Clinical Observation of Treating Ulcerative Colitis with Acupuncture at Front Mu Points Combined with Oral Mesalazine
-
摘要:
目的 观察针刺募穴治疗溃疡性结肠炎的临床疗效。 方法 收集昆明市中医医院2022年8月至 2023年6月收治的溃疡性结肠炎患者60例。随机数字表法,分为对照组、联合组各30例,治疗方法为连续8周予对照组口服美沙拉嗪,联合组美沙拉嗪口服结合针刺募穴。从治疗前后临床疗效、肠镜结果评分 (the baron score,Baron)、结肠粘膜愈合评分(colonic mucosal healingscore,Geboes)3个方面进行比较,并随访3月,计算联合组、对照组疾病复发率。 结果 临床疗效联合组高于对照组(P < 0.05),总有效率分别为 93.33%、67.67%,治疗后,疾病活动指数、Baron 评分、Geboes 评分较治疗前下降(P < 0.05),联合组治疗后疾病活动指数、Baron 评分、Geboes 评分比对照组低(P < 0.05)。 比较治疗后3月的疾病复发率,发现联合组低于对照组。 结论 针刺募穴明显改善溃疡性结肠炎临床症状,相较于对照组患者,降低了复发机率,安全可靠,未见严重不良反应。 Abstract:Objective To observe the clinical efficacy of acupuncture at Front Mu point in the treatment of ulcerative colitis. Methods Sixty patients with ulcerative colitis treated at the Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital in Kunming from August 2022 to June 2023 were collected. Using a random number table method, 30 cases were assigned to each of the control group and the combined group. The treatment method involved administering oral mesalazine to the control group for a continuous period of 8 weeks, while the combined group received both oral mesalazine and acupuncture at front Mu points. The clinical efficacy, colonoscopy results score (Baron score), and colonic mucosal healing score (Geboes) before and after treatment were compared. Follow-up was conducted at 3 months to calculate the recurrence rate in the combination and control groups. Results The total effective rate in the combination group was higher than that in the control group (P < 0.05), with rates of 93.33% and 67.67%, respectively. After treatment, the disease activity index, Baron score, and Geboes score decreased compared to before treatment (P < 0.05), and the combination group had a lower disease activity index, Baron score, and Geboes score than the control group after treatment (P < 0.05). Comparing the recurrence rates at 3 months post-treatment, the combination group was lower than the control group. Conclusion Acupuncture at Front Mu Point can significantly improve the clinical symptoms of ulcerative colitis, reduce the recurrence rate compared to patients in the control group, and is safe and reliable without serious adverse reactions. -
Key words:
- Ulcerative colitis /
- Mesalazine /
- Front Mu point /
- Clinical efficacy /
- Recurrence rate
-
表 1 溃疡性结肠炎症状评分标准
Table 1. Ulcerative colitis symptom scoring criteria
临床表现 0分 1分 2分 3分 腹泻 无 腹泻 < 4次/d 腹泻4~6次/d 腹泻 > 4次/d 腹痛 无 轻微疼痛,偶尔发作 腹部疼痛,每天发作数次 腹部疼痛或绞痛 脓血便 无 少量脓血便 脓血便为主 全部为脓血便或纯血 表 2 2组患者性别及疾病严重程度比较[n(%)]
Table 2. Comparison of gender and disease severity between two groups of patients [n(%)]
特征 联合组 对照组 χ2 P 性别 3.267 0.071 男 17(56.7) 20(66.7) 女 13(43.3) 10(33.3) 严重程度 0.267 0.606 轻度 15(50.0) 13(43.3) 中度 15(50.0) 17(56.7) 表 3 2组患者年龄及病程比较($ \bar x \pm s $)
Table 3. Comparison of age and disease duration between two groups of patients ($ \bar x \pm s $)
特征 联合组 对照组 t P 年龄(岁) 34.27 ± 8.33 32.07 ± 8.92 0.987 0.328 病程(a) 2.42 ± 1.19 3.01 ± 1.13 −1.810 0.075 表 4 2组患者治疗前后临床疗效比较[n(%)]
Table 4. Comparison of clinical efficacy before and after treatment between two groups of patients [n(%)]
组别 n 疗效 总有效率(%) Z P 治愈 显效 有效 无效 联合组 30 4 6 18 2 93.33 −22.233 0.026* 对照组 30 2 4 14 10 67.67 *P < 0.05。 表 5 不同组别治疗前后各种评分差异比较[M(P25,P75)]
Table 5. Comparison of differences in various scores before and after treatment between different groups [M(P25,P75)]
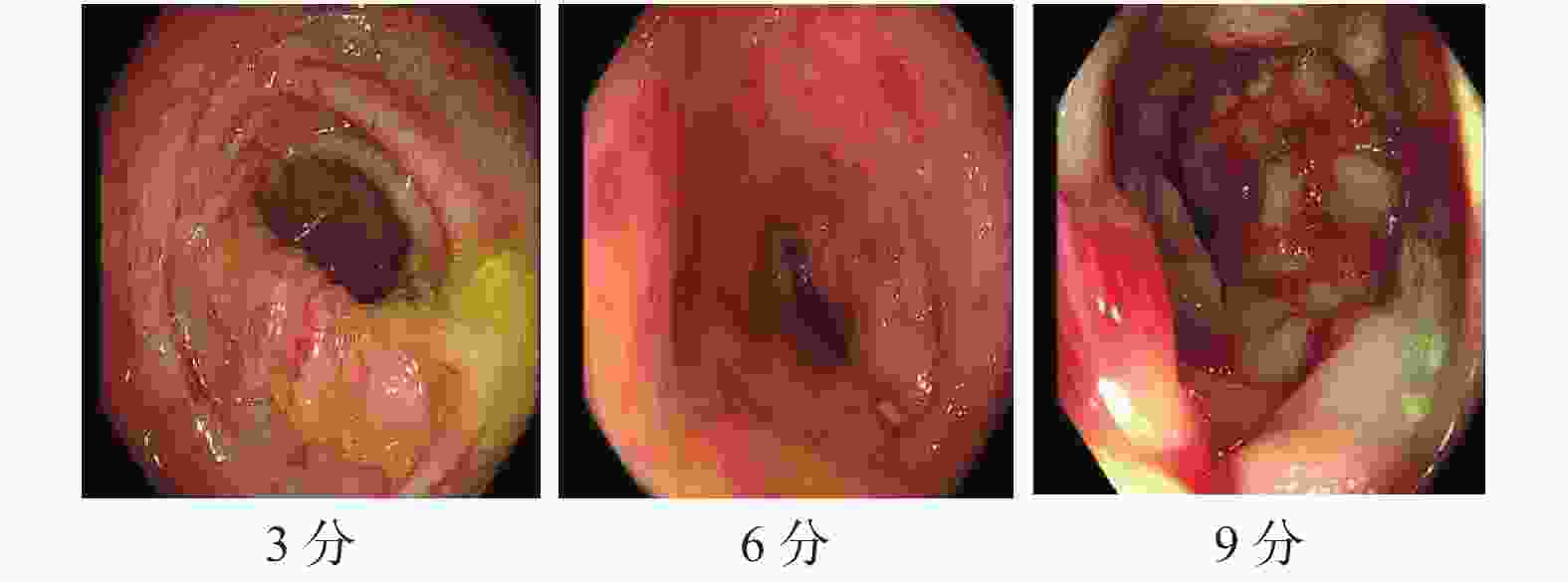
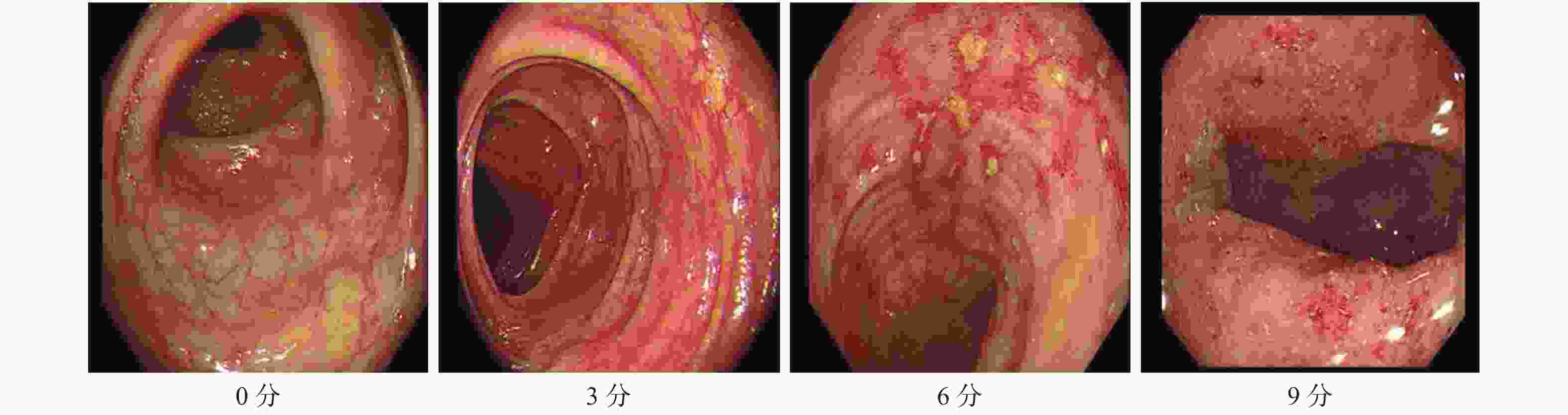
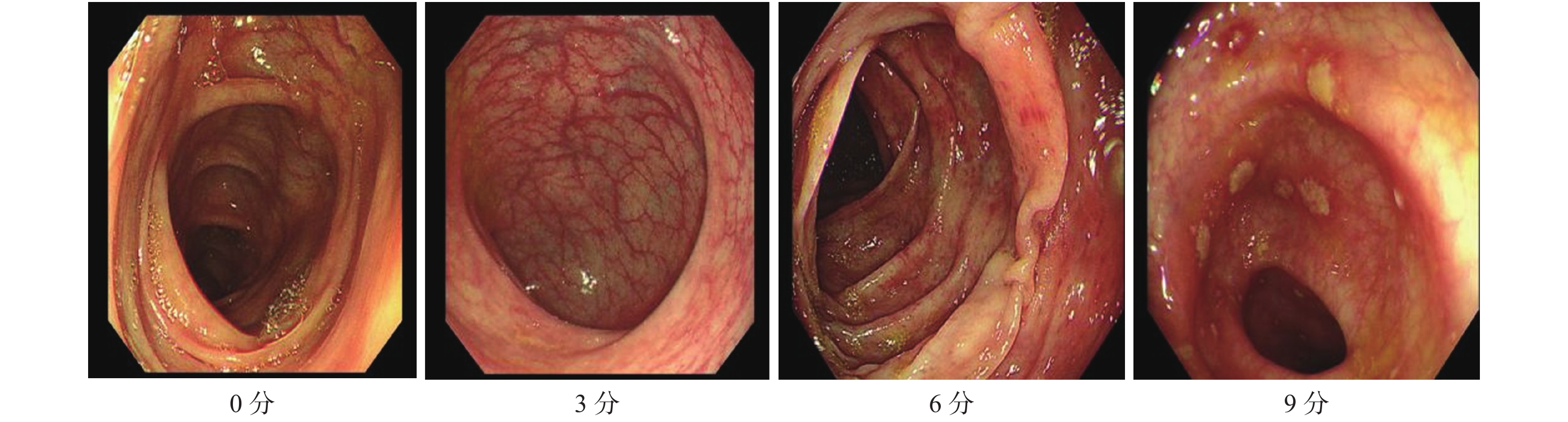
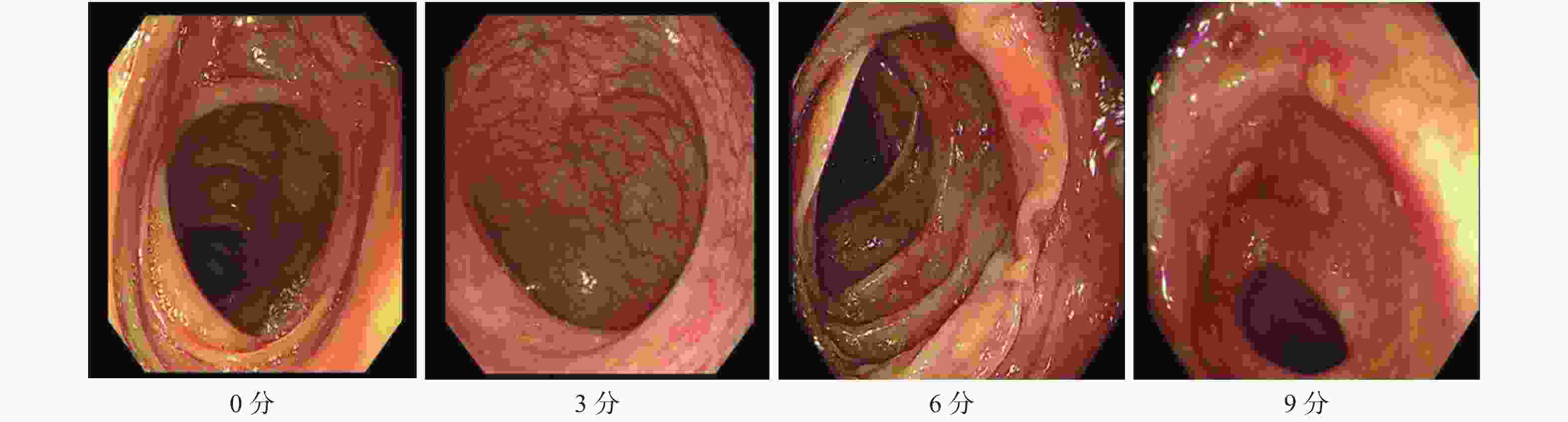
评分项 疾病活动指数 Baron评分 Geboes指数 联合组 治疗前 6.5(6,8) 6(3,9) 3(2,5) 治疗后 4(1,4) 3(0,3) 1(1,2) Z −4.740 −4.582 −4.579 P < 0.001* < 0.001* < 0.001* 对照组 治疗前 7(5,8) 6(3,9) 3(2,5) 治疗后 4.5(3,6) 3(3,6) 2(1,3) Z −4.15 −3.394 −3.869 P < 0.001* < 0.001* < 0.001* Za −0.203 −0.174 −0.559 P 0.839 0.862 0.576 Zb −2.418 −2.897 −2.304 P 0.016* 0.004* 0.021* *P < 0.05;a:联合组与对照组治疗前比较;b:联合组与对照组治疗后比较。 -
[1] Warren S,Sommers S C. Pathogenesis of ulcerative colitis[J]. The American Journal of Pathology,1949,25(4):657-679. [2] Jewell D P, Sutherland L R, McDonald J W D, et al. Ulcerative colitis[J]. Evidence‐based Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 2010, 12: 232-247. [3] Gajendran M,Loganathan P,Jimenez G,et al. A comprehensive review and update on ulcerative colitis[J]. Disease-a-month,2019,65(12):100851. doi: 10.1016/j.disamonth.2019.02.004 [4] Rashid N S Lui, Siew C Ng. The same intestinal inflammatory disease despite different genetic risk factors in the East and West?[J]. Inflammatory Intestinal Diseases,2016,1(2):78-84. doi: 10.1159/000446625 [5] Kamm M A,Lichtenstein G R,Sandborn W J,et al. Randomised trial of once-or twice-daily MMX mesalazine for maintenance of remission in ulcerative colitis[J]. Gut,2008,57(7):893-902. doi: 10.1136/gut.2007.138248 [6] Ham M,Moss A C. Mesalamine in the treatment and maintenance of remission of ulcerative colitis[J]. Expert Review of Clinical Pharmacology,2012,5(2):113-123. doi: 10.1586/ecp.12.2 [7] Li R,Huang X,Yang L,et al. Integrated analysis reveals the targets and mechanisms in immunosuppressive effect of mesalazine on ulcerative colitis[J]. Frontiers in Nutrition,2022,9:867692. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.867692 [8] Sehgal P,Colombel J F,Aboubakr A,et al. Systematic review: safety of mesalazine in ulcerative colitis[J]. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics,2018,47(12):1597-1609. [9] 李星霞,孙习鹏,陈燕,等. 临床药师参与美沙拉秦引起心脏毒性的药物治疗 1 例[J]. 临床药物治疗杂志,2020,18(6):78-81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3384.2020.06.015 [10] Joos S,Wildau N,Kohnen R,et al. Acupuncture and moxibustion in the treatment of ulcerative colitis: a randomized controlled study[J]. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology,2006,41(9):1056-1063. doi: 10.1080/00365520600580688 [11] Wang X,Zhao N,Sun Y,et al. Acupuncture for ulcerative colitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials[J]. BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies,2020,20:1-10. doi: 10.1186/s12906-019-2780-5 [12] Cabioglu M T,Kaya Y,Surucu H S. Neurophysiologic basis of front-Mu points[J]. Neuroanatomy,2009,8:32-35. [13] Chen Y,Zhao Y,Tan R Y S,et al. The influence of stomach back-shu and front-mu points on insular functional connectivity in functional dyspepsia rat models[J]. Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine: eCAM,2021,2021:2771094. [14] 李军祥,陈誩. 溃疡性结肠炎中西医结合诊疗共识意见2017年)[J]. 中国中西医结合消化杂志,2018,26(2):105-120. [15] 郑筱萸. 中药新药临床研究指导原则(试行)[S]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2002, 72: 151-156. [16] 何建伟,丁益宏,韩晓梅,等. 愈疡合剂直肠滴注疗法对溃疡性结肠炎大肠湿热型患者中医证候、血清IL-6、IL-10、TNF-α 水平的影响[J]. 四川中医,2021,39(10):98-101. [17] 孟梦,周强,朱春洋,等. 张声生教授辨治溃疡性结肠炎中医临证经验[J]. 世界中医药,2022,17(6):838-842. [18] Zheng S,Xue T,Wang B,et al. Chinese medicine in the treatment of ulcerative colitis: The mechanisms of signaling pathway regulations[J]. The American Journal of Chinese Medicine,2022,50(7):1781-1798. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X22500756 [19] Li G G,Bai G,Jiao Z. Correlation between traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) syndromes of ulcerative colitis and enteroscope[J]. Chinese Archives of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2022,40(2):90-93. [20] Kucharzik T,Koletzko S,Kannengiesser K,et al. Ulcerative colitis-diagnostic and therapeutic algorithms[J]. Deutsches Ä rzteblatt International,2020,117(33-34):564-574. [21] Karagozian R,Burakoff R. The role of mesalamine in the treatment of ulcerative colitis[J]. Therapeutics and Clinical Risk Management,2007,3(5):893-903. [22] Sicilia B,García-López S,González-Lama Y,et al. GETECCU 2020 guidelines for the treatment of ulcerative colitis. Developed using the GRADE approach[J]. Gastroenterologia y hepatologia,2020,43:1-57. [23] Burri E,Maillard M H,Schoepfer A M,et al. Treatment algorithm for mild and moderate-to-severe ulcerative colitis: an update[J]. Digestion,2020,13(25):2-15. [24] 贾文睿,苏晓兰,甄建华,等. 近20年针灸治疗溃疡性结肠炎研究进展[J]. 针灸临床杂志,2020,36(5):99-103. [25] Song G,Fiocchi C,Achkar J P. Acupuncture in inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Inflammatory Bowel Diseases,2019,25(7):1129-1139. doi: 10.1093/ibd/izy371 [26] Bao C,Wu L,Wang D,et al. Acupuncture improves the symptoms,intestinal microbiota,and inflammation of patients with mild to moderate Crohn’s disease: A randomized controlled trial[J]. E Clinical Medicine,2022,45:101300. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101300 [27] 毕婷婷. 针灸治疗溃疡性结肠炎的临床研究进展[J]. 中国民间疗法,2019,27(23):106. [28] 纪 丽, 高宗跃. 针刺合中药保留灌肠联合西药治疗溃疡性结肠炎的疗效 及对炎症因子水平、肠黏膜屏障指标的影响[ J] . 中医研究, 2022, 35(11): 29-33. [29] 薛丹,蔡敬宙,韩棉梅,等. 俞募配穴温针灸疗法在治疗溃疡性结肠炎中的应用[J]. 广东医学,2018,39(15):2377-2380. [30] 李皓月,梁浩. 电针天枢穴对溃疡性结肠炎大鼠 TLR4/NF-κB 信 号通路的影响[J]. 新中医,2018,50(12):20-24. [31] Yan J,Zhang H,Chen C T,et al. Effects of electroacupuncture at Shangjuxu (ST 37) on interleukin-1beta and interleukin-4 in the ulcerative colitis model rats[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2009,29(1):60-63. doi: 10.1016/S0254-6272(09)60033-9 -





 下载:
下载: