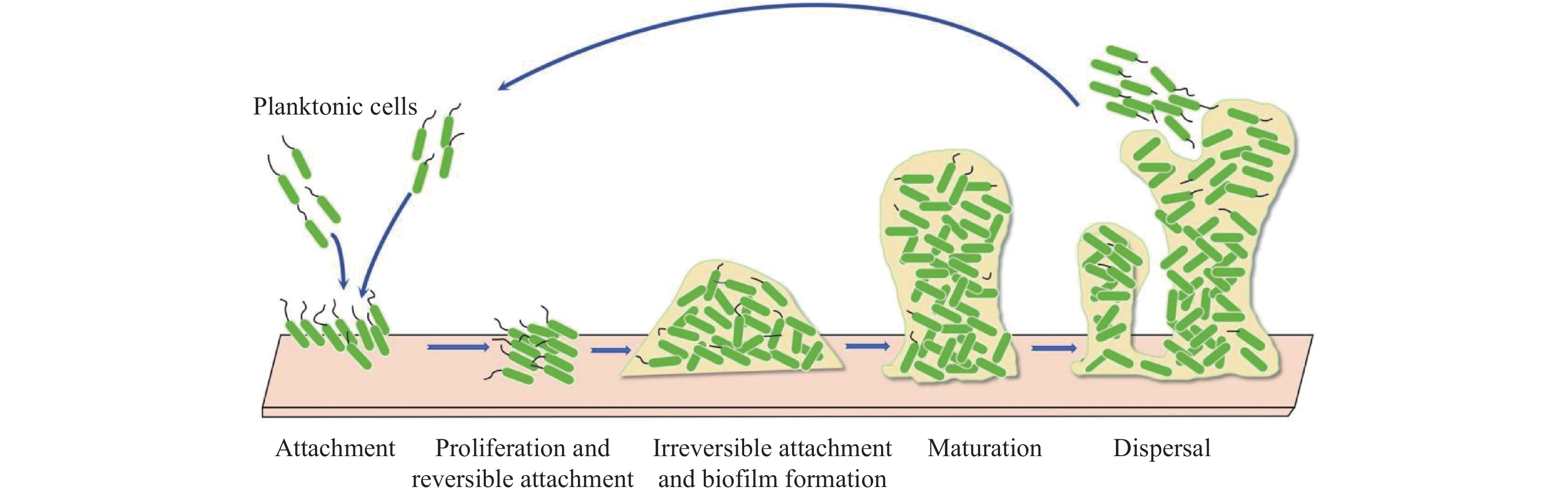
|
[1]
|
Li S,Duan W,Lei Y,et al. Effects of lipid emulsions on the formation of Escherichia coli-Candida albicans mixed-species biofilms on PVC[J]. Sci Rep,2021,11(1):16929. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-96385-6
|
|
[2]
|
Mei J,Xu D,Wang L,et al. Biofilm microenvironment-responsive self-assembly nanoreactors for all-stage biofilm associated Infection through bacterial cuproptosis-like death and macrophage re-rousing[J]. Adv Mater,2023,35(36):e2303432. doi: 10.1002/adma.202303432
|
|
[3]
|
Li Q,Liu Q,Wang Z,et al. Biofilm homeostasis Interference therapy via 1O2-Sensitized hyperthermia and Immune microenvironment re-rousing for biofilm-associated Infections elimination[J]. Small,2023,19(22):e2300592. doi: 10.1002/smll.202300592
|
|
[4]
|
Xu Q,Chen S,Jiang L,et al. Sonocatalytic hydrogen/hole-combined therapy for anti-biofilm and infected diabetic wound healing[J]. Natl Sci Rev,2023,10(5):nwad063. doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwad063
|
|
[5]
|
杨政鸿,何大千,宁明杰,等. 不同3D打印精度制作的生物材料表面形貌对表皮葡萄球菌生物膜形成影响[J]. 昆明医科大学学报,2022,43(2):12-17. doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220228
|
|
[6]
|
张国婧,万子琳,王小燕,等. 表皮葡萄球菌胞间黏附素基因操纵子对细菌与真菌混合生物膜相关炎症作用影响的体内研究[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2021,35(10):1328-1335.
|
|
[7]
|
Lei Y,Xu Y,Jing P,et al. The effects of TGF-β1 on staphylococcus epidermidis biofilm formation in a tree shrew biomaterial-centered infection model[J]. Ann Transl Med,2021,9(1):57. doi: 10.21037/atm-20-4526
|
|
[8]
|
李民杰. 大肠杆菌运动调控在生物材料植入感染中的作用研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明医科大学, 2021.
|
|
[9]
|
Wang X,Zhang J,Chen W,et al. Study on the effects of estradiol in staphylococcus epidermidis device-related capsule formation[J]. Aesthetic Plast Surg,2020,44(2):558-569. doi: 10.1007/s00266-019-01567-3
|
|
[10]
|
Karygianni L,Ren Z,Koo H,et al. Biofilm matrixome: Extracellular components in structured microbial communities[J]. Trends Microbiol,2020,28(8):668-681. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2020.03.016
|
|
[11]
|
Rosman C W K,van Dijl J M,Sjollema J. Interactions between the foreign body reaction and Staphylococcus aureus biomaterial-associated infection. Winning strategies in the derby on biomaterial implant surfaces[J]. Crit Rev Microbiol,2022,48(5):624-640. doi: 10.1080/1040841X.2021.2011132
|
|
[12]
|
Zarkan A,Liu J,Matuszewska M,et al. Local and universal action: The paradoxes of Indole signalling in bacteria[J]. Trends Microbiol,2020,28(7):566-577. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2020.02.007
|
|
[13]
|
Bjarnsholt T,Buhlin K,Dufrêne Y F,et al. Biofilm formation-what we can learn from recent developments[J]. J Intern Med,2018,284(4):332-345. doi: 10.1111/joim.12782
|
|
[14]
|
Arciola C R,Campoccia D,Montanaro L. Implantinfections: adhesion,biofilm formation and immune evasion[J]. Nat Rev Microbiol,2018,16(7):397-409. doi: 10.1038/s41579-018-0019-y
|
|
[15]
|
羊扬,刘云,张信军,等. 大肠杆菌群体感应系统的研究进展[J]. 中国兽医学报,2018,38(8):1624-1631. doi: 10.16303/j.cnki.1005-4545.2018.08.27
|
|
[16]
|
Flemming H C,Wuertz S. Bacteria and archaea on earth and theirabundance in biofilms[J]. Nat Rev Microbiol,2019,17(4):247-260. doi: 10.1038/s41579-019-0158-9
|
|
[17]
|
吴丽娜,董鹏程,张一敏,等. 大肠杆菌生物膜形成特性及控制措施的研究进展[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(15):307-313. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20180910-100
|
|
[18]
|
Berne C,Ellison C K,Ducret A,et al. Bacterial adhesion at the single-cell level[J]. Nat Rev Microbiol,2018,16(10):616-627. doi: 10.1038/s41579-018-0057-5
|
|
[19]
|
Arnaouteli S,Bamford N C,Stanley-Wall N R,et al. Bacillus subtilis biofilm formation and social interactions[J]. Nat Rev Microbiol,2021,19(9):600-614. doi: 10.1038/s41579-021-00540-9
|
|
[20]
|
Filipović U,Dahmane R G,Ghannouchi S,et al. Bacterial adhesion on orthopedic implants[J]. Adv Colloid Interface Sci,2020,283:102228. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2020.102228
|
|
[21]
|
Yan J,Bassler B L. Surviving as a community: Antibiotic tolerance and persistence in bacterial biofilms[J]. Cell Host Microbe,2019,26(1):15-21. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2019.06.002
|
|
[22]
|
Yin W,Wang Y,Liu L,et al. Biofilms: The microbial "protective clothing" in extreme environments[J]. Int J Mol Sci,2019,20(14):3423. doi: 10.3390/ijms20143423
|
|
[23]
|
Roy R,Tiwari M,Donelli G,et al. Strategies for combating bacterial biofilms: A focus on anti-biofilm agents and their mechanisms of action[J]. Virulence,2018,9(1):522-554. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2017.1313372
|
|
[24]
|
Del Pozo J L. Biofilm-related disease[J]. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther,2018,16(1):51-65. doi: 10.1080/14787210.2018.1417036
|
|
[25]
|
Balzan S,de Almeida Quadros C,de Cleva R,et al. Bacterial translocation: Overview of mechanisms and clinical impact[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol,2007,22(4):464-471. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2007.04933.x
|
|
[26]
|
Krawczyk B,Śledzińska A,Szemiako K,et al. Characterisation of Escherichia coli isolates from the blood of haematological adult patients with bacteraemia: Translocation from gut to blood requires the cooperation of multiple virulence factors[J]. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis,2015,34(6):1135-1143. doi: 10.1007/s10096-015-2331-z
|
|
[27]
|
Azimi S,Klementiev A D,Whiteley M,et al. Bacterial quorum sensing during Infection[J]. Annu Rev Microbiol,2020,74:201-219. doi: 10.1146/annurev-micro-032020-093845
|
|
[28]
|
Coquant G,Grill J P,Seksik P. Impactof N-acyl-homoserine lactones,quorum sensing molecules,on gut Immunity[J]. Front Immunol,2020,11:1827. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01827
|
|
[29]
|
Ahmed U K B,Ballard J D. Autoinducing peptide-based quorum signaling systems in clostridioides difficile[J]. Curr Opin Microbiol,2022,65:81-86. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2021.10.017
|
|
[30]
|
Yi L,Dong X,Grenier D,et al. Research progress of bacterialquorum sensing receptors: Classification,structure,function and characteristics[J]. Sci Total Environ,2021,763:143031.
|
|
[31]
|
Khera R,Mehdipour A R,Bolla J R,et al. Cryo-EM structures of pentameric autoinducer-2 exporter from Escherichia coli reveal its transport mechanism[J]. EMBO J,2022,41(18):e109990. doi: 10.15252/embj.2021109990
|
|
[32]
|
Huang S,Liu X,Yang W,et al. Insights into adaptive mechanisms of extreme acidophiles[J]. Msystems,2022,7(2):e0149121. doi: 10.1128/msystems.01491-21
|
|
[33]
|
Kim C S,Gatsios A,Cuesta S,et al. Characterization of autoinducer-3 structure and biosynthesis in E. coli[J]. ACS Cent Sci,2020,6(2):197-206. doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.9b01076
|
|
[34]
|
Cui B,Chen X,Guo Q,et al. The cell-cell communication signal indole controls the physiology and interspecies communication of acinetobacter baumannii[J]. Microbiol Spectr,2022,10(4):e0102722. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01027-22
|
|
[35]
|
Wu S,Liu J,Liu C,et al. Quorum sensing for population-level control of bacteria and potential therapeutic applications[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci,2020,77(7):1319-1343. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03326-8
|
|
[36]
|
Yaikhan T,Chuerboon M,Tippayatham N,et al. Indole and derivatives modulate biofilm formation and antibiotic tolerance of klebsiella pneumoniae[J]. Indian J Microbiol,2019,59(4):460-467. doi: 10.1007/s12088-019-00830-0
|
|
[37]
|
Rattanaphan P,Mittraparp-Arthorn P,Srinoun K,et al. Indole signaling decreases biofilm formation and related virulence of Listeria monocytogenes[J]. FEMS Microbiol Lett,2020,367(14):fnaa116. doi: 10.1093/femsle/fnaa116
|
|
[38]
|
Li Y,Feng T,Wang Y. The role of bacterial signaling networks in antibiotics response and resistance regulation[J]. Mar Life Sci Technol,2022,4(2):163-178. doi: 10.1007/s42995-022-00126-1
|
|
[39]
|
Ganin H,Kemper N,Meir S,et al. Indole derivatives maintain the status quo between beneficial biofilms and their plant hosts[J]. Mol Plant Microbe Interact,2019,32(8):1013-1025.
|
|
[40]
|
Denamur E,Clermont O,Bonacorsi S,et al. The population genetics of pathogenic Escherichia coli[J]. Nat Rev Microbiol,2021,19(1):37-54. doi: 10.1038/s41579-020-0416-x
|
|
[41]
|
Gorelika O,Rogada A,Holoidovskyb L,et al. Meijlerb. Indole intercepts the communication between enteropathogenic E. coli and vibrio cholerae[J]. Gut Microbes,2022,14(1):2138677. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2022.2138677
|
|
[42]
|
韩茵,孙苗苗,王建平,等. 吲哚作为细菌细胞间信号分子的研究进展[J]. 微生物学通报,2015,42(4):736-748. doi: 10.13344/j.microbiol.china.140629
|
|
[43]
|
Wang J,Zhang C,Childers W S. A biosensor for detection of Indole metabolites[J]. ACS Synth Biol,2021,10(7):1605-1614. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.1c00090
|
|
[44]
|
Fiore A,Murray P J. Tryptophan and indole metabolism in immune regulation[J]. Curr Opin Immunol,2021,70:7-14. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2020.12.001
|
|
[45]
|
杨刚,张云露,李思明,等. 色氨酸对肠屏障免疫的调控作用研究进展[J]. 中国畜牧杂志,2021,57(4):6-10+16. doi: 10.19556/j.0258-7033.20200517-03
|
|
[46]
|
Kumar A,Russell R M,Hoskan M A,et al. Indole sensing regulator (IsrR) promotes virulence gene[J]. mBio,2022,13(4):e0193922. doi: 10.1128/mbio.01939-22
|
|
[47]
|
Han T H,Lee J H,Cho M H,et al. Environmental factors affecting indole production in Escherichia coli[J]. Res Microbiol,2011,162(2):108-116. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2010.11.005
|
|
[48]
|
Li G,Young K D. Indole production by the tryptophanase TnaA in Escherichia coli is determined by the amount of exogenous tryptophan[J]. Microbiology (Reading),2013,159(2):402-410.
|
|
[49]
|
Boon N,Kaur M,Aziz A,et al. The signaling molecule Indole Inhibits Induction of the AR2 acid resistance system in Escherichia coli[J]. Front Microbiol,2020,11:474. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00474
|
|
[50]
|
Kumar A,SperandioV. Indole signaling at the host-microbiota-pathogen Interface[J]. mBio,2019,10(3):e01031-19.
|
|
[51]
|
Kim J,Shin B,Park C,et al. Indole-Induced activities of β-Lactamase and efflux pump confer ampicillin resistance in pseudomonas putida KT2440[J]. Front Microbiol,2017,8:433.
|
|
[52]
|
Cheng C,Yan X,Liu B,et al. SdiA enhanced the drug resistance of cronobacter sakazakii and suppressed Its motility,adhesion and biofilm formation[J]. Front Microbiol,2022,13:901912. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.901912
|
|
[53]
|
Mayer C,Borges A,Flament-Simon S C,et al. Quorum sensing architecture network in Escherichia coli virulence and pathogenesis[J]. FEMS Microbiol Rev,2023,47(4):fuad031. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuad031
|
|
[54]
|
Xuan G,Dou Q,Kong J,et al. Pseudomonas aeruginosa resists phage Infection via eavesdropping on Indole signaling[J]. Microbiol Spectr,2023,11(1):e0391122. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03911-22
|
|
[55]
|
Kim J,Park W. Indole: A signaling molecule or a mere metabolic byproduct that alters bacterial physiology at a high concentration?[J]. J Microbiology,2015,53(7):421-428. doi: 10.1007/s12275-015-5273-3
|
|
[56]
|
Wang Y,Bian Z,Wang Y. Biofilm formation and inhibition mediated by bacterial quorum sensing[J]. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol,2022,106(19-20):6365-6381. doi: 10.1007/s00253-022-12150-3
|
|
[57]
|
Liu W,Tang Q,Meng L,et al. Interbacterial chemical communication‐triggered nascent proteomics[J]. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl,2023,62(5):e202214010. doi: 10.1002/anie.202214010
|
|
[58]
|
Sun F,Yuan Q,Wang Y,et al. Sub-minimum inhibitory concentration ceftazidime inhibits Escherichia coli biofilm formation by influencing the levels of the ibpA gene and extracellular indole[J]. Chemother,2020,32(1):7-14. doi: 10.1080/1120009X.2019.1678913
|
|
[59]
|
Feng W,Zhang L,Yuan Q,et al. Effect of sub-minimal inhibitory concentration ceftazidime on the pathogenicity of uropathogenic Escherichia coli[J]. Microb Pathog,2021,151:104748. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2021.104748
|
|
[60]
|
Lee J,Page R,García-Contreras R,et al. Structure and function of the E. coli protein YmgB: A protein critical for biofilm formation and acid-resistance[J]. J Mol Biol,2007,373(1):11-26. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.07.037
|
|
[61]
|
Domka J,Lee J,Wood T K. YliH (BssR) and YceP (BssS) regulate Escherichia coli K-12 biofilm formation by influencing cell signaling[J]. Appl Environ Microbiol,2006,72(4):2449-2459. doi: 10.1128/AEM.72.4.2449-2459.2006
|






 下载:
下载: