Correlation Between TyG Index,MHR and Coronary Lesions,Myocardial Ischemia in Patients with Coronary Heart Disease,and the Value of Combined Detection
-
摘要:
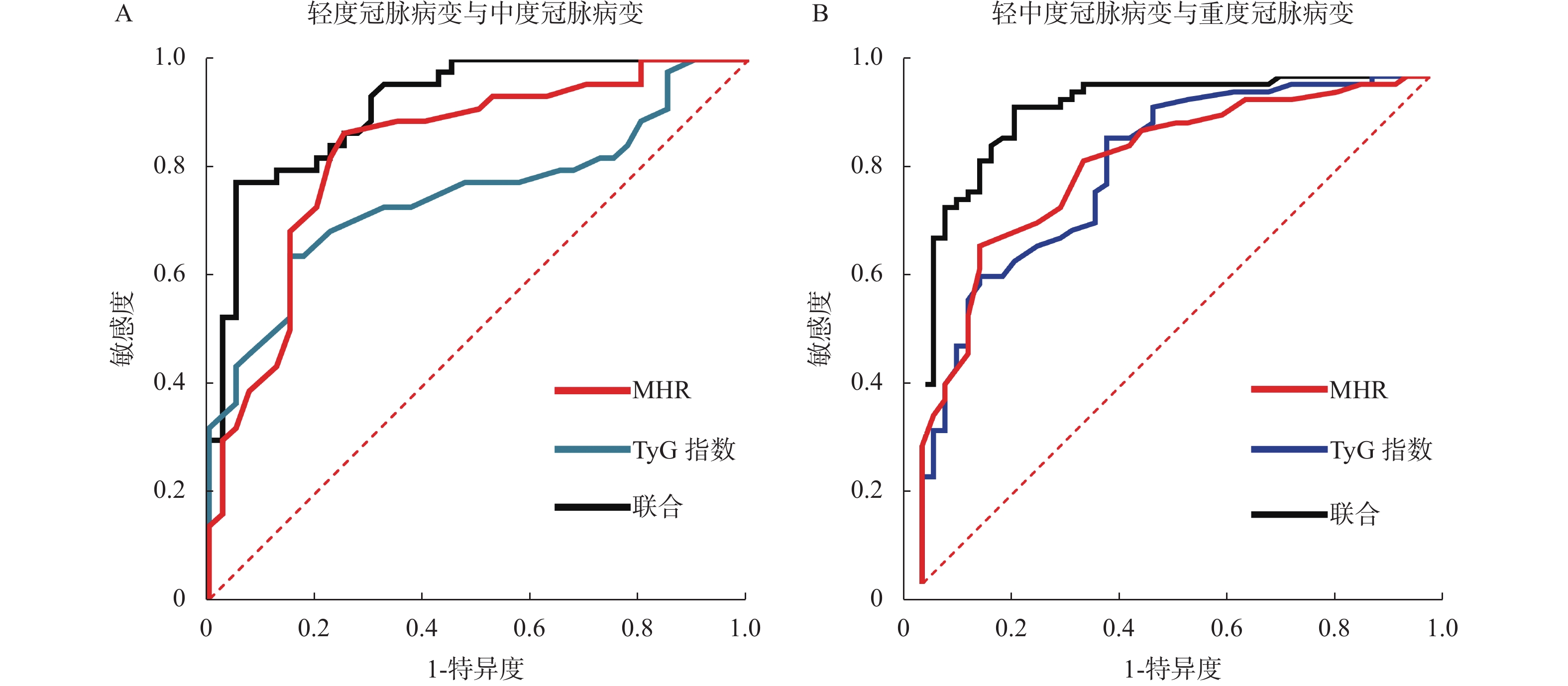
目的 探讨三酰甘油葡萄糖(triglyceride glucose index,TyG)指数、单核细胞数/高密度脂蛋白胆固醇比值(monocyte to high-density lipo-protein cholesterol ratio,MHR)与冠心病(coronary heart disease,CHD)冠脉病变、心肌缺血程度的相关性,并分析二者对冠脉病变、心肌缺血程度的预测价值。 方法 选取中国人民解放军联勤保障部队第九二O医院2019年1月至2022年1月CHD患者作为研究组(n = 150),另选取同期健康体检者作为对照组(n = 75)。对比分析2组TyG指数、MHR。依据Gensini积分评估冠脉病变程度,并比较不同冠脉病变、心肌缺血程度患者TyG指数、MHR,并分析其与Gensini积分、心肌缺血程度相关性。受试者工作特征(receiver operating characteristic,ROC)曲线及曲线下面积(area under curve,AUC)评价TyG指数、MHR及两者联合检测对冠脉病变、心肌缺血程度的预测价值。 结果 研究组TyG指数、MHR分别为(4.12±0.35)、(0.26±0.08)×109,均高于对照组的(4.94±0.55)、(0.43±0.12)×109,且重度冠脉病变TyG指数、MHR > 中度冠脉病变 > 轻度冠脉病变,急性心肌梗死TyG指数、MHR > 不稳定型心绞痛 > 稳定型心绞痛(P < 0.05);TyG指数、MHR与Gensini积分呈正相关(r = 0.621、0.635,P < 0.05),其与心肌缺血程度呈正相关(r = 0.617、0.642,P < 0.05)。TyG指数、MHR联合鉴别轻度冠脉病变与中度冠脉病变的AUC为0.917,大于两者单独鉴别0.749、0.832,联合鉴别轻中度冠脉病变与重度冠脉病变的AUC为0.935,大于两者单独鉴别0.770、0.767(P < 0.05)。TyG指数、MHR联合鉴别稳定型心绞痛与不稳定型心绞痛的AUC为0.922,大于两者单独鉴别0.812、0.824,联合鉴别稳定型心绞痛不稳定型心绞痛与急性心肌梗死的AUC为0.913,大于两者单独鉴别0.708、0.714(P < 0.05)。 结论 TyG指数、MHR均与Gensini积分、心肌缺血程度呈正相关,二者联合检测对冠脉病变、心肌缺血程度的评估具有更高应用价值。 -
关键词:
- 冠心病 /
- 三酰甘油葡萄糖指数 /
- 单核细胞数/高密度脂蛋白胆固醇比值 /
- 心肌缺血
Abstract:Objective To investigate the correlation of triacylglycerol glucose(TyG) index, monocyte to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio(MHR) with coronary artery disease and myocardial ischemia degree in coronary heart disease(CHD), and to analyze the two Predictive value of coronary artery disease and myocardial ischemia degree. Methods CHD patients from the 920th Hospital of the Chinese People's Liberation Army Joint Logistics Support Force from January 2019 to January 2022 were selected as the study group(n = 150), and healthy physical examination subjects from the same period were selected as the control group(n = 75). The TyG index and MHR of the two groups were compared and analyzed. The extent of coronary artery disease was evaluated based on the Gensini score, and the TyG index and MHR of patients with different coronary lesions and myocardial ischemia were compared, and their correlation with Gensini score and myocardial ischemia was analyzed. The predictive value of TyG index, MHR, and the combined detection of both for coronary lesions and myocardial ischemia was evaluated using receiver operating characteristic(ROC) curves and area under the curve(AUC). Results The TyG index and MHR of the study group were(4.12±0.35) and(0.26±0.08) ×109, respectively, which were higher than those of the control group(4.94±0.55) and(0.43±0.12) ×109, and the TyG index and MHR of severe coronary artery disease > moderate coronary artery disease > mild coronary artery disease, acute myocardial infarction TyG index, MHR > unstable angina pectoris > stable angina pectoris(P < 0.05); TyG index and MHR were positively correlated with Gensini score(r = 0.621, 0.635, P < 0.05), and positively correlated with the severity of myocardial ischemia(r = 0.617, 0.642, P < 0.05). The AUC of TyG index and MHR for the joint identification of mild coronary artery disease and moderate coronary artery disease was 0.917, which was greater than the AUCs of 0.749 and 0.832 for the two conditions individually. The AUC of TyG index and MHR for the joint identification of mild to moderate coronary artery disease and severe coronary artery disease was 0.935, which was greater than the AUCs of 0.770 and 0.767 for the two conditions individually(P < 0.05). The AUC of TyG index and MHR for the joint identification of stable angina pectoris and unstable angina pectoris was 0.922, which was greater than the AUCs of 0.812 and 0.824 for the two conditions individually. The AUC of TyG index and MHR for the joint identification of stable angina pectoris, unstable angina pectoris, and acute myocardial infarction was 0.913, which was greater than the AUCs of 0.708 and 0.714 for the two conditions individually(P < 0.05). Conclusions TyG index and MHR are positively correlated with Gensini score and myocardial ischemia degree. The combined detection of the two has a higher application value in the evaluation of coronary artery disease and myocardial ischemia degree. -
表 1 2组患者一般资料比较[n(%)/$ \bar x \pm s $]
Table 1. Comparison of general data between two groups of patients[n(%)/$ \bar x \pm s $]
组别 n 性别 年龄(岁) 体质量指数(kg/m2) 吸烟史 饮酒史 男 女 有 无 有 无 研究组 150 87(58.00) 63(42.00) 58.75±4.53 24.32±1.15 86(57.33) 64(42.67) 53(35.33) 97(64.67) 对照组 75 40(53.33) 35(46.67) 58.86±4.60 24.41±1.18 44(58.67) 31(41.33) 36(48.00) 39(52.00) t/χ2 0.443 0.171 0.549 0.036 3.355 P 0.506 0.865 0.584 0.849 0.067 表 2 2组患者TyG指数、MHR比较($ \bar x \pm s $)
Table 2. Comparison of TyG index and MHR between two groups of patients($ \bar x \pm s $)
组别 n TyG指数 MHR(×109) 研究组 150 4.12±0.35 0.26±0.08 对照组 75 4.94±0.55 0.43±0.12 t 13.583 12.633 P < 0.001* < 0.001* *P < 0.05。 表 3 研究组不同Gensini积分患者TyG指数、MHR比较($ \bar x \pm s $)
Table 3. Comparison of TyG index and MHR in patients with different Gensini scores in the study group($ \bar x \pm s $)
组别 n TyG指数 MHR(×109) 轻度冠脉病变患者 43 4.76±0.12 0.33±0.08 中度冠脉病变患者 39 4.90±0.15# 0.40±0.10# 重度冠脉病变患者 68 5.08±0.20△# 0.51±0.13△# F 49.501 37.152 P < 0.001* < 0.001* *P < 0.05;与中度冠脉病变患者比较,△P < 0.05;与轻度冠脉病变患者比较,#P < 0.05。 表 4 研究组不同心肌缺血程度患者TyG指数、MHR比较($ \bar x \pm s $)
Table 4. Comparison of TyG index and MHR in patients with different degrees of myocardial ischemia in the study group($ \bar x \pm s $)
组别 n TyG指数 MHR(×109) 稳定型心绞痛患者 40 4.74±0.11 0.32±0.06 不稳定型心绞痛患者 44 4.89±0.15# 0.39±0.08# 急性心肌梗死患者 66 5.09±0.21△# 0.52±0.13△# F 54.527 52.848 P < 0.001* < 0.001* *P < 0.05;与不稳定型心绞痛患者比较,△P < 0.05;与稳定型心绞痛患者比较,#P < 0.05。 表 5 TyG指数、MHR与Gensini积分、心肌缺血程度的相关性
Table 5. Correlation between TyG index,MHR and Gensini score,myocardial ischemia degree
指标 Gensini积分 心肌缺血程度 r P r P TyG指数 0.621 < 0.001* 0.617 < 0.001* MHR 0.635 < 0.001* 0.642 < 0.001* *P < 0.05。 -
[1] Dibben G O,Faulkner J,Oldridge N,et al. Exercise-based cardiac rehabilitation for coronary heart disease: A meta-analysis[J]. Eur Heart J,2023,44(6):452-469. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehac747 [2] 赵媛媛,田雅楠,付亚磊,等. 联合检测hs-CRP、NLR、MHR对冠心病的预测价值[J]. 现代临床医学,2021,47(3):181-184. [3] 司月乔,范文俊,高秀鑫,等. TyG指数与稳定性冠心病及冠状动脉钙化斑块负荷的相关性[J]. 天津医药,2020,48(9):875-880. [4] 陈素琴,黎明江,吴限,等. TyG指数与2型糖尿病患者冠状动脉病变相关性研究[J]. 疑难病杂志,2017,16(8):761-764. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6450.2017.08.002 [5] 马伟利,刘奇峰,宝凤梅,等. NLR和MHR及二者联合在诊断冠心病患者行经皮冠状动脉介入术后发生支架内再狭窄中的应用价值[J]. 广西医学,2021,43(8):913-916. [6] 刘晓腾,张英,金凤表,等. 老年高血压合并不稳定型心绞痛患者γ-谷氨酰基转移酶与血小板比值单核细胞与高密度脂蛋白胆固醇比值与冠状动脉病变程度的相关性[J]. 中华老年医学杂志,2020,39(11):1264-1268. [7] 段运霞,周荣,贺杰. 冠心病患者MHR与冠脉狭窄程度的相关性及其临床意义[J]. 心脏杂志,2019,31(3):282-285. [8] 夏铭蔚,邵正斌,梁国庆,等. 冠心病患者血小板参数、血清IL-6与冠脉病变程度的关系分析[J]. 中国循证心血管医学杂志,2019,11(1):63-66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-4055.2019.01.16 [9] 付建平,张俊岭,扈晓霞,等. 血清缺血修饰白蛋白和同型半胱氨酸水平与冠心病患者心肌缺血程度的关系研究[J]. 实用心脑肺血管病杂志,2019,27(4):13-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-5971.2019.04.002 [10] Task Force Members,Montalescot G,Sechtem U,et al. 2013 ESC guidelines on the management of stable coronary artery disease: The Task Force on the management of stable coronary artery disease of the European Society of Cardiology[J]. Eur Heart J,2013,34(38):2949-3003. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/eht296 [11] Wang Y,Lv Q B, Li Y,et al. TGensini score values for predicting periprocedural myocardial infarction: An observational study analysis[J]. Medicine (Baltimore),2022,101(29):e29491. [12] 付琳,王敏,李瑾. 冠心病病人载脂蛋白B/载脂蛋白A1、胱抑素C、血清胆红素水平变化及其与冠状动脉病变严重程度的相关性[J]. 中西医结合心脑血管病杂志,2022,20(7):1287-1292. [13] 牛茼,王婉,李天天,等. 妊娠期糖尿病和/或非酒精性脂肪肝代谢相关因素分析及TyG指数在妊娠期对代谢疾病的诊断价值[J]. 中国医药导报,2020,17(12):97-100,108. [14] 张梦玮,徐长江,段洋,等. 利用TyG指数评估急性心肌梗死患者的预后[J]. 中国循证心血管医学杂志,2021,13(4):499-503. [15] 张梦玮,王宇,段洋,等. TyG指数及TyG指数联合Grace评分对急性心肌梗死患者预后的预测价值[J]. 临床心血管病杂志,2021,37(2):113-117. [16] 桑婉玥,王雪华,李红建,等. 单核细胞与高密度脂蛋白胆固醇比值对中青年原发性高血压患者左心室肥厚的筛检价值[J]. 中华高血压杂志,2021,29(11):1118-1122. [17] 孔祥勇,余华,冯克福,等. 单核细胞与高密度脂蛋白胆固醇比值在冠心病合并高尿酸血症患者中的变化及其与冠心病患者冠状动脉狭窄程度的关系研究[J]. 实用心脑肺血管病杂志,2020,28(7):37-40,53. [18] Wang L,Cong H L,Zhang J X,et al. Triglyceride-glucose index predicts adverse cardiovascular events in patients with diabetes and acute coronary syndrome[J]. Cardiovasc Diabetol,2020,19(1):80-90. doi: 10.1186/s12933-020-01054-z [19] 李虹敏,张跃,袁梦,等. 单核细胞与高密度脂蛋白胆固醇比值对老年急性心肌梗死患者新发心房颤动的预测价值[J]. 中华老年心脑血管病杂志,2021,23(3):229-232. [20] 徐慧,刘芳. 单核细胞计数/高密度脂蛋白胆固醇比值与早发冠心病的相关性分析[J]. 临床心血管病杂志,2020,36(8):709-713. -






 下载:
下载: