Simultaneous Imaging of Ureter and Abdominal Aorta and Its Application in Open Surgery for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
-
摘要:
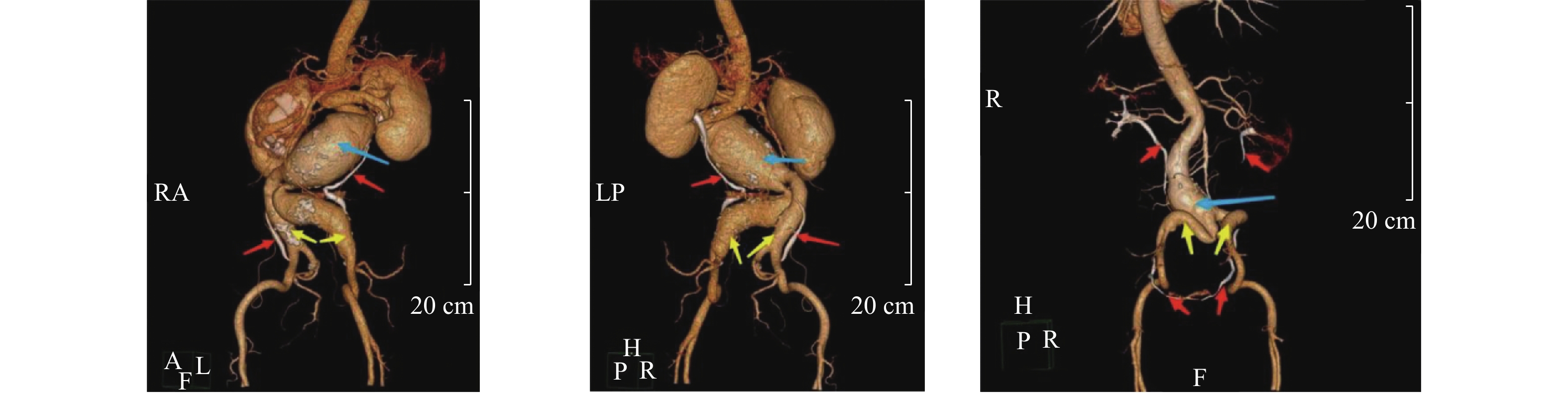
目的 探讨输尿管和腹主动脉同期显影技术以及该技术在临床应用中的效果和在腹主动脉瘤开放手术中的应用价值。 方法 2021年8月至2023年5月期间昆明医科大学第二附属医院心脏血管外科有24例患者接受开放手术治疗,并在术前行输尿管和腹主动脉同期显影检查。根据这部分患者在行同期显影检查时操作参数调整及显影结果介绍该技术,并对该技术在24例腹主动脉瘤开放手术中的应用进行探讨,阐述该技术在腹主动脉瘤开放手术治疗中对输尿管保护的价值。 结果 输尿管和腹主动脉同期显影检查时首次注射40 mL造影剂后4~5 min进行CTA扫描得到的CT和3D图像上输尿管大部分节段显示良好,与周围组织关系较为清楚;输尿管和腹主动脉同期显影与术中探查对输尿管异常的检出率没有差异(P > 0.05),24例行开放手术治疗的患者未出现输尿管损伤,与对照组20例患者对比,输尿管损伤发生率有统计学差异( P < 0.05)。 结论 输尿管和腹主动脉同期显影检查时,首次注射40 mL造影剂后4~5 min进行CTA扫描对输尿管显影良好,可以清楚区分输尿管、腹主动脉及周围粘连组织,辅助输尿管定位,在腹主动脉瘤开放手术中应用有助于术前发现输尿管狭窄、周围粘连等情况,避免术中输尿管损伤。 -
关键词:
- 输尿管和腹主动脉同期显影 /
- 腹主动脉瘤开放手术 /
- 输尿管损伤
Abstract:Objective To investigate the simultaneous ureter and abdominal aorta imaging technique, its clinical effect and application value in the open surgery of abdominal aortic aneurysm. Method From August 2021 to May 2023, 24 patients underwent open surgery in the Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, and the ureter and abdominal aorta were simultaneously imaged before surgery. Based on the adjustment of operating parameters and the results of the simultaneous development examination in these patients, the application of this technique in 24 cases of open surgery for abdominal aortic aneurysm was discussed, and the value of this technique for ureteral protection in open surgery for abdominal aortic aneurysm was expounded. Result During the simultaneous imaging of the ureter and abdominal aorta, CTA scans were performed 4-5 minutes after the first injection of 40 ml contrast agent. Most segments of the ureter were well displayed on CT and 3D images, and their contrast with surrounding tissues was relatively clear; There was no difference in the detection rate of ureteral abnormalities between simultaneous imaging of the ureter and abdominal aorta and intraoperative exploration (P > 0.05). There was no ureteral injury in 24 patients who underwent open surgery, and there was a statistical difference in the incidence of ureteral injury compared to the control group of 20 patients ( P < 0.05). Conclusion During the simultaneous imaging of the ureter and abdominal aorta, CTA scan performed 4-5 minutes after the first injection of 40 ml contrast agent showed good imaging of the ureter. It can clearly distinguish the ureter, abdominal aorta, and surrounding adhesive tissue, assist in ureteral localization, and its application in open surgery for abdominal aortic aneurysm can help to detect ureteral stenosis, peripheral adhesion, and other conditions before surgery, and avoid intraoperative ureteral injury. -
表 1 开放手术患者输尿管异常检出率差异比较3~4 min组(1)
Table 1. Comparison of differences in the detection rate of ureteral abnormalities in patients undergoing open surgery(1)
同期显影检查 术中探查 合
计+ − + 2 0 2 − 1 12 13 合计 3 12 15 采用配对卡方检验计算出P = 1.000a > 0.05(a表示采用连续性修正)。 表 1 开放手术患者输尿管异常检出率差异比较5~6 min组(2)
Table 1. Comparison of differences in the detection rate of ureteral abnormalities in patients undergoing open surgery (2)
同期显影检查 术中探查 合
计+ − + 1 0 1 − 1 7 8 合计 2 7 9 采用配对卡方检验计算出P=1.000a >0.05(a表示采用连续性修正)。 表 2 输尿管损伤发生率比较[n(%)]
Table 2. Comparison of the incidence of ureteral injury [n(%)]
检查方式 术中无
输尿管损伤术中出现
输尿管损伤χ2 p 同期显影 24/24(100) 0/24(0) 0.386a < 0.05 CTA 17/20(85) 3/20(15) 注:a表示采用连续性修正。 -
[1] Harrie kurvers,Frank J Veith,Evan C,et al. Discontinuous,staccato growth of abdominal aortic aneurysms[J]. Journal of the American College of Surgeons,2004,199(5):709-715. [2] 张韬,郭伟. 腹主动脉瘤诊断和治疗中国专家共识(2022版)[J]. 中国实用外科杂志,2022,42(04):380-387. doi: 10.19538/j.cjps.issn1005-2208.2022.04.03 [3] Erbel raimund,Aboyans victor,Boileau catherine,et al. 2014 ESC Guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of aortic diseases: Document covering acute and chronic aortic diseases of the thoracic and abdominal aorta of the adult. The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Aortic Diseases of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC)[J]. European Heart Journal,2014,35(41):2873-926. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehu281 [4] 李哲昀,王利新,符伟国. 最新腹主动脉瘤腔内治疗指南解读[J]. 中国普外基础与临床杂志,2021,28(11):1414-1417. [5] Rao Vallabhaneni S,McWilliams R G,Anbarasu A,et al. Perianeurysmal Fibrosis: a Relative Contraindication to Endovascular Repair[J]. European Journal of Vascular & Endovascular Surgery,2001,22(6):535-541. [6] 罗明尧,舒畅,陈冬,等. 以主动脉夹层和腹主动脉瘤为例谈中国主动脉疾病诊疗研究现状[J]. 临床外科杂志,2021,29(12):1196-1199. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6483.2021.12.029 [7] Maureen K sheehan,Paula K,Shireman fred N,et al. Ureteral injury during aortic aneurysm repair by the retroperitoneal approach[J]. Annals of Vascular Surgery,2001,15(4):481-484. doi: 10.1007/s100160010125 [8] Adams john R,Mata john A,Culkin daniel J,et al. Ureteral injury in abdominal vascular reconstructive surgery[J]. Urology,1992,39(1):77-81. doi: 10.1016/0090-4295(92)90047-Z [9] Dalsing michael C ,Bihrle richard,Lalka stephen G,et al. Vascular surgery-associated ureteral injury:zebras do exist[J]. Annals of Vascular Surgery,1993,7(2):180-186. doi: 10.1007/BF02001013 [10] Bright thomas C,Peters paul C. Ureteral injuries secondary to operative procedures: Report of 24 cases[J]. Urology,1977,9(1):22-26. doi: 10.1016/0090-4295(77)90277-1 [11] 顾建华,孙大林,卢定友,石全,许晶晶. 分次团注结合双能量扫描在CTU检查中的应用价值[J]. 中国CT和MRI杂志,2016,14(9):110-113. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5131.2016.09.036 [12] Rud Erik,Galtung kristina flor,Lauritzen peter maehre,et al. Examining the upper urinary tract in patients with hematuria-time to revise the CT urography protocol?[J]. European Radiology,2020,30(3):1664-1670. doi: 10.1007/s00330-019-06521-0 -






 下载:
下载: