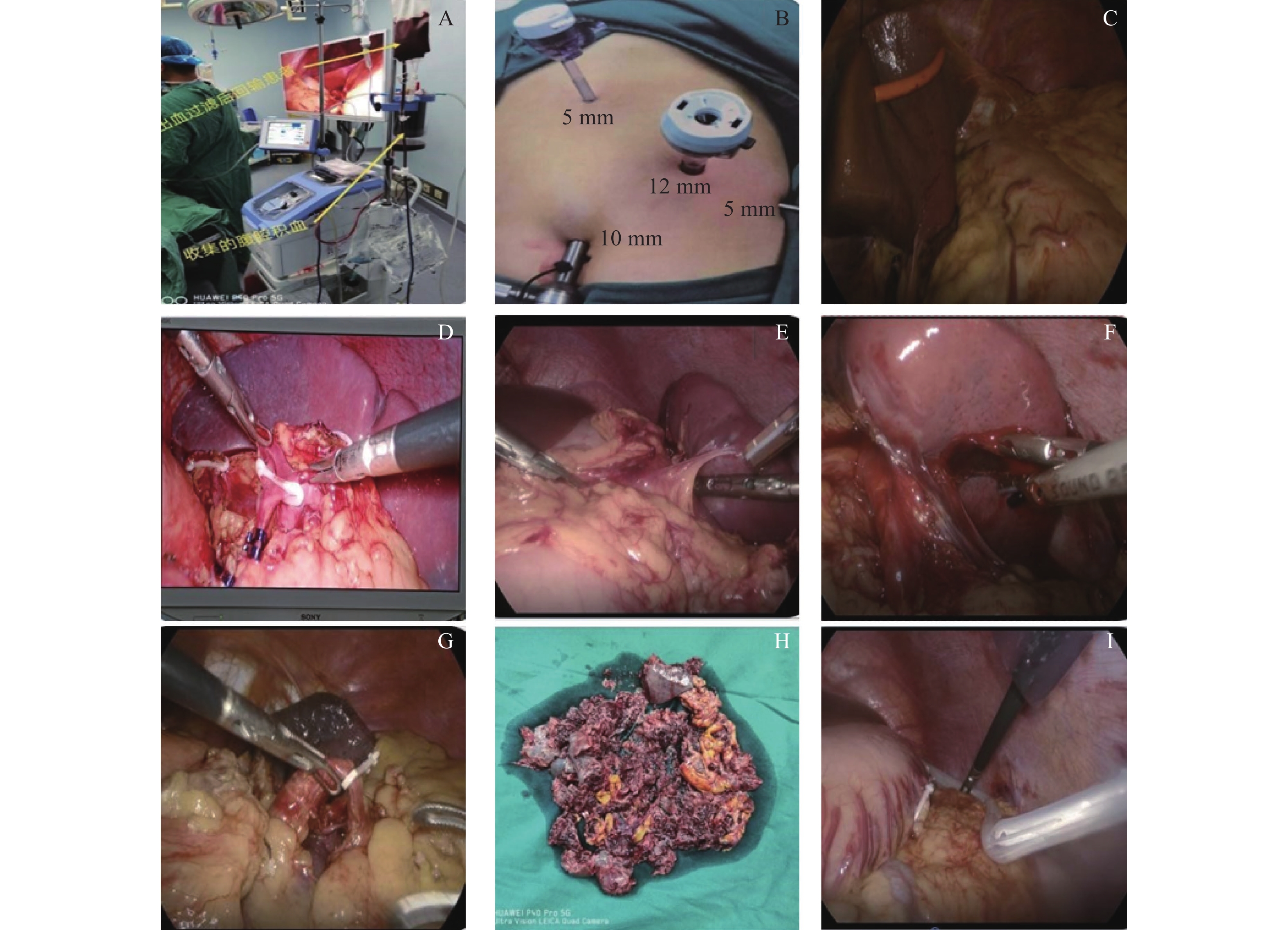
The Application Value of Laparoscopic Splenectomy in Traumatic Splenectomy
-
摘要:
目的 探讨在外科临床中极其常见的脾破裂患者中使用腔镜技术进行脾脏切除的优缺性。 方法 回顾分析云南省保山市第二人民医院在2012年5月至2022年10月期间普外科收治的外伤性脾破裂患者61例。所收集的资料中有25例患者行腹腔镜脾切除术(LS),将其纳入观察组;有36例患者行开腹手术(OS),将其纳入对照组。利用倾向性评分按 1:1 比例匹配,最终 LS 和 OS各纳入 25 例。观察组(LS 组)中男性患者 16 例,女性患者 9 例,年龄(43.92±21.24)岁,年龄范围在 16~75 岁;对照组(OS 组)中男性患者 19例,女性患者 6 例,年龄(35.20±16.28)岁,年龄范围在 14~65 岁。比较2组手术全期各项指标(出血量、术后镇痛时间、手术时间等)以及住院费用、术后并发症等。 结果 经过倾向性平分后2组基线资料满足可比性要求。LS 组手术时间(157.16±43.47)min、腹腔积液 98.00(50.00,100.00)mL、术中出血量 800.00(500.00,1000.00)mL、术中输血量 450.00(400.00,601.25)mL、术后首次排气(40.32 ±13.36) h 、术后首次下床时间 48.00(48.00,72.00)h、引流管拔除时间(72.96±21.33) h、术后镇痛时间 24.00(24.00,48.00) h、 住院时间 12.00 (10.00,14.00) d,优于 OS 组手术时间(184.20 ±63.14)min、积液量 100.00 mL(100.00,200.00)、术中出血量1000.00 (800.00,1750.00) mL、术中输血量 1200.00(461.00,1200.00) mL、术后首次排气(58.56±18.43) h、术后首次下床时间 72.00 (48.00,120.00) h、 引流管拔除时间(102.72±43.00) h、术后镇痛 时间 48.00(36.00,96.00) h、住院时间 14(11.50,17.00) d,数据差异均有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。LS 组住院费用 2.18(1.68,2.58)万元略高于 OS 组住院费用 1.77(1.51,2.18)万元,但整体 差距不大。 结论 LS 在手术时间、术中控制出血量、术中输血量、术后排气、术后下床时间、镇痛药使用时间、腹腔积液、术后并发症等方面均相对于 OS 有优势,更加有利于患者恢复并且提升预后生存品质,更符合现代医学发展。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the advantages and disadvantages of laparoscopic splenectomy in patients with splenic rupture, which is very common in surgical practice. Methods The data of 61 patients with traumatic splenic rupture admitted to the Second People’s Hospital of Baoshan from May 2012 to October 2022 were retrospectively analyzed. Among the collected data, 25 patients underwent laparoscopic splenectomy and were included in the observation group. Thirty-six patients underwent open surgery (OS) and were included in the control group. The orientation score was matched in 1∶1 ratio, and finally LS and OS were included in 25 cases each. In the observation group (LS group), there were 16 males and 9 females, aged (43.92±21.24) years old, ranging from 16 to 75 years old. In the control group (OS group), there were 19 male patients and 6 female patients, aged (35.20±16.28) years old, ranging from 14 to 65 years old. The indexes (blood loss, postoperative analgesic time, operation time, etc.), hospitalization cost and postoperative complications were compared between the two groups during the whole operation period. Results The baseline data of the two groups met the requirement of comparability after the propensity bisection. The operation time of LS group was (157.16±43.47) min, abdominal fluid was 98.00 (50.00, 100.00) mL, intraoperative blood loss was 800.00 (500.00, 1000.00) mL, intraoperative blood transfusion was 450.00 (400.00, 601.25) mL. The first postoperative exhaust was (40.32±13.36) h. The first time of getting out of bed after the operation was 48.00 (48.00, 72.00) h, drainage tube removal time was (72.96±21.33) h, and the postoperative analgesia time was 24.00 (24.00, 48.00) h. The hospital stay was 12.00 (10.00, 14.00) d, which was better than the operating time (184.20±63.14) min, with the effusion volume being 100.00 (100.00, 200.00) mL, intraoperative bleeding volume being 1000.00 (800.00, 1750.00) mL, intraoperative blood transfusion beting 1200.00 (461.00, 1200.00) mL. The first postoperative exhaust (58.56±18.43) h, first postoperative time of getting out of bed 72.00 (48.00, 120.00) h, drainage tube removal time was (102.72±43.00) h , the postoperative analgesia time was 48.00 (36.00, 96.00) h, and the hospital stay time 14 (11.50, 17.00) d was statistically significant (all P < 0.05). The hospitalization cost of LS group was 21800 yuan (1.68, 25800 yuan), slightly higher than that of OS groupof 17 700 yuan (15 100, 21 800 yuan), but the overall difference was not significant. Conclusion LS has the advantages over OS in terms of operation time, intraoperative blood loss control, intraoperative blood transfusion amount, postoperative exhaust, postoperative getting out of bed time, analgesic drug use time, abdominal effusion, postoperative complications, etc. It is more conducive to the recovery of patients and the improvement of the prognosis and survival quality, and more in line with the development of modern medicine. -
表 1 LS 组和 OS 组患者术前资料对比[n(%)/(
$\bar x \pm s $ )]Table 1. Comparison of preoperative data between LS group and OS group [n(%)/(
$\bar x \pm s $ )]项目 LS 组(n = 25) OS 组(n = 25) χ2/t P 年龄(岁) 43.92 ± 21.24 35.20 ± 16.28 1.629 0.110 性别 0.857 0.355 男性 16(64.00) 19(76.00) 女性 9 (36.00) 6(24.00) 脾脏破裂分型a 1.486 0.662 Ⅰ型 13(52.00) 17(68.00) Ⅱ型 8 (32.00) 6(24.00) Ⅲ型 2 (8.00) 1(4.00) Ⅳ型 2 (8.00) 1(4.00) 注:LS:腹腔镜下脾切除术;OS:开服脾切除术;a:脾脏破裂分型根据 2000 年中华医学会外科分会第六届全国脾脏外科学术研讨分级标准划分。 表 2 LS 组和 OS 组患者手术指标和术后并发症比较[(
$\bar x \pm s $ )/M(Q1,Q3)/n(%)]Table 2. Comparison of surgical indexes and postoperative complications between LS group and OS group [(
$\bar x \pm s $ )/M(Q1,Q3)/n(%)]项目 LS 组(n = 25) OS 组(n = 25) χ2/t P 手术时间(min) 152.16 ± 43.47 184.20 ± 63.14 −2.090 0.042* 术中出血量(mL) 800.00(500.00,1000.00) 1000.00(800.00,1750.00) −2.578 0.010* 术中输血量(mL) 450.00(400.00,601.25) 1200.00(461.00,1200.00) −2.074 0.038* 术后首次排气(h) (40.32 ± 13.36) (58.56 ± 18.43) −4.006 < 0.001* 术后首次下床(h) 48.00(48.00,72.00) 72.00(48.00,120.00) −2.725 0.006* 引流管拔除(h) (72.96 ± 21.33) (102.72 ± 43.00) −3.100 0.003* 腹腔积液(mL) 98.00(50.00,100.00) 100.00(100.00,200.00) −2.817 0.005* 术后镇痛(h) 24.00(24.00,48.00) 48.00(36.00,96.00) −3.080 0.002* 住院时间(d) 12.00 (10.00,14.00) 14.00 (11.50,17.00) −2.597 0.009* 住院费用(万元) 2.18(1.68,2.58) 1.77(1.51,2.18) −2.164 0.030* 术后并发症 a 8.420 0.004* 胸腔积液 1.00(4.0) 3.00(12.0) 胰瘘 1.00 (4.0) 5.00(20.0) 肝衰竭 0.00 1.00(4.0) 切口感染 0.00 2.00(8.0) 注:LS:腹腔镜下脾切除术;OS:开腹脾切除术;a:总计并发症比较结果,LS组 2 例(8.0%)发生术后并发症,OS 组 11 例(44.0%)发生术后并发症;*P < 0.05。 -
[1] 张海文,蔺广荣,徐怀勇,等. 腹腔镜脾切除联合选择性贲门周围血管离断术的临床疗效[J]. 腹腔镜外科杂志,2022,27(6):415-418. [2] Torre L A,Bray F,Siegel R L,et al. Global cancer statistics,2012[J]. CA:A Cancer Journal for Clinicians,2015,65(2):87-108. doi: 10.3322/caac.21262 [3] Asoglu O,Ozmen V,Gorgun E,et al. Does the early ligation of the splenic artery reduce hemorrhage during laparoscopic splenectomy?[J]. Surgical Laparoscopy,Endoscopy & Percutaneous Techniques,2004,14(3):118-121. [4] Gupta R A,Das R,Verma G R. A rare case of post-splenectomy gastric volvulus managed by laparoscopic anterior gastropexy[J]. Journal of Minimal Access Surgery,2017,13(2):161-163. doi: 10.4103/0972-9941.195581 [5] Park A, Targarona E M, Trías M. Laparoscopic surgery of the spleen: State of the art [J]. Langenbeck’s Archives of Surgery, 2001, 386(3): 230-239. [6] Winslow E R,Brunt L M. Perioperative outcomes of laparoscopic versus open splenectomy: A meta-analysis with an emphasis on complications[J]. Surgery,2003,134(4):647-653. [7] Li Y,Cui L,Zhang W,et al. Laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation for traumatic splenic rupture[J]. The Journal of Surgical Research,2013,185(2):711-716. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2013.06.018 [8] Habermalz B,Sauerland S,Decker G,et al. Laparoscopic splenectomy: The clinical practice guidelines of the European Association for Endoscopic Surgery (EAES)[J]. Surgical Endoscopy,2008,22(4):821-848. doi: 10.1007/s00464-007-9735-5 [9] 第六届全国脾脏外科学术研讨会“脾脏损伤程度分级”标准[J] . 腹部外科, 2001, 14(4): 198. [10] Chen W,Zheng R,Baade P D,et al. Cancer statistics in China,2015[J]. CA:A Cancer Journal for Clinicians,2016,66(2):115-132. doi: 10.3322/caac.21338 [11] 陶亮,谢志杰,高书峰,等. 62例创伤性脾破裂行腹腔镜脾切除的临床经验[J]. 中华普通外科杂志,2019,34(5):428-430. [12] Fisichella P M,Wong Y M,Pappas S G,et al. Laparoscopic splenectomy: Perioperative management,surgical technique,and results[J]. Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery:Official Journal of the Society for Surgery of the Alimentary Tract,2014,18(2):404-451. [13] Koshenkov V P,Németh Z H,Carter M S. Laparoscopic splenectomy: Outcome and efficacy for massive and supramassive spleens[J]. American Journal of Surgery,2012,203(4):517-522. doi: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2011.05.014 [14] 范瑞芳,柴福录,刘宏斌,等. 自体输血在外伤性肝脾破裂手术中的应用[J]. 西北国防医学杂志,2001,22(4):345-346. [15] Grossi U,Crucitti A,D'amato G,et al. Laparoscopic splenectomy for atraumatic splenic rupture[J]. International Surgery,2011,96(1):87-89. doi: 10.9738/1382.1 [16] Vecchio R,Cacciola E,Lipari G,et al. Laparoscopic splenectomy reduces the need for platelet transfusion in patients with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura[J]. JSLS:Journal of the Society of Laparoendoscopic Surgeons,2005,9(4):415-418. [17] Weiss C A,3Rd,Kavic S M,Adrales G L,et al. Laparoscopic splenectomy: What barriers remain?[J]. Surgical Innovation,2005,12(1):23-29. doi: 10.1177/155335060501200104 [18] 裴磊,李春明,黄涛,等. 腹腔镜与传统脾切除术治疗创伤性脾破裂的疗效对比研究[J]. 腹腔镜外科杂志,2019,24(8):577-581. [19] 陈晶,张悦,杨雨,等. 程序化腹腔镜脾切除或脾部分切除术在创伤性脾破裂诊治中的应用[J]. 中华普通外科杂志,2018,33(10):878-879. [20] 黄无浪,张旭华,张亮. 腹腔镜脾切除术治疗外伤性Ⅲ级脾破裂的安全性及有效性[J]. 实用临床医学,2022,23(6):7-8. -






 下载:
下载: