Application of Nanopore Sequencing in Tumor with Infection
-
摘要:
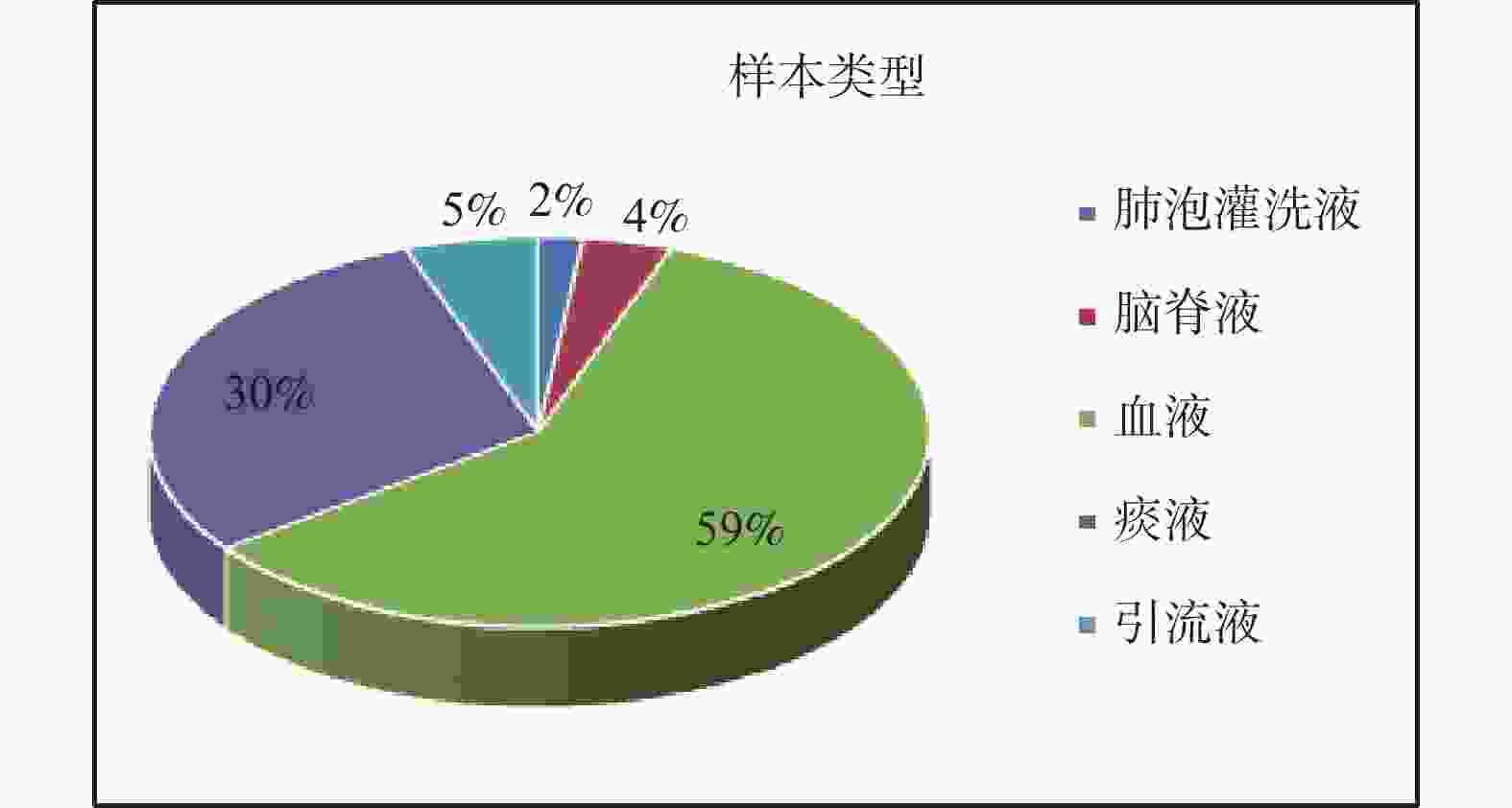
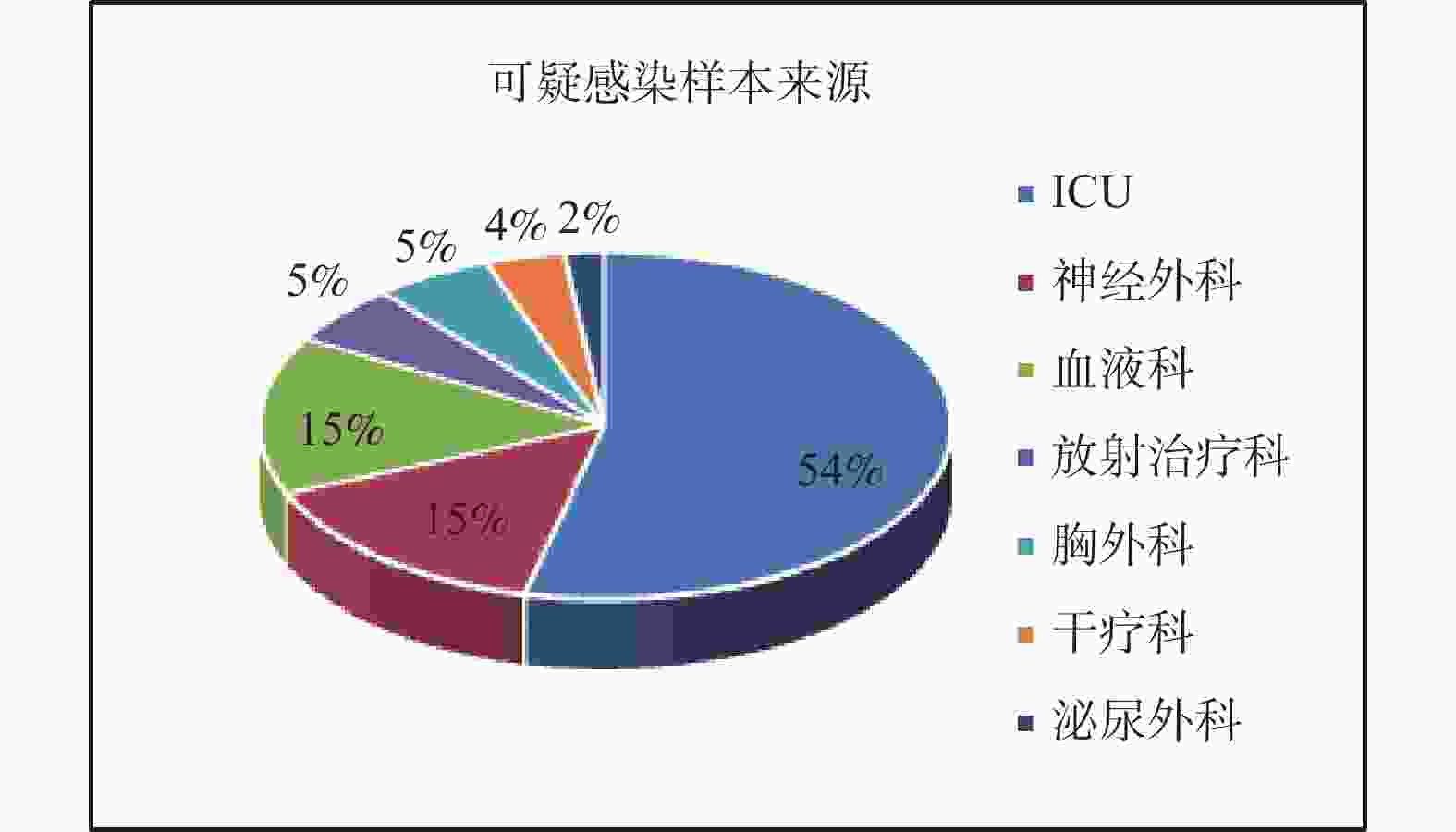
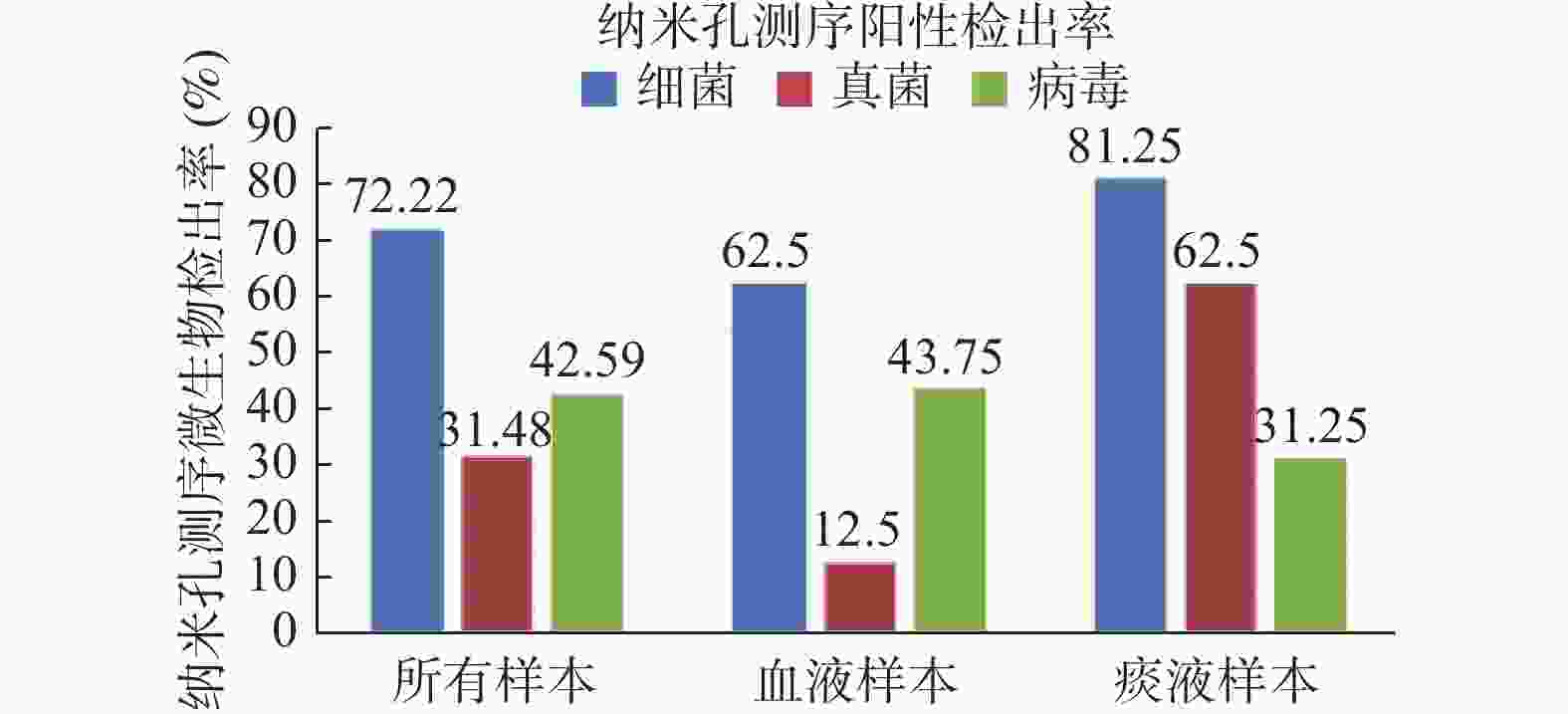
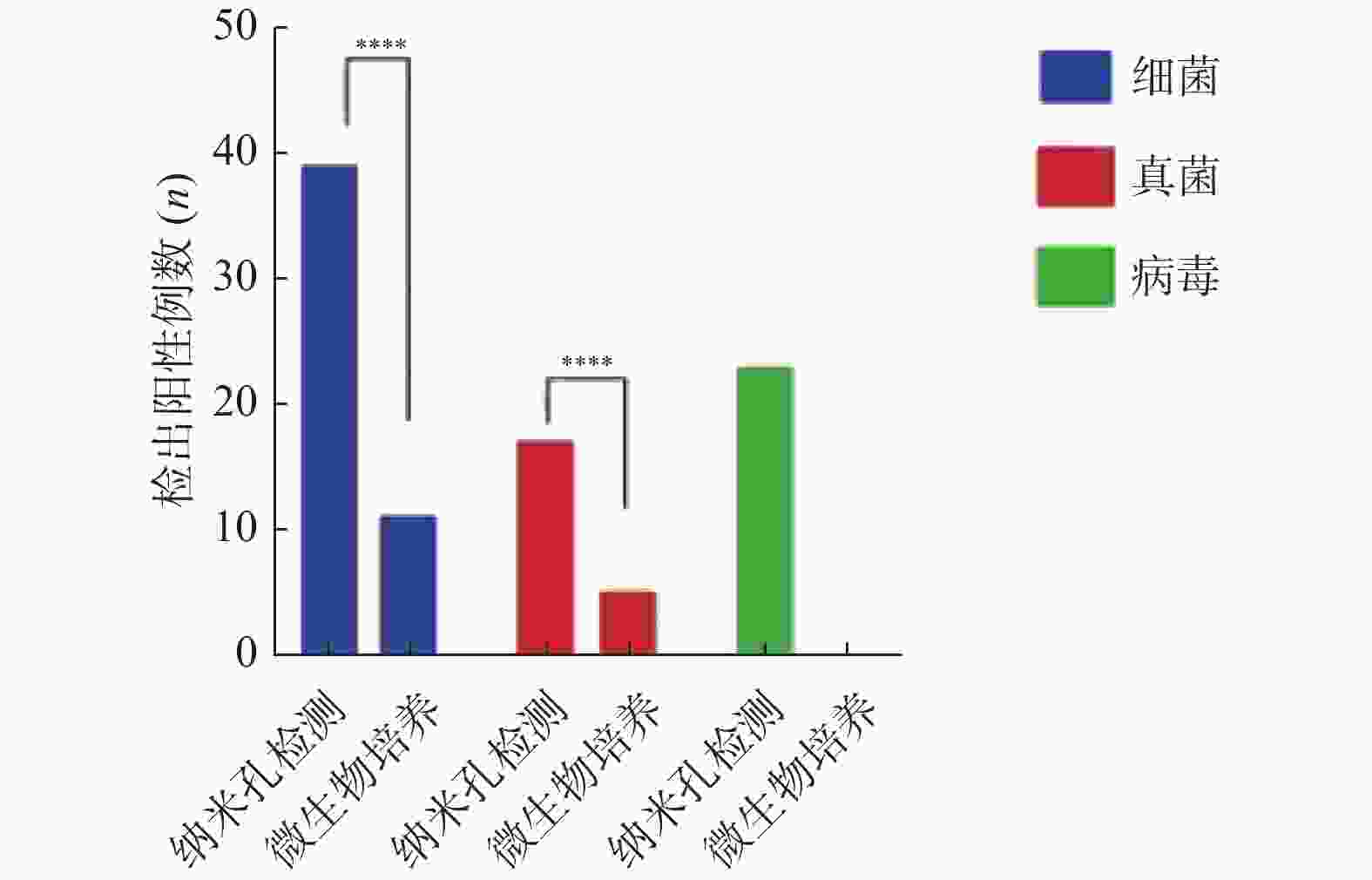
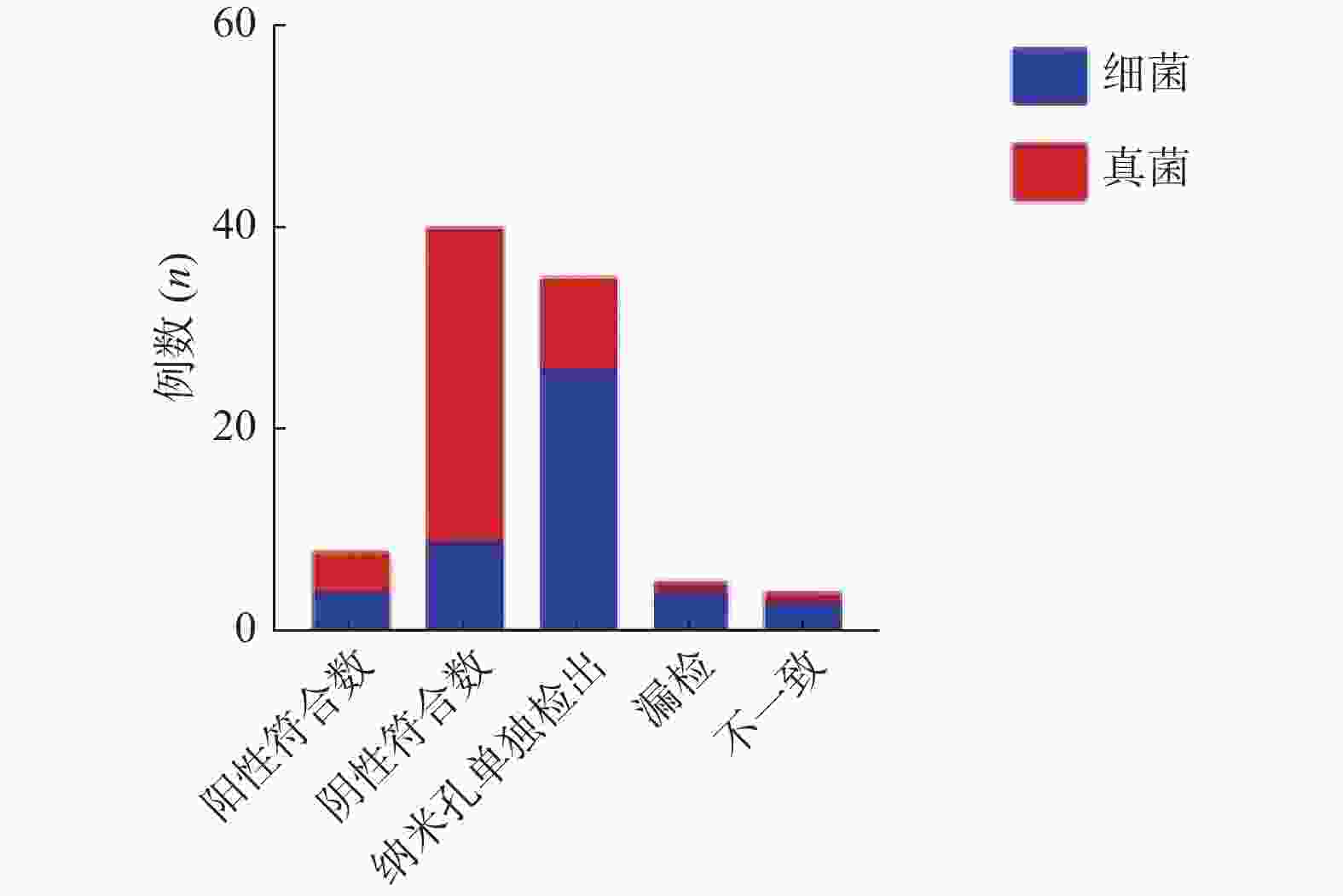
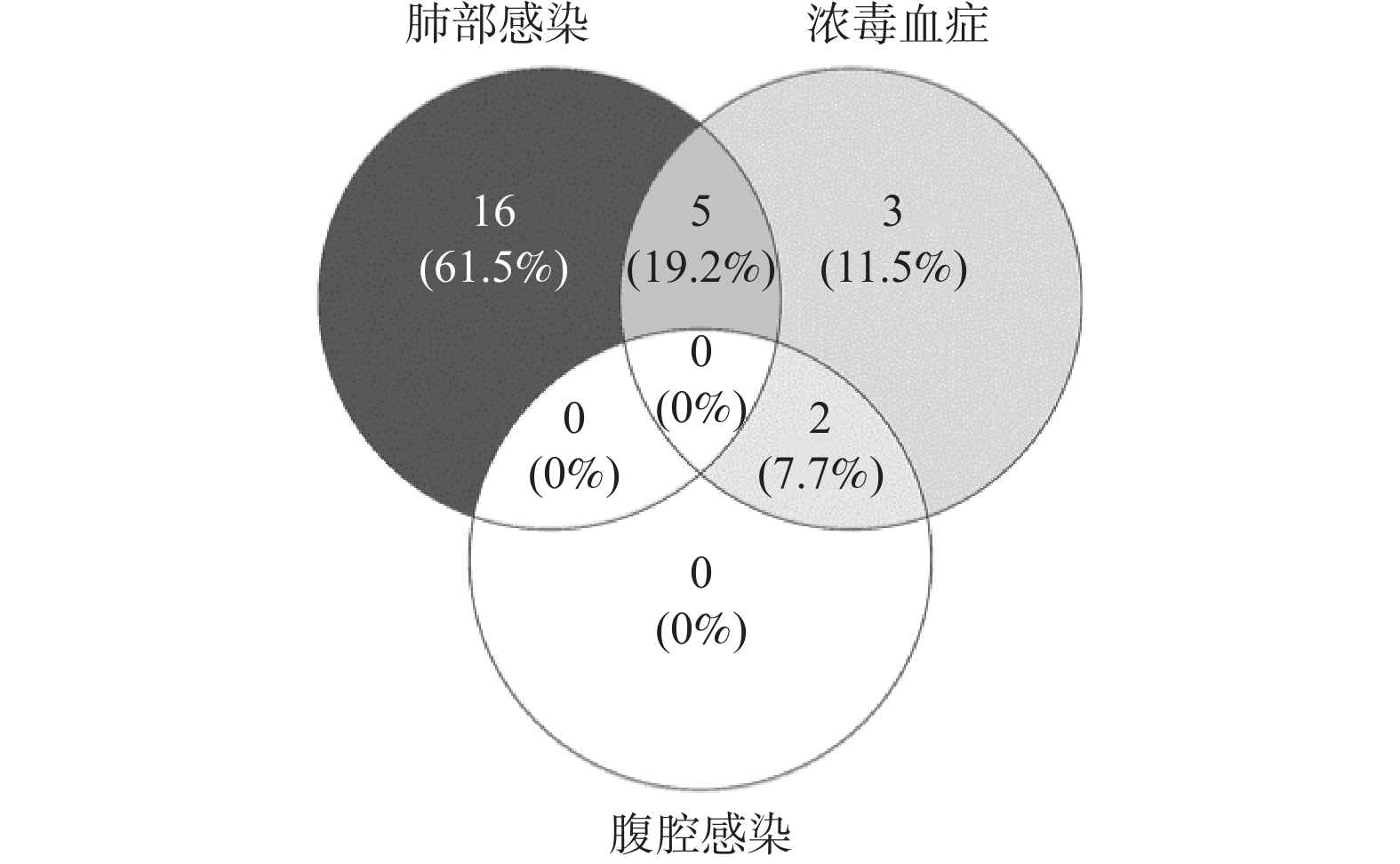
目的 评估纳米孔测序在肿瘤患者并发感染性疾病中的临床应用价值,为肿瘤患者感染性疾病的快速、灵敏诊断提供新的检测方法。 方法 收集2022年7月至8月云南省肿瘤医院36例疑似感染的肿瘤患者样本46份,利用纳米孔测序鉴定样本中的病原微生物。 结果 纳米孔测序细菌检出率72.22%,真菌检出率31.48%,病毒检出率42.59%。细菌和真菌检出率均较微生物培养法(23.91%和10.87%)明显升高(χ2 = 23.19 ,P < 0.0001;χ2 = 13.14 ,P= 0.0003)。纳米孔测序结果与微生物培养结果比较,检出的细菌和真菌种属明显增多。 结论 纳米孔测序鉴定病原微生物具有检出率高,检测病原菌种属广,诊断快速的优势,在肿瘤并发感染性疾病的诊断中具有潜在的临床应用价值。 Abstract:Objective To evaluate the clinical application value of nanopore sequencing in tumor patients with concurrent infectious diseases and to provide a new detection method for rapid and sensitive diagnosis of infectious diseases in tumor patients. Methods Samples of inpatients with suspected infections from July to August 2022 at Yunnan Cancer Hospital were collected, and pathogenic microorganisms in the samples were identified using nanopore sequencing. Results Forty-six samples from 36 patients with suspected infection were collected. Nanopore sequencing detected 72.22% of bacteria, 31.48% of fungi, and 42.59% of viruses. Both bacterial and fungal detection rates were significantly higher (χ2 = 23.19 , P < 0.0001; χ2 = 13.14 , P = 0.0003) than the results by microbiological culture method (23.91% and 10.87%). The nanopore sequencing results showed significantly more bacterial and fungal species detected compared to microbial culture results. Conclusions Nanopore sequencing for the identification of pathogenic microorganisms has the advantages of high detection rate, wide detection of pathogenic genera, and rapid diagnosis. It has potential clinical application in the diagnosis of tumor-associated infectious diseases. -
Key words:
- Nanopore sequencing /
- Tumor /
- Infection /
- Pathogenic microorganisms /
- Microbial culture
-
表 1 纳米孔测序检出的病原微生物种属(n)
Table 1. Pathogenic microbial species detected by nanopore sequencing (n)
检出细菌种属 检出例数 检出真菌种属 检出例数 检出病毒例数 检出例数 铜绿假单胞菌 3 白色念珠菌 3 人疱疹病毒6型 3 肺炎链球菌 4 热带念珠菌 3 人类疱疹病毒1型 2 血液链球菌 1 葡萄牙棒孢酵母 2 EB病毒 10 大肠埃希氏菌 1 似平滑念珠菌 3 人巨细胞病毒 6 肺炎克雷伯菌 2 克柔念珠菌 3 人疱疹病毒7型 1 屎肠球菌 6 耶氏肺孢子菌 1 细环病毒 5 戈登链球菌 1 限制性马拉色菌 1 JC病毒 1 内氏放线菌 2 解脂耶氏酵母菌 1 人类疱疹病毒1型 2 口腔链球菌 1 清酒念珠菌 1 杰氏棒杆菌 2 光滑念珠菌 1 鲍曼不动杆菌 4 酿酒酵母 1 荧光假单胞菌 2 蜡样芽孢杆菌 1 蕈状芽孢杆菌 1 棉子糖球菌 1 阴道加德纳菌 2 副流感嗜血杆菌 2 产气克雷伯菌 1 金黄色葡萄球菌 3 维隆气单胞菌 1 产碱假单胞菌 1 缓症链球菌 1 阿氏肠杆菌 1 枯草芽孢杆菌 1 斯氏假单胞菌 1 路登葡萄球菌 1 栖稻假单胞菌 1 54份样本中共检测出细菌27种,9份样本同时检出2种细菌;真菌11种,3份样本同时检出2种真菌;病毒7种,5份样本同时检出2种病毒,1份样本同时检出3种病毒。 表 2 微生物培养检出的微生物种属(n)
Table 2. Pathogenic microbial species detected by microbial culture (n)
检出细菌种属 检出
例数检出真菌种属 检出
例数耐碳青霉烯铜绿假单胞菌 1 白色念珠菌 2 革兰氏阳性杆菌 1 克柔念珠菌 1 鲍曼不动杆菌 1 光滑念珠菌 3 耐碳青霉烯鲍曼不动杆菌 1 产酸克雷伯菌 1 超广谱B内酰胺酶大肠埃希菌 1 耐甲氧西林凝固酶阴性葡萄球菌 1 肠膜明串珠菌 1 超广谱B内酰胺酶 肺炎克雷伯菌 1 肺炎克雷伯 1 阴沟肠杆菌 1 46份样本中共检测出细菌9种,每一份样本均只检出1种细菌;真菌3种,1份样本同时检出2种真菌。 -
[1] Zheng Y,Chen Y,Yu K,et al. Fatal infections among cancer patients:A population-based study in the United States[J]. Infectious Diseases and Therapy,2021,10(2):871-895. [2] Zorina T, Styche A. Infectious diseases in cancer patients: An overview[M]. Shurin M R, ThanavalaY, Ismail N. Infection and Cancer: Bi-Directorial Interactions. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2015: 295-311. [3] Huang G,Huang Q,Zhang G,et al. Point-prevalence surveys of hospital-acquired infections in a Chinese cancer hospital: from 2014 to 2018[J]. Journal of Infection and Public Health,2020,13(12):1981-1987. [4] Kumar A,Roberts D,Wood K E,et al. Duration of hypotension before initiation of effective antimicrobial therapy is the critical determinant of survival in human septic shock[J]. Critical Care Medicine,2006,34(6):1589-1596. [5] Petersen L M,Martin I W,Moschetti W E,et al. Third-generation sequencing in the clinical laboratory:Exploring the advantages and challenges of Nanopore sequencing[J]. Journal of Clinical Microbiology,2019,58(1):e01315-e01319. [6] Ryan R W,Louise M J,Kathryn E H. Assembling the perfect bacterial genome using Oxford Nanopore and Illumina sequencing[J]. Plos Computational Biology,2023,19(3):e1010905. [7] Gu W,Deng X,Lee M,et al. Rapid pathogen detection by metagenomic next-generation sequencing of infected body fluids[J]. Nature Medicine,2021,27(1):115-124. [8] Jain M,Olsen H E,Paten B,et al. The Oxford Nanopore MinION:Delivery of Nanopore sequencing to the genomics community[J]. Genome Biology,2016,17(1):239. [9] Wang Y,Zhao Y,Bollas A,et al. Nanopore sequencing technology,bioinformatics and applications[J]. Nature biotechnology,2021,39(11):1348-1365. [10] 刘晔,许小毛. 基于纳米孔测序技术的临床检测研究进展[J]. 中华检验医学杂志,2022,45(3):296-299. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn114452-20210618-00383 [11] 庄子,孟雨桐,刘润旸,等. 纳米孔测序技术及其在病原学诊断中的应用[J]. 江苏大学学报(医学版),2023,33(1):1-12. [12] 闫冬明,赵宁,赵春春,等. 纳米孔测序技术研究进展[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志,2020,31(3):380-384. doi: 10.11853/j.issn.1003.8280.2020.03.029 [13] Ciuffreda L,Rodriguez-perez H,Flores C. Nanopore sequencing and its application to the study of microbial communities[J]. Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal,2021,19:1497-1511. [14] Markwart R,Saito H,Harder T,et al. Epidemiology and burden of sepsis acquired in hospitals and intensive care units: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Intensive Care Medicine,2020,46(8):1536-1551. [15] Taylo L H,Latham S M,Woolhouse M E. Risk factors for human disease emergence[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B,Biological Sciences,2001,356(1411):983-989. [16] 吴泽刚,顾剑,郑红云,等. 纳米孔测序在血流感染中的应用[J]. 华西医学,2022,37(8):1166-1169. [17] Holland T,Fowler V G Jr,Shelburne S A III. Invasive gram-positive bacterial infection in cancer patients[J]. Clinical Infectious Diseases,2014,59(suppl_5):S331-S334. [18] 刘晔,孙高远,李贺鑫,等. 纳米孔测序技术在下呼吸道感染细菌性病原检测的临床应用[J]. 中华检验医学杂志,2021,44(4):328-334. [19] Stefan C P,Hall A T,Graham A S,et al. Comparison of Illumina and Oxford Nanopore sequencing technologies for pathogen detection from clinical matrices using molecular inversion probes[J]. The Journal of Molecular Diagnostics: JMD,2022,24(4):395-405. [20] Sheka D,Alabi N,Gordon P M K. Oxford Nanopore sequencing in clinical microbiology and infection diagnostics[J]. Briefings in Bioinformatics,2021,22(5):1-18. [21] Batovska J,Lynch S E,Rodoni B C,et al. Metagenomic arbovirus detection using MinION nanopore sequencing[J]. Journal of Virological Methods,2017,249:79-84. [22] 叶福强,李鹏,韩一芳,等. 基于纳米孔测序技术的呼吸道病原体快速确认[J]. 分子诊断与治疗杂志,2020,12(2):127-132,150. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6929.2020.02.003 -





 下载:
下载: