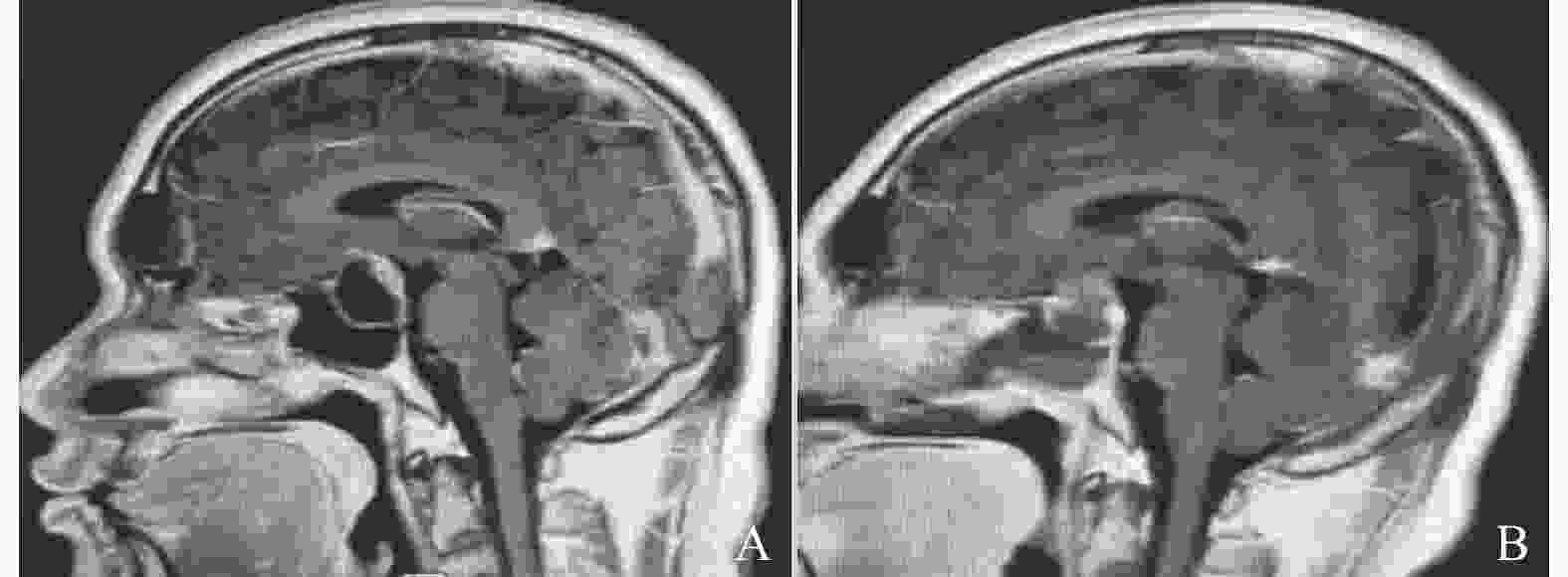
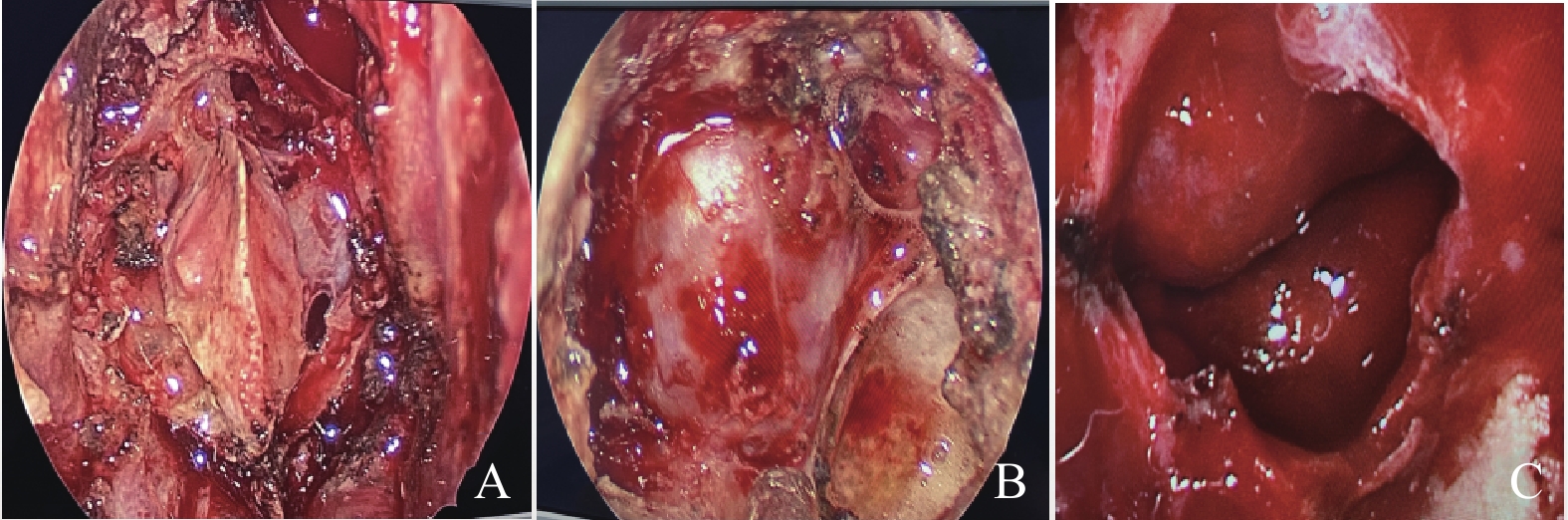
Clinical Study of Neuronavigation-assisted Endoscopic Transnasal Sphenoid Approach for Resection of Pituitary Tumors
-
摘要:
目的 探讨全麻下神经导航定位辅助内镜下经鼻蝶入路切除垂体腺瘤的临床应用疗效及前景。 方法 收集阳江市人民医院神经外科2018年9月至2023年4月垂体腺瘤手术患者共68例,分为2组:实验组34例(神经导航定位辅助内镜下经鼻蝶入路切除垂体腺瘤),对照组34例(显微镜经鼻蝶入路切除垂体腺瘤),分析评价2组手术相关指标,并发症指标,手术前后内分泌激素指标。 结果 肿瘤全切几率在术后影像学对比中实验组高于对照组,差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。手术时间、出血量、住院时间、手术出血量及术后患者激素指标对比,实验组低于对照组,差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。 结论 神经导航辅助内镜下经鼻蝶入路切除垂体腺瘤具有创伤小、安全、高效、住院时间短、全切率高等优点,值得临床推广应用。 Abstract:Objective To explore and analyze the clinical application efficacy and prospect of neuronavigation positioning assisted endoscopic transnasal sphenoid approach for resection of pituitary adenomas under general anesthesia. Methods A total of 68 patients who underwent pituitary adenoma surgery at the Neurosurgery Department of Yangjiang People's Hospital from September 2018 to April 2023 were collected and divided into two groups: an experimental group of 34 patients(neuronavigation-assisted endoscopic transsphenoidal approach for pituitary adenoma resection) and a control group of 34 patients(microscopic transsphenoidal approach for pituitary adenoma resection). The surgery-related indicators, complication indicators, and preoperative and postoperative endocrine hormone indicators were analyzed and evaluated in both groups. Results The probability of total tumor resection in the experimental group was significantly higher than that in the control group in postoperative imaging comparison, with statistical significance(P<0.05). The comparison of surgical time, bleeding volume, hospitalization time, surgical bleeding volume, and postoperative patient hormone indicators showed that the experimental group was significantly lower than the control group, and the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05). Conclusions Neuronavigation positioning assisted endoscopic transnasal sphenoid approach for resection of pituitary adenoma has the advantages of small trauma, safety, high efficiency, short hospital stay, and high total resection rate. This represents a novel and effective strategy for wide clinical application. -
Key words:
- Neural navigation /
- Neuroendoscope /
- Microscope /
- Pituitary adenoma
-
表 1 2组间一般资料比较[n(%)/
$ \bar x \pm s $ ]Table 1. Comparison of general information between two groups[n(%)/
$ \bar x \pm s $ ]组别 n 性别 年龄(岁) 病程(a) 肿瘤直径(cm) 男 女 实验组 34 18(52.94) 16(47.05) 48.13 ± 3.11 2.48 ± 1.06 2.81 ± 1.06 对照组 34 15(44.11) 19(55.88) 49.22 ± 1.36 2.32 ± 1.50 2.85 ± 0.67 χ2/t 0.401 0.902 0.212 0.310 P 0.841 0.986 0.647 0.639 表 2 2组手术相关指标对比 [
$ \bar x \pm s $ /n(%)]Table 2. Comparison of surgical related indicators between two groups [
$ \bar x \pm s$ /n(%)]组 别 n 手术时间(min) 术中出血量(mL) 住院时间(d) 全切率 实验组 34 94.25 ± 3.23 97.63 ± 1.56 9.34 ± 1.16 30/(88.2) 对照组 34 125.34 ± 2.36 148.33 ± 5.13 13.28 ± 1.56 21/(61.7) t/χ2 9.012 15.206 8.912 10.213 P 0.041* 0.035* 0.047* 0.043* 与对照组相关手术指标比较,*P<0.05。 表 3 2组相关并发症指标对比[n(%)]
Table 3. Comparison of two groups of related complications indicators[n(%)]
组 别 n 电解质紊乱(n) 垂体功能障碍(n) 一过性尿崩(n) 脑脊液漏(n) 颅内感染(n) 并发症发生几率 实验组 34 6 1 2 2 0 11(32.35) 对照组 34 9 3 4 2 1 19(55.88) χ2 7.823 P 0.035* 与对照组并发症发生几率对比,*P<0.05。 表 4 2组手术前后内分泌激素指标对比(
$ \bar x \pm s $ )Table 4. Comparison of endocrine hormone indicators before and after surgery between two groups(
$ \bar x \pm s $ )组别 n GH(ng/mL) PRL(ng/mL) 治疗前 治疗后 治疗前 治疗后 实验组 34 33.86 ± 1.53 3.15 ± 1.08 21.45 ± 2.35 5.82 ± 1.07 对照组 34 34.25 ± 1.46 7.02 ± 1.03 28.25 ± 2.71 8.92 ± 1.56 t 8.132 9.954 P 0.048 0.039 与对照组术前后生长激素与泌乳素对比,*P<0.05。 -
[1] Asa S L,Ezzat S. The pathogenesis of pituitary tumours[J]. Nat Rev Cancer,2002,2(11):836-849. doi: 10.1038/nrc926 [2] 张亚卓,王忠诚,刘业剑,等. 内镜经鼻蝶入路手术治疗垂体瘤[J]. 中国微侵袭神经外科杂志,2007,12(2):51-54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-122X.2007.02.002 [3] 李储忠,朱海波,宗绪毅,等. 我国外镜神经外科发展史[J]. 中国现代神经疾病杂志,2019,19(4):232-234. [4] 赵浥,王希,魏栋,等. 显微镜及神经内镜经鼻蝶窦手术治疗垂体瘤的对比研究[J]. 临床神经外科杂志,2022,19(5):583-542. [5] Ishikawa M,Ota Y,Naritaka H,et al. Endoscopic ultrasound imaging with high flow mode for endonasal transsphenoidal pituitary surgery[J]. J Clin Neurosci,2021,89(7):329-335. [6] Kalyvas A,Millesi M,Gentili F. Endoscopic extra-capsular resection of a giant pituitary adenoma:How I do it[J]. Acta Neurochir (Wien),2021,163(6):1711-1715. doi: 10.1007/s00701-021-04833-z [7] Van Gompel J,Atkinson JLD,Choby G,et al. Pituitary tumor surgery: Comparison of endoscopic and microscopic techniques at a single Center[J]. Mayo Clin Proc,2021,96(8):2043-2057. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.03.028 [8] Inoue A,Kohno S,Ohnishi T,et al. Tricks and traps of ICG endoscopy for effectively applying endoscopic transsphenoidal surgery to pituitary adenoma[J]. Neurosurg Rev,2021,44(4):2133-2143. doi: 10.1007/s10143-020-01382-4 [9] Singh H,Essayed W I,Cohen-Gadol A,et al. Resection of pituitary tumor:Endoscopic versus microscopic[J]. Journal of Neuro-oncology,2016,130(2):309-317. doi: 10.1007/s11060-016-2124-y [10] Saeki N,Horigushi K,Murai H,et al. Endoscopic endonasal pituitary and skull base surgery[J]. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo),2010,50(9):756-764. doi: 10.2176/nmc.50.756 [11] Peto I,Abou H,White G,et al. Sources of residuals after endoscopic transsphenoidal surgery for large and giant pituitary adenomas[J]. Acta Neurochir (Wien),2020,162(10):2341-2351. doi: 10.1007/s00701-020-04497-1 [12] Tao C,Cheng G,Chen Y,et al. Early outcomes of endoscopic endonasal approach pituitary adenomas resection with minimal nasal injury[J]. Medicine (Baltimore),2021,100(46):27843. [13] Rahimli T, Hidayetov T, Yusifli Z, et al. Endoscopic endonasal approach to giant pituitary adenomas: surgical outcomes and review of the literature[J]. World Neurosurg, 2021, 149(5): 1043-1055. 补充期号Rahimli T,Hidayetov T,Yusifli Z,et al. Endoscopic endonasal approach to giant pituitary adenomas:Surgical outcomes and review of the literature[J]. World Neurosurg,2021,149(5):1043-1055. [14] Pojskić M,Arnautouvic A,Kovasevic M,et al. Combined microsurgical,endoscopic and neuronavigation assisted transseptal-transsphenoidal resection of pituitary tumors[J]. Acta Med Acad,2020,49(11):14-22. [15] Dai W,Zhuang G,Ling H,et al. Systematic review and network meta-analysis assess the comparative efficacy and safety of transsphenoidal surgery for pituitary tumor[J]. Neurosurg Rev,2021,44(1):515-527. doi: 10.1007/s10143-020-01240-3 [16] Abhinav K, Matthew T, Oliver T, et al. Managing complications of endoscopic transsphenoidal surgery in pituitary adenomas[J]. Expert Rev Endocrinol Metab, 2020, 15(5): 311-319. 期号Abhinav K,Matthew T,Oliver T,et al. Managing complications of endoscopic transsphenoidal surgery in pituitary adenomas[J]. Expert Rev Endocrinol Metab,2020,15(5):311-319. [17] Van Furth W,De Vries F,Lobatto D J,et al. Endoscopic surgery for pituitary tumors[J]. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am,2020,49(3):487-503. doi: 10.1016/j.ecl.2020.05.011 -






 下载:
下载: