Value of Three-dimensional Rectal Intraluminal Ultrasound Combined with Couplant Contrast for Surgical Guidance of Perianal Necrotising Fasciitis
-
摘要:
目的 探讨三维直肠腔内超声结合耦合剂造影在肛周坏死性筋膜炎的手术指导价值。 方法 对40例临床诊断为肛周坏死性筋膜炎的患者,同一病例术前均进行常规三维直肠腔超声检查(常规组)和耦合剂造影检查(造影组)2种检查,分别观察原发灶内口,深、浅筋膜坏死及肛提肌损伤情况,与手术结果对比,分析常规组和造影组观察内容诊断敏感性。 结果 常规组和造影组2种方法相比较,对原发灶内口显示率由70% 增加到97.5% ;深筋膜坏死显示率由50%增加到 88.8% ;浅筋膜显示率由70% 增加到 100% ;肛提肌损伤显示率由62.5% 增加到 97.2%(P < 0.05)。 结论 三维直肠腔内超声结合耦合剂造影较常规三维直肠腔超声对肛周坏死性筋膜炎原发灶内口,深、浅筋膜坏死,肛提肌损伤检出准确率显著提高,有利于指导临床医生制定最佳的手术方式,提高手术成功率。 Abstract:Objective To explore the application value of Three-Dimensional rectal cavity ultrasound combined with contrast agent imaging in necrotizing fasciitis of the anal region. Methods Before surgery, standard three-dimensional rectal cavity ultrasound examinations(referred to as the conventional group) and contrast agent imaging examinations(referred to as the imaging group) were conducted for 40 patients clinically diagnosed with anal region necrotizing fasciitis. Separate observations were made for the primary lesion, as well as for the depth and superficial necrosis of the fascia, and injuries to the anal sphincter muscle. Comparative analysis with surgical results was undertaken to assess the diagnostic sensitivity of both the conventional and imaging groups. Results In comparing the conventional group with the imaging group, the rates of primary lesion visibility rose significantly from 70% to 97.5%, deep fascial necrosis visibility increased from 50% to 88.8%, superficial fascia visibility improved from 70% to 100%, and the visibility of anal sphincter muscle injury escalated from 62.5% to 97.2%, all demonstrating statistical significance at P < 0.05. Conclusions Three-dimensional rectal cavity ultrasound combined with contrast agent imaging exhibits significantly enhanced accuracy in identifying primary lesions associated with perianal necrotizing fasciitis, as well as the necrosis affecting deep and superficial fascia, in contrast to conventional three-dimensional rectal cavity ultrasound. This advancement offers more precise guidance for clinicians in devising surgical plans, thereby augmenting the success rate of surgical interventions. -
Key words:
- Necrotizing fasciitis /
- Rectal intracavitary ultrasound /
- Contrast agent /
- Imaging
-
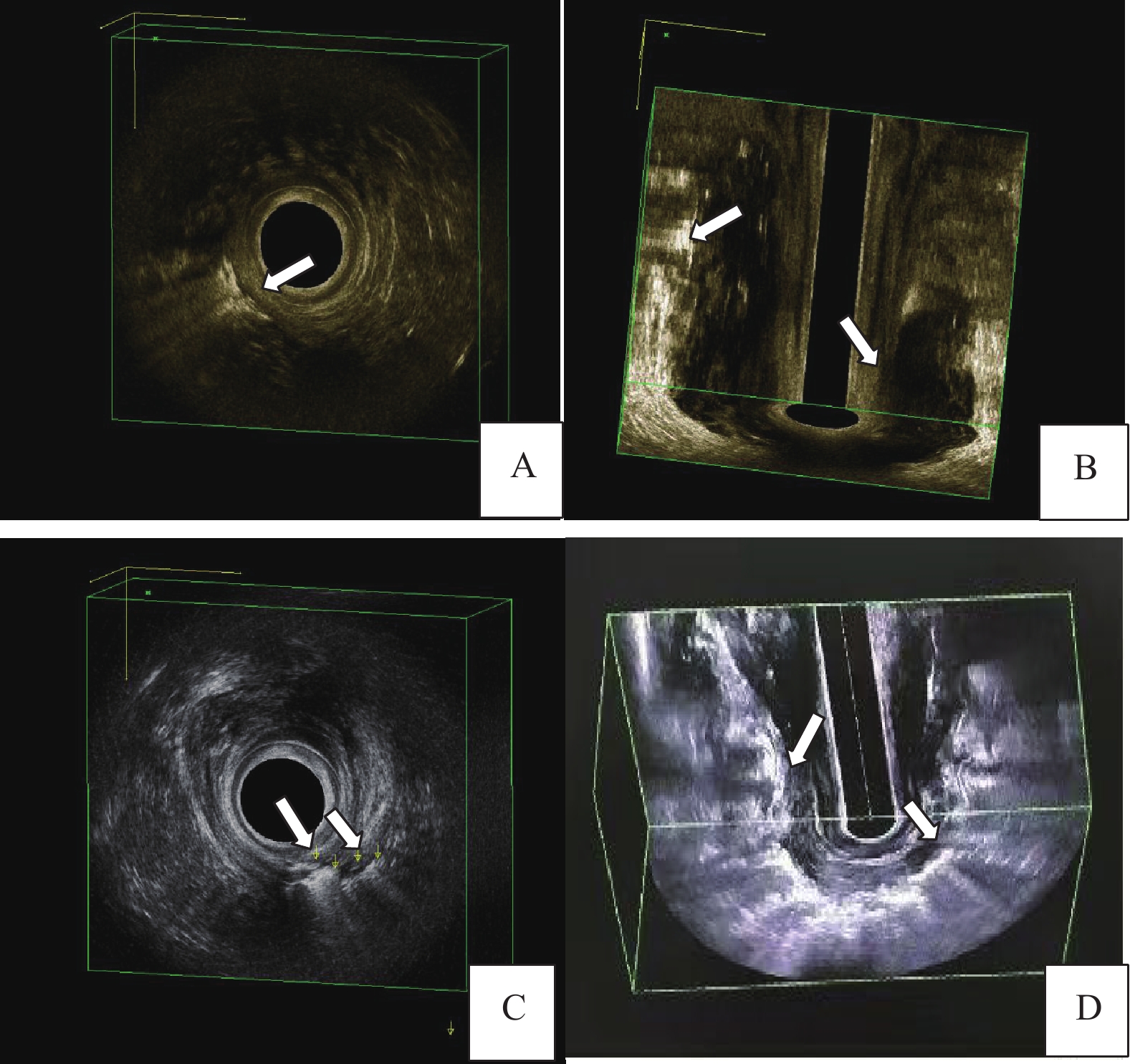
图 1 常规腔内超声与造影腔内超声诊断肛周坏死性筋膜炎各项指标的图像
A:常规组腔内超声声像图,箭头所示为浅筋膜坏死;B:常规组腔内超声声像图,箭头所示分别为深筋膜坏死合并高位多间隙脓肿;C:造影组腔内超声声像图,箭头所示分别为浅筋膜坏死和原发灶内口;D:造影组腔内超声声像图,箭头所示分别为浅筋膜坏死、深筋膜坏死。
Figure 1. Images of parameters of perianal necrotizing fasciitis diagnosed by conventional and contrast-enhanced intracavitary ultrasonography.
表 1 常规腔内超声与造影腔内超声在诊断肛周坏死性筋膜炎各项指标的显示率比较(%)
Table 1. Comparison of the display rate between conventional and contrast-enhanced intracavitary ultrasonography in the diagnosis of perianal necrotizing fasciitis (%)
检测项目 常规腔内超声显示率 造影腔内超声显示率 McNemar’s chi-squared P 原发灶内口 70.0 (28/40) 97.5 (39/40) 9.091 0.003* 深筋膜坏死 50.0 (18/36) 88.8 (32/36) 12.071 < 0.001* 浅筋膜坏死 70.0 (28/40) 100 .0(40/40) 10.083 0.001* 肛提肌受累 62.5 (20/36) 97.2 (35/36) 13.067 < 0.001* *P < 0.05。 -
[1] 吴长君. 肛肠疾病超声诊断图谱第2版[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2019: 190 [2] 李玲华,王琼. 三维直肠腔内超声联合体表超声诊断坏死性筋膜炎1例[J]. 中国超声医学杂志,2016,32(3):288. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0101.2016.03.038 [3] Tao X C,Hu D C,Yin L X,et al. Necrotizing fasciitis of cryptoglandular infection treated with multiple incisions and thread-dragging therapy: A case report[J]. World Journal of Clinical Cases,2021,9(28):8537. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i28.8537 [4] 中国医师学会肛肠医师分会临床指南工作委员会. 肛周坏死性筋膜炎临床诊治中国专家共识(2019版)[J]. 中华胃肠外科杂志,2019,22(7):689-693. [5] Kwee R M,Kwee T C. Diagnostic performance of MRI and CT in diagnosing necrotizing soft tissue infection: A systematic review[J]. Skeletal Radiology,2022,40(3):1-10. [6] Al-Qurayshi Z,Nichols R L,Killackey M T,et al. Mortality risk in necrotizing fasciitis: National prevalence,trend,and burden[J]. Surgical Infections,2020,21(10):840-852. doi: 10.1089/sur.2019.277 [7] Saad E,Tummala A,Agab M,et al. Gemella morbillorum as the culprit organism of post-colonoscopy necrotizing perineal soft tissue infection in a diabetic patient with crohn’s disease[J]. Journal of Medical Cases,2022,13(3):99-103. doi: 10.14740/jmc3896 [8] 林秋,竺平,孙桂东. 肛周坏死性筋膜炎的诊治进展[J]. 世界华人消化杂志,2010,18(32):3428-3431. [9] 刘洪,王锦,伍静,等. 肛周坏死性筋膜炎的诊断及治疗[J]. 现代预防医学,2010,37(22):4349-4351. [10] 吴媛媛,李志,冷羽,等. 肛周坏死性筋膜炎误诊一例及文献复习[J]. 河南外科学杂志,2022,28(5):41-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-8991.2022.5.hnwkxzz202205013 [11] 吴昕,马志强,于健春,等. 坏死性筋膜炎的诊断和治疗[J]. 中国普外基础与临床杂志,2014,21(10):1289-1291. doi: 10.7507/1007-9424.20140307 [12] Paz Maya S, Dualde Beltrán D, Lemercier P, et al. Necrotizing fasci-itis: An urgent diagnosis [ J ] . Skeletal Radiol, 2014, 43(5) : 577-589. [13] Hadeed G J,Smith J,O′Keeffe T,et al. Early surgical intervention and its impact on patients presenting with necrotizing soft tissue infections: a single academic center experience[J]. Emerg Trauma Shock,2016,9(1):22-27. doi: 10.4103/0974-2700.173868 [14] Lahham S,Shniter I,Desai M,et al. Point of care ultrasound in the diagnosis of necrotizing fasciitis[J]. The American Journal of Emergency Medicine,2022,51(3):397-400. [15] 孙建设,刘婷婷. 高频超声在肛周坏死性筋膜炎的诊断价值[J]. 实用医技杂志,2017,24(2):154-155. [16] 陈东,陈海涛,李支尧,等. 直肠腔内360°超声和腔内矢状面超声在全段直肠癌术前TN分期和环周切缘中的应用价值[J]. 昆明医科大学学报,2020,41(7):38-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-4706.2020.07.007 [17] Lin C N,Hsiao C T,Chang C P,et a1. The relationship betweenfluid accumulation in ultrasonography and the diagnosis and prognosis of patients with necrotizing fasciitis[J]. UltrasoundMed Biol,2019,45(7):1545-1550. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2019.02.027 [18] 陈蝶,吴晶晶,陈开良,等. 坏死性筋膜炎1例并文献复习[J]. 中国临床医学影像杂志,2022,33(8):607-608. -






 下载:
下载: