Application of Difficult Intravenous Access Score in Paediatric Peripheral Venepuncture
-
摘要:
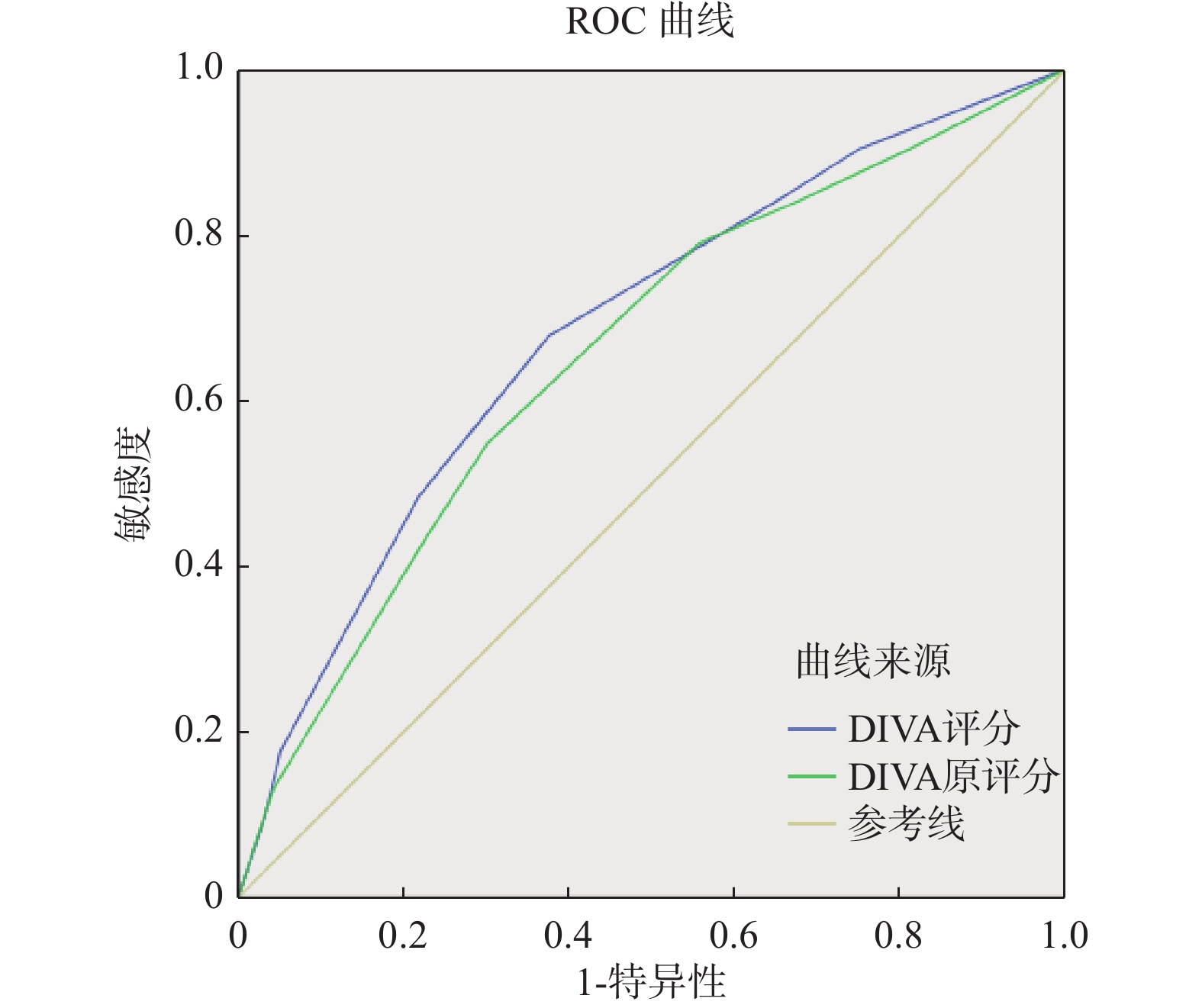
目的 验证困难静脉通路评分在儿科外周静脉穿刺中的有效性,探讨其在儿科静脉通路留置策略中的适用性。 方法 采用便利抽样法选取云南昆明一家三级甲等医院儿科的住院患儿作为研究对象。使用Riker的三变量儿童困难静脉通路评估工具(DIVA评分)对374名接受静脉穿刺置管的患儿进行评估。采用ROC曲线下面积、灵敏度、特异度和约登指数等指标对该工具的预测价值进行评价。 结果 DIVA评分与国外常模比较,差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05)。研究中穿刺失败组与穿刺成功组患儿DIVA评分比较,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.001)。随着DIVA评分由0递增至6,对应患儿的首次静脉穿刺成功率逐渐由92.9%下降至54.5%。DIVA评分ROC曲线下面积为0.648。当总分为3分时,量表预测价值最大。 结论 儿童三变量DIVA评分对儿童困难静脉通路有一定的识别能力且预测准确度较好,可用于儿科外周静脉穿刺前的评估。 Abstract:Objective To verify the validity of difficult venous access score in pediatric peripheral venipuncture and explore its applicability in pediatric venous access indwelling strategy. Methods The convenience sampling method was used to select inpatients in the pediatric department of a tertiary hospital in Kunming, Yunnan Province as the research subjects. Riker’ s three-variable pediatric Difficult Intravenous Access(DIVA) Assessment Tool was used to evaluate 374 children undergoing venipuncture catheterization. The predictive value of the tool was evaluated using indicators such as the area under the ROC curve, sensitivity, specificity, and Youden index. Results Comparing this DIVA score with Riker’ s study, the difference was not statistically significant(P > 0.05). In contrast, the difference in DIVA scores between the failed puncture group and the successful puncture group was statistically significant(P < 0.001). As the DIVA score increased from 0 to 6, the first venipuncture success rate of the corresponding children gradually decreased from 92.9% to 54.5%. The area under the ROC curve of the DIVA score was 0.648. When the total score was 3 points, the scale had the greatest predictive value. Conclusion The three-variable DIVA score has a certain ability to identify difficult venous access in children. It has a good prediction accuracy, and can be used for evaluation before pediatric peripheral venipuncture. -
表 1 患儿DIVA评分与首次穿刺成功情况[(n=374),n(%)]
Table 1. DIVA scores and success rate of first attempt at IV cannulation [(n=374),n(%)]
DIVA总分 n 穿刺失败 穿刺成功 0 84(22.5) 6(7.1) 78(92.9) 1 36(9.6) 4(11.1) 32(88.9) 2 95(25.4) 10(10.5) 85(89.5) 3 61(16.3) 12(19.7) 49(80.3) 4 71(19.0) 19(26.8) 52(73.2) 5 11(2.9) 5(45.5) 6(54.5) 6 16(4.3) 6(37.5) 10(62.5) 合计 374(100) 表 2 DIVA评分与Riker原评分比较[n(%)]
Table 2. Comparison between DIVA score and Riker’ s original score [n(%)]
组别 n 效果 有效 无效 国外常模 366 260(71.0) 106(29.0) DIVA评分 372 274(73.1) 98(26.3) χ² 0.632 P 0.427 表 3 穿刺失败组和成功组患儿的DIVA评分比较[(
$\bar x \pm s $ ),n=374]Table 3. Comparison of DIVA scores among children in the failed puncture group and the successful group [(
$\bar x \pm s $ ),n=374]穿刺结果 DIVA评分 失败(n=62) 3.18±1.675 成功(n=312) 2.07±1.617 t 4.880 P <0.001* *P < 0.05 表 4 Hosmer-Lemeshow检验结果
Table 4. Hosmer-Lemeshow test results of DIVA score and Riker’s original score
项目 χ² df P DIVA评分 0.948 4 0.918 Riker原评分 1.403 5 0.924 -
[1] House D R,Cheptinga P,Rusyniak D E,et al. Qualitative study of healthcare providers’ current practice patterns and barriers to successful rehydration for pediatric diarrheal illnesses in Kenya[J]. Peer J,2017,6(5):e3829. [2] Parker S I A,Benzies K M,Hayden K A. A systematic review: effectiveness of pediatric peripheral intravenous catheterization strategies[J]. J Adv Nurs,2017,73(7):1570-1582. doi: 10.1111/jan.13211 [3] Petroski A,Frisch A,Joseph N,et al. Predictors of difficult pediatric intravenous access in a community Emergency Department[J]. J Vasc Access,2015,16(6):521-526. doi: 10.5301/jva.5000411 [4] 闫亚敏,龚梅,李爱求,等. 儿科外周静脉留置针穿刺成功率的调查及影响因素分析[J]. 中国实用护理杂志,2016,32(20):1558-1561. [5] Kim M J,Park J M,Rhee N,et al. Efficacy of vein viewer in pediatric peripheral intravenous access: A randomized controlled trial[J]. European Journal of Pediatrics,2012,171(7):1121-1125. doi: 10.1007/s00431-012-1713-9 [6] 钱海兴,闫亚敏. 困难静脉通路评估工具的研究进展[J]. 中国实用护理杂志,2017,33(31):2477-2480. [7] Schults J,Rickard C,Kleidon T,et al. Difficult peripheral venous access in children: An international survey and critical appraisal of assessment tools and escalation pathways[J]. J Nurs Scholarship,2019,51(5):537-546. doi: 10.1111/jnu.12505 [8] Yen K,Riegert A,Gorelick M H. Derivation of the DIVA score: A clinical prediction rule for the identification of children with difficult intravenous access[J]. Pediatr Emerg Care,2008,24(3):143-147. doi: 10.1097/PEC.0b013e3181666f32 [9] Riker M W,Kennedy C,Winfrey B S,et al. Validation and refinement of the difficult intravenous access score: A clinical prediction rule for identifying children with difficult intravenous access[J]. Acad Emerg Med,2011,18(11):1129-1134. doi: 10.1111/j.1553-2712.2011.01205.x [10] Gregg S C,Murthi S B,Sisley A C,et al. Ultrasound-guided peripheral intravenous access in the intensive care unit[J]. J Crit Care,2010,25(3):514-519. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2009.09.003 [11] Kuensting L L,DeBoer S,Holleran R,et al. Difficult venous access in children: Taking control[J]. J Emerg Nurs,2009,35(5):419-424. doi: 10.1016/j.jen.2009.01.014 [12] Fields J M,Dean A J,Todman R W,et al. The effect of vessel depth,diameter,and location on ultrasound- guided peripheral intravenous catheter longevity[J]. Am J Emerg Med,2012,30(7):1134-1140. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2011.07.027 [13] Schoenfeld E,Boniface K,Shokoohi H. ED technicians can successfully place ultrasound-guided intravenous catheters in patients with poor vascular access[J]. Am J Emerg Med,2011,29(5):496-501. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2009.11.021 [14] Au A K,Rotte M J,Grzybowski R J,et al. Decrease in central venous catheter placement due to use of ultrasound guidance for peripheral intravenous catheters[J]. Am J Emerg Med,2012,30(9):1950-1954. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2012.04.016 [15] 儿童静脉输液治疗临床实践循证指南工作组. 儿童静脉输液治疗临床实践循证指南[J]. 中国循证儿科杂志,2021,16(1):1-42. [16] Lee S U,Jung J Y,Ham E M,et al. Factors associated with difficult intravenous access in the pediatric emergency department[J]. The Journal of Vascular Access,2020,21(2):180-185. doi: 10.1177/1129729819865709 [17] Reigart J R,Chamberlain K H,Eldridge D,et al. Peripheral intravenous access in pediatric inpatients[J]. Clinical Pediatrics,2012,51(5):468-472. doi: 10.1177/0009922811435164 [18] 王俊峰,章仲恒,周支瑞,等. 临床预测模型: 模型的验证[J]. 中国循证心血管医学杂志,2019,11(2):141-144. [19] Alba A C,Agoritsas T,Walsh M,et al. Discrimination and calibration of clinical prediction models: Users’ guides to the medical literature[J]. JAMA,2017,318(14):1377-1384. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.12126 [20] Demir D,Inal S. Does the Use of a vein visualization device for peripheral venous catheter placement increase success rate in pediatric patients?[J]. Pediatr Emerg Care,2019,35(7):474-479. doi: 10.1097/PEC.0000000000001007 [21] Hartman J H,Bena J F,Morrison S L,et al. Effect of adding a pediatric vascular access team component to a pediatric peripheral vascular access algorithm[J]. J Pediatr Health Care,2020,34(1):4-9. doi: 10.1016/j.pedhc.2019.06.004 [22] Shaukat H,Neway B,Breslin K,et al. Utility of the DIVA score for experienced emergency department technicians[J]. Br J Nurs,2020,29(2):S35-S40. doi: 10.12968/bjon.2020.29.2.S35 [23] 杨艳,杨葵英,徐健华. 静脉血管评估分级配合输液信息卡在儿科门急诊中的应用[J]. 护理研究,2012,26(28):2662-2663. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6493.2012.28.032 [24] 余忠祥,邓毅书,董燕鸿,等. 外周静脉评估及静脉穿刺的层级管理[J]. 护理管理杂志,2011,11(10):749-751. [25] Paterson R S, Chopra V, Brown E, et al. Selection and insertion of vascular access devices in pediatrics: A systematic review[J]. Pediatrics, 2020, 145(Supplement 3): S243-S268. [26] Ballard H A,Hajduk J,Cheon E C,et al. Clinical and demographic factors associated with pediatric difficult intravenous access in the operating room[J]. Pediatric Anesthesia,2022,32(7):792-800. doi: 10.1111/pan.14438 [27] Larsen P, Eldridge D, Brinkley J, et al. Pediatric peripheral intravenous access: Does nursing experience and competence really make a difference? J Infus Nurs, 2010, 33(4): 226-235. -






 下载:
下载: