Influence of Medication Compliance of Type 2 Diabetes Chronic Disease Management Patients in Two Communities of Kunming on Disease Control
-
摘要:
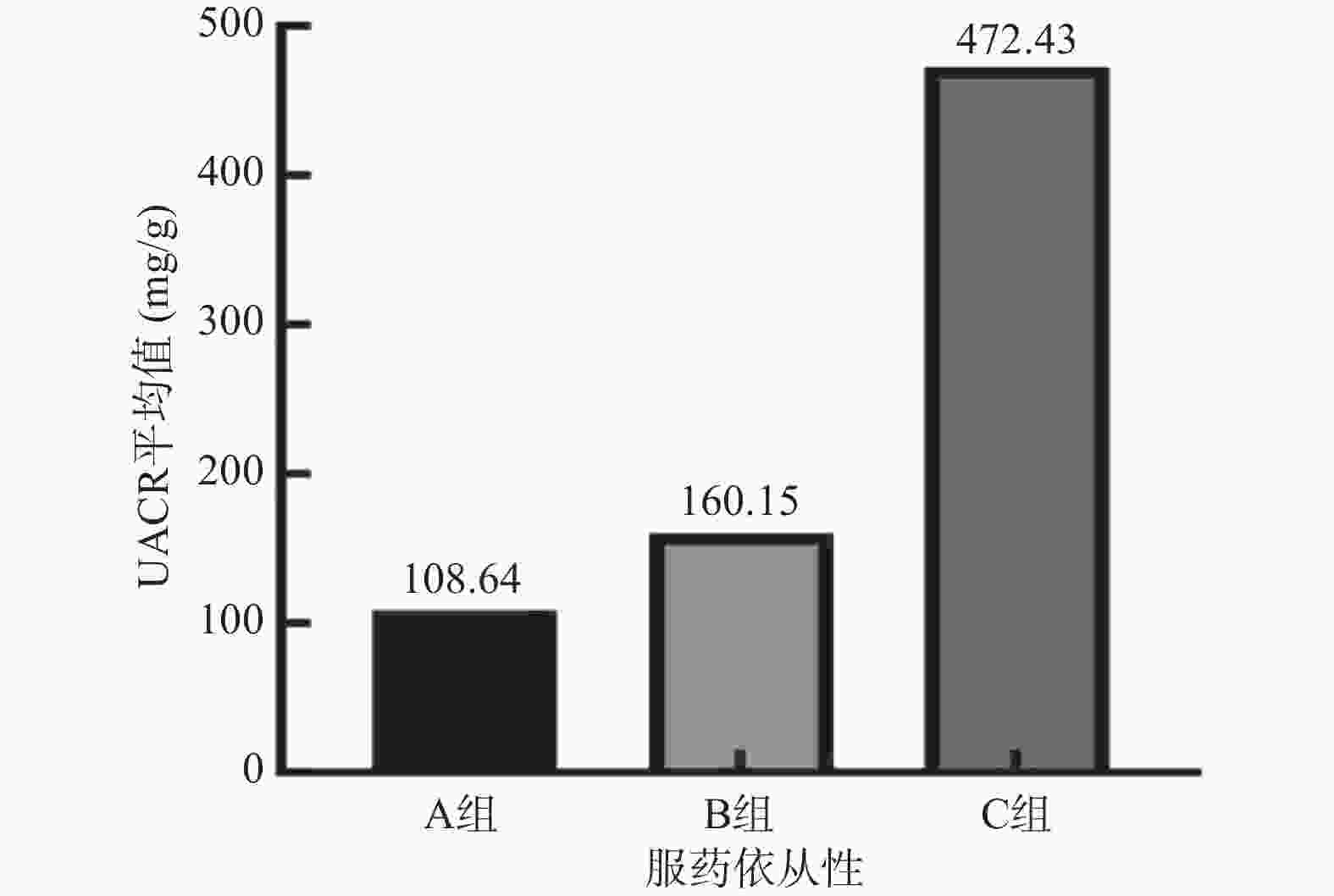
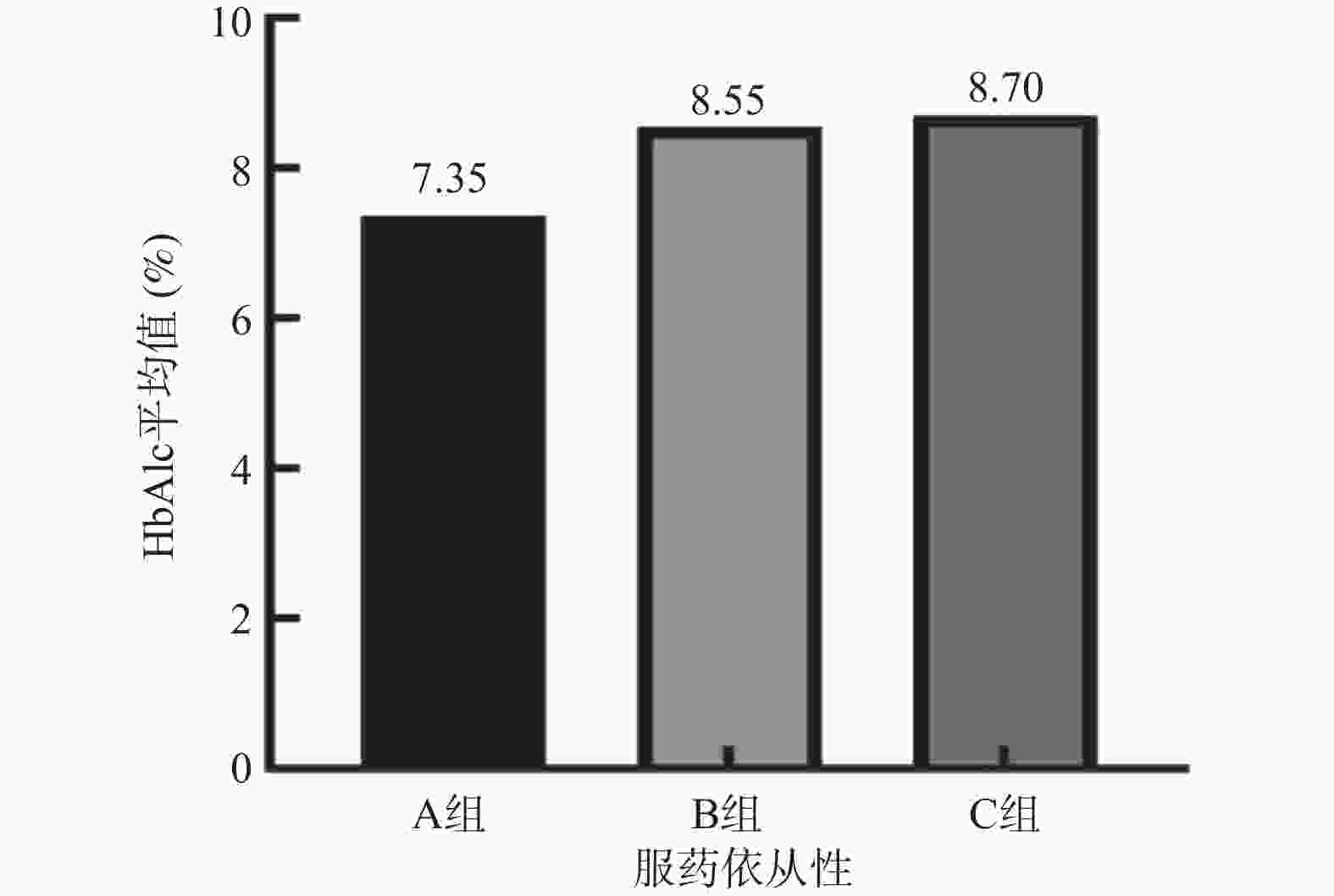
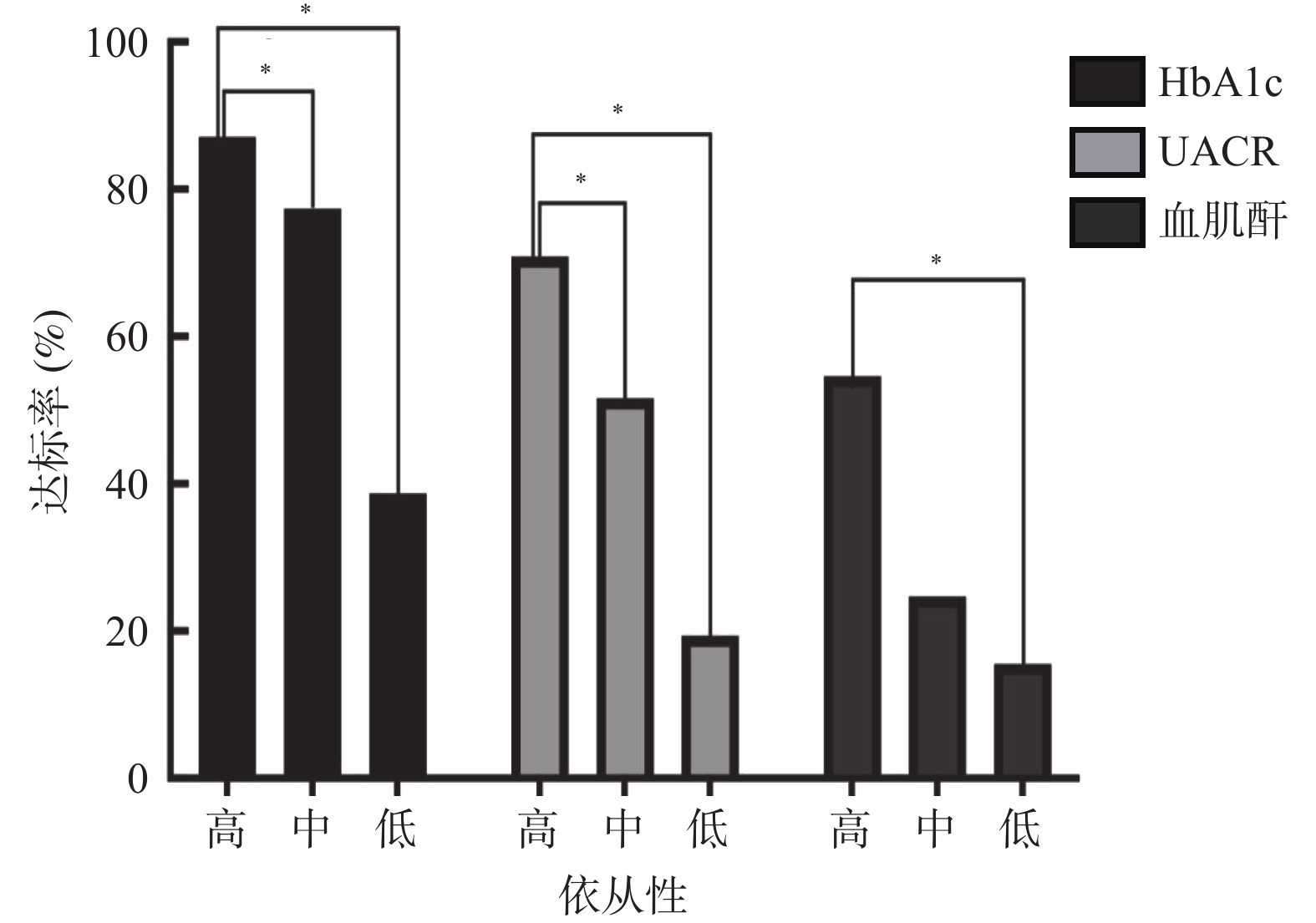
目的 分析昆明市2社区2型糖尿病(type 2 diabetes,T2DM)慢病管理患者服药依从性对病情控制的影响。 方法 选取2021年12月至2022年7月昆明市官渡、小板桥2个社区纳入慢病管理的2型糖尿病患者138例,完善基本信息采集、糖化血红蛋白(HbAlc)等相关检查,进行Morisliy服药依从性量表(8-item Morisky medication adherence scale,MMAS-8)问卷调查,分析服药依从性高(A组)、中(B组)、低(C组)3组的HbAlc等指标水平,并进行统计学分析。 结果 A组病例数占22.5%,B组占44.9%,C组占32.6%。2组间的尿白蛋白肌酐比(UACR)、HbA1c、血肌酐差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。A组患者UACR、HbAlc、血肌酐水平低于B组、C组患者,UACR、HbAlc、血肌酐与用药依从率存在相关性,呈负相关( P<0.05)。 结论 昆明市官渡社区、小板桥2社区2型糖尿病慢病管理患者服药依从性高的患者比例仅为22.5%。依从性越高,患者UACR、HbAlc、血肌酐水平越低,两者之间存在相关性,提示应将服药的依从性作为社区糖尿病慢病管理中重点之一,并应加强对患者服药依从性的干预。 Abstract:Objective To analyze the influence of medication compliance of chronic type 2 diabetes management patients on disease control in two communities in Kunming. Methods A total of 138 patients with type 2 diabetes who were included in chronic disease management in Guandu and Xiaobanqiao communities of Kunming were selected from December 2021 to September 2022. Basic information collection and HbAlc and other related tests were improved. A questionnaire survey of 8-item Morisliy medication adherence scale (MMAS-8) was conducted to analyze the levels of HbAlc and other indexes of three groups with high (group A), medium (group B), and low (group C) adherence, and to conduct statistical analysis. Results Group A accounted for 22.5%, group B for 44.9%, and group C for 32.6%. There were significance differences in urinary albumin creatinine ratio (UACR), HbA1c and blood creatinine among the three groups (P < 0.05). The levels of UACR, HbAlc and serum creatinine in group A were lower than those in group B and group C, and there was a negative correlation between UACR, HbAlc and serum creatinine and medication compliance rate ( P < 0.05). Conclusion In the Guandu Community and Xiaobanqiao community of Kunming, only 22.5% of patients with chronic type 2 diabetes had high medication compliance. The higher the compliance, the lower the level of UACR, HbAlc and serum creatinine, there is a correlation between the two, suggesting that medication compliance should be regarded as one of the key points in the management of chronic diabetes mellitus in the community, and the intervention of patients' medication compliance should be strengthened. -
表 1 Morisky服药依从性问卷(MMAS-8)
Table 1. Morisky medication adherence scale(MMAS-8)
条目 1.您是否出现忘记服药的情况? □是 □否 2.在过去2周里您是否出现有一天或几天忘记服药的情况?□是 □否 3.治疗过程中,当您觉得症状加重或出现其他症状时,您是否在未告知医生的情况下自行减少药量或停止服药?□是 □否 4.当您外出旅行或长时间离家时,您是否出现过忘记随身携带药物的情况?□是 □否 5.昨天您是否按医嘱服药了?□是 □否 6.当您觉得自己的血糖已经得到控制时,您是否停止过服药? □是 □否 7.您是否觉得坚持治疗计划存在困难?□是□否 8. 您是否觉得记住按时按量服药很困难?□从不 □偶尔 □有时 □经常 □所有时间 表 2 各分组基本特征[n(%)/ $\bar x \pm s $/M(P25,P75)]
Table 2. Basic characteristics of each group [n(%)/ $\bar x \pm s $/M(P25,P75)]
项目 A组 (n=31) B组 (n=62) C组 (n=45) H/F/χ2 P 年龄(岁) 65.0(55.0,69.0) 65.0(60.0,70.0) 66.0(55.0,69.0) 1.251 0.535 性别(男/女) 15(48.40) 30(48.40) 25(55.60) 0.623 0.732 学历(初中及以下) 15(48.40) 40(64.50) 30(66.70) 2.999 0.223 病程(a) 7.4±4.2 8.6±5.9 8.5±5.60 0.540 0.584 BMI(kg/m2) 25.7±3.2 26.2±6.3 25.3±3.2 0.420 0.658 收缩压(mmHg) 133.4±13.2 137.7±15.0 134.7±14.1 1.151 0.319 舒张压(mmHg) 82.5±7.8 82.1±10.7 80.8±8.8 0.358 0.700 FPG(mmol/L) 7.1(5.8,8.0) 8.32(6.2,10.6) 8.0(6.4,10.5) 4.369 0.113 HbAlc(%) 7.4(6.9,7.8) 7.9(7.0,9.5) 8.1(7.3,9.7) 7.922 0.019* UACR(mg/g) 11.9(6.0,30.0) 25.5(9.9,59.09) 34.4(11.2,248.7) 7.372 0.025* TG(mmol/L) 1.9(1.6,2.9) 2.0(1.4,3.1) 1.9(1.2,2.7) 1.386 0.5 TC(mmol/L) 4.8(4.3,6.0) 5.1(4.6,5.7) 5.2(4.5,5.9) 0.768 0.681 LDL-C(mmol/L) 3.1(2.5,3.7) 3.1(2.7,3.6) 3.5(2.6,3.9) 1.47 0.48 HDL-C(mmol/L) 1.2(1.0,1.4) 1.2(1.0,1.4) 1.2(1.0,1.4) 0.151 0.927 血肌酐(μmol/L) 63.3±13.7 62.6±21.4 82.1±28.2 11.138 <0.001* 是否诊断高血压(是) 10(32.20) 10(19.40) 11(24.40) 1.901 0.386 是否诊断冠心病(是) 3(0.09) 4(0.06) 2(0.04) 0.825 0.662 是否诊断脑梗(是) 6(0.19) 4(0.06) 6(0.19) 3.553 0.169 是否诊断糖尿病相关并发症(是) 12(0.39) 25(0.40) 14(0.31) 1.002 0.606 *P<0.05。 表 3 服药依从性评分与UACR、HbAlc、血肌酐相关性分析
Table 3. Correlation analysis of medication compliance with UACR,HbAlc and serum creatinine
指标 服药依从性评分 r P UACR −0.220 0.012* HbAlc −0.213 0.009* 血肌酐 −0.279 0.001* *P<0.05。 -
[1] 杨斯曼,张曦,周梦萍,等. 全科医疗核心特征功能对糖尿病患者治疗依从性的影响研究[J]. 中国全科医学,2022,25(1):62-69. [2] Khan M A B,Hashim M J,King J K,et al. Epidemiology of type 2 diabetes - global burden of disease and forecasted trends[J]. J Epidemiol Glob Hea,2020,10(1):107-111. [3] 杨华,张艳,李春燕. 2型糖尿病老年患者用药依从性与糖化血红蛋白控制的相关性分析[J]. 中国药物滥用防治杂志,2023,29(3):445-458. [4] 中华医学会糖尿病学分会. 中国2型糖尿病防治指南(2017年版)[J]. 中华糖尿病杂志,2018,10(1):4-67. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-5809.2018.01.003 [5] Morisky D E,Ang A,Ktousel-wood M,et al. Predictive validity of a medication adherence measure in an outpatient setting[J]. J Clin Hypertens,2008,10(5):348-354. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-7176.2008.07572.x [6] 翁艳君. 中文版MMAS-8在T2DM患者中的信效度评价及应用研究 [D]. 昆明: 昆明医科大学, 2018. [7] 米艳丽. 观察社区糖尿病慢病管理对患者血糖控制、治疗依从性的影响情况[J]. 中国社区医师,2020,36(33):182-183. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-614x.2020.33.089 [8] 孔灵芝. 中国慢性病防治规划解读[J]. 中国慢性病预防与控制,2012,20(5):502-503. [9] 王剑,马陈芳,丁嘉寅,等. 老年高血压合并糖尿病患者服药依从性的影响因素[J]. 中华高血压杂志,2022,30(11):1085-1089. [10] Balkhi B,Alwhaibi M,Alqahtani N,et al. Oral antidiabetic medication adherence and glycaemic control among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A cross-sectional retrospective study in a tertiary hospital in Saudi Arabia[J]. BMJ Open,2019,9(7):e029280. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2019-029280 [11] 周忠梅,程晓亮,班立丽,等. 基于MMC平台的2型糖尿病患者用药依从性现状调查[J]. 临床合理用药,2023,16(11):18-23. [12] Wang X,Luo J F,QI L,et al. Adherence to self-monitoring of blood glucose in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes: Current status and influential factors based on electronic questionnaires[J]. Patient Prefer Adherence,2019,13:1269-1282. doi: 10.2147/PPA.S211668 [13] 路孝琴,任振勇,瓮学清. 北京方庄社区全科医疗门诊糖尿病患者依从性及其与病情控制间的关系[J]. 中国全科医学,2004,7(12):884-886. [14] 李奇星. 某社区2型糖尿病患者自我管理联合社区干预效果[J]. 甘肃医药,2022,41(2):150-157. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2725.2022.2.gsyy202202019 [15] Wakui N, Ozawa M, Yanagiya T, et al. Factors associated with medication compliance in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A cross-sectional study [J]. Front Public Health, 2021, 9: 771593. [16] The Lancet Diabetes E. Diabetes education: The key to a brighter tomorrow[J]. Lancet Diabetes Endo,2022,10(12):827. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(22)00323-0 [17] Chawla S P S,Kaur S,Bharti A,et al. Impact of health education on knowledge,attitude,practices and glycemic control in type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. J Fam Med Prim Care,2019,8(1):261-268. doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_228_18 [18] 田茂英. 社区糖尿病的健康教育[J]. 饮食保健,2020,7(44):274. [19] 王冯彬,高敏,陈雪莹,等. 社区2型糖尿病患者家庭支持与血糖控制关联研究[J]. 首都公共卫生,2020,14(2):79-81. -





 下载:
下载: