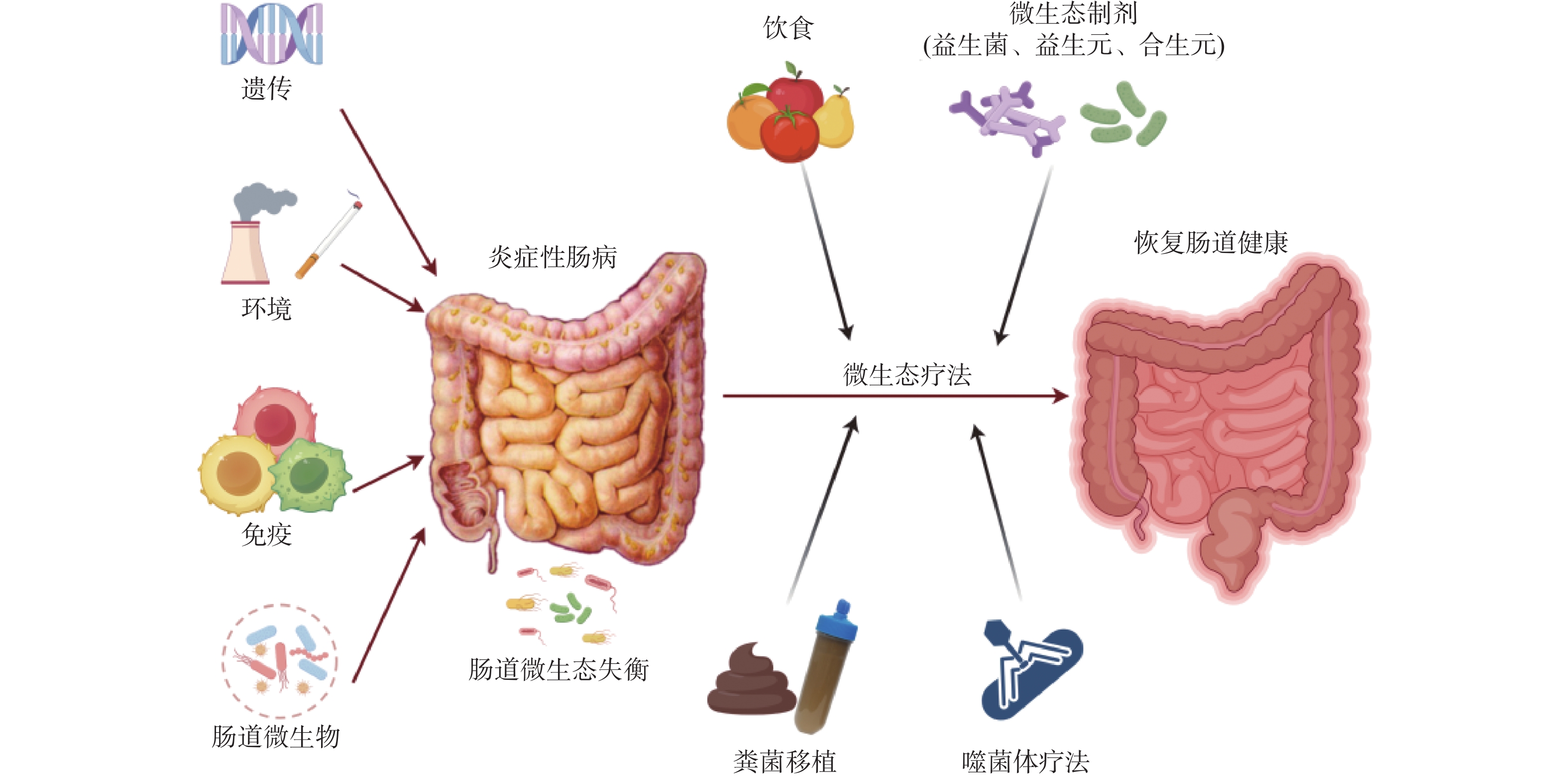
|
[1]
|
Mak W Y,Zhao M,Ng S C,et al. The epidemiology of inflammatory bowel disease: East meets west[J]. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology,2020,35(3):380-389. doi: 10.1111/jgh.14872
|
|
[2]
|
包云丽,汪哲,唐海茹,等. 1990-2019年中国炎症性肠病疾病负担及变化趋势分析[J]. 中国全科医学,2023,26(36):4581-4586.
|
|
[3]
|
Xu L,He B,Sun Y,et al. Incidence of inflammatory bowel disease in urban China: A nationwide population-based study[J]. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology,2023,21(13): 3379-3386. e29.
|
|
[4]
|
Ng S C,Shi H Y,Hamidi N,et al. Worldwide incidence and prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease in the 21st century: A systematic review of population-based studies[J]. The Lancet,2017,390(10114):2769-2778. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32448-0
|
|
[5]
|
Nakase H,Sato N,Mizuno N,et al. The influence of cytokines on the complex pathology of ulcerative colitis[J]. Autoimmunity Reviews,2022,21(3):103017. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2021.103017
|
|
[6]
|
Caparr ó s E,Wiest R,Scharl M,et al. Dysbiotic microbiota interactions in Crohn’ s disease[J]. Gut Microbes,2021,13(1):1949096. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2021.1949096
|
|
[7]
|
Lee M,Chang E B. Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) and the microbiome—Searching the crime scene for clues[J]. Gastroenterology,2021,160(2):524-537. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.09.056
|
|
[8]
|
Hu Y,Chen Z,Xu C,et al. Disturbances of the gut microbiota and microbiota-derived metabolites in inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Nutrients,2022,14(23):5140. doi: 10.3390/nu14235140
|
|
[9]
|
Schirmer M,Garner A,Vlamakis H,et al. Microbial genes and pathways in inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology,2019,17(8):497-511. doi: 10.1038/s41579-019-0213-6
|
|
[10]
|
Kennedy J M,De Silva A,Walton G E,et al. A review on the use of prebiotics in ulcerative colitis[J]. Trends Microbiol,2023,Published online .
|
|
[11]
|
Li W,Sun Y,Dai L,et al. Ecological and network analyses identify four microbial species with potential significance for the diagnosis/treatment of ulcerative colitis (UC)[J]. BMC Microbiology,2021,21(1):138. doi: 10.1186/s12866-021-02201-6
|
|
[12]
|
Pittayanon R,Lau J T,Leontiadis G I,et al. Differences in gut microbiota in patients with vs without inflammatory bowel diseases: A systematic review[J]. Gastroenterology,2020,158(4): 930-946. e1.
|
|
[13]
|
Waters J L,Ley R E. The human gut bacteria Christensenellaceae are widespread,heritable,and associated with health[J]. BMC Biology,2019,17(1):83. doi: 10.1186/s12915-019-0699-4
|
|
[14]
|
Hu W,Gao W,Liu Z,et al. Biodiversity and physiological characteristics of novel Faecalibacterium prausnitzii strains isolated from human feces[J]. Microorganisms,2022,10(2):297. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10020297
|
|
[15]
|
Wang X,Ni J,You Y,et al. SNX10‐mediated LPS sensing causes intestinal barrier dysfunction via a caspase‐5‐dependent signaling cascade[J]. The EMBO Journal,2021,40(24):e108080. doi: 10.15252/embj.2021108080
|
|
[16]
|
Duerkop B A,Kleiner M,Paez-Espino D,et al. Murine colitis reveals a disease-associated bacteriophage community[J]. Nature Microbiology,2018,3(9):1023-1031. doi: 10.1038/s41564-018-0210-y
|
|
[17]
|
Zuo T,Lu X J,Zhang Y,et al. Gut mucosal virome alterations in ulcerative colitis[J]. Gut,2019,68(7):1169-1179. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2018-318131
|
|
[18]
|
Cao Z,Fan D,Sun Y,et al. The gut ileal mucosal virome is disturbed in patients with Crohn’ s disease and exacerbates intestinal inflammation in mice[J]. Nature Communications,2024,15(1):1638. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-45794-y
|
|
[19]
|
Clooney A G,Sutton T D S,Shkoporov A N,et al. Whole-virome analysis sheds light on viral dark matter in inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Cell Host & Microbe,2019,26(6): 764-778. e5.
|
|
[20]
|
Ventin-Holmberg R,Eberl A,Saqib S,et al. Bacterial and fungal profiles as markers of infliximab drug response in inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Journal of Crohn’ s and Colitis,2021,15(6):1019-1031. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjaa252
|
|
[21]
|
Limon J J,Tang J,Li D,et al. Malassezia is associated with Crohn’ s disease and exacerbates colitis in mouse models[J]. Cell Host & Microbe,2019,25(3): 377-388. e6.
|
|
[22]
|
Rahabi M,Jacquemin G,Prat M,et al. Divergent roles for macrophage C-type lectin receptors,Dectin-1 and mannose receptors,in the intestinal inflammatory response[J]. Cell Reports,2020,30(13): 4386-4398. e5.
|
|
[23]
|
Torres J,Bonovas S,Doherty G,et al. ECCO guidelines on therapeutics in Crohn’ s disease: Medical treatment[J]. Journal of Crohn’ s & colitis,2020,14(1):4-22.
|
|
[24]
|
中华医学会消化病学分会炎症性肠病学组,中国炎症性肠病诊疗质量控制评估中心. 中国溃疡性结肠炎诊治指南(2023年·西安)[J]. 中华炎性肠病杂志(中英文),2024,8(1):33-58.
|
|
[25]
|
中华医学会消化病学分会炎症性肠病学组,中国炎症性肠病诊疗质量控制评估中心. 中国克罗恩病诊治指南(2023年·广州)[J]. 中华炎性肠病杂志(中英文),2024,8(1):2-32.
|
|
[26]
|
Peters V,Bolte L,Schuttert E M,et al. Western and carnivorous dietary patterns are associated with greater likelihood of IBD development in a large prospective population-based cohort[J]. J Crohns Colitis,2022,16(6):931-939. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjab219
|
|
[27]
|
Adolph T E,Meyer M,Schwärzler J,et al. The metabolic nature of inflammatory bowel diseases[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol,2022,19(12):753-767. doi: 10.1038/s41575-022-00658-y
|
|
[28]
|
Narula N,Wong E C L,Dehghan M,et al. Association of ultra-processed food intake with risk of inflammatory bowel disease: Prospective cohort study[J]. BMJ,2021,374:n1554.
|
|
[29]
|
Fritsch J,Garces L,Quintero M A,et al. Low-fat,high-fiber diet reduces markers of inflammation and dysbiosis and improves quality of life in patients with ulcerative colitis[J]. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology,2021,19(6): 1189-1199. e30.
|
|
[30]
|
Wang S,Martins R,Sullivan M C,et al. Diet-induced remission in chronic enteropathy is associated with altered microbial community structure and synthesis of secondary bile acids[J]. Microbiome,2019,7(1):126. doi: 10.1186/s40168-019-0740-4
|
|
[31]
|
Jakubczyk D,Leszczy ń ska K,G ó rska S. The effectiveness of probiotics in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)-A critical review[J]. Nutrients,2020,12(7):1973. doi: 10.3390/nu12071973
|
|
[32]
|
Sun M,Liu Y,Song Y,et al. The ameliorative effect of Lactobacillus plantarum-12 on DSS-induced murine colitis[J]. Food & Function,2020,11(6):5205-5222.
|
|
[33]
|
Yao S,Zhao Z,Wang W,et al. Bifidobacterium longum: Protection against inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Journal of Immunology Research,2021,2021:1-11.
|
|
[34]
|
Chen Y,Zhang M,Ren F. A role of exopolysaccharide produced by Streptococcus thermophilus in the intestinal inflammation and mucosal barrier in caco-2 monolayer and dextran sulphate sodium-induced experimental murine colitis[J]. Molecules,2019,24(3):513. doi: 10.3390/molecules24030513
|
|
[35]
|
Kang M,Choi H J,Yun B,et al. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SCGB1 alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice through immune regulation[J]. Journal of Medicinal Food,2021,24(7):709-719. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2021.K.0044
|
|
[36]
|
Choi E J,Lee H J,Kim W J,et al. Enterococcus faecalis EF-2001 protects DNBS-induced inflammatory bowel disease in mice model[J]. PLoS One,2019,14(2):e0210854. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0210854
|
|
[37]
|
Tursi A,Brandimarte G,Papa A,et al. Treatment of relapsing mild-to-moderate ulcerative colitis with the probiotic VSL#3 as adjunctive to a standard pharmaceutical treatment: A double-blind,randomized,placebo-controlled study[J]. American Journal of Gastroenterology,2010,105(10):2218-2227. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2010.218
|
|
[38]
|
Li S C,Hsu W F,Chang J S,et al. Combination of Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis shows a stronger anti-inflammatory effect than individual strains in HT-29 cells[J]. Nutrients,2019,11(5):969. doi: 10.3390/nu11050969
|
|
[39]
|
Dore M P,Rocchi C,Longo N P,et al. Effect of probiotic use on adverse events in adult patients with inflammatory bowel disease: A retrospective cohort study[J]. Probiotics and Antimicrobial Proteins,2020,12(1):152-159. doi: 10.1007/s12602-019-9517-0
|
|
[40]
|
Gibson G R,Hutkins R,Sanders M E,et al. Expert consensus document: The international scientific association for probiotics and prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of prebiotics[J]. Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology,2017,14(8):491-502.
|
|
[41]
|
Wilson B,Eyice Ö,Koumoutsos I,et al. Prebiotic galactooligosaccharide supplementation in adults with ulcerative colitis: Exploring the impact on peripheral blood gene expression,Gut Microbiota,and Clinical Symptoms[J]. Nutrients,2021,13(10):3598. doi: 10.3390/nu13103598
|
|
[42]
|
Valcheva R,Koleva P,Mart í nez I,et al. Inulin-type fructans improve active ulcerative colitis associated with microbiota changes and increased short-chain fatty acids levels[J]. Gut Microbes,2019,10(3):334-357. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2018.1526583
|
|
[43]
|
Ikegami S,Nakamura M,Honda T,et al. Efficacy of 1-kestose supplementation in patients with mild to moderate ulcerative colitis: A randomised,double-blind,placebo-controlled pilot study[J]. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics,2023,57(11):1249-1257.
|
|
[44]
|
Xue Z,Li R,Liu J,et al. Preventive and synbiotic effects of the soluble dietary fiber obtained from lentinula edodes byproducts and Lactobacillus plantarum LP90 against dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2023,103(2):616-626. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.12173
|
|
[45]
|
Amiriani T,Rajabli N,Faghani M,et al. Effect of Lactocare® synbiotic on disease severity in ulcerative colitis: A randomized placebo-controlled double-blind clinical trial[J]. Middle East Journal of Digestive Diseases,2019,12(1):27-33. doi: 10.15171/mejdd.2020.160
|
|
[46]
|
Costello S P,Hughes P A,Waters O,et al. Effect of fecal microbiota transplantation on 8-week remission in patients with ulcerative colitis: A randomized clinical trial[J]. JAMA,2019,321(2):156. doi: 10.1001/jama.2018.20046
|
|
[47]
|
Haifer C,Paramsothy S,Kaakoush N O,et al. Lyophilised oral faecal microbiota transplantation for ulcerative colitis (LOTUS): A randomised,double-blind,placebo-controlled trial[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol,2022,7(2):141-151. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(21)00400-3
|
|
[48]
|
Boicean A,Birlutiu V,Ichim C,et al. Fecal microbiota transplantation in inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Biomedicines,2023,11(4):1016. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11041016
|
|
[49]
|
Xu Z,Dong X,Yang K,et al. Association of adherent-invasive Escherichia coli with severe gut mucosal dysbiosis in Hong Kong Chinese population with Crohn’ s disease[J]. Gut Microbes,2021,13(1):1994833. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2021.1994833
|
|
[50]
|
Galtier M,De Sordi L,Sivignon A,et al. Bacteriophages targeting adherent invasive Escherichia coli strains as a promising new treatment for Crohn’ s disease[J]. Journal of Crohn’ s and Colitis,2017,11(7):jjw224.
|
|
[51]
|
Federici S,Kredo-Russo S,Valdés-Mas R,et al. Targeted suppression of human IBD-associated gut microbiota commensals by phage consortia for treatment of intestinal inflammation[J]. Cell,2022,185(16): 2879-2898. e24.
|





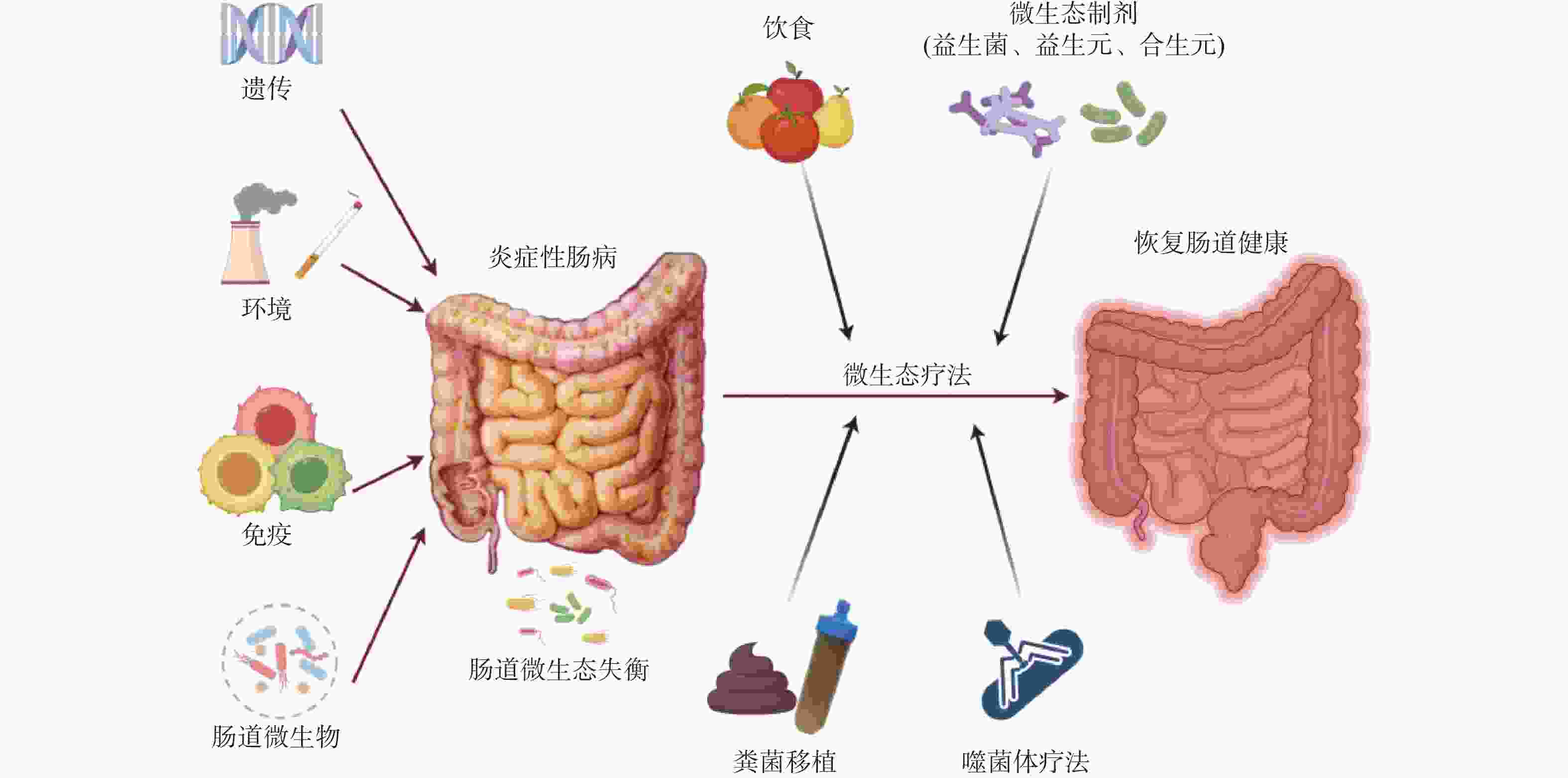
 下载:
下载: