Value of Binary Logit Regression Model Based on FNA-Tg and Serum Tg for Determining Lymph Node Metastasis or Recurrence of Thyroid Cancer
-
摘要:
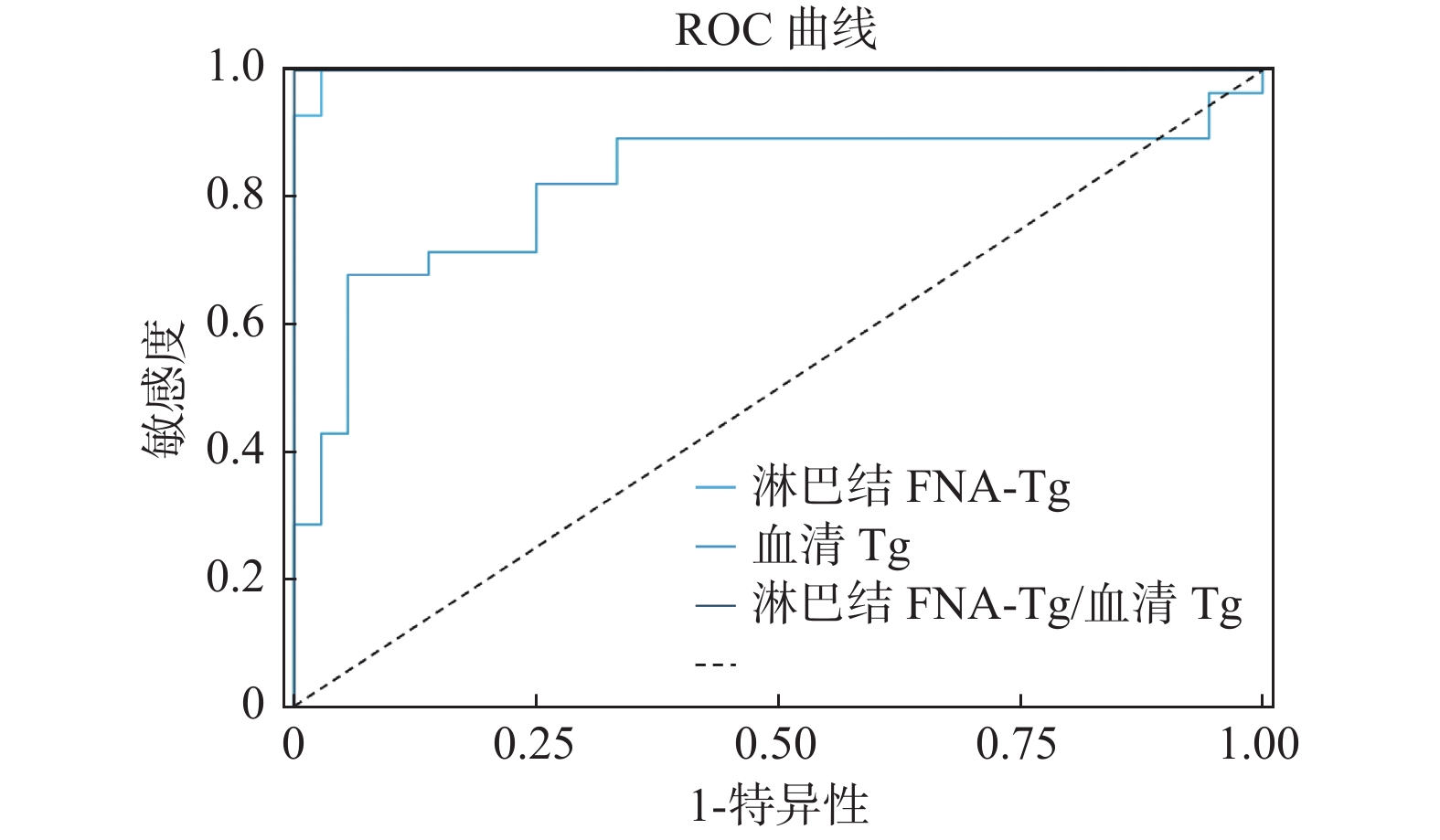
目的 通过二元Logit回归分析患者淋巴结细针细胞学穿刺洗脱液甲状腺球蛋白测定值(FNA-Tg值)、血清甲状腺球蛋白值(血清Tg值)及其比值,建立对甲状腺癌淋巴结转移、复发情况的预测模型。 方法 (1)收集术前为分化型甲状腺癌伴可疑淋巴结转移患者64例。(2)通过ROC曲线初步评估FNA-Tg值、血清Tg值及其比值对淋巴结良恶性鉴别的诊断价值。(3)使用二元Logit回归分析进一步评价上述3项指标的诊断价值并建立预测模型。 结果 (1)ROC曲线:淋巴结FNA-Tg对应的AUC值为0.998(95% CI 99.27%~100.34%),切点值为0.82;血清Tg对应的AUC值为0.824(95% CI 70.64%~94.14%),切点值为18.27;淋巴结FNA-Tg/血清Tg对应的AUC值为1.000(95% CI 100.00%~100.00%),切点值为0.461。(2)二元Logit回归全进入法3项自变量同时存在,二元Logit回归全进入法3项自变量同时存在,FNA-Tg值、血清Tg值及其比值3项P值均 > 0.05,模型3项自变量同时存在对淋巴结良恶性无诊断价值;二元Logit回归全进入法淋巴结FNA-Tg单一变量。淋巴结FNA-Tg可以解释88%淋巴结良恶性的变化,P = 0.038 < 0.05,回归系数2.68,OR值14.587,预测模型公式为:In(p/1-p) = -4.122 + 2.680*淋巴结FNA-Tg,似然比检验P = 0.000 < 0.001,AIC值14.386,BIC值18.704,总体预测准确率为95.31%;二元Logit回归全进入法血清Tg单一变量,血清Tg能解释淋巴结良恶性27.8%的变化原因,P = 0.000 < 0.001,回归系数0.164,OR值1.179,预测模型公式为:In(p/1-p) = -2.466 + 0.164*血清Tg,似然比检验P = 0.000 < 0.001,AIC值67.33,BIC值71.648,总体预测准确率为75%。 结论 术前FNA-Tg、血清Tg及其比值在判定甲状腺结节良恶性有很好的诊断价值。基于FNA-Tg、血清Tg的二元Logit回归模型公式能较好的预测甲状腺癌患者淋巴结转移、复发的情况。 Abstract:Objective To establish a prediction model for lymph node metastasis and recurrence of thyroid cancer by analyzing patients’ lymph node FNA-Tg values, serum Tg values, and their ratios by binary logit regression. Methods 1. 64 patients with preoperative differentiated thyroid cancer with suspected lymph node metastasis were collected. 2. The diagnostic value of FNA-Tg value, serum Tg value, and their ratios for the differentiation of benign and malignant lymph nodes were initially evaluated by the ROC curve. 3. The diagnostic value of the above three indices was further evaluated by binary logit regression analysis and a prediction model was established. Results 1. ROC curve: the AUC value corresponding to lymph node FNA-Tg was 0.998 (95% CI 99.27%-100.34%), with a cut point value of 0.82; the AUC value corresponding to serum Tg was 0.824 (95% CI 70.64%-94.14%), with a cut point value of 18.27; the AUC value corresponding to lymph node FNA-Tg/serum Tg The AUC value of FNA-Tg/serum Tg in lymph nodes was 1.000 (95% CI 100.00%-100.00%), and the cut point value was 0.461. 2. Binary logit regression all-entry method with the simultaneous presence of three independent variables: i) Binary logit regression all-entry method with the simultaneous presence of three independent variables: FNA-Tg value, serum Tg value and their ratios all had P values > 0.05, and the model The simultaneous presence of three independent variables has no diagnostic value for benign and malignant lymph nodes; ii) Binary Logit regression all-entry method lymph node FNA-Tg single variable results: lymph node FNA-Tg could explain 88% of the variation in benign and malignant lymph nodes, P = 0.038 < 0.05, regression coefficient 2.68, OR value 14.587, prediction model formula was: In (p/1-p) = -4.122 + 2.680* lymph node FNA-Tg, likelihood ratio test P = 0.000 < 0.001, AIC value 14.386, BIC value 18.704, overall prediction accuracy of 95.31%; iii) Binary Logit regression all-entry method serum Tg single variable results: serum Tg explained 27.8% of the variation in benign and malignant lymph nodes , P = 0.000 < 0.001, regression coefficient 0.164, OR 1.179, prediction model formula: In (p/1-p) = -2.466 + 0.164*serum Tg, likelihood ratio test P = 0.000 < 0.001, AIC value 67.33, BIC value 71.648, overall prediction accuracy 75%. Conclusions 1. Preoperative FNA-Tg, serum Tg and their ratios have good diagnostic value in determining the benignity and malignancy of thyroid nodules. 2. The binary logit regression model (stepwise method) formula based on serum Tg can better predict the benignity and malignancy of thyroid nodules. -
Key words:
- Ultrasound /
- Fine needle aspiration /
- Thyroglobulin /
- Regression model
-
表 1 ROC结果AUC汇总
Table 1. AUC Summary of ROC results
标题 AUC 标准误 p 95% CI 淋巴结FNA-Tg 0.998 0.003 0.000* 0.993 ~ 1.003 血清Tg 0.824 0.060 0.000* 0.706 ~ 0.941 淋巴结FNA-Tg/血清Tg 1.000 0.000 0.000* 1.000 ~ 1.000 *P < 0.05。 表 2 ROC最佳界值结果
Table 2. The optimal boundary value results of ROC
标题 AUC 最佳界值 敏感度 特异度 Cut-off 淋巴结FNA-Tg 0.998 0.972 1.000 0.972 0.820 血清Tg 0.824 0.623 0.679 0.944 18.270 淋巴结FNA-Tg/血清Tg 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.000 0.461 表 3 二元Logit回归分析结果汇总
Table 3. Summary of binary Logit regression analysis results
项 回归系数 标准误 z 值 Wald χ2 p 值 OR值 OR值95% CI 淋巴结FNA-Tg −0.988 119.973 −0.008 0.000 0.993 0.372 0.000~4.92 血清Tg 0.978 112.840 0.009 0.000 0.993 2.659 0.000~2.98 淋巴结FNA-Tg/血清Tg 47.852 2517.846 0.019 0.000 0.985 6.0x1020 0.000~null 截距 −36.735 2041.715 −0.018 0.000 0.986 0.000 0.000~null 因变量:术后病理结果,McFadden R方: 1.000 Cox & Snell R方:0.746 Nagelkerke R方:1.000。 表 4 二元Logit回归分析结果汇总
Table 4. Summary of binary Logit regression analysis results
项 回归系数 标准误 z 值 Wald χ2 p 值 OR值 OR值95% CI 淋巴结FNA-Tg 2.680 1.290 2.078 4.319 0.038 14.587 1.165~182.660 截距 −4.122 1.252 −3.293 10.841 0.001 0.016 0.001~0.189 因变量:术后病理结果 McFadden R方: 0.882 Cox & Snell R方:0.701 Nagelkerke R方:0.940。 表 5 二元Logit回归预测准确率汇总
Table 5. Summary of accuracy rate of binary Logit regression prediction
预测值 预测准确率 预测错误率 0 1 真实值 0 35 1 97.22% 2.78% 1 2 26 92.86% 7.14% 汇总 95.31% 4.69% 表 6 二元Logit回归分析结果汇总
Table 6. Summary of binary Logit regression analysis results
项 回归系数 标准误 z 值 Wald χ2 P 值 OR值 OR值95% CI 血清Tg 0.164 0.042 3.924 15.397 0.000 1.179 1.086 ~ 1.280 截距 −2.466 0.645 −3.825 14.628 0.000 0.085 0.024 ~ 0.301 因变量:术后病理结果 McFadden R 方: 0.278 Cox & Snell R 方:0.317 Nagelkerke R 方:0.425。 表 7 二元Logit回归预测准确率汇总
Table 7. Summary of accuracy rate of binary Logit regression prediction
预测值 预测准确率 预测错误率 0 1 真实值 0 28 8 77.78% 22.22% 1 8 20 71.43% 28.57% 汇总 75.00% 25.00% -
[1] Cooper D S,Doherty G M,Haugen,et al. Revised American Thyroid Association management guidelines for patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer[J]. Thyroid,2009,19(11):1167-1214. doi: 10.1089/thy.2009.0110 [2] Brito J P,Gionfriddo M R,Al Nofal A,et al. The accuracy of thyroid nodule ultrasound to predict thyroid cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab,2014,99(4):1253-1263. doi: 10.1210/jc.2013-2928 [3] 谭石,姚宏伟,贾建文,等. 超声引导下细针穿刺在甲状腺小结节诊断中的应用[J]. 中国微创外科杂志,2014,14(12):1065-1067. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6604.2014.12.001 [4] 董屹婕,詹维伟. 超声引导下细针穿刺在甲状腺结节诊断和鉴别诊断中的价值[J]. 中国实用外科杂志,2015,35(6):613-619. [5] Johnson N A,Tublin M E. Postoperative surveillance of differentiatedthyroid carcinoma: rationale,techniques,and controversies[J]. Radiology,2008,249(2):429-444. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2492071313 [6] Uruno T,Miyauchi A,Shimizu K,et al. Usefulness of thyroglobulin measurement in fine-needle aspiration biopsy specimens for diagnosingcervical lymph node metastasis in patients with papillary thyroid cancer[J]. World J Surg,2005,29(4):483-485. doi: 10.1007/s00268-004-7701-0 [7] Jeon S J,Kim E,Park J S,et al. Diagnostic benefit of thyroglobulin Measurement in fine-needle aspiration for diagnosing metastatic cervical lymph nodes from papillary thyroid cancer: correlations with US features[J]. Korean J Radiol,2009,10(2):106-111. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2009.10.2.106 [8] Sigstad E,Heilo A,Paus E,et al. The usefulness of detecting thyroglobulin in fine-needle aspirates from patients with neck lesions using a sensitive thyroglobulin assay[J]. Diagn Cytopathol,2007,35(12):761-767. doi: 10.1002/dc.20726 [9] Kim D W,Jeon S J,Kim C G. Usefulness of thyroglobulin measurement inneedle washouts of fine-needle aspiration biopsy for the diagnosis ofcervical lymph node metastases from papillary thyroid cancer before thyroidectomy[J]. Endocrine,2012,42(2):399-403. doi: 10.1007/s12020-012-9636-9 [10] Snozek C L,Chambers E P,Reading C C,et al. Serum thyroglobulin,high-resolution ultrasound,and lymph node thyroglobulin in diagnosis of differentiated thyroid carcinoma nodal metastases[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab,2007,92(11):4278-4281. doi: 10.1210/jc.2007-1075 [11] Sohn Y M,Kim M J,Kim E K,et al. Diagnostic performance of thyroglobulin value in indeterminate range in fine needle aspiration washout fluid from lymph nodes of thyroid cancer[J]. Yonsei Med J,2012,53(1):126-131. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2012.53.1.126 [12] Salmaslıolu A,Erbil Y,Cıtlak G,et al. Diagnostic value of thyroglobulin measurement in fine-needle aspiration biopsy for detecting metastatic lymph nodes in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma[J]. Langenbecks Arch Surg,2011,396(1):77-81. doi: 10.1007/s00423-010-0723-1 [13] Bournaud C,Charrié A,Nozières C,et al. Thyroglobulin measurement in fine-needle aspirates of lymph nodes in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer: a simple definition of the threshold value,with emphasis on potential pitfalls of the method[J]. Clin Chem Lab Med,2010,48(8):1171-1177. [14] Wu L M,Gu H Y,Qu X H,et al. The accuracy of ultrasonography in the preoperative diagnosis of cervical lymph node metastasis in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma: a meta-analysis[J]. Eur J Radiol,2012,81(8):1798-1805. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2011.04.028 [15] Leboulleu x S,Girard E,Rose M,et al. Ultrasound criteria of malignancy for cervical lymph nodes in patients followed up for differentiated thyroid cancer[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab,2007,92(9):3590-3594. doi: 10.1210/jc.2007-0444 [16] Kessler A,Rappaport Y,Blank A,et al. Cystic appearance of cervicallymph nodes is characteristic of metastatic papillary thyroid carcinoma[J]. J Clin Ultrasound,2003,31(1):21-15. doi: 10.1002/jcu.10130 [17] Pacini F,Schlumberger M,Dralle H,et al. European consensus for the management of patients with differentiated thyroid carcinoma of thefollicular epithelium[J]. Eur J Endocrinol,2006,154(6):787-803. doi: 10.1530/eje.1.02158 [18] 周好,陈海珍,陈曦等. 细针穿刺洗脱液测定甲状腺球蛋白鉴别转移淋巴结性质[J]. 外科理论与实践,2012,17(1):17-20. -






 下载:
下载: