Effects of MMP-1 and MMP-7 on Pulmonary Hypertension in Rats
-
摘要:
目的 探究MMP-1和MMP-7在肺动脉高压(pulmonary arterial hypertension,PAH)发展中的作用。 方法 采用ELISA检测PAH患者血清中的MMPs(MMP-1、MMP-2、MMP-7、MMP-9、MMP-10、MMP-14)的含量并选择出2种MMPs进行动物体内实验。收集临床信息并比较PAH患者和健康人的体重指数(body mass index, BMI)、NYHA心功能等级、6 min步行距离(6 min walking distance,6MWD)、脑钠肽(brain natriuretic peptide,BNP)、平均肺动脉压(mean pulmonary arterial pressure,mPAP)、甘油三酯(triglyceride,TGs)、低密度脂蛋白(low-density lipoprotein,LDL)、总胆固醇(total cholesterol,TC)、血红蛋白(hemoglobin,HB)、心率(heart rate,HR)等指标的差异。采用野百合碱诱导PAH大鼠模型,然后使用过表达MMP-1质粒和shMMP-7质粒分别上调和下调PAH大鼠中MMP-1和MMP-7的表达。通过苏木精-伊红染色法 ( hematoxylin-eosin staining,HE)观察肺动脉病理变化,Masson染色观察肌纤维和胶原纤维的变化,免疫荧光检测α-SMA和VWF,对左心室、右心室和室间隔进行称重后计算右心室肥厚指数。 结果 与健康人相比,PAH患者血清中的MMP-1(P < 0.0001)、MMP-2(P < 0. 001)、MMP-7(P < 0.01)、MMP-9(P < 0.001)、MMP-10(P < 0.001)、MMP-14(P < 0.01)含量升高,6MWD降低(P < 0.05),BNP含量升高(P < 0.001),NYHA分级升高(P < 0.0001)。与对照组相比,PAH大鼠的MMP-1(P < 0.0001)和MMP-7(P < 0.0001)在肺组织中蛋白表达升高,右心室肥厚指数增加(P < 0.0001),肺动脉血管增厚(P < 0.05),胶原纤维沉积增多(P < 0.05),α-SMA(P < 0.05)和VWF(P < 0.05)在血管中表达增多。与PAH组相比,在PAH大鼠中过表达MMP-1促进PAH发展,而干扰MMP-7则延缓其发展。 结论 MMPs(MMP-1、MMP-2、MMP-7、MMP-9、MMP-10、MMP-14)在肺动脉高压患者血清中升高。MMP-1和MMP-7促进肺动脉高压大鼠模型的肺动脉血管重塑、肺纤维化和右心室功能不全。 Abstract:Objective To explore the effects of MMP-1 and MMP-7 on pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). Methods The contents of MMPs (MMP-1, MMP-2, MMP-7, MMP-9, MMP-10, MMP-14) in the serum of PAH patients and healthy controls were detected and two MMPs were selected for in vivo experiments. Clinical information was collected and body mass index (BMI), NYHA cardiac function class, 6 min walking distance (6MWD), brain natriuretic peptide (BNP), mean pulmonary arterial pressure (mPAP), triglyceride (TGs), low-density lipoprotein (LDL), total cholesterol (TC), hemoglobin (HB), heart rate (HR) were compared between PAH patients and healthy controls. The PAH rat model was induced by monocrotaline, and then MMP-1 overexpression plasmid and shMMP-7 plasmid were used to up-regulate and down-regulate the expression of MMP-1 and MMP-7, respectively. Hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining was used to observe the pathological of PAH, Masson staining was used to observe the changes of muscle fibers and collagen fibers, and immunofluorescence was used to detect the expression of α-SMA and VWF. The left ventricle, right ventricle and interventricular septum were weighed and the right ventricular hypertrophy index was calculated. Results The serum levels of MMP-1 (P < 0.0001), MMP-2 (P < 0.001), MMP-7 (P < 0.01), MMP-9 (P < 0.001), MMP-10 (P < 0.001) and MMP-14 (P < 0.01) in PAH patients were significantly higher than those in healthy controls. 6MWD was significantly decreased (P < 0.05), BNP level was increased (P < 0.001), NYHA class was increased (P < 0.0001). Compared with the control group, the protein expression of MMP-1 (P < 0.0001) and MMP-7 (P < 0.0001) in lung tissue, right ventricular hypertrophy index (P < 0.0001), pulmonary artery vascular thickness (P < 0.05), and collagen fiber deposition (P < 0.05) were increased in PAH rats. The expressions of α-SMA (P < 0.05) and VWF (P < 0.05) in blood vessels were increased in PAH rats than control rats. Compared with PAH group, overexpression of MMP-1 in PAH rats promoted the development of PAH, while interference with MMP-7 delayed its development. Conclusions The serum levels of MMPs (MMP-1, MMP-2, MMP-7, MMP-9, MMP-10, MMP-14) are increased in patients with PAH. MMP-1 and MMP-7 promote pulmonary artery remodeling, pulmonary fibrosis and right ventricular dysfunction in PAH rats. -
Key words:
- MMP-1 /
- MMP-7 /
- Pulmonary arterial hypertension
-
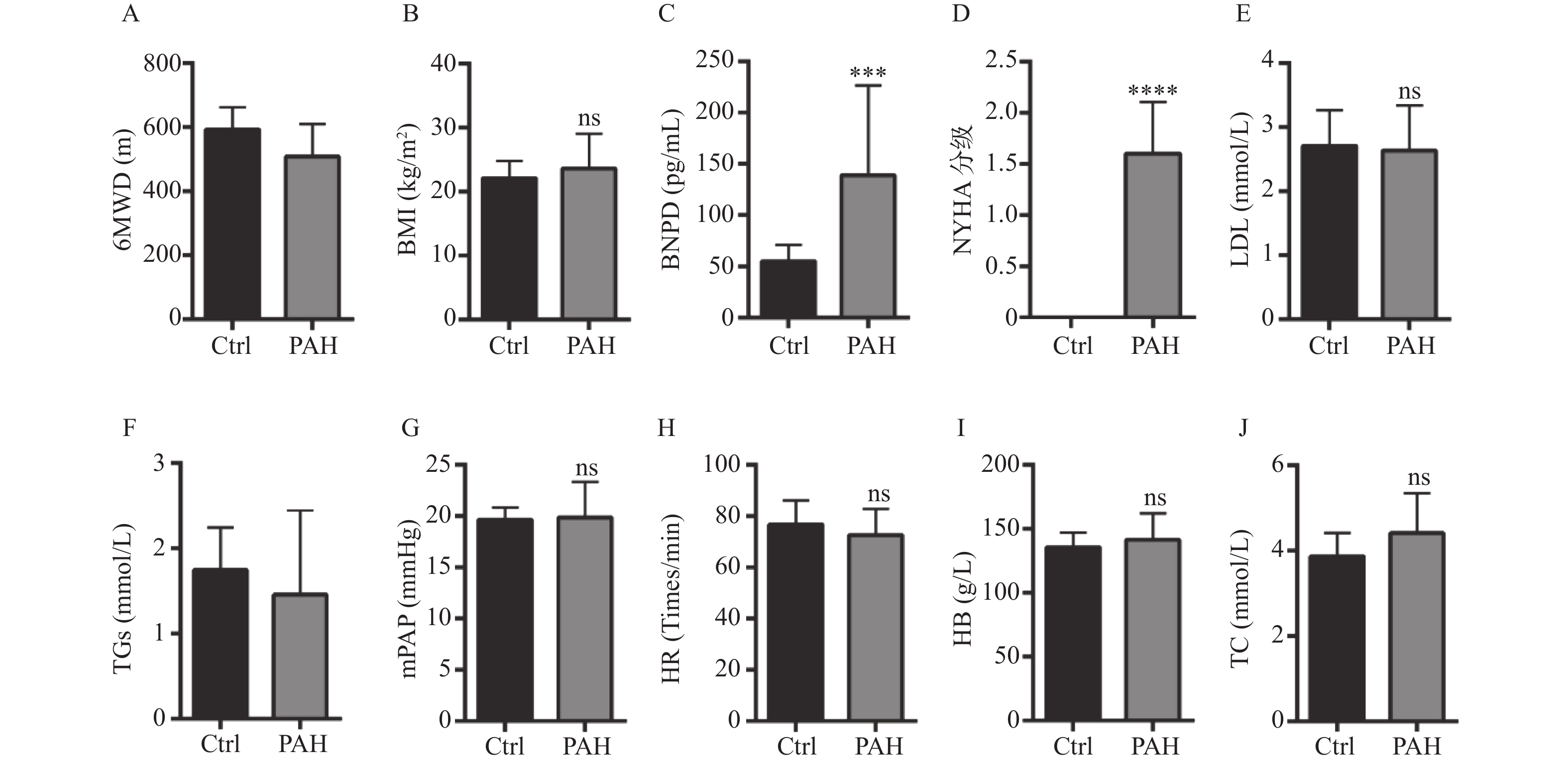
图 1 健康人和PAH患者临床指标的差异
A:比较健康人与PAH组的6MWD差异;B:比较健康人与PAH组的BMI差异;C:比较健康人与PAH组的BNP差异;D:比较健康人与PAH组的NYHA分级差异;E:比较健康人与PAH组的LDH差异;F:比较健康人与PAH组的TGs差异;G:比较健康人与PAH组的mPAP差异;H:比较健康人与PAH组的HR差异;I:比较健康人与PAH组的HB差异;J:比较健康人与PAH组的TC差异。*P < 0.05,***P < 0.001,****P < 0.0001。
Figure 1. Differences of clinical indicators between healthy people and patients with PAH
图 2 Ctrl组与PAH患者血清中MMPs的水平
A:ELISA试剂盒检测健康人和PAH患者MMP-1水平;B:ELISA试剂盒检测健康人和PAH患者MMP-2水平;C:ELISA试剂盒检测健康人和PAH患者MMP-7水平;D:ELISA试剂盒检测健康人和PAH患者MMP-9水平;E:ELISA试剂盒检测健康人和PAH患者MMP-10水平;F:ELISA试剂盒检测健康人和PAH患者MMP-14水平。**P < 0.01,***P < 0.001,****P < 0.0001。
Figure 2. Concentration levels of MMPs in serum of patients with Ctrl group and PAH
图 3 筛选3个shMMP-7干扰质粒对MMP-7蛋白水平和mRNA水平的干扰效率
A和B:western blot检测比较3个shMMP-7干扰质粒对MMP-7蛋白表达的干扰效率; C:qRT-PCR检测比较3个shMMP-7干扰质粒对MMP-7 mRNA的干扰效率。*P < 0.05,**P < 0.01,***P < 0.001,****P < 0.0001。
Figure 3. Interference efficiency of three shMMP-7 interfering plasmids screened on MMP-7 protein level and mRNA level
图 5 MMP-1过表达质粒和MMP-7干扰质粒对PAH的蛋白表达水平和病理作用
A-C:western blot检测过表达MMP-1质粒和干扰MMP-7质粒的转染效率; D:HE染色观察MMP-1和MMP-7对PAH的形态学影响(40×);E:Masson染色观察MMP-1和MMP-7对PAH肌纤维和胶原纤维的影响(40×)。****P < 0.0001。
Figure 5. Protein expression levels and pathological effects of MMP-1 overexpression plasmid and MMP-7 interference plasmid on PAH
表 1 临床PAH患者和健康人的基线资料表[
$ \bar x \pm s $ /n(%)]Table 1. Baseline data table of clinical PAH patients and healthy individuals [
$ \bar x \pm s $ /n(%)]项目 健康人(n = 16) PAH患者(n = 15) 年龄(岁) 31.69 ± 11.45 69.07 ± 11.11 性别(女性) 10(62.50) 4(26.67) BMI(cm/kg2) 22.13 ± 2.68 23.60 ± 5.49 NYHA心功能等级 0 16(100.00) 0(0.00) 1 0(0.00) 6(40.00) 2 0(0.00) 9(60.00) 6MWD(m) 593.00 ± 69.19 508.67 ± 102.102 BNP(pg/mL) 55.19 ± 15.71 139.13 ± 89.37 mPAP(mmHg) 19.62 ± 1.20 19.86.25 ± 3.46 HR(次/min) ≤80 11(68.75) 10(66.67) > 80 5(31.25) 5(33.33) TGs(mmol/L) 1.74 ± 0.50 1.45 ± 0.99 LDL(mmol/L) 2.71 ± 0.55 2.63 ± 0.70 TC(mmol/L) 3.87 ± 0.55 4.41 ± 0.94 HB(g/L) 135.56 ± 11.37 141.47 ± 20.43 -
[1] Deng L,Blanco F J,Stevens H,et al. Microrna-143 activation regulates smooth muscle and endothelial cell crosstalk in pulmonary arterial hypertension[J]. Circ Res,2015,117(10):870-883. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.306806 [2] Boutet K,Montani D,Jaïs X,et al. Therapeutic advances in pulmonary arterial hypertension[J]. Ther Adv Respir Dis,2008,2(4):249-265. doi: 10.1177/1753465808094762 [3] Liu Y,Zhang H,Yan L,et al. Mmp-2 and mmp-9 contribute to the angiogenic effect produced by hypoxia/15-hete in pulmonary endothelial cells[J]. J Mol Cell Cardiol,2018,121:36-50. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2018.06.006 [4] Tuder R M,Stacher E,Robinson J,et al. Pathology of pulmonary hypertension[J]. Clin Chest Med,2013,34(4):639-650. doi: 10.1016/j.ccm.2013.08.009 [5] George J,Sun J,D'armiento J. Transgenic expression of human matrix metalloproteinase-1 attenuates pulmonary arterial hypertension in mice[J]. Clin Sci (Lond),2012,122(2):83-92. doi: 10.1042/CS20110295 [6] Takahashi J,Orcholski M,Yuan K,et al. Pdgf-dependent β-catenin activation is associated with abnormal pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell proliferation in pulmonary arterial hypertension[J]. FEBS Lett,2016,590(1):101-109. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.12038 [7] Safdar Z,Tamez E,Chan W,et al. Circulating collagen biomarkers as indicators of disease severity in pulmonary arterial hypertension[J]. JACC Heart Fail,2014,2(4):412-421. doi: 10.1016/j.jchf.2014.03.013 [8] Pittayapruek P,Meephansan J,Prapapan O,et al. Role of matrix metalloproteinases in photoaging and photocarcinogenesis[J]. Int J Mol Sci,2016,17(6):868. doi: 10.3390/ijms17060868 [9] Yao J,Xiong M,Tang B,et al. Simvastatin attenuates pulmonary vascular remodelling by down-regulating matrix metalloproteinase-1 and -9 expression in a carotid artery-jugular vein shunt pulmonary hypertension model in rats[J]. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg,2012,42(5):e121-127. doi: 10.1093/ejcts/ezs445 [10] Lee E,Grodzinsky A J,Libby P,et al. Human vascular smooth muscle cell-monocyte interactions and metalloproteinase secretion in culture[J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol,1995,15(12):2284-2289. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.15.12.2284 [11] Lepetit H,Eddahibi S,Fadel E,et al. Smooth muscle cell matrix metalloproteinases in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension[J]. Eur Respir J,2005,25(5):834-842. doi: 10.1183/09031936.05.00072504 [12] Chi P L,Cheng C C,Hung C C,et al. Mmp-10 from m1 macrophages promotes pulmonary vascular remodeling and pulmonary arterial hypertension[J]. Int J Biol Sci,2022,18(1):331-348. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.66472 [13] Galiè N,Hoeper M M,Humbert M,et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension[J]. Eur Respir J,2009,34(6):1219-1263. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00139009 [14] Yancy C W,Jessup M,Bozkurt B,et al. 2013 accf/aha guideline for the management of heart failure: Executive summary: A report of the american college of cardiology foundation/american heart association task force on practice guidelines[J]. Circulation,2013,128(16):1810-1852. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0b013e31829e8807 [15] Condon D F,Agarwal S,Chakraborty A,et al. Novel mechanisms targeted by drug trials in pulmonary arterial hypertension[J]. Chest,2022,161(4):1060-1072. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2021.10.010 [16] Benza R L,Miller D P,Gomberg-Maitland M,et al. Predicting survival in pulmonary arterial hypertension: Insights from the registry to evaluate early and long-term pulmonary arterial hypertension disease management (reveal)[J]. Circulation,2010,122(2):164-172. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.898122 [17] Voelkel N F,Gomez-Arroyo J,Abbate A,et al. Pathobiology of pulmonary arterial hypertension and right ventricular failure[J]. Eur Respir J,2012,40(6):1555-1565. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00046612 [18] Harbaum L,Rhodes C J,Wharton J,et al. Mining the plasma proteome for insights into the molecular pathology of pulmonary arterial hypertension[J]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med,2022,205(12):1449-1460. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202109-2106OC [19] Overall C M,López-Otín C. Strategies for mmp inhibition in cancer: Innovations for the post-trial era[J]. Nat Rev Cancer,2002,2(9):657-672. doi: 10.1038/nrc884 [20] Drwal E,Rak A,Tworzydło W,et al. "Real life" polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (pah) mixtures modulate hcg,hpl and hplgf levels and disrupt the physiological ratio of mmp-2 to mmp-9 and vegf expression in human placenta cell lines[J]. Reprod Toxicol,2020,95:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.reprotox.2020.02.006 [21] Schäfer M,Ivy D D,Nguyen K,et al. Metalloproteinases and their inhibitors are associated with pulmonary arterial stiffness and ventricular function in pediatric pulmonary hypertension[J]. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol,2021,321(1):H242-h252. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00750.2020 [22] Thenappan T,Chan S Y,Weir E K. Role of extracellular matrix in the pathogenesis of pulmonary arterial hypertension[J]. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol,2018,315(5):H1322-h1331. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00136.2018 [23] Frisdal E,Gest V,Vieillard-Baron A,et al. Gelatinase expression in pulmonary arteries during experimental pulmonary hypertension[J]. Eur Respir J,2001,18(5):838-845. doi: 10.1183/09031936.01.00084601 [24] Uzui H,Lee J D,Shimizu H,et al. The role of protein-tyrosine phosphorylation and gelatinase production in the migration and proliferation of smooth muscle cells[J]. Atherosclerosis,2000,149(1):51-59. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9150(99)00295-6 [25] George S J,Johnson J L,Angelini G D,et al. Adenovirus-mediated gene transfer of the human timp-1 gene inhibits smooth muscle cell migration and neointimal formation in human saphenous vein[J]. Hum Gene Ther,1998,9(6):867-877. doi: 10.1089/hum.1998.9.6-867 [26] Botney M D,Liptay M J,Kaiser L R,et al. Active collagen synthesis by pulmonary arteries in human primary pulmonary hypertension[J]. Am J Pathol,1993,143(1):121-129. [27] Wei B,Du J,Li J,et al. The modulating effect of l-arginine on collagen metabolism of pulmonary artery in pulmonary hypertension induced by a left-to-right shunt[J]. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi,2002,82(18):1273-1275. [28] Dieffenbach P B,Mallarino Haeger C,Rehman R,et al. A novel protective role for matrix metalloproteinase-8 in the pulmonary vasculature[J]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med,2021,204(12):1433-1451. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202108-1863OC [29] Wright J L,Tai H,Wang R,et al. Cigarette smoke upregulates pulmonary vascular matrix metalloproteinases via tnf-alpha signaling[J]. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol,2007,292(1):L125-133. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00539.2005 [30] Saunders W B, Bayless K J, Davis G E. Mmp-1 activation by serine proteases and mmp-10 induces human capillary tubular network collapse and regression in 3d collagen matrices[J]. J Cell Sci, 2005, 118(Pt 10): 2325-2340. [31] Cui N,Hu M,Khalil R A. Biochemical and biological attributes of matrix metalloproteinases[J]. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci,2017,147:1-73. [32] Arvidsson M,Ahmed A,Bouzina H,et al. Matrix metalloproteinase 7 in diagnosis and differentiation of pulmonary arterial hypertension[J]. Pulm Circ,2019,9(4):1-8. [33] Rosanò L,Spinella F,Di Castro V,et al. Endothelin receptor blockade inhibits molecular effectors of kaposi's sarcoma cell invasion and tumor growth in vivo[J]. Am J Pathol,2003,163(2):753-762. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63702-9 [34] Stenmark K R,Fagan K A,Frid M G. Hypoxia-induced pulmonary vascular remodeling: Cellular and molecular mechanisms[J]. Circ Res,2006,99(7):675-691. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000243584.45145.3f -






 下载:
下载: