Association between TMTC1 Gene Polymorphisms and Schizophrenia
-
摘要:
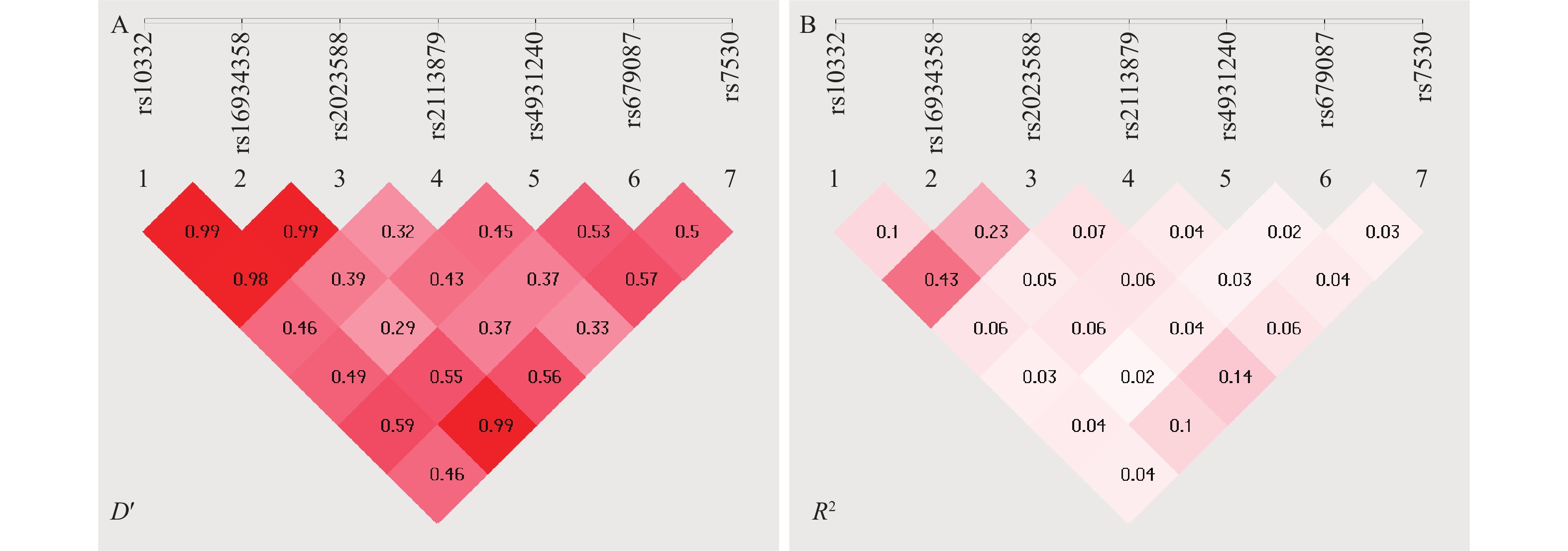
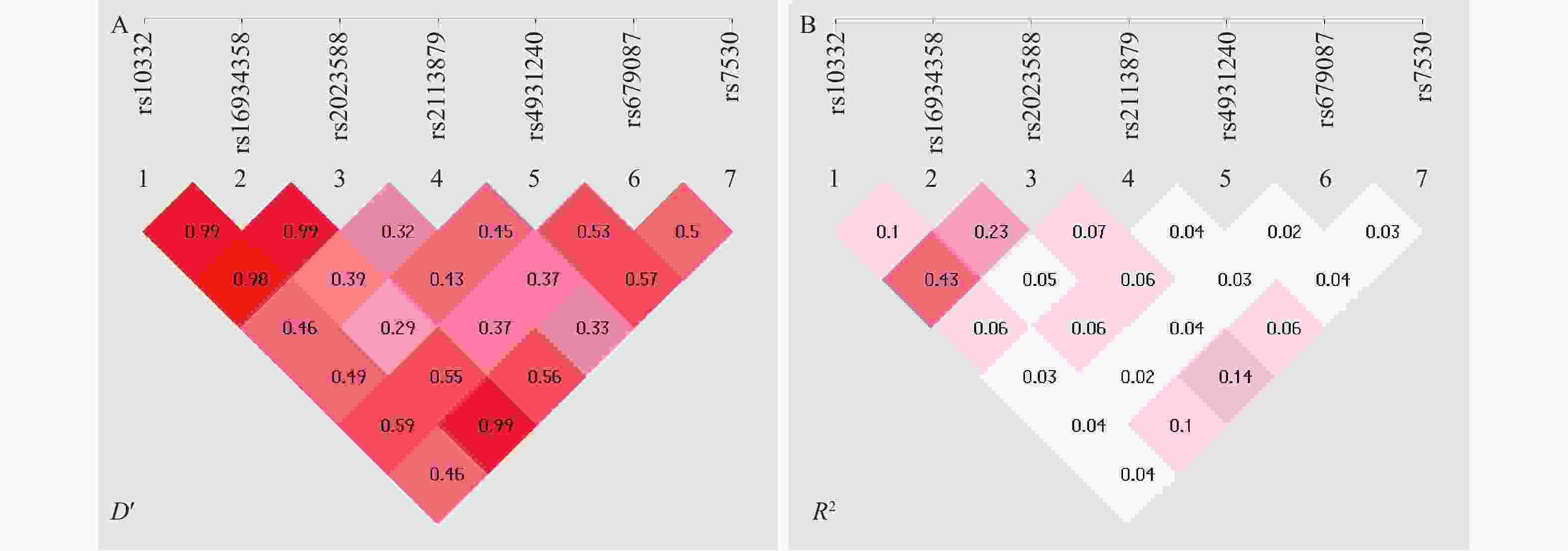
目的 探讨TMTC1基因单核苷酸多态性与精神分裂症的相关性。 方法 共纳入207例精神分裂症患者和186例健康对照。采用SNPscan TM多重SNP分型技术,对TMTC1基因7个SNP位点进行基因分型检测,比较等位基因、基因型和单倍型之间的差异,并分析在不同的遗传模式下SNP位点与精神分裂症易感性的相关性。 结果 7个SNP位点的基因型分布均符合Hardy-Weinberg平衡;7个位点的等位基因频率和基因型频率分布在2组间差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05)。不同遗传模式下7个SNP位点多态性均与精神分裂症发病风险无关(P > 0.05);但rs10332与rs16934358、rs10332与rs2023588、rs16934358与rs2023588、rs16934358与rs7503之间存在高度连锁不平衡。 结论 TMTC1基因rs7503、rs10332、rs2023588、rs16934358、rs2113879、rs679087、rs4931240位点多态性与精神分裂症无关,需要扩大样本量和筛选新的SNP位点进一步分析。 Abstract:Objective To explore the association between single nucleotide polymorphisms of TMTC1 gene and schizophrenia. Methods A total of 207 patients with schizophrenia and 186 healthy controls were included in the study. SNPscanTM multiplex SNP genotyping technology was used to perform genetic typing of 7 SNP loci in the TMTC1 gene. Differences in allele frequencies, genotypes, and haplotypes were compared, and the correlation between SNP loci and susceptibility to schizophrenia was analyzed under different genetic models. Results The genotype distribution of the 7 SNP sites loci is consistent with Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. There was no statistically significant difference in the allele and genotype frequency distribution of the 7 loci between the two groups (P > 0.05). The polymorphisms of the 7 SNP loci under different genetic models are not associated with the risk of schizophrenia (P > 0.05). However, there is a high degree of linkage disequilibrium (LD) between rs10332 and rs16934358, rs10332 and rs2023588, rs16934358 and rs2023588, rs16934358 and rs7503. Conclusion The polymorphisms of the TMTC1 gene at rs7503, rs10332, rs2023588, rs16934358, rs2113879, rs679087, and rs4931240 sites are not associated with schizophrenia. Further analysis is needed by increasing the sample size and screening for new SNP loci. -
Key words:
- Schizophrenia /
- TMTC1 /
- Single nucleotide polymorphism /
- Linkage disequilibrium
-
表 1 2组TMTC1基因SNP位点等位基因频率分布[n(%)]
Table 1. Allele frequency distribution of SNP sites in two groups of TMTC1 gene [n(%)]
SNP 分层 等位基因 病例组 对照组 χ2 P rs10332 总样本 C 286(69. 1) 261(70.2) 0.107 0.742 T 128(30.9) 111(29.8) 男性 C 103(66.9) 162(71.1) 0.752 0.385 T 51(33.1) 66(28.9) 女性 C 183(70.4) 99(68.8) 0. 117 0.731 T 77(29.6) 45(31.3) rs16934358 总样本 T 337(81.4) 301(80.9) 0.030 0.861 C 77(18.6) 71(19. 1) 男性 T 128(83. 1) 183(80.3) 0.494 0.481 C 26(16.9) 45(19.7) 女性 T 209(80.4) 118(81.9) 0.146 0.702 C 51(19.6) 26(18. 1) rs2023588 总样本 T 209(50.5) 190(51.1) 0.027 0.868 C 205(49.5) 182(48.9) 男性 T 76(49.4) 118(51.8) 0.212 0.644 C 78(50.6) 110(48.2) 女性 T 133(51.2) 72(50.0) 0.049 0.824 C 127(48.8) 72(50.0) rs2113879 总样本 A 247(59.7) 210(56.5) 0.829 0.362 G 167(40.3) 162(43.5) 男性 A 90(58.4) 130(57.0) 0.076 0.782 G 64(41.6) 98(43.0) 女性 A 157(60.4) 80(55.6) 0.891 0.345 G 103(39.6) 64(44.4) rs4931240 总样本 T 311(75.1) 279(75.0) 0.001 0.968 C 103(24.9) 93(25.0) 男性 T 117(76.0) 170(74.6) 0.098 0.754 C 37(24.0) 58(25.4) 女性 T 194(74.6) 109(75.7) 0.057 0.810 C 66(25.4) 35(24.3) rs679087 总样本 C 319(77.1) 287(77.2) 0.001 0.974 A 95(22.9) 85(22.8) 男性 C 118(76.6) 180(78.9) 0.289 0.591 A 36(23.4) 48(21.1) 女性 C 201(77.3) 107(74.3) 0.461 0.497 A 59(22.7) 37(25.7) rs7503 总样本 A 289(69.8) 252(67.7) 0.389 0.532 G 125(30.2) 120(32.3) 男性 A 114(74.0) 153(67.1) 2.092 0.148 G 40(26.0) 75(32.9) 女性 A 175(67.3) 99(68.8) 0.088 0.766 G 85(32.7) 45(31.3) 表 2 2组TMTC1基因SNP位点的基因型频率分布[n(%)]
Table 2. Genotype frequency distribution of SNP sites in two groups of TMTC1 gene [n(%)]
SNP 分层 基因型 病例组 对照组 χ2 P rs10332 总样本 CC 101(48.8) 92(49.5) 0.224 0.885 CT 84(40.6) 77(41.4) TT 22(10.6) 17(9.1) 男性 CC 36(46.8) 59(51.8) 0.729 0.694 CT 31(40.3) 44(38.6) TT 10(13.0) 11(9.6) 女性 CC 65(50.0) 33(45.8) 0.487 0.784 CT 53(40.8) 33(45.8) TT 12(9.2) 6(8.3) rs16934358 总样本 TT 137(66.2) 122(65.6) 0.046 0.976 TC 63(30.4) 57(30.6) CC 7(3.4) 7(3.8) 男性 TT 55(71.4) 73(64.0) 2.002 0.367 TC 18(23.4) 37(32.5) CC 4(5.2) 4(3.5) 女性 TT 82(63.1) 49(68. 1) 1.389 0.499 TC 45(34.6) 20(27.8) CC 3(2.3) 3(4.2) rs2023588 总样本 TT 47(22.7) 46(24.7) 0.350 0.840 TC 115(55.6) 98(52.7) CC 45(21.7) 42(22.6) 男性 TT 20(25.9) 29(25.4) 0.860 0.649 TC 36(46.8) 60(52.6) CC 21(27.3) 25(21.9) 女性 TT 27(20.8) 17(23.6) 1.288 0.525 TC 79(60.8) 38(52.8) CC 24(18.5) 17(23.6) rs2113879 总样本 AA 74(35.7) 63(33.9) 1.336 0.512 AG 99(47.8) 84(45.2) GG 34(16.4) 39(21.0) 男性 AA 30(39.0) 41(36.0) 0.222 0.894 AG 30(39.0) 48(42. 1) GG 17(22.1) 25(21.9) 女性 AA 44(33.8) 22(30.6) 1.462 0.481 AG 69(53.1) 36(50.0) GG 17(13.1) 14( 19.4) rs4931240 总样本 TT 117(56.5) 107(57.5) 0.376 0.828 TC 77(37.2) 65(34.9) CC 13(6.3) 14(7.5) 男性 TT 46(59.7) 66(57.9) 0.089 0.956 TC 25(32.5) 38(33.3) CC 6(7.8) 10(8.8) 女性 TT 71(54.6) 41(56.9) 0.122 0.941 TC 52(40.0) 27(37.5) CC 7(5.4) 4(5.6) rs679087 总样本 CC 124(59.9) 110(59.1) 0.261 0.877 CA 71(34.3) 67(36.0) AA 12(5.8) 9(4.8) 男性 CC 44(57. 1) 71(62.3) 0.636 0.727 CA 30(39.0) 38(33.3) AA 3(3.9) 5(4.4) 女性 CC 80(61.5) 39(54.2) 1.583 0.453 CA 41(31.5) 29(40.3) AA 9(6.9) 4(5.6) rs7503 总样本 AA 98(47.3) 87(46.8) 1.527 0.465 GA 93(44.9) 78(41.9) GG 16(7.7) 21( 11.3) 男性 AA 43(55.8) 51(44.7) 2.295 0.317 GA 28(36.4) 51(44.7) GG 6(7.8) 12(10.5) 女性 AA 55(42.3) 36(50.0) 3.337 0.189 GA 65(50.0) 27(37.5) GG 10(7.7) 9(12.5) 表 3 不同遗传模式下2组TMTC1基因SNP位点多态性[n(%)](1)
Table 3. SNP polymorphisms of two groups of TMTC1 gene under different genetic patterns [n(%)](1)
SNP 分层 等位基因 病例组 对照组 OR(95% CI) P rs10332 共显性 C/C 101(48.8) 92(49.5) 1 0.92 C/T 84(40.6) 77(41.4) 1.06(0.68~1.65) T/T 22( 10.6) 17(9. 1) 0.91(0.44~1.90) 显性 C/C 101(48.8) 92(49.5) 1 0.91 C/T-T/T 106(51.2) 94(50.5) 1.03(0.67~1.56) 隐性 C/C-C/T 185(89.4) 169(90.9) 1 0.74 T/T 22(10.6) 17(9. 1) 0.89(0.44~1.80) 超显性 C/C-T/T 123(59.4) 109(58.6) 1 0.75 C/T 84(40.6) 77(41.4) 1.07(0.70~1.65) 对数加性 - - - 0.99(0.72~1.36) 0.95 rs16934358 共显性 T/T 137(66.2) 122(65.6) 1 0.95 T/C 63(30.4) 57(30.6) 1.04(0.65~1.65) C/C 7(3.4) 7(3.8) 0.86(0.28~2.69) 显性 T/T 137(66.2) 122(65.6) 1 0.94 T/C-C/C 70(33.8) 64(34.4) 1.02(0.65~1.59) 隐性 T/T-T/C 200(96.6) 179(96.2) 1 0.78 C/C 7(3.4) 7(3.8) 0.85(0.28~2.63) 超显性 T/T-C/C 144(69.6) 129(69.3) 1 0.85 T/C 63(30.4) 57(30.6) 1.05(0.66~1.65) 对数加性 - - - 0.99(0.68~1.45) 0.98 rs2023588 共显性 T/T 47(22.7) 46(24.7) 1 0.86 T/C 115(55.6) 98(52.7) 0.87(0.52~1.47) C/C 45(21.7) 42(22.6) 0.98(0.52~1.81) 显性 T/T 47(22.7) 46 (24.7) 1 0.68 T/C-C/C 160(77.3) 140(75.3) 0.90(0.55~1.48) 隐性 T/T-T/C 162(78.3) 144(77.4) 1 0.79 C/C 45(21.7) 42(22.6) 1.07(0.64~1.78) 超显性 T/T-C/C 92(44.4) 88(47.3) 1 0.57 T/C 115(55.6) 98(52.7) 0.88(0.58~1.35) 对数加性 - - - 0.99(0.72~1.34) 0.92 rs2113879 共显性 A/A 74(35.8) 63(33.9) 1 0.77 A/G 99(47.8) 84(45.2) 1.09(0.68~1.75) G/G 34(16.4) 39(21.0) 1.25(0.68~2.29) 显性 A/A 74(35.8) 63(33.9) 1 0.58 A/G-G/G 133(64.2) 123(66.1) 1.13(0.73~1.76) 隐性 A/A-A/G 173(83.6) 147(79.0) 1 0.52 G/G 34(16.4) 39(21.0) 1.19(0.69~2.05) 超显性 A/A-G/G 108(52.2) 102(54.8) 1 0.98 A/G 99(47.8) 84(45.2) 1.01(0.66~1.54) 对数加性 - - - 1.11(0.83~1.50) 0.47 rs4931240 共显性 T/T 117(56.5) 107(57.5) 1 1.00 T/C 77(37.2) 65(35.0) 0.98(0.63~1.53) C/C 13(6.3) 14(7.5) 1.00(0.42~2.38) 显性 T/T 117(56.5) 107(57.5) 1 0.94 T/C-C/C 90(43.5) 79(42.5) 0.98(0.64~1.51) 隐性 T/T-T/C 194(93.7) 172(92.5) 1 0.98 C/C 13(6.3) 14(7.5) 1.01(0.43~2.36) 超显性 T/T-C/C 130(62.8) 121(65.0) 1 0.93 T/C 77(37.2) 65(35.0) 0.98(0.63~1.52) 对数加性 - - - 0.99(0.71~1.39) 0.96 rs679087 共显性 C/C 124(59.9) 110(59.1) 1 0.90 C/A 71(34.3) 67(36.0) 1.11(0.71~1.73) A/A 12(5.8) 9(4.8) 0.98(0.37~2.55) 显性 C/C 124(59.9) 110(59.1) 1 0.70 C/A-A/A 83(40.1) 76(40.9) 1.09(0.71~1.67) 隐性 C/C-C/A 195(94.2) 177(95.2) 1 0.90 A/A 12(5.8) 9(4.8) 0.94(0.37~2.42) 超显性 C/C-A/A 136(65.7) 119(64.0) 1 0.65 C/A 71(34.3) 67(36.0) 1.11(0.71~1.72) 对数加性 - - - 1.05(0.74~1.50) 0.79 表 3 不同遗传模式下2组TMTC1基因SNP位点多态性[n(%)](2)
Table 3. SNP polymorphisms of two groups of TMTC1 gene under different genetic patterns [n(%)](2)
SNP 分层 等位基因 病例组 对照组 OR(95% CI) P rs7503 共显性 A/A 98(47.3) 87(46.8) 1 0.60 G/A 93(44.9) 78(41.9) 1.06(0.68~1.65) G/G 16(7.7) 21(11.3) 1.47(0.69~3.15) 显性 A/A 98(47.3) 87(46.8) 1 0.60 G/A-G/G 109(52.7) 99(53.2) 1.12(0.73~1.71) 隐性 A/A-G/A 191(92.3) 165(88.7) 1 0.33 G/G 16(7.7) 21(11.3) 1.44(0.69~2.98) 超显性 A/A-G/G 114(55.1) 108(58.1) 1 0.97 G/A 93(44.9) 78(41.9) 0.99(0.65~1.52) 对数加性 - - - 1.15(0.83~1.59) 0.40 表 4 TMTC1基因的单倍型分布情况[n(%)]
Table 4. Haplotype distribution of the TMTC1 gene [n(%)]
单倍型 等位基因构成 病例组 对照组 χ2 P OR (95% CI) H1 CTTGTCA 35(0.084) 33(0.088) 0.043 0.835 0.948 (0.576~ 1.560) H2 TTCATCG 13(0.031) 13(0.034) 0.076 0.781 0.895(0.409~ 1.956) H3 TTCATCA 61(0.147) 47(0.126) 0.728 0.393 1.194(0.793~ 1.799) H4 CTTGTCG 37(0. 089) 37(0.099) 0.233 0.628 0.888 (0.550~ 1.434) H5 CTTATCG 22(0.053) 22(0.059) 0.133 0.714 0.892 (0.485~ 1.640) H6 CCCGCCA 25(0.060) 20(0.053) 0.159 0.689 1.131 (0.617~2.072) H7 CCCGTCA 13(0.031) 12(0.032) 0.004 0.945 0.972(0.438~ 2.158) H8 CTTACCG 15(0.036) 11(0.029) 0.271 0.602 1.233(0.559~ 2.721) -
[1] 郝伟, 陆林主编. 精神病学[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2018: 85-86. [2] Sullivan P F,Kendler K S,Neale M C. Schizophrenia as a complex trait:Evidence from a meta-analysis of twin studies[J]. Archives of General Psychiatry,2003,60(12):1187. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.60.12.1187 [3] Mealer R G,Williams S E,Daly M J,et al. Glycobiology and schizophrenia: A biological hypothesis emerging from genomic research[J]. Molecular Psychiatry,2020,25(12):3129-3139. doi: 10.1038/s41380-020-0753-1 [4] Qing L,Liu L,Zhou L,et al. Sex-dependent association of mineralocorticoid receptor gene (NR3C2) DNA methylation and schizophrenia[J]. Psychiatry Research,2020,292:113318. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2020.113318 [5] 青丽丽. NR3C1和NR3C2基因SNP和甲基化与精神分裂症的关联性及调控机制研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明医科大学, 2022. [6] Birnbaum R,Weinberger D R. Genetic insights into the neurodevelopmental origins of schizophrenia[J]. Nature Reviews Neuroscience,2017,18(12):727-740. doi: 10.1038/nrn.2017.125 [7] Williams S E,Mealer R G,Scolnick E M,et al. Aberrant glycosylation in schizophrenia: A review of 25 years of post-mortem brain studies[J]. Molecular Psychiatry,2020,25(12):3198-3207. doi: 10.1038/s41380-020-0761-1 [8] Larsen I S B,Narimatsu Y,Joshi H J,et al. Discovery of an O-mannosylation pathway selectively serving cadherins and protocadherins[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,2017,114(42):11163-11168. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1708319114 [9] Graham J B,Sunryd J C,Mathavan K,et al. Endoplasmic reticulum transmembrane protein TMTC3 contributes to O-mannosylation of E-cadherin,cellular adherence,and embryonic gastrulation[J]. Molecular Biology of the Cell,2020,31(3):167-183. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E19-07-0408 [10] Jerber J,Zaki M S,Al-Aama J Y,et al. Biallelic mutations in TMTC3,encoding a transmembrane and TPR-containing protein,lead to cobblestone lissencephaly[J]. American Journal of Human Genetics,2016,99(5):1181-1189. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2016.09.007 [11] Farhan S M K,Nixon K C J,Everest M,et al. Identification of a novel synaptic protein,TMTC3,involved in periventricular nodular heterotopia with intellectual disability and epilepsy[J]. Human Molecular Genetics,2017,26(21):4278-4289. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddx316 [12] Runge C L,Indap A,Zhou Y,et al. Association of TMTC2 with human nonsyndromic sensorineural hearing loss[J]. JAMA Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery,2016,142(9):866-872. [13] Li J,Akil O,Rouse S L,et al. Deletion of TMTC4 activates the unfolded protein response and causes postnatal hearing loss[J]. Journal of Clinical Investigation,2018,128(11):5150-5162. doi: 10.1172/JCI97498 [14] Sunryd J C,Cheon B,Graham J B,et al. TMTC1 and TMTC2 are novel endoplasmic reticulum tetratricopeptide repeat-containing adapter proteins involved in calcium homeostasis[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry,2014,289(23):16085-16099. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.554071 [15] Ngô H M,Zhou Y,Lorenzi H,et al. Toxoplasma modulates signature pathways of human epilepsy,neurodegeneration & cancer[J]. Scientific Reports,2017,7(1):11496. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-10675-6 [16] Ben-Mahmoud A,Kishikawa S,Gupta V,et al. A cryptic microdeletion del(12)(p11.21p11.23) within an unbalanced translocation t(7;12)(q21.13;q23.1) implicates new candidate loci for intellectual disability and Kallmann syndrome[J]. Scientific Reports,2023,13(1):12984. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-40037-4 [17] Fagerberg L,Hallström B M,Oksvold P,et al. Analysis of the human tissue-specific expression by genome-wide integration of transcriptomics and antibody-based proteomics[J]. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics,2014,13(2):397-406. -





 下载:
下载: