An Economical Method for Cultivation and Identification of Mast Cell Derived from Suckling Rabbit Bone Marrow
-
摘要:
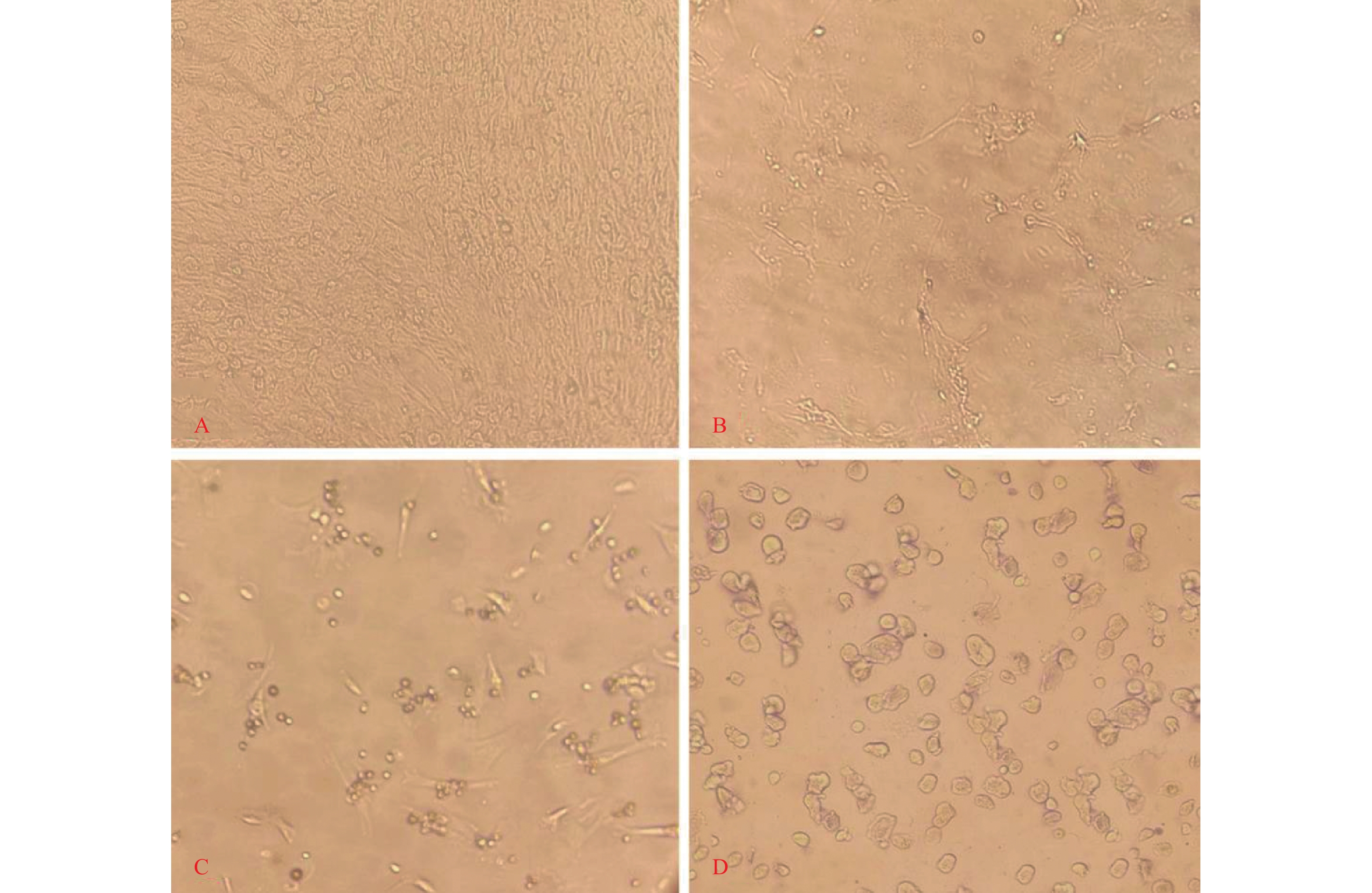
目的 通过一种操作简单的体外诱导培养体系获得更加成熟、更具有典型特征的肥大细胞。 方法 将乳兔的骨髓吹出放入含DMEM高糖培养基中,隔天换液,待细胞铺满,改用F12诱导培养基,隔天换液,镜下观察有细胞变圆时,更换为1640促成熟培养基,隔7 d换液,直至细胞诱导成熟。利用甲苯胺蓝染色检测其功能,流式细胞仪检测表面CD117及FcεR1α表达结果。 结果 6周后甲苯胺蓝染色可观察到:加入β-巯基乙醇的可得到含较多异染颗粒的细胞。采用流式细胞术进行检测:加入β-巯基乙醇时:CD117+、FcεRIα+双阳性细胞的比例为 96.2%,与不加β-巯基乙醇相比有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。 结论 利用SCF、IL-3及β-巯基乙醇可以成功诱导出兔骨髓来源的肥大细胞,为下一步对兔进行炎性损伤研究提供了依据,使后续基础及临床研究成为可能。 Abstract:Objective To obtain more mature mast cells with more typical characteristics through a simple and well-operated in vitro induction culture system. Methods The bone marrow of suckling rabbits was blown out and put into high glucose medium containing DMEM, and the medium was changed every other day. When the cells were confluent, F12 induction medium was used, and the medium was changed every other day. When the cells became round under the microscope, 1640 maturation medium was replaced, and the medium was changed every 7 days until the cells were induced to mature. Toluidine blue staining was used to detect its function, and flow cytometry was used to detect the surface expression of CD117 and FcεR1α. Results After 6 weeks, toluidine blue staining showed that the cells containing more metachromatic particles could be obtained by adding β-mercaptoethanol. Flow cytometry showed that the proportion of CD117+ and FcεRIα+ double positive cells in the presence of β-mercapto ethanol was 96.2%, which was significantly higher than that in the absence of β-mercapto ethanol (P < 0.05). Conclusion The use of SCF, IL-3 and β-mercaptoethanol can successfully induce mast cells derived from rabbit bone marrow, which provides foundation for the future research on inflammatory injury in rabbits, and makes subsequent basic and clinical research possible. -
Key words:
- Suckling rabbit /
- Bone marrow /
- Mast cells /
- Induction
-
表 1 不同浓度β-巯基乙醇诱导后CD117+ FcεRIα+肥大细胞的比例
Table 1. The proportion of CD117+ FcεRIα+ mast cells induced by different concentrations of β-mercaptoethanol
β-巯基乙醇
(mol/L)实验次数 CD117+ FcεRIα+
肥大细胞的比例(%)P 0 5 48.97 ± 3.12 0.7069 10×10−5 5 95.64 ± 4.66# 与β-巯基乙醇浓度为0 mol/L比较,#P < 0.05。 -
[1] Kaartinen M,Penttilä A,Kovanen P T. Accumulation of activated mast cells in the shoulder region of human coronary atheroma,the predilection site of atheromatous rupture[J]. Circulation,1994,90(4):1669-1678. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.90.4.1669 [2] Spinas E,Kritas S K,Saggini A,et al. Role of mast cells in atherosclerosis: a classical inflammatory disease[J]. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol,2014,27(4):517-521. doi: 10.1177/039463201402700407 [3] Sun W,Pang Y,Liu Z,et al. Macrophage inflammasome mediates hyperhomocysteinemia-aggravated abdominal aortic aneurysm[J]. J Mol Cell Cardiol,2015,81:96-106. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2015.02.005 [4] Kovanen P T,Bot I. Mast cells in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease-Activators and actions[J]. Eur J Pharmacol,2017,816:37-46. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2017.10.013 [5] Conti P,Lessiani G,Kritas S K,et al. Mast cells emerge as mediators of atherosclerosis: special emphasis on IL-37 inhibition[J]. Tissue Cell,2017,49(3):393-400. doi: 10.1016/j.tice.2017.04.002 [6] Maaninka K,Nguyen S D,Mäyränpää M I,et al. Human mast cell neutral proteases generate modified LDL particles with increased proteoglycan binding[J]. Atherosclerosis,2018,275:390-399. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2018.04.016 [7] Oliveira S H,Lukacs N W. Stem cell factor: a hemopoietic cytokine with important targets in asthma[J]. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy,2003,2(4):313-318. [8] Irani A M,Nilsson G,Miettinen U,et al. Recombinant human stem cell factor stimulates differentiation of mast cells from dispersed human fetal liver cells[J]. Blood,1992,80(12):3009-3021. [9] Kaartinen M,Penttilä A,Kovanen P T. Mast cells of two types differing in neutral protease composition in the human aortic intima. Demonstration of tryptase- and tryptase/Chymase -containing mast cells in normal intimas,fatty streaks,and the shoulder region of atheromas[J]. Arterioscler Thromb,1994,14(6):966-972. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.14.6.966 [10] Bot I,Shi G P,Kovanen P T. Mast cells as effectors in atherosclerosis[J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol,2015,35(2):265-271. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.114.303570 [11] Ribatti D. The development of human mast cells. an historical reappraisal[J]. Exp Cell Res,2016,342(2):210-215. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2016.03.013 [12] Kritas S K,Saggini A,Cerulli G,et al. Interrelationship between IL-3 and mast cells[J]. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents,2014,28(1):17-21. [13] Ito T,Smrž D,Jung M Y,et al. Stem cell factor programs the mast cell activation phenotype[J]. J Immunol,2012,188(11):5428-5437. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1103366 [14] Meurer S K,Neß M,Weiskirchen S,et al. Isolation of mature (peritoneum-derived) mast cells and immature (bone marrow-derived) mast cell precursors from mice[J]. PLoS One,2016,11(6):e0158104. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0158104 [15] Sayed S O,Dyson M. Histochemical heterogeneity of mast cells in rat dermis[J]. Biotech Histochem,1993,68(6):326-32. doi: 10.3109/10520299309105638 -






 下载:
下载: