Metabolomics of Siha Supernatant in Cervical Cancer Cells with Down-regulated HPV16 E6/E7 Expression
-
摘要:
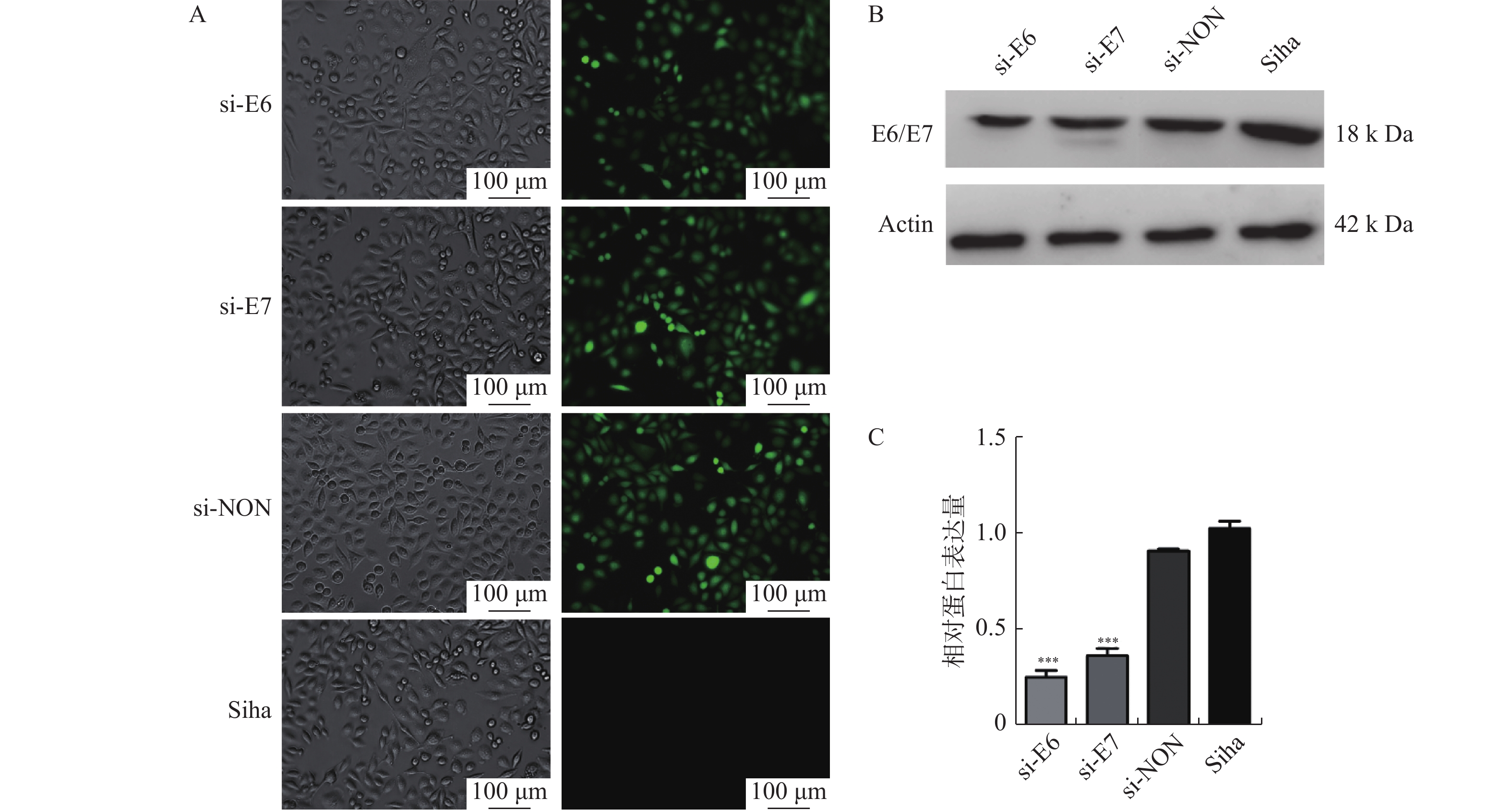
目的 基于核磁共振氢谱(1H NMR)代谢组学筛选抑制HPV16 E6/E7表达,检测宫颈癌Siha细胞中差异代谢物以及相关通路,以明确感染高危型HPV16宫颈癌发生的关键代谢标志物。 方法 通过RNAi片段转染Siha细胞下调E6/E7表达,分为正常对照组(Siha细胞)、空载组(si-NON)、si-E6 组与si-E7组,并验证其转染效率。利用1H NMR 代谢组学技术揭示干扰Siha细胞中E6/E7表达后所涉及的差异代谢物;结合MetaboAnalyst 5.0在线软件,得到改变的差异性代谢物和相关的代谢途径。 结果 荧光倒置显微镜观察细胞荧光存在;Western blotting检测结果显示,与Siha组比较,si-E6 组与si-E7组中E6/E7的表达量降低(F=145.8,P<0.001);下调E6/E7表达后,检测13种共有差异代谢物,包括异亮氨酸(Isoleucine),亮氨酸(Leucine),缬氨酸(Valine);MetaboAnalyst 5.0在线软件分析结果提示,以上代谢物主要涉及氨酰-tRNA生物化学合成途径;异亮氨酸、亮氨酸和缬氨酸的生物化学合成途径;酪氨酸、苯丙氨酸以及色氨酸的生物化学合成等10条代谢途径。 结论 HPV16感染后通过改变葡萄糖及氨基酸相关代谢促进宫颈癌的进展,为宫颈癌的防治提供理论依据。 -
关键词:
- HPV16 E6/E7 /
- 宫颈癌 /
- 代谢组学
Abstract:Objective To detecte the differential metabolites and related pathways in Siha cells of cervical cancer by screening the inhibition of HPV16 E6/E7 expression based on 1H NMR metabolomics so as to identify the key metabolic markers involved in the development of high-risk HPV16 cervical cancer. Methods Siha cells were transfected with RNAi fragments to down-regulate the expression of E6/E7, which were divided into the normal control group(Siha cells), no-load group(si-NON), si-E6 group and si-E7 group, and their transfection efficiency was verified. 1H NMR metabolomics was used to reveal the differential metabolites involved in interfering E6/E7 expression in Siha cells. Combined with MetaboAnalyst 5.0 online software, differential metabolites and related metabolic pathways were obtained. Results Fluorescence was observed by inverted fluorescence microscope. Western blotting results showed that compared with Siha group, the expression of E6/E7 in si-E6 group and si-E7 group was decreased(F=145.8, P < 0.001). After down-regulating the expression of E6/E7, 13 common differential metabolites, including Isoleucine, Leucine and valine, were detected. The results of MetaboAnalyst 5.0 online software analysis suggested that the above metabolites were mainly involved in the biochemical synthesis pathway of aminoacyl-trNA, biochemical synthesis pathway of isoleucine, Leucine and valine; There were 10 metabolic pathways of tyrosine, phenylalanine and tryptophan biochemical synthesis. Conclusion After HPV16 infection, changes of glucose and amino acid metabolism can promote the progression of cervical cancer, which provide a theoretical basis for the prevention and treatment of cervical cancer. -
Key words:
- HPV E6/E7 /
- Cervical cancer /
- Metabolomics
-
表 1 E6 RNAi、E7 RNAi片段引物序列
Table 1. Primer sequences of E6 RNAi and E7 RNAi fragments
基因名 引物序列 E6 RNAi 上游 TGCTGATGTATAGTTGTTTGCAGCTCGTTTTGGCCACTGACTGACGAGCTGCACAACTATACAT 下游 CCTGATGTATAGTTGTGCAGCTCGTCAGTCAGTGGCCAAAACGAGCTGCAAACAACTATACATC E7 RNAi 上游 TGCTGTTGTAATGGGCTCTGTCCGGTGTTTTGGCCACTGACTGACACCGGACAGCCCATTACAA 下游 CCTGTTGTAATGGGCTGTCCGGTGTCAGTCAGTGGCCAAAACACCGGACAGAGCCCATTACAAC 表 2 RNA干扰组与非干扰租1HNMR谱经过OPLS-DA分析获得的主要差异性代谢物及其相关系数
Table 2. Otherness metabolites of different cell samples using OPLS-DA based on different normalization methods and its correlation coefficients
序号 代谢物 化学位移/(mg/L) 归属 相关系数r si-NON/si-/E6 si-NON/si-/E6 Siha/si-E6 Siha/si-E7 1 异亮氨酸 0.93(t) δ-CH3 −0.84 −0.74 −0.93 −0.77 2 亮氨酸 0.95(d),0.97(d) δ-CH3,δ-CH3 −0.88 −0.74 −0.94 −0.83 3 缬氨酸 0.98(d),1.04(d) CH3,CH3,α-CH2 −0.84 −0.79 −0.89 −0.85 4 丙氨酸 1.47(d),3.76(q) CH3,α-CH 0.72 0.47 0.55 0.56 5 酪氨酸 3.95(dd),6.89(d),7.18(d) CH2,α-CH,H3/H5 −0.59 −0.69 −0.92 −0.83 6 苯丙氨酸 7.32(d),7.37(m),7.42(m) H2/H6,H4,H3/H5 −0.59 −0.51 −0.91 −0.84 7 甲基组氨酸 7.03(s),7.74(s) H4,H2 0.65 0.45 0.96 0.91 8 α-葡萄糖 3.53(dd),3.72(dd),5.23(d),3.84(ddd) C-H2,halfCH2−CH6,C-H1 −0.80 −0.87 −0.83 −0.71 9 β-葡萄糖 3.24(t),3.40(t),3.47(ddd),3.70(dd),
3.90(dd),4.64(d),C-H4,C-H5,halfCH2−CH6,C-H1 −0.72 −0.7 −0.81 −0.68 10 乳酸 1.33(d),4.11(q) CH3,CH 0.59 0.58 0.66 0.53 11 乙酸 1.91(s) CH3 −0.54 −0.94 −0.73 −0.69 12 甲酸 8.44(s) CH 0.49 0.41 0.91 0.63 13 β-羟丁酸 1.18(t),4.17(dd) γ-CH3,β-CH −0.63 −0.67 −0.65 s:单峰;d:双重峰;t:三重峰;q:四重峰;m:多重峰;dd:双重双重峰;ddd:双重双重双重峰。 表 3 下调Siha细胞E6/E7蛋白后10条相关代谢通路
Table 3. 10 metabolic pathways associated with down-regulation of E6/E7 protein in SIHA cells
代谢通路名称 总计 表达 数目 原始P值 差异倍数 Holm校对 错误检出率 影响 氨酰-tRNA生物合成 48 0.37161 6 0.00000051598 6.2874 0.000043342 0.000043342 0 缬氨酸、亮氨酸和
异亮氨酸的生物合成8 0.061935 3 0.000019458 4.7109 0.001615 0.000817 0 苯丙氨酸、酪氨酸和
色氨酸的生物合成4 0.030968 2 0.000327 3.4854 0.026817 0.009157 1 糖酵解/糖异生 26 0.20129 3 0.000835 3.0784 0.067623 0.017532 0.35714 苯丙氨酸合成途径 10 0.077419 2 0.00239 2.6216 0.19121 0.040153 0.02399 缬氨酸、亮氨酸和异亮氨酸降解 40 0.30968 3 0.002983 2.5254 0.23565 0.04176 0 苯丙氨酸代谢途径 22 0.17032 2 0.01165 1.9337 0.90873 0.1398 0.06065 丙酮酸代谢途径,
乙醛酸和
二羧酸代谢32 0.24774 2 0.023961 1.6205 1 0.25159 0 酮体的合成与降解 5 0.03871 1 0.038163 1.4184 1 0.35619 0 泛醌和其他萜类-醌生物合成 9 0.069677 1 0.067728 1.1692 1 0.56891 0 -
[1] Wang H,Hu H,Luo Z,et al. miR-4454 up-regulated by HPV16 E6/E7 promotes invasion and migration by targeting ABHD2/NUDT21 in cervical cancer[J]. Bioscience Reports,2020,40(9):1-12. [2] Zhou Z,Yang H,Yang L,et al. Human papillomavirus type 16 E6 and E7 gene variations associated with cervical cancer in a Han Chinese population[J]. Infection,Genetics and Evolution:Journal of Molecular Epidemiology and Evolutionary Genetics in Infectious Diseases,2019,73(4):13-20. [3] Hasan Y,Furtado L,Tergas A,et al. A phase 1 trial assessing the safety and tolerability of a therapeutic DNA vaccination against HPV16 and HPV18 E6/E7 oncogenes after chemoradiation for cervical cancer[J]. International Journal of Radiation Oncology,Biology,Physics,2020,107(3):487-498. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2020.02.031 [4] Tang J,Li D,He L,et al. HPV 16 E6/E7 promote the glucose uptake of GLUT1 in lung cancer through downregulation of TXNIP due to inhibition of PTEN phosphorylation[J]. Frontiers in Oncology,2020,10(11):559543. [5] Wang H, Lu Y, He L, et al. viaHPV16 E6/E7 promote the translocation and glucose uptake of GLUT1 by PI3K/AKT pathway relieving miR-451 inhibitory effect on CAB39 in lung cancer cells[J]. Therapeutic Advances in Chronic Disease, 2020, 11(9): 2040622320957143. [6] Diggle C,Pitt E,Roberts P,et al. N;-3 and n;-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids induce cytostasis in human urothelial cells independent of p53 gene function[J]. Journal of Lipid Research,2000,41(9):1509-1515. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2275(20)33463-5 [7] Kim D,Allwood J,Moore R,et al. A metabolomics investigation into the effects of HIV protease inhibitors on HPV16 E6 expressing cervical carcinoma cells[J]. Molecular BioSystems,2014,10(3):398-411. doi: 10.1039/C3MB70423H [8] Li X,Zhou X,Zeng M,et al. PAX1Methylation of gene promoter in the prediction of concurrent chemo-radiotherapy efficacy in cervical cancer[J]. Journal of Cancer,2021,12(17):5136-5143. doi: 10.7150/jca.57460 [9] 王丹萍,周佳娣,王伟,等. 新疆乌鲁木齐市健康体检女性HPV感染情况及其基因型分布分析[J]. 新疆医学,2023,53(3):321-324. [10] Koc S,Yuksel D,Kayikcioglu F. Colposcopic histopathology results of patients over 50: Is HPV genotyping useful?[J]. Current Problems in Cancer,2022,46(1):100764. doi: 10.1016/j.currproblcancer.2021.100764 [11] Gandhi S,Nor Rashid N,Mohamad Razif M,et al. Proteasomal degradation of p130 facilitate cell cycle deregulation and impairment of cellular differentiation in high-risk human papillomavirus 16 and 18 E7 transfected cells[J]. Molecular Biology Reports,2021,48(6):5121-5133. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06509-4 [12] Warburg O,Wind F,Negelein E. The metabolism of tumors in the body[J]. J Gen Physiol,1927,8(6):519-530. doi: 10.1085/jgp.8.6.519 [13] Vander Heiden M G,Locasale J W,Swanson K D,et al. Evidence for an alternative glycolytic pathway in rapidly proliferating cells[J]. Science,2010,329(5998):1492-1499. doi: 10.1126/science.1188015 [14] 阿仙姑·哈斯木,努尔满古力·肉孜,徐丽秀,等. 宫颈癌发生与肿瘤组织代谢物变化及代谢途径的分析研究[J]. 新疆医科大学学报,2018,41(5):521-527,533. [15] 海燕,美力班·吐尔逊,阿仙姑·哈斯木. Pin1通过调控脂质代谢关键酶影响宫颈癌细胞的增殖及凋亡[J]. 昆明医科大学学报,2023,44(1):1-6. [16] 马建红,高亚婷,万子华,等. 糖代谢与宫颈癌关系及其致病机制的研究进展[J]. 国际妇产科学杂志,2023,50(3):275-280. [17] 蔡鑫,熊蓉,范佳杨,等. 沉默ENO1对人宫颈癌HeLa细胞增殖、迁移、侵袭能力的影响[J]. 山西医科大学学报,2020,51(7):616-622. [18] Xu L,Li J,Tursun M,et al. Receptor for activated C kinase 1 promotes cervical cancer lymph node metastasis via the glycolysis-dependent AKT/mTOR signaling[J]. Int J Oncol,2022,61(1):83. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2022.5373 [19] Hensley C T,Wasti A T,De Berardinis R J,et al. Glutamine and cancer: Cell biology,physiology,and clinical opportunities[J]. J Clin Invest,2013,123(9):3678-3684. doi: 10.1172/JCI69600 [20] 王林琳,孙振亮. 氨基酸转运体在肿瘤代谢中的研究进展[J]. 生物技术进展,2022,12(01):50-56. [21] Hoppe-Seyler K,Honegger A,Bossler F,et al. Viral E6/E7 oncogene and cellular hexokinase 2 expression in HPV-positive cancer cell lines[J]. Oncotarget,2017,8(63):106342-106351. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.22463 [22] Zhang R,Su J,Xue S L,et al. HPV E6/p53 mediated down-regulation of miR-34a inhibits warburg effect through targeting LDHA in cervical cancer[J]. Am J Cancer Res,2016,6(2):312-320. [23] 刘迎春. TG2及HPV16-E6蛋白在宫颈鳞癌中的表达研究[D]. 衡阳: 南华大学硕士学位论文, 2015. -






 下载:
下载: