Effects of Scutellarin on MMP2,MMP9 and TIMP-1 Protein in Liver of Obese Rats with Chronic Liver Injury by High Glucose and Fat Diet
-
摘要:
目的 研究在高脂高糖饮食诱导建立的肥胖大鼠慢性肝损伤肝脏纤维化模型中,灯盏乙素(SCU)对其发病机制的影响,探讨SCU能否通过促进MMP2、MMP9,抑制TIMP-1的表达改善肝脏纤维化程度。 方法 采用高脂高糖饮食诱导慢性肝损伤肝脏纤维化模型,SCU和姜黄素(CUR)灌胃治疗8周后,HE染色观察肝组织病理变化 ;Masson染色观察胶原纤维在肝脏中的沉积;Western blot和免疫组织化学染色观察肝脏组织TIMP-1、MMP2、MMP9的表达。 结果 在肝脏组织中,模型组大鼠肝细胞形态不规则细胞水肿,并有大量脂肪空泡出现,汇管区有蓝色胶原纤维沉积,不同剂量的SCU和CUR干预后,脂肪空泡减少,肝细胞肿胀情况减少,纤维化程度得到改善。在大鼠肝细胞中,模型组MMP2、MMP9蛋白表达下调(P < 0.01),不同剂量SCU和CUR干预后MMP2、MMP9蛋白表达上调(P < 0.01);模型组TIMP-1蛋白表达上调(P < 0.01),不同剂量SCU和CUR治疗后TIMP-1蛋白表达下调(P < 0.01),没有很明显的剂量依赖性。 结论 SCU可能通过促进MMP2、MMP9,抑制TIMP-1蛋白的表达,减少ECM的积累改善肥胖引起的肝脏纤维化。 -
关键词:
- 慢性肝损伤肝脏纤维化 /
- 灯盏乙素 /
- 基质金属蛋白酶 /
- 基质金属蛋白酶组织抑制剂
Abstract:Objective To investigate the effect of scutellarin (SCU) on liver fibrosis in obese rats with chronic liver injury induced by high-fat and high-sugar diet, and to explore the possibility of SCU to ameliorate the degree of liver fibrosis by promoting the expression of MMP2 and MMP9 and inhibiting the expression of TIMP-1. Methods The model of chronic liver injury and liver fibrosis was induced by high-fat and high-sugar diet. After 8 weeks of intragastric administration of SCU and curcumin (CUR), HE staining was used to observe the pathology of liver tissue; Masson staining was used to detect the deposition of collagen fibers in liver tissue; and western blot and immunohistochemical staining were used to observe the expression of TIMP-1, MMP2 and MMP9 in liver tissue. Results In the model group, hepatocytes were swollen with irregular hepatocyte morphology, a large number of fat vacuoles, and blue collagen fibers were deposited in the confluent area. After different doses of SCU and CUR intervention, the fat vacuoles were reduced, the swelling of hepatocytes was decreased, and the degree of fibrosis was improved. In liver tissue cells, the protein expressions of MMP2 and MMP9 were down-regulated in the model group (P < 0.01), and up-regulated after treatment with different doses of SCU and CUR (P < 0.01). The expression of TIMP-1 protein was up-regulated in the model group (P < 0.01), and down-regulated after treatment with different doses of SCU and CUR (P < 0.01), and the dose dependence was not significant. Conclusion SCU may improve liver fibrosis caused by obesity by promoting MMP2 and MMP9, inhibiting the expression of TIMP-1 protein and reducing the accumulation of ECM. -
Key words:
- Liver fibrosis in chronic liver injury /
- Scutellarin /
- MMPs /
- TIMPs
-
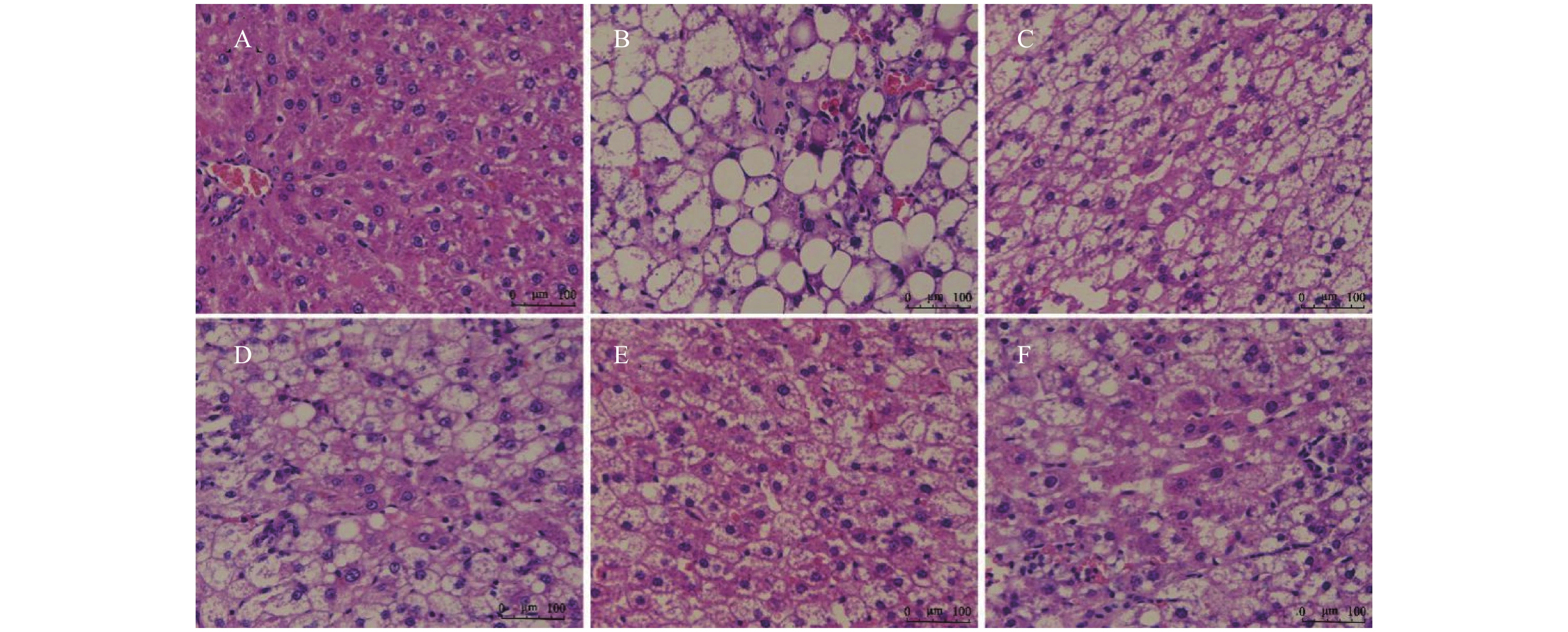
图 4 肝脏组织细胞MMP2、MMP9、TIMP-1蛋白的表达(×400)
A:正常组MMP2表达;B:模型组MMP2表达;C:SCU-25 MMP2表达; D:SCU-50 MMP2表达;E:SCU-100 MMP2表;F:CUR-200 MMP2表达;G:正常组MMP9表达;H:模型组MMP9表达;I:SCU-25 MMP9表达;J:SCU-50 MMP9表达;K:SCU-100 MMP9表达;L:CUR-200 MMP9表达;M:正常组TIMP-1表达;N:模型组TIMP-1表达;O:SCU-25 TIMP-1表达;P:SCU-50 TIMP-1表达;Q:SCU-100 TIMP-1表达;R:CUR-200 TIMP-1表达。与正常组比较,#P < 0.05;与模型组比较,*P < 0.05。
Figure 4. Expression of MMP2,MMP9,TIMP-1 proteins in liver tissue cells(×400)
-
[1] George J,Tsuchishima M,Tsutsumi M. Metabolism of N-nitrosodimethylamine,methylation of macromolecules,and development of hepatic fibrosis in rodent models[J]. J Mol Med (Berl),2020,98(9):1203-1213. doi: 10.1007/s00109-020-01950-7 [2] Oakley F. Interrogating mechanisms of liver fibrosis with omics[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol,2022,19(2):89-90. doi: 10.1038/s41575-021-00567-6 [3] Jun J H,Park S Y,Park S,et al. Formyl peptide receptor 2 alleviates hepatic fibrosis in liver cirrhosis by vascular remodeling[J]. Int J Mol Sci,2021,22(4):2-13. [4] Perez-Is L,Collazos J,de la Fuente B,et al. 24-month decline of non-invasive liver fibrosis markers in HCV-mono and HCV/HIV coinfection after direct-acting antiviral therapy[J]. Sci Rep,2022,12(1):3828. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-07548-y [5] George J,Tsutsumi M,Tsuchishima M. MMP-13 deletion decreases profibrogenic molecules and attenuates N-nitrosodimethylamine-induced liver injury and fibrosis in mice[J]. J Cell Mol Med,2017,21(12):3821-3835. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13304 [6] Xie H,Su D,Zhang J,et al. Raw and vinegar processed Curcuma wenyujin regulates hepatic fibrosis via bloking TGF-beta/Smad signaling pathways and up-regulation of MMP-2/TIMP-1 ratio[J]. J Ethnopharmacol,2020,246(1):111768. [7] Li X M,Peng J H,Sun Z L,et al. Chinese medicine CGA formula ameliorates DMN-induced liver fibrosis in rats via inhibiting MMP2/9,TIMP1/2 and the TGF-beta/Smad signaling pathways[J]. Acta Pharmacol Sin,2016,37(6):783-793. doi: 10.1038/aps.2016.35 [8] Attia H,Al-Rasheed N,Mohamad R,et al. The antifibrotic and fibrolytic properties of date fruit extract via modulation of genotoxicity,tissue-inhibitor of metalloproteinases and nuclear factor- kappa B pathway in a rat model of hepatotoxicity[J]. BMC Complement Altern Med,2016,16(1):414. doi: 10.1186/s12906-016-1388-2 [9] Peng L,Wen L,Shi Q F,et al. Scutellarin ameliorates pulmonary fibrosis through inhibiting NF-kappaB/NLRP3-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition and inflammation[J]. Cell Death Dis,2020,11(11):978. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-03178-2 [10] 王银辉,耿玲,李辉. 灯盏乙素抗大鼠肝纤维化作用的研究[J]. 中国中药杂志,2015,40(10):1999-2003. [11] 杨永锐,王丽媛,李海雯,等. 灯盏乙素抑制NOX的表达改善非酒精性脂肪性肝病肝脏纤维化的研究[J]. 昆明医科大学学报,2022,43(7):38-45. [12] Piche M E,Tchernof A,Despres J P. Obesity phenotypes,diabetes,and cardiovascular diseases[J]. Circ Res,2020,126(11):1477-1500. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.316101 [13] Polyzos S A,Kountouras J,Mantzoros C S. Obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease:From pathophysiology to therapeutics[J]. Metabolism,2019,92(4):82-97. [14] Devaraj E,Perumal E,Subramaniyan R,et al. Liver fibrosis:Extracellular vesicles mediated intercellular communication in perisinusoidal space[J]. Hepatology,2022,76(1):275-285. doi: 10.1002/hep.32239 [15] Roehlen N,Crouchet E,Baumert T F. Liver fibrosis:Mechanistic concepts and therapeutic perspectives[J]. Cells,2020,9(4):2-43. [16] Aydin M M,Akcali K C. Liver fibrosis[J]. Turk J Gastroenterol,2018,29(1):14-21. doi: 10.5152/tjg.2018.17330 [17] 李晋,徐尚福,李远洋,等. 小柴胡汤对肝纤维化大鼠肝脏MMP-2、TIMP-2表达的影响[J]. 辽宁中医杂志,2018,45(5):1066-1068. doi: 10.13192/j.issn.1000-1719.2018.05.053 [18] Ye J,Zeng B,Zhong M,et al. Scutellarin inhibits caspase-11 activation and pyroptosis in macrophages via regulating PKA signaling[J]. Acta Pharm Sin B,2021,11(1):112-126. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2020.07.014 [19] Miao Z,Lai Y,Zhao Y,et al. Scutellarein aggravated carbon tetrachloride-induced chronic liver injury in gut microbiota-dysbiosis mice[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med,2020,2020(11):8811021. [20] Mansour-Ghanaei F,Pourmasoumi M,Hadi A,et al. Efficacy of curcumin/turmeric on liver enzymes in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials[J]. Integr Med Res,2019,8(1):57-61. doi: 10.1016/j.imr.2018.07.004 [21] Dkab C,Zzb C,Lc A,et al. Curcumin blunts epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocytes to alleviate hepatic fibrosis through regulating oxidative stress and autophagy[J]. Redox Biology,2020,36(5):101600. [22] Zhang L,Pan X,Xu L,et al. Mitochondria-targeted curcumin loaded CTPP-PEG-PCL self-assembled micelles for improving liver fibrosis therapy[J]. RSC Adv,2021,11(10):5348-5360. doi: 10.1039/D0RA09589C [23] Medeiros T,Saraiva G N,Moraes L A,et al. Liver fibrosis improvement in chronic hepatitis C after direct acting-antivirals is accompanied by reduced profibrogenic biomarkers-a role for MMP-9/TIMP-1[J]. Dig Liver Dis,2020,52(10):1170-1177. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2020.05.004 -






 下载:
下载: