Clinical Significance of Ultrasound Signs Combined Diagnosis in Acute Appendicitis of Children
-
摘要:
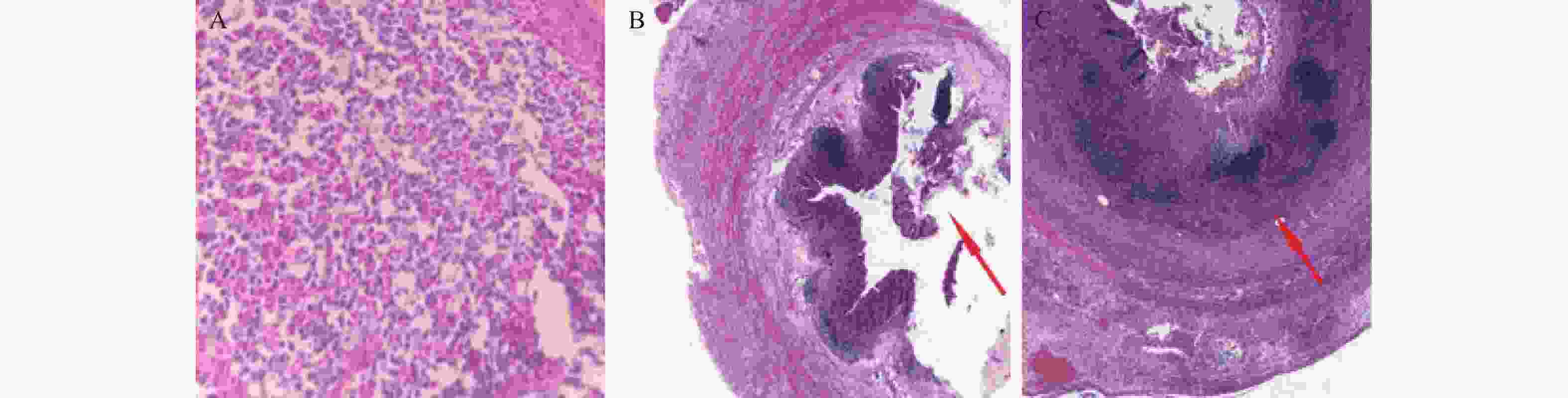
目的 探讨在急性阑尾炎患儿诊断中,超声征象的特点及诊断意义。 方法 以81例急性阑尾炎患儿为研究对象,将81例急性阑尾炎患儿依病理检测结果分为2组:进展性阑尾炎患儿34例(41.98%),单纯性阑尾炎患儿47例(58.02%)。通过超声检测的间接征象、直接征象,以及病理检查资料,并借助ROC曲线分析超声征象联合应用的曲线下面积(area under curve,AUC),进行综合分析,对患儿超声检查结果进行评分。 结果 进展组患儿超声检测的管壁连续性中断/层次清晰度不高、管腔积液、阑尾周围或腹腔积液、阑尾周围高回声、盲肠、回肠壁增厚检出率均高于单纯组(P < 0.05);进展组超声间接征象、直接征象、联合征象评分均高于单纯组(P < 0.05);ROC (receiver oprating characteristic)曲线下,联合征象诊断灵敏度、特异度、阳性预测值和阴性预测值分别为98.77%、97.53%、98.77%、96.30%均高于间接征象、直接征象,AUC为0.902高于间接征象、直接征象(P < 0.05)。 结论 超声检测征象联合诊断,能够为急性阑尾炎患儿的早期诊断提供客观证据,且还可实现对疾病动态监测,从而有利于临床治疗方案的制定。 Abstract:Objective To explore the characteristics and diagnostic significance of ultrasound signs in the diagnosis of acute appendicitis in children. Methods This study focused on 81 children with acute appendicitis and divided them into two groups based on pathological examination results: 34 children with severe progressive appendicitis (41.98%) and 47 children with simple appendicitis (58.02%). By analyzing the indirect and direct signs of ultrasound detection, as well as pathological examination data, and using ROC curve analysis to analyze the area under the curve (area under curve, AUC) of ultrasound signs combined, a comprehensive analysis is conducted to score the ultrasound examination results of children. Results The detection rates of wall continuity interruption/low-level clarity, intraluminal fluid accumulation, periappendiceal or abdominal fluid accumulation, periappendiceal hyperechogenicity, cecal and ileal wall thickening in the advanced group were higher than those in the simple group (P < 0.05); The scores of indirect, direct, and combined ultrasound signs in the progressive group were higher than those in the simple group (P < 0.05); Under the ROC curve, the sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value of combined signs were 98.77%, 97.53%, 98.77%, and 96.30%, respectively, higher than those of indirect signs and direct signs. The AUC was 0.835, higher than those of indirect signs and direct signs (P < 0.05). Conclusion The combined diagnosis of ultrasound examination signs can provide objective evidence for the early diagnosis of acute appendicitis in children, and can also achieve dynamic monitoring of the disease, which is conducive to the formulation of clinical treatment plans. -
Key words:
- Ultrasonic signs /
- Acute appendicitis in children /
- Combined diagnosis
-
表 1 2组患儿基线资料比较
Table 1. Comparison of baseline data between two groups of pediatric patients($ \bar x \pm s $)
指标 单纯组(n=47) 进展组(n=34) t/χ2 P 性别 男 26(55.32) 18(52.94) 0.038 0.125 女 21(44.68) 16(47.06) 年龄(岁) 7.28±1.12 7.31±1.24 0.114 0.057 发病到入院
时间(d)1.11±0.06 1.12±0.05 0.793 0.362 穿孔现象 32(68.09) 24(70.59) 0.053 0.254 表 2 2组急性阑尾炎患儿超声征象检查结果[n(%)]
Table 2. Ultrasound findings of two groups of children with acute appendicitis [n(%)]
征象 单纯组(n=47) 进展组(n=34) χ2 P 管径增宽 47(100.00) 33(97.06) 0.369 0.323 管壁增厚 46(97.87) 33(97.06) 1.857 0.068 管壁连续性中断/层次清晰度不高 21(44.68) 30(88.24) 32.458 0.012* 管腔积液 11(23.40) 15(44.12) 5.584 0.021* 粪石 19(40.43) 19(55.88) 2.058 0.052 阑尾周围或腹腔积液 19(40.43) 27(79.41) 19.817 0.001* 阑尾周围高回声 25(53.19) 30(88.24) 25.458 0.000* 肠系膜淋巴结肿大 18(38.30) 9(26.47) 2.258 0.067 盲肠、回肠壁增厚 21(44.68) 22(64.71) 6.182 0.016* *P<0.05。 表 3 2组急性阑尾炎患儿超声征象评分结果比较($\bar x \pm s$)
Table 3. Comparison of ultrasound sign scores between two groups of children with acute appendicitis ($\bar x \pm s$)
分组 单纯组
(n=47)进展组
(n=34)t P 间接征象 2.18±0.87 3.41±1.11 5.589 0.018* 直接征象 3.09±0.92 3.89±1.22 3.366 0.033* 联合征象 5.27±1.15 7.30±1.88 6.016 0.002* *P<0.05。 表 4 超声征象在急性阑尾炎分型诊断中的应用效能
Table 4. Application efficacy of ultrasound signs in the classification diagnosis of acute appendicitis
超声征象 灵敏度(%) 特异度(%) 阳性预测值(%) 阴性预测值(%) 截断值 AUC 95%CI 间接征象 88.24 93.62 90.91 91.67 1 0.625 0.512~0.693 直接征象 95.74* 94.12* 95.74* 94.12* 2 0.721* 0.684~0.759 联合征象 98.77*# 97.53*# 98.77*# 96.30* 3 0.902*# 0.768~0.921 与间接征象比较,*P<0.05;与直接征象比,#P<0.05。 -
[1] 毕世玥,王玉,熊晓苓,等. 超声对儿童急性阑尾炎的诊断价值[J]. 临床超声医学杂志,2023,25(12):986-989. [2] 张登奎,曹苏成,苗振军. 多层螺旋CT诊断急性阑尾炎的临床应用效果[J]. 吉林医学,2023,44(10):2762-2765. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0412.2023.10.021 [3] 刘钱洋. 5岁及以下儿童急性阑尾炎严重程度的分层特征研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆医科大学, 2022. [4] 赵辉萍. 急性阑尾炎的MSCT征象与病理分型的相关性分析[J]. 现代医用影像学,2023,32(08):1463-1466. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7035.2023.08.021 [5] 李晶莹,杨丽丽,朱苗苗,等. 小儿急性阑尾炎的临床特点及复杂性阑尾炎影响因素分析[J]. 中国妇幼保健,2023,38(11):2065-2068. [6] 乔艳,义娟,刘小毅,等. 高频彩色多普勒超声在阑尾炎患者中的应用[J]. 山西医药杂志,2022,51(21):2431-2433. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-9926.2022.21.009 [7] 路婧,黎新艳,杨水华,等. 超声征象诊断儿童急性阑尾炎合并穿孔的价值[J]. 广西医学,2022,44(09):947-950. [8] 罗建彬. 阑尾超声检查评分系统在成人急性阑尾炎诊断中的应用[J]. 中国医学影像学杂志,2016,24(8):580-584. [9] 黄兰,何琛波,罗元臣,等. 儿童阑尾炎的超声特征与病理分型分析[J]. 中国医学物理学杂志,2023,40(01):83-86. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-202X.2023.01.014 [10] 沃佳静,李丹红. 超声在三种病理类型急性阑尾炎诊断中的应用价值[J]. 浙江创伤外科,2021,26(05):990-991. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-7147.2021.05.093 [11] 路娟,吴梦琦,沈琪. 超声特征、Alvarado评分与血液炎症标志物水平联合检测在小儿阑尾炎诊断和分型中的意义[J]. 临床和实验医学杂志,2021,20(14):1553-1557. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4695.2021.14.028 [12] Kanimozhi V,Anis A,Gopinathan K,et al. Acute appendicitis in infants – A report of two cases[J]. Journal of Indian Association of Pediatric Surgeons,2022,27(6):63-67. [13] 伍卫如. 高频超声联合CRP检测在小儿阑尾炎中的诊断价值分析[J]. 中国现代药物应用,2021,15(10):51-54. [14] 张碧宏,史妙丽,李性希,等. 超声间接征象对小儿急性阑尾炎诊断价值分析[J]. 影像研究与医学应用,2020,4(12):16-18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-3807.2020.12.008 [15] Ayşe K,Fuat A T,Zeynep F A,et al. Two-dimensional shear wave elastography can improve the diagnostic accuracy of ultrasonography in acute appendicitis[J]. Journal of Ultrasound,2022,26(2):15-20. [16] 张爱华,周守群,郭婉清,等. 超声征象对阑尾周围脓肿的诊断价值分析[J]. 中外医学研究,2021,19(32):80-83. [17] 吴斌,宋庆文. 超声诊断阑尾炎周围脓肿的临床价值及准确率分析[J]. 实用医学影像杂志,2023,24(4):301-304. [18] 易婷华,蔡东传,黄春荣,等. 高频和低频超声检查在阑尾炎间接超声征象中的诊断价值分析[J]. 临床医学工程,2020,27(04):393-394. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-4659.2020.04.0393 [19] 施银春. 超声检查在不同类型急性阑尾炎诊断中的应用效果观察[J]. 中国药物与临床,2020,20(7):1092-1093. -





 下载:
下载:



