Correlation between Plasma proBDNF Level and Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome with Depressive Symptoms
-
摘要:
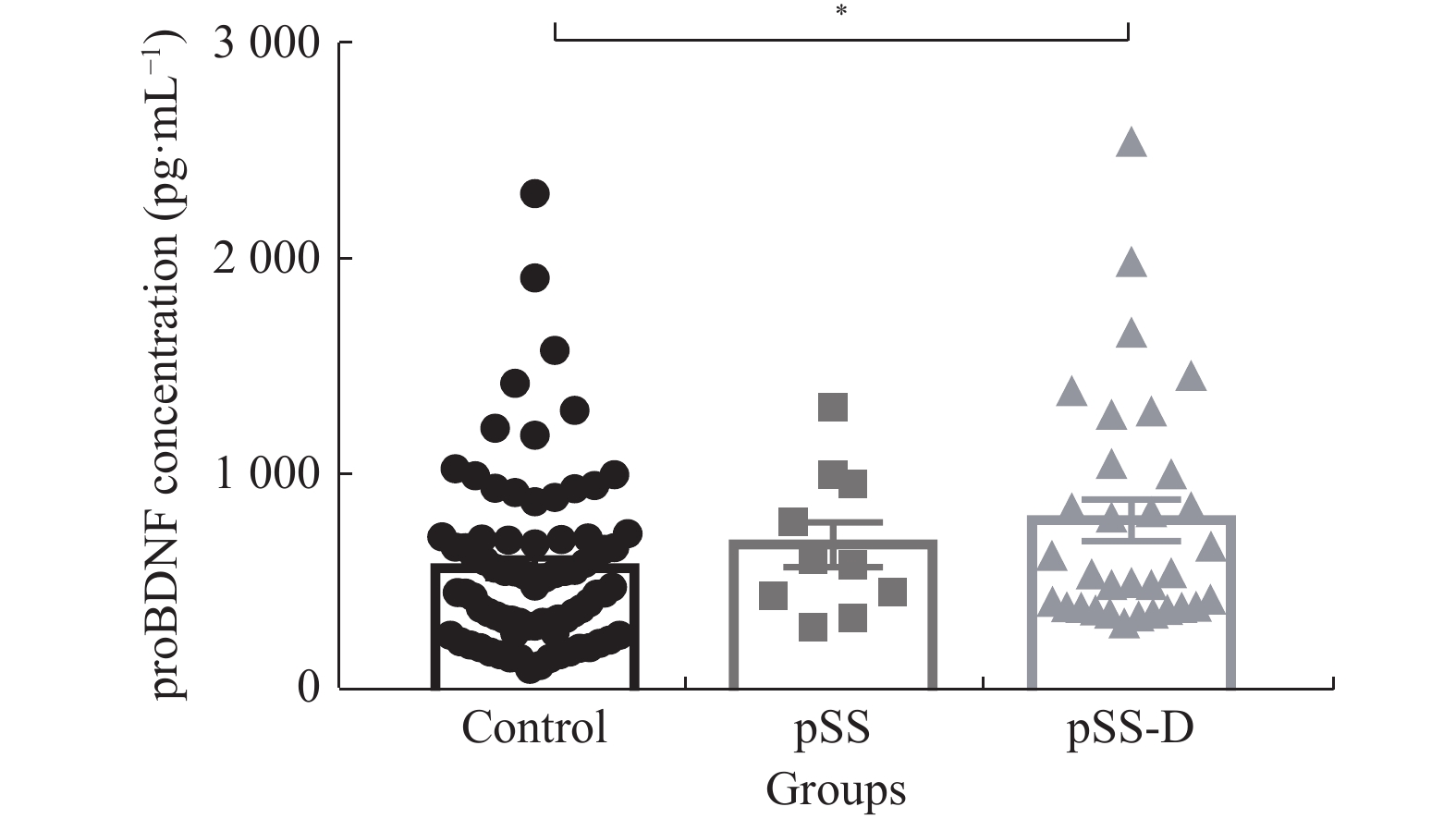
目的 了解血浆proBDNF水平在原发性干燥综合征(pSS)患者伴抑郁症状中的作用,并对相关因素进行探讨,为早期干预提供参考。 方法 采用自制一般情况调查表及PHQ-9量表对42例pSS患者及81例健康对照进行调查,并对42例pSS患者采用应对方式问卷(SCSQ)、社会支持评定量表(SSRS)进行调查和评分,欧洲抗风湿病联盟pSS病情活动度量表(ESSDAI)评估pSS疾病活动度。取得知情同意后抽取外周血3~5 mL,检测血浆中proBDNF的水平。 结果 pSS伴随抑郁症状患者血浆proBDNF水平升高最为明显(P < 0.05),较少的社会支持是pSS伴随抑郁症状的危险因子。 结论 proBDNF可能参与了pSS伴随抑郁症状的发病机制,pSS患者合并抑郁症状时需要更多的社会支持。 -
关键词:
- 原发性干燥综合征 /
- 脑源性神经营养因子前体 /
- 心理社会因素
Abstract:Objective To study the role of plasma proBDNF level in patients with primary Sjogren's syndrome (pSS) with depressive symptoms, and to explore related factors, so as to provide evidence for early intervention. Methods A total of 42 pSS patients and 81 healthy controls were investigated with self-made general information questionnaire and PHQ-9 scale, and 42 pSS patients were investigated and scored with Coping style questionnaire (SCSQ) and social support rating scale (SSRS). European Antirheumatic Association pSS Disease Activity Scale (ESSDAI) was used to evaluate the disease activity of pSS. After informed consent was obtained, 3-5 ml peripheral blood was collected to detect the level of proBDNF. Results The increase of plasma proBDNF level in patients with pSS complicated with depressive symptoms was the most significant (P < 0.05), and less social support was a risk factor. Conclusion ProBDNF may be involved in the pathogenesis of pSS with depressive symptoms, and these patients need more social support. -
表 1 对照组、pSS组和pSS-D组一般人口学资料的比较[n(%)/M(P25,P75)/(
$ \bar x \pm s$ )]Table 1. Comparison of the demographic data among control group,pSS group and pSS-D group [n(%),M(P25,P75),(
$ \bar x \pm s$ )]项目 对照组 pSS组 pSS-D组 χ2/t/F P (n = 81) (n = 12) (n = 30) 性别
男
女
3(3.7)
78(96.3)
0(0)
12(100)
2(6.7)
28(93.3)0.868 0.769 年龄 43.72 ± 9.26 45.50 ± 10.05 47.57 ± 10.51 1.776 0.174 PHQ-9 2.30 ± 0.84 3.08 ± 1.08 7.90 ± 2.06a 216.047 0.001* 病程(月) − 42(2.25,60.00) 24(10.50,72.00) 185.500 0.878 ESDAI评分 − 2(2.00,3.00) 2(2.00,3.00) 144.500 0.271 pSS-D组与对照组及pSS组PHQ-9得分差异均有统计学意义,*P < 0.05。 表 2 pSS组和pSS-D组实验室指标的比较[(
$\bar x \pm s $ ),g/L]Table 2. Comparison of laboratory indicators between pSS and pSS-D groups [(
$\bar x \pm s $ ),g/L]项目 pSS组 pSS-D组 t P 球蛋白 36.54 ± 2.82 36.86 ± 1.54 −0.107 0.916 IgG 19.60 ± 1.94 19.72 ± 1.04 −0.060 0.952 IgA 2.55 ± 0.36 2.64 ± 0.35 −0.161 0.873 IgM 1.37 ± 0.24 1.44 ± 0.16 −0.239 0.812 C3 1.01 ± 0.06 1.05 ± 0.04 −0.499 0.621 C4 0.19 ± 0.02 0.23 ± 0.02 −1.169 0.250 ESR(mmH2O/h) 26.08 ± 6.70 32.07 ± 4.90 −0.677 0.503 CRP(mg/L) 4.27 ± 1.44 3.00 ± 0.55 1.010 0.319 表 3 pSS组和pSS-D组在SCSQ 、SSRS总分及SSRS3个维度得分间的比较(
$\bar x \pm s $ )Table 3. Comparison of SCSQ,SSRS total score and SSRS scores between pSS and pSS-D groups (
$\bar x \pm s $ )项目 pSS组(n = 12) pSS-D组(n = 30) t P SCSQ 10.916 ± 5.248 9.067 ± 4.989 1.070 0.291 SSRS总分 45.09 ± 9.137 37.39 ± 8.135 2.614 0.013* 主观支持 10.45 ± 4.156 9.29 ± 3.133 0.971 0.338 客观支持 25.82 ± 3.816 21.45 ± 6.115 2.745 0.010* 对社会支持
利用度7.73 ± 2.970 7.68 ± 2.286 0.057 0.995 *P < 0.05。 -
[1] 韩晓蕾,石磊,任夏瑾,等. 原发性干燥综合征患者睡眠质量情况及其对病情影响分析[J]. 中华风湿病学杂志,2022,26(3):179-184. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn141217-20210604-00227 [2] Goulabchand R,Castille E,Navucet S,et al. The interplay between cognition,depression,anxiety,and sleep in primary Sjogren’s syndrome patients[J]. Scientific Reports,2022,12(1):13176. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-17354-1 [3] Cui Y,Xia L,Li L,et al. Anxiety and depression in primary Sjögren’s syndrome:A cross-sectional study[J]. BMC Psychiatry,2018,18(1):131. doi: 10.1186/s12888-018-1715-x [4] Milic V,Grujic M,Barisic J,et al. Personality,depression and anxiety in primary Sjögren’s syndrome-Association with sociodemographic factors and comorbidity[J]. PLoS One,2019,14(1):e0210466. [5] Grygiel-Górniak B,Limphaibool N,Puszczewicz M. Cytokine secretion and the risk of depression development in patients with connective tissue diseases[J]. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci,2019,73(6):302-316. doi: 10.1111/pcn.12826 [6] Fauchais A,Lalloué F,Lise M,et al. Role of endogenous brain-derived neurotrophic factor and sortilin in B cell survival[J]. J Immunol,2008,181(5):3027-3038. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.5.3027 [7] Schuhmann B,Dietrich A,Sel S,et al. A role for brain-derived neurotrophic factor in B cell development[J]. J Neuroimmunol,2005,163(1-2):15-23. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2005.01.023 [8] Wang Z,Wu J,Zhong F,et al. Upregulation of proBDNF in the mesenteric lymph nodes in septic mice[J]. Neurotox Res,2019,36(3):540-550. doi: 10.1007/s12640-019-00081-3 [9] Luo R,Luo C,Zhong F,et al. ProBDNF promotes sepsis-associated encephalopathy in mice by dampening the immune activity of meningeal CD4 T cells[J]. J Neuroinflammation,2020,17(1):169. doi: 10.1186/s12974-020-01850-0 [10] Zhou L,Xiong J,Lim Y,et al. Upregulation of blood proBDNF and its receptors in major depression[J]. J Affect Disord,2013,150(3):776-784. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2013.03.002 [11] Shiboski C H,Shiboski S C,Seror R,et al. 2016 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism Classification Criteria for Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome:A Consensus and Data-Driven Methodology Involving Three International Patient Cohorts[J]. Arthritis Rheumatol,2017,69(1):35-45. [12] Aloe L,Bracci-Laudiero L,Bonini S,et al. The expanding role of nerve growth factor: from neurotrophic activity to immunologic diseases[J]. Allergy,1997,52(9):883-894. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1997.tb01247.x [13] Strom T,Evrin P E,Karlsson A. Serum beta-2-microglobulin in Sjögren’s syndrome[J]. Scand J Rheumatol,1978,7(2):97-100. doi: 10.3109/03009747809098844 [14] Lapchak P A,Araujo D M,Hefti F. Systemic interleukin-1 beta decreases brain-derived neurotrophic factor messenger RNA expression in the rat hippocampal formation[J]. Neuroscience,1993,53(2):297-301. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(93)90196-M [15] Hu Z L,Luo C,Hurtado P R,et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor precursor in the immune system is a novel target for treating multiple sclerosis[J]. Theranostics,2021,11(2):715-730. doi: 10.7150/thno.51390 [16] Fauchais A L,Ahmed Boumédiène,Fabrice Lalloué,et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and nerve growth factor correlate with T-cell activation in primary Sjogren's syndrome[J]. Scand J Rheumatol,2009,38(1):50-57. doi: 10.1080/03009740802378832 [17] Pertovaara M,Silvennoinen O,Isomäki P. Cytokine-induced STAT1 activation is increased in patients with primary Sjögren’s syndrome[J]. Clin Immunol,2016,165:60-67. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2016.03.010 [18] Hou R,Garner M,Holmes C,et al. Peripheral inflammatory cytokines and immune balance in generalised anxiety disorder: case-controlled study[J]. Brain,Behavior,and Immunity,2017,62:212-218. [19] Liu H T,Lin Y N,Tsai M C,et al. Baicalein exerts therapeutic effects against endotoxin-induced depression-like behavior in mice by decreasing inflammatory cytokines and increasing brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels[J]. Antioxidants (Basel),2022,11(5):947. doi: 10.3390/antiox11050947 [20] 杨敏,刘荣,周润华,等. 原发性干燥综合征患者抑郁症患病率调查及相关因素分析[J]. 中华风湿病学杂志,2013,17(6):387-391. -






 下载:
下载: