Effect of Nicorandil on Inflammation-related Markers after PCI Intervention in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndromes
-
摘要:
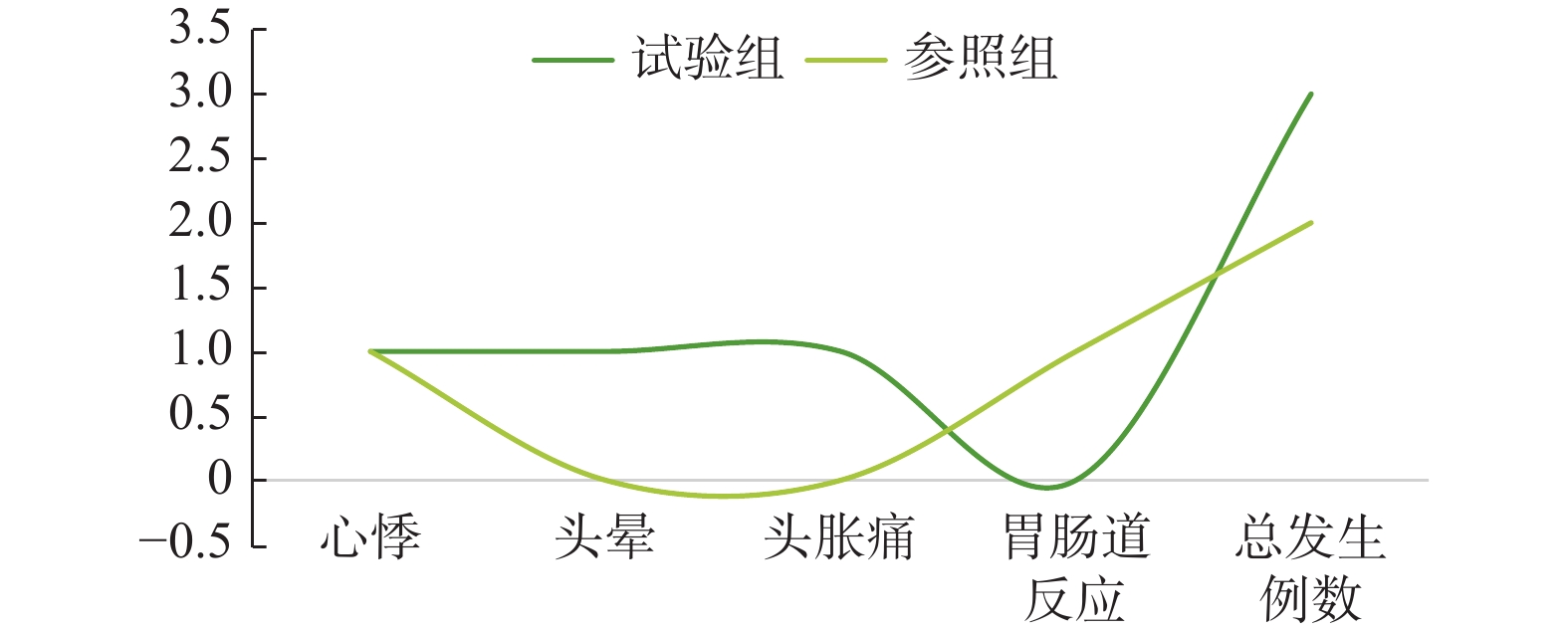
目的 探讨急性冠脉综合征(acute coronary syndrome,ACS)患者经皮冠状动脉介入治疗(percutaneous coronary intervention,PCI)后采用尼可地尔治疗后对炎性相关指标的影响,评估其对血管内皮功能的影响。 方法 将2022年8月至2023年1月于大连医科大学附属第二医院心血管内科行PCI治疗的66例ACS患者作为研究样本,按照完全随机设计法分成对照组和试验组,每组33例。对照组行常规疗法,试验组用尼可地尔治疗。比较2组患者血清中的炎性指标、同型半胱氨酸(hcy)和不良反应情况。 结果 尼可地尔治疗后,对照组术后炎性相关因子水平高于试验组,差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05);尼可地尔治疗后Hcy水平低于对照组,差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05);试验组不良反应率高于对照组,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。 结论 尼可地尔应用在老年ACS患者PCI术后疗效确切,能优化血管相关炎性指标,降低同型半胱氨酸水平改善冠状动脉血管内皮功能,适合进一步推广。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the effects of treatment with nicorandil after Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) in patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS) on inflammation-related markers, and to assess its effects on vascular endothelial function. Methods Sixty-six ACS patients who underwent PCI in the Department of Cardiovascular Medicine of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University from August 2022 to January 2023 were used as the study sample, and were divided into the control group and the experimental group according to the method of completely randomized design, with 33 cases in each group. The control group was treated with conventional therapy, and the experimental group was treated with nicorandil. Inflammatory indexes, homocysteine (Hcy) and adverse reactions in serum were compared between the two groups. Results After nicorandil treatment, the levels of postoperative inflammation-related factors in the control group were higher than that in the experimental group, and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05); The levels of Hcy after nicorandil treatment were lower than that in the control group, and the difference was statistically significant ( P < 0.05); and the rate of adverse reactions in the experimental group was higher than that in the control group, and there was no statistical difference ( P > 0.05). Conclusion Nicorandil application in elderly ACS patients after PCI has a definite efficacy, can optimize the vascular-related inflammatory indexes, reduce homocysteine levels to improve coronary vascular endothelial function, and is suitable for further promotion. -
Key words:
- Acute coronary syndrome /
- Inflammatory indicators /
- Nicorandil
-
表 1 2组患者基线资料情况比较 [n(%)]
Table 1. Comparison of baseline information between the two groups [n(%)]
项目 对照组(n=33) 试验组(n=33) χ2/t P 性别 男 20(60.6) 22(66.7) 0.524 0.469 女 13(39.4) 11(33.3) 年龄(岁) 69.93±7.45 69.88±7.33 1.137 0.259 起病时间(月) 15.64±4.17 15.87±4.09 −0.389 0.698 阿司匹林肠溶片 33(100.0) 33(100.0) − − 硫酸氢氯吡格雷片 33(100.0) 33(100.0) − − 阿托伐他汀钙片 33(100.0) 33(100.0) − − ACEI/ARB类药物 24(72.7) 21(63.6) 0.581 0.446 β受体阻滞剂 29(87.9) 31(93.9) 0.721 0.675 预扩球囊扩张 33(100.0) 33(100.0) − − 后扩球囊扩张 26(78.8) 21(63.6) 1.726 0.189 支架成功开通 33(100.0) 33(100.0) − − TIMI血流3级 33(100.0) 33(100.0) − − 表 2 2组患者炎性因子水平相比( $\bar x \pm s$,n=33)
Table 2. Comparison of the inflammatory factor levels between the two groups( $\bar x \pm s$,n=33)
组别 IL-6(pg/mL) TNF-α(pg/mL) hs-CRP(mg/L) 治疗前 治疗后 治疗前 治疗后 治疗前 治疗后 对照组 4.62±1.05 4.14±0.28 110.52±2.49 10.63±1.18 9.61±0.32 8.05±0.24 试验组 4.65±1.02 3.26±0.11 110.71±2.60 7.61±1.20 9.74±0.29 4.04±0.15 t 0.118 16.804 0.303 10.308 1.729 81.393 P 0.907 <0.001* 0.763 <0.001* 0.089 <0.001* 与治疗前比较,*P<0.05。 表 3 2组患者治疗前后Hcy水平比较( $ \bar x \pm s $, n=33)
Table 3. Comparison of Hcy levels before and after treatment between the two groups( $ \bar x \pm s $, n=33)
组别 治疗前 治疗后 t P 对照组 12.96±1.20 10.90±2.62 4.106 <0.001* 试验组 12.90±1.13 7.08±2.66 11.568 <0.001* t 0.209 5.877 P 0.835 <0.001* 与治疗前比较,*P<0.05. -
[1] 刘康,姜子超,凌维维,等. 静脉应用尼可地尔对急性冠脉综合征患者冠脉灌注及临床预后的影响[J]. 解放军医学院学报,2022,43(1):40-44. [2] Chen W,Ni M,Huang H,et al. Chinese expert consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of coronary microvascular diseases (2023 Edition)[J]. MedComm,2023,4(6):438. doi: 10.1002/mco2.438 [3] Groenland F T W,Ziedses des Plantes A C,Scoccia A,et al. Post percutaneous coronary intervention physiology in patients presenting with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction[J]. Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc,2023,49(10):1013-1019. [4] Milasinovic D,Nedeljkovic O,Maksimovic R,et al. Coronary microcirculation: The next frontier in the management of STEMI[J]. J Clin Med,2023,12(4):1602. doi: 10.3390/jcm12041602 [5] 杨月霞,刘中慧,王怀新. 尼可地尔对急性ST段抬高型心肌梗死患者Tp-Te间期和Tp-Te/QT以及预后的影响[J]. 临床急诊杂志,2023,24(11):567-572. [6] Rao S,Bhardwaj R,Negi P C,et al. No reflow phenomenon in CAD patients after percutaneous coronary intervention: A prospective hospital based observational study[J]. Indian Heart J,2023,75(2):156-159. doi: 10.1016/j.ihj.2023.02.002 [7] 王亚红,肖红艳,彭齐. 尼可地尔治疗急性冠脉综合征的疗效及对冠脉微循环血清炎症指标的影响[J]. 河北医学,2020,26(10):1750-1754. [8] Jing T,Wang Y,Li Y,et al. Diagnosis,treatment,and management for chronic coronary syndrome: A systematic review of clinical practice guidelines and consensus statements[J]. Int J Clin Pract,2023,12(6):95-98. [9] 钱灿,诸帆,厉强. 通心络胶囊联合前列地尔、尼可地尔对急性冠脉综合征患者行PCI术后心肌损伤和血脂水平的影响[J]. 新中医,2021,53(17):66-69. [10] 蒋芳勇,陈慧生,黄山松. 他汀联合尼可地尔对急性冠脉综合征患者PCI术后缺血再灌注损伤的作用研究[J]. 黑龙江医药,2020,33(4):744-746. [11] Lu Y,Wang Y,Zhou B. Predicting long-term prognosis after percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with acute coronary syndromes: A prospective nested case-control analysis for county-level health services[J]. Front Cardiovasc Med,2023,10(6):129. [12] 张晓东. 集采与原研氯吡格雷对冠心病患者PCI术后的疗效及成本对比研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明医科大学, 2022. [13] 李璇璇. 尼可地尔对老年急性冠脉综合征患者经皮冠状动脉介入治疗术后血管内皮功能及炎性因子的影响[D]. 石家庄: 河北医科大学, 2019. [14] Rao N D,Lemaitre R N,Sitlani C M,et al. Dietary magnesium,c-reactive protein and interleukin-6: the strong heart family study[J]. PLoS One,2023,18(12):296-298. [15] Liu Z,Li Y,Cheng F,et al. Homocysteine combined with apolipoprotein b as serum biomarkers for predicting carotid atherosclerosis in the oldest-old[J]. Clin Interv Aging,2023,18(1):1961-1972. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S428776 [16] Bouzidi N,Gamra H. Relationship between serum interleukin-6 levels and severity of coronary artery disease undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention[J]. BMC Cardiovasc Disord,2023,23(1):586. doi: 10.1186/s12872-023-03570-8 [17] 王学彬,司伟,李敬文,等. 尼可地尔在急性冠脉综合征经皮冠状动脉介入治疗后的应用[J]. 世界临床药物,2022,43(11):1451-1456. [18] Tang N,Chen X,Li K,et al. Myocardial perfusion in ST-Segment elevation myocardial infarction patients after percutaneous coronary intervention: Influencing factors and intervention strategies[J]. Cureus,2023,15(8):841-842. [19] Marano P,Wei J,Merz C N B. Coronary microvascular dysfunction: What clinicians and investigators should know[J]. Curr Atheroscler Rep,2023,25(8):435-446. doi: 10.1007/s11883-023-01116-z -






 下载:
下载: