Possible Roles of MiR-219-5p Targeting SOX5 in the Development of Oral Cancer
-
摘要:
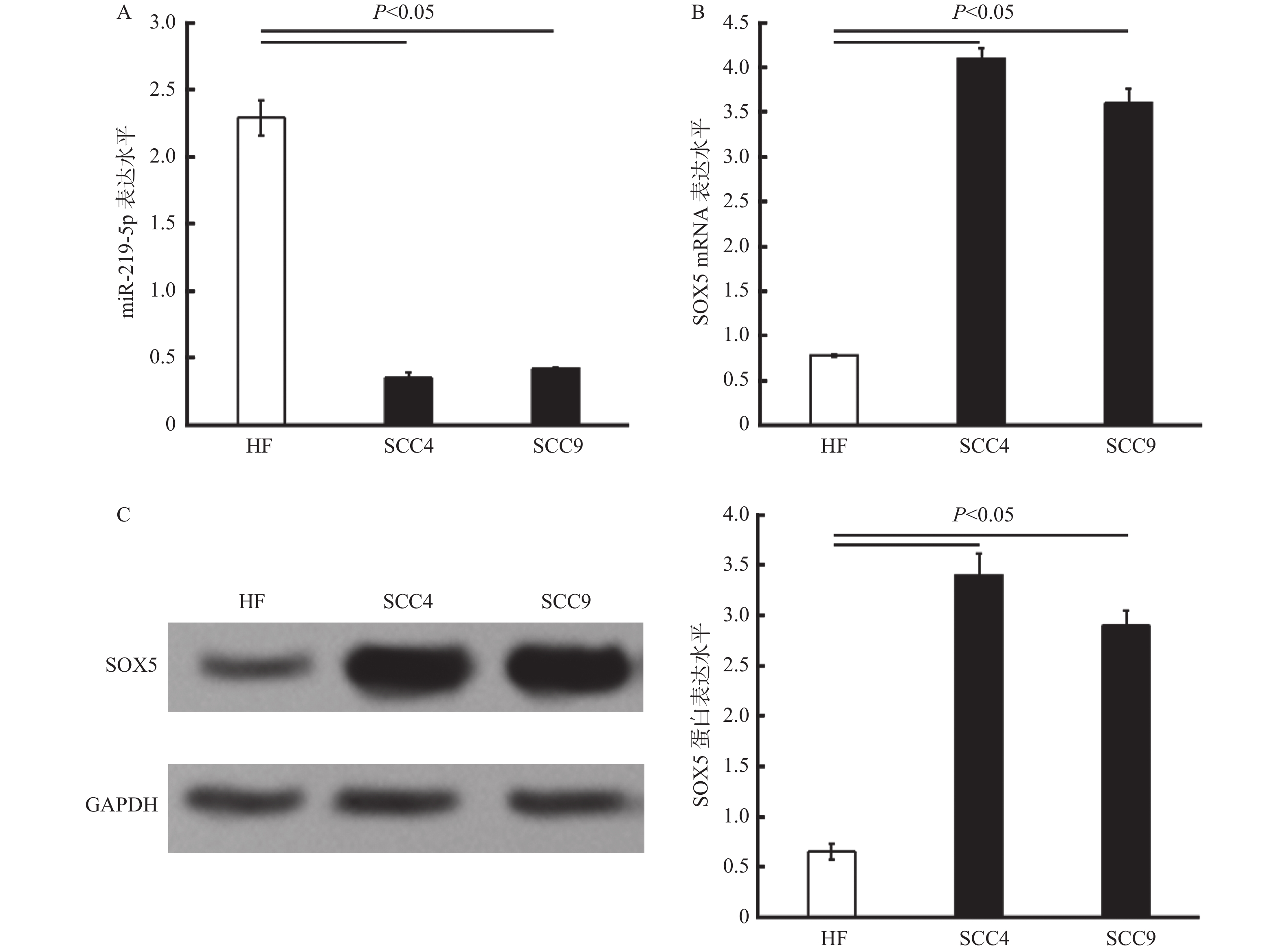
目的 研究miR-219-5p 与SOX5在口腔鳞状细胞癌中是否存在差异性表达,并探讨miR-219-5p 对SOX5的靶向调控作用, 方法 运用口腔鳞状细胞癌细胞株SCC4及SCC9,人正常皮肤成纤维细胞系(HF)作为对照,对miR-219-5p与SOX5在个细胞系中的表达情况进行检测(RT-qPCR、Western blot);并在SCC4及SCC9细胞株中验证miR-219-5p对SOX5表达的靶向调控作用。 结果 与正常人纤维细胞相比,miR-219-5p的表达水平显著降低,而SOX5的表达水平显著增加,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);miR-219-5p与SOX5的表达水平具有负相关(P < 0.05);在SCC4及SCC9细胞中,miR-219-5p通过结合3' 非编码区(3'-UTR)靶向调控SOX5的表达。 结论 miR-219-5p可能通过对SOX5的靶向调控参与了口腔鳞状细胞癌的发生发展,为协助临床预后评估和/或筛选治疗的新候选药物提供了科学依据。 -
关键词:
- 口腔癌细胞 /
- miR-219-5p /
- SOX5 /
- 靶向调控
Abstract:Objectives To explore whether the expressions of miR-219-5p and / or SRY-related high-mobility-group box 5 (SOX5) in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells are differ from normal cells. We also aim to confirm the transcription regulation in SOX5 by miR-219-5p. Methods Human oral squamous cell lines SCC4 and SCC9 were employed. The expression levels of miR-219-5p and SOX5 were detected in cancer cells (indicated by RT-qPCR and Western blot). Genetic analysis and luciferase assay were employed to verify whether miR-219-5p targets SOX5 by binding to the specific region of 3'-UTR. Results Our data showed that high miR-219-5p and low SOX5 levels were detected in vitro SCC4 and SCC9 cells (P < 0.05). miR-219-5p was negatively correlated with SOX5 expression. Genetic analysis and luciferase assay revealed that miR-291-5p regulated SOX5 expression by targeting the 3'untranslated region (3'-UTR) of the SOX5 mRNA. Conclusions This study demonstrates that miR-219-5p is involved in the development and prognosis of oral cancer by targeting the expression of SOX5, and can be a novel candidate for clinical prognosis and/or therapy. -
Key words:
- Oral cancer cells /
- miR-219-5p /
- SOX5 /
- Target regulation
-
图 2 miR-219-5p靶向3’-UTR特异性序列调控SOX5
A:miRMine预测人SOX5 mRNA序列中miR-219-5p可能的结合位点,红色标注的为miR-219-5p与SOX5 mRNA靶向结合的潜在位点;B:根据预测结果设计的miR-219-5p与SOX5 mRNA靶向结合潜在位点的突变序列(黄色标示);3’UTR,3’非编码区;C:SCC4细胞的双荧光素酶报告实验结果;D:SCC9细胞的双荧光素酶报告实验结果。SOX5 3'UTR-wt,SOX5 3'UTR结合位点野生型组(未突变组);SOX5 3'UTR-mut,SOX5 3'UTR结合位点突变组;miR-NC,miR-219-5p空白对照剂转染;miR-219-5p,miR-219-5p转染。
Figure 2. miR-219-5p regulates SOX5 by binding to specific sites in 3’-UTR
图 3 在口腔癌细胞SCC4及SCC9中miR-219-5p靶向调控SOX5的表达
A:miR-219-5p在SCC4细胞中对SOX5 mRNA水平的表达调控; B:miR-219-5p在SCC9细胞中对SOX5 mRNA水平的表达调控;C:miR-219-5p在SCC4细胞中对SOX5蛋白水平的表达调控,上方为Western blot检测的蛋白印迹图,GAPDH为内对照,下方SOX5蛋白水平的定量统计直方图;D:miR-219-5p在SCC9细胞中对SOX5蛋白水平的表达调控,上方为Western blot检测的蛋白印迹图,GAPDH为内对照,下方SOX5蛋白水平的定量统计直方图。
Figure 3. miR-219-5p regulates the expression of SOX5 in SCC4 and SCC9
-
[1] Johnson D E,Burtness B,Leemans C R,et al. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers,2020,6(1):92. doi: 10.1038/s41572-020-00224-3 [2] Tandon P,Dadhich A,Saluja H,et al. The prevalence of squamous cell carcinoma in different sites of oral cavity at our Rural Health Care Centre in Loni,Maharashtra-a retrospective 10-year study[J]. Contemp Oncol (Pozn),2017,21(2):178-183. [3] Wang L,Ye S,Wang J,et al. HuR Stabilizes lnc-Sox5 mRNA to Promote Tongue Carcinogenesis[J]. Biochemistry (Mosc),2017,82(4):438-445. [4] Song S,Fajol A,Tu X,et al. miR-204 suppresses the development and progression of human glioblastoma by targeting ATF2[J]. Oncotarget,2016(43):70058-70065. [5] Livak K J,Schmittgen T D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method[J]. Methods,2001,25(4):402-8. doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262 [6] Huang D Y,Lin Y T,Jan P S,et al. Transcription factor SOX-5 enhances nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression by down-regulating SPARC gene expression[J]. J Pathol,2008,214(4):445-55. [7] Wang D,Han S,Wang X,et al. SOX5 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cell invasion via regulation of Twist1 in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Med Oncol,2015,32(2):461. [8] Pei X H,Lv X Q,Li H X. Sox5 induces epithelial to mesenchymal transition by transactivation of Twist1[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun,2014,446(1):322-327. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.02.109 [9] Hu J,Tian J,Zhu S,et al. Sox5 contributes to prostate cancer metastasis and is a master regulator of TGF-β-induced epithelial mesenchymal transition through controlling Twist1 expression[J]. Br J Cancer,2018,118(1):88-97. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2017.372 [10] Meng X,Lou Q Y,Yang W Y,et al. The role of non-coding RNAs in drug resistance of oral squamous cell carcinoma and therapeutic potential[J]. Cancer Commun (Lond),2021,41(10):981-1006. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12194 [11] Macfarlane L A,Murphy P R. MicroRNA: Biogenesis,Function and role in cancer[J]. Curr Genomics,2010,11(7):537-561. doi: 10.2174/138920210793175895 [12] Hurník P,Chyra Z,Ševčíková T,et al. Epigenetic Regulations of Perineural Invasion in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma[J]. Front Genet,2022,13:848557. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.848557 [13] Maruyama T,Nishihara K,Umikawa M,et al. MicroRNA-196a-5p is a potential prognostic marker of delayed lymph node metastasis in early-stage tongue squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Oncol Lett,2018,15(2):2349-2363. [14] Xin H,Feng Z,Yao C. SNHG1/miR-145-5p/KLF5 Axis Participates in Regulating the Proliferation and Migration of Oral Squamous Cell Cancer[J]. J Healthc Eng.,2022,2022:2053271. [15] Wei C,Zhang X,He S,et al. MicroRNA-219-5p inhibits the proliferation,migration,and invasion of epithelial ovarian cancer cells by targeting the Twist/Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway[J]. Gene,2017,637:25-32. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2017.09.012 [16] Li C,Dong J,Han Z,Zhang K. MicroRNA-219-5p Represses the Proliferation,Migration,and Invasion of Gastric Cancer Cells by Targeting the LRH-1/Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway[J]. Oncol Res,2017,25(4):617-627. doi: 10.3727/096504016X14768374457986 [17] Wang Q,Zhu L,Jiang Y,et al. miR-219-5p suppresses the proliferation and invasion of colorectal cancer cells by targeting calcyphosin[J]. Oncol Lett,2017,13(3):1319-1324. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.5570 [18] Xiong G B,Zhang G N,Xiao Y,et al. MicroRNA-219-5p functions as a tumor suppressor partially by targeting platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha in colorectal cancer[J]. Neoplasma,2015,62(6):855-863. doi: 10.4149/neo_2015_104 [19] Huang L X,Hu C Y,Jing L,et al. microRNA-219-5p inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of colorectal cancer by targeting lymphoid enhancer-binding factor 1[J]. Cancer Sci,2017,108(10):1985-1995. doi: 10.1111/cas.13338 -






 下载:
下载: