Association between MPV,PDW,PCT and Cardiac Function in Patients with Pulmonary Hypertension
-
摘要:
目的 研究肺动脉高压(PH)患者平均血小板体积(MPV)、血小板分布宽度(PDW)和降钙素原(PCT)水平与心功能的关系及对心力衰竭诊断的价值。 方法 选取2021年10月至2022年10月成都市第三人民医院PH患者103例(PH组)同期健康体检者103例(对照组)为样本,入组第1天采集患者空腹外周静脉血并检测MPV、PDW和PCT水平,同时测量左室射血分数(LVEF)并采用纽约心脏协会(NYHA)分级标准评估心功能,根据心力衰竭诊断结果将PH患者分为衰竭组和未衰竭组,然后分析MPV、PDW和PCT与PH患者心功能的关系及对心力衰竭诊断价值。 结果 PH组MPV、PDW和PCT水平均高于对照组,LVEF低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);随着NYHA分级增加,MPV、PDW和PCT水平呈升高趋势,LVEF呈下降趋势,各组比较差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);衰竭组(n = 65)MPV、PDW和PCT水平均高于未衰竭组(n = 38),LVEF低于未衰竭组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);MPV、PDW和PCT水平与NYHA心功能分级和LVEF均具有显著正相关性(P < 0.05);MPV、PDW和PCT水平对PH患者心力衰竭诊断均具有良好参考价值,AUC分别为0.816、0.897和0.825,三者联合诊断AUC为0.952,与3项指标单独应用相比,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。 结论 RDW、PDW和PCT与PH患者心功能存在密切联系,可为PH患者心力衰竭诊治提供参考信息。 Abstract:Objective To study the association between mean platelet volume(MPV), platelet distribution width(PDW) and procalcitonin(PCT) and cardiac function in patients with pulmonary hypertension(PH) and their diagnostic value on heart failure. Methods 103 patients with PH(PH group) in the 3rd People's Hospital of Chengdu from October 2021 to October 2022 and 103 healthy subjects with physical examination(control group)were selected as study subjects. Fasting peripheral venous blood was collected on the 1st day of admission and MPV, PDW and PCT were detected. The left ventricular ejection fraction(LVEF) was measured and the cardiac function was evaluated by New York Heart Association(NYHA) grading criteria. The patients with PH were divided into failure group and non-failure group according to the diagnosis results of heart failure. The relations of MPV, PDW and PCT with cardiac function in patients with PH and the diagnostic value on heart failure were analyzed. Results The levels of MPV, PDW, and PCT were all higher in the experimental group compared to the control group, while the LVEF was lower, and these differences were statistically significant(P < 0.05); as the NYHA classification increased, the levels of MPV, PDW, and PCT showed an increasing trend, while LVEF showed a decreasing trend, and the differences between the groups were statistically significant(P < 0.05); in the heart failure group n = 65, the levels of MPV, PDW, and PCT were higher compared to the non-heart failure group n = 38, while LVEF was lower, and these differences were statistically significant(P < 0.05). The levels of MPV, PDW, and PCT werr significantly positively correlated with NYHA functional classification and LVEF(P < 0.05). The levels of MPV, PDW, and PCT had good reference value for the diagnosis of heart failure in PH patients, with AUC values of 0.816, 0.897, and 0.825 respectively, and the combined diagnostic AUC is 0.952, which wass statistically different from the application of the three indicators alone(P < 0.05). Conclusion RDW, PDW and PCT are closely related to cardiac function in patients with PH, and can provide reference information for diagnosis and treatment of heart failure in patients with PH. -
表 1 PH组和对照组基线资料比较[n(%)/$\bar x \pm s$]
Table 1. Comparison of baseline data between PH group and control group[n(%)/$ \bar x \pm s $]
分组 n 性别 年龄(岁) BMI(kg/m2) 男 女 PH组 103 57 46 41.98±10.35 23.64±2.79 对照组 103 54 49 42.59±10.84 23.18±2.95 χ2/t 0.176 0.413 1.150 P 0.675 0.680 0.252 表 2 PH组和对照组MPV、PDW和PCT水平比较($\bar x \pm s$)
Table 2. Comparison of MPV,PDW and PCT between PH group and control group($ \bar x \pm s $)
分组 n MPV(fL) PDW(%) PCT(ng/mL) LVEF(%) PH组 103 17.49±2.61 17.42±2.94 0.63±0.21 51.87±4.62 对照组 103 10.57±1.98 10.26±1.73 0.25±0.07 60.54±3.46 t 4.172 5.864 3.905 15.244 P < 0.001* < 0.001* < 0.001* < 0.001* *P < 0.05。 表 3 不同NYHA分级患者MPV、PDW和PCT水平比较($\bar x \pm s$)
Table 3. Comparison of MPV,PDW and PCT in patients with different NYHA grades($ \bar x \pm s $)
NYHA
分级n MPV(fL) PDW(%) PCT
(ng/mL)LVEF(%) Ⅰ级 34 16.23±2.17 15.08±2.46 0.53±0.14 56.72±4.39 Ⅱ级 29 16.94±2.38a 17.32±2.89a 0.61±0.17a 52.43±4.51a Ⅲ级 23 18.02±2.63ab 18.64±3.01ab 0.68±0.20ab 48.96±4.07ab Ⅳ级 17 20.39±2.81abc 20.73±3.25abc 0.79±0.24abc 45.18±3.82abc F 13.398 16.825 8.488 34.914 P < 0.001* < 0.001* < 0.001* < 0.001* 与NYHA分级Ⅰ级比较,aP < 0.05;与NYHA分级Ⅱ级比较,bP < 0.05;与NYHA分级Ⅲ级比较,cP < 0.05;*P < 0.05。 表 4 衰竭组和未衰竭组MPV、PDW、PCT和LVEF比较($\bar x \pm s$)
Table 4. Comparison of MPV,PDW,PCT and LVEF between failure group and non-failure group($ \bar x \pm s $)
分组 n MPV(fL) PDW(%) PCT(ng/mL) LVEF(%) 衰竭组 65 16.52±2.41 16.04±2.57 0.59±0.18 49.36±4.27 未衰竭组 38 19.15±2.78 17.83±2.91 0.70±0.20 56.18±4.03 t 5.047 3.247 2.872 9.153 P <0.001* 0.002* 0.005* <0.001* *P < 0.05。 表 5 PH患者MPV、PDW和PCT水平与心功能的相关性分析
Table 5. Correlation of MPV,PDW and PCT and cardiac function in patients with PH
参数 NYHA分级 LVEF r P r P MPV 0.397 0.014* 0.417 0.003* PDW 0.406 0.008* 0.435 <0.001* PCT 0.382 0.025* 0.394 0.019* *P < 0.05。 表 6 MPV、PDW和PCT水平对PH患者心力衰竭诊断价值分析
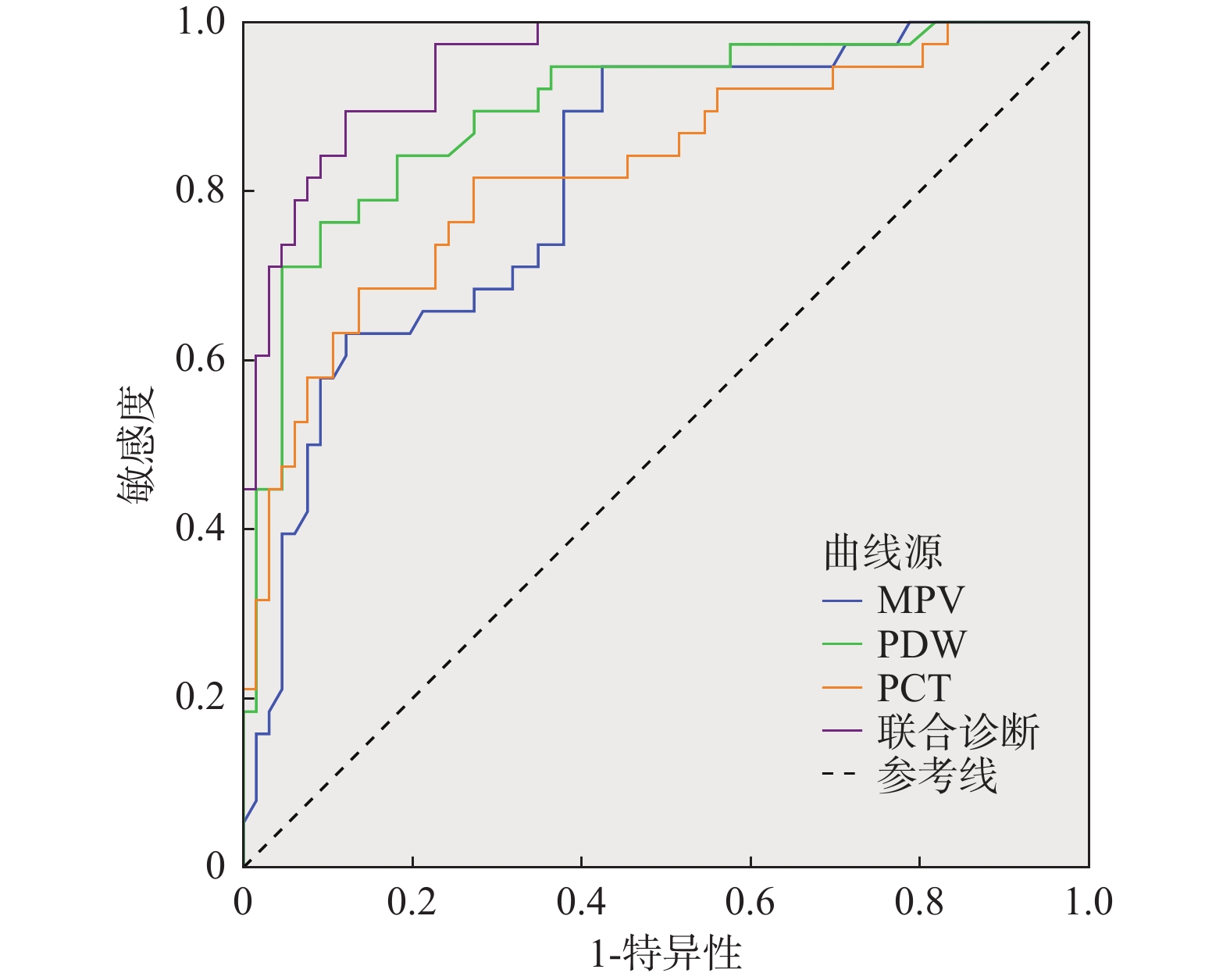
Table 6. Diagnostic value of MPV,PDW and PCT on heart failure in patients with PH
参数 最佳阈值 约登指数 敏感度(%) 特异度(%) AUC 95%CI MPV > 16.73 0.523 94.74 57.58 0.816 0.728~0.885 PDW > 15.01 0.672 76.32 90.91 0.897 0.822~0.948 PCT > 0.59 0.548 68.42 86.36 0.825 0.738~0.892 联合诊断 − 0.774 89.47 87.88 0.952 0.892~0.984 -
[1] Singh Y,Lakshminrusimha S. Pathophysiology and management of persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn[J]. Clin Perinatol,2021,48(3):595-618. doi: 10.1016/j.clp.2021.05.009 [2] 蒋殿虎,陈志旺,白书昌,等. 不同左心室舒张末压慢性射血分数保留性心力衰竭患者超声心动图参数差异分析[J]. 中国医学物理学杂志,2021,38(5):596-601. [3] Delcea C,Buzea C A,Vîjan A E,et al. The platelet to lymphocyte ratio in heart failure: A comprehensive review[J]. Rom J Intern Med,2023,61(2):84-97. [4] Sato M,Asagai S,Harada G,et al. Platelet volume indices correlate to severity of heart failure and have prognostic value for both cardiac and thrombotic events in patients with congenital heart disease[J]. Heart Vessels,2022,37(12):2107-2118. doi: 10.1007/s00380-022-02112-0 [5] Menghoum N,Beauloye C,Lejeune S,et al. Mean platelet volume: A prognostic marker in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction[J]. Platelets,2023,34(1):2188965. doi: 10.1080/09537104.2023.2188965 [6] Möckel M,de Boer R A,Slagman A C,et al. Improve management of acute heart failure with ProcAlCiTonin in EUrope: Results of the randomized clinical trial IMPACT EU Biomarkers in Cardiology (BIC) 18[J]. Eur J Heart Fail,2020,22(2):267-275. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.1667 [7] 左路广,张惠,谢桂芳,等. 血清降钙素原水平在非感染因素所致心力衰竭患者病程中的变化[J]. 中国医药,2021,16(10):1525-1528. [8] 中华医学会呼吸病学分会肺栓塞与肺血管病学组,中国医师协会呼吸医师分会肺栓塞与肺血管病工作委员会,全国肺栓塞与肺血管病防治协作组,等. 中国肺动脉高压诊断与治疗指南(2021版)[J]. 中华医学杂志,2021,101(1):11-51. [9] 中华医学会心血管病学分会心力衰竭学组,中国医师协会心力衰竭专业委员会,中华心血管病杂志编辑委员会. 中国心力衰竭诊断和治疗指南2018[J]. 中华心血管病杂志,2018,46(10):760-789. [10] 赵智慧,姜莉,王俊青. 实时三维超声心动图评价不同左室构型高血压病患者左房功能[J]. 临床超声医学杂志,2021,23(3):236-239. [11] Castiglione V,Aimo A,Vergaro G,et al. Biomarkers for the diagnosis and management of heart failure[J]. Heart Fail Rev,2022,27(2):625-643. doi: 10.1007/s10741-021-10105-w [12] 张颖,田毅,朱紫薇,等. 门控心肌灌注/代谢显像动态评估小型猪室壁瘤模型左心室功能及心室重构[J]. 中华核医学与分子影像杂志,2019,39(7):420-422. [13] 张玉海,李力兵,王亮,等. 间充质干细胞治疗肺动脉高压所致右心衰竭的研究进展[J]. 中华胸心血管外科杂志,2022,38(8):504-507. [14] Al-Qazazi R,Lima P D A,Prisco S Z,et al. Macrophage-NLRP3 Activation promotes right ventricle failure in pulmonary arterial hypertension[J]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med,2022,206(5):608-624. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202110-2274OC [15] Cassady S J,Ramani G V. Right heart failure in pulmonary hypertension[J]. Cardiol Clin,2020,38(2):243-255. doi: 10.1016/j.ccl.2020.02.001 [16] 陆云燕,魏文娟. 平均血小板体积与慢性心力衰竭的相关性[J]. 心脑血管病防治,2019,19(6):531-533. [17] 王婷,赵连山,张亮,等. 血小板体积分布宽度评估急性心力衰竭患者预后的价值[J]. 中国分子心脏病学杂志,2022,22(3):4668-4673. [18] Yaku A,Inagaki T,Asano R,et al. Regnase-1 prevents pulmonary arterial hypertension through mRNA degradation of interleukin-6 and platelet-derived growth factor in alveolar macrophages[J]. Circulation,2022,146(13):1006-1022. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.122.059435 [19] Delaney C,Davizon-Castillo P,Allawzi A,et al. Platelet activation contributes to hypoxia-induced inflammation[J]. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol,2021,320(3):L413-L421. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00519.2020 [20] Siniarski A,Gąsecka A,Borovac J A,et al. Blood coagulation disorders in heart failure: From basic science to clinical perspectives[J]. J Card Fail,2023,29(4):517-526. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2022.12.012 [21] Hanna A,Frangogiannis N G. Inflammatory cytokines and cemokines as therapeutic targets in heart failure[J]. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther,2020,34(6):849-863. doi: 10.1007/s10557-020-07071-0 [22] Said E A,Al-Reesi I,Al-Shizawi N,et al. Defining IL-6 levels in healthy individuals: A meta-analysis[J]. J Med Virol,2021,93(6):3915-3924. doi: 10.1002/jmv.26654 [23] 余志艳,彭松,江涛,等. 慢性肺源性心脏病患者血清白细胞介素-6、降钙素原、D-二聚体、N端B型脑钠肽前体与心功能分级和预后的关系研究[J]. 现代生物医学进展,2022,22(24):4714-4719,4724. [24] 陈保花,Agyekum GA,何婷婷,等. 雌二醇/睾酮比值、白细胞介素6、降钙素原水平与慢性心衰的关系[J]. 中国循证心血管医学杂志,2021,13(12):1496-1501. [25] Velissaris D,Zareifopoulos N,Lagadinou M,et al. Procalcitonin and sepsis in the emergency department: An update[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci,2021,25(1):466-479. [26] 梁彦群,王文棣,范文文. PCT、D-dimer和NT-proBNP水平及肺功能与儿童喘息性疾病相关肺动脉高压关系[J]. 青岛大学学报(医学版),2021,57(4):589-592. -






 下载:
下载: