Overexpression of ZIC1 Gene Inhibits Proliferation of Pleural Mesothelioma Cells by Activating P53 Signaling Pathway
-
摘要:
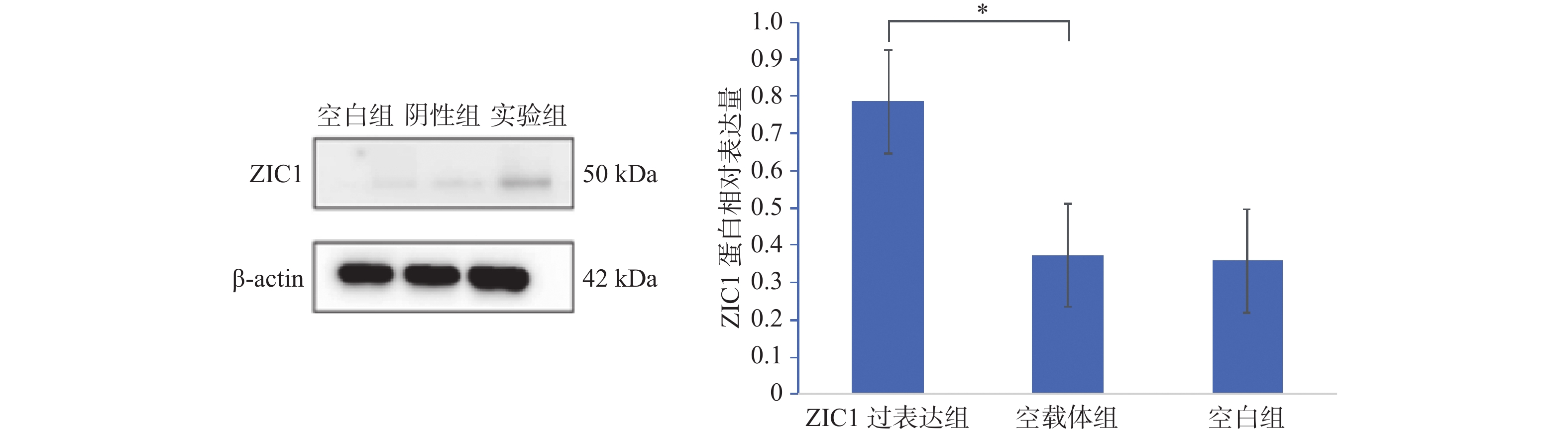
目的 探讨小脑锌指结构1(ZIC1) 基因过表达对胸膜间皮瘤SMC-1细胞增殖、凋亡的影响以及相应的机制。 方法 用携带ZIC1 基因的慢病毒颗粒转染SMC-1细胞作为过表达组,用空载慢病毒颗粒感染SMC-1细胞作为空载体组,将常规培养未进行转染的SMC-1细胞作为空白对照组,采用Western blot在蛋白水平检测3组细胞中ZIC1蛋白的表达情况;采用CCK-8细胞增殖试验检测各组细胞增殖能力,Hoechst-PI双染法检测各组细胞凋亡情况;采用Western blot检测P53介导的细胞凋亡信号通路的主要基因P53、P21、MDM2及P53磷酸化位点Ser392蛋白表达水平。 结果 与空载组和对照组相比,ZIC1过表达组中ZIC1蛋白的表达明显增高,差异有统计学意义(F = 4.665,P = 0.036);ZIC1过表达组中肿瘤细胞的增殖活性明显减弱,而肿瘤细胞的凋亡明显增加,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);ZIC1基因过表达组中P53信号通路中的主要基因P53、P21、MDM2及P53-Ser392蛋白表达均明显增加(P < 0.05)。 结论 ZIC1基因过表达可以抑制胸膜间皮瘤SMC-1细胞增殖,促进其凋亡,其可能的机制为通过上调P53基因磷酸化位点的表达激活P53基因介导的细胞凋亡信号通路来实现。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the effect of cerebellar zinc finger structure 1 (ZIC1) gene overexpression on the proliferation and apoptosis of pleural mesothelioma cells (SMC-1 cells) and the corresponding molecular mechanism. Methods SMC-1 cells were transfected with lentivirus particles carrying ZIC1 gene as the experimental group, infected with empty lentivirus particles as the control group, and conventional cultured untransfected SMC-1 cells as the blank control group. Western blot was used to detect the expression of ZIC1 protein in the three groups. CCK-8 cell proliferation assay was used to detect the proliferation ability of each group, and Hoechst-PI double staining was used to detect the apoptosis of each group. The protein expression levels of P53, P21, MDM2 and P53 phosphorylation site Ser392 in P53-mediated apoptosis signaling pathway were detected by Western blot. Results Compared with the empty vector group and the control group, the expression of ZIC1 protein in the ZIC1 overexpression group was significantly increased, with a statistically significant difference (F = 4.665, P = 0.036). Compared with the control group, the proliferation ability of SMC-1 cells in the ZIC1 overexpression group was significantly reduced, while the apoptosis of tumor cells was significantly increased, with a statistically significant difference (P < 0.05). The main genes P53, P21, MDM2, and P53 Ser392 protein expression in the P53 signaling pathway in the ZIC1 gene overexpression group were significantly increased. Conclusion Overexpression of ZIC1 gene can inhibit the proliferation of pleural mesothelioma SMC-1 cells and promote their apoptosis. The possible mechanism is to activate the P53 gene mediated apoptosis signaling pathway by upregulating the expression of P53 gene phosphorylation sites. -
Key words:
- ZIC1 /
- Pleural mesothelioma cells /
- P53 signal pathway /
- Proliferation /
- Apoptosis
-
表 1 ZIC1在各组细胞中的蛋白表达
Table 1. The ZIC1 protein expression in tumor cells of each group
组别 ZIC1过表达组 空载体组 空白组 F P 相对表达量 0.785±0.021 0.373±0.019 0.358±0.022 4.665 0.036* *P < 0.05。 表 2 各实验组在不同时间点的 OD值
Table 2. The optical density value of each group cell at different time points
分组 8 h 12 h 24 h 36 h 48 h 72 h ZIC1过表达组 0.677±0.016 0.788±0.018 0.913±0.021 0.988±0.017 1.023±0.022 1.165±0.020 空载体组 0.798±0.022 0.878±0.024 1.233±0.023 1.355±0.016 2.238±0.023 3.266±0.018 空白组 0.836±0.023 0.955±0.027 1.311±0.026 1.402±0.022 2.548±0.028 3.476±0.023 -
[1] Baas P,Schouwink H,Zoetmulder F A. Malignant pleural mesothelioma[J]. Ann Oncol,1998,9(2):139-149. doi: 10.1023/A:1008239116237 [2] Saddoughi S A,Abdelsattar Z M,Blackmon S H. National trends in the epidemiology of malignant pleural mesothelioma: A national cancer data base study[J]. The Annals of Thoracic Surgery,2018,105(2):432-437. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2017.09.036 [3] Perera N D,Mansfield A S. The evolving therapeutic landscape for malignant pleural mesothelioma[J]. Current Oncology Reports,2022,24(11):1413-1423. doi: 10.1007/s11912-022-01302-3 [4] Han W,Cao F,Gao X J,et al. ZIC1 acts a tumor suppressor in breast cancer by targeting survivin[J]. International Journal of Oncology,2018,53(3):937-948. [5] Iyer A S,Shaik M R,Raufman J P,et al. The roles of zinc finger proteins in colorectal cancer[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2023,24(12):10249. doi: 10.3390/ijms241210249 [6] Ge Q,Hu Y,He J,et al. Zic1 suppresses gastric cancer metastasis by regulating Wnt/β‐catenin signaling and epithelial‐mesenchymal transition[J]. The FASEB Journal,2020,34(2):2161-2172. doi: 10.1096/fj.201901372RR [7] Hou Y,Chen K,Liao R,et al. LINC01419-mediated epigenetic silencing of ZIC1 promotes metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma through the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway[J]. Laboratory Investigation,2021,101(5):570-587. doi: 10.1038/s41374-021-00539-z [8] Thottappillil N,Gomez-Salazar MA,Xu M,et al. ZIC1 dictates osteogenesis versus adipogenesis in human mesenchymal progenitor cells via a Hedgehog dependent mechanism[J]. Stem Cells,2023,41(9):862-76. doi: 10.1093/stmcls/sxad047 [9] Sun J,Hu L,Bok S,et al. A vertebral skeletal stem cell lineage driving metastasis[J]. Nature,2023,621(7979):602-609. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06519-1 [10] 莫世贤,邓勇军,刘焕鹏,等. Fibulin-3 表达对恶性胸膜间皮瘤细胞的影响[J]. 中国病理生理杂志,2019(3):448-453. [11] Scherpereel A,Wallyn F,Albelda S M,et al. Novel therapies for malignant pleural mesothelioma[J]. The Lancet Oncology,2018,19(3):e161-e72. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30100-1 [12] Bronte G,Incorvaia L,Rizzo S,et al. The resistance related to targeted therapy in malignant pleural mesothelioma: Why has not the target been hit yet?[J]. Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology,2016,107:20-32. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2016.08.011 [13] Liu S,Liu X,Lin X,et al. Zinc finger proteins in the war on gastric cancer: Molecular mechanism and clinical potential[J]. Cells,2023,12(9):1314. doi: 10.3390/cells12091314 [14] Ma G,Dai W,Sang A,et al. Roles of ZIC family genes in human gastric cancer[J]. International Journal of Molecular Medicine,2016,38(1):259-266. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2016.2587 [15] Hata AN,Rowley S,Archibald H L,et al. Synergistic activity and heterogeneous acquired resistance of combined MDM2 and MEK inhibition in KRAS mutant cancers[J]. Oncogene,2017,36(47):6581-6591. doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.258 [16] Shen W,Tong D,Chen J,et al. Silencing oncogene cell division cycle associated 5 induces apoptosis and G1 phase arrest of non‐small cell lung cancer cells via P53‐p21 signaling pathway[J]. Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis,2022,36(5):e24396. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24396 [17] Lucchesi C A,Zhang J,Ma B,et al. Disruption of the Rbm38-eIF4E complex with a synthetic peptide Pep8 increases P53 expression[J]. Cancer Research,2019,79(4):807-818. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-2209 [18] Ma Z,Liu X,Zhang Q,et al. Carvedilol suppresses malignant proliferation of mammary epithelial cells through inhibition of the ROS-mediated PI3K/AKT signaling pathway[J]. Oncology Reports,2019,41(2):811-818. [19] Nicolaou S T,Kannan S,Warwicker J,et al. Activation of P53: How phosphorylated Ser15 triggers sequential phosphorylation of P53 at Thr18 by CK1δ[J]. Proteins:Structure,Function,and Bioinformatics,2022,90(12):2009-2022. doi: 10.1002/prot.26393 -






 下载:
下载: