miR-218-5p Inhibits the Development of Colon Cancer by Regulating LAYN
-
摘要:
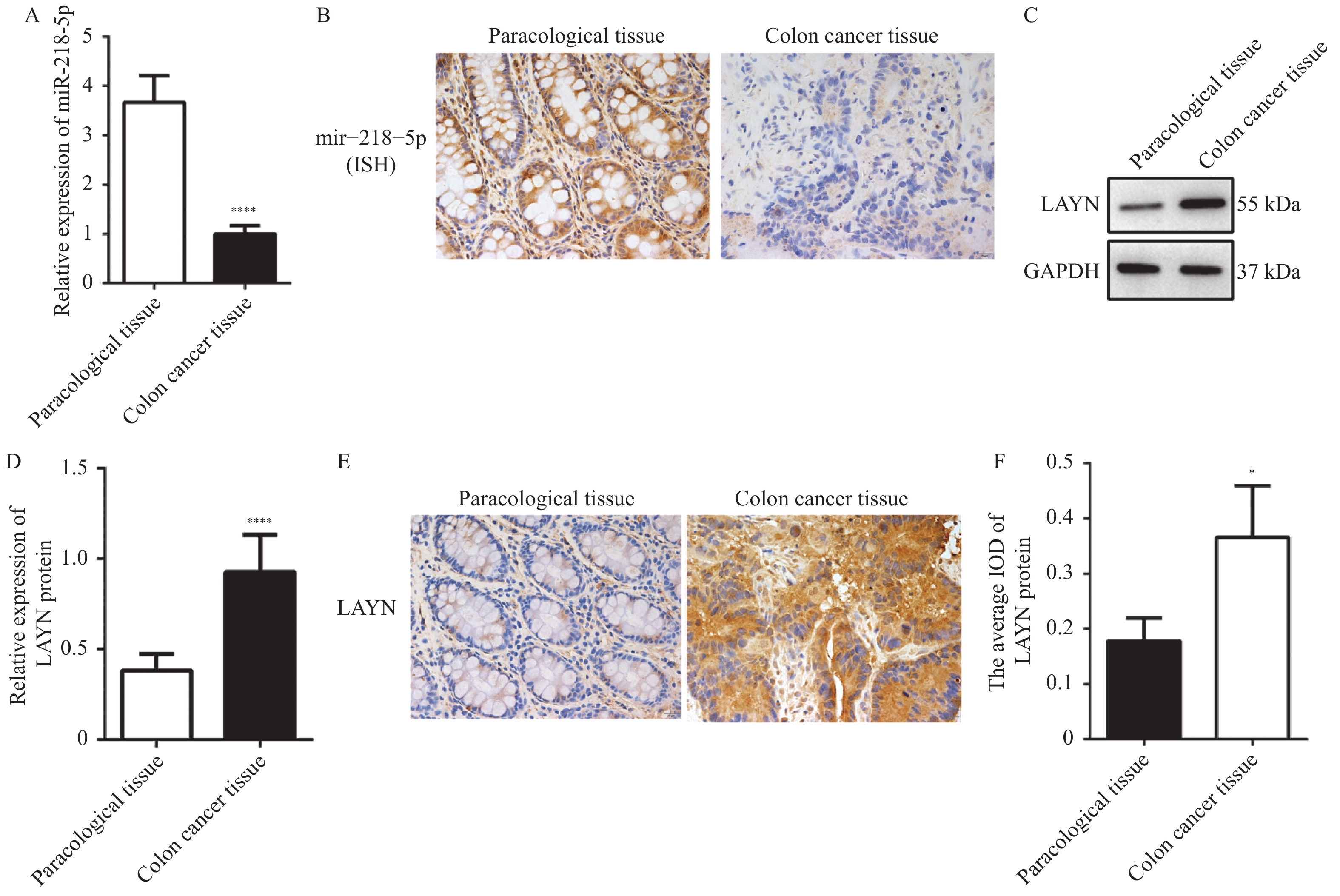
目的 探讨miR-218-5p和LAYN在结肠癌中的表达水平以及二者的调控关系对结肠癌进展的影响。 方法 采用RT-qPCR对结肠癌组织、癌旁组织以及细胞系中的miR-218-5p的表达进行检测。采用Western blot对结肠癌组织、癌旁组织和细胞系中的LAYN蛋白表达水平进行检测。采用原位杂交(in situ hybridizsation,ISH)实验对结肠癌组织和癌旁组织中的miR-218-5p的表达进行检测。采用免疫组化(immunohistochemistry,IHC)实验对结肠癌组织和癌旁组织中的LAYN蛋白分布和表达进行检测。采用双荧光素酶实验对miR-218-5p与LAYN的3’ -非翻译区(rn-translation region,UTR)的结合关系进行检测。采用CCK-8对细胞的增殖进行检测;采用Transwell法对细胞的侵袭能力进行检测;采用流式细胞术对细胞的凋亡水平进行检测;采用Western blot对细胞中cleaved Caspase3表达水平进行检测。 结果 在结肠癌组织和结肠癌细胞系中,miR-218-5p表达降低并且HT-29细胞中表达最低(P < 0.0001),LAYN表达升高并且HT-29细胞中表达最高(P < 0.05)。双荧光素酶报告基因实验结合Western blot实验表明miR-218-5p可以结合在LAYN的3′ UTR区域并抑制其蛋白表达(P < 0.01)。在细胞实验中,过表达miR-218-5p抑制细胞增殖(P < 0.05)、侵袭(P < 0.001)并增加凋亡(P < 0.01)和cleaved Caspase3蛋白的表达(P < 0.01);过表达LAYN促进细胞增殖(P < 0.05)、侵袭(P < 0.001)并减少凋亡(P < 0.0001)和cleaved Caspase 3蛋白的表达(P < 0.01),同时过表达miR-218-5p和LAYN部分逆转了上述变化。 结论 在结肠癌组织中,miR-218-5p表达水平降低,细胞实验表明miR-218-5p通过靶向调控LAYN抑制细胞的侵袭和增殖,促进其凋亡。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the expression level of miR-218-5p and LAYN in colon cancer and the effects of their regulatory relationship on the progress of colon cancer. Methods RT-qPCR was used to detect the expression of miR-218-5p in colon cancer tissues, adjacent tissues, and cell lines. Western blot was used to detect the expression level of LAYN protein in colon cancer tissues, adjacent tissues, and cell lines. The in situ hybridization(ISH) was used to detect the expression of miR-218-5p in colon cancer and adjacent tissues. Immunohistochemical(IHC) experiment was used to detect the distribution and expression of LAYN protein in colon cancer tissues and adjacent tissues. The dual luciferase experiment was used to detect the binding relationship between miR-218-5p and 3'- rn-translation region(UTR) of LAYN. CCK-8 was used to detect the cell proliferation. Transwell was used to detect the invasion ability of cells. The flow cytometry was used to detect the apoptosis level of cells. Western blot was used to detect the expression level of cleaved Caspase3 in cells. Results The expression of miR-218-5p decreased in colon cancer tissues and colon cancer cell lines, with the lowest expression in HT-29 cells(P < 0.0001), and the expression of LAYN increased and the highest expression in HT-29 cells(P < 0.05). The double luciferase reporter gene experiment(P < 0.01) combined with Western blot experiment(P < 0.01) showed that miR-218-5p could bind to the 3'UTR region of LAYN and inhibit its protein expression. In cell experiments, overexpression of miR-218-5p inhibited cell proliferation(P < 0.05), invasion(P < 0.001), and increased apoptosis(P < 0.01), and the expression of cleaved Caspase3 protein(P < 0.01). Overexpression of LAYN promoted cell proliferation(P < 0.05), invasion(P < 0.001), and decreased apoptosis(P < 0.0001) and the expression of cleaved Caspase3 protein(P < 0.01), while overexpression of miR-218-5p and LAYN partially reversed the above changes. Conclusion The expression level of miR-218-5p is decreased in colon cancer tissues. Cell experiments show that miR-218-5p inhibits cell invasion and proliferation and promotes cell apoptosis through targeted regulation of LAYN. -
Key words:
- Colon cancer /
- miR-218-5p /
- LAYN /
- Invasion /
- Proliferation /
- Apoptosis
-
图 3 过表达miR-218-5p抑制HT29细胞增殖、侵袭并诱导凋亡
A:RT-qPCR检测miR-218-5pmimic的转染效率;B:CCK-8检测细胞的增殖能力;C:Transwell检测细胞的侵袭能力;D:Annexin V FITC/PI细胞凋亡实验检测细胞的凋亡水平;E:Western blot检测cleaved Caspase3表达水平;与mimic NC组比较,*P < 0.05,**P < 0.01,***P < 0.001,****P < 0.0001。
Figure 3. Overexpression of miR-218-5p inhibits the proliferation,invasion and induces apoptosis of HT29 cells
-
[1] 顾晋,汪建平. 中国结直肠癌诊疗规范(2023版)[J]. 协和医学杂志,2023,14(4):706-733. [2] Sung H,Ferlay J,Siegel R L,et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin,2021,71(3):209-249. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660 [3] Yang Y,Meng W J,Wang Z Q. MicroRNAs in colon and rectal cancer - novel biomarkers from diagnosis to therapy[J]. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets,2020,20(8):1211-1226. doi: 10.2174/1871530320666200506075219 [4] Garo L P,Ajay A K,Fujiwara M,et al. MicroRNA-146a limits tumorigenic inflammation in colorectal cancer[J]. Nat Commun,2021,12(1):2419. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-22641-y [5] Zhou X G,Huang X L,Liang S Y,et al. Identifying miRNA and gene modules of colon cancer associated with pathological stage by weighted gene co-expression network analysis[J]. Onco Targets Ther,2018,11:2815-2830. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S163891 [6] Tammi M I,Oikari S,Pasonen-Seppänen S,et al. Activated hyaluronan metabolism in the tumor matrix - causes and consequences[J]. Matrix Biol,2019,78-79:147-164. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2018.04.012 [7] Pan J H,Zhou H,Cooper L,et al. LAYN is a prognostic biomarker and correlated with immune infiltrates in gastric and colon cancers[J]. Front Immunol,2019,10:6. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00006 [8] 李哲轩, 张阳, 周彤, 等. 2020全球癌症统计报告解读[J]. 2021, 7(2): 14. [9] Iacona J R, Lutz C S. miR‐146a‐5p: Expression, regulation, and functions in cancer[J], 2019, 10(4): e1533. [10] Huang X,Zhu X,Yu Y,et al. Dissecting miRNA signature in colorectal cancer progression and metastasis[J]. Cancer Lett,2021,501:66-82. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2020.12.025 [11] Payandeh Z,Khalili S,Somi M H,et al. PD-1/PD-L1-dependent immune response in colorectal cancer[J]. J Cell Physiol,2020,235(7-8):5461-5475. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29494 [12] Wang H. MicroRNAs and apoptosis in colorectal cancer[J]. Int J Mol Sci,2020,21(15):5353. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155353 [13] Zhang N,Hu X,Du Y,et al. The role of miRNAs in colorectal cancer progression and chemoradiotherapy[J]. Biomed Pharmacother,2021,134:111099. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.111099 [14] Ilm K,Fuchs S,Mudduluru G,et al. MACC1 is post-transcriptionally regulated by miR-218 in colorectal cancer[J]. Oncotarget,2016,7(33):53443-53458. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10803 [15] Yu H,Gao G,Jiang L,et al. Decreased expression of miR-218 is associated with poor prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer[J]. Int J Clin Exp Pathol,2013,6(12):2904-2911. [16] Deng M,Zeng C,Lu X,et al. miR-218 suppresses gastric cancer cell cycle progression through the CDK6/Cyclin D1/E2F1 axis in a feedback loop[J]. Cancer Lett,2017,403:175-185. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.06.006 [17] Pu Y,Wei J,Wu Y,et al. THUMPD3-AS1 facilitates cell growth and aggressiveness by the miR-218-5p/SKAP1 axis in colorectal cancer[J]. Cell Biochem Biophys,2022,80(3):483-494. doi: 10.1007/s12013-022-01074-4 [18] Liu Q Z,Yu H R,Wang L P,et al. Up-regulation of PUM1 by miR-218-5p promotes colorectal tumor-initiating cell properties and tumorigenesis by regulating the PI3K/AKT axis[J]. J Gastrointest Oncol,2023,14(1):233-244. doi: 10.21037/jgo-23-6 [19] Liu M,Yin K,Guo X,et al. Diphthamide biosynthesis 1 is a novel oncogene in colorectal cancer cells and is regulated by miR-218-5p[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem,2017,44(2):505-514. doi: 10.1159/000485087 [20] De Simone M,Arrigoni A,Rossetti G,et al. Transcriptional landscape of human tissue lymphocytes unveils uniqueness of tumor-infiltrating T regulatory cells[J]. Immunity,2016,45(5):1135-1147. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.10.021 -






 下载:
下载: