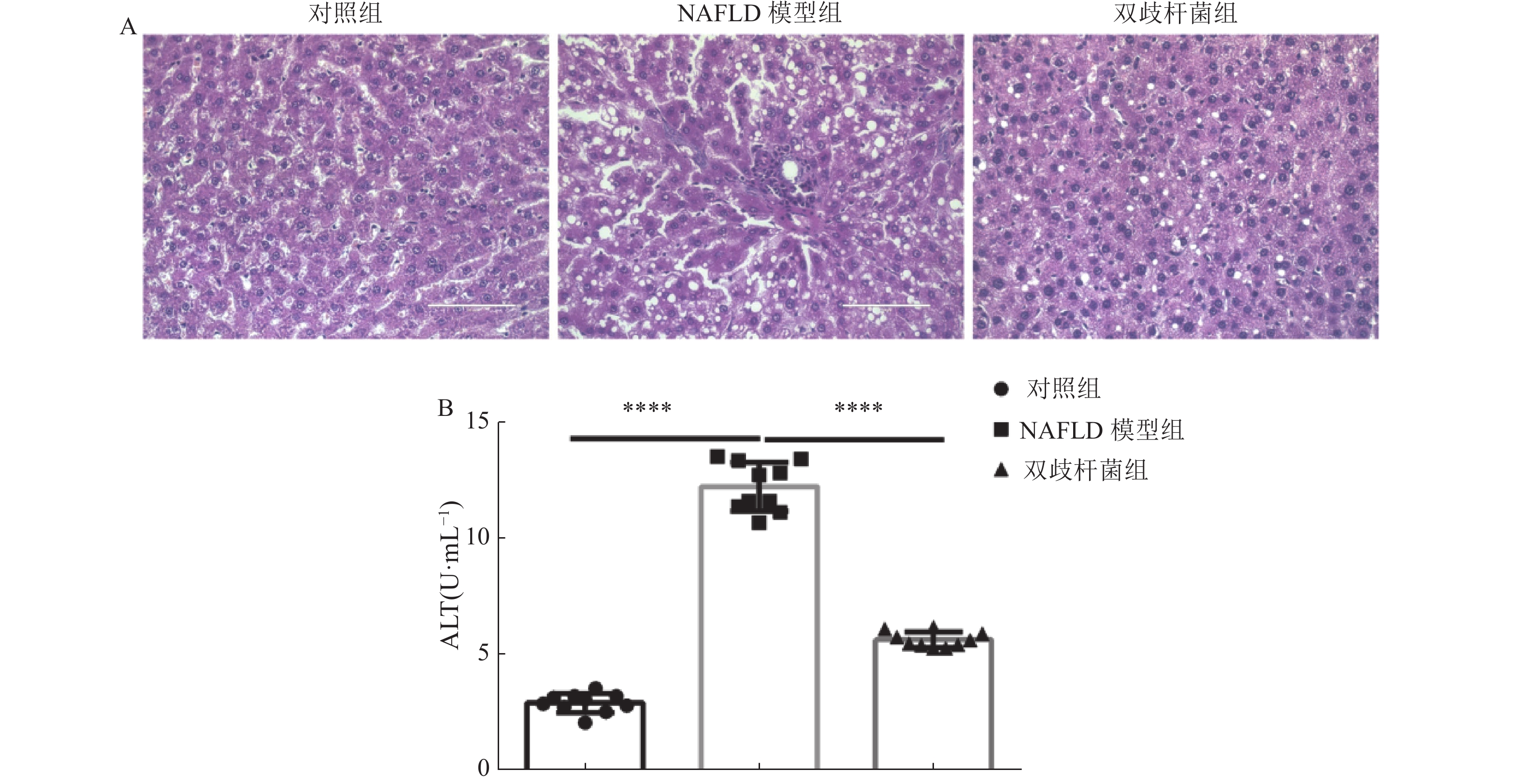
|
[1]
|
Wagner R,Eckstein S S,Yamazaki H,et al. Metabolic implications of pancreatic fat accumulation[J]. Nat Rev Endocrinol,2022,18(1):43-54. doi: 10.1038/s41574-021-00573-3
|
|
[2]
|
Kwan S Y,Jiao J,Joon A,et al. Gut microbiome features associated with liver fibrosis in Hispanics,a population at high risk for fatty liver disease[J]. Hepatology,2022,5(4):955-967.
|
|
[3]
|
Kolodziejczyk A A,Zheng D,Shibolet O,et al. The role of the microbiome in NAFLD and NASH[J]. EMBO Mol Med,2019,11(2):e9302. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201809302
|
|
[4]
|
Safari Z,Gérard P. The links between the gut microbiome and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci,2019,76(8):1541-1558. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03011-w
|
|
[5]
|
Hu H,Lin A,Kong M,et al. Intestinal microbiome and NAFLD: Molecular insights and therapeutic perspectives[J]. J Gastroenterol,2020,55(2):142-158. doi: 10.1007/s00535-019-01649-8
|
|
[6]
|
Aron-Wisnewsky J,Vigliotti C,Witjes J,et al. Gut microbiota and human NAFLD: Disentangling microbial signatures from metabolic disorders[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol,2020,17(5):279-297. doi: 10.1038/s41575-020-0269-9
|
|
[7]
|
Lau L H S,Wong S H. Microbiota,obesity and NAFLD[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol,2018,1061:111-125.
|
|
[8]
|
Canfora E E,Meex R C R,Venema K,et al. Gut microbial metabolites in obesity,NAFLD and T2DM[J]. Nat Rev Endocrinol,2019,15(5):261-273. doi: 10.1038/s41574-019-0156-z
|
|
[9]
|
Fan Y,Pedersen O. Gut microbiota in human metabolic health and disease[J]. Nat Rev Microbiol,2021,19(1):55-71. doi: 10.1038/s41579-020-0433-9
|
|
[10]
|
Bana B,Cabreiro F. The microbiome and aging[J]. Annu Rev Genet,2019,53:239-261. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-112618-043650
|
|
[11]
|
Suez J,Zmora N,Segal E,et al. The pros,cons,and many unknowns of probiotics[J]. Nat Med,2019,25(5):716-729. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0439-x
|
|
[12]
|
Qian X,Si Q,Lin G,et al. Bifidobacterium adolescentis is effective in relieving type 2 diabetes and may be related to its dominant core genome and gut microbiota modulation capacity[J]. Nutrients,2022,14(12):2479. doi: 10.3390/nu14122479
|
|
[13]
|
Fang Z,Pan T,Li L,et al. Bifidobacterium longum mediated tryptophan metabolism to improve atopic dermatitis via the gut-skin axis[J]. Gut Microbes,2022,14(1):2044723. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2022.2044723
|
|
[14]
|
Eng J M,Estall J L. Diet-induced models of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Food for thought on sugar,fat,and cholesterol[J]. Cells,2021,10(7):1805.P. doi: 10.3390/cells10071805
|
|
[15]
|
Zeng H,Larson K J,Cheng WH,et al. Advanced liver steatosis accompanies an increase in hepatic inflammation,colonic,secondary bile acids and Lactobacillaceae/Lachnospiraceae bacteria in C57BL/6 mice fed a high-fat diet[J]. J Nutr Biochem,2020,78:108336. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2019.108336
|
|
[16]
|
Yuan G,Tan M,Chen X. Punicic acid ameliorates obesity and liver steatosis by regulating gut microbiota composition in mice[J]. Food Funct,2021,12(17):7897-7908. doi: 10.1039/D1FO01152A
|
|
[17]
|
Wang H,Wang Q,Yang C,et al. Bacteroides acidifaciens in the gut plays a protective role against CD95-mediated liver injury[J]. Gut Microbes,2022,14(1):2027853. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2022.2027853
|
|
[18]
|
Nishimura N,Kaji K,Kitagawa K,et al. Intestinal permeability is a mechanical rheostat in the pathogenesis of liver cirrhosis[J]. Int J Mol Sci,2021,22(13):6921. doi: 10.3390/ijms22136921
|
|
[19]
|
Do M H,Oh M J,Lee H B,et al. Bifidobacterium animalis ssp. lactis MG741 reduces body weight and ameliorates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease via improving the gut permeability and amelioration of inflammatory cytokines[J]. Nutrients,2022,14(9):1965. doi: 10.3390/nu14091965
|
|
[20]
|
Wang W,Xu A L,Li Z C,et al. Combination of probiotics and salvia miltiorrhiza polysaccharide alleviates hepatic steatosis via gut microbiota modulation and insulin resistance improvement in high fat-induced NAFLD mice[J]. Diabetes Metab J,2020,44(2):336-348. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2019.0042
|
|
[21]
|
Yang X,Mo W,Zheng C,et al. Alleviating effects of noni fruit polysaccharide on hepatic oxidative stress and inflammation in rats under a high-fat diet and its possible mechanisms[J]. Food Funct,2020,11(4):2953-2968. doi: 10.1039/D0FO00178C
|
|
[22]
|
Wang X,Shi L,Wang X,et al. MDG-1,an Ophiopogon polysaccharide,restrains process of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease via modulating the gut-liver axis[J]. Int J Biol Macromol,2019,141(3):1013-1021.
|
|
[23]
|
Tong A J,Hu R K,Wu L X,et al. Ganoderma polysaccharide and chitosan synergistically ameliorate lipid metabolic disorders and modulate gut microbiota composition in high fat diet-fed golden hamsters[J]. J Food Biochem,2020,44(1):e13109.
|
|
[24]
|
Dehhaghi M, Kazemi Shariat Panahi H, Guillemin GJ. Microorganisms, tryptophan metabolism, and kynurenine pathway: A complex interconnected loop influencing human health status [J]. Int J Tryptophan Res, 2019, 12(2): 1178646919852996.
|
|
[25]
|
Arnoriaga-Rodríguez M,Mayneris-Perxachs J,Burokas A,et al. Obesity impairs short-term and working memory through gut microbial metabolism of aromatic amino acids[J]. Cell Metab,2020,32(4):548-560,e7. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.09.002
|
|
[26]
|
Zhao Z H,Xin F Z,Xue Y,et al. Indole-3-propionic acid inhibits gut dysbiosis and endotoxin leakage to attenuate steatohepatitis in rats[J]. Exp Mol Med,2019,51(9):1-14.
|






 下载:
下载: