Differential Diagnosis of Benign and Malignant Ovarian Tumors Based on Convolutional Neural Network
-
摘要:
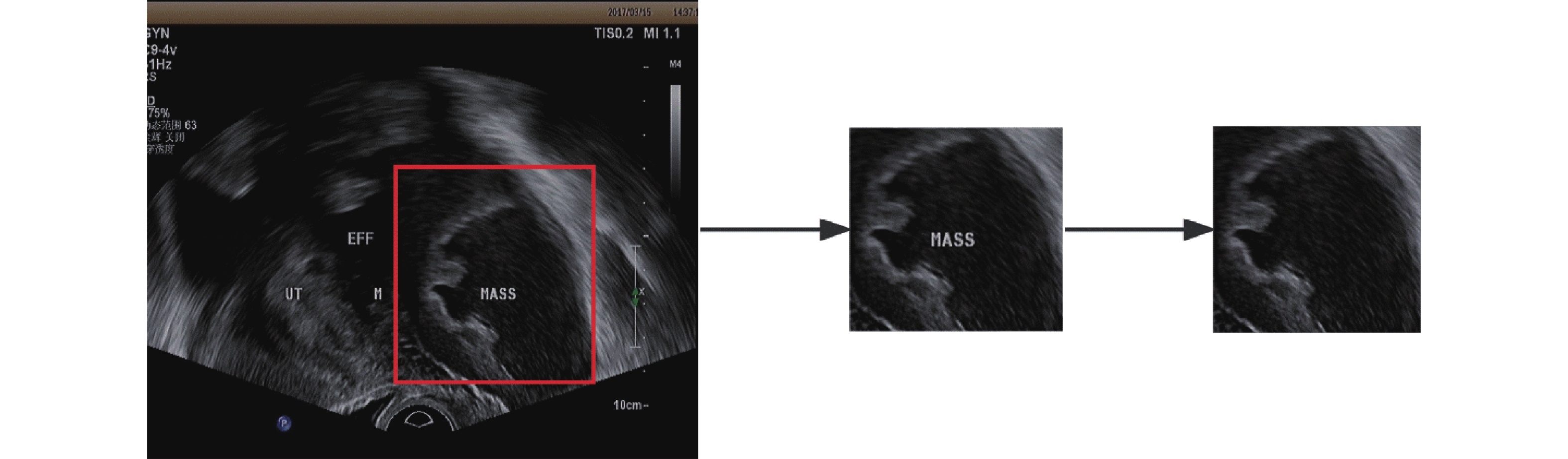
目的 建立卷积神经网络卵巢肿瘤超声诊断模型,探讨其在卵巢良恶性肿瘤鉴别诊断中的价值。 方法 收集2015年6月至2022年9月于昆明医科大学第二附属医院接受超声检查,并获得细胞学或组织病理证实的卵巢良性、恶性肿瘤超声图像各200张,共400张卵巢肿瘤超声图像。图像以1∶3的比例分为训练集和验证集。基于卷积神经网络构建训练并验证VGG16、MobileNet-V2 2个诊断模型,同时选取高年资、低年资2名超声医生进行训练集超声图像诊断,以病理结果为金标准,评估2个诊断模型和超声医生鉴别卵巢良恶性的效能。 结果 VGG16模型诊断卵巢肿瘤良恶性的灵敏度、特异度、准确度分别为80.67%,79.33%,80.00%;MobileNet-V2模型诊断卵巢肿瘤良恶性的灵敏度、特异度、准确度分别为89.33%,93.33%,91.33%;MobileNet-V2模型诊断效能最优,且MobileNet-V2、VGG16模型诊断效能均优于超声医生(P < 0.05)。 结论 卷积神经网络卵巢肿瘤诊断模型具有较好诊断价值,其中MobileNet-V2模型能准确地判断卵巢肿瘤超声图像的良恶性。 Abstract:Objective To establish a convolutional neural network model for ultrasound diagnosis of ovarian tumors and explore its value in distinguishing between benign and malignant ovarian tumors. Methods A total of 400 ovarian tumor ultrasound images, including 200 benign and 200 malignant tumors, were collected from June 2015 to September 2022 at the Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University. These images were confirmed by cytology or histopathology. The images were divided into a training set and a validation set in a 1∶3 ratio. Two diagnostic models, VGG16 and MobileNet-V2 were constructed based on convolutional neural networks for training and validation. A senior and a junior sonographers were selected to diagnose the ultrasound images in the training set. The performance of the two diagnostic models and the ultrasound doctors in distinguishing between benign and malignant ovarian tumors was evaluated using the pathological results as the gold standard. Results The sensitivity, specificity and accuracy of VGG16 model in diagnosing the benign and malignant nature of ovarian tumors were 80.67%, 79.33% and 80.00% respectively. The sensitivity, specificity and accuracy of MobileNet-V2 were 89.33%, 93.33% and 91.33% respectively. The MobileNet-V2 model had the best diagnostic performance, and both the MobileNet-V2 and VGG16 models had better diagnostic performance than ultrasound doctors (P < 0.05). Conclusion The convolutional neural network ovarian tumor diagnostic model has good diagnostic value, with the MobileNet-V2 model accurately determining the benign or malignant nature of ovarian tumor ultrasound images. -
Key words:
- Convolutional neural network /
- Ovarian tumors /
- Ultrasonic diagnosis
-
表 1 收集图片病理结果统计表(
$ \bar x \pm s$ )Table 1. Statistical tables of pathological results from collected image (
$ \bar x \pm s$ )病理结果 超声图片例数(n) 年龄(岁) 良性肿瘤 200
33.84 ± 9.15成熟畸胎瘤 64 子宫内膜异位囊肿 57 纤维瘤 4 纤维-卵泡膜细胞瘤 1 囊腺瘤 73 炎性病变 1 恶性肿瘤 200
54.32 ± 10.70浆液性癌 68 黏液性癌 10 子宫内膜样腺癌 8 透明细胞癌 22 未分类腺癌 31 上皮内癌 2 生殖细胞恶性肿瘤 8 性索-间质恶性肿瘤 10 转移性肿瘤 6 交界性肿瘤 35 合计 400 48.34 ± 13.47 表 2 Mobilenet-V2、VGG16、与超声医生诊断能力比较
Table 2. Comparision of diagnosis performance among MobileNet-V2,VGG16 and ultrasound doctors in validation sets
诊断模型 参数 Kappa值 准确率(%) 灵敏度(%) 特异度(%) 阳性预测值(%) 阴性预测值(%) Mobilenet-V2 91.33 89.33 93.33 93.06 89.74 0.827* VGG16 80.00 80.67 79.33 79.61 80.41 0.600* 高年资医生 78.00 75.33 80.67 77.93 78.06 0.560* 低年资医生 66.33 66.67 66.00 66.23 66.44 0.327 *P < 0.05。 -
[1] 狄文,胡媛. 卵巢癌的大数据研究[J]. 中国实用妇科与产科杂志,2018,34(1):18-22. doi: 10.19538/j.fk2018010105 [2] Reid F,Bhatla N,Oza A M,et al. The World Ovarian Cancer Coalition Every Woman Study: Identifying challenges and opportunities to improve survival and quality of life[J]. Int J Gynecol Cancer,2021,31(2):238-244. doi: 10.1136/ijgc-2019-000983 [3] La Vecchia C. Ovarian cancer: Epidemiology and risk factors[J]. Eur J Cancer Prev,2017,26(1):55-62. doi: 10.1097/CEJ.0000000000000217 [4] 张家雨,何昕晖,宫婷婷,等. 肉类摄入与卵巢癌发病及预后关系的研究进展[J]. 肿瘤防治研究,2019,46(5):490-496. [5] Trinidad C V,Tetlow A L,Bantis L E,et al. Reducing ovarian cancer mortality through early detection: Approaches using circulating biomarkers[J]. Cancer Prev Res (Phila),2020,13(3):241-252. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-19-0184 [6] Kim G R,Lee E,Kim H R,et al. Convolutional neural network to stratify the malignancy risk of thyroid nodules: Diagnostic performance compared with the American college of radiology thyroid imaging reporting and data system implemented by experienced radiologists[J]. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol,2021,42(8):1513-1519. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A7149 [7] Hejduk P,Marcon M,Unkelbach J,et al. Fully automatic classification of automated breast ultrasound (ABUS) imaging according to BI-RADS using a deep convolutional neural network[J]. Eur Radiol,2022,32(7):4868-4878. doi: 10.1007/s00330-022-08558-0 [8] Mitrea D,Badea R,Mitrea P,et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma automatic diagnosis within CEUS and B-Mode ultrasound images using advanced machine learning methods[J]. Sensors (Basel),2021,21(6):1-31. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3057283 [9] 李睿,许祥丛,林静怡,等. 基于卷积神经网络的超声影像肝癌自动分类[J]. 生物化学与生物物理进展,2023,50(3):668-675. doi: 10.16476/j.pibb.2022.0101 [10] 曹宇,邢素霞,逄键梁,等. 基于改进的VGG-16卷积神经网络的肺结节检测[J]. 中国医学物理学杂志,2020,37(7):940-944. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-202X.2020.07.026 [11] 高慧明. 基于卷积神经网络的肺结节检测及良恶性分类方法研究[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学, 2019. [12] Han Y,Ma Y,Wu Z,et al. Histologic subtype classification of non-small cell lung cancer using PET/CT images[J]. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging,2021,48(2):350-360. doi: 10.1007/s00259-020-04771-5 [13] Alshammari A. Construction of VGG16 convolution neural network (VGG16_CNN) classifier with NestNet-Based segmentation paradigm for brain metastasis classification[J]. Sensors (Basel),2022,22(20):1-19. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2022.3211123 [14] Altun S,Alkan A,Altun I. LSS-VGG16: Diagnosis of lumbar spinal stenosis with deep learning[J]. Clin Spine Surg,2023,36(5):E180-E190. doi: 10.1097/BSD.0000000000001418 [15] 刘雪纯,刘大铭,常佳鑫,等. 基于MobileNet V2迁移学习的中药材图像识别[J]. 长江信息通信,2022,35(7):33-37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1131.2022.07.009 [16] 易振通,吴瑰,官端正,等. 轻量化卷积神经网络的研究综述[J]. 工业控制计算机,2022,35(10):109-111. [17] Palczynski K,Smigiel S,Gackowska M,et al. IoT application of transfer learning in hybrid artificial intelligence systems for acute lymphoblastic leukemia classification[J]. Sensors (Basel),2021,21(23):1-12. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3128120 [18] Srinivasu P N,SivaSai J G,Ijaz M F,et al. Classification of skin disease using deep learning neural networks with MobileNet V2 and LSTM[J]. Sensors (Basel),2021,21(8):1-27. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3063942 [19] Yu C J,Yeh H J,Chang C C,et al. Lightweight deep neural networks for cholelithiasis and cholecystitis detection by point-of-care ultrasound[J]. Comput Methods Programs Biomed,2021,211:106382. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2021.106382 [20] Martinez-Mas J,Bueno-Crespo A,Khazendar S,et al. Evaluation of machine learning methods with Fourier Transform features for classifying ovarian tumors based on ultrasound images[J]. PLoS One,2019,14(7):e219388. -






 下载:
下载: