Effects of Paroxetine and Sulpiride in the Treatment of Social Phobia in Young Women and Its Effects on Neurotransmitter and Sleep Structure
-
摘要:
目的 探讨帕罗西汀、舒必利联合治疗年轻女性社交恐惧效果及对神经递质、睡眠结构的影响。 方法 选取2021年2月至2023年2月张家口市沙岭子医院102例年轻女性社交恐惧患者,随机数字表法分为2组,各51例。对照组采取帕罗西汀,研究组采取帕罗西汀+舒必利,连续治疗3个月。统计2组治疗效果、神经递质[5-羟色胺(5-HT)、多巴胺(DA)、γ-氨基丁酸(GABA)、髓过氧化物酶(MPO)]、睡眠结构、社交焦虑(LASA)、社交恐惧(SPS)及社会适应能力(SAFE)评分、不良事件发生风险。 结果 研究组治疗总有效率88.24%较对照组70.59%高(P<0.05);治疗1个月、3个月后研究组血清DA、MPO水平低于对照组,5-HT、GABA水平高于对照组(P<0.05);治疗1个月、3个月后研究组睡眠转换次数、Ⅰ期+Ⅱ期占比较对照组低,Ⅲ期+Ⅳ期、REM期占比较对照组高(P<0.05);治疗1个月、3个月后研究组LASA、SPS、SAFE评分较对照组降低(P<0.05);研究组不良事件发生率13.73%与对照组9.80%比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。 结论 帕罗西汀与舒必利联合能改善年轻女性社交恐惧症患者睡眠结构,调节血清神经递质水平,减轻社交恐惧症状,提高社会适应力,且具有一定安全性。 Abstract:Objective To explore the effects of paroxetine and sulpiride in the treatment of social phobia in young women and the effects on neurotransmitters and sleep structure. Methods 102 young female patients with social phobia in our hospital from February 2021 to February 2023 were selected and divided into 2 groups with 51 cases in each group by random number table method. The control group was treated with Paxil, and the study group was treated with Paxil + sulpiride for 3 months. Treatment effect, neurotransmitters [5-hydroxytryptamine(5-HT), dopamine(DA), gamma-aminobutyric acid(GABA), myeloperoxidase(MPO)], sleep structure, social anxiety(LASA), social fear(SPS) and social Results The research group's overall effective rate of treatment is 88.24%, which is higher than the control group's 70.59%(P<0.05). 1 month and 3 months after treatment, the research group's serum levels of DA and MPO are lower than those of the control group, while the levels of 5-HT and GABA are higher than those of the control group(P<0.05). 1 month and 3 months after treatment, the research group's sleep transition frequency and the proportion of stage I + stage II are lower than those of the control group, while the proportion of stage III + stage IV and REM stage are higher than those of the control group(P<0.05). 1 month and 3 months after treatment, the research group's LASA, SPS, and SAFE scores are lower than those of the control group(P<0.05); The incidence of adverse events in the research group is 13.73% compared to 9.80% in the control group, with no statistically significant difference(P>0.05). Conclusion Paroxetine and sulpiride combined can improve the sleep structure of young women with social phobia, regulate serum neurotransmitter levels, alleviate social anxiety symptoms, improve social adaptability, and have a certain level of safety. -
Key words:
- Social phobia /
- Sulpride /
- Paroxetine /
- Sleep structure /
- Neurotransmitter
-
表 1 2组治疗效果比较[n(%)]
Table 1. Comparison of treatment effects between two groups [n(%)]
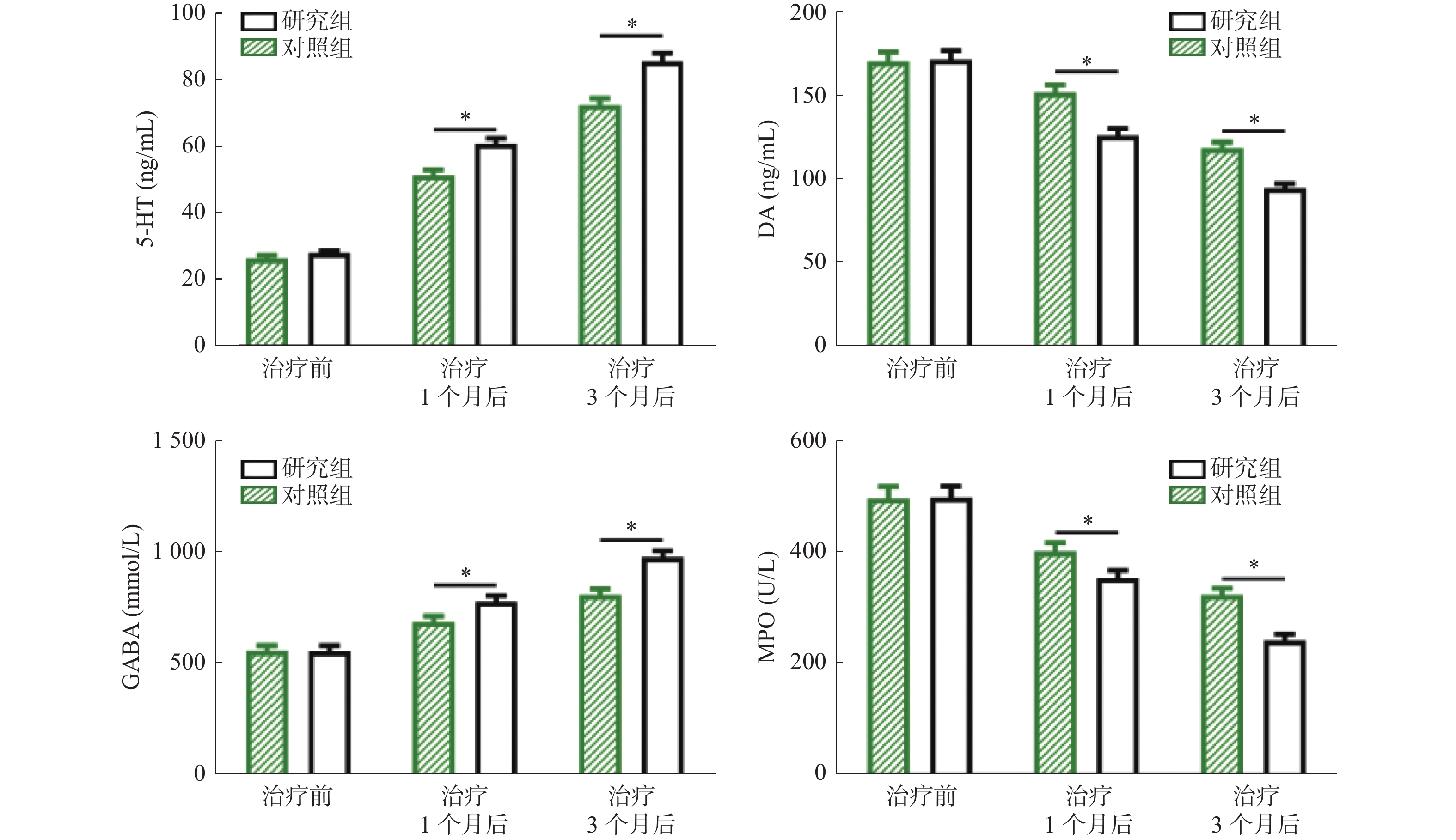
组别 n 显效 有效 无效 总有效率 对照组 51 10(19.61) 26(50.98) 15(29.41) 36(70.59) 研究组 51 14(27.45) 30(58.82) 6(11.76) 45(88.24) χ2 4.857 P 0.028* *P<0.05。 表 2 2组神经递质比较($ \bar x \pm s$)
Table 2. Comparison of neurotransmitters between two groups ($ \bar x \pm s$)
组别 n 5-HT(ng/mL) DA(ng/mL) GABA(mmol/L) MPO(U/L) 对照组 51 治疗前 26.23±3.12 170.92±20.24 558.58±88.91 495.91±75.58 治疗1个月后 51.19±5.56 152.21±16.65 689.89±90.56 400.12±58.21 治疗3个月后 72.27±7.23 118.87±13.48 811.01±94.42 322.27±42.28 研究组 51 治疗前 27.89±2.65 172.05±18.91 557.42±89.56 497.12±73.77 治疗1个月后 60.64±5.81 126.60±14.53 781.12±93.56 352.52±49.69 治疗3个月后 85.44±8.62 95.12±9.46 981.12±100.03 240.05±40.41 F/P时间 348.152/<0.001* 429.407/<0.001* 430.842/<0.001* 307.528/<0.001* F/P组间 168.094/<0.001* 198.095/<0.001* 260.408/<0.001* 134.910/<0.001* F/P交互 226.482/<0.001* 276.046/<0.001* 315.620/<0.001* 268.402/<0.001* *P<0.05。 表 3 2组睡眠结构比较($ \bar x \pm s $)
Table 3. Comparison of sleep structures between two groups ($ \bar x \pm s $)
组别 n 睡眠转换次数(次) 睡眠结构百分比(%) REM期 Ⅰ期+Ⅱ期 Ⅲ期+Ⅳ期 对照组 51 治疗前 201.12±26.65 8.85±1.52 80.90±9.95 10.20±1.55 治疗1个月后 120.20±11.38 13.04±1.95 73.35±5.46 13.12±1.86 治疗3个月后 65.56±5.34 17.75±2.03 63.38±5.11 17.96±2.23 研究组 51 治疗前 198.98±27.78 9.33±1.36 81.76±8.23 10.12±1.68 治疗1个月后 95.51±9.63 15.87±2.00 66.13±6.39 16.23±2.14 治疗3个月后 45.42±4.41 20.20±2.36 56.56±4.98 21.88±2.76 F/P时间 625.842/<0.001* 306.393/<0.001* 93.460/<0.001* 264.752/<0.001* F/P组间 125.684/<0.001* 154.756/<0.001* 35.429/<0.001* 29.840/<0.001* F/P交互 394.028/<0.001* 228.406/<0.001* 55.184/<0.001* 162.486/<0.001* *P<0.05。 表 4 2组LASA、SPS、SAFE评分比较($ \bar x \pm s$,分)
Table 4. Comparison of LASA,SPS,and SAFE scores between two groups ($ \bar x \pm s $,points)
组别 n LASA SPS SAFE 对照组 51 治疗前 15.54±1.96 25.01±2.90 37.56±5.34 治疗1个月后 13.42±1.50 20.11±2.66 31.16±3.40 治疗3个月后 9.22±0.67 11.38±1.26 25.74±1.35 研究组 51 治疗前 16.12±1.30 24.42±3.38 38.38±4.41 治疗1个月后 11.38±1.16 17.79±2.53 27.85±2.63 治疗3个月后 6.40±0.58 8.81±1.02 23.38±1.12 F/P时间 306.158/<0.001* 158.160/<0.001* 168.405/<0.001* F/P组间 124.536/<0.001* 16.818/<0.001* 20.674/<0.001* F/P交互 245.422/<0.001* 64.856/<0.001* 59.418/<0.001* *P<0.05。 表 5 5组不良反应比较[n(%)]
Table 5. Comparison of adverse reactions among 5 groups [n(%)]
组别 n 失眠 早醒 食欲减退 恶心呕吐 总发生率 对照组 51 1(1.96) 0(0.00) 2(3.92) 2(3.92) 5(9.80) 研究组 51 2(3.92) 2(3.92) 1(1.96) 3(5.88) 7(13.73) χ2 0.378 P 0.539 -
[1] Tibi L,Asher S,van Oppen P,et al. The correlates of social phobia in OCD: Findings from a large clinical sample[J]. Br J Clin Psychol,2021,60(3):312-332. doi: 10.1111/bjc.12292 [2] Probst T,Berger T,Meyer B,et al. Social phobia moderates the outcome in the EVIDENT study: A randomized controlled trial on an Internet-based psychological intervention for mild to moderate depressive symptoms[J]. J Consult Clin Psychol,2020,88(1):82-89. doi: 10.1037/ccp0000441 [3] Li L,Han Z,Li L,et al. Effectiveness of paroxetine for poststroke depression: A meta-analysis[J]. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis,2020,29(5):104664. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2020.104664 [4] Naguy A. Sulpiride for autism spectrum disorder[J]. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord,2021,23(5):20l02822. [5] 王春雨,储华. 文拉法辛联合舒必利治疗社交恐惧症的临床疗效[J]. 临床合理用药杂志,2019,12(12):83-84. doi: 10.15887/j.cnki.13-1389/r.2019.12.040 [6] 中华医学会精神科分会. CCMD-3中国精神障碍分类与诊断标准[M]. 山东科学技术出版社, 2001: 43. [7] 何燕玲,张明园. LieboWitZ社交焦虑量表的信度和效度研究[J]. 诊断学理论与实践,2004,3(2):89-93. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2870.2004.02.009 [8] 叶冬梅,钱铭怡,刘兴华,等. 社会交往焦虑量表和社交恐惧量表的修订[J]. 中国临床心理学杂志,2007,15(2):115-117. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3611.2007.02.002 [9] Duan S,Lee M,Wolf J,et al. Higher depressive symptoms predict lower social adaptive functioning in children and adolescents with ASD[J]. J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol,2022,51(2):203-210. doi: 10.1080/15374416.2020.1750020 [10] Caponnetto P,Triscari S,Maglia M,et al. The simulation game-virtual reality therapy for the treatment of social anxiety disorder: A systematic review[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health,2021,18(24):13209. doi: 10.3390/ijerph182413209 [11] Alomari N A,Bedaiwi S K,Ghasib A M,et al. Social anxiety disorder: Associated conditions and therapeutic approaches[J]. Cureus,2022,14(12):e32687. [12] Muris P,Ollendick T H. Selective mutism and its relations to social anxiety disorder and autism spectrum disorder[J]. Clin Child Fam Psychol Rev,2021,24(2):294-325. doi: 10.1007/s10567-020-00342-0 [13] Villanueva J,Meyer AH,Mikoteit T,et al. Having versus not having social interactions in patients diagnosed with depression or social phobia and controls[J]. PLoS One,2021,16(4):e0249765. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0249765 [14] 赵春龙,张涛. 左侧背外侧前额叶rTMS联合帕罗西汀治疗抑郁症的效果及对患者血清神经递质的影响[J]. 海南医学,2023,34(5):629-632. [15] 周岩,李莹,郝腾,等. 益气养心安神汤联合帕罗西汀对抑郁症失眠气郁痰阻证患者HAMD、CGI评分的影响[J]. 辽宁中医杂志,2023,50(1):62-65. [16] Leisman G,Sheldon D. Tics and emotions[J]. Brain Sci,2022,12(2):242. doi: 10.3390/brainsci12020242 [17] 李杰,赵金香,魏丽宁,等. 度洛西汀联合小剂量舒必利治疗躯体化障碍随机对照研究[J]. 河北医药,2020,42(23):3560-3563. [18] 张孜,杨烨,李晓琳,等. 基于治疗药物浓度监测的舒必利剂量校正浓度的影响因素分析[J]. 中国临床药理学杂志,2023,39(1):13-16. [19] 杨柳,周云云. 帕罗西汀联合小剂量舒必利治疗社交恐惧合并抑郁的疗效[J]. 中国健康心理学杂志,2018,26(6):4. doi: 10.13342/j.cnki.cjhp.2018.06.003 [20] Dos Santos R G,Bouso J C,Alcázar-Córcoles M Á,et al. Efficacy,tolerability,and safety of serotonergic psychedelics for the management of mood,anxiety,and substance-use disorders: A systematic review of systematic reviews[J]. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol,2018,11(9):889-902. doi: 10.1080/17512433.2018.1511424 [21] 郭虹,李云鹏,王超敏,等. 艾司西酞普兰联合心理疗法对焦虑症患者睡眠质量、生活质量和血清神经递质水平的影响[J]. 现代生物医学进展,2021,21(6):1059-1063. doi: 10.13241/j.cnki.pmb.2021.06.013 [22] Aledavood T,Torous J,Triana Hoyos A M,et al. Smartphone-based tracking of sleep in depression,anxiety,and psychotic disorders[J]. Curr Psychiatry Rep,2019,21(7):49. doi: 10.1007/s11920-019-1043-y -






 下载:
下载: