Effects and Mechanisms of Xueshuantong on the Cognitive Function and Abnormal Neural Excitability in Mice with Alzheimer’ s Disease
-
摘要:
目的 探究血栓通[主要有效成分为三七皂苷(panax notoginseng,PNS)]对阿尔茨海默症(Alzheimer’s disease,AD)模型小鼠认知功能及神经兴奋性的影响,并探讨其潜在分子机制。 方法 用APP/PS1小鼠作为AD研究动物模型,在小鼠淀粉样蛋白尚未检测到阶段(2月龄)开始每日以60 mg/kg对血栓通组(APP/PS1+PNS)行灌胃给药,每日1次,连续给药6个月(给药至8月龄);对照组小鼠予同等体积的0.9%氯化钠(APP/PS1+vehicle)灌胃处理,同月龄野生型小鼠予0.9%氯化钠灌胃处理作为正常对照组(WT+ vehicle),每组各15只。6个月后,新物体识别实验、Morris水迷宫实验检测小鼠的认知功能;EEG脑电检测、Western blot、细胞表面生物素化试验以检测各组小鼠皮质与海马中BACE1的活性、Nav1.1α的分布、表达以及Navβ2的表达与酶解情况(Navβ2的酶解片段Navβ2 full length及Navβ2-CTF表达检测)。 结果 新物体识别实验显示,与对照组APP/PS1小鼠相比,血栓通用药后APP/PS1小鼠的辨别指数(discrimination index,DI)上升(P < 0.05);Morris水迷宫检测结果发现,血栓通灌胃6个月后小鼠在探索实验中逃避潜伏期缩短(P < 0.05),撤除平台后在目标象限停留时间增加(P < 0.05)、穿梭平台次数增加(P < 0.05);EEG脑电检测结果发现,血栓通给药后减少了APP/PS1小鼠棘波放电出现的频率(P < 0.05)。血栓通给药后显著降低了BACE1蛋白水平的表达(P < 0.05),而全长片段Navβ2的蛋白水平显著上升(P < 0.05),并纠正了Nav1.1α在神经元内外的异常分布(P < 0.05)。 结论 血栓通可以改善AD模型小鼠的学习记忆能力、纠正大脑异常兴奋性,其作用机制可能与抑制BACE1的活性从而减少Navβ2由 APP/PS1诱导的过度酶解,纠正皮质、海马神经元Nav1.1α的异常表达与分布,调节神经元的兴奋性有关。 Abstract:Objective To explore the possible effects and the underlying molecular mechanisms of xueshuantong [The main active component is panax notoginseng (PNS)] on the cognitive function and neural excitability of mice with Alzheimer’ s disease (AD). Methods The APP/PS1 mice were used as an animal model for AD research, at the stage when amyloid protein was not detected in mice (2 months of age). Mice in the xueshuantong group (APP/PS1+PNS) were administered by gavage once a day at a dose of 60 mg/kg for six months (for 8 months of age). The mice of the control group were given 0.9% sodium chloride (APP/PS1+Vehicle) intragastric treatment of the same volume, while the wild-type mice of the same age were given 0.9% sodium chloride intragastric treatment as the normal control group (WT+Vehicle) (15 mice in each group, n=15). After six months, the cognitive function of the mice was evaluated by the Novel Object Recognition (NOR) task and Morris Water Maze (MWM) test. The activity of BACE1, the distribution and expression of Nav1.1α, as well as the expression and enzymatic hydrolysis of Navβ2 (Navβ2 full-length and Navβ2-CTF fragments) in cortex and hippocampus were detected by EEG, Western blot and cell surface biotinylation assay, respectively. Results The NOR task showed that compared with the mice in the APP/PS1+Vehicle group, the Discrimination index (DI) of mice in the APP/PS1 group was significantly increased after xueshuantong administration (P < 0.05). The MWM test found that, the escape latency of the mice in the xueshuantong group was shortened followed six months in gastric administration (P < 0.05), while the stay time in the target quadrant and the number of platforms significantly increased (P < 0.05) after the removal of the platform. The results of EEG recording showed that xueshuantong reduced the frequency of spike-wave discharges in APP/PS1 mice (P < 0.05). Furthermore, xueshuantong significantly reduced the expression of BACE1 (P < 0.05). In the APP+PNS group, the expression of Navβ2 full-length was increased (P < 0.05), as well as corrected the abnormal distribution of Nav1.1α inside and outside of neurons (P<0.05). Conclusion Treatment with xueshuantong can significantly improve the learning and memory ability and correct the abnormal excitability of the brain in AD model mice. The mechanism may be related to the inhibition of BACE1 activity, the reduction of APP/PS1-induced excessive enzyme digestion of Navβ2, the correction of the abnormal expression and distribution of Nav1.1α in cortical and hippocampal neurons, as well as the subsequent regulation of neuronal excitability. -
Key words:
- Xueshuantong /
- Alzheimer’ s disease /
- Cognition /
- BACE1 /
- The enzymolysis of Navβ2 /
- The distribution of Nav1.1α
-
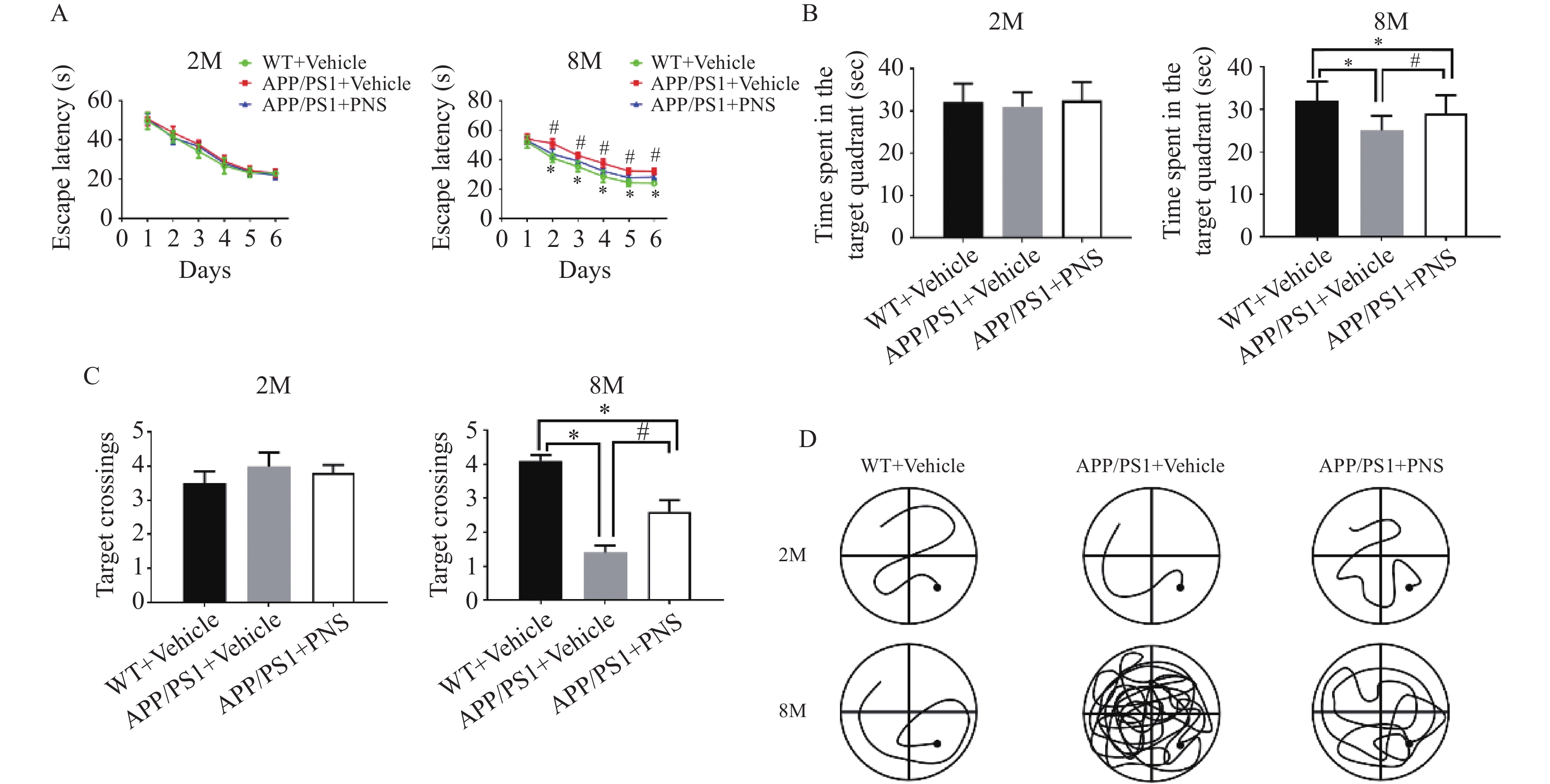
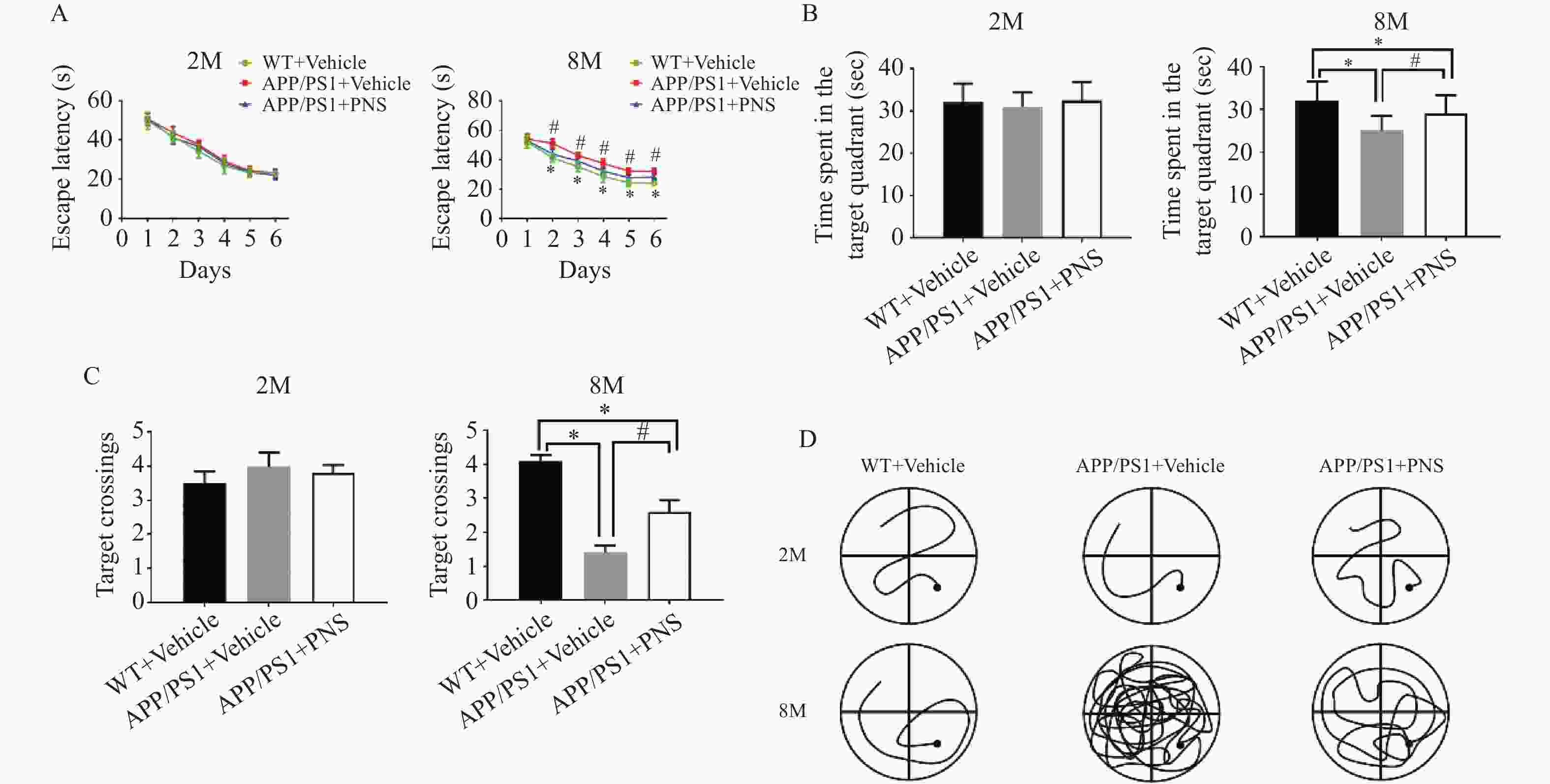
图 1 Morris水迷宫任务显示血栓通对APP/PS1小鼠空间学习记忆变化的影响
A:各组小鼠在训练期间从第1天到第6天的逃避潜伏期;B:探针实验测试期间在目标象限所花费的时间;C:探针实验中在目标平台的穿梭次数;D:探针实验中APP/PS1小鼠的游泳路径。($ \bar x \pm s $,n=15),*P < 0.05 vs. WT+Vehicle,#P<0.05 vs. APP/PS1+PNS。
Figure 1. Morris water maze task shows the effect of xueshuantong on spatial learning and memory changes in APP/PS1 mice
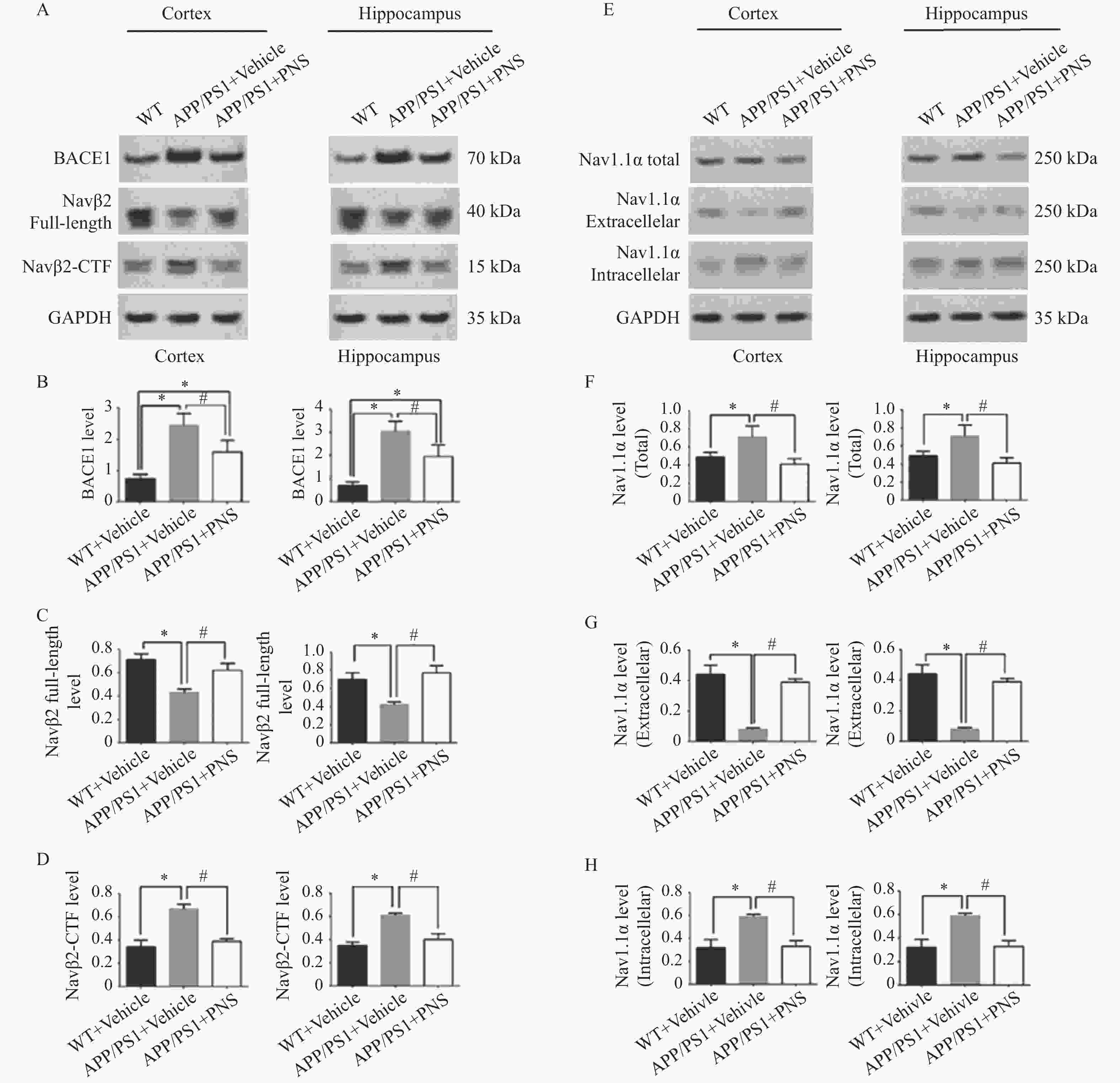
图 4 血栓通改变APP/PS1小鼠中Nav1.1α的分布和Navβ2的裂解
A:各组小鼠额叶皮层和海马中BACE1、Navβ2全长、Navβ2-CTF的蛋白电泳图;B:各组小鼠额叶皮层和海马中BACE1的蛋白表达比较;C:各组小鼠额叶皮层和海马中Navβ2全长的蛋白表达比较;D:各组小鼠额叶皮层和海马中Navβ2-CTF的蛋白表达比较;E:各组小鼠额叶皮层和海马中的Nav1.1α的总量、细胞外Nav1.1α和细胞内Nav1.1α的蛋白电泳图;F:各组小鼠额叶皮层和海马中Nav1.1α总量的蛋白表达比较;G:各组小鼠额叶皮层和海马中细胞外Nav1.1α的蛋白表达比较;H:各组小鼠额叶皮层和海马中细胞外Nav1.1α的蛋白表达比较。($ \bar x \pm s $,n=15),*P<0.05 vs. WT+ Vehicle,#P<0.05 vs. APP/PS1 + PNS。
Figure 4. Xueshuantong alters Nav1.1α distribution and Navβ2 cleavage in APP/PS1 mice
-
[1] Grossberg G T, Tong G, Burke A D, et al. Present Algorithms and future treatments for Alzheimer's disease. [J] Journal of Alzheimer's Disease, 2019, 67(4): 1157-1171. [2] 王高瑞,陈姿羽,吴辉,等. 基于网络药理学和实验验证的血栓通改善缺血性脑微循环障碍作用机制研究[J]. 药学学报,2022,57(7):2077-2086. [3] Liu L,Zhang Q,Xiao S,et al. Inhibition of shear-induced platelet aggregation by xueshuantong via targeting piezo1 channel-mediated Ca2+ signaling pathway[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology,2021,12:606245. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.606245 [4] Han S,Chen Y,Wang J,et al. Anti-thrombosis effects and mechanisms by xueshuantong capsule under different flow conditions[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology,2019,10(FEB):35. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00035 [5] Zhang J,Guo F,Zhou R,et al. Proteomics and transcriptome reveal the key transcription factors mediating the protection of Panax notoginseng saponins (PNS) against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury[J]. Phytomedicine,2021,92:153613. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153613 [6] Peiran L,Ying L,Mingzhuo Z,et al. The development of a Panax notoginseng medicinal liquor processing technology using the response surface method and a study of its antioxidant activity and its effects on mouse melanoma B16 cells[J]. Food & Function,2017,8(11):4251-4264. [7] Han J Y,Li Q,Ma Z Z,et al. Effects and mechanisms of compound Chinese medicine and major ingredients on microcirculatory dysfunction and organ injury induced by ischemia/reperfusion[J]. Pharmacology & Therapeutics,2017,177:146-173. [8] Zhong L,Zhou X L,Liu Y S,et al. Estrogen receptor α mediates the effects of notoginsenoside R1 on endotoxin-induced inflammatory and apoptotic responses in H9c2 cardiomyocytes[J]. Molecular Medicine Reports,2015,12(1):119-126. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.3394 [9] Lee C Y,Hsieh S L,Hsieh S,et al. Inhibition of human colorectal cancer metastasis by notoginsenoside R1,an important compound from Panax notoginseng[J]. Oncol Rep,2017,37(1):399-407. doi: 10.3892/or.2016.5222 [10] Li W,Wu Y,Wan M,et al. Simultaneous determination of three saponins in human plasma after oral administration of compound danshen dripping pills by LC-MS/MS and its application in a pharmacokinetic study[J]. J Pharm Biomed Anal,2019,169:254-259. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2019.03.008 [11] Jian W,Yu S,Tang M,et al. A combination of the main constituents of Fufang Xueshuantong Capsules shows protective effects against streptozotocin-induced retinal lesions in rats[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology,2016,182:50-56. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.11.021 [12] Gao L,Zhao H,Liu Q,et al. Improvement of hematoma absorption and neurological function in patients with acute intracerebral hemorrhage treated with Xueshuantong[J]. Journal of the Neurological Sciences,2012,323(1-2):236-240. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2012.09.028 [13] Li Z,Li H,Zhao C H,et al. Protective effect of notoginsenoside R1 on an APP/PS1 mouse model of Alzheimer & aposs disease by up-regulating insulin degrading enzyme and inhibiting Aβ accumulation[J]. CNS & Neurological Disorders-Drug Targets,2015,14(3):360-369. [14] Huang J L,Xin J,Xin T,et al. Neuroprotective properties of panax notoginseng saponins via preventing oxidative stress injury in SAMP8 mice[J]. Evidence-Based Complementray and Alternative Medicine,2017,2017:8713561. [15] Huang J,Wu D,Wang J,et al. Effects of Panax notoginseng saponin on α,β,and γ secretase involved in Aβ deposition in SAMP8 mice[J]. Neuroreport,2014,25(2):89-93. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0000000000000048 [16] Xi Y,Yan B,Wang Y C,et al. Sodium channel voltage-gated beta 2 plays a vital role in brain aging associated with synaptic plasticity and expression of COX5A and FGF-2[J]. Mol Neurobiol,2016,53(2):955-967. doi: 10.1007/s12035-014-9048-3 [17] Tao H,Xiao Z,Rui M,et al. Navβ2 knockdown improves cognition in APP/PS1 mice by partially inhibiting seizures and APP amyloid processing[J]. Oncotarget,2017,8(59):99284-99295. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.21849 [18] Hu T,Li S S,Lu M N,et al. Neuroprotection induced by Nav beta 2-knockdown in APP/PS1 transgenic neurons is associated with NEP regulation[J]. Nature Reviews Neuroscience,2019,20(2):2002-2011. [19] Lee M,Kim D,Shin H S,et al. High-density EEG recordings of the freely moving mice using polyimide-based microelectrode[J]. Journal of Visualized Experiments Jove,2011(47):2562. [20] Corbett B F,Leiser S C,Ling H,et al. Sodium channel cleavage is associated with aberrant neuronal activity and cognitive deficits in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease[J]. Journal of Neuroscience,2013,33(16):7020-7026. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2325-12.2013 [21] Sheena LP,Regan,Phil G,et al. Growth hormone during in vitro fertilization in older women modulates the density of receptors in granulosa cells,with improved pregnancy outcomes[J]. Fertility and Sterility,2018,110(7):1298-1310. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2018.08.018 [22] Huang Y,Guo B,Shi B,et al. Chinese herbal medicine xueshuantong enhances cerebral blood flow and improves neural functions in Alzheimer's disease mice[J]. Journal of Alzheimers Disease,2018,63(3):1089-1107. doi: 10.3233/JAD-170763 [23] Liu H,Liang J P,Li P B,et al. Core bioactive components promoting blood circulation in the traditional chinese medicine compound xueshuantong capsule (CXC) based on the relevance analysis between chemical HPLC fingerprint and in vivo biological effects[J]. Plos One,2014,9(11):e112675. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112675 [24] Cheret C,Willem M,Fricker F R,et al. Bace1 and Neuregulin-1 cooperate to control formation and maintenance of muscle spindles[J]. Embo Journal,2013,32(14):2015-2028. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2013.146 [25] Filser S,Ovsepian S V,Masana M,et al. Pharmacological inhibition of BACE1 impairs synaptic plasticity and cognitive functions[J]. Biological Psychiatry,2015,77(8):729-739. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2014.10.013 [26] Zhu K,Xiang X,Filser S,et al. Beta-site amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme 1 inhibition impairs synaptic plasticity via seizure protein 6[J]. Biological Psychiatry,2016,83(5):428-437. [27] Wong H K,Sakurai T,Oyama F,et al. Beta Subunits of voltage-gated sodium channels are novel substrates of beta-site amyloid precursor protein-cleaving enzyme (BACE1) and gamma-secretase[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry,2005,280(24):23009-23017. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M414648200 -





 下载:
下载: