Study on the Relationship Between OAT1 Expression and Renal Osteodystrophy in Rats with Chronic Renal Failure
-
摘要:
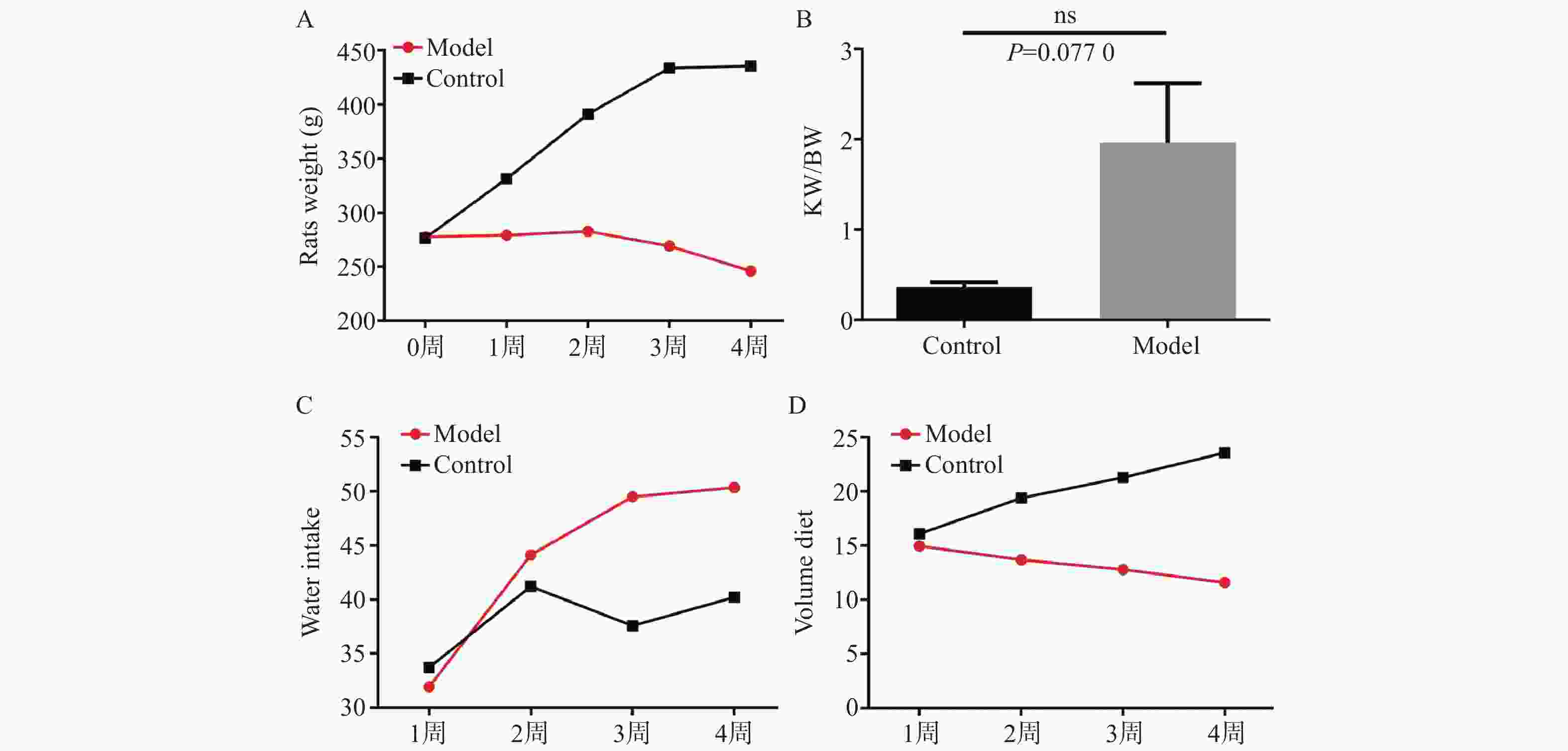
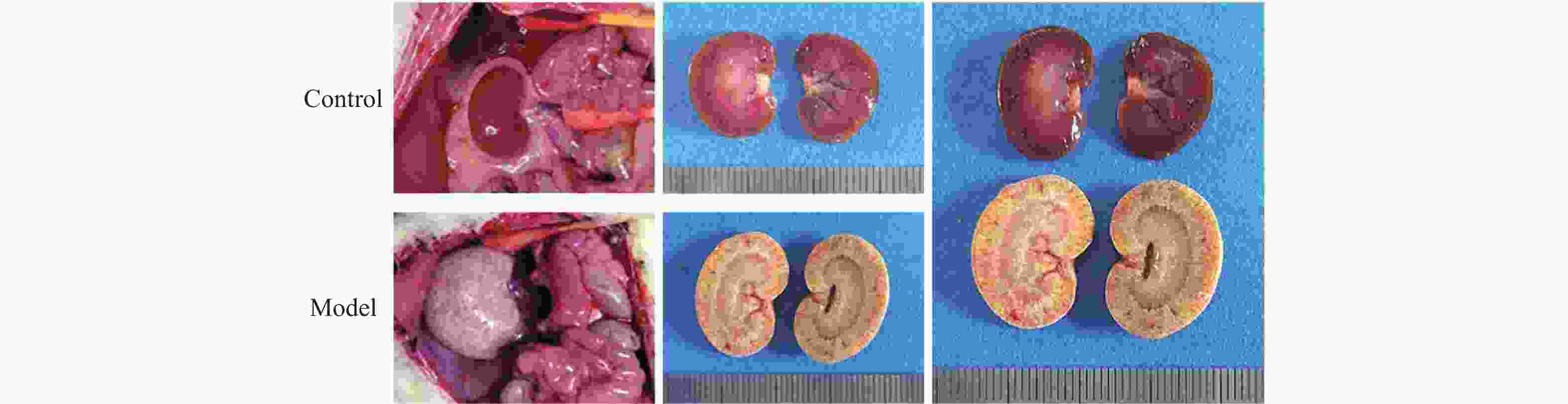
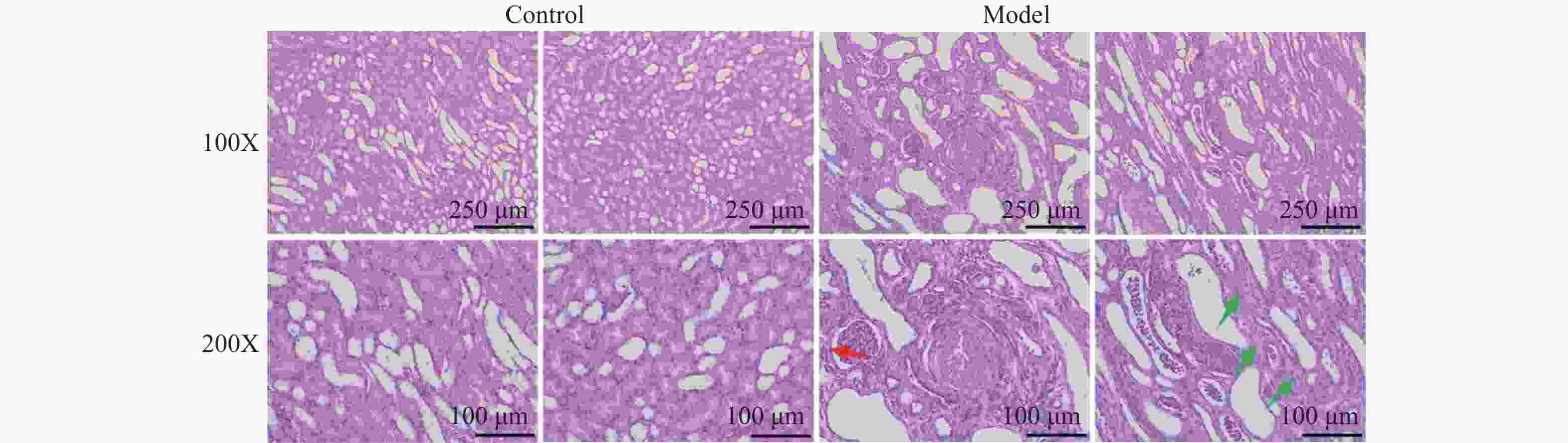
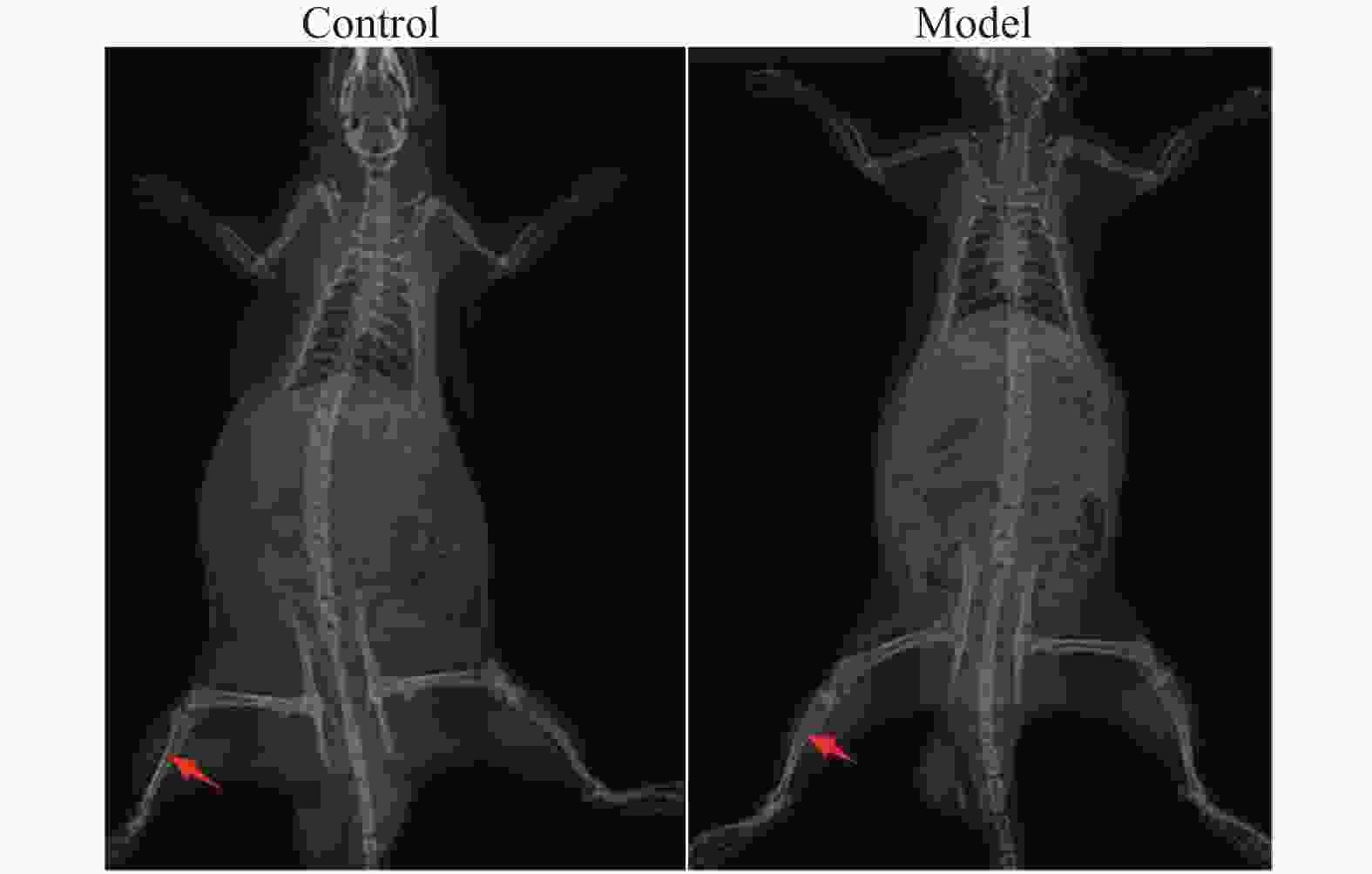
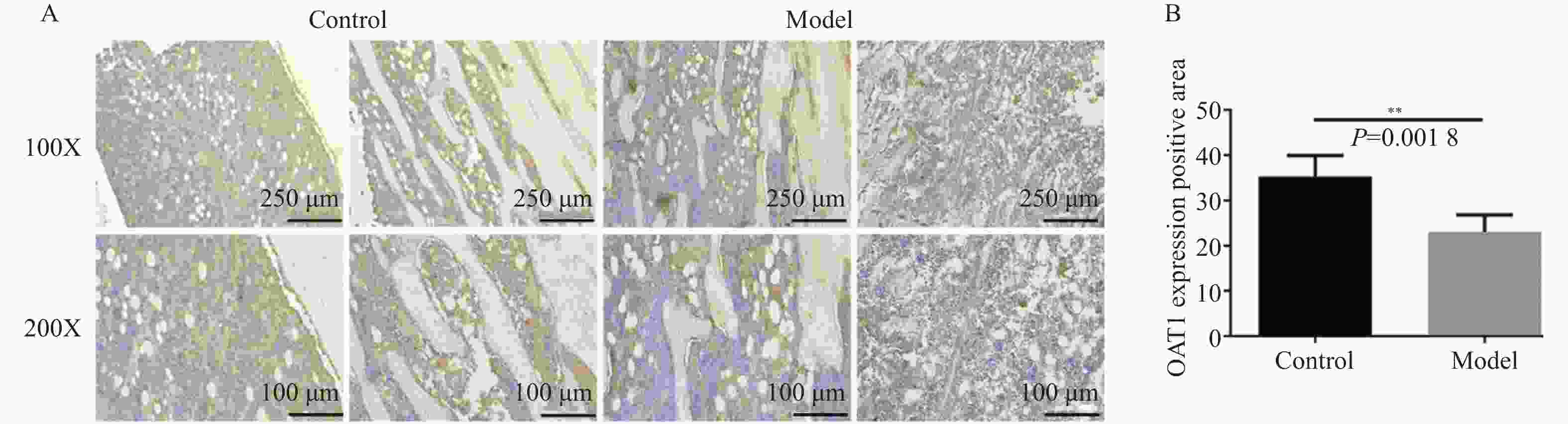
目的 研究慢性肾衰竭时导致骨细胞有机阴离子转运蛋白(organic anion transporter,OAT)表达的变化,探讨OAT1表达对骨代谢的影响。 方法 将SD大鼠随机分为对照组(Control,n=6)和模型组(Model,n=6)。模型组采用“单肾切除+腺嘌呤灌胃法”建立大鼠慢性肾衰竭模型,通过血常规分析仪测定大鼠血清的红细胞(red blood cell,RBC)、血红蛋白(hemoglobin,Hb);通过全自动生化分析仪测定肌酐(creatinine,Cr)、尿素氮(urea nitrogen,BUN)、尿酸(uric acid,UA)、血钙(Ca2+)、血磷(P3+)等指标;对大鼠肾脏进行病理学检查;X线拍片检查大鼠胫骨标本;免疫组化检查骨组织OAT1表达。 结果 模型组大鼠的骨密度低于对照组;模型组大鼠钙磷代谢失调,并且骨组织结合OAT1值远低于对照组,差异具有统计学意义(P=0.0018)。 结论 慢性肾功衰竭影响OAT1在骨组织中的表达,导致钙磷代谢失调,从而加重肾性骨营养不良。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the changes of OAT expression in bone cells in chronic renal failure (CRF)and involved mechanism, and to explore the effect of OAT expression on bone metabolism. Methods Randomly divide the rats into a control group (n=6)and a model group (n=6).The model group established a rat chronic renal failure model using "single nephrectomy+adenine gavage" method, and the red blood cell (RBC) and hemoglobin (HGB)of the rat body were measured using a blood routine analyzer; Measure indicators such as creatinine (Cr), urea nitrogen (BUN), uric acid (UA), blood calcium (Ca2+), and blood phosphorus (P3+) using a fully automated biochemical analyzer; Pathological examination of rat kidneys; X-ray examination of rat tibia; Immunohistochemical examination of bone tissue OAT1 level. Results The bone density of the model group rats is lower than that of the control group;The calcium and phosphorus metabolism of rats in the model group was in metabolic disorder, and the OAT1 value of bone tissue binding was much lower than that of the control group(P=0.0018), which was statistically significant. (P=0.0018) Conclusion Chronic renal failure affected the binding ability of OAT1 in bone tissue, leading to the metabolic disorder for calcium absorption and phosphorus metabolism, thus aggravating renal osteodystrophy (P<0.05). -
Key words:
- Organic anion transporter /
- Chronic renal failure /
- Osteodystrophy
-
表 1 不同组间大鼠的肾功能指标比较($ \bar x \pm s $,n=6)
Table 1. Comparison of renal function indicators among different groups of rats($\bar x \pm s$,n=6)
组别 n 红细胞(RBC,×1012/L) 血红蛋白(Hb,g/L) 尿素氮(BUN,mmol/L) 肌酐(Cr,µmol/L) 模型组 6 6.742±0.480 119±7.457 142.8±25.85** 374.2±51.97** 对照组 6 7.763±2.488 146.2±52.53 17.86±1.063 40.81±0.593 t − 0.987 1.254 11.83 15.71 P − 0.3456 0.0649 <0.001** <0.001** 与对照组比较,*P<0.05,**P<0.01。 表 2 不同组间大鼠的尿酸、钙和磷水平($ \bar x \pm s $,n=6)
Table 2. Uric acid,calcium,and phosphorus levels in rats of different groups($ \bar x \pm s $,n=6)
组别 n 尿酸(UA,µmol/L) Ca2+ (mmol/L) P3+ (mmol/L) 模型组 6 162.8±46.92** 2.290±0.179** 5.535±1.433** 对照组 6 72.04±11.45 2.006±0.050 2.181±0.232 t − 4.604 3.752 5.661 P − 0.001** 0.0038** 0.0002** 与对照组比较,*P<0.05,**P<0.01。 -
[1] 陆汝江,李玲,高丽辉. 有机阴离子转运蛋白在肾脏尿酸排泄中的作用研究进展[J]. 国际药学研究杂志,2019,46(10):405-410. [2] Hou G,Jin M,Ye Z,et al. Ameliorative effects of soybean soluble polysaccharide on adenine-induced chronic renal failure in mice[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,170(4):4032-4076. [3] Enomoto A, Niwa T. Roles of organic anion transporters in the progression of chronic renal failure[J]. Ther Apher Dial, 2007(Suppl 1): S27-31. [4] Ahn S,Nigam S. Toward a systems level understanding of organic anion and other multispecific drug transporters: A remote sensing and signaling hypothesis[J]. Mol Pharmacol,2009,76(3):481-90. [5] Bytyqi C,Bytyqi D,Shabani B,et al. Correction of severe K-nees valgus deformities in a patient with renal osteodystrophy[J]. J Am Acad Orthop Surg Glob Res Rev,2022,6(6):1-4. [6] Modest J,Sheth H,Gohh R,et al. Osteomalacia and renal osteodystrophy[J]. R I Med J,2022,97(10):22-27. [7] Abdalbary M, Sobh M, Elnagar S, et al. Management of osteoporosis in patients w-ith chronic kidney disease[J]. Osteoporos Int, 2022, 33(10): 2259-2274. [8] 孙保党. 血液灌流联合血液透析治疗慢性肾功能衰竭合并肾性骨营养不良患者的疗效及对血磷、血钙及甲状旁腺激素水平的影响[J]. 系统医学,2022,33(10):2259-2274. [9] Suzuki T,Toyohara T,Akiyama Y,et al. Transcriptional regulation of organic anion transporting polypeptide SLCO4C1 as a new therapeutic modality to prevent chronic kidney disease[J]. J Pharm Sci,2012,339(1):3696-3707. [10] Wang L,Sweet D. Interaction of natural dietary and herbal anionic compou-nds and flavonoids with human organic anion transporters 1(SLC22A6),3(S-LC22A8),and 4(SLC22A11)[J]. Evidence-based Complement Altern Med,2013,4(2):1-7. [11] Duan P,You G. Short-term regulation of organic anion transporters[J]. Phar-macol Ther,2010,125(1):55-61. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2009.08.002 [12] 陈剑泉,罗美玲,刘玲苑,等. 慢性肾功能衰竭患者血清脂蛋白及尿酸水平与肾功能损害的相关性研究[J]. 吉林医学,2020,41(41):2887-2899. [13] 赵萍. 血清脂蛋白尿酸水平变化与慢性肾功能衰竭患者肾功能损害的相关性分析[J]. 基层医学论坛,2022,26(1):19-21. [14] Sharma S,Gupta A. Adynamic bone disease: Revisited[J]. Nefrologia,2022,42(3):8-14. doi: 10.1016/j.nefro.2020.11.012 [15] Hochrath K,Ehnert S,Ackert-Bicknell C L,et al. Modeling hepatic osteodystr-ophy in Abcb4 deficient miced[J]. Bone,2013,55(3):501-511. [16] Khairallah P,Nickolas T. Bone and mineral disease in kidney transplant r-ecipients[J]. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol,2022,17(1):121-130. doi: 10.2215/CJN.03410321 [17] Enomoto A, Niwa T. Roles of organic anion transporters in the progression of chronic renal failure [J]. Ther Apher Dial, 2007, 11(Supplement 1): 27-31. [18] 张圆圆,靳培培,宛哲,等. 腺嘌呤诱导慢性肾功能衰竭并发心血管病变大鼠模型的分析[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2023,29(1):1-11. [19] 叶毅. 血液透析联合血液灌流治疗慢性肾衰竭合并矿物质-骨代谢异常的临床效果[J]. 中外医学研究,2018,16(139):40-42. [20] Shi B,Zhang Y,Huang B,et al. The system profile of renal drug transporter-s in tubulointerstitial fibrosis model and consequent effect on pharmacok-inetics[J]. Molecules,2022,27(17):4531-4540. [21] 陈丽,唐文庄,朱美娟,等. 利拉鲁肽通过下调TGF-β1和α-SMA对慢性肾功能衰竭大鼠的治疗作用[J]. 临床肾脏病杂志,2020,20(9):901-906. [22] 徐晓琳. 骨化三醇治疗维持性血液透析肾衰竭患者对高转运骨营养不良的影响及安全性分析[J]. 中国医师进修杂志,2022,45(10):946-949. [23] Liu N, Wang L, Yang T, et al. EGF receptor in hibit-ion alleviates hyperuric-emic nephropathy[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 26(10): 2716-2729. [24] 李明慧,吴铠礽,陈哲,等. 高尿酸血症肾病小鼠模型的优化及效果评价[J]. 药学学报,2022,57(6):1673-1678. [25] 李发双,李玲,高丽辉. 有机阴离子转运蛋白研究进展[J]. 国际药学研究杂志,2017,44(9):931-940. [26] 杨振,李会影,刘建璇,等. 参芪颗粒对腺嘌呤致大鼠慢性肾功能衰竭模型的作用研究[J]. 中国医学创新,2022,19(1):7-11. -





 下载:
下载: