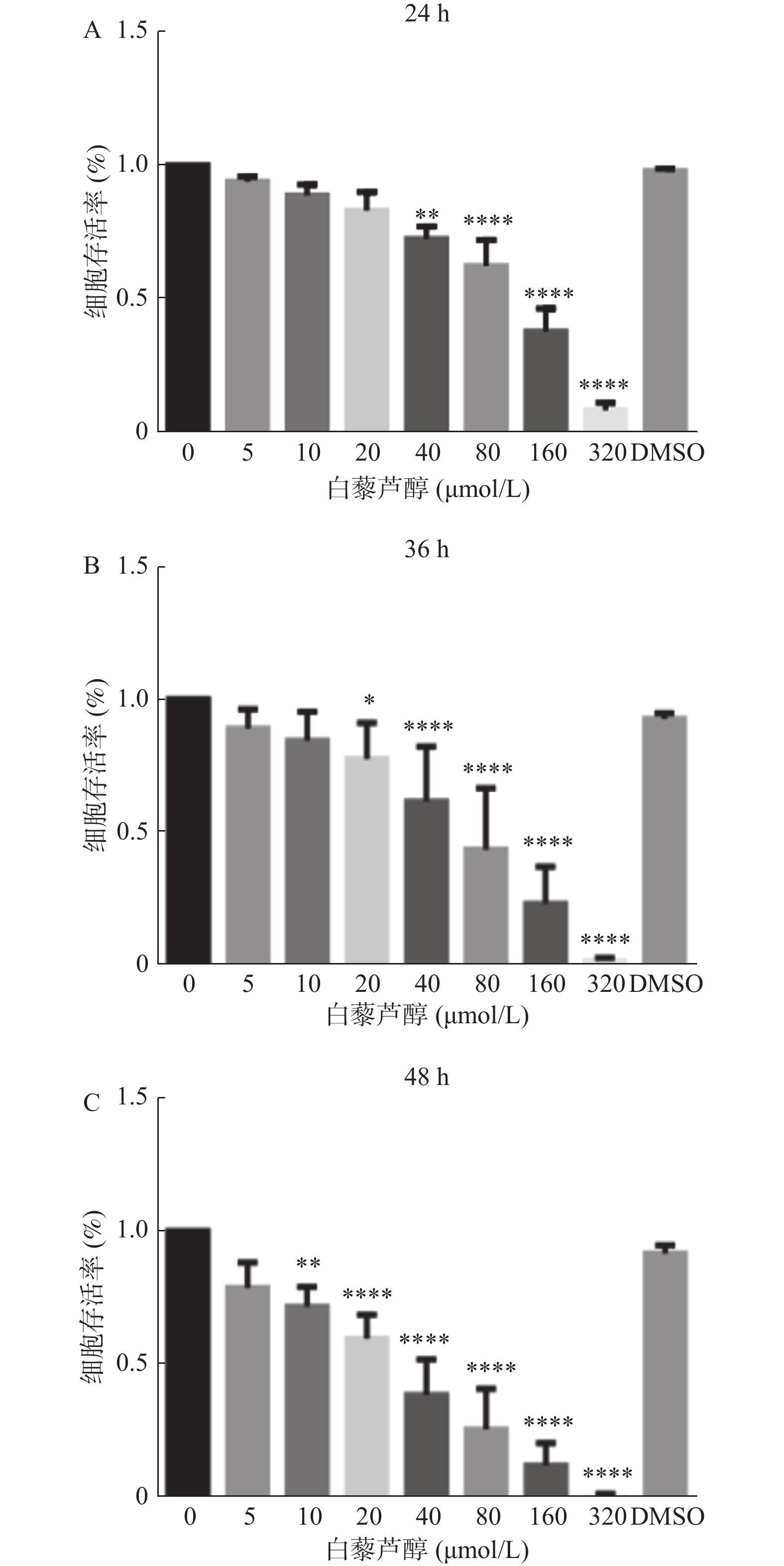
|
[1]
|
陈瑶,李思维. 鼻咽癌放疗敏感性的研究进展[J]. 华夏医学,2016,1(30):167-171. doi: 10.19296/j.cnki.1008-2409.2017-01-053
|
|
[2]
|
Farooqi A A,Khalid S,Ahmad A. Regulation of cell signaling pathways and mirnas by resveratrol in different cancers[J]. Int J Mol Sci,2018,19(3):217-225.
|
|
[3]
|
Kim S E,Shin S H,Lee J Y,et al. Resveratrol induces mitochondrial,apoptosis and inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells[J]. Nutr Cancer,2018,70(1):125-135. doi: 10.1080/01635581.2018.1397708
|
|
[4]
|
Yang Sun,Qian-Mei Zhou,Yi-Yu Lu,et al. Resveratrol inhibits the migration and metastasis of mda-mb-231 human breast cancer by reversing tgf-β1-induced epithelial- mesenchymal transition[J]. Molecules,2019,24:1131-1147. doi: 10.3390/molecules24061131
|
|
[5]
|
Li Yuan,Mengmeng Zhou,Dawei Huang,et al. Resveratrol inhibits the invasion and metastasis of colon cancer through reversal of ithelial-Mesenchymal Transition via the Akt/GSK-3β/Snail signaling pathway[J]. Molecular Medicine Reports,2019,20:2783-2795.
|
|
[6]
|
Yi-Ching Chuang,Ming-Chang Hsieh,Chia-Chieh Lin,et al. Pinosylvin inhibits migration and invasion of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cancer cells via regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and inhibition of MMP-2[J]. Oncol Rep,2021,46(1):143. doi: 10.3892/or.2021.8094
|
|
[7]
|
Dong-Fang Meng,Rui Sun,Guo-Ying Liu,et al. S100A14 suppresses metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by inhibition of NF-kB signaling through degradation of IRAK1[J]. Oncogene,2020,39(30):5307-5322. doi: 10.1038/s41388-020-1363-8
|
|
[8]
|
Qian Fei,Ming-Yu Du,Lu-Xi Qian,et al. Feedback loop in miR-449b-3p/ADAM17/ NF-κB promotes metastasis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J]. Cancer Med,2019,Oct,8(13):6049-6063.
|
|
[9]
|
Yangyang Xiao,Jilin Qing,Baoxuan Li,et al. TIM-3 participates in the invasion and metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma via SMAD7/ SMAD2/SNAIL1 Axis-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition[J]. OncoTargets and Therapy,2020,13:1993-2006. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S237222
|
|
[10]
|
J Hou,J Yan,XY Ren,et al. Long noncoding RNA ROR1-AS1 induces tumor metastasis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by sponging miR-375 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J]. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences,2020,24:174-180.
|
|
[11]
|
W Chen,X Ren,J Wu,et al. HSP27 associates with epithelial-mesenchymal transition stemness and radioresistance of salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma[J]. Cell Mol Med,2018,22(4):2283-2298. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13510
|
|
[12]
|
SH Chol,JK Nam,BY Kim,et al. HSPB1 inhibits the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition to suppress pulmonary fibrosis and lung tumorigenesis[J]. Cancer Res,2016,76(5):1019-1030. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-0952
|
|
[13]
|
Y Zhang,X Tao,G Jin,et al. A targetable molecular chaperone HSP27 confers aggressiveness in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Theranostics,2016,6(4):558-570. doi: 10.7150/thno.14693
|
|
[14]
|
W Deng, Y Zhang, L Gu, et al. Heat shock protein27 downstream of P38-PI3K/Akt signaling antagonizes melatonin-induced apoptosis of SGC-7901 gastric cancer cells [J]. Cancer Cell Int, 2016, doi: 10.1186/s12935-016-0283-8.
|
|
[15]
|
T Cordonnier,JL Bishop,M Shiota,et al. Hsp27 regulates EGF/β-catenin mediated epithelial to mesenchymal transition in prostate cancer[J]. International journal of cancer,2015,136(6):496-507. doi: 10.1002/ijc.29122
|
|
[16]
|
Yuanyuan Tang,Xiuzhen Sun,Shen Yu,et al. Inhibition of Ezrin suppresses cell migration and invasion in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J]. Oncol Lett,2019,Jul;18(1):553-560.
|
|
[17]
|
L Wang,M Fan,C Zeng,et al. Expression and purification of a rapidly degraded protein,TMEM8B-a,in mammalian cell line[J]. Protein Expr Purif.,2018,151:38-45. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2018.06.002
|
|
[18]
|
Chunmei Fan,Hongke Qu,Fang Xiong,et al. CircARHGAP12 promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma migration and invasion via ezrin-mediated cytoskeletal remodeling[J]. cancer Lett,2021,496:41-56. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2020.09.006
|
|
[19]
|
Y Li,Z Lin,B Chen,et al. Ezrin/NF-kB activation regulates epithelial- mesenchymal transition induced by EGF and promotes metastasis of colorectal cancer[J]. Biomed Pharmacother,2017,92:140-148. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.05.058
|
|
[20]
|
Zijian Liu, Jinlan He, Jiaqi Han, et al. m6A Regulators Mediated Methylation Modification Patterns and Tumor Microenvironment Infiltration Characterization In Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma [J]. Front Immunol, 2022 ;doi: 10.3389/fimmu. 2021.762243.
|
|
[21]
|
C Lin,J Zong,W Lin,et al. EBV-miR-BART8-3p induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and promotes metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells through activating NF-κB and Erk1/2 pathways[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res,2018,37(1):283-295. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-0953-6
|
|
[22]
|
Gastón Repossi,Undurti N Das,Aldo Renato Eynard. Molecular Basis of the Beneficial Actions of Resveratrol[J]. Arch Med Res,2020,51(2):105-114. doi: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2020.01.010
|
|
[23]
|
Y Jiao,H Li,Y Liu,et al. Resveratrol inhibits the invasion of glioblastoma -initiating cells via down-regulation of the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. Nutrients,2015,7:4383-4402. doi: 10.3390/nu7064383
|
|
[24]
|
Y Y Lan,F H Chang,J H Tsai,et al. Epstein-Barr virus Rta promotes invasion of bystander tumor cells through paracrine of matrix metalloproteinase 9[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun,2018,503(3):2160-2166. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.08.006
|
|
[25]
|
Li Chen,Guoxiang Lin,Kaihua Chen,et al. VEGF promotes migration and invasion by regulating EMT and MMPs in nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J]. J Cancer,2020,11(24):7291-7301. doi: 10.7150/jca.46429
|






 下载:
下载: