Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Nilotinib Versus Dasatinib as Second-Line Treatment of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
-
摘要:
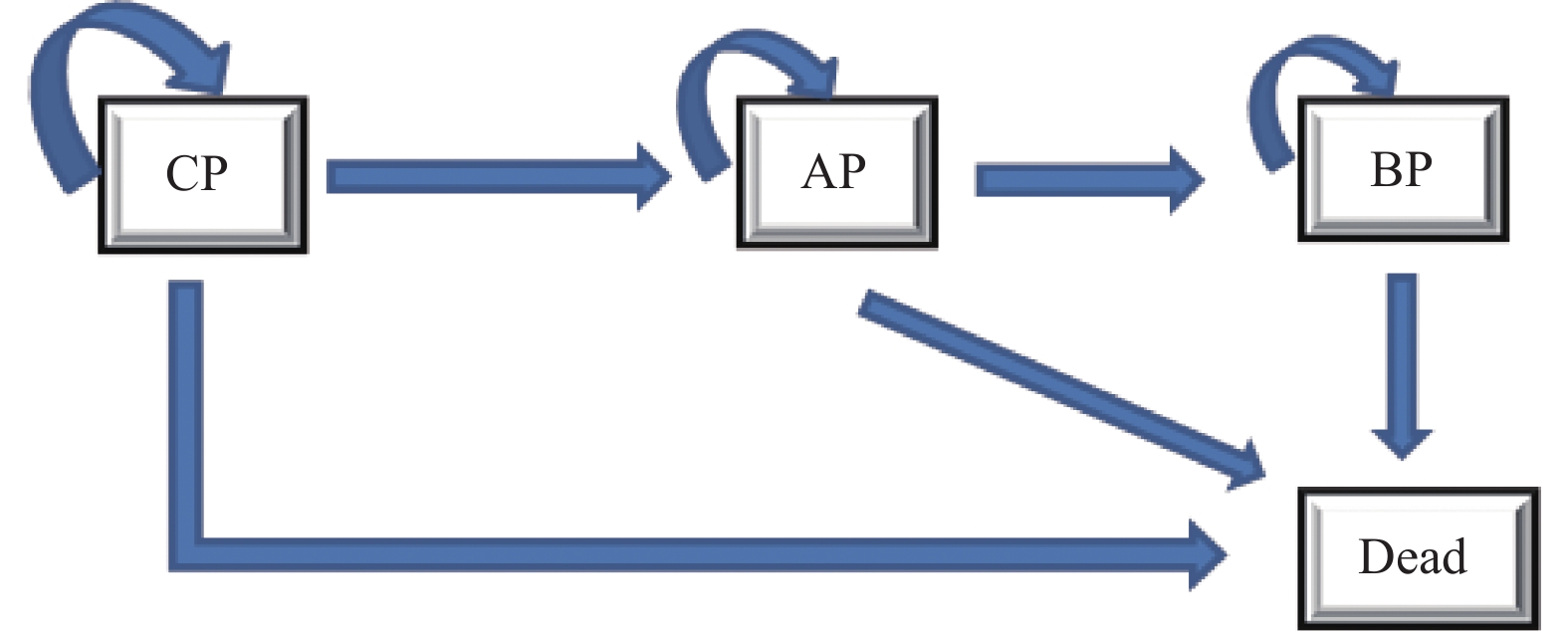
目的 评估费城染色体阳性慢性髓性白血病慢性期(Ph+CML-CP)患者中对伊马替尼耐药或不耐受的二线尼洛替尼与达沙替尼的成本效果。 方法 建立状态转移马尔可夫(Markov)模型进行成本效用分析,模型包括4种健康状态:慢性期(CP),加速期(AP),急变期(BP)和死亡。尼洛替尼与达沙替尼治疗的无进展生存率,疾病进展发生率,总生存率等有关临床参数来源于既往发表的研究和专家意见,健康状态效用值来源于文献。通过Treeage软件以增量成本效果比(ICER)作为评价指标,对尼洛替尼和达沙替尼2个方案的总产出和总成本进行评价,并通过单变量、概率敏感性分析评估模型稳定性。 结果 与选用达沙替尼治疗相比,选用尼洛替尼治疗的ICER 为182487.71元·QALY-1,低于3倍2021年全国人均GDP。敏感性分析显示主要的影响参数有贴现率,达沙替尼价格和尼洛替尼价格,模型结果稳定。 结论 选用尼洛替尼相对达沙替尼用于对伊马替尼耐药或不耐受的Ph+CML-CP患者治疗具有成本效用优势。 Abstract:Objective To evaluate the cost-effectiveness of nilotinib versus dasatinib in the second-line treatment of Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase. Methods Establish a Markov model for cost-effectiveness analysis, including four health states: chronic phase (CP), accelerated phase (AP), blast phase (BP), and death. Clinical parameters related to progression-free survival rates, disease progression rates, overall survival rates, etc. for treatment with nilotinib and dasatinib are derived from previously published studies and expert opinions, while health state utility values are sourced from the literature. Using Treeage software, the incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) was used as an evaluation metric to assess the total output and total costs of the two schemes of nilotinib and dasatinib, and model stability is evaluated through univariate and probabilistic sensitivity analyses. Results Compared with using dasatinib for treatment, the ICER for using nilotinib treatment is 182487.71 yuan per QALY, which is less than 3 times the national per capita GDP in 2021. Sensitivity analysis showed that the main influencing parameters are the discount rate, dasatinib price, and nilotinib price, and the model results are stable. Conclusion Nilotinib has a cost-utility advantage over dasatinib in the treatment of Ph+CML-CP patients who are resistant or intolerent to imatinib. -
Key words:
- Nilotinib /
- Dasatinib /
- Chronic myeloid leukemia /
- Cost-effectiveness analysis /
- Second-line treatment
-
表 1 状态转移概率
Table 1. Transition probability
表 2 药品成本
Table 2. Drug cost
药品名称 规格 生产产家 价格(元/盒) 达沙替尼 50 mg/片,60片/盒 AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals LP 7274.16 20 mg/片,60片/盒 3607.00 50 mg/片,7片/盒 正大天晴药业集团股份有限公司 377.11 20 mg/片,7片/盒 186.99 50 mg/片,7片/盒 石药集团欧意药业股份有限公司 373.25 20 mg/片,7片/盒 185.08 尼洛替尼 200 mg/粒,120粒/盒 Novartis PharmaSte 11030.40 150 mg/粒,120粒/盒 8850.00 药品价格来源于药智网(https://www.yaozh.com/)。 表 3 成本与效用参数
Table 3. Cost and utility parameters
参数模型 均值 下限 上限 概率分布 文献来源 药品成本(元/d) 尼洛替尼CP期#
尼洛替尼AP期#
尼洛替尼BP期#367.68(295)
367.68(295)
367.68(295)275.76(221.25)
275.76(221.25)
275.76(221.25)404.45(324.5)
404.45(324.5)
404.45(324.5)Gamma
Gamma
Gamma药智网
药智网
药智网达沙替尼CP期
达沙替尼AP期
达沙替尼BP期242.47
362.71
362.71106.64
159.52
159.52266.72
398.98
398.98Gamma
Gamma
Gamma药智网
药智网
药智网其他成本 (元) 门诊挂号费 15.00 10.50 19.50 Gamma * 全血细胞计数和外周血分类 24.00 16.80 31.20 Gamma * 骨髓细胞遗传学分析、荧光原位杂交 642.00 449.40 834.60 Gamma * 定量聚合酶链反应检测BCR-ABL 350.00 245.00 455.00 Gamma * 聚合酶链反应扩增BCR-ABL转录本后测序 1292.00 904.40 1679.60 Gamma * 效用值 CP期使用尼洛替尼效用值 0.810 0.648 0.972 Beta [16] CP期使用达沙替尼效用值 0.780 0.624 0.936 Beta [17] AP期效用值 0.650 0.520 0.780 Beta [18] BP期效用值 0.53 0.424 0.636 Beta [12] 死亡 0 Beta 不良反应 1563.32 1094.32 2023.32 Gamma [17] 贴现率(%) 5 0 8 Beta [19] #括号内为数值尼洛替尼用量为300 mg q12 h ;* 2022年云南省三级甲等医院收费标准。 表 4 成本效果分析
Table 4. Cost-effectiveness results
治疗方案 尼洛替尼用法用量 QALYs 总成本/元 ICER/元·QALY−1 达沙替尼 8.77 257929.14 尼洛替尼 400 mg q12 h(100%) 9.11 319830.67 182487.71 300 mg q12 h(45.9%) 9.11 292090.70 100709.42 -
[1] 中华医学会血液学分会. 慢性髓性白血病中国诊断与治疗指南(2020年版)[J]. 中华血液学杂志,2020,(5):353-364. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-2727.2020.05.001 [2] Morel F,Ka C,Le Bris MJ,et al. Deletion of the 5' abl region in Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myeloid leukemia[J]. Leukemia,2003,17(2):473-474. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2402816 [3] Melo J V. The diversity of BCR-ABL fusion proteins and their relationship to leukemia phenotype[J]. Blood,1996,88(7):2375-2384. doi: 10.1182/blood.V88.7.2375.bloodjournal8872375 [4] Baccarani M,Cortes J,Pane F,et al. Chronic myeloid leukemia: An update of concepts and management recommendations of European Leukemia Net[J]. J Clin Oncol,2009,27(35):6041-6051. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.25.0779 [5] Mace M L,Dahl J,Jabbour E J. Which tyrosine-kinase inhibitor to use first in chronic phase chronic myelogenous leukemia?[J]. Expert Opin Pharmacother,2015,16(7):999-1007. [6] Radich J P, Deininger M, Abboud C N, et al. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: Chronic myelogenous leukemia (2023, Version 1) [M/OL]. [2023-1-23]. https://www.nccn.org//login?ReturnURL=https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/cml.pdf [7] 陈琳,杨敏,程国华. 尼洛替尼与达沙替尼二线治疗慢性髓系白血病的药物经济学评价[J]. 肿瘤,2016,36(6):698-704,710. [8] 徐伟,高楠,马丽,等. 大剂量伊马替尼、达沙替尼和尼洛替尼治疗慢性髓性白血病的成本效用分析[J]. 中国医院药学杂志,2017,37(19):1974-1978. [9] Bonifacio M,Maheshwari V,Tran D,et al. Economic model to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of second-line nilotinib versus dasatinib for the treatment of Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myeloid leukemia (CML-CP) in Italy[J]. Pharmacoecon Open,2022,6(1):95-104. doi: 10.1007/s41669-021-00286-3 [10] Li N,Yang X,Fan L,et al. Nilotinib versus dasatinib as second-line therapy in patients with Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase who are resistant or intolerant to imatinib: A cost-effectiveness analysis based on real-world data[J]. J Med Econ,2017,20(4):328-336. doi: 10.1080/13696998.2016.1261032 [11] Yue X,Hincapie A L,Li Y,et al. Safety and cost-effectiveness of ponatinib versus other tyrosine kinase inhibitors as second-line therapy in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia in the United States[J]. Leuk Lymphoma,2022,63(4):946-954. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2021.2002320 [12] Giles F J,Coutre P D L,Pinilla-Ibarz J,et al. Nilotinib in imatinib-resistant or imatinib-intolerant patients with chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase: 48-month follow-up results of a phase II study[J]. Leukemia,2013,27(1):107-112. doi: 10.1038/leu.2012.181 [13] Shah N P,Kim D W,Kantarjian H M,et al. Potent transient inhibition of BCR-ABL with dasatinib 100 mg daily achieves rapid and durable cytogenetic responses and high transformation-free survival rates in chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia patients with resistance,suboptimal response or into[J]. Heamatologica,2010,95(2):232-240. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2009.011452 [14] Griffin J D,Guerin A,Chen L,et al. Comparing nilotinib with dasatinib as second-line therapies in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia resistant or intolerant to imatinib - a retrospective chart review analysis[J]. Curr Med Res Opin,2013,29(6):623-631. doi: 10.1185/03007995.2013.789012 [15] Shah N P,Guilhot F,Cortes J E,et al. Long-term outcome with dasatinib after imatinib failure in chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia: Follow-up of a phase 3 study[J]. Blood,2014,123(15):2317-2324. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-10-532341 [16] Kulpeng W,Sompitak S,Jootar S,et al. Cost-utility analysis of dasatinib and nilotinib in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia refractory to first-line treatment with imatinib in Thailand[J]. Clin Ther,2014,36(4):534-543. [17] Huang X,Jiang Q,Hu J,et al. Four-year follow-up of patients with imatinib-resistant or intolerant chronic myeloid leukemia receiving dasatinib: Efficacy and safety[J]. Front Med,2018,13(3):344-353. [18] Padula W V,Larson R A,Dusetzina S B,et al. Cost-effectiveness of tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment strategies for chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase after generic entry of imatinib in the United States[J]. J Natl Cancer Inst,2016,108(7):djw003. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djw003 [19] 刘国恩. 中国药物经济学评价指南(2020中英双语版)[M]. 北京: 中国市场出版社, 2020: 27-47. [20] Nguyen J T,Cole A L,Leech A A,et al. Cost-effectiveness of first-line tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy initiation strategies for chronic myeloid leukemia[J]. Value Health,2020,23(10):1292-1299. doi: 10.1016/j.jval.2020.05.019 [21] Li N,Zheng B,Cai H F. et al. Cost effectiveness of imatinib,dasatinib,and nilotinib as first-line treatment for chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia in china[J]. Clin Drug Investig,2018,38(1):79-86. doi: 10.1007/s40261-017-0587-z [22] Cai D,Shi S,Jiang S,et al. Estimation of the cost-effective threshold of a quality-adjusted life year in China based on the value of statistical life[J]. Eur J Health Econ,2022,23(4):607-615. doi: 10.1007/s10198-021-01384-z -





 下载:
下载: