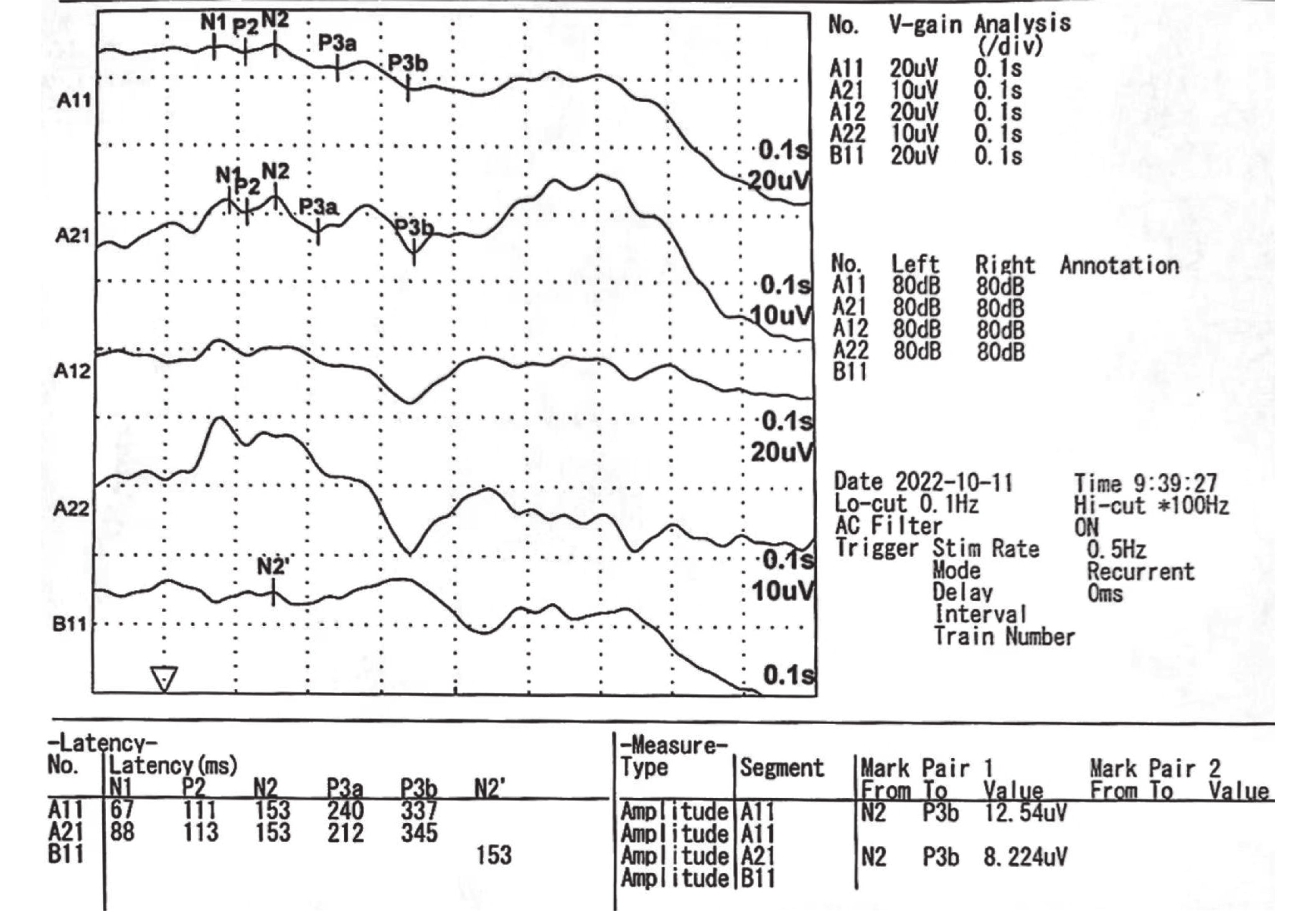
The Value of Urinary AD7c-NTP and P300 in the Diagnosis of AD-derived MCI
-
摘要:
目的 探讨联合尿AD7c-NTP水平检测与P300检查在AD源性轻度认知功能障碍(MCI)诊断中的价值。 方法 选取健康对照组78例,MCI组72例,AD组108例,通过MMSE及ADL量表评定,采用酶联免疫吸附法(ELLSA)测定各组患者尿液中AD7c-NTP值及对各组患者进行事件相关电位(ERP)P300检查。 结果 尿液AD7c-NTP含量检测及事件相关电位(ERP)P300检查潜伏期时间在健康对照组、MCI组及AD组中均有不同,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);进行两两比较,健康对照组与MCI组、MCI组与AD组、健康对照组与AD组均有不同,差异具有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。 结论 尿AD7c-NTP水平升高直接提示轻度认知功能障碍(MCI)至AD过程中神经元受损情况;而P300检查异常提示脑功能受损,二者具有共同的病理生理学过程。通过联合检验学与功能学检查,可以有效提高早期AD的检出率,从而可以作为临床早期诊断、治疗AD的重要参考指标,同时也可以作为筛查MCI与早期AD的参考依据。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the value of urine AD7c-NTP level test combined with ERP P300 in the diagnosis of AD-derived mild cognitive impairment (MCI). Methods 78 healthy subjects in control group, 72 in MCI group and 108 in AD group were selected and assessed by MMSE and ADL scale. AD7c-NTP levels in urine of each group were determined by enzyme-linked immunosoradsorption method (ELLSA) and event-related potential (ERP) P300 tests were performed in each group. Results Urine AD7c-NTP and latent time of ERP P300 were siginificantly different among healthy control group, MCI group and AD group (P < 0.05). Pair-wise comparison showed that urine AD7c-NTP and latent time of ERP P300 were different among healthy control and MCI group, MCI group and AD group, and healthy control and AD group (P < 0.05). Conclusion The elevated AD7c-NTP in urine in this study indicated the neuronal damage from mild cognitive impairment (MCI) to AD. The abnormal P300 indicates the impaired brain function, and the two have the same pathophysiological process. These results showed that the detection rate of early AD can be effectively improved through the combination of laboratory and functional examination, which can be used as an important reference index for early diagnosis and treatment of AD, as well as a reference basis for screening MCI and early AD. -
表 1 实验研究对象一般资料比较 [(
$ \bar x \pm s $ )/n(%)]Table 1. Comparison of general data of experimental subjects [(
$ \bar x \pm s $ )/n(%)]项目 健康对照组 MCI AD χ2/F P 性别(男/女) 36/42 22/50 48/60 4.629 0.99 年龄(岁) 60.48 ± 6.93 60.8 ± 7.14 68.8 ± 7.20 41.89 0.000* 受教育年限(a) 9.35 ± 2.98 8.90 ± 2.50 8.51 ± 2.27 2.55 0.08 *P < 0.05。 表 2 MMSE及ADL评分在不同分组中的比较[(
$ \bar x \pm s $ )/n(%)]Table 2. Comparison of MMSE and ADL scores in different groups [(
$ \bar x \pm s $ )/n(%)]项目 健康对照组 MCI AD χ2/F P MMSE评分(分) 26.61 ± 1.76 20.33 ± 2.39 11.05 ± 2.59 1063.7 0.001* ADL评分(分) 7.07 ± 3.31 19.06 ± 1.72 34.40 ± 5.78 954.54 0.001* *P < 0.05。 表 3 尿AD7c-NTP水平与P300在不同分组中的比较[(
$ \bar x \pm s $ )/n(%)]Table 3. Urinary AD7c-NTP levels compared with P300 in different groups[(
$ \bar x \pm s $ )/n(%)]项目 健康对照组 MCI AD F P 尿AD7c-NTP(ng/mL) 0.82±0.14 1.50±0.48 2.55±0.75 228.15 0.001* P300潜伏期(ms) 330.7±16.41 363.7±15.29 389.3±26.64 174.6 0.001* *P < 0.05。 表 4 单独尿液AD7c-NTP水平检测、P300检查及两者联合检查对MCI的诊断效能
Table 4. Diagnostic efficacy of urine AD7c-NTP level alone,P300 and combined tests for MCI
项目 AUC(95%CI) 标准
错误a渐近
显著bP 尿AD7c-NTP 0.843(0.777~0.909) 0.034 0.000 0.001* P300潜伏期 0.830(0.764~0.897) 0.034 0.000 0.001* 2指标联合检测 0.929(0.892~0.967) 0.019 0.000 0.001* a.按非参数假定; b.原假设:真区域 = 0.5。*P < 0.05。 -
[1] 王雪莹,李明,卢志明,等. 阿尔茨海默病生物标志物应用指南及研究进展[J]. 中华预防医学杂志,2022,56(3):262-269. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112150-20210916-00902 [2] Knopman D S,Petersen R C. Mild cognitive impairment and midementia: A clinical perspective[J]. Mayo Clin Proc,2014,89(10):1452-1459. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2014.06.019 [3] Lane C A,Hardy J,Schott J M. Alzheimer’s disease[J]. European Journal of Neurology,2018,25(1):59-70. doi: 10.1111/ene.13439 [4] 中国痴呆与认知障碍写作组,中国医师协会神经内科医师分会认知障碍疾病专业委员会. 2018中国痴呆与认知障碍诊治指南(二): 阿尔茨海默病诊治指南[J]. 中华医学杂志,2018,98,(13):971-977. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2018.13.004 [5] 杨青,贾杰. 阿尔茨海默病相关指南及专家共识解读-全周期康复新视角[J]. 中国医刊,2021,56(1):22-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1070.2021.01.007 [6] 邹扬,任汝静,王刚. 阿尔茨海默病: 从临床诊断标准到神经病理诊断标准的进展和重塑[J]. 内科理论与实践,2015,10(2):131-134. [7] 孙梦莎,顾鸣敏. 阿尔茨海默病早期诊断研究进展[J]. 中国现代神经疾病杂志,2018,18(3):213-221. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6731.2018.03.011 [8] 李晓丹. 阿尔茨海默病生物标志物AD7c-NTP的研究现状[J]. 检验医学与临床床,2021,18(20):3056-3058. [9] 张立,刘洁,李蓉,等. 老年阿尔茨海默病患者脑电图和ERP内源性P300诱发电位变化特点及意义[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2022,42(20):5053-5057. [10] Gibbons H. Event-related brain potentials of temporal generalization: The P300 span marks the transition between time perception and time estimation[J]. Behavioral Neuroscience,2022,136(5):430-444. doi: 10.1037/bne0000530 [11] 戴文豪,陈杰,谢平,等. 运动相关皮层电位研究的知识图谱分析[J]. 中国生物医学工程学报,2022,41(3):360-369. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-8021.2022.03.012 [12] 马喆喆,巩尊科,温炜婷,等. 脑卒中注意障碍患者事件相关电位P300与注意评定量表的相关性分析[J]. 中国康复医学杂志,2022,37(8):1113-1115. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1242.2022.08.020 [13] Janca A,Ustün T B,Early T S,et al. The ICD-10 symptom checklist: A companion to the ICD-10 classification of mental and behavioural disorder[J]. Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology,1993,28(5):239-242. doi: 10.1007/BF00788743 [14] Sperling R A,Aisen P S,Beckett L A,et al. Toward defining the preclinical stages of Alzheimer,s disease: Recommendations from the national institute on aging-Alzheimer,s association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer,s disease[J]. Alzheimers Dement,2011,7(3):280-292. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2011.03.003 [15] Tsai L H,Madabhushi R. Alzheimer’s disease:A protective factor for the ageing brain[J]. NatLlre,2014,507(7493):439-440. [16] 张李娜,崔莉,刘智,等. 尿液AD7c-NTP检测在阿尔茨海默病早期诊断中的价值[J]. 脑与神经疾病杂志,2021,29(3):170-173. [17] 邹永明,田志岩,张惠红,等. 不同类型痴呆患者阿尔茨海默病相关神经丝蛋白水平和嗅觉功能差异的比较[J]. 中华老年医学杂志,2018,37(7):738-742. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-9026.2018.07.003 [18] 方涵,杨再兴. 阿尔茨海默病脑脊液和替代基质中生物标志物的研究进展[J]. 浙江临床医学,2020,22(4):596-598. [19] Levy S,McConville M,Lazaro G A,et al. Competitive ELISA studies of neural thread protein in urine in Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis,2007,21(1):24-33. doi: 10.1002/jcla.20159 [20] 闫金秋,巩尊科,马喆喆,等. 经颅直流电刺激在脑卒中后执行功能障碍患者中的临床研究[J]. 神经疾病与精神卫生,2022,22(1):34-39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6574.2022.01.007 [21] Yerlikaya D,Hünerli-Gündüz D,Fide E,et al. The reliability of P300 and the influence of age,gender and education variables in a 50 years and older normative sample[J]. Int J Psychophysiol,2022,181:1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2022.08.002 [22] Olichney J,Xia J,Church K J, et al. Predictive power of cognitive biomarkers in neurodegenerative disease drug development: Utility of the P300 event-related potential[J]. Neural Plasticity,2022,2022:2104880. [23] 张玉蓉,方堃,王芳,等. 不同尿AD7c-NTP水平的体检人群血尿酸水平与胰岛素抵抗的关系[J]. 重庆医学,2021,50(10):1672-1675. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8348.2021.10.011 [24] 曹友林,余青龙,王振国,等. AD相关神经丝蛋白、尿酸、hs-CRP水平与老年腔隙性脑梗死患者认知功能受损程度的相关性[J]. 临床和实验医学杂志志,2022,21(10):1030-1034. -






 下载:
下载: