2020 Vol. 41, No. 11
2020, 41(11): 18-24.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20201128
Abstract:
Objective To isolate the enterovirus(EV)from 595 stool samples collected from hand, foot and mouth disease(HFMD)patients from Wenshan prefecture of Yunnan province in 2019 and to analyze the epidemiology of EVs and the genetic characteristics of coxsackievirus A16(CV-A16). Methods Virus isolated from 595 stool samples was carried out and the VP1 gene of 74 positive samples was amplified and identified by sequencing and the genetic characteristics and molecular epidemiology of CV-A16 were analyzed. Results Seventy-four strains of EVs were isolated from 595 samples with an isolation rate of 12.44(74/595), of which, 72 strains were enterovirus species A(EV-A), accounting for 97.30%(72/74), 2 strains were EV-B, accounting for 2.70%(2/74), EV-C and EV-D viruses were not isolated. Among EV-A viruses, CV-A6 was most frequently isolated, accounting for 61.11%(44/72), CV-A16 was the second, accounting for 19.44%(14/72), 9 strains were CV-A10, accounting for 12.50%(9/72). The genetic characteristics analysis showed that all 14 strains of CV-A16 belonged to subgenotype B1, they were further divided into 2 subgenotypes(B1a and B1b), among which, 8 strains were B1a subgenotype, 6 strains were B1b subgenotype. Conclusions The main etiology of HFMD in Wenshan prefecture in 2019 was CV-A6, CV-A16 was the second. Two subgenotypes(B1a and B1b)of CV-A16 co-circulated in Wenshan prefecture in 2019.
2020, 41(11): 30-37.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20201124
Abstract:
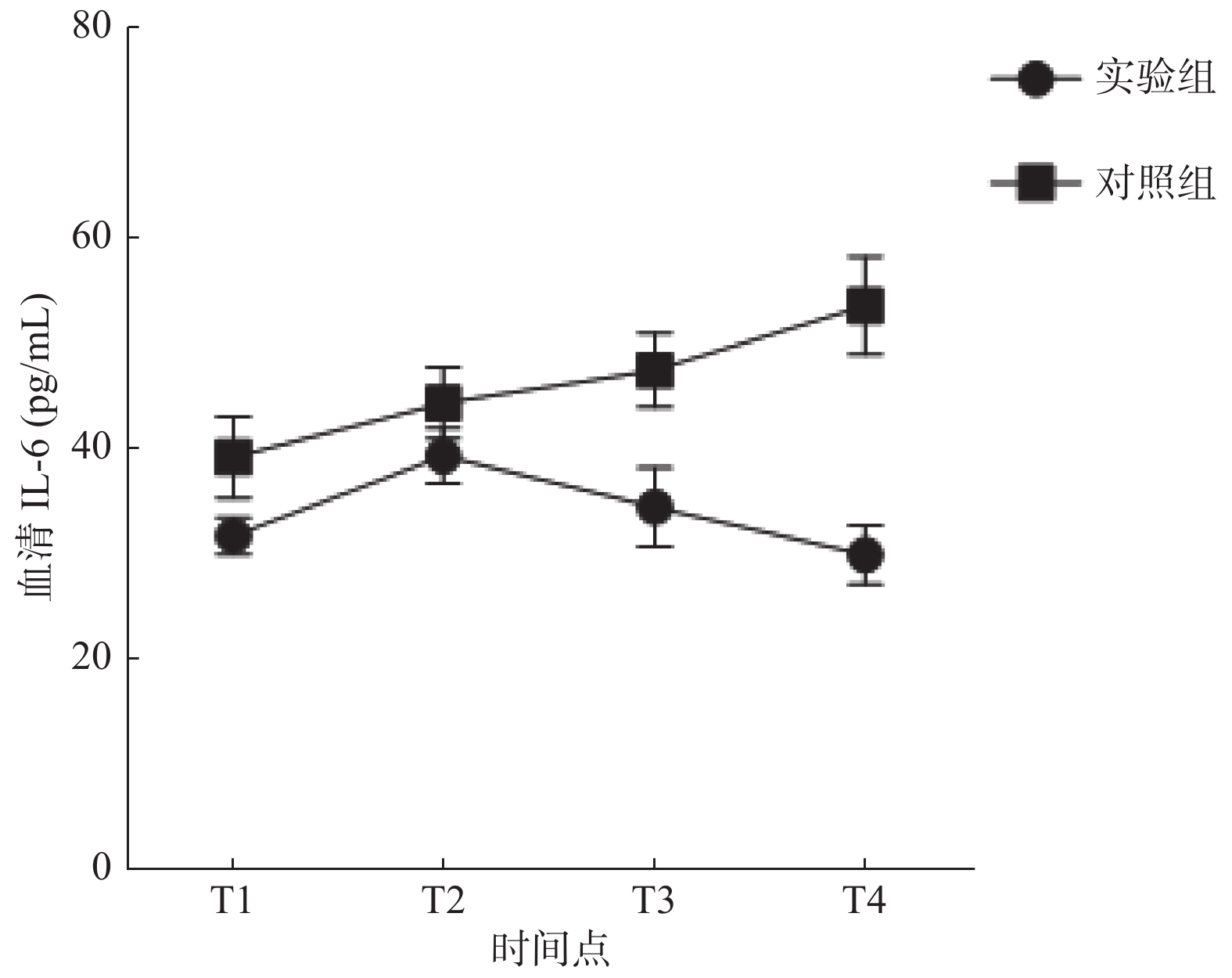
Objective To investigate the effects of dexmedetomidine (DEX) on inflammatory response and expression of inflammatory factors in lung tissue of rats with smoke inspiratory lung injury. Methods Seventy-eight healthy and clean adult SD rats were selected from the same batch. Among them, the rats were randomly selected to be injured in the smoke chamber(six rats died)and divided into experimental group (DEX 4.5 ug/kg static injection, n = 32) and control group (same amount of normal saline static injection, n = 32). The remaining 8 rats were used as the blank group without any intervention.According to the different time points of administration, the experimental group and the control group were divided into 4 subgroups, with 8 in each group. The DEX solution was injected through the tail-vein at 4 time points after the smoke injury: half an hour (T1), 12 hours (T2), 24 hours (T3) and 48 hours (T4), respectively.Blood samples were dissected and collected half an hour after administration, and serum and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid levels of tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) were measured by ELISA. Lung tissue was taken to observe the pathological changes of bronchi and alveoli at each time point after injury, and the results were compared with those of the healthy group. Results Compared with the healthy rats in the blank group, all the injured rats were successfully modeled.Compared with the control group, the serum and alveolar lavage fluid of the experimental group showed reduced levels of TNF-αand IL-6 (P < 0.05), especially in the T4stage. TNF-αand IL-6 in the serum of the control group increased continuously with time ( P < 0.05), while TNF-αand IL-6 in the experimental group first increased and then decreased, reaching a peak at 12 hours, and then decreased slowly ( P < 0.05). In alveolar lavage fluid, the inflammatory cytokines in the experimental group increased first and then decreased with time, in which il-6 decreased after reaching the peak at 12 hours, and TNF- radiation decreased after reaching the peak at 24 hours ( P < 0.05). Compared with the healthy group, a large number of inflammatory cells were observed around the alveoli of rats in the experimental group and control group under the light microscope. Moderate and severe inflammatory reactions were dominant in the control group, and mild inflammatory reactions were dominant in the experimental group ( P < 0.05). Conclusion Dexmedetomidine can significantly down-regulate the expression of inflammatory factors in rats with inhalation lung injury, promote the repair of lung tissue injury, and thus play a protective role in lung.
2020, 41(11): 1-6.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20201107
Abstract:
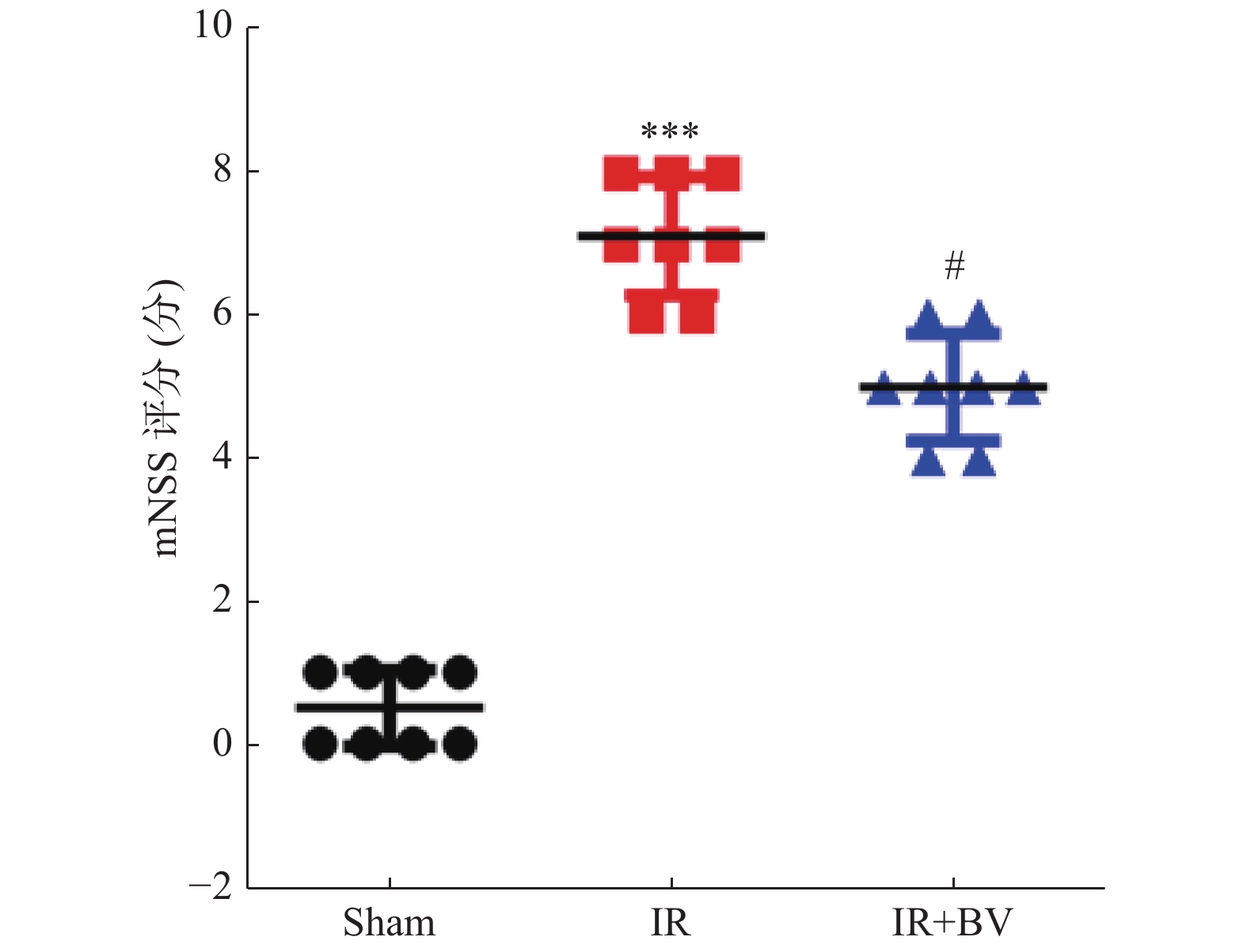
Objective To investigate the protective effect and underlying mechanism of biliverdin on cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Methods The middle cerebral artery occlusion model(MCAO)was established by inserting nylon thread, after biliverdin treatment, the neurological deficit were evaluated by modified neurological severity score, the brain water content were detected by dry and wet weight method, the cerebral infarction were detected by TTC staining, the activation of microglia in ischemic brain tissue were marked by Iba-1/DAPI staining, the expression of TNF-α were detected by immunofluorescence staining, the protein expression of Iba-1/CD68 were detected by Western blot. Results Compared with the IR group, after biliverdin treatment, the neurological deficits were improved(P < 0.05), Meanwhile, the brain water content was reduced(P < 0.05), and the cerebral infarction were attenuated(P < 0.05). What's more, the microglia expression and Iba-1/CD68 protein expression were decreased(P < 0.05)and the inflammatory factor TNF-α expression was also reduced(P < 0.05). Conclusion Biliverdin may attenuate cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting microglia activation in rats.
2020, 41(11): 7-11.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20201103
Abstract:
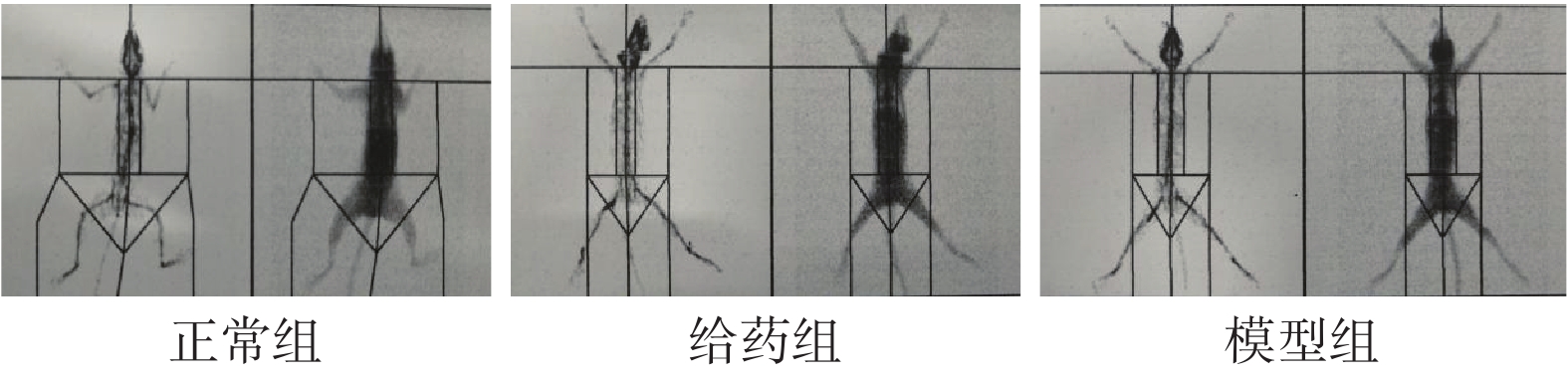
Objective To observe the effect of osteoking on bone density and bone biomechanics in a postmenopausal osteoporotic fracture(OPF)model tree shrew. Methods Female western Yunnan subspecies tree shrews were subjected to bilateral ovariectomy and hysterectomy to establish an osteoporosis(OP)model, and after 180 days, bone density(BMD)was measured in tree shrews, and 20 OP modeling successes were randomly and equally divided into administration(3 mL/kg)and model groups(equal volume of 0.9% sodium chloride solution). Ten tree shrews with the same volume of large omentum removed were divided into normal groups(equal volume of 0.9% sodium chloride solution). The tree shrews in the drug-administered and model groups were subjected to right hindlimb tibial fracture surgery to establish the OPF model. The administration group was given one dose of saline every 2 d for 90 d, and the remaining group was given the same dose of saline. Results Compared with the normal group, the BMD of whole body(including head), lumbar + pelvic, cervical-caudal, left pelvis, right pelvis, lumbar spine, lumbar + sacral, and whole body(excluding head)were significantly reduced to different degrees in the administered and model groups, and the differences were statistically significant(P < 0.05). Compared with the model group, the BMD of the whole body(including the head), lumbar + pelvic, cervical-caudal, left pelvis, lumbar spine, and lumbar + sacral were significantly increased in the administration group, and the differences were statistically significant(P < 0.05), while the BMD of the right pelvis and whole body(excluding the head)were not statistically different. In terms of bone biomechanics, energy absorption was significantly increased in the administered group compared to the normal group, while maximum load and structural stiffness were not statistically difference; the maximum load, structural stiffness, and energy absorption capacity of the model group were all significantly reduced, and the differences were statistically significant(P < 0.05). The maximum load, structural stiffness, and energy absorption capacity of the model group were all significantly reduced compared to the drug-administered group, and the differences were statistically significant(P < 0.05). Conclusion Osteoking can improve both BMD and bone biomechanics in the OPF model of tree shrew.
2020, 41(11): 12-17.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20201101
Abstract:
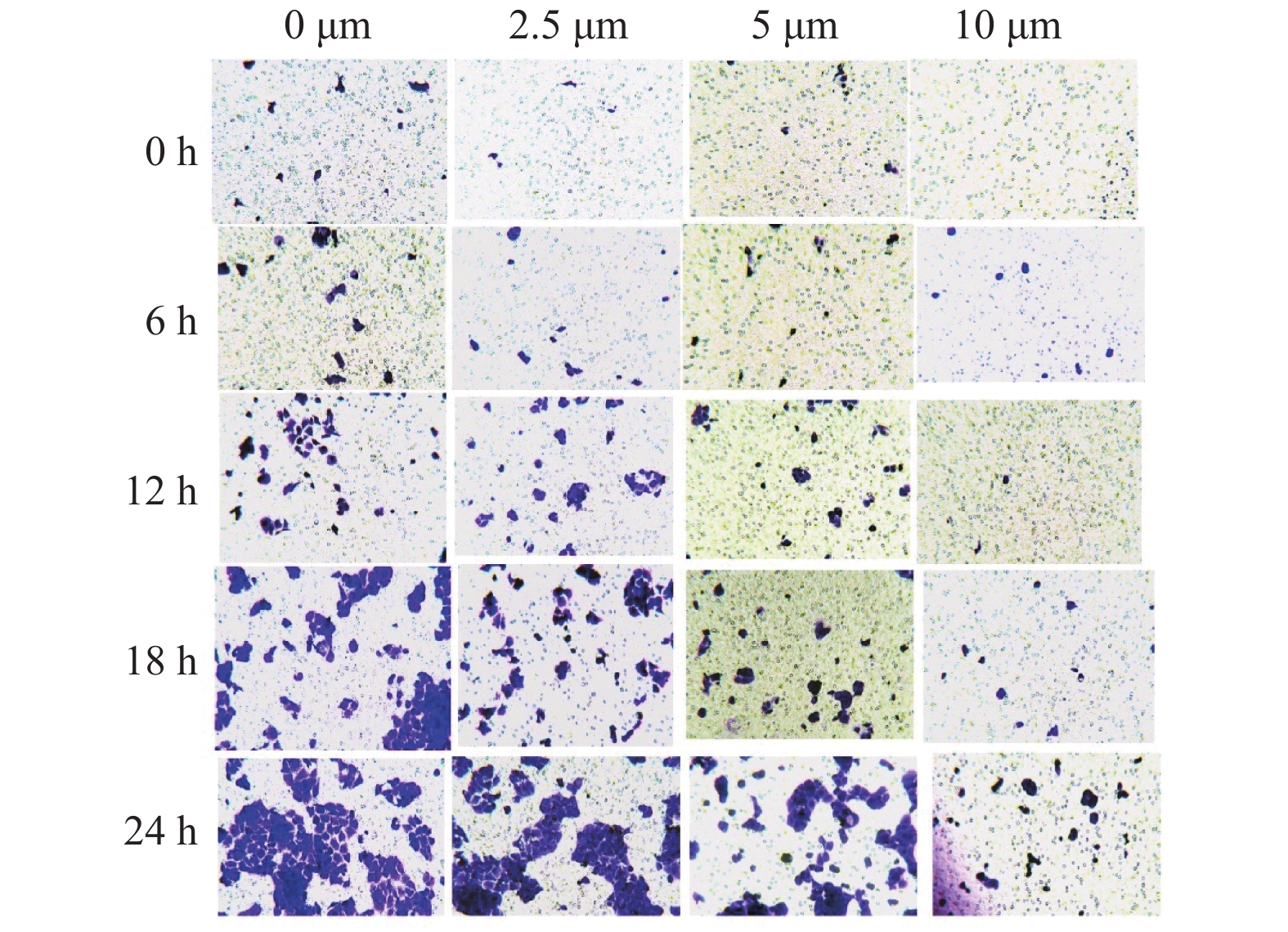
Objective To observe the effect of gossypol acetate acid(GAA)on the invasion of human tongue squamous cell carcinoma Cal-27 cells in vitro. Methods GAA of different concentrations(0 μmol/L, 2.5 μmol/L, 5.0 μmol/L, 10.0 μmol/L)was acted on Cal-27 cells, Transwell experiment was employed to detect the inhibitory effect of GAA on the invasion of Cal-27 cells. The effect of gossypol acetate on MMP-2 and MMP-9 mRNA expression was quantified by qRT-PCR. The effect of gossypol acetate acid on MMP-2 and MMP-9 protein expression was analyzed by Western-Blot experiment. Results Cell Transwell chamber experiment showed that GAA could inhibit the migration of human tongue squamous cell carcinoma Cal-27 cells, and the amount of invasion decreased with the increase in concentration. The difference between the control group and the experimental group was statistically significant(P < 0.05). qRT-PCR experiment and Western-blot results showed that the expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9 mRNA and proteins was significantly reduced after Cal-27 cells of human tongue squamous cell carcinoma was treated with GAA, and the difference between the control group and the experimental group was statistically significant(P < 0.05). Conclusions GAA can reduce the invasiveness of tongue squamous cell carcinoma Cal-27 cells. And GAA can reduce the mRNA and protein expression levels of MMP-2 and MMP-9 of human tongue squamous cell carcinoma Cal-27 cells.
2020, 41(11): 25-29.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20201117
Abstract:
Objective To study the antagonistic effect of total flavonoids of Panax notoginseng on osteoporosis induced by glucocorticoid and its possible mechanism. Methods Fifty female SD rats(SPF-grade)weighing about 170 g were randomly divided into five groups(10 / group): normal control group, model group(hormone group)and high, medium and low dose treatment group(hormone + drug group)of total flavonoids of Panax notoginseng. Dexamethasone(2.5 mg/kg)was injected intramuscularly twice a week in the model group and total flavonoids of Panax notoginseng treatment groups. At the same time, the three treatment groups were given total flavonoids of Panax notoginseng 275 mg/(kg·d), 137.5 mg/(kg·d)and 68.75 mg/(kg·d)by intragastric administration once a day. The experimental period was 9 weeks. After 9 weeks, bone mineral density(BMD)and indexes reflecting biomechanical properties of femur, serum biochemical indexes were measured. Results Compared with the normal group, the bone mineral density of femur, bone biomechanical properties and the serum calcium level decreased significantly, the serum phosphorus level and the serum alkaline phosphatase activity increased significantly in the model group(P < 0.05). Compared with the model group, the bone mineral density, bone biomechanical properties and the serum calcium level increased significantly, the serum phosphorus level and the serum alkaline phosphatase activity decreased significantly in the high and medium dose treatment group of total flavonoids of Panax notoginseng(P < 0.05). Conclusions Total flavonoids of Panax notoginseng can increase the bone density and improve the biomechanical properties of bone in glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis rats. It has an antagonistic effect on osteoporosis induced by glucocorticoid. The mechanism of action is related to the inhibition of bone absorption and the imbalance of calcium and phosphorus metabolism induced by glucocorticoid.
2020, 41(11): 38-43.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20201111
Abstract:
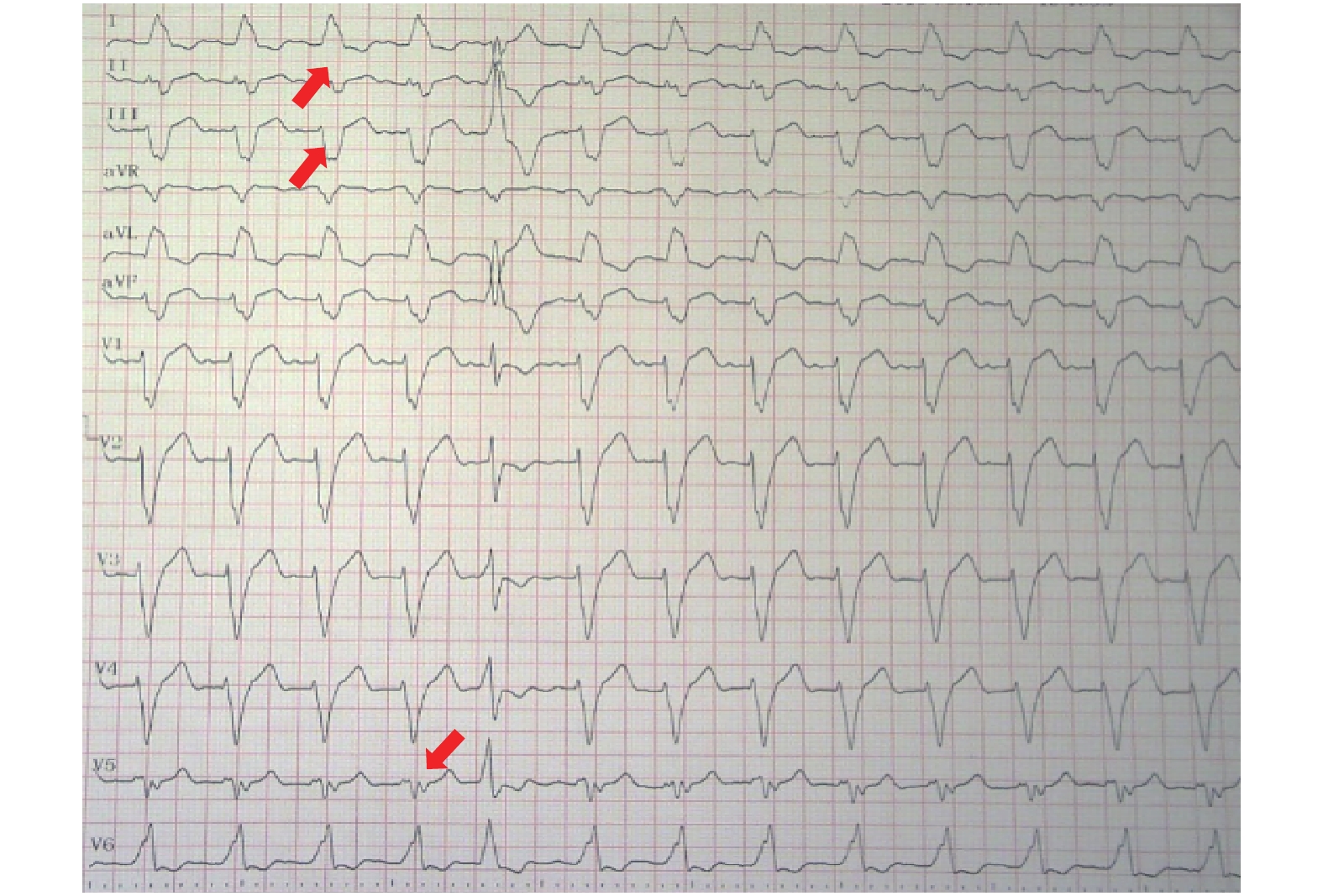
Objestive To investigate the association between characteristics of Fragmented QRS(fQRS)before and after CRT implantation and response to CRT. Methods Patients with heart failure planned for CRT were enrolled. The 12-lead ECGs before and after CRT were analyzed. The presence of fQRs was confirmed according to the definition in previous studies. Echocardiography imagines were obtained before and 6 months after the CRT implantation. Results The study included 108 patients(78 male, 72.2%)with a mean age of 56.5 ± 11.9 years. Totally 75 patients(69.4%)responded to CRT with significantly increased mean LVEF(from 30.71±1.92 to 50.61±2.57, P < 0.001)and decreased LVESV(from 195.26±78.79 to 156.55±84.44, P < 0.001). After CRT implantation, the number of leads with fQRS remained unchanged in responders(6.25±2.68 vs. 6.03±2.54, P= 0.57 before and after CRT respectively)but increased in non-responders(6.18±2.20 vs.7.36±2.61, P = 0.013 before and after CRT respectively). In the multivariate logistic analysis, a decreased number of leads with fQRS and shortened QRS duration immediately after CRT implantation was found to be a predictor of response to CRT. Conclusions In patients undergoing CRT, new fQRS as well as an increased number of leads with fQRS in 12-lead ECG immediately after CRT implantation predicts non-response to CRT and may help in the decision making in heart failure patients.
2020, 41(11): 44-48.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20201131
Abstract:
Objective To explore the difference in the incidence of complications and hospitalization time between exchange transfusion combined with intensive phototherapy and single intensive phototherapy in the treatment of neonatal hyperbilirubinemia. Methods We retrospectively analyzed the data of 121 hyperbilirubinemia in term infants. We compared the difference in the incidence of complications and the hospitalization time between the exchange transfusion combined with intensive phototherapy and single intensive phototherapy in the treatment of neonatal hyperbilirubinemia. We also studied the incidences of anemia when we use different volume ratios of red blood cells and plasma. Results There were more complications in the group of exchange transfusion combined with intensive phototherapy than the intensive phototherapy group, otherwise there was no difference in the hospitalization time between the two groups. The incidence of anemia of the 1:1 exchange transfusion group was higher than that of the 2:1 exchange group. Conclusions All neonates with hyperbilirubinemia should be considered phototherapy for 4 hours or 6 hours and reassess whether they need exchange transfusion therapy to reduce the incidence of complications. If the exchange transfusion therapy is used, it is suggested that the volume ratios of red blood cells to plasma is 2:1 rather than 1:1.
2020, 41(11): 49-54.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20201106
Abstract:
Objective To explore the effect and cost-effectiveness ratio of Integrated Chinese and Western medicine in the treatment of MDR-TB, and to find the best treatment plan. Methods Four hundreds cases of MDR-TB patients in Kunming Third People's Hospital from April 2017 to October 2019 were collected and randomly divided into observation group (200 cases) and control group (200 cases). The control group was treated with Western Medicine Anti Tuberculosis Program: 4D(Pto)LZEV(Mfx)AmkCsCfz/8D(Pto)LZEV(Mfx)CsCfz(D: Isoniazidp-aminosalicylate, Pro: propylthioisoniamine, L: rifapentine, Z: pyrazinamide, E: ethambutol, V: levofloxacin, MFX: moxifloxacin, AMK: amikacin, CS: cycloserine, CFZ: clofazimine). On the basis of the control group, the observation group used antituberculosis Bufei Decoction according to the type of symptoms. The absolute values of CD3+, CD4+, CD8+ in peripheral blood T-lymphocyte subsets, the negative conversion rate of sputum bacteria, the effective rate of focus absorption, the rate of cavity closure, the improvement rate of symptoms in traditional Chinese medicine, the incidence of adverse reactions and the total effective rate of treatment were compared between the two groups after treatment, and the economic evaluation was made by cost-effectiveness analysis. Results At the end of treatment, the absolute values of CD3+, CD4+, CD8+ in the peripheral blood T lymphocyte subsets of the observation group were significantly higher than those of the control group (P < 0.05). The negative rate of sputum bacteria was 86.5% in the observation group and 60.5% in the control group. The effective rate of absorption was 88.5% in the observation group and 58.0% in the control group. The cavity closure rate of the observation group and the control group was 52.0% / 34.5% respectively. The improvement rate of TCM symptoms in the observation group and the control group was 90.5% / 67.0% respectively. The total effective rate of the observation group and the control group was 93.5% / 80.0% respectively. There was significant difference between the two groups (P < 0.01). The incidence of adverse reactions in the observation group and the control group was 5.0% / 9.0% respectively, there was no significant difference between the two groups (P > 0.05). In the economic evaluation, the cost-effectiveness ratio of the observation group and the control group is 31205.9 yuan / 31746.4 yuan respectively, and the incremental cost-effectiveness ratio is 28002.9 yuan. The sensitivity analysis results are consistent with the cost-effectiveness ratio results. Conclusion The combination of traditional Chinese and Western medicine in the treatment of MDR-TB is better than western medicine in improving the efficacy and economic evaluation, which is worthy of clinical promotion.
2020, 41(11): 68-71.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20201123
Abstract:
Objective To explore the effect of aerobic exercise and nutrition management on malnutrition in patients with maintenance hemodialysis. Methods Forty-seven patients with maintenance hemodialysis were given aerobic exercise and nutritional management for 48 weeks, and the conduct self-comp-arison were taken with their nutritional status, protein and calorie intake as well as nutritional indexes before and after the management. Results After aerobic exercise and nutritional management, the patients' nutritional status was significantly improved compared with that before management(P < 0.05). Protein, caloric intake, upper arm muscle circumference on the same side, triceps thickness without internal fistula, serum prealbumin, albumin and hemoglobin all increased which compared with that before management( P < 0.05). Conclusion Reasonable and effective nutrition management and aerobic exercise can significantly improve the nutritional status of patients with maintenance hemodialysis.
2020, 41(11): 143-149.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20201104
Abstract:
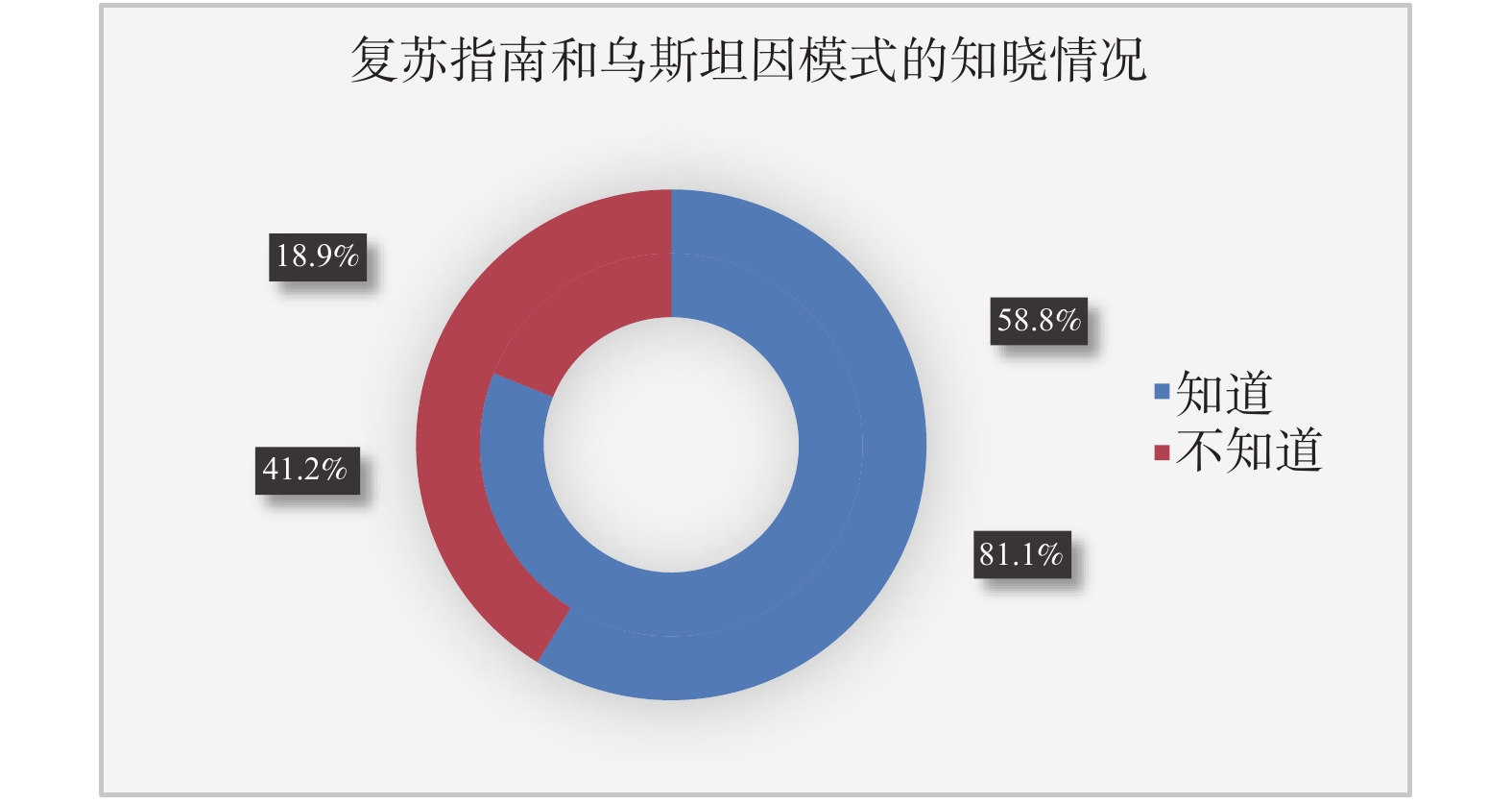
Objective To investigate the knowledge of the Utstein model and the criteria for evaluating the success of resuscitation among Chinese medical staffs. Method A random sampling survey was conducted among the medical staffs in Mainland of China. Results Only 58.8% of the participants had heard of the Utstein model. The awareness rate of the Utstein model was mostly related to whether the participant works in a department where registered the results of resuscitation, nurses, males, young people, senior professional titles and highly educated individuals, staff works in cardiac emergency-related department had a higher awareness rate of Utstein model. However, the awareness rate of high level hospital group was lower than that of the low level hospital group, the group who received a training within 6 months did not have a higher awareness rate than the group who had no training more than 2 years. 84.5% of participants considered that post-defibrillation survival was a standard for successful resuscitation. Additionally, 24.9%, 33.4%, and 18.4% of participants believed that judgment indicators lasted more than 30 seconds, more than 20 minutes, or more than 24 hours indicated successful resuscitation, respectively. Conclusions The awareness rate of Utsteinmodel among the medical staff is low, and the understanding of the term “success of resuscitation” is very confusing in China. It is urgent to strengthen the popularization and application of the Utstein registration model.
2020, 41(11): 62-67.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20201120
Abstract:
Objective To observe the changes of intestinal flora in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and the role in occurrence and development of the disease. Methods One hundred and fifty patients who were diagnosed as NAFLD and 60 healthy controls were randomly selected. Used the relative quantification of Real Time PCR to detecte the expression level of DNA of target bacteria. Results Compared to the control group, the quantity of Lactobacillus and Eubacterium rectale in NAFLD patients were significant increased, Bifidobacterium and Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron were decreased. Conclusion The quantity of Lactobacillus, Eubacterium rectale, Bifidobacterium, Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron in patients with NAFLD may exist structural imbalance of intestinal flora, gut microbiome probably participate in the occurrence and development of NAFLD, improve the intestinal flora imbalance has a certain treatment value in NAFLD.
2020, 41(11): 72-77.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20201105
Abstract:
Objective To compare the effects of two fluid management regimens, goal-directed fluid therapy(GDFT)and restrictive fluid therapy, on patients undergoing thoracoabdominal combined endoscopic esophagectomy for esophageal cancer in the context of prophylactic intravenous pump infusion of low-dose methoxamine 1.0~2.5 μg/(kg·min), in order to provide more optimal fluid management for such patients. Methods Thirty-six patients were scheduled to undergo thoracoabdominal combined with laparoscopic radical esophagectomy foresophageal cancer were divided into goal-directed liquid therapy group(Group G)and restrictive liquid therapy group(Group R)according to random number table method. Group G patients were managed with SVV value of 8%~10%, CI > 2.5 L/(min·m2)as the target. The restrictive infusion regimen was used in group R. HR, MAP, SVV, CO, CI and SV were monitored and recorded before anesthesia induction(T0), after anesthesia induction(T1), two lung ventilation for 15 min(T2), one lung ventilation for 15 min(T3), two lung ventilation for 15 min(T4)after lung recruitment and operation completion(T5); intraoperative infusion volume, crystalloid volume, colloid volume, urine volume, blood loss, the usage of methoxamine and the occurrence of early postoperative complications were recorded. Results At the time points of T4 and T5, the HR of group G was lower than that of group R, and the difference was statistically significant(P < 0.05). The MAP, SVV, CO, CI and SV of group G were higher than those of group R, and the difference was statistically significant(P < 0.05). In terms of fluid intake and output, the total fluid volume in group G was less than that in group R, in which the decrease of crystalloid fluid was the main factor, and the difference was statistically significant(P < 0.05), while the colloidal fluid volume in group G was more than that in group R, the difference was statistically significant(P < 0.05); the intraoperative urine volume in group R was significantly more than that in group G, and the difference was statistically significant(P < 0.05). In terms of complications, the incidence of postoperative nausea and vomiting, cough and expectoration in group G was lower than that in group R. The difference of the pain complications was statistically significant(P < 0.05). Conclusion GDFT combined with low-dose methoxamine is more suitable for fluid management in patients undergoing thoracoabdominal combined laparoscopic esophagectomy for esophageal cancer.
2020, 41(11): 83-87.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20201122
Abstract:
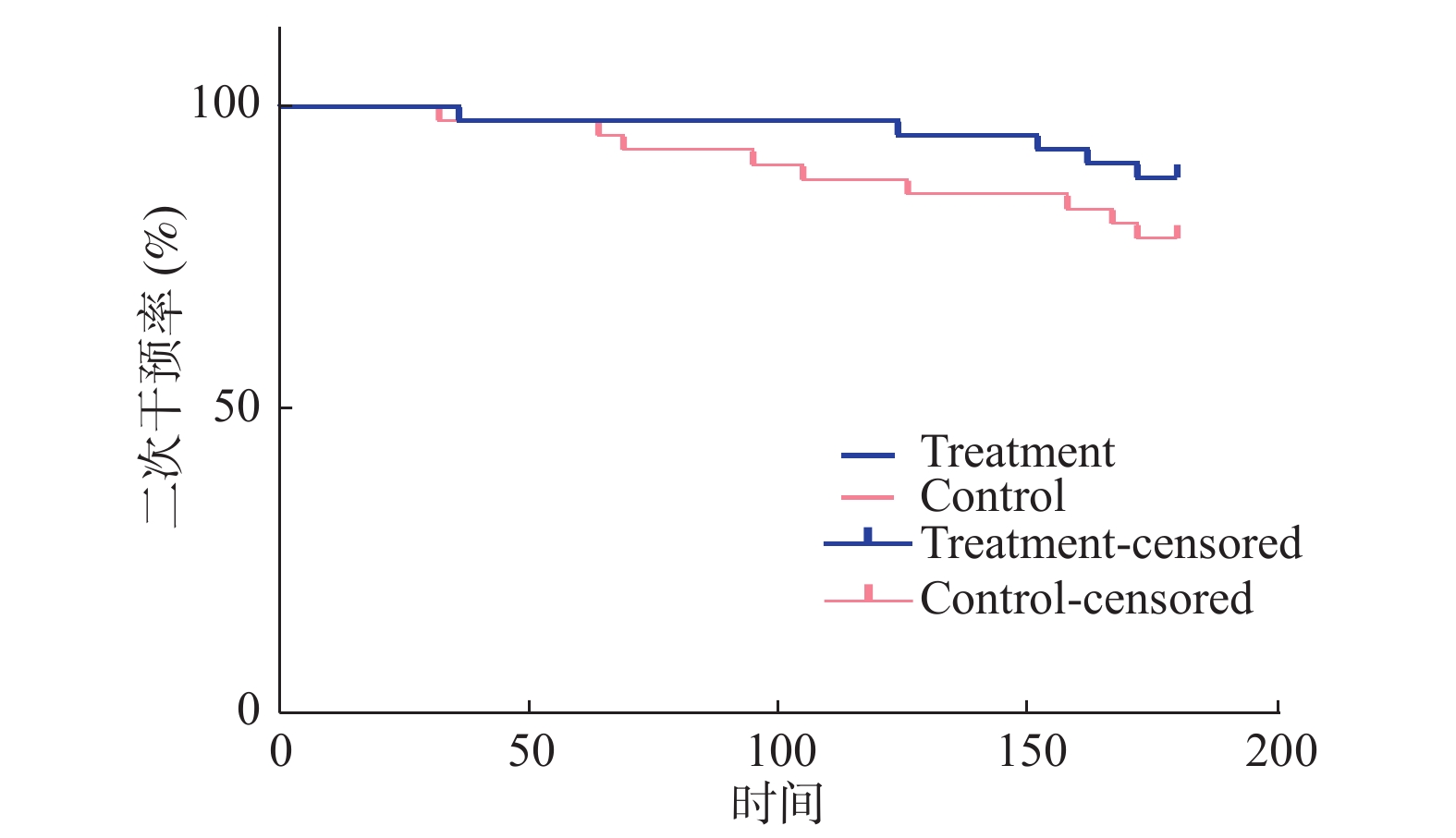
Objective To study the efficacy and safety of rivaroxaban after stent implantation of the femoral popliteal atherosclerosis occlusion stent. Methods Eighty-seven patients who met the criteria were randomly divided into 45 cases in the treatment group and 42 cases in the control group. There was no statistically significant difference in the general information between the two groups. The treatment group was given rivaroxaban tablets 10 mg each time, po, qd and aspirin enteric-coated tablets 100 mg each time, po, qd; the control group was given aspirin enteric-coated tablets 100 mg, po, qd each time, both groups were given Atorvastatin 10 mg, po, qd and Beraprost sodium tablets 40 μg, po, tid, all patients were urged to quit smoking. Observe the relevant efficacy indicators such as ABI, claudication distance, stent restenosis, stent mural thrombosis, and secondary intervention rate of the two groups of patients on the day of postoperative day, 3 months and 6 months after treatment, and the safety indicators such as adverse drug reactions, major adverse cardiacand cerebrovascular events, minor and major bleeding, the results were analyzed statistically. Results At 6 months, there were differences in the stent mural thrombosis, ankle brachial index and claudication distance between the two groups(P < 0.05), no significant difference in in-stent restenosis(P > 0.05), There was no statistically significant difference in the log-rank test of the second intervention rate between the two groups(P > 0.05), and there was no statistical difference in safety comparison between the two groups(P > 0.05). Conclusion Rivaroxaban combined with aspirin can significantly reduce stent mural thrombosis and delay the decline in postoperative ABI and claudication distance, which may benefit the long-term prognosis of patients.
2020, 41(11): 88-92.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20201108
Abstract:
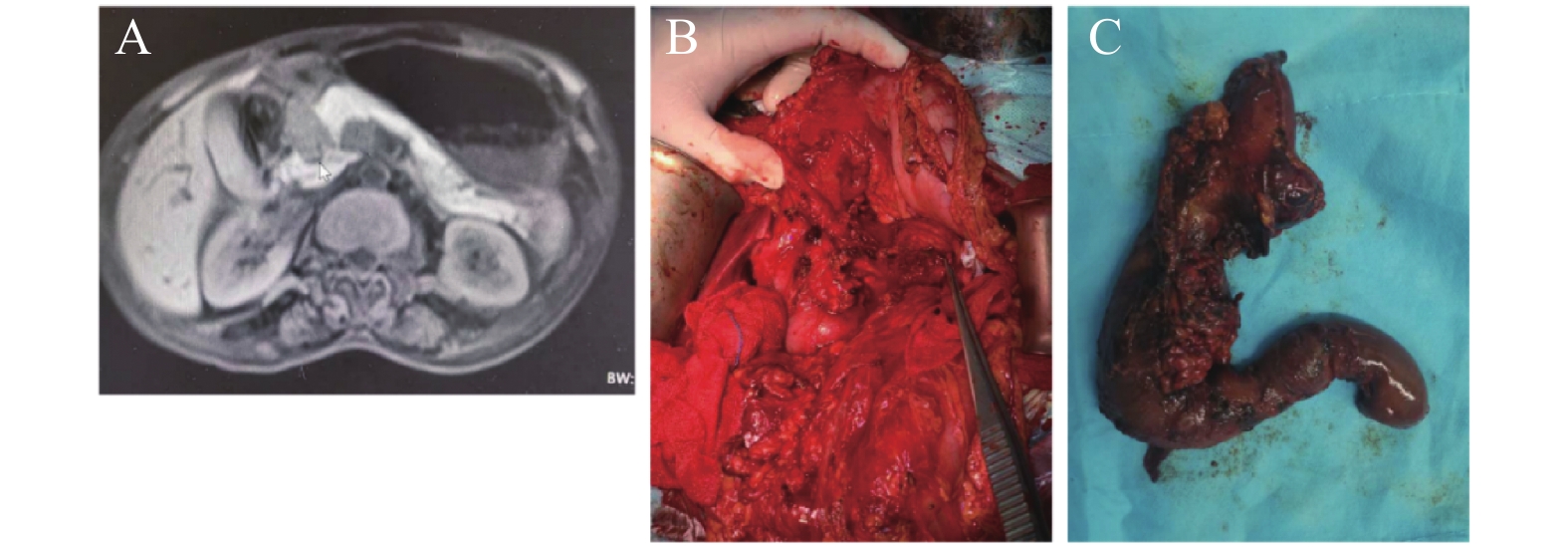
Objective To evaluate the value of emergency pancreaticoduodenectomy in the treatment of blunt duodenal and pancreatic head trauma. Methods Twenty one patients's clinical data who were treated in the second affiliated hospital of Kunming Medical University during January 2018 to January 2020 due to blunt duodenal and pancreatic trauma is retrospectively analyzed. Five patients underwent EPD: 4 males and 1 female; The rest of the patients without emergency pancreatoduodenectomy were non-EPD group, there are 16 cases: 13 males and 3 females. Two groups were compared in terms of average age, average operation time, average intraoperative blood loss, postoperative complications, mortality, average hospital stay and other indicators. Results In the EPD group, the average age was 28.60±5.18 years, the average operative time was 270.00±47.43 minutes, the intraoperative blood loss was 450.00±165.83 ml, the average length of hospitalization was 15.00±4.85 days, there was 1 case of postoperative pancreatic fistula, 1 case of localized effusion, and no postoperative death. In the non-EPD group: the average age was 40.81±12.48 years; the average operative time was 266.88±96.73 minutes; the intraoperative blood loss was 695.63±399.02; the average length of hospital stay was 53.19±27.58 days. There were 11 cases of postoperative pancreatic fistula, 5 cases of bile fistula, 6 cases of intestinal fistula, 12 cases of infection, 9 cases of localized effusion and 3 cases of postoperative death. The average age in the EPD group was significantly lower than in the non-EPD group(P < 0.05). The average hospital stay and the incidence of postoperative infection complications in the emergency pancreaticoduodenal surgery group were significantly lower than in the non-EPD group(P < 0.05). 16 patients were followed up in outpatient clinics for 3-24 months, and the average follow-up time was 11.64±5.57 months. EPD group didn't have any postoperative complications. In the non EPD group, 3 patients recovered after gastrojejunostomy due to duodenal stenosis from 1 to 5 months after discharge, and 1 patient improved after endoscopic plastic stent implantation due to benign biliary stricture 7 months after discharge. Conclusions EPD is safe and feasible for the patients with blunt duodenal and pancreatic head trauma, especially for who have been injured for less than 24 hours and whose abdominal infection has not widespread. In this case, Chen's pancreaticoduodenal anastomosis is an important guarantee for successful surgery.
2020, 41(11): 98-102.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20201125
Abstract:
Objective To study the preventive and therapeutic effect of dexmedetomidine hydrochloride on shivering reaction of caesarean section patients during combined spinal-epidural anesthesia. Methods Sixty patients undergoing caesarean section under combined spinal-epidural anesthesia in Yan'an Hospital affiliated to Kunming Medical University from September to December in 2019 were randomly divided into experimental group and control group.0.5 μg/kg. Dexmedetomidine hydrochloride was pumped within 10 minutes immediately after the umbilical cord was cut off in the experimental group. The control group was given the same dose of saline. The ECG, BP, HR, SpO2, RR, sedation(according to Ramsay sedation score), shivering reaction(according to Wrench grade)and nausea and vomiting were observed continuously before anesthesia(T0), 5 minutes after anesthesia(T1), at the time of fetal delivery(T2), 10 minutes after fetal delivery(T3), at the end of operation(T4). Results The level of shivering reaction in the experimental group was lower than that in the control group(P < 0.05). There was no significant difference in BP, HR, SpO2 between the two groups at corresponding time points(P > 0.05). Ramsay sedation score at T3 and T4 was significantly higher than that at T0 in the experimental group(P < 0.05), and significantly higher than that in the control group(P < 0.05). Conclusion The application of dexmedetomidine during combined spinal-epidural anesthesia in cesarean section can effectively prevent and treat shivering reaction.
2020, 41(11): 103-108.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20201121
Abstract:
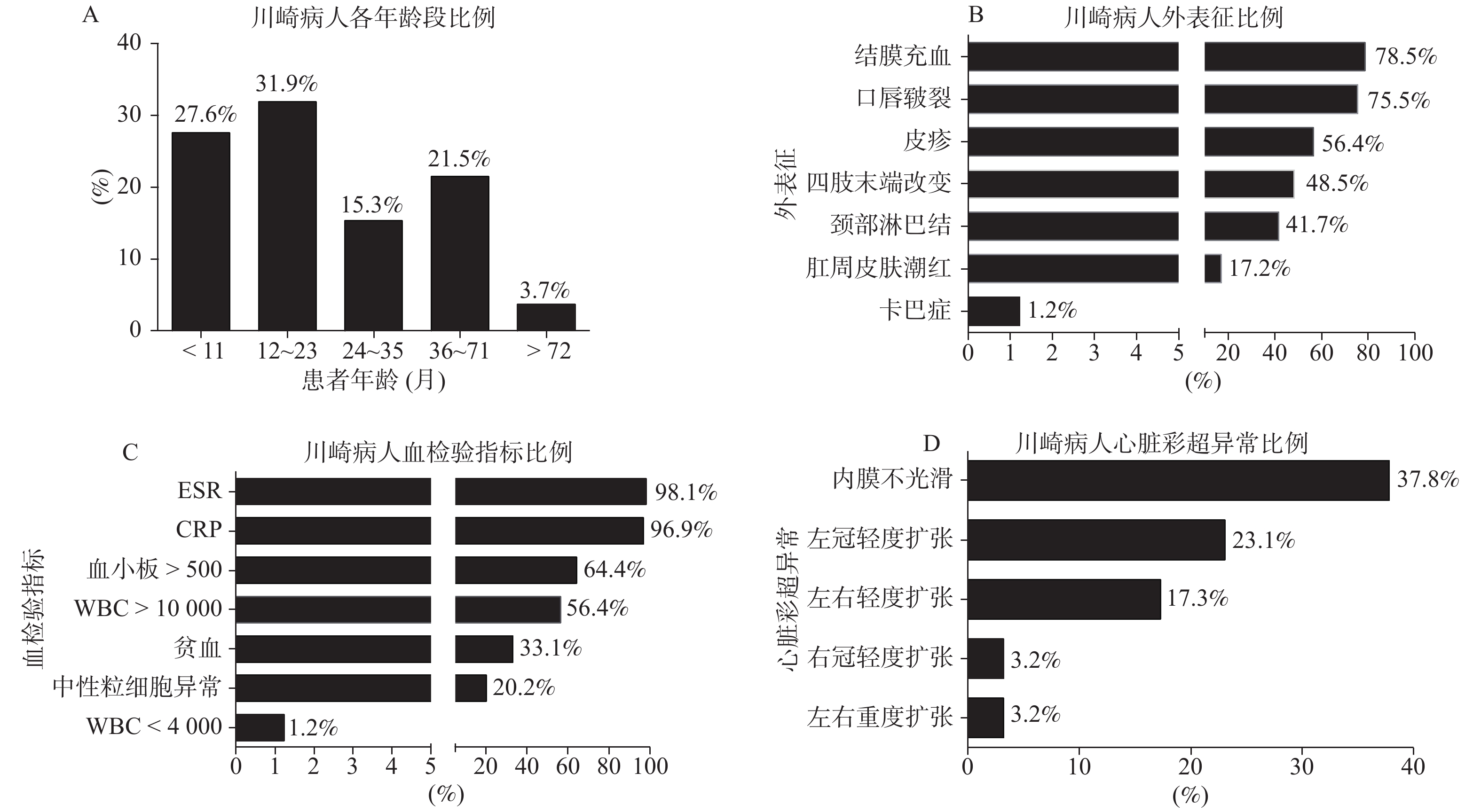
Objective To investigate the incidence and clinical features of Kawasaki disease(KD)among children in Yunnan province. Methods A total of 163 patients with Kawasaki disease were studied retrospectively. All of them were treated in the Third People's Hospital of Yunnan Province in Kunming from January 2013 to December 2018. The clinical features and lymphocyte subpopulations in the patients with Kawasaki disease were analyzed. Results 59.51% of the patients were 0~2 years old. Patients had conjunctival congestion, chapped lips, rash, abnormal erythrocyte sedimentation rate(ESR), elevated C-reactive protein(CRP), platelet count greater than 500, and white blood cell(WBC)greater than 10 000. In addition, extremity changes, cervical lymphadenopathy, perianal skin flushing, kappa disease, anemia, neutrophil abnormalities, and WBC less than 4000 were also detected in patients with Kawasaki disease. The results of color Doppler ultrasound showed that the intima of Kawasaki patients was not smooth and the left and right coronary arteries were dilated. CD19+ was increased in 93.66% of Kawasaki disease patients, and other lymphocyte subsets were also changed. CD3+CD8+ and CD3+CD4+ were significantly correlated with age(Pearson Correlation Coefficicient > 0.2). Conclusion Children under 2 years old are susceptible groups, and there are significant immunologic disorders in acute phase in the patients with Kawasaki disease. It is more scientific and reasonable to diagnose Kawasaki disease by combining the characteristics of Kawasaki disease, blood parameters, cardiac color Doppler ultrasound and lymphocyte subsets.
2020, 41(11): 109-113.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20201102
Abstract:
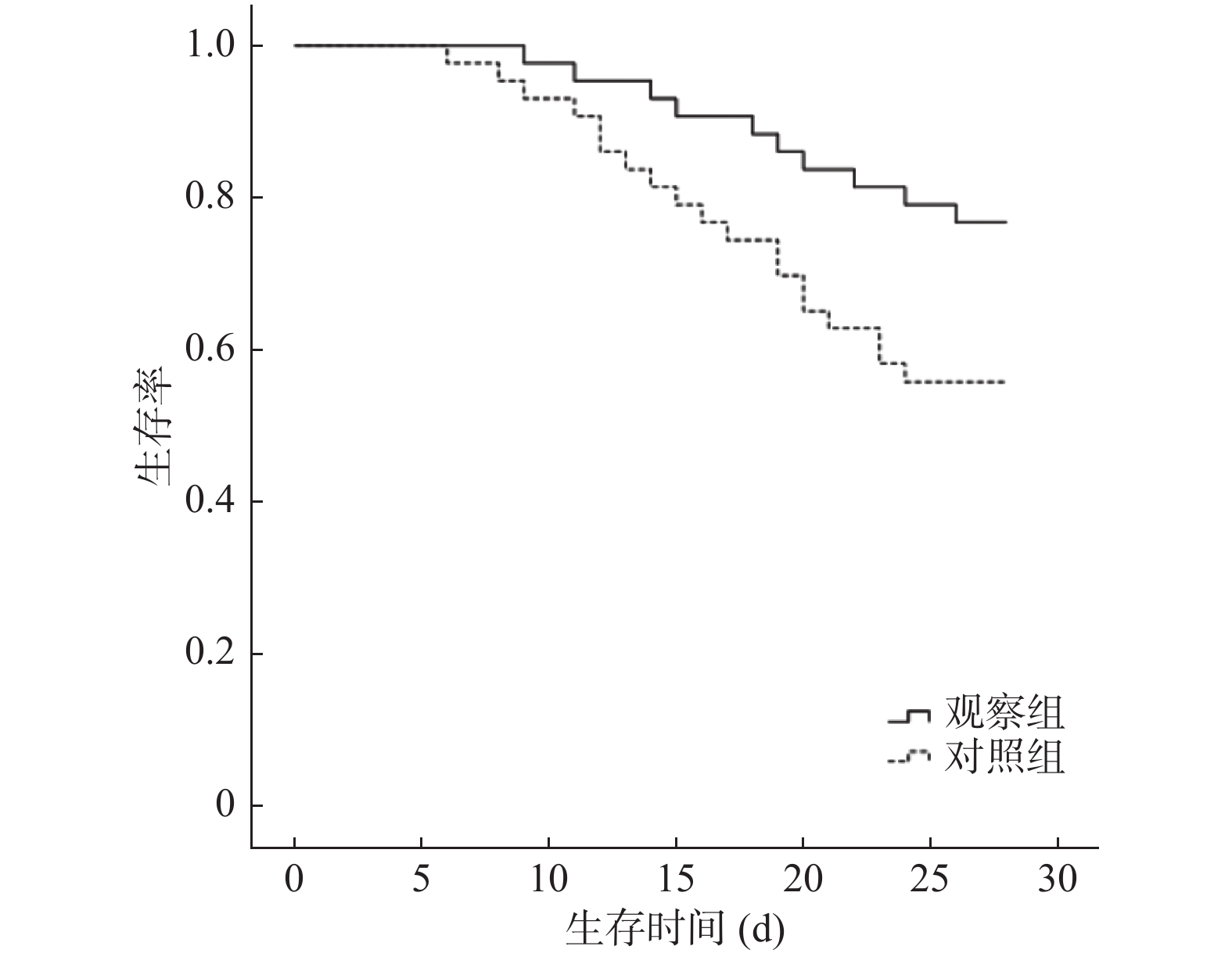
Objective To explore the effect of ulinastatin combined with continuous renal replacement therapy(CRRT)on inflammatory factors and 28-day all-cause mortality in severe burns. Methods A selection of 86 patients with severe burns admitted to the Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University from January 2017 to August 2019 were divided into CRRT group and Ulinastatin combined CRRT group according to the random number table, with 43 cases in each group. CRRT group: conventional treatment + CRRT, ulinastatin combined with CRRT group: combined with ulinastatin on the basis of CRRT group for 7 consecutive days. Compare the critical scores(APACHEⅡ score, SOFA score, Marshall score), serum inflammatory factors(TNF-α, IL-6, IL-8), antibiotics and vasoactive drugs before treatment and 7 days after treatment between the two groups. The duration of mechanical ventilation and 28-day all-cause mortality. The Kaplan-Meier survival curve was drawn to analyze the 28-day survival of the two groups of patients. Results Before treatment, there was no significant difference in APACHEⅡ, SOFA, and Marshall scores between the two groups of patients(P > 0.05). The scores of the two groups of patients after 7 days of treatment were significantly lower than those before treatment(P < 0.05). The APACHEⅡ, SOFA, and Marshall scores of the patients in the Ulinastatin combined CRRT group were significantly lower than those in the CRRT group after 7 days of treatment(P < 0.05). Before treatment, the differences in serum TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-8 between the two groups were not statistically significant(P > 0.05). After 7 days of treatment, serum TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-8 of the two groups were lower than before treatment(P < 0.05). The serum TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-8 of patients in the ulinastatin combined CRRT group were significantly lower than those in the CRRT group after 7 days of treatment(P < 0.05). There was a statistically significant difference in 28-day all-cause mortality between the ulinastatin combined CRRT group and the CRRT group(23.26% vs 44.19%, P < 0.05). Conclusion Ulinastatin combined with CRRT in the treatment of severe burn patients can reduce APACHEⅡ, SOFA and Marshall scores, serum TNF-α, IL-6, IL-8 levels and 28-day all-cause mortality, shorten the treatment time, and have better efficacy and high safety.
2020, 41(11): 114-118.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20201109
Abstract:
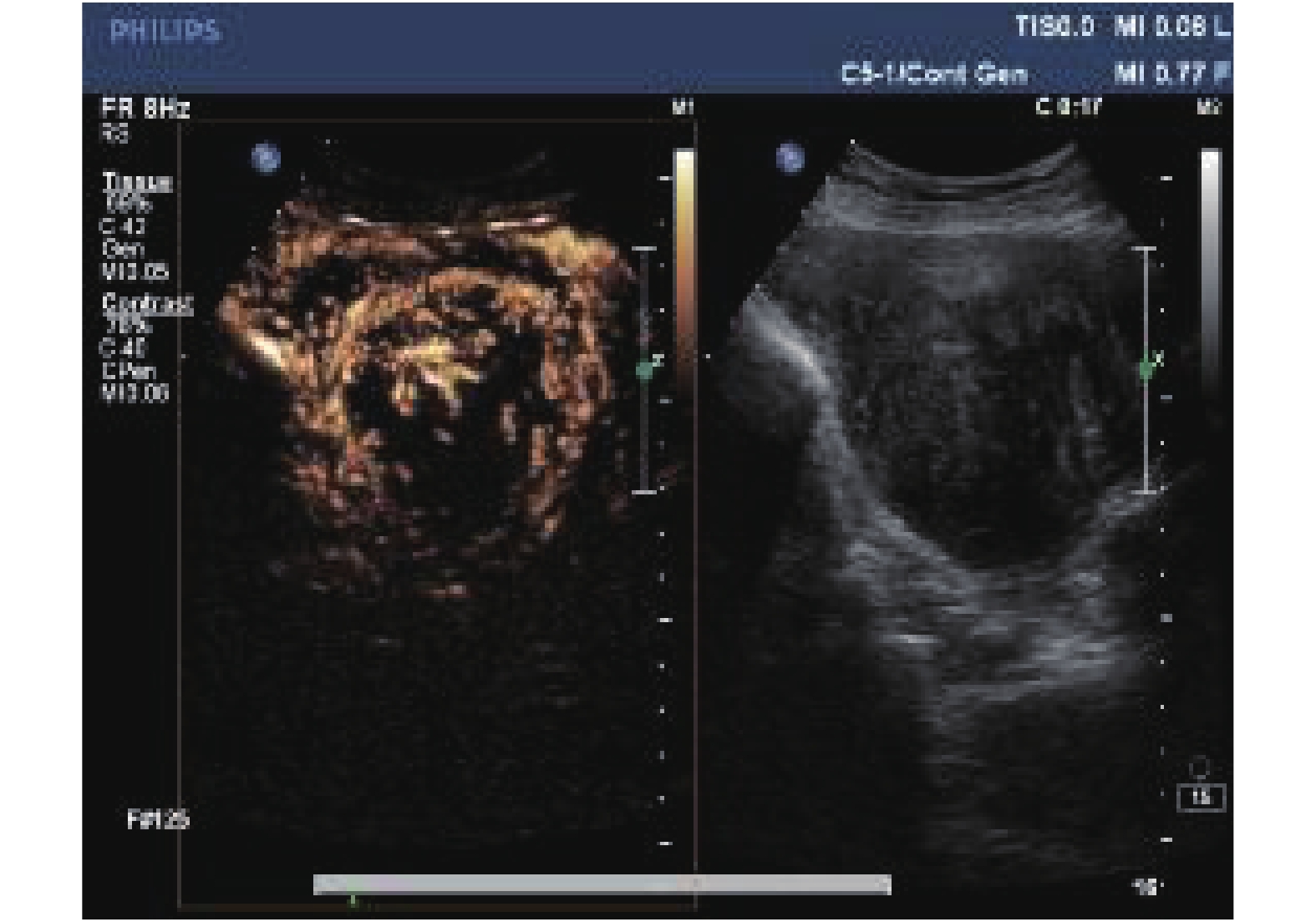
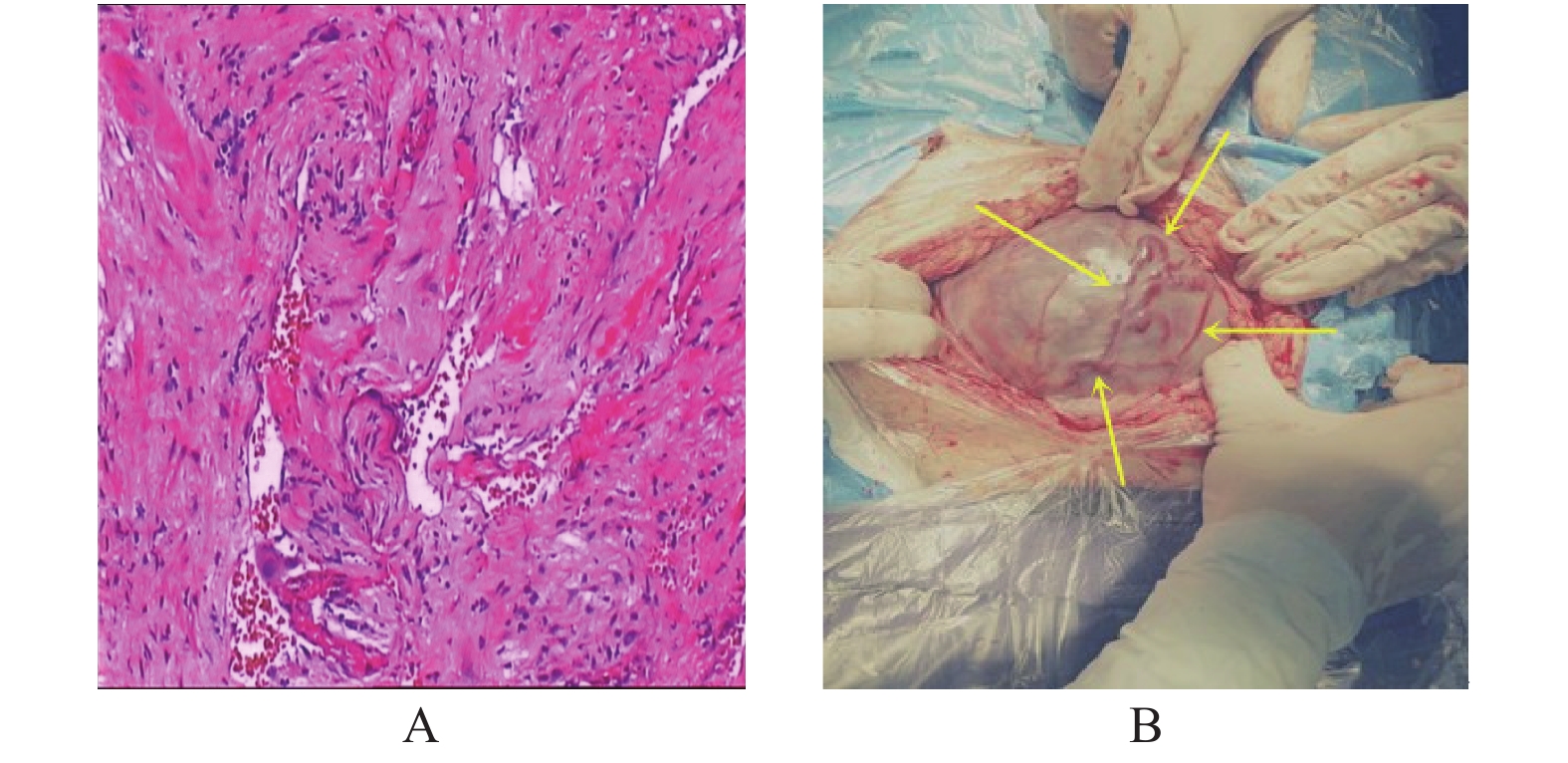
Objective To evaluate the differential diagnosis of uterine adenomyosis and uterine fibroids by intravenous contrast-enhanced ultrasound(CEUS). Methods Routine ultrasonography and intravenous CEUS were performed in patients with uterine fibroids and adenomyosis in the department of obstetrics and gynecology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University from December 2017 to December 2019. The results of postoperative pathological examination were compared, the accuracy of conventional ultrasound and intravenous CEUS was analyzed, and the characteristics of CEUS for uterine fibroids and adenomyosis were also analyzed. Results 1. The accuracy rates of conventional ultrasound and CEUS in the diagnosis of uterine fibroids were 92% and 98%, respectively, with statistically significant differences(P < 0.05). The accuracy of adenomyosis diagnosis was 91% and 100%, respectively, with statistically significant difference(P < 0.05). 2. According to intravenous contrast-enhanced ultrasonography, the onset time of adenomyosis was earlier than that of adenomyoma, and the peak time was earlier than that of uterine fibroids, and the peak intensity was lower than that of uterine fibroids, with statistically significant difference(P < 0.05). Conclusions 1. Intravenous CEUS is superior to conventional ultrasonography in the diagnosis of adenomyosis and uterine fibroids. 2. Adenomyosis and hysteromyoma have different characteristic changes in contrast-enhanced ultrasonography, which can be used as the key point to differentiate them.
2020, 41(11): 119-123.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20201112
Abstract:
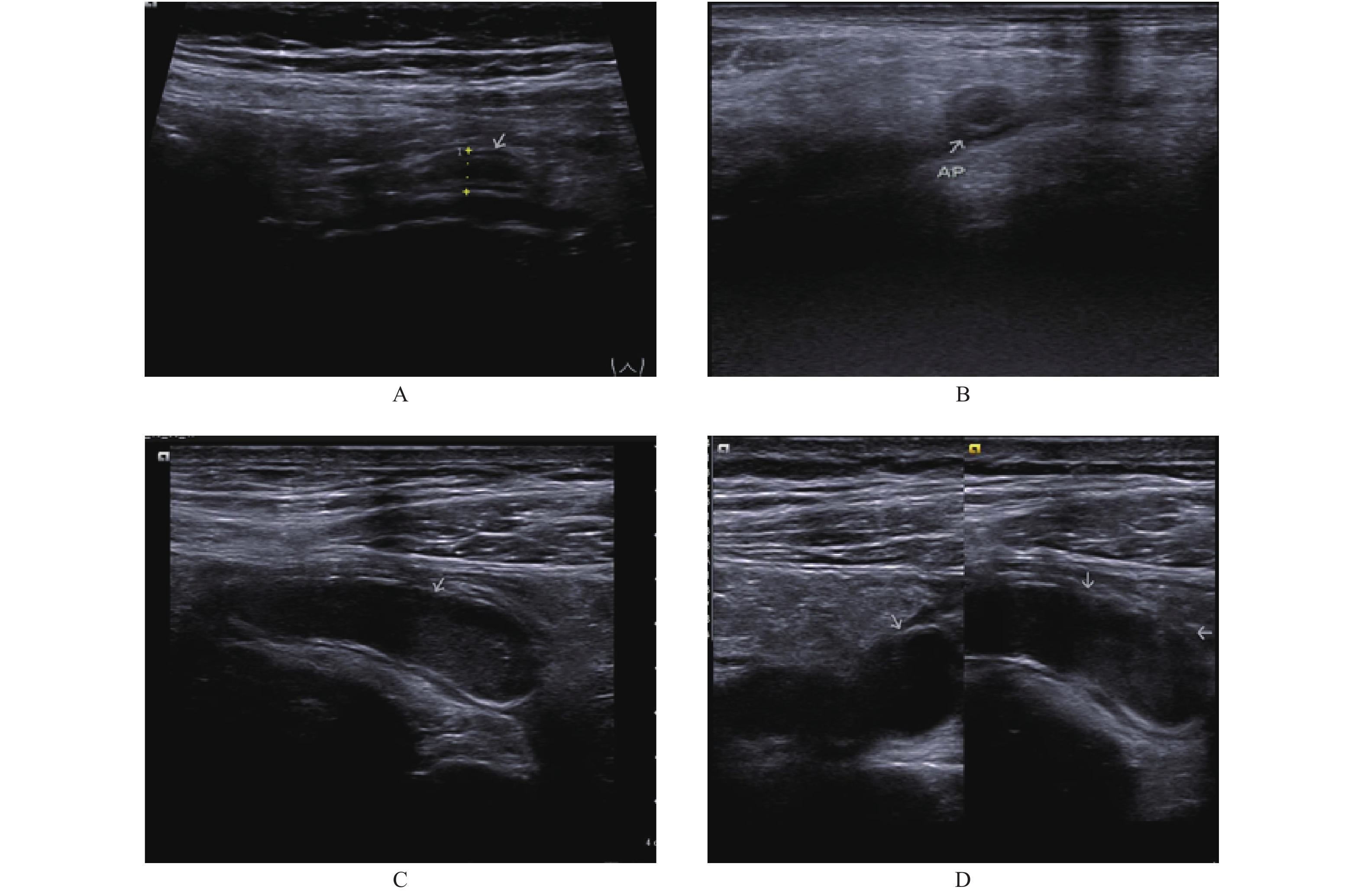
Objective To analyze the application value of ultrasound scoring combined with enhanced flow in dangerous placenta previa(PPP)combined with placenta accreta, in order to improve the ultrasonic diagnosis accuracy of PPP combined with placenta accreta. Methods From January 2017 to June 2019, 60 cases of pregnant and lying-in women with suspected PPP combined placental implantation in the Second People's Hospital of Yunnan Province were studied.Two-dimensional, ultrasound scoring and e-flow examination methods were routinely used in all pregnant women for the classification of PPP combined with placental implantation. Clinical surgery and pathological results were used as the gold standard for comparison, and the diagnostic efficacy of ultrasound scoring, e-flow and ultrasound scoring combined with e-flow for PPP combined with placental implantation was compared. Results Among 60 pregnant women with suspected PPP combined with placental implantation, the sensitivity of ultrasound scoring combined with e-flow was higher than that of ultrasound scoring(P < 0.05). The accuracy of ultrasonic scoring combined with E-flow was higher than that of ultrasonic scoring combined with e-flow(P < 0.05). The diagnostic efficiency of ultrasound scoring combined with e-flow in PPP with placental implantation was higher than that of single ultrasound scoring or e-flow. Conclusion Ultrasound scoring combined with E-flow has a higher diagnostic efficiency in the diagnosis of PPP combined with placental implantation. It is a combined examination method to promote the value and can provide guidance for clinical treatment.
2020, 41(11): 124-129.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20201115
Abstract:
Objective To analyze the low birth weight(LBW)situation and related risk factors of newborns born to HIV-positive pregnant women. Methods A total of 194 HIV-positive pregnant women who were hospitalized in Kunming Third People's Hospital for delivery from January 2013 to May 2018 were selected as the research subjects. Information on pregnant women includes demographic characteristics, history of obstetrics and gynecology, history of antiretroviral drugs, HIV transmission route, and HIV disease status(including CD4 count, HIV RNA viral load and hemoglobin at the time of enrollment). Logistic regression analysis was used to determine the risk factors related to LBW. Results Among 194 infants, 38(19.6%)were LBW(< 2500 g). There were significant differences between LBW infants and non-LBW infants in entry weight, antiretroviral treatment during pregnancy, entry CD4 count, entry HIV RNA viral load and gestational age at delivery(P < 0.05). Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that the body weight was light at entry(OR = 2.14, 95% CI = 0.84~4.05, P = 0.013), and CD4 count at entry(OR = 6.02, 95% CI = 1.50~24.13, P < 0.001), HIV RNA viral load at entry(OR = 3.34, 95% CI = 1.70~6.55, P < 0.001)and gestational age at delivery(OR = 12.90, 95% CI = 2.03~81.88, P < 0.001)were independent risk factor for LBW. Conclusions The status of HIV disease in pregnant women is related to neonatal LBW. Prenatal screening and diagnosis of HIV are essential for the early prevention and treatment of mother-to-child transmission of HIV and reducing adverse pregnancy outcomes.
2020, 41(11): 130-133.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20201126
Abstract:
Objective To explore the application value of viral load testing in diagnosing HIV antibody indeterminate cases. Methods The COBAS TaqMan HIV-1 Test v2.0 and CD4 cell count in 102 cases of indeterminate HIV antibody from The Third People's Hospital of Kunming from January 2016 to December 2019 were detected in one week. Patients were followed up to get the blood samples again two to four weeks later for the retest by Western blotting(WB). The results of the two methods were compared. Results A total 102 cases of blood samples showed unclear WB test result, with 86 cases proved to be HIV positive by follow-up WB test, VL test results of 19 samples more than 20 IU/ml and 2 samples below detection limit 20 IU/ml. 16 cases got confirmed diagnosis of negative HIV antibody by follow-up WB test, and their VL were all TND. Conclusions HIV antibody detection results can be identificated fastly and accurately by high precision detection of viral load. And the time for follow-up will be.shorten.The disease can be accurately judged early. The National Technical Specification for AIDS Testing(2015 Revision)also states that viral load testing as an effective auxiliary detection method for indeterminate samples of HIV antibody. High-precision detection of viral load is of great significance.
2020, 41(11): 134-137.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20201127
Abstract:
Objectives To explore the relationship between sperm abnormality and genital ureaplasma urealytieum(UU) infection, and discuss how do they interact with each other. Methods Three hundreds and forty-seven patients with male infertility were divided into UU-positive and UU-negative groups based on if they suffered UU infection. Subsequently, two groups were observed in terms of quality of sperm(including sperm count, sperm density, sperm mobility and proportion of forward motile sperm), liquefaction time and rate of sperm abnormalities. After the UU-positive group was treated with azithromycin and became UU-negative, sperm was recollected from them for analysis. Results Before the UU-positive group was treated, all of its sperm indicators were lower than the UU-negative group(P < 0.01). After they were treated and became negative, the sperm count, sperm density, mobility, proportion of Grade A sperm and ratio of Grade A+B sperm increased by 20.59%, 16.44%, 19.56%, 24.89% and 32.69% respectively, while the sperm deformity rate declined by 1.39%. In particular, the liquefaction rate increased from 20.11% before treatment to 92.53% after the group was treated and became UU-negative. The effects of treatment were evident, and differences were statistically significant before and after treatment(P < 0.01). Compared with the UU-negative group, the differences were not statistically significant(P > 0.05). Conclusions Male genital ureaplasma urealytieum infection may weaken sperm quality, particularly prolong liquefaction time of sperm and increase male infertility, Once UU infection is detected, prompt treatment is needed, so as to reduce male infertility.
2020, 41(11): 138-142.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20201110
Abstract:
Objective To explore the influence of low-dose alprostadil on patients' pulmonary artery pressure(PAP)and hemodynamics in orthotopic liver transplantation. Methods From March 2018 to September 2019, 22 patients undergoing orthotopic liver transplantation in The First People's Hospital of Kunming were selected and then they were randomly assigned into two groups. Experimental group(12 cases)was continuously pumped with alprostadil(1.5 ng/kg·min)through internal jugular vein; control group(10 cases)was continuously pumped with the same amount of saline through internal jugular vein. Finally the mean pulmonary artery pressure(MPAP)and hemodynamics of the two groups at different times of the surgery were compared. Results There was no significant difference between the two groups in basic information(age, gender, height, weight, ASA classification)(P > 0.05)and basic information in liver transplantation(infusion, concentrated red blood cell concentrate infusion, plasma infusion, blood loss, urine, operation time and anhepatic period time)(P > 0.05), also there was no statistically significant difference in MPAP and hemodynamics between the two groups at different times of the surgery(P > 0.05). Conclusion Continuous pumping of 1.5ng/kg·min alprostadil during orthotopic liver transplantation has little effect on PAP and hemodynamics.
2020, 41(11): 150-153.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20201130
Abstract:
Objective To study the duration of anoxia tolerance in patients with different weight, so as to discuss obese patients with oxygen reserve capacity. Methods Twenty-two aldut patients undergoing elective surgery, ASAⅠ~Ⅱ, aged 20~50, were divided into 3 groups according to Body Mass Index (BMI = High/Weight2): group A (BMI≤25 kg/m2), group B (BMI25~29.9 kg/m2) and group C (BMI≥30 kg/m2). Each patients received routine induction, while respiratory arrest control ventilation (VT: 8 mL/kg, R: 12次/min, PEEP: 5 cm H2O). Glidescope to trachea intubation in two minutes, fiber bronchoscope to ensure the position of the endotracheal tube without error quickly and fix the endotracheal tube. No patients were not ventilated until SpO2 decreased to 93%. Baseline BMI, HR, blood pressure, SpO2, the duration of SpO2 fell from 100% to 97% and 93% (T97, T93). Results There were statistically significant differences in the airless safety time T97, T93 between the three groups of patients. BMI and T97 and T93 had negative correlation with BMI. Conclusion With the increase of BMI in twenty-two patients, the airless safety time will be shortened significantly.
2020, 41(11): 158-164.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20201113
Abstract:
Objective To understand the cognitive status and influencing factors of clinical nurses at all levels of medical institutions in Yunnan Province for the treatment of peripheral venous puncture and central venous catheter(PICC), and to provide evidence for improving the PICC maintenance capacity measures in this area. Methods A stratified sampling method was used to survey 4297 clinical nurses in 67 hospitals in Yunnan Province. Results PICC maintenance related knowledge average score was 52.19±12.38 points, with 1.56% of excellent rate, 31.86% of qualified rate, and 66.58% fo failed rate. Hospital level, whether intravenous infusion or PICC nursing team members, education, professional title, monthly maintenance cases, the total number of training received were important factors influencing the score(P < 0.05). Conclusions The clinical nurses at all levels of medical institutions in Yunnan Province have poor overall knowledge of PICC-related maintenance knowledge. Hospitals at all levels should strengthen training for each hospital's specific conditions and explore appropriate training methods to improve nurses' cognitive level.
2020, 41(11): 165-170.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20201114
Abstract:
Objective To determine the influencing factors of the compliance of patients with diabetic cataract after discharge from day surgery through continuing motivational interviews. Methods A total of 108 cases of patients with diabetic cataract surgery in the day were randomly selected from Renji Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiaotong Nuiversity School of Medicine from January 2018 to January 2019, and were randomly divided into observation and control group. All patients accepted the hospital health education at the same time, and were continuously observed once a month for 6 months after discharge. The patients in the control group were reviewed about the health status and medication compliance, and were guided according to the review results. The patients in the observation group were treated by continuous motivated interview to understand the factors that affect the appointment compliance of patients after discharge, the application effect of continuous motivated interview was analyzed and the targeted continuous interview plan was formed. The nursing staffs were responsible for interview and health education. The follow-up compliance of patients in the two groups was compared. Results The awareness rate was 77.77%(42/54)in the observation group and 38.89%(21/54)in the control group. The patients in the observation group had 74.07%, 81.48 and 85.19% compliance at 1, 3 and 6 months after discharge, while the patients in the control group had 38.89%, 48.15 and 57.41% compliance at 1, 3 and 6 months after discharge. The incidence of adverse reactions after discharge was 9.26% in the observation group and 37.04% in the control group, and the comparison between the groups was statistically significant(P < 0.05). Conclusions Continuing motivational interview can significantly improve the compliance of diabetic cataract patients after discharge from day surgery, and continuous interview after discharge can ensure the quality of nursing at home and reduce the incidence of adverse reactions, which has a high clinical application value.
2020, 41(11): 56-61.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20201119
Abstract:
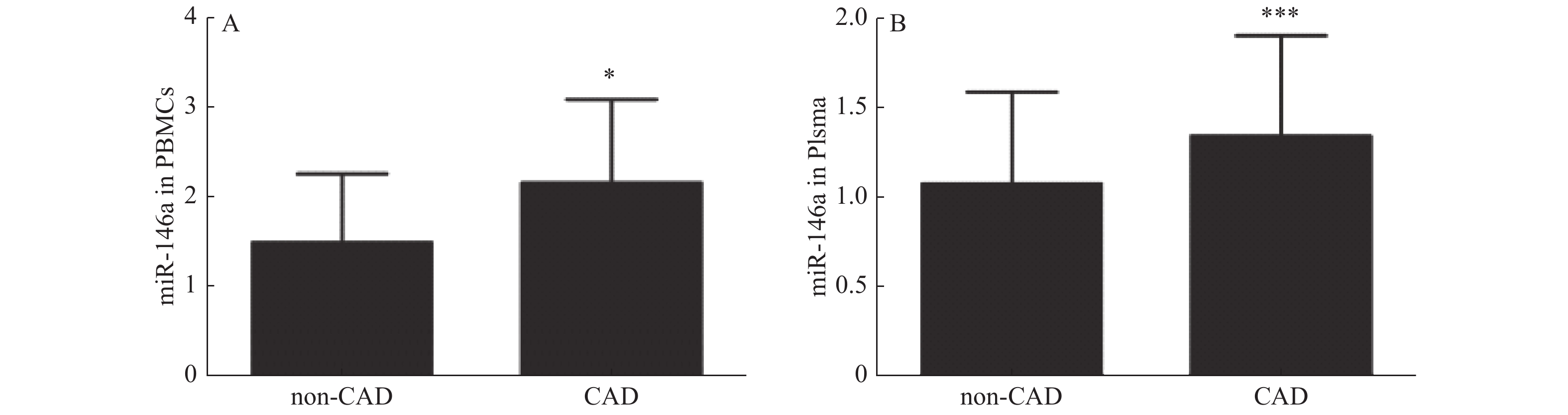
Objectives To investigate the association between microRNA-146a(miR-146a)and the plaque stability in patients with coronary heart disease. Methods Real-time PCR was used to measure miR-146a expression in 324 patients. ELISA was used to measure the level of hs-CRP, IL-6 and IL-8. Coronary angiography was used to evaluate the degree of coronary artery stenosis. Intravascular ultrasound(IVUS)was used to evaluate the plaque stability of coronary stenotic lesions. Results (1)The levels of hs-CRP, IL-6 and IL-8 were significantly increased in the UAP and AMI groups compared with the CPS groups(P < 0.01).(2)The miR-146a expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells(PBMCs)and plasma was significantly higher in CAD patients than those in non-CAD group(P < 0.05, P < 0.001).(3)The miR-146a expression in PBMCs was higher in SAP, UAP and AMI group than CPS group(P < 0.01, P < 0.001, P < 0.001). The expression patterns of miR-146a in plasma was consistent with that of PBMCs.(4)The expression of miR-146a in PBMCs and plasma were significantly higher in vulnerable plaque group than those in stable plaque group(P < 0.05).(5)The level of miR-146a in PBMCs and plasma was significantly higher in soft plaque group than those in fibrous plaque group and calcified plaque group(P < 0.05). Conclusions The expression of miR-146a is associated with the plaque stability of coronary stenotic lesions.
2020, 41(11): 78-82.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20201118
Abstract:
Objective To explore the clinical value of ultrasound in the diagnosis of acute appendicitis. Methods The clinical data of 423 cases of acute appendicitis treated in our hospital from 2019 to 2020 were retrospectively analyzed to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of ultrasonography for acute appendicitis. The results of lumen diameter, tube wall thickness, tube wall thickening in the right lower abdominal ileocecal part, local effusion in the right lower abdomen, and local strong echo comparison for different types of appendicitis were analyzed. Results A total of 374 cases of acute appendicitis were detected by ultrasound, and the diagnostic accuracy was 88.4%(374/423). The lumen diameter and wall thickness(mm)of appendicitis with acute appendicitis were(7.1±1.3)and(3.2±0.9), the lumen diameter and wall thickness(mm)of appendicitis with acute suppurative appendicitis were(10.0±1.9)and(4.3±1.1), and the lumen diameter and wall thickness of appendicitis with acute gangrenous appendicitis were(12.4±2.2)and(5.3±1.3), respectively, with statistically significant differences among the three groups(P < 0.05). Acute gangrene appendicitis and acute suppurative appendicitis combined with thickening of ileocecal wall, local effusion in the right lower abdomen, local strong echo and lymph node enlargement were all higher than those in acute simple appendicitis, and the differences were statistically significant(P < 0.05). Conclusion Ultrasonography can provide a clear basis for the diagnosis of different pathological types of acute appendicitis.
2020, 41(11): 154-157.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20201129
Abstract:
Objective To evaluate the effect of mixed situational simulation teaching on improving the doctor-patient communication skills of pediatric residents. Methods From September 2016 to December 2019 in our hospital of pediatrics rotation, a total of 56 students receiving resident standardization training in accordance with the standards of parity method were divided into two groups, each group of 28. In the experimental group, students were given the hybrid scenario teaching methods - scene simulation combined with standardized patients and Seminar teaching method, students in the control group adopted the basic teaching method, then we analyzed the theory and the practice operation assessment scores, the satisfaction on teaching, and the improvement rate of the communication ability of students receiving resident standardization training. Results Compared with the data of the control group, the experimental group had higher satisfaction degree, better assessment scores, higher improvement rate of communication ability, and there was a difference between the two groups(P < 0.05). Conclusion In the teaching of pediatrics, adopting the mixed situation simulation teaching method scientifically can improve the doctor-patient communication ability of the trainees in the standardized training of pediatric rotation resident physicians, and comprehensively improve the clinical competence.


 Email
Email RSS
RSS