Analysis of Breastfeeding Duration and Influencing Factors of Children Aged 0-5 Years in Yunnan Province
-
摘要:
目的 了解云南省0~5岁儿童母乳喂养持续时间现状,探讨母乳喂养持续时间的影响因素。 方法 利用第六次国家卫生服务调查云南省的数据,选取云南省1582名0~5岁儿童作为研究对象,应用Kaplan-Meier法和Cox回归分析母乳喂养持续时间的影响因素。 结果 云南省0~5岁儿童母乳喂养持续时间均值为9.29个月,地区、辅食添加时间、吸吮时间和家庭收入是母乳喂养持续时间的主要影响因素(P < 0.05)。 结论 云南省0~5岁儿童母乳喂养持续时间与WHO和我国儿童母乳喂养指导建议均存在着较大的差距,面对当前的情况相关部门应进一步提高重视。 Abstract:Objective To understand the current situation of breastfeeding duration in children aged 0-5 years in Yunnan Province, and to explore the influencing factors of breastfeeding duration. Methods Using the data of the 6th National Health Service Survey in Yunnan Province, 1582 children aged 0~5 years in Yunnan Province were selected as the research subjects, and the Kaplan-Meier method and Cox regression were used to analyze the influencing factors of breastfeeding duration. Results The mean duration of breastfeeding for children aged 0~5 years in Yunnan Province was 9.29 months, and region, time of complementary food addition, time of suckling and family income were the main factors influencing the duration of breastfeeding. Conclusion The duration of breastfeeding for children aged 0~5 years in Yunnan Province deviates significantly from the recommendations provided by both the World Health Organization(WHO) and China's child breastfeeding guidelines. Given the current situation, the relevant departments must enhance their focus on this issue. -
Key words:
- Breastfeeding /
- Duration /
- Influence factors /
- Survival analysis
-
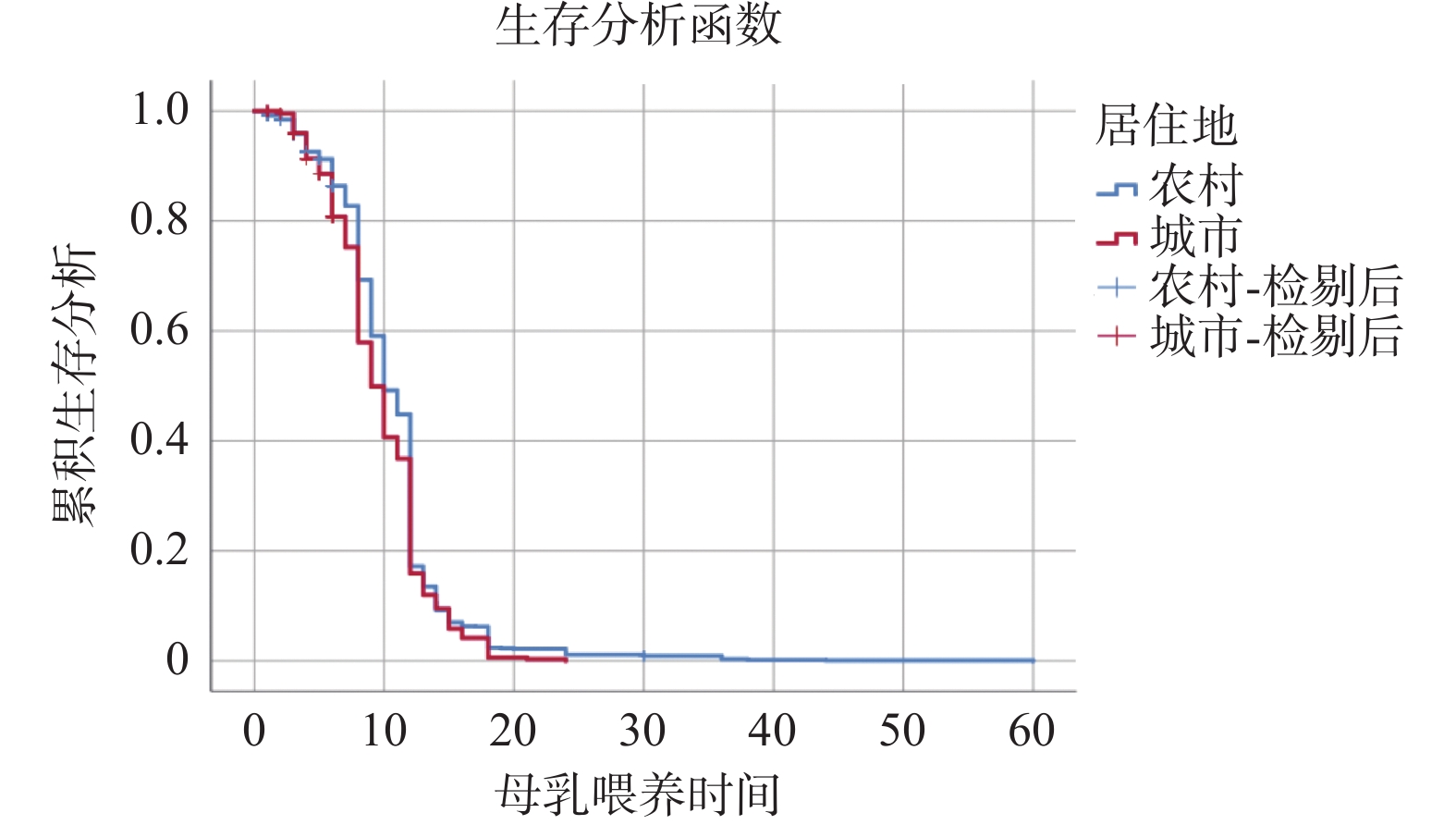
表 1 母乳喂养持续时间的Kaplan-Meier分析[n (%)]
Table 1. Kaplan-Meier analysis of breastfeeding duration [n (%)]
影响因素 人数 已断乳人数 截尾比(%) 中位数 χ2 P 地区 农村 1272(80.40) 1098(81.39) 13.68 10.46 11.67 <0.001* 城市 310(19.60) 251(18.61) 19.03 9.89 民族 汉族 1059(66.94) 912(67.61) 13.88 10.30 0.27 0.76 少数民族 523(33.06) 437(32.39) 16.44 10.41 家庭收入(元) 0~ 351(22.19) 298(22.09) 15.1 10.85 8.37 0.036* 10000~ 399(25.22) 343(25.43) 14.04 10.5 25000~ 467(29.52) 406(30.10) 13.06 10.33 50000~ 365(23.07) 302(22.39) 17.26 9.74 医疗服务可及性 好(<30 min) 1386(87.61) 1177(87.25) 15.08 10.28 0.78 0.52 差(≥30 min) 196(12.39) 172(12.75) 12.24 10.76 辅食添加时间(月) ≤6 1142(72.19) 987(73.16) 13.57 10.31 9.73 0.027* >6 440(27.81) 362(26.84) 17.73 10.48 第1次吸吮时间 出生1 h内 736(46.52) 642(47.59) 12.77 10.3 7.95 0.039* 出生1 h到24 h 322(20.35) 277(20.53) 13.98 10.16 出生24 h后 524(33.12) 430(31.88) 17.94 10.51 儿童贫血情况 是 131(8.29) 126(9.34) 13.98 10.39 5.09 0.12 否 1451(91.71) 1345(90.66) 14.85 10.42 母亲就业情况 在业 1283(81.10) 1102(81.69) 14.11 10.26 1.02 0.38 未在业 299(18.90) 247(18.31) 17.39 10.69 *P<0.05。 表 2 母乳喂养持续时间影响因素的Cox回归分析
Table 2. Cox regression analysis of factors influencing the duration of breastfeeding
因素 β SE Wald P Exp(β) 95%CI 家庭收入(元) 50000~ 1 0~ −0.28 0.16 3.92 0.05 0.56 0.49~0.87 10000~ −0.29 0.14 4.33 0.04* 0.75 0.57~0.98 25000~ −0.29 0.15 4.01 0.04* 0.82 0.39~0.92 地区 城市 1 农村 −0.51 0.17 9.55 0.002* 0.60 0.44~0.82 辅食添加时间 >6个月 1 ≤6个月 0.50 0.36 46.81 <0.001* 1.12 1.02~1.42 吸吮时间 出生24 h后 1 出生1 h内 −1.85 0.53 3.60 0.04* 0.46 0.35~0.87 出生1 h
到24 h内−0.97 0.58 3.84 0.53 0.40 0.19~1.24 *P<0.05。 -
[1] Victora C G,Bahl R,Barros A J,et al. Breastfeeding in the 21st century: Epidemiology,mechanisms,and lifelong effect[J]. Lancet,2016,387(10017):475-490. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)01024-7 [2] Gupta A,Suri S,Dadhich J P,et al. The world breastfeeding trends initiative: Implementation of the global strategy for infant and young child feeding in 84 countries[J]. J Public Health Policy,2019,40(1):35-65. doi: 10.1057/s41271-018-0153-9 [3] 黄永玲,张唯敏,方亮. 安徽省贫困地区儿童母乳喂养持续时间及其影响因素[J]. 中国儿童保健杂志,2017,25(11):1150-1152. doi: 10.11852/zgetbjzz2017-25-11-19 [4] 李沛霖,刘鸿雁. 中国儿童母乳喂养持续时间及影响因素分析——基于生存分析方法的研究[J]. 人口与发展,2017,23(2):100-112. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1668.2017.02.011 [5] 王帅,谢学勤,张耀光. 中国国家卫生服务调查回顾与思考[J]. 中国卫生信息管理杂志,2021,18(1):9-15. [6] 刘稳,李士雪. 山东儿童纯母乳喂养持续时间及影响因素分析[J]. 中国儿童保健杂志,2016,24(4):410-412. doi: 10.11852/zgetbjzz2016-24-04-21 [7] 刘岚, 王旭明, 李国晖, 等 云南农村居民哮喘的患病现状及社会人口学和生活行为的影响因素[J]. 昆明医科大学学报, 2022, 43(12): 41-46. [8] 汪之顼,盛晓阳,苏宜香. 《中国0~2岁婴幼儿喂养指南》及解读[J]. 营养学报,2016,38(2):105-109. [9] 扎西德吉,次旦卓嘎,扎西达娃. 西藏自治区0~5岁儿童母乳喂养持续时间及影响因素分析——基于西藏第六次国家卫生服务调查项目[J]. 高原科学研究,2021,5(4):67-73. [10] 杨严政,周玉娥,李团,等. 昆明市4个区母乳喂养现状及影响因素分析[J]. 昆明医科大学学报,2023,44(6):40-46. doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230624 [11] 曾果, 黄璐娇, 芮溧, 等. 西南城乡婴幼儿母乳喂养行为比较研究[C]. 中国营养学会第十一次全国营养科学大会暨国际DRIs研讨会, 2013: 193-194. [12] Tang K,Liu Y,Meng K,et al. Breastfeeding duration of different age groups and its associated factors among Chinese women: A cross-sectional study[J]. Int Breastfeed J,2019,14:19. doi: 10.1186/s13006-019-0212-2 [13] 胡珊珊,王晓晔,李争,等. 影响我国母乳喂养持续时间相关因素的系统评价[J]. 中国儿童保健杂志,2020,28(10):1131-1134,1139. doi: 10.11852/zgetbjzz2020-0309 [14] 裘美娟,房玥晖,连怡遥,等. 中国六省市0~24月龄婴幼儿的喂养状况调查研究[J]. 营养学报,2022,44(5):426-429,435. [15] 中华医学会儿科学分会儿童保健学组,中华医学会围产医学分会,中国营养学会妇幼营养分会,《中国儿科杂志》编辑委员会. 母乳喂养促进策略指南(2018版)[J]. 中华儿科杂志,2018,56(4):261-266. [16] 柳晓珍. 中国儿童母乳喂养的健康效益及影响因素研究—于2011年CHNS数据的经验验证[D]. 杭州: 浙江工商大学, 2015. -





 下载:
下载: