Spatiotemporal Expression Profiles of miR-25 in Siniperca chuatsi and Prediction Analysis of Its Targeting Core Circadian Clock Genes
-
摘要:
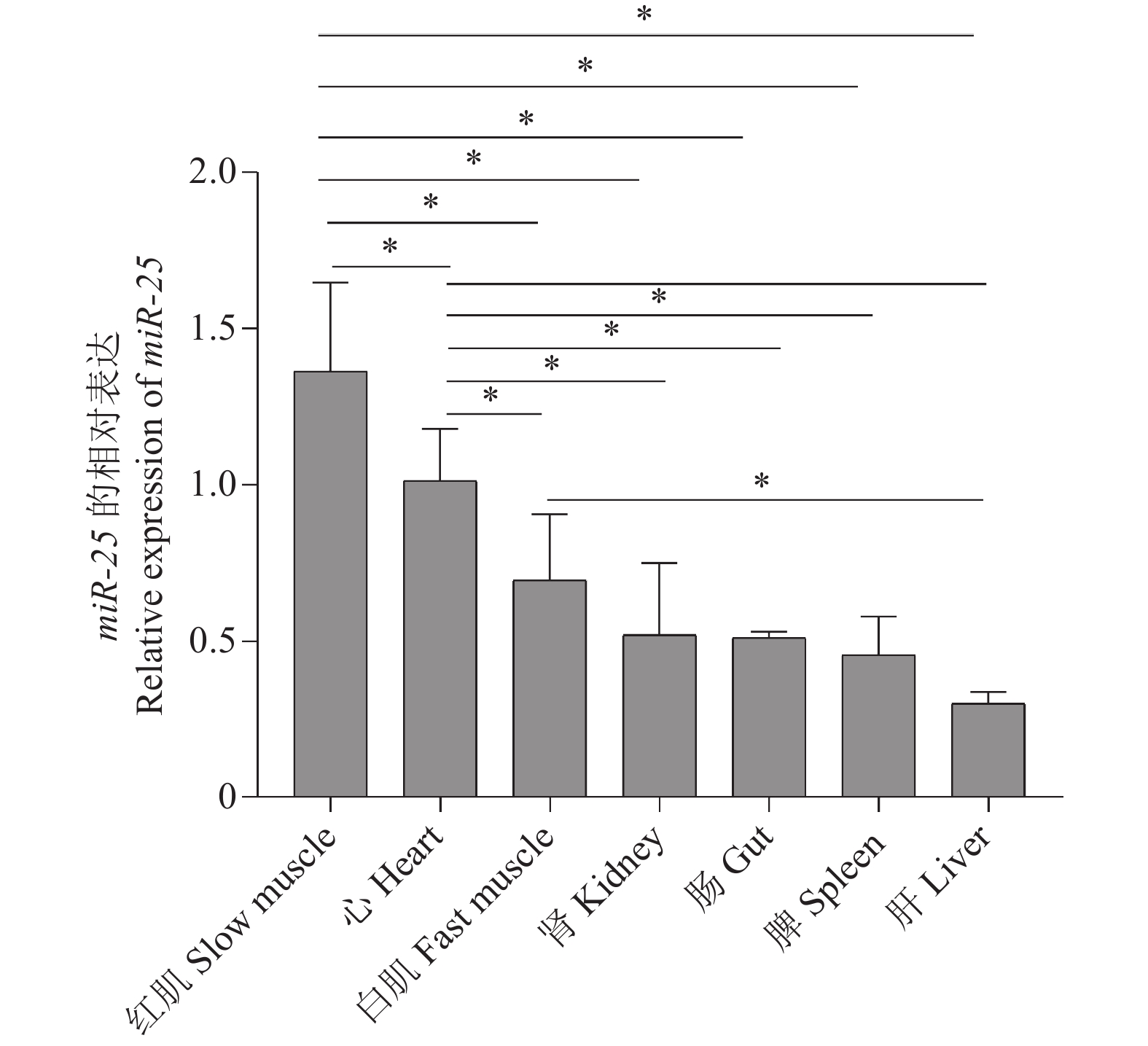
目的 研究miR-25在鳜的时空表达特征,预测其靶向核心生物钟基因,对其可能存在的生物学意义进行探讨。 方法 采用实时荧光定量PCR分析miR-25在鳜各组织以及不同阶段胚胎中的表达特征,并利用TargetScan对其靶向核心生物钟基因进行预测分析。 结果 miR-25在鳜红肌和心肌中的表达量较高(P < 0.05),而在鳜脾、肾、肠以及肝中的表达量较低,且这4个组织中的表达量,差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05);miR-25在鳜胚胎的2细胞期表达量较高(P < 0.05),随着胚胎发育,其表达水平逐渐降低。靶基因预测结果显示,节律基因Arntl2、Nr1d2b mRNA的3’UTR区域存在miR-25的靶位点。 结论 miR-25在胚胎发育过程中呈母源性表达,并且可能在鳜红肌和心肌中具有重要的调控意义,此外miR-25可能通过靶向调节Arntl2、Nr1d2b的表达来调控鳜生物节律,为后续研究miR-25的生理作用以及调控昼夜节律从而预防相关疾病提供参考依据。 Abstract:Objective To study the spatiotemporal expression profiles of miR-25 in the Chinese perch(Siniperca chuatsi), to predict its targeting core Circadian clock genes, and to explore its possible biological significance. Methods Real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR was used to analyze the expression characteristics of miR-25 in various tissues and embryos at different stages of Siniperca chuatsi, and TargetScan was used to predict its targeted core clock genes. Results The expression level of miR-25 was higher in the red muscle and heart (P < 0.05), while it was lower in the spleen, kidney, intestine, and liver of the Chinese perch. However, the expression level difference in these four tissues was not statistically significant (P > 0.05). The expression level of miR-25 was higher in the phase 2 of cell cycle in embryos (P < 0.05), and it gradually decreased as the embryos developed. Target gene prediction results showed that the 3’UTR region of the rhythmic genes Arntl2 and Nr1d2b mRNA contained target sites for miR-25. Conclusion miR-25 exhibited maternal expression during embryonic development and may have important regulatory significance in the red muscle and heart of Chinese perch. Additionally, miR-25 may regulate the circadian rhythm by targeting the expression of Arntl2 and Nr1d2b, providing a reference for further research on the physiological effects of miR-25 and the regulation of circadian rhythm to prevent related diseases. -
Key words:
- Siniperca chuatsi /
- miR-25 /
- Expression pattern /
- Target gene prediction
-
表 1 实时荧光定量PCR引物
Table 1. The Primer Sequences for RT-qPCR
名称 引物序列(5’-3’) sch-miR-25 F CATTGCACTTGTCTCGGTCTG U6 R TTTGGCTCTCTTGGCACGGAT U6 F ACGGACAGCTGAAGAACAAGT -
[1] Makeyev E V,Maniatis T. Multilevel regulation of gene expression by microRNAs[J]. Science,2008,319(5871):1789-1790. doi: 10.1126/science.1152326 [2] Schmiedel J M,Klemm S L,Zheng Y N,et al. Gene expression. MicroRNA control of protein expression noise[J]. Science,2015,348(6230):128-132. doi: 10.1126/science.aaa1738 [3] 丁小丽,胡蓉. microRNA-25在肿瘤中的研究进展[J]. 重庆医学,2017,46(4):545-548. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8348.2017.04.042 [4] Sárközy M,Kahán Z,Csont T. A myriad of roles of miR-25 in health and disease[J]. Oncotarget,2018,9(30):21580-21612. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.24662 [5] Yang L Q,Li L N,Chang P,et al. MiR-25 regulates gastric cancer cell growth and apoptosis by targeting EGR2[J]. Frontiers in Genetics,2021,12:690196. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.690196 [6] 李卿,李轶君,张国锐. miR-25对食管癌EC109细胞侵袭和迁移能力的影响及临床意义[J]. 天津医药,2022,50(4):357-362. [7] 董超,黄远丽,徐正丰. miR-25在乳腺癌组织、细胞的表达及对细胞增殖的影响[J]. 山东医药,2018,58(9):31-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2018.09.009 [8] 王博,田园园,孙成飞,等. 翘嘴鳜microRNA转录组分析及生长相关miRNA鉴定[J]. 基因组学与应用生物学,2017,36(2):603-613. doi: 10.13417/j.gab.036.000603 [9] Huang W,Ramsey K M,Marcheva B,et al. Circadian rhythms,sleep,and metabolism[J]. Clin Invest,2011,121(6):2133-2141. doi: 10.1172/JCI46043 [10] Ketelauri P,Scharov K,von Gall C,et al. Acute circadian disruption due to constant light promotes Caspase 1 activation in the mouse hippocampus[J]. Cells,2023,12(14):1836. doi: 10.3390/cells12141836 [11] Park I,Kim D,Kim J,et al. MicroRNA-25 as a novel modulator of circadian Period2 gene oscillation[J]. Experimental & Molecular Medicine,2020,52(9):1614-1626. [12] 朱鑫,叶苏杭,李源,等. 鳜miR-21的时空表达特征及短期饥饿胁迫下的适应性节律表达调控[J]. 中国水产科学,2022,29(5):665-672. doi: 10.12264/JFSC2021-0520 [13] 朱鑫,秦家鑫,何雅芝,等. 翘嘴鳜miR-125b的时空表达特征及饥饿对其节律性表达的调控[J]. 基因组学与应用生物学,2023,42(1):34-43. doi: 10.13417/j.gab.042.000034 [14] Kelu J J,Pipalia T G,Hughes S M. Circadian regulation of muscle growth independent of locomotor activity[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,2020,117(49):31208-31218. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2012450117 [15] 刘希良,宾石玉,王开卓,等. 翘嘴鳜的人工繁殖与胚胎发育观察[J]. 广西师范大学学报(自然科学版),2013,31(2):100-106. [16] Chu W Y,Liu L S,Li Y L,et al. Systematic identification and differential expression profiling of MicroRNAs from white and red muscles of siniperca chuatsi[J]. Curr Mol Med,2013,13(8):1397-1407. doi: 10.2174/15665240113139990059 [17] Livak K J,Schmittgen T D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method[J]. Methods,2001,25(4):402-408. doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262 [18] Wang B,Xu M T,Li M M,et al. MiR-25 promotes cardiomyocyte proliferation by targeting FBXW7[J]. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids,2020,19:1299-1308. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2020.01.013 [19] Li H Z,Xie Y M,Liu Y S,et al. Alteration in microRNA-25 expression regulate cardiac function via renin secretion[J]. Exp Cell Res,2018,365(1):119-128. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2018.02.029 [20] 任秀美奥,姚旭东,蒙亚琦,等. miR-449b对绵羊早期胚胎发育的影响[J]. 中国畜牧兽医,2022,49(7):2661-2668. doi: 10.16431/j.cnki.1671-7236.2022.07.024 [21] Giraldez A J,Mishima Y,Rihel J,et al. Zebrafish miR-430 promotes deadenylation and clearance of maternal mRNAs[J]. Science,2006,312(5770):75-79. doi: 10.1126/science.1122689 [22] Li X,Zhang W B,Fu J,et al. MicroRNA-451 is downregulated in the follicular fluid of women with endometriosis and influences mouse and human embryonic potential[J]. Reprod Biol Endocrinol,2019,17(1):96. doi: 10.1186/s12958-019-0538-z -






 下载:
下载: