Hsa-let-7a-5p Regulates Proliferation and Apoptosis of Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells
-
摘要:
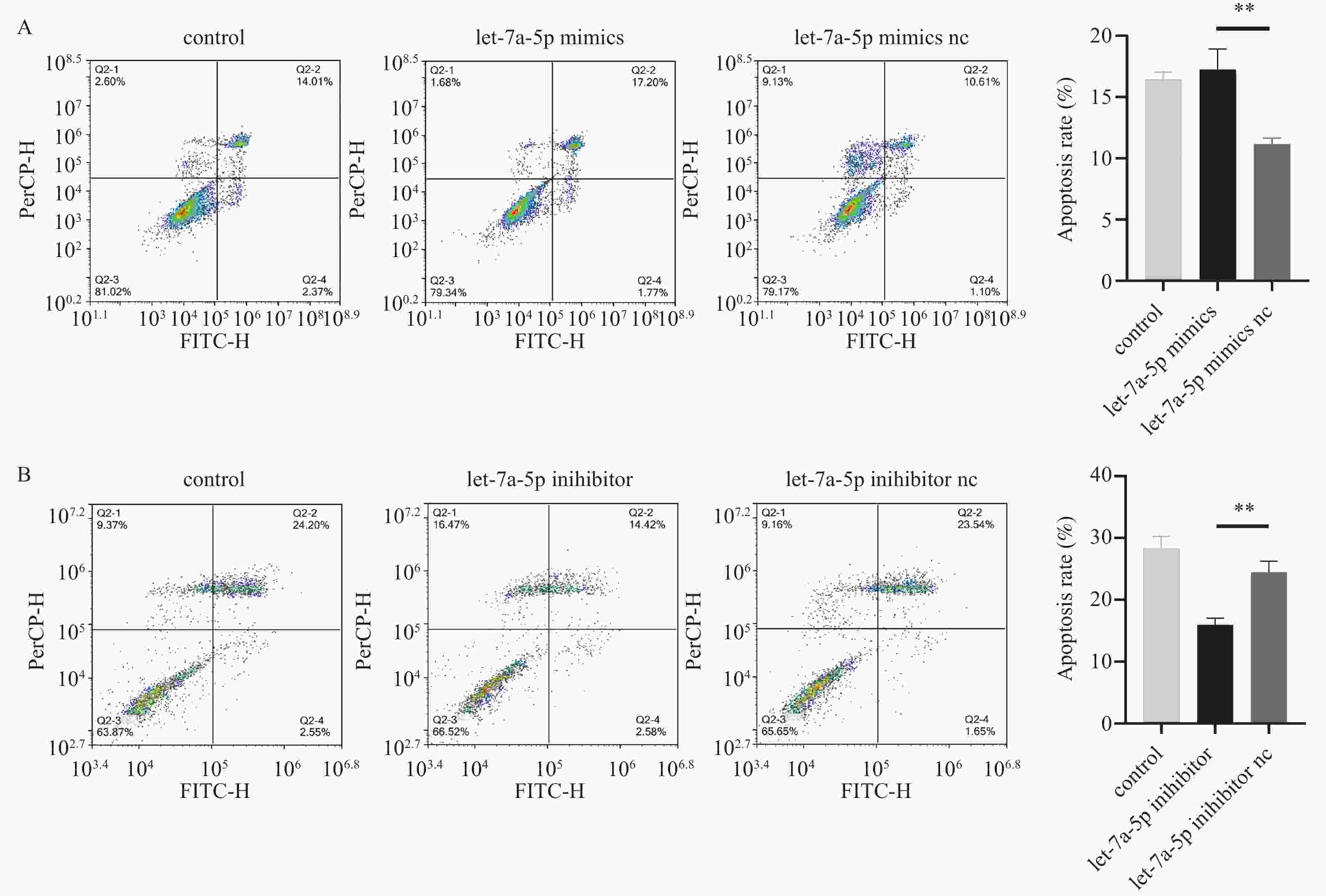
目的 探讨hsa-let-7a-5p对牙周膜干细胞(periodontal ligament stem cells,PDLSCs)增殖及凋亡的影响。 方法 将let-7a-5p mimics、mimics nc、let-7a-5p inhibitor、inhibitor nc转染进入PDLSCs,通过RT-qPCR测定转染效率,通过CCK-8、细胞周期、EdU实验检测let-7a-5p对PDLSCs增殖的影响,通过细胞凋亡实验检测PDLSCs的凋亡率。 结果 let-7a-5p成功转染进入PDLSCs。let-7a-5p mimics可抑制PDLSCs增殖能力(P < 0.05),促进PDLSCs凋亡(P < 0.01)。let-7a-5p inhibitor可促进PDLSCs增殖能力(P < 0.05),抑制PDLSCs凋亡(P < 0.01)。 结论 hsa-let-7a-5p可抑制PDLSCs增殖,促进PDLSCs凋亡。 -
关键词:
- hsa-let-7a-5p /
- microRNA /
- 牙周膜干细胞 /
- 增殖 /
- 凋亡
Abstract:Objective To investigate the effect of hsa-let-7a-5p on the proliferation and apoptosis of periodontal ligament stem cells (PDLSCs). Methods let-7a-5p mimics, mimics nc, let-7a-5p inhibitor, and inhibitor nc were transfected into PDLSCs, and transfection efficiency was measured by RT-qPCR. The effects of let-7a-5p on PDLSCs proliferation were evaluated by CCK-8, cell cycle, and EdU experiments, while the apoptosis rate of PDLSCs was detected by apoptosis experiments. Results let-7a-5p was successfully transfected into PDLSCs. let-7a-5p mimics inhibited cell proliferation (P < 0.05) and promoted cell apoptosis of PDLSCs (P < 0.01). let-7a-5p inhibitor promoted cell proliferation (P < 0.05) and inhibited cell apoptosis of PDLSCs (P < 0.01). Conclusion hsa-let-7a-5p can inhibit the proliferation of PDLSCs and promote the apoptosis of PDLSCs. -
Key words:
- hsa-let-7a-5p /
- microRNA /
- Periodontal ligament stem cell /
- Proliferation /
- Apoptosis
-
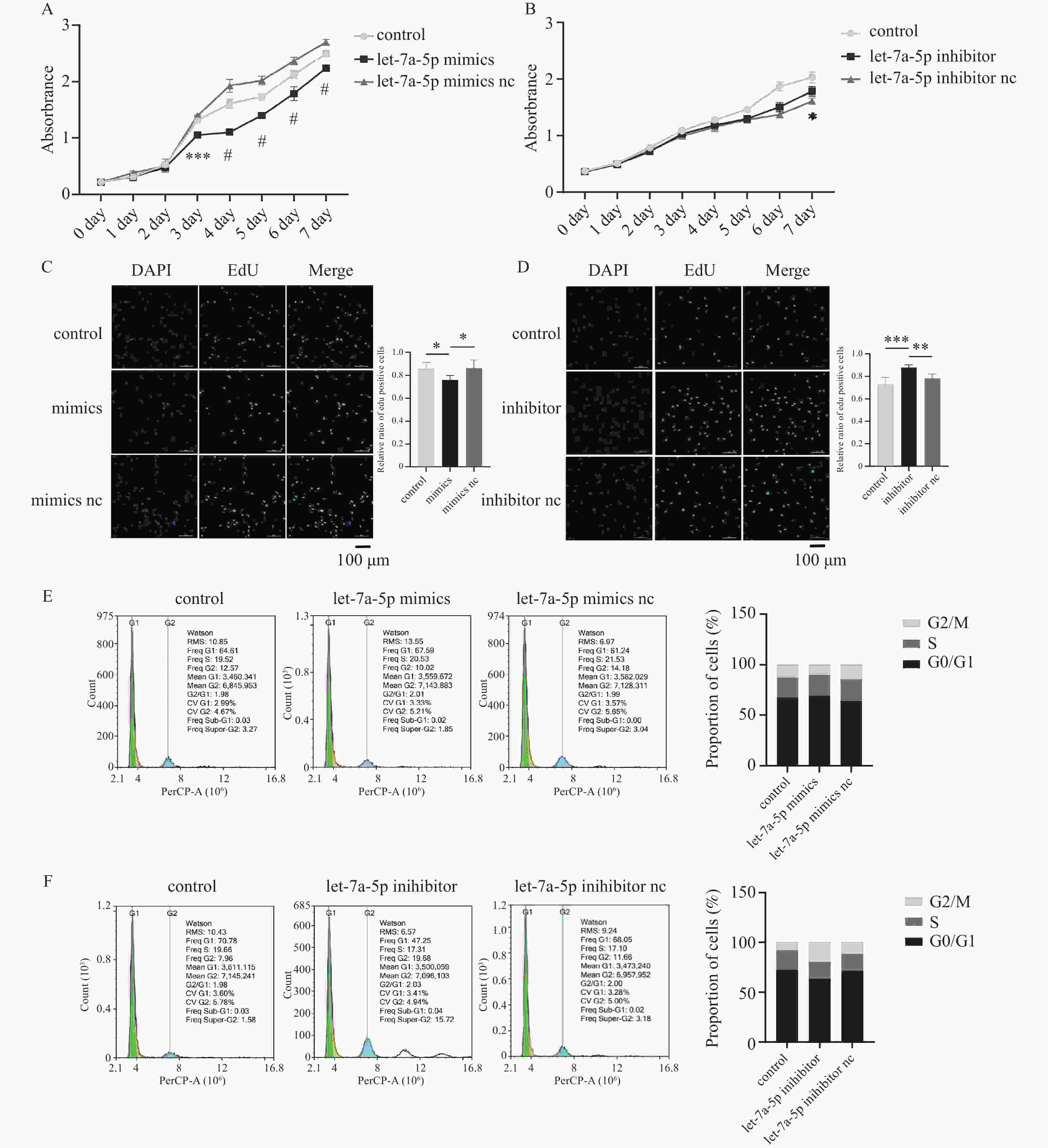
图 2 let-7a-5p抑制牙周膜干细胞增殖
A:CCK-8探究let-7a-5p mimics对PDLSCs增殖的影响,n = 4;B:CCK-8探究let-7a-5p inhibitor对PDLSCs增殖的影响,n = 4;C:EdU实验探究let-7a-5p mimics对PDLSCs增殖的影响,n = 5;D:EdU实验探究let-7a-5p inhibitor对PDLSCs增殖的影响,n = 5;E:细胞周期探究let-7a-5p mimics对PDLSCs增殖的影响;F:细胞周期探究let-7a-5p inhibitor对PDLSCs增殖的影响。*P < 0.05,**P < 0.01,***P < 0.001,#P < 0.0001。
Figure 2. let-7a-5p inhibits periodontal ligament stem cell proliferation
-
[1] Kwon T,Lamster I B,Levin L. Current concepts in the management of periodontitis[J]. International Dental Journal,2021,71(6):462-476. doi: 10.1111/idj.12630 [2] Isola G,Santonocito S,Lupi S M,et al. Periodontal health and disease in the context of systemic diseases[J]. Mediators of Inflammation,2023,2023:9720947. [3] Păunică I,Giurgiu M,Dumitriu AS,et al. The bidirectional relationship between periodontal disease and diabetes mellitus-A review[J]. Diagnostics (Basel),2023,13(4):681. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13040681 [4] Seo B M,Miura M,Gronthos S,et al. Investigation of multipotent postnatal stem cells from human periodontal ligament[J]. Lancet,2004,364(9429):149-155. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(04)16627-0 [5] Zhao X,Lin H,Ding T,et al. Overview of the main biological mechanisms linked to changes in periodontal ligament stem cells and the inflammatory microenvironment[J]. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B,2023,24(5):373-386. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B2200576 [6] Luan X,Zhou X,Trombetta-eSilva J,et al. MicroRNAs and periodontal homeostasis[J]. J Dent Res,2017,96(5):491-500. doi: 10.1177/0022034516685711 [7] Huang P,Jia L. MicroRNA-28-5p as a potential diagnostic biomarker for chronic periodontitis and its role in cell proliferation and inflammatory response[J]. J Dent Sci,2022,17(4):1501-1509. doi: 10.1016/j.jds.2022.04.031 [8] Venugopal P,Koshy T,Lavu V,et al. Differential expression of microRNAs let-7a,miR-125b,miR-100,and miR-21 and interaction with NF-kB pathway genes in periodontitis pathogenesis[J]. J Cell Physiol,2018,233(8):5877-5884. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26391 [9] Lee Y H,Na H S,Jeong S Y,et al. Comparison of inflammatory microRNA expression in healthy and periodontitis tissues[J]. Biocell,2011,35(2):43-49. doi: 10.32604/biocell.2011.35.043 [10] Lee N H,Lee E,Kim Y S,et al. Differential expression of microRNAs in the saliva of patients with aggressive periodontitis: A pilot study of potential biomarkers for aggressive periodontitis[J]. J Periodontal Implant Sci,2020,50(5):281-290. doi: 10.5051/jpis.2000120006 [11] Ma L,Rao N,Jiang H,et al. Small extracellular vesicles from dental follicle stem cells provide biochemical cues for periodontal tissue regeneration[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther,2022,13(1):92. doi: 10.1186/s13287-022-02767-6 [12] Li Q,Yang G,Li J,et al. Stem cell therapies for periodontal tissue regeneration: A network meta-analysis of preclinical studies[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther,2020,11(1):427. doi: 10.1186/s13287-020-01938-7 [13] Tomokiyo A,Wada N,Maeda H. Periodontal ligament stem cells: Regenerative potency in periodontium[J]. Stem Cells Dev,2019,28(15):974-985. doi: 10.1089/scd.2019.0031 [14] Jin H Y,Gonzalez-Martin A,Miletic A V,et al. Transfection of microRNA mimics should be used with caution[J]. Front Genet,2015,6:340. [15] Esau C C. Inhibition of microRNA with antisense oligonucleotides[J]. Methods,2008,44(1):55-60. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2007.11.001 [16] Robertson B,Dalby A B,Karpilow J,et al. Specificity and functionality of microRNA inhibitors[J]. Silence,2010,1(1):10. doi: 10.1186/1758-907X-1-10 [17] Campani V,De Rosa G,Misso G,et al. Lipid nanoparticles to deliver miRNA in cancer[J]. Curr Pharm Biotechnol,2016,17(8):741-749. doi: 10.2174/138920101708160517234941 [18] Johnson C D,Esquela-Kerscher A,Stefani G,et al. The let-7 microRNA represses cell proliferation pathways in human cells[J]. Cancer Res,2007,67(16):7713-7722. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-1083 [19] Chen Z,Qiu J,Gao Y,et al. Study on the mechanism of let-7a-5p in regulating the proliferation in cervical cancer cells[J]. Clin Transl Oncol,2022,24(8):1631-1642. doi: 10.1007/s12094-022-02810-1 [20] Yu J J,Pi W S,Cao Y,et al. Let-7a inhibits osteosarcoma cell growth and lung metastasis by targeting Aurora-B[J]. Cancer Manag Res,2018,10:6305-6315. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S185090 [21] Liu C,Chen Z,Fang M,et al. MicroRNA let-7a inhibits proliferation of breast cancer cell by downregulating USP32 expression[J]. Transl Cancer Res,2019,8(5):1763-1771. doi: 10.21037/tcr.2019.08.30 [22] Chen Y,Qiao L,Zhang Z,et al. Let-7a inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis of human asthmatic airway smooth muscle cells[J]. Exp Ther Med,2019,17(5):3327-3334. [23] James N,Kini S,Pai S,et al. Comparative evaluation of corneal storage medias used as tooth avulsion medias in maintaining the viability of periodontal ligament cells using the cell counting kit-8 assay[J]. Clin Cosmet Investig Dent,2022,14:87-94. doi: 10.2147/CCIDE.S314478 [24] Sun X,Zhang C,Jin H,et al. Flow cytometric analysis of T lymphocyte proliferation in vivo by EdU incorporation[J]. Int Immunopharmacol,2016,41:56-65. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2016.10.019 [25] Rieger A M. Flow cytometry and cell cycle analysis: An overview[J]. Methods Mol Biol,2022,2579:47-57. [26] Xu X,Lai Y,Hua Z C. Apoptosis and apoptotic body: Disease message and therapeutic target potentials[J]. Biosci Rep,2019,39(1):BSR20180992. doi: 10.1042/BSR20180992 [27] Zhang J,Dong X,Yan Q,et al. Galectin-1 inhibited LPS-induced autophagy and apoptosis of human periodontal ligament stem cells[J]. Inflammation,2021,44(4):1302-1314. doi: 10.1007/s10753-021-01417-y [28] Liu L,Zhao J,Peng Y,et al. miR-let-7a-5p inhibits invasion and migration of hepatoma cells by regulating BZW2 expression[J]. Onco Targets Ther,2020,13:12269-12279. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S278954 [29] Cai K,Wan Y,Sun G,et al. Let-7a inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis by targeting EZH2 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells[J]. Oncol Rep,2012,28(6):2101-2106. doi: 10.3892/or.2012.2027 [30] Ersahin T,Tuncbag N,Cetin-Atalay R. The PI3K/AKT/mTOR interactive pathway[J]. Mol Biosyst,2015,11(7):1946-1954. doi: 10.1039/C5MB00101C [31] Xia Z,Li Q,Tang Z. Network pharmacology,molecular docking,and experimental pharmacology explored Ermiao wan protected against periodontitis via the PI3K/AKT and NF-κB/MAPK signal pathways[J]. J Ethnopharmacol,2023,303:115900. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115900 -






 下载:
下载: