Clinicopathological Features and Prognosis of Mucinous Breast Carcinoma
-
摘要:
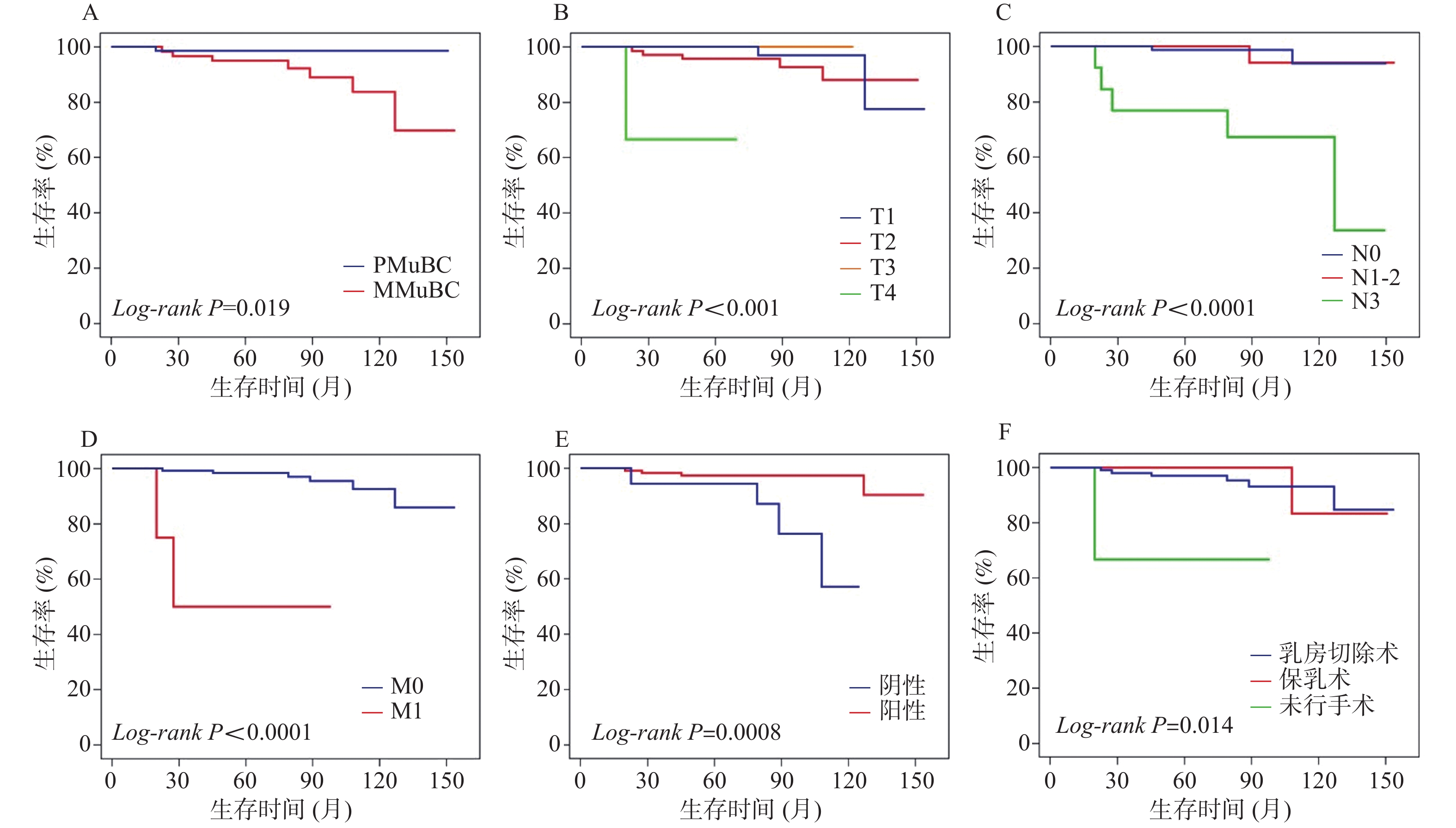
目的 探讨乳腺粘液腺癌(mucinous breast carcinoma,MuBC)的临床病理特征及其与预后的关系,为患者个性化治疗方案的制订提供参考。 方法 回顾性收集2008年1月至2021年9月云南省肿瘤医院收治的139例MuBC患者的临床及病理资料,将其分为76例单纯型粘液腺癌(pure mucinous breast carcinoma,PMuBC)组和63例混合型粘液腺癌(mixed mucinous breast carcinoma,MMuBC)组并进行比较。采用COX比例风险回归模型确定MuBC的预后因素,Kaplan-Meier法和log-rank检验用于生存分析。 结果 PMuBC组的10 a总生存率较MMuBC组高(98.6% vs 83.7%,P = 0.019)。PMuBC组淋巴结未受累的比例(81.6% vs 47.6%,P < 0.001)高于MMuBC组。COX多因素分析显示:肿瘤大小为T1期(P = 0.005)、肿瘤大小为T2期(P = 0.006)和PR阳性(P = 0.033)是预后的保护因素。淋巴结受累达N3期(P = 0.052)与合并远处转移(P = 0.025)是预后的危险因素。 结论 肿瘤大小、淋巴结转移情况、是否远处转移和PR状态是MuBC的独立预后因素,PMuBC较MMuBC淋巴结转移率低、PR阳性率高,预后更好。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the clinicopathological characteristics of mucinous breast carcinoma (MuBC) and its relationship with prognosis, so as to provide reference for patients to make a personalized treatment plan. Methods The clinical and pathological data of 139 MuBC patients admitted to Yunnan Cancer Hospital from January 2008 to September 2021 were retrospectively collected. They were divided into pure mucinous breast carcinoma (PMuBC) group (n = 76) and mixed mucinous breast carcinoma (MMuBC) group (n = 63), and compared between two groups. COX proportional hazards regression model was used to determine the prognostic factors of MuBC.Kaplan-Meier and log-rank tests were used for survival analysis. Results The 10-year overall survival rate of PMuBC group was higher than that of MMuBC group (98.6% vs 83.7%, P = 0.019). The proportion of uninvolved lymph nodes (81.6% vs 47.6%, P < 0.001) in PMuBC group was higher than those in MMuBC group.COX multivariate analysis showed that tumor size was stage T1 (P = 0.005), tumor size was stage T2 (P = 0.006) and positive PR (P = 0.033) were prognostic protective factors. Lymph node involvement reached stage N3 (P = 0.052) and distant metastasis (P = 0.025) are prognostic risk factors. Conclusions Tumor size, lymph node metastasis, distant metastasis and PR status are independent prognostic factors for MuBC. Compared with MMuBC, PMuBC has lower lymph node metastasis rate, higher positive rate of PR and better prognosis. -
Key words:
- Mucinous breast carcinoma /
- Pathological feature /
- Prognosis /
- Survival
-
表 1 139例MuBC患者的特征及不同病理类型的比较[n(%)]
Table 1. Characteristics of 139 patients with MuBC and comparison of different pathological types [n(%)]
变量 总MuBC(n = 139) PMuBC(n = 76) MMuBC(n = 63) χ2/W P 诊断年龄 0.028 0.868 ≤45岁 54(38.8) 30(39.5) 24(38.1) > 45岁 85(61.2) 46(60.5) 39(61.9) 绝经 3.578 0.059 是 65(46.8) 30(39.5) 35(55.6) 否 74(53.2) 46(60.5) 28(44.4) T分期 4363 0.822 T1 52(37.4) 28(36.8) 24(38.1) T2 77(55.4) 42(55.3) 35(55.5) T3 7(5.0) 5(6.6) 2(3.2) T4 3(2.2) 1(1.3) 2(3.2) N分期 4486.5 < 0.001* N0 92(66.2) 62(81.6) 30(47.6) N1-2 34(24.5) 11(14.5) 23(36.5) N3 13(9.3) 3(3.9) 10(15.9) M分期 0.490 0.484 M1 4(2.9) 1(1.3) 3(4.8) M0 135(97.1) 75(98.7) 60(95.2) ER状态 0.968 0.325 阳性 130(93.5) 73(96.1) 57(90.5) 阴性 9(6.5) 3(3.9) 6(9.5) PR状态 3.801 0.051 阳性 121(87.1) 70(92.1) 51(81.0) 阴性 18(12.9) 6(7.9) 12(19.0) HER-2状态 7.038 0.031* 扩增 12(8.6) 4(5.3) 8(12.7) 未扩增 76(54.7) 49(64.5) 27(42.9) 未知 51(36.7) 23(30.3) 28(44.4) 手术方式 8.722 0.006* 未行手术 3(2.2) 2(2.6) 1(1.6) 乳房切除术 108(77.7) 52(68.4) 56(88.9) 保乳术 28(20.1) 22(28.9) 6(9.5) 化疗 6.637 0.010* 是 110(79.1) 54(71.1) 56(88.9) 否 29(20.9) 22(28.9) 7(11.1) 放疗 0.932 0.334 是 60(43.2) 30(39.5) 30(47.6) 否 79(56.8) 46(60.5) 33(52.4) 内分泌治疗 11.357 0.003* 是 106(76.3) 63(82.9) 43(68.3) 否 11(7.9) 8(10.5) 3(4.8) 未知 22(15.8) 5(6.6) 17(27.0) 结局 4.421 0.035* 死亡 8(5.8) 1(1.3) 7(11.1) 生存 131(94.2) 75(98.7) 56(88.9) *P < 0.05。 表 2 139例MuBC患者的COX单因素和多因素分析
Table 2. COX univariate and multivariate analysis of 139 MuBC patients
变量 单因素分析 多因素分析 HR(95%CI) P HR(95%CI) P 诊断年龄 ≤45岁 参考 > 45岁 0.43(0.10~1.81) 0.249 病理类型 PMBC 参考 MMBC 8.13(1.00~66.17) 0.050* 5.49(0.33~92.12) 0.237 绝经 否 参考 是 0.75(0.18~3.14) 0.693 T分期 T4 参考 T1 0.03(0.002~0.38) 0.007* 0.006(0~0.22) 0.005* T2 0.05(0.005~0.53) 0.013* 0.007(0~0.24) 0.006* T3 0(0~) 0.986 0(0~) 0.991 N分期 N0 参考 N1-2 1.29(0.12~14.26) 0.835 1.10(0.08~15.38) 0.942 N3 16.01(3.09~83.01) 0.001* 9.78(0.98~97.90) 0.052 M分期 M0 参考 M1 24.67(4.45~136.71) < 0.001* 61.03(1.66~2240.00) 0.025* ER状态 阴性 参考 阳性 22.28(0~无限大) 0.652 PR状态 阴性 参考 阳性 0.12(0.03~0.53) 0.005* 0.05(0.004~0.79) 0.033* 化疗 否 参考 是 26.36(0.006~114558.7) 0.444 放疗 否 参考 是 1.43(0.36~5.79) 0.614 手术方式 未行手术 参考 乳房切除术 0.09(0.01-0.80) 0.031* 7.55(0.21~277.94) 0.272 保乳术 0.06(0.003-0.94) 0.045* 28.68(0.23~3536.36) 0.172 *P < 0.05; CI:置信区间;HR:风险比。 -
[1] Sung H,Ferlay J,Siegel R L,et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin,2021,71(3):209-249. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660 [2] Leil,Yu X,Chen B,et al. Clinicopathological characteristics of mucinous breast cancer: A retrospective analysis of a 10-Year study[J]. PLoS One,2016,11(5):e0155132. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0155132 [3] Budzik M P,Fudalej M M,Badowska-Kozakiewicz A M. Histopathological analysis of mucinous breast cancer subtypes and comparison with invasive carcinoma of no special type[J]. Sci Rep,2021,11(1):5770. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-85309-z [4] Gannon L M,Cotter M B,Quinn C M. The classification of invasive carcinoma of the breast[J]. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther,2013,13(8):941-954. doi: 10.1586/14737140.2013.820577 [5] Marrazzo E,Frusone F,Milana F,et al. Mucinous breast cancer: A narrative review of the literature and a retrospective tertiary single-centre analysis[J]. Breast,2020,49:87-92. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2019.11.002 [6] Li C I. Risk of mortality by histologic type of breast cancer in the United States[J]. Horm Cancer,2010,1(3):156-165. doi: 10.1007/s12672-010-0016-8 [7] Hu T,Huang J,Fang K. Overall survival in patients with mucinous carcinoma of breast:A population-based study[J]. Int J Gen Med,2021,14:9991-10001. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S343137 [8] Cserni G. Histological type and typing of breast carcinomas and the WHO classification changes over time[J]. Pathologica,2020,112(1):25-41. doi: 10.32074/1591-951X-1-20 [9] Castaneda C A,Andrés E,Barcena C,et al. Behaviour of breast cancer molecular subtypes through tumour progression[J]. Clin Transl Oncol,2012,14(6):481-485. doi: 10.1007/s12094-012-0827-x [10] Rakha E A,Tse G M,Quinn C M. An update on the pathological classification of breast cancer[J]. Histopathology,2023,82(1):5-16. doi: 10.1155/2022/1230812 [11] Sas-KorczyŃska B,MituŚ J,Stelmach A,et al. Mucinous breast cancer - clinical characteristics and treatment results in patients treated at the Oncology Centre in Kraków between 1952 and 2002[J]. Contemp Oncol (Pozn),2014,18(2):120-123. [12] 西部多中心临床合作流行病学调查组. 我国乳腺癌发病年龄前移 [J]. 中国肿瘤临床与康复, 2015, 22(10): 1274. [13] Tseng H S,Lin C,Chan S E,et al. Pure mucinous carcinoma of the breast: clinicopathologic characteristics and long-term outcome among Taiwan residents women[J]. World J Surg Oncol,2013,11:139. doi: 10.1186/1477-7819-11-139 [14] Cao A Y,He M,Liu Z B,et al. Outcome of pure mucinous breast carcinoma compared to infiltrating ductal carcinoma: a population-based study from China[J]. Annals of Surgical Oncology,2012,19(9):3019-3027. doi: 10.1245/s10434-012-2322-6 [15] Pan B,Yao R,Shi J,et al. Prognosis of subtypes of the mucinous breast carcinoma in Chinese women: a population-based study of 32-year experience (1983-2014)[J]. Oncotarget,2016,7(25):38864-38875. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8778 [16] Zhang M,Teng X D,Guo X X,et al. Clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis of mucinous breast carcinoma[J]. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol,2014,140(2):265-2659. doi: 10.1007/s00432-013-1559-1 [17] Skotnicki P,Sas-Korczynska B,Strzepek L,et al. Pure and mixed mucinous carcinoma of the breast: A comparison of clinical outcomes and treatment results[J]. The Breast Journal,2016,22(5):529-534. doi: 10.1111/tbj.12621 [18] Yu P,Liu P,Zou Y,et al. Breast-conserving therapy shows better prognosis in mucinous breast carcinoma compared with mastectomy: A SEER population-based study[J]. Cancer Med,2020,9(15):5381-5391. doi: 10.1002/cam4.3202 [19] Di Saverio S,Gutierrez J,Avisar E. A retrospective review with long term follow up of 11,400 cases of pure mucinous breast carcinoma[J]. Breast Cancer Res Treat,2008,111(3):541-547. doi: 10.1007/s10549-007-9809-z [20] Zhou X,Zheng Z,Li Y,et al. The clinical features and prognosis of patients with mucinous breast carcinoma compared with those with infiltrating ductal carcinoma: a population-based study[J]. BMC Cancer,2021,21(1):536. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08262-0 [21] Wu S L,Gai J D,Yu X M,et al. A novel nomogram and risk classification system for predicting lymph node metastasis of breast mucinous carcinoma:A SEER-based study[J]. Cancer Med,2022,11(24):4767-4783. [22] Komenaka I K,El-Tameer M B,Troxel A,et al. Pure mucinous carcinoma of the breast[J]. The American Journal of Surgery,2004,187(4):528-532. doi: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2003.12.039 [23] Barkley C R,Ligibel J A,Wong J S,et al. Mucinous breast carcinoma: a large contemporary series[J]. American Journal of Surgery,2008,196(4):549-551. doi: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2008.06.013 [24] Gwark S C,Lee H S,Lee Y,et al. Clinical implication of HER2 status in hormone receptor-positive mucinous breast cancer[J]. Annals of Surgical Oncology,2019,26(7):2166-2174. doi: 10.1245/s10434-019-07332-9 [25] Kangleon-Tan H L,Sim J,You J Y,et al. Omission of chemotherapy for hormone receptor-positive and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative breast cancer:patterns of treatment and outcomes from the Korean Breast Cancer Society Registry[J]. Ann Surg Treat Res,2022,103(6):313-322. [26] Kim H S,Lee J U,Yoo T K,et al. Omission of chemotherapy for the treatment of mucinous breast cancer: A nationwide study from the Korean breast cancer society[J]. J Breast Cancer,2019,22(4):599-612. doi: 10.4048/jbc.2019.22.e46 [27] Chen R,Wang Y,Li T,et al. Oncotype DX 21-gene test has a low recurrence score in both pure and mixed mucinous breast carcinoma[J]. Oncol Lett,2021,22(5):771. doi: 10.3892/ol.2021.13032 -






 下载:
下载: