2021 Vol. 42, No. 1
2021, 42(1): 12-16.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210111
Abstract:
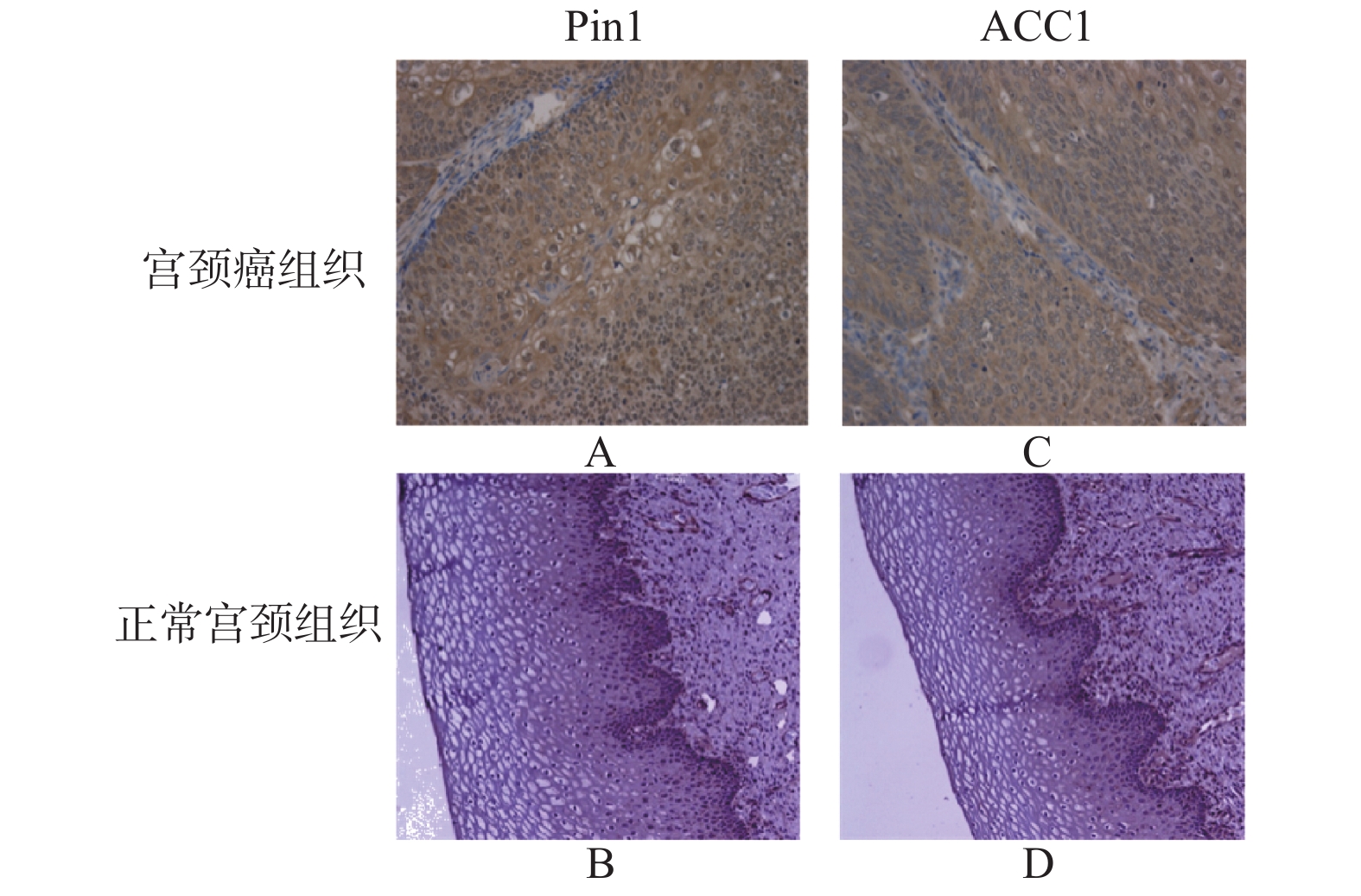
Objective To investigate the effect of peptide-based prolinyl isomerase(Pin1)protein on lipid metabolism in cervical cancer cells. Methods The expression of Pinl and ACC1 protein in chronic cervical cancer and cervical cancer tissues was detected by immunohistochemistry. Western blotting and RT-PCR were used to detect the background expression of Pin1 gene in SiHa, C33a and H8 cells of cervical cancer, and RNA interference was used to detect the expression of Pin1 in C33a cells of cervical cancer. The influence of Pin1 protein expression on ACC1 protein expression in cervical cancer cells was detected by Western blotting. Lipid-soluble fluorescence staining(bodipy493/503)was used to observe the changes in the content of neutral fat in cervical cancer cells before and after transfection with low expression of lentivirus Pin1. Results Compared with chronic cervicitis, the expression of Pin1 and ACC1 in cervical cancer tissues was significantly up-regulated(P < 0.05), and the expression of Pin1 and ACC1 in cervical cancer tissues was positively correlated(r = 4.45, P < 0.05). Compared with C33a cells, the expression level of Pin1 protein in SiHa cells was relatively low, so C33a cells were selected for transfection with lentivirus with low Pin1 expression. After the transfection with lentivirus with low Pin1 expression in C33a cells, the protein expression levels of Pin1 and ACC1 were significantly decreased( P < 0.05). Compared with normal control group and negative control group, the content of intracellular neutral fatty acids transfected with lentivirus with low Pin1 expression was decreased. Conclusion The expression of Pin1 protein is involved in lipid metabolism in cervical cancer cells, and the specific regulatory mechanism remains to be studied.
2021, 42(1): 38-45.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210101
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the effect of exosomes divided from human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on the polarization of tumor-associated macrophages, and to preliminarily discuss their influence on glioma cell lines. Methods Exosomes divided from human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells were extracted and identified by scanning electron microscopy and western blot. The glioma cell line SHG449 was divided into three groups: SHG449 group: SHG449 cells without special treatment; SHG449+M0 group: SHG449 cells co-cultured with M0 macrophages; SHG449+M0+exosome group: SHG449 cells co-cultured with M0 macrophages, and then exosomes labeled with PKH-67 were added to the M0 cells. The mRNA expression of M1 biomarkers(iNOS and CD68)and M2 markers(Arginase and CD206)were detected by qPCR, and the content of IL-1β, TNF-α, CCL22 and TGF-β in the supernatant of SHG449 cells were detected by ELISA. The proliferation and apoptosis of SHG449 cell line were detected by CCk8 and flow cytometry. Results (1)Exosomes secreted by human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells were successfully extracted and entered into M0-type macrophages.(2)Macrophage morphology was transformed after exosome was intaken by SHG449-induced polarized macrophages, and the expression of M2 macrophages markers Arginase, CD206, CCL22 and TGF-β were decreased(Arginase: P < 0.01, CD206: P < 0.05, CCL22: P < 0.05, TGF-β: P < 0.01), while the expression of M1 macrophages markers iNOS, CD68, IL-1β and TNF-α increased(iNOS: P < 0.01, CD68: P < 0.01, L-1β: P < 0.000 1, TNF-α: P < 0.001).(3)Macrophage polarization induced by exosomes resulted in decreased proliferation( P < 0.05) and increased apoptotic( P < 0.000 1) of glioma cells. Conclusion Exosomes derived from human bone marrow stromal cells can inhibit the polarization of tumor-associated macrophages to the M2 phenotype and induce their polarization to the M1 phenotype, and regulate the tumor immune microenvironment, thereby suppressing the development of glioma.
2021, 42(1): 1-5.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210112
Abstract:
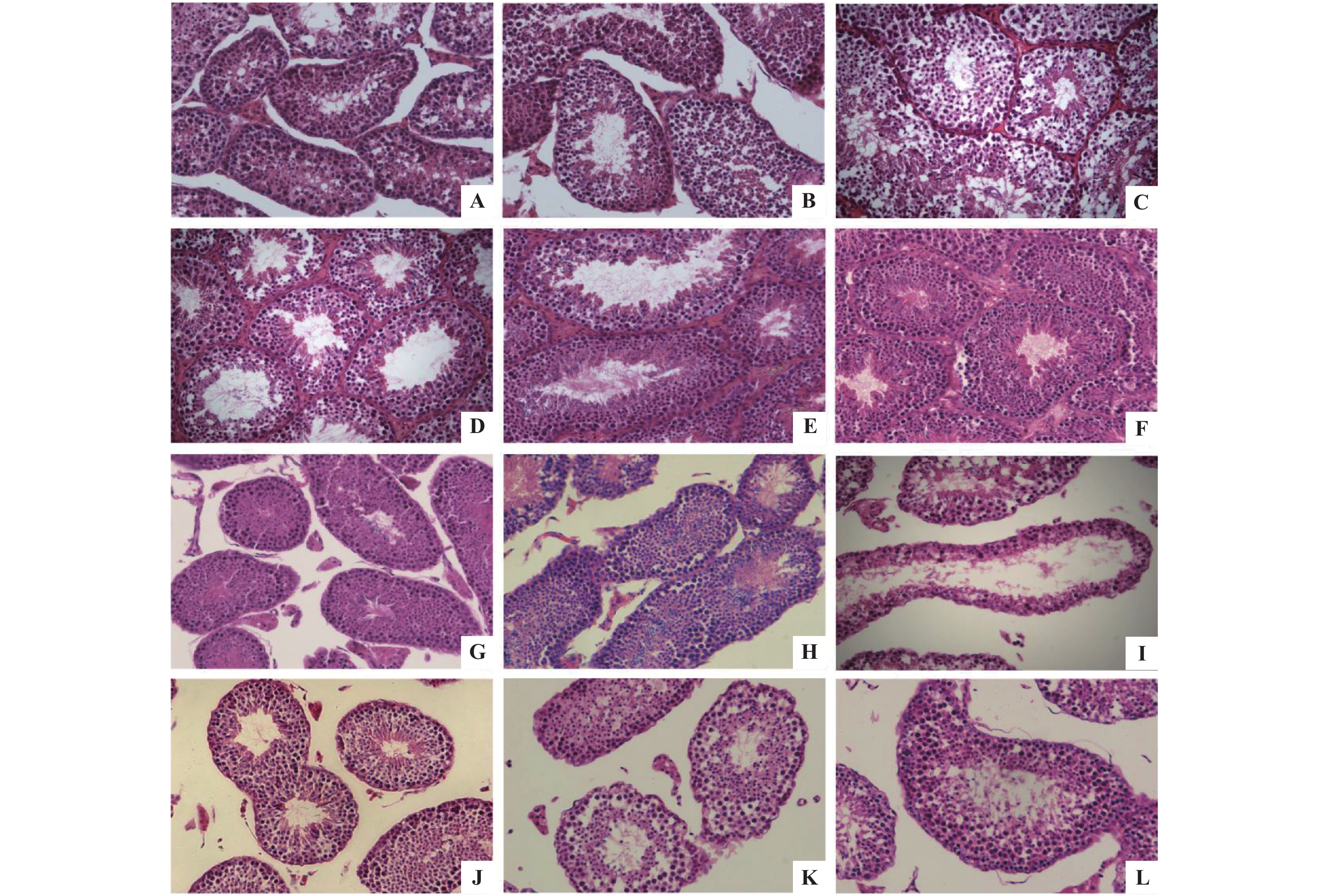
Objective To study the expression characteristics of MCM7 protein during spermatogenesis of artificially domesticated tree shrews and whether there are seasonal differences in its expression, so as to provide basic experimental data for reproductive research using tree shrews as animal models. Methods 12 groups of adult male artificially domesticated tree shrews testis tissues of different months were used as the materials and immunohistochemical detection of MCM7 protein was performed on the paraffin tissue sections. Results MCM7 protein was expressed in spermatogonia and some primary spermatocyte of the testes in artificially domesticated tree shrews. Compared with the other months in the whole year, the positive cell rate of MCM7 protein was significantly different in February and March (P < 0.05). Conclusions MCM7 protein may play a role in the DNA replication of spermatogonia and primary spermatocytes during the spermatogenesis of artificially domesticated tree shrews, and there was seasonal difference in the activity of MCM7 protein expression.
2021, 42(1): 6-11.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210134
Abstract:
Objective To comparatively study the anti-inhibitory and bacteriostatic effects of RDD and RDC gel so as to provide the laboratory basis for the development and utilization of the resin. Methods The model of the mouse pinna swelling induced by xylene and granuloma induced by cotton ball was adopted to test the anti-inflammatory effects of two kinds of the resin gel and the bacteriostatic effects of two kinds of the resin gel on Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Propionibacterium Acne, Candida albicans and Escherichia coli were compared by means of broth medium colorimetry. Results Compared with the blank control group in the test of auricle swelling induced by xylene, momethasone furoate gel(0.1 mg/) and high dose(12 mg/) of RDD gel inhibited the auricle swelling in mice(P < 0.05), but there were no statistical differences in the other two groups(P > 0.05); Compared with the momethasone furoate o gel group, the blank control group and the high dose RDD group had the significant difference(P < 0.05), but there were no statistical differences in the other two groups(P > 0.05). Compared with the blank control group in the experiment of granuloma model caused by cotton ball, the low dose RDC gel group had inhibitory effect on granulomal in mice, but there were no statistical differences in the other two groups(P > 0.05); Compared with the mometasone furoate group, the blank control group and the high dose RDD blood group had the significant differences(P < 0.05) but there were no statistical differences in the other groups(P > 0.05). The two kinds of resin gels had the inhibition to Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Propionibacterium Acne, Candida albicans and Escherichia coli. The minimal inhibitory concentration(MIC) of RDC gel was 50mg/mL and RDD gel was 200mg/mL for staphylococcus aureus and staphylococcus epidermidis; the MIC of propionibacterium acnes RDD gel and dragon resin gel were 100 mg/mL and 50 mg/mL, ; the MIC of Candida albicans RDD gel and RDC gel were 100 mg/mL and 200 mg/mL, respectively; the MIC of E. coli RDD gel and RDC gel were 100 mg/mL. Conclusion Both RDD gel and RDC gel have the anti-inflammatory and bacteriostatic effects. The RDC gel is superior to RDD gel in inhibiting granuloma of mouse cotton ball and fighting against Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis and Propionibacterium Acne; the effect of RDD gel on inhibiting auricle swelling induced by xylene in mice is better than that of RDC gel. There is the same bacteriostatic effect in the two kinds of resin gel on E. coli.
2021, 42(1): 17-22.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210106
Abstract:
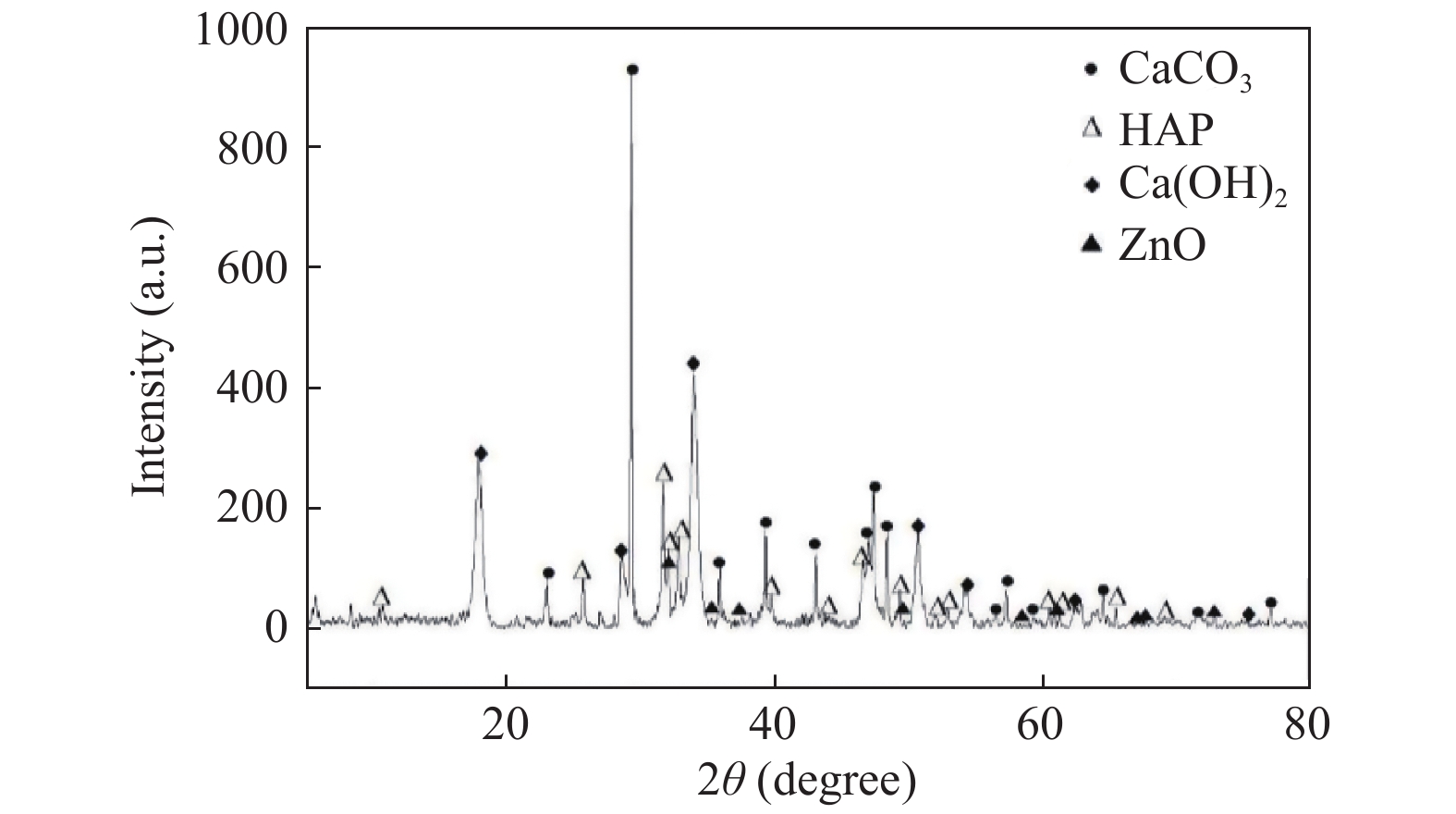
Objective To explore the process of modifying coral hydroxyapatite by nmZnO under the different conditions. Methods Coral hydroxyapatite was modified by zinc nitrate sol-gel method at 70 ℃ in weak acid environment. White granular porous composite materials were obtained by ultrasonic, rotary stirring, drying and calcination. The surface characteristics of the modified materials were observed by scanning electron microscope. Results The results showed that the distribution and size of nmzno particles on the coral hydroxyapatite surface were different under the different raw material ratios. In the process of heat treatment, different holding temperature and holding time would lead to the change of carbon removal effect and structural integrity of materials. Conclusion Coral hydroxyapatite surface can be modified by zinc nitrate sol-gel method. The particle size of nano zinc oxide is less than 100 nanometers. The agglomeration problem of nano-particles is solved.
2021, 42(1): 23-28.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20201245
Abstract:
Objective To explore the feasibility and characteristics of magnetic microbead anterior chamber injection inducing ocular hypertension model, and to study the role of OCT in model evaluation. Methods C57BL/6 mice were divided into the normal group, control group and experimental group. The normal group was not treated. The intraocular pressure fluctuations were detected before the surgery and on the first day after the surgery; After 3 weeks of modeling, fluorescent gold retrograde labeling was performed, and after 4 weeks of modeling, OCT was used to detect the thickness of para-optical nerve fibers in two groups of mice, and the number of RGCs in each group was counted by parallel retinal plating. Results After the injection of magnetic fluorescent microbeads into the anterior chamber of the mice, the microbeads were able to be evenly distributed at the angle of the anterior chamber to block the angle. In the experimental group, the intraocular pressure of the mice began to increase 1 day after the injection, and the average intraocular pressure was 19.37 ± 4.38 mmHg. The intraocular pressure decreased slightly after three weeks. In the 4th week, OCT was used to detect the thickness of RNFL. The thickness of RNFL in the experimental group was 27.67 ± 6.15 μm, which was significantly thinner than that in the control group. The difference between the two groups was statistically significant(p = 0.0082). After detecting OCT, RGCs were counted in wholemount retina and the RGCs in the experimental group were 203.83 ± 26.35, which was significantly reduced compared with the control group, and the difference was statistically significant(p = 0.0094). Conclusion The injection of magnetic microbeads in the anterior chamber of mice can induce a sustained and stable increase in intraocular pressure and cause a significant decrease in the number of RGCs. RGC damage can be found by non-invasive, rapid, and repeated detection of the thickness of the nerve fiber layer by OCT.
2021, 42(1): 29-37.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210144
Abstract:
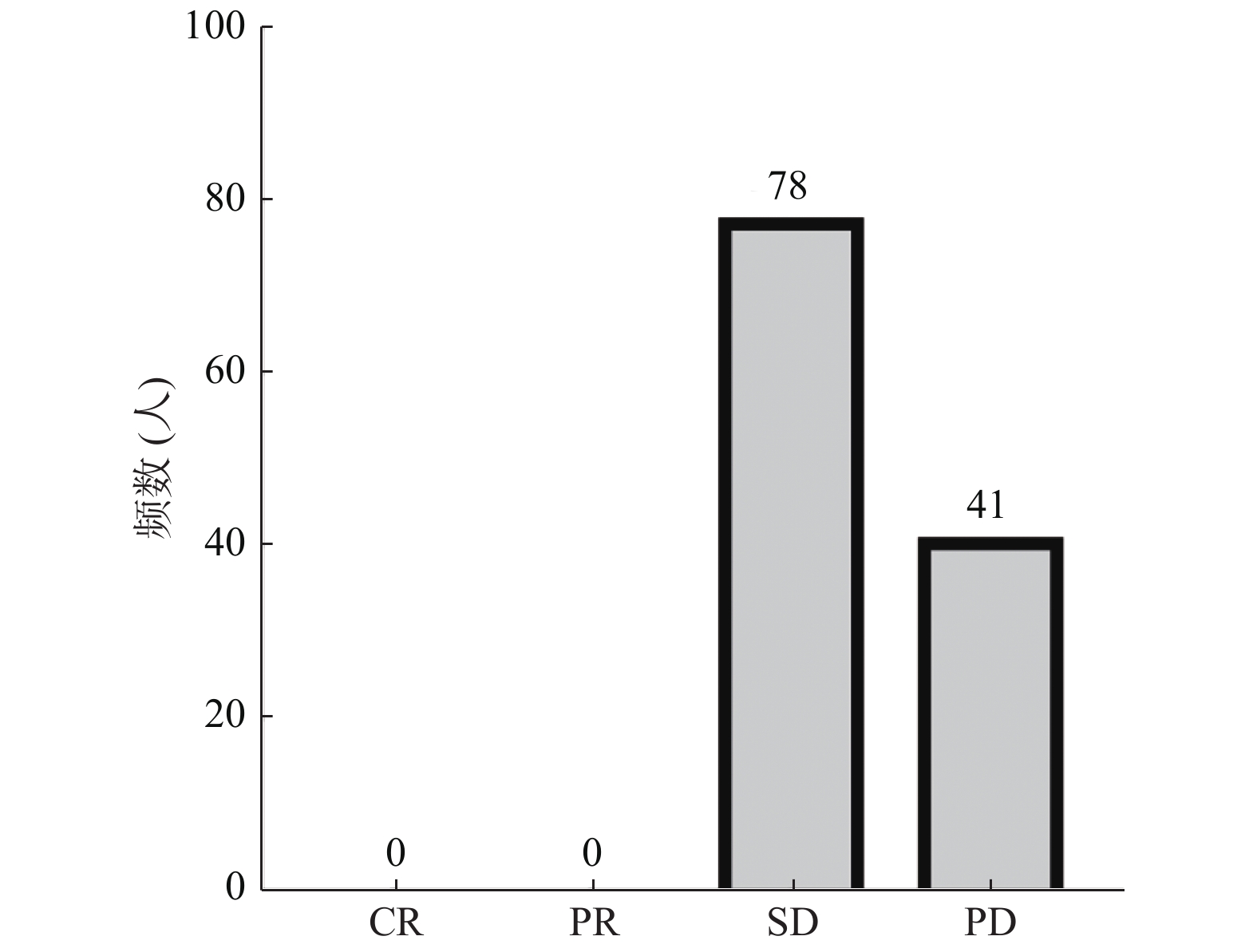
Objective The purpose of this study was to develop a scoring system to predict chemotherapy resistance of osteosarcoma, which could guide doctors to better choose the appropriate treatment. Methods 119 cases of osteosarcoma with neoadjuvant chemotherapy were diagnosed by pathology at the Third Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University between January 2013 and December 2017 and the covariates including general situation, blood indexes, initial diagnosis, treatment mode, therapeutic effect and survival were analyzed. Results According to RECIST 1.1, 78 of 119 patients were evaluated as stable disease(SD group)and 41 as progressive disease(PD group); There was signifcant difference in staging, initial visit time, initial tumor size, neoadjuvant chemotherapy cycle, types of chemotherapy drugs, lymphocyte/leukocyte prechemotherapy, neutrophils/lymphocytes prechemotherapy, albumin prechemotherapy, ALP prechemotherapy, Uric acid prechemotherapy, BUN after the chemotherapy, uric acid after the chemotherapy, LDL prechemotherapy, TGF-β score, TCNR between SD group and PD group(P < 0.05). Metastasis had no significant effect on the efficacy of chemotherapy. According to the ROC curve, the best cut-off value showed staging≥III, neoadjuvant chemotherapy cycle≤3, Lymphocyte/leukocyte prechemotherapy≤0.32, neutrophils/lymphocytes ≤1.98, albumin prechemotherapy, ≥48 g/L, BUN after the chemotherapy≥4.22 mmol/L, uric acid after the chemotherapy≥305 umol/L. TGF-β score≥8.5 was the risk factor for chemotherapy resistance in patients with osteosarcoma.3. Patients with one risk factors add 1, and 0-3 were classified as group 1. 4-6 were listed as group 2; 7-9 were listed as group 3 and there was no statistically significant difference between the three groups. Conclusion This study explored the clinical factors related to chemotherapy resistance of osteosarcoma.
2021, 42(1): 46-50.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210127
Abstract:
Objective To study the effect of tumor antigen loaded DC-CIK on the microenvironment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Methods The antigen of HCC coming from resected HCC and peripheral blood mononuclear cells were isolated from healthy donors. The cells were divided into 4 groups as DC, Ag-DC, CIK and Ag-DC-CIK according to the loading of HCC antigen or coculture of DC-CIK or not. Cell phenotype of 4 groups were evaluated by FCM. Furthermore, levels of IL-6, IL-10 and IFN-γ; expression of VEGF and MMP-2、MMP-3、MMP-9mRNA were observed. Results The contents of CD80, CD86 in group Ag-DC and CD3+CD56+, CD8+CD56+ double positive cells in group Ag-DC-CIK elevated significantly(P < 0.05). The level of IL-6 and IFN-γdecreased significantly in group Ag-DC-CIK(P < 0.05). Expression of VEGF and MMP-2, MMP-3, MMP-9mRNA also reduced significantly in group Ag-DC-CIK(P < 0.05). Conclusion Coculture of DC and CIK on the basis of loading HCC antigen shows the stronger activity and reduces the expression of relating factors about inflammation, angiopoiesis and fibrosis in HePG2 microenvironment.
2021, 42(1): 51-58.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210103
Abstract:
Objectives To investigate and analyze the health lifestyle of medical students and the impact factors of social and demographic characteristics. Methods A total of 2, 278 medical students were randomly selected and their health lifestyle information was collected and analyzed by using questionnaire scoring scale. Results When controlling other variables, gender, grade, and father's education level predicted total healthy lifestyle score were 0.039, 0.012, 0.032, respectively(P < 0.05); exercise behaviour was predicted partially by gender, grade, and family monthly income(0.031、0.003、0.0045, P < 0.05); regular behaviour was modulated by gender, grade, family monthly income, and father's educational level(0.022、0.0015、0.0001, P < 0.05); nutrition behaviour was affected partially by family monthly income and father's educational level(P < 0.05); health risk behaviour was modulated by gender, mother's education level, and family monthly income(P < 0.05); health responsibility was modulated by gender, grade, and father's educational level(P < 0.05); social support was modulated by gender, grade, and father's educational level(P < 0.05); stress management was modulated by gender, grade, and mother's education level(P < 0.05); life appreciation was modulated by grade and mother's educational level(P < 0.05). Conclusions Medical students' healthy lifestyles are influenced by gender, grade, family monthly income and father's and mother's education level. These influences can be used as a predictor of healthy lifestyle of medical students.
2021, 42(1): 59-63.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210110
Abstract:
Objective The aim of this study is to analyze the factors affecting re-admission to hospitals of the patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease(COPD)in Yunnan province based on the diagnosis related groups(DRGs). Methods Clustering sampling method was used to select COPD patients who were re-admitted to a top three hospital in Yunnan province from 2017 to 2019, and random sampling method was used to choose COPD patients who received the treatment in any hospitals during the same period without re-admission. Results The average age of COPD patients in the re-admission group, the proportion of residents living in kunming, the ratio of 0-10 km away from the hospital, the average relative weight RW and the average length of hospital stay in the re-admission group were all higher than those in the non-readmission group(P < 0.01), while returning to the group of COPD patients(farmers or the unemployed), the proportion of patients using ventilator, and the proportion of patients with disease course less than 1 year were significantly higher than those in the re-admission group(P < 0.01). Multiple linear regression analysis showed that the older the patient, the urban location of residence, the longer the course of illness, the more severe the illness, and the longer the average length of stay, the greater the likelihood of re-admission for COPD patients(P < 0.01). Conclusion To grade the patients, who is older, having longer duration of living in Kunming city, having longer course, with high Relative Weight, having the breath machine treatment, in the specific DRG groups,having longer average hospitalization time by relevant feedback on the DRGs data platform. The top three hospital should develop targeted treatment and clinical pathway to the patients who are in a critical condition. And for patients who are in better status can get medical care in a closer community hospital. In this way, we can reduce the number of COPD patients who are in admitted to hospital repeatedly, reduce the economic burden of patients reasonably, improve the quality of life.
2021, 42(1): 64-67.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210136
Abstract:
Objective To study the expression of HIF-1α in the serum of CKD patients, analyze the relationship between it and serum fibrosis index PⅢNP, and the clinical indicators of CKD patients, and explore the clinical application value of HIF-1α in CKD. Methods A total of 63 CKD patients were randomly selected as the research object, and the research objects were grouped according to the CKD stage. 30 patients in CKD1-2 were in group A, 17 patients in CKD3 were in group B, and 16 patients in CKD4-5 were in group C.ELISA method was used to detect the expression of HIF-1α and PⅢNP in the serum of the enrolled patients, and the clinical data of the enrolled patients were collected, including gender, age, blood routine, liver function, renal function, ions, and 24-hour urine protein. Results HIF-1α was positively correlated with PⅢNP, Scr, BUN, γ-GT(P < 0.05), negatively correlated with GFR, HB, Blood calcium( P < 0.05), There was no correlation with NLR, PLR, ALB, Phosphorus and 24-hour urine protein( P > 0.05). Conclusion HIF-1α is associated with serum fibrosis indexes, renal function, CKD complications, and may be involved in the progression of CKD disease, which can be used as one of the indicators for evaluating CKD.
2021, 42(1): 94-98.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210142
Abstract:
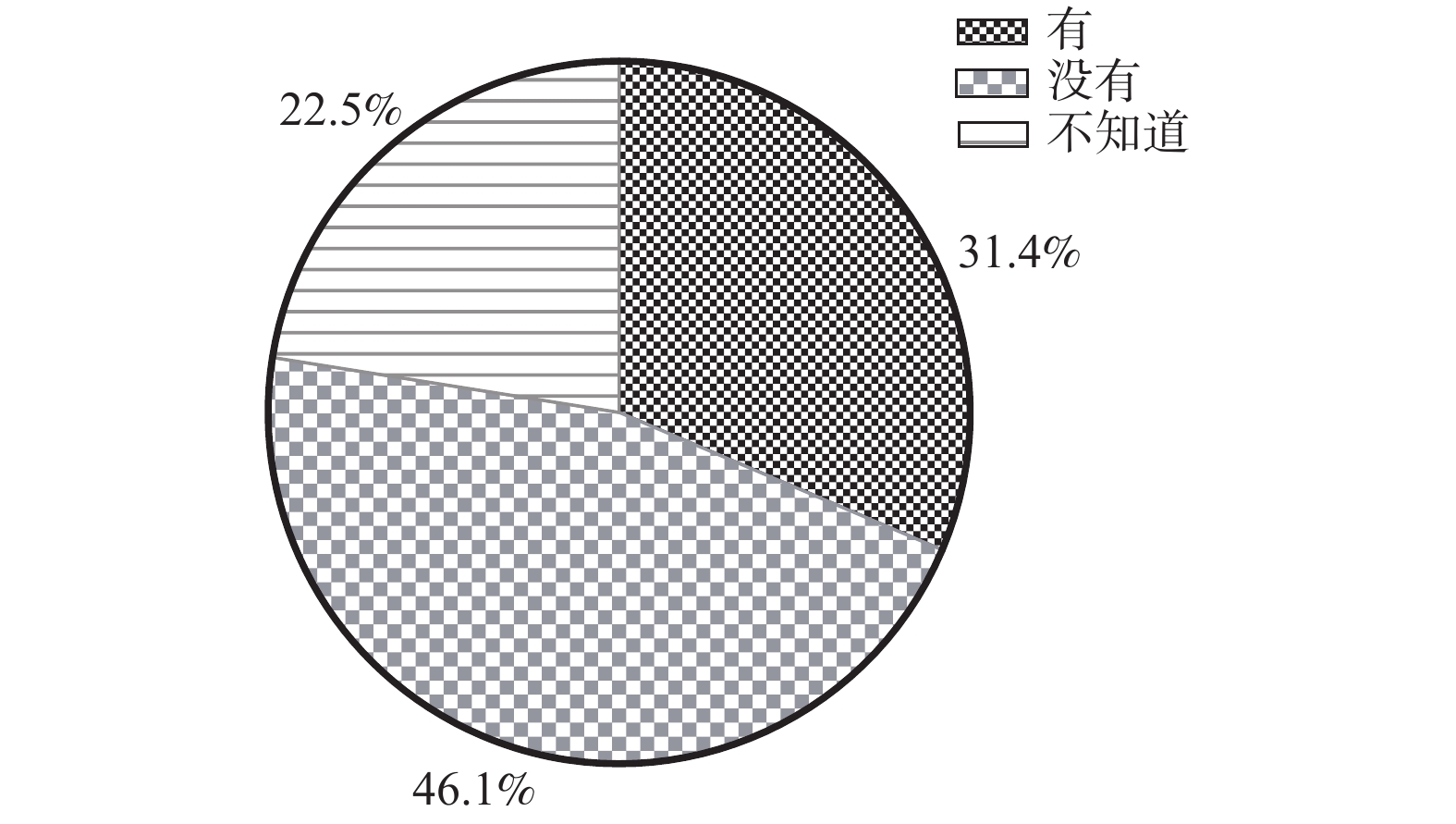
Objective The aim of this study is to assess the malocclusion status, the risk factors and the parental awareness about deciduous malocclusion among 3-to-5-year-old children in Kunming. Methods Multistage stratified random sampling method was conducted to examine the occlusion and caries status of 480 3-to-5-year-old children in Kunming. Information of the parental awareness on malocclusion was collected using a questionnaire. Data were analyzed by the Chi-square test and binary logistic regression analysis. Results 430 children were recruited, the prevalence of malocclusion was 69.3%. Among them, the most common type of malocclusion was deep overbite(82.2%), followed by deep overjet(24.5%), and the minimum prevalence was the edge-to-edge occlusion(0.7%). And there was a significant difference between the feeding methods and the prevalence of malocclusion(P < 0.05). In genetic, there was a significant difference between crossbite and genetic( P < 0.05). As to oral bad habits, there was a correlation between the biting habit and deep overjet, and between the bruxism and deep overbite( P < 0.05). The results of binary logistic regression analysis showed that the bruxism was a risk factor of deciduous malocclusion(OR = 1.256, P < 0.05). The result of parental questionnaire showed that merely 31.4% of parents payed attention to children's occlusal problem. Conclusion The prevalence of malocclusion is high among 3-to-5-year-old childrein with primary dentition in Kunming. Many factors are related to malocclusion of primary dentition. And parents pay less attention to the children's occlusion.
2021, 42(1): 124-129.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210102
Abstract:
Objective To study the clinical characteristics, treatment and prognosis of necrotizing pneumonia (NP) in children. Method The clinical data of 46 patients with NP admitted to the Department of Respiratory Medicine of Kunming Children's Hospital from April 2017 to April 2020 were collected retrospectively. According to the etiological score, the patients were divided into mycoplasma pneumoniae necrotizing pneumonia (MPNP) group and bacterial necrotizing pneumonia (BNP) group. The clinical manifestations, laboratory examination results, imaging features, bronchoscopic manifestations, treatment process and prognosis of the two groups were compared later. Methods Of the 46 NP cases, 30 were MPNP and 16 were BMP. The age of children in MPNP group was significantly higher than that in BNP group. There was no significant difference between the total fever days in MPNP group and the total fever days in BNP group. The proportion of patients with shortness of breath and in need of oxygen therapy was significantly higher in BNP group than that in MPNP group. There was no significant difference between the two groups in the proportion of respiratory failure requiring mechanical ventilation. Laboratory tests showed that BNP had the higher white blood cell count and PCT c-reactive protein (CRP) than MPNP children. Imaging examination showed that the necrotic lesion in MPNP group was significantly later than that in BNP group. There was no significant difference in the proportion of pleural effusion between the two combinations. Electronic bronchoscopy revealed that there were a variety of inflammatory changes in the characteristics of tracheal and bronchial mucosa, bronchial lumen and secretions of MPNP children. The bronchial mucosa, lumen and secretions of BNP were mainly suppurative. After the effective treatment, the two groups of patients improved and were discharged from the hospital without any death. There was no significant difference in length of stay between the two groups. There was no significant difference in the absorption time between the two groups. Conclusion Patients with NP have the long fever, long hospital stay, long imaging absorption, and severe and diverse bronchoscopy. Fever and cough for more than 10 days, pleural effusion, CRP for more than 80 mg/L, and ricin-like alveolar lavage fluid may be the risk factors for NP development. NP has a good prognosis after the active and effective treatment.
2021, 42(1): 130-134.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210122
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the risk factors associated with the vascular crisis after the digits replantation and provide the evidence for the improvement of the replantation survival rate. Methods From Jan. 2016 to Dec. 2018, 26 cases(29 digits)suffered by digit amputation were collected and analyzed retrospectively. Survival rate of replantation was summarized and functional evaluation was performed at the last follow-up. Statistical methods were used to analyze the risk factors associated with vascular crisis after digits replantation. Results 25 cases(28 digits)were followed up and the follow-up period raged from 9 to 28 months(mean 18.4 months). 25 cases(28 digits)survived during the last follow-up, and the standard evaluation of digits replantation function of Chinese medical association hand surgery branch was used to evaluate the function. 16 digits function was excellent, 5 digits good, 4 digits better and 3 digits poor, and the rate of excellent and good was 75%. There were statistically significant differences between the vascular crisis group and non-vascular crisis group during the process of injury-operation time, vein transplantation and functional evaluation(P < 0.05). Conclusion There are many factors affecting the survival of digits replantation. Strictly shortening the time interval from injury to operation and improving the quality of vein transplantation can reduce the occurrence of vascular crisis and finally improve the survival rate of the replanted digit.
The Application Value of CT Pulmonary Blood Flow Distribution in the Diagnosis of Pulmonary Embolism
2021, 42(1): 135-141.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210128
Abstract:
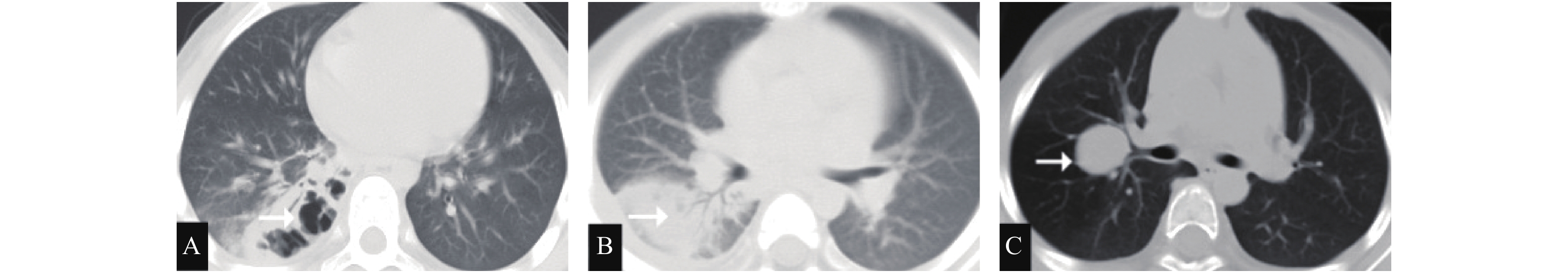
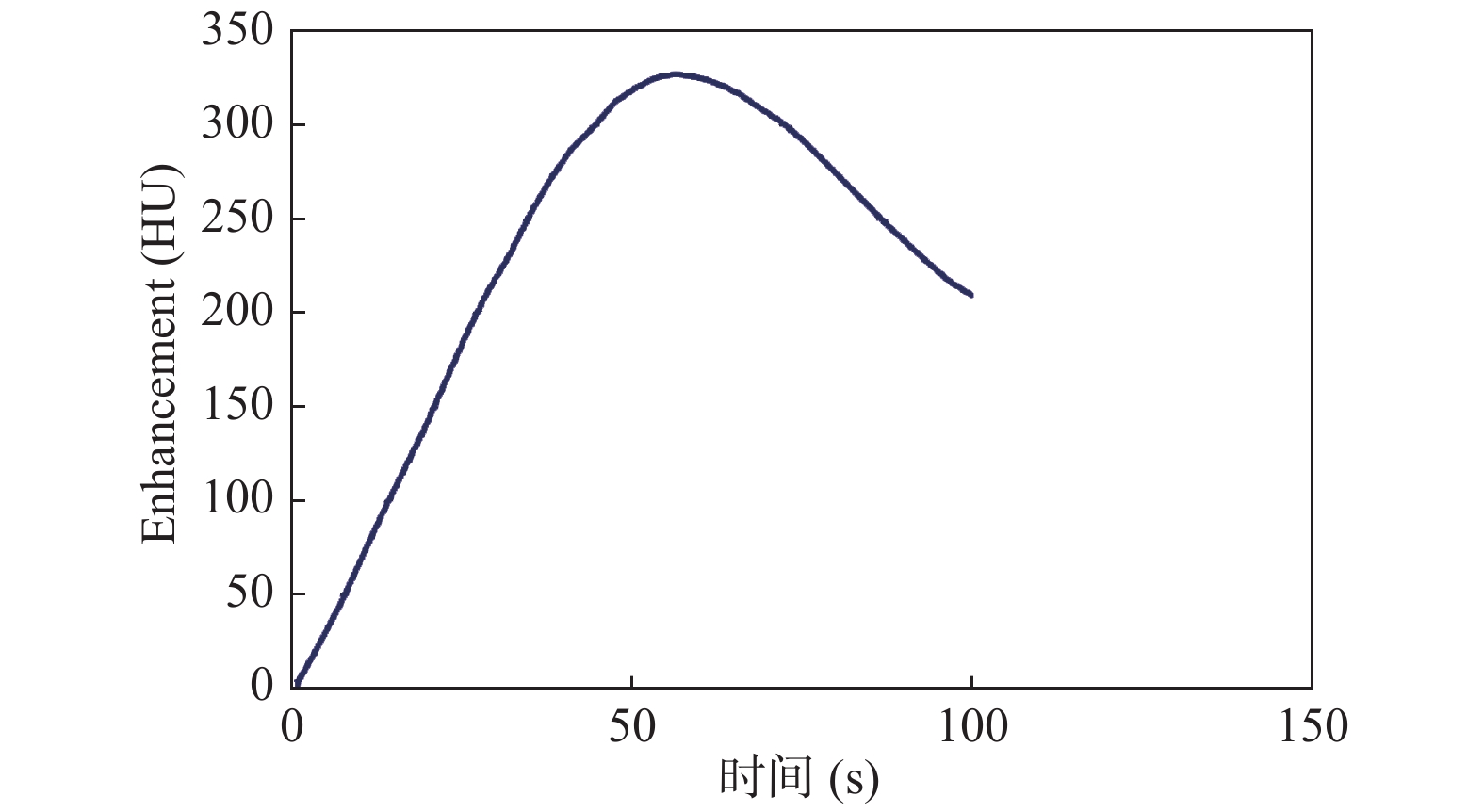
Objective To explore the feasibility of CT pulmonary blood flow distribution in the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism. Methods Using the imaging efficiency of the imaging agent, the corresponding mapping mechanism was established by processing the image with skill. The blood flow distribution of the lung lobe was observed by color development method, and the pulmonary blood perfusion was speculated. Results After the imaging agent was injected, the imaging agent flowed with the blood and passed its imaging efficiency, resulting in changes in the CT value on the CT image. Through the original CT image of the lungs, the embolism can be found. After the development, the blue area of the color map image appeared at the end of the embolized blood vessel. Observing the embolized area directly from the color map was easier and more efficient than CTA and nuclear medicine analysis. Conclusion CT pulmonary blood flow distribution angiography is to describe the blood flow distribution of the pulmonary lobes through the analysis of color map images, and has an auxiliary role in the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism. It is worthy of further research and clinical application.
2021, 42(1): 142-146.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210126
Abstract:
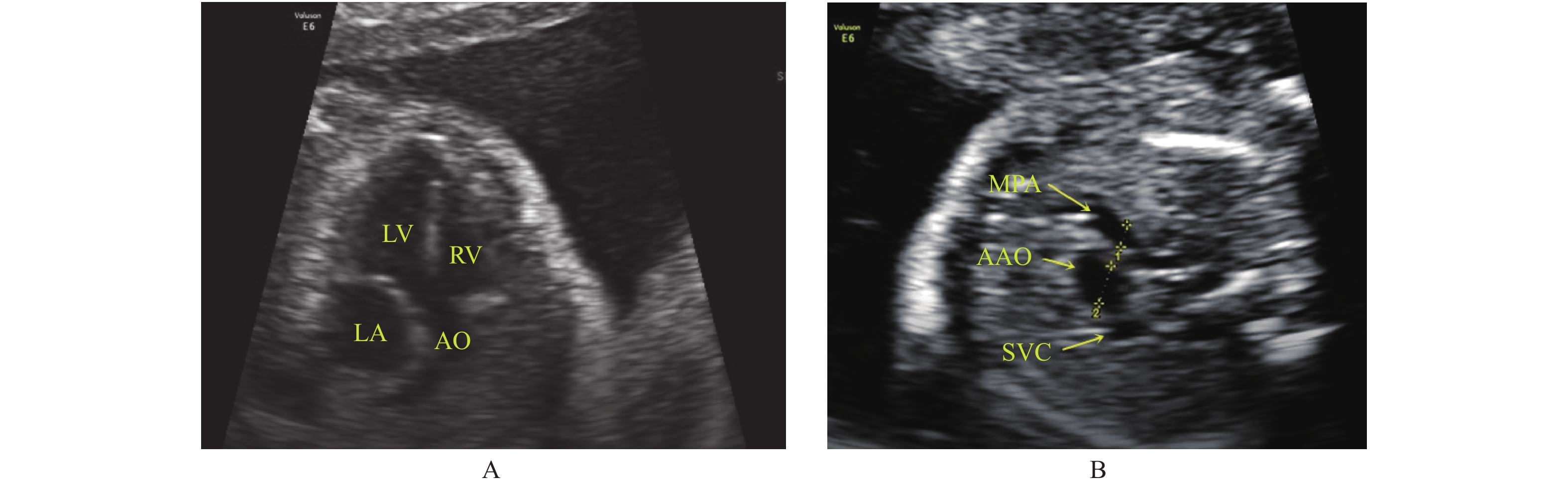
Objective To analyze the value of echocardiography in the diagnosis of fetal tetralogy of Fallot(TOF). Methods 558 pregnant women who underwent fetal echocardiography in the department of ultrasound of the Second People's Hospital of Yunnan Province from January 2017 to June 2019 were selected as the research objects. The pathological anatomy after the induction of labor and the results of postpartum echocardiography follow-up were as used the gold standard to calculate the prenatal echocardiography. The diagnosis sensitivity, specificity, accuracy rate were shown, and the sound image characteristics of TOF were analyzed. Results A total of 558 pregnant women underwent the echocardiographic examination. After the induction of labor, pathological anatomy and postpartum echocardiographic follow-up results confirmed a total of 25 cases of TOF fetus. Prenatal echocardiography detected 26 cases of TOF fetus, 20 cases of typical TOF with pulmonary artery stenosis, 3 cases of pulmonary atresia with ventricular septal defect, 2 cases of TOF with absent pulmonary valve, 2 cases of misdiagnosis, and 1 case of missed diagnosis. The diagnostic sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, misdiagnosis rate and missed diagnosis rate of prenatal echocardiography were approximately 96%(24/25), 99.62%(531/533), 99.46%(555/558), 0.38%(2/533)and 4%(1/25), respectively. It is mainly characterized by ventricular septal defect, aortic straddling, pulmonary artery stenosis, atresia, and absence of pulmonary valve. Conclusion Prenatal fetal echocardiography is the most important imaging method for the diagnosis of TOF, and it has important clinical guiding significance for evaluating the prognosis of the fetus.
2021, 42(1): 68-71.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210130
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the positive rate, gene mutation type and distribution characteristics of thalassemia gene screening patients in the First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University. Methods A retrospective analysis was made on 2376 cases of thalassemia gene screening patients in the First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University from April 1, 2017 to December 31, 2018. The parameters of thalassemia gene and blood cell analysis (Hb, MCV, MCH, RDW) were statistically analyzed. Results (1) Among 2376 cases of thalassemia gene screening, 817 were positive for thalassemia gene, the positive rate was 34.39%, of which 392 cases were positive for α thalassemia gene, accounting for 47.98% of the total positive samples; 398 were positive samples of βthalassemia gene, accounting for 48.71% of the total positive samples; 27 cases were αβcompound thalassemia gene positive samples, accounting for 3.30% of the total positive samples. (2) 392 positive samples of αthalassemia gene were αα/--SEA、αα/-α3.7、αα/ααCS、αα/-α4.2 and -α3.7/--SEA genotypes, accounting for 50.51%, 32.91%, 4.34%, 3.57% and 2.55%, respectively; CD26, CD41-42, CD17, IVS II654, nt28 genotypes were the main positive samples of β thalassemia gene, accounting for 25.38%, 23.37%, 20.60%, 20.60% and 3.27% of thalassemia gene. Conclusion The incidence rate of thalassemia in Yunnan is still high, of which CD26 is the largest in beta thalassemia, which is totally different from that in other provinces and cities in China.
2021, 42(1): 72-75.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210121
Abstract:
Objective To analyze the efficacy and safety of levosimendan in patients with heart failure caused by severe coronary heart disease. Methods From January 2018 to January 2020, 40 patients who were hospitalized with the diffuse coronary artery disease were selected and divided into two groups according to the selection of levosimendan or not, with 20 cases in each group. Cardiac function index, myocardial enzymes, BNP, liver and kidney function changes and adverse reactions of the two groups were collected and analyzed. Results After the corresponding treatment, it was found that changes in cardiac function were statistically significant(P < 0.05)and differences in myocardial enzymes and BNP were statistically significant(P < 0.05)between the two groups. Also, there was no significant difference in liver and kidney function(P > 0.05)and the incidence of adverse reactions was not statistically significant(P > 0.05). Conclusion The effect of levosimendan on severe coronary heart disease is obvious and the side effects of the drug are small.
2021, 42(1): 76-80.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210135
Abstract:
Objective To compare the effects of balloon dilatation and reoperation on benign biliary-enteric anastomotic stenosis. Methods From February 2009 to June 2019, 41 patients with benign biliary and intestinal anastomotic stenosis treated in the Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University were retrospectively analyzed, including 18 cases in the balloon dilatation treatment group and 23 cases in the reoperation group. And the treatment time, treatment effect and related complications in the two groups were compared. Results Compared with the re-operation group, the balloon dilatation treatment group had the shorter treatment time and fewer treatment-related complications (P < 0.05) and there was no significant difference in cure rate, recurrence rate and postoperative cholangitis between the two groups (P > 0.05) but the cure rate of balloon dilation treatment group was slightly higher.. Conclusion Balloon dilatation has a higher cure rate and fewer complications in the treatment of benign biliary-enteric anastomotic stenosis, and it is a safe, effective, and reliable treatment for benign biliary-enteric anastomotic stenosis.
2021, 42(1): 81-84.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210109
Abstract:
Objective To study the prevalence and different clinical manifestations of hospitalized children with rotavirus infection in Kunming. Methods The clinical data of 1570 cases of children hospitalized with rotavirus infection from 2014 to 2018 in Kunming Children`s Hospital were collected and the retrospective analysis of population characteristics, time distribution and different clinical features were conducted. Results Of the 1570 children with rotavirus infection, 987 were male and 583 were female. Age composition: six to 24 months of age(79%), average age: (12.9±9.24)months. Winter(December to February of the following year)is the peak season of illness(46.8%). There were 380 children only presenting with digestive symptoms, the hospitalization days are(7.07±4.49)d. There were 1 190 children incorporative presenting with extraintestinal symptoms which occupy a proportion of 75.8%, the hospitalization days are(9.09±3.65)d; In these cases, most of children who were hospitalized between year 2014 and year 2017 were likely to have extraintestinal symptoms, but the symptoms are rare in 2018. Children aged 3 months to 3 years old are more likely to have extraintestinal symptoms. Conclusion The incidence of extraintestinal injury or complications after rotavirus infection is high.
2021, 42(1): 85-88.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210124
Abstract:
Objective To explore the clinical significance of changes of coagulation tetrad and D-dimer(D-D)and pregnancy outcome in infertile women before and after IVF assisted pregnancy. Methods 115 cases of in vitro fertilization and embryo transfer were collected from June to November 2016 in the Department of Reproductive Medicine, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University. Four coagulation and DD indexes were detected before and after IVF assisted pregnancy. According to whether the patients were pregnant, they were divided into the pregnancy group(69 cases)and non-pregnancy group(46 cases). The changes of PT, APTT, FIB, TT and DD before and after IVF assisted pregnancy were compared between the two groups to see if there were any differences. Results The mean values of FIB and DD after IVF assisted pregnancy in pregnancy group were significantly higher than those before IVF assisted pregnancy(3.502±0.773、1.718±1.107 vs 2.875±0.625、0.706±3.101), while TT was significantly lower than that before IVF assisted pregnancy(3.502±0.773 vs 2.875±0.635), with significant difference(P < 0.05); DD after IVF assisted pregnancy in non-pregnancy group was significantly higher than that before IVF assisted pregnancy(2.058±1.507 vs 0.294±0.244), while TTF was significantly lower. The difference was significant before IVF assisted pregnancy(16.094±0.862 vs 16.830±1.697)(P < 0.05). There was no significant difference in coagulation and DD between the pregnant group and non-pregnant group before and after IVF(P > 0.05). Conclusion Detection of PT, APTT, FIB, TT and DD before and after IVF-ET assisted pregnancy in infertile women is helpful to detect abnormal coagulation function in time and improve the success rate of IVF-ET pregnancy in infertile women.
2021, 42(1): 89-93.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210141
Abstract:
Objective to observe the efficacy and safety in the clinic practice of Propofol Tenofavir Fumarate(TAF)as a treatment of Chronic Hepatitis B(CHB) Method A total of 180 Chronic-Hepatitis-B patients who had taken TDF antiviral therapy for 48 to 49 weeks were chosen between January 2018 and February 2020. They were further separated into two groups regarding to the following treatments: one continues TDF treatment while the other replaces with TAF. The comparison was made based on the clinic efficacy and renal safety from such two groups after a 48-week continuous medication. Results TAF group showed a statistical difference significantly better in HBV-DNA inhibition rate, ALT normalization rate, and HBeAg serum conversion with χ2 = 10.250, P = 0.001 and χ2 = 6.871, P = 0.009, and χ2 = 3.881, P = 0.049 respectively. In terms of the safety, TAF group also demonstrates a difference significantly lower in the urinary α1 microglobulin abnormal rate with χ2 = 13.703, P = 0.000. On the other hand, there was no significant difference in bloom β2 microglobulin among the groups owning to P values ≥ 0.05. Conclusion With the statistical comparison between TAF and TDF treatments in this clinic study, TAF is observed to have a stronger antiviral effectiveness, fewer side effects such as less induced harm to the renal function, and reduce the risks deriving from the liver cirrhosis and cancer.
2021, 42(1): 99-105.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210115
Abstract:
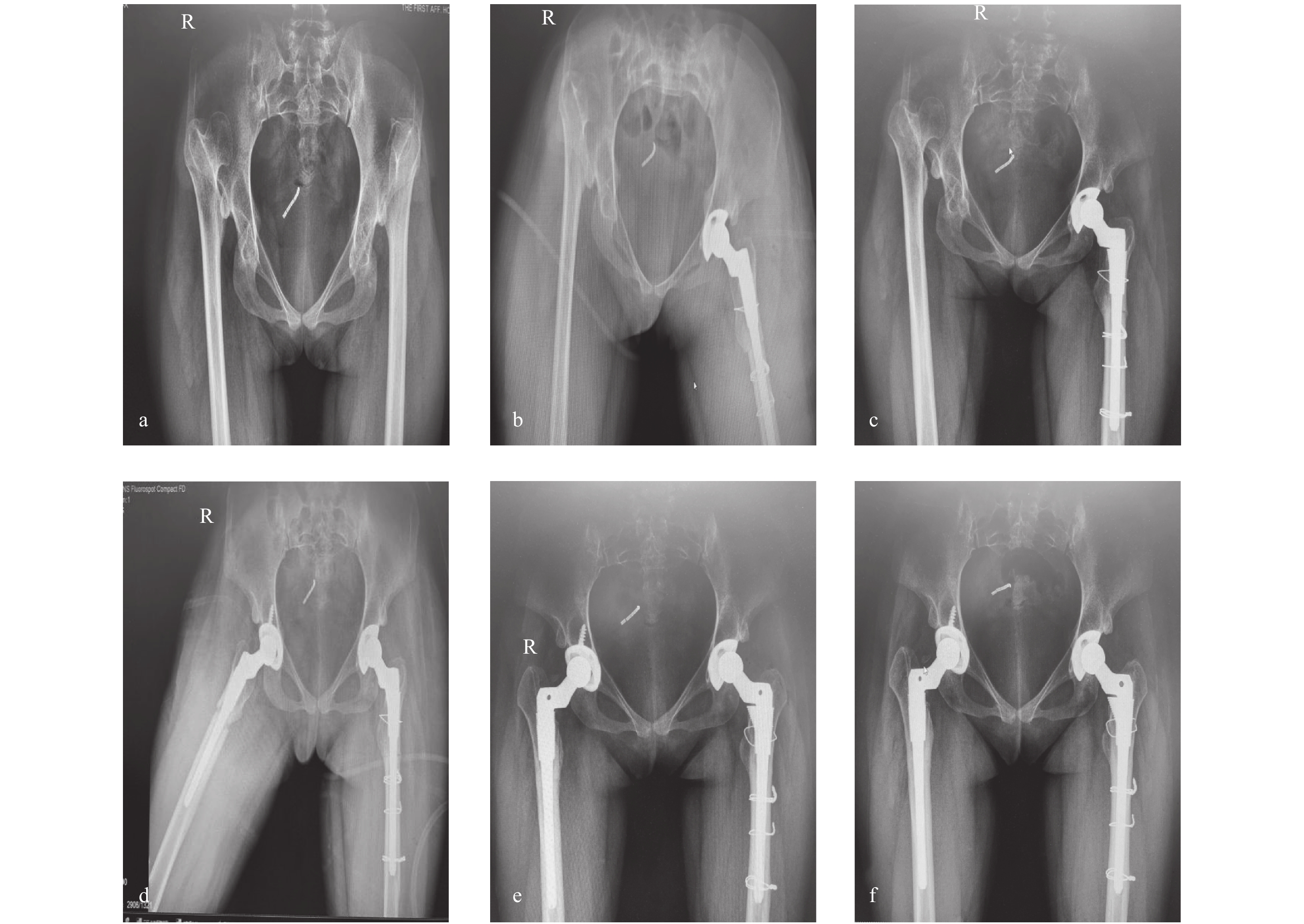
Objective To compare the clinical efficacy of modular S-ROM femoral prosthesis and monoblock Wagner Cone femoral prosthesis used in total hip arthroplasty for the treatment of Crowe type IV developmental dysplasia of the hip. Methods Retrospective study was conducted in 58 patients(65 hips) undergoing total hip arthroplasty for the treatment of Crowe type IV developmental dysplasia of the hip between January 2014 to August 2018, including 33 patients(37 hips) with modular S-ROM prosthesis and 25 patients(27 hips) with monoblock Wagner Cone prosthesis. The general data, operative time, intraoperative blood loss during the postoperative hospitalization, bone union time, Harris score, VAS score and perioperative complication rate were compared between the two groups. Results There was no significant difference in the perioperative complication rate during the postoperative hospitalization, Harris score and VAS score in the last follow-up between the two groups. The operative time was (135.7perat)min in the S-ROM group and (113.3n the)min in the Wagner Cone group, and there was a significant difference between the two groups (P < 0.05). The intraoperative blood loss was (469.7±43.6)ml in the S-ROM group and (410.4 rence between the two groups (and there was a significant difference between the two groups (P < 0.05). The bone healing time of Wagner Cone group was significantly longer than that of S-ROM group (P < 0.05). Conclusion The application of both the modular S-ROM andmonoblock Wagner Cone femoral prosthesis with subtrochanteric shortening osteotomy in total hip arthroplasty for the treatment of Crowe type IV developmental dysplasia of the hip has a good clinical efficacy. The monoblock Wagner Cone prosthesis has the shorter operative time and less intraoperative blood loss, and the modular S-ROM prosthesis has shorter bone healing time.
2021, 42(1): 106-109.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210113
Abstract:
Objective To compare the vaginal microecological results of newly diagnosed patients with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and healthy women, and to explore the etiology, diagnosis and treatment of PCOS patients. Methods 80 newly diagnosed PCOS patients were selected as the study group, and 80 healthy patients in the physical examination group were selected as the control group. The vaginal secretions of two groups of subjects were tested for trichomonas, fungi, flora density, white blood cells, dominant bacteria, Nugent score and AV score. The above vaginal microecological indicators of the two groups were compared to analyze whether the vaginal microecological disorders of the two groups were imbalanced. Results The detection rate of trichomonas in the two groups of subjects was zero. The comparison of the dominant bacteria, fungus detection rate, AV score, Nugent score and vaginal infection between the two groups was statistically significant (P < 0.05). There was no significant difference in the density of white blood cells and flora between the two groups of subjects (all P > 0.05). Conclusion The composition of the vaginal flora of PCOS patients is significantly different from the normal vaginal microecological environment. It is a new treatment for PCOS and the dynamic observation of the microecological status of PCOS patients can be used as an important indicator for evaluating POCS patients after the treatment.
2021, 42(1): 110-114.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210118
Abstract:
Objective To the investigate the safety and efficacy of reverse use tirofiban and contrast agent through thrombus suction catheter after occlusion artery route in hyperthrombotic load patients with acute myocardial infarction. Methods From July 2018 to October 2019, 376 acute STEMI patients treated by emergency percutaus coronary intervention were admitted to the hospital successively. According to the different treatment methods, the 376 acute STEMI patients were divided into the study group (n = 54) and the control group (n = 322). The effects of two different routes of administration on postoperative myocardial perfusion(TIMI flow grades) and the incidence of severe hemorrhage, stroke and serious cardiac adverse events during hospitalization were compared. Results The preoperative thrombotic load of the study group was significantly higher than that of the control group (3.23±0.95 vs 2.14±0.66, P < 0.05). There was no significant difference in the incidence of intraoperative complications (P > 0.05), and there was no significant difference in the postoperative rate of TIMI 3 between the two groups (95.3% vs 96.3, P > 0.05). There was no significant infference to the incidence of severe hemorrhage, stroke during PCI and serious cardiac adverse events during the hospitalization between the two groups(P > 0.05). Conclusion With the use of tirofiban and contrast agent through thrombus suction catheter after the occlude artery route, it can effectively improve the myocardial perfusion and reduce the perioperative risk of acute STEMI patients with hyperthrombotic load and it is worthy of further study.
2021, 42(1): 115-123.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210104
Abstract:
Objective Cone-beam computed tomography(CBCT)was used to observe the anatomical structure of the mandibular canal in the mandible, providing theoretical basis for dental implants and alveolar surgery. Methods According to the inclusion and exclusion criteria, a total of 339 cases of CBCT imaging data were collected; all the cases were divided into groups on the basis of age and gender; and the anatomy and position of the mandibular canal was measured and analyzed. Results The lengths from mandibular canal to alveolar ridge crest, buccal bone plate, the lingual bone plate and the root apex were statistically significant among the different age and gender groups(P < 0.05); the lengths from mandibular canal and the inferior margin of the mandible was statistically significant among age groups(P < 0.05), but there was no statistical significance in gender groups(P > 0.05). Conclusion The location of the mandibular canal are highly variable. The mandibular canal runs in the mandible from the distal to the medial, from the tongue to the buccal side and gradually approaches the alveolar crest. The use of CBCT can clearly demonstrate the three-dimensional location of the mandibular canal in the mandible, which has great clinical guidance and reference value for the mandibular surgery and implant surgery.
2021, 42(1): 147-151.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210129
Abstract:
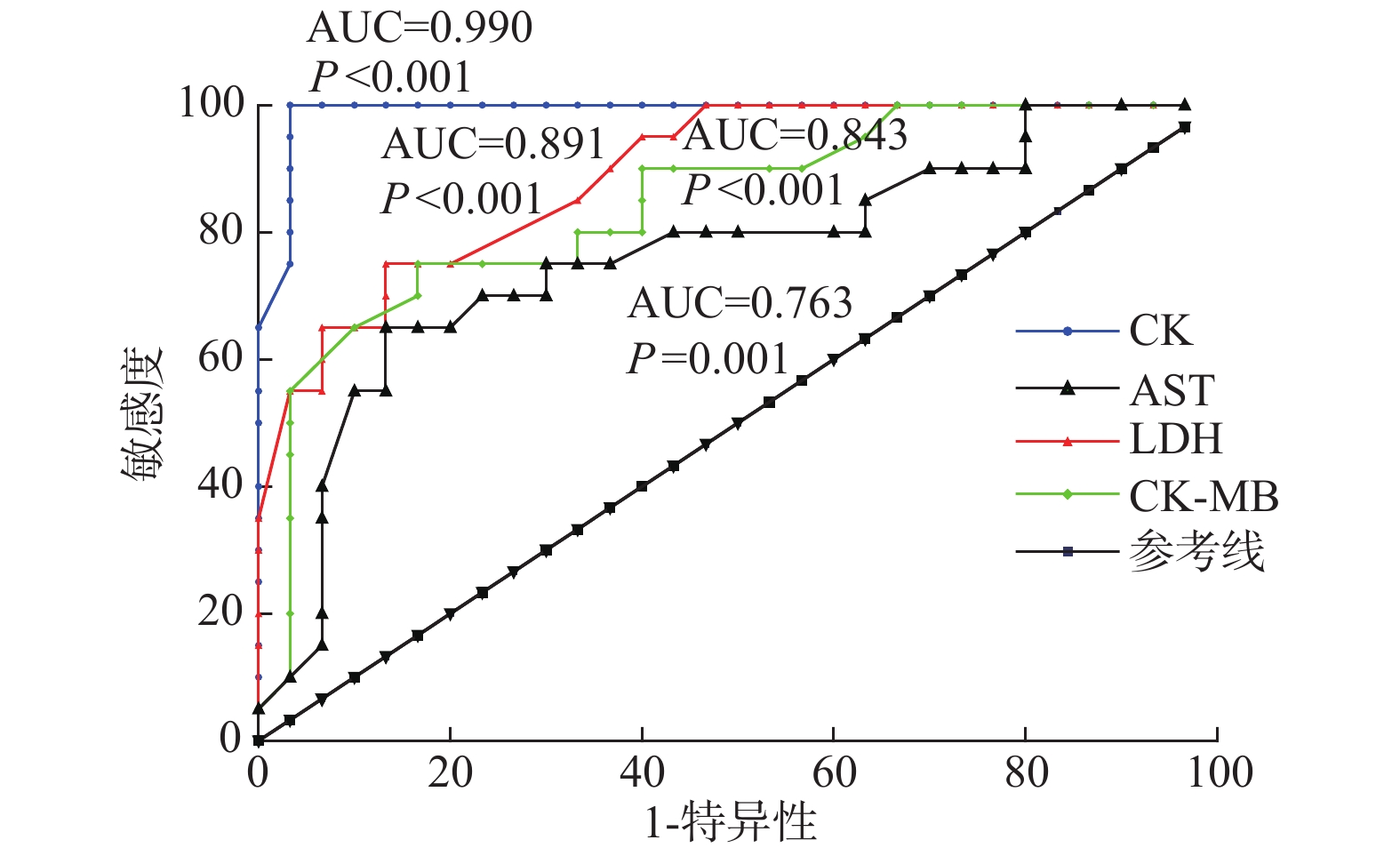
Objective To investigate the correlation between myocardial enzymes and the severity of type 1 diabetic ketoacidosis in children. Methods From January 2016 to December 2019, thirty children with type 1 diabetes and DKA treated in Anhui Provincial Children's Hospital were selected as the research objects, and twenty children with type 1 diabetes and non-DKA during the same period were selected as the control group to analyze the correlation between myocardial enzymes and disease severity. Results The serum levels of LDH, CK, CK-MB and AST in children with DKA were significantly higher than those in the control group(all P < 0.05). Serum CK, LDH, CK-MB, AST had certain predictive value for DKA in patients with type 1 diabetes, the area under the ROC curve AUC was 0.990(95%CI: 0.969~1.011), 0.891(95%CI: 0.805~0.977), 0.843(95%CI: 0.731~0.956), 0.763(95%CI: 0.622~0.905). The levels of LDH and CK in children with DKA increased gradually with the progression of the disease(F = 39.251, 11.458; P < 0.001, < 0.001). Compared with the remission period, the serum levels of LDH, CK, CK-MB and AST in children with DKA increased during the acute phase, and the differences were statistically significant(all P < 0.05). Multivariate Logistic regression analysis showed that CK and LDH were the independent risk factors for DKA(OR = 1.582, 1.651, P < 0.05). Spearman correlation analysis showed that CK and LDH were positively correlated with the progression of DKA(r = 0.933, 0.793, P < 0.0001, < 0.0001). Conclusion As the disease progresses, myocardial enzymes in patients with DKA gradually increase, and dynamic monitoring of changes in myocardial enzymes in patients is of great significance for the disease evaluation and treatment.
2021, 42(1): 152-156.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210114
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the effect of laser artificial shrinkage on the pregnancy outcome of single blastocysts transfer with different developmental days and stages in in the frozen-thawed cycles Methods The clinical data of 336 cases of frozen thawed single blastocyst transplantation cycles in reproductive center of Yulin maternal and Children Health Hospital in Guangxi were analyzed retrospectively. According to whether laser shrinkage was performed, the patients were divided into laser shrinkage group(227 cases)and non-shrinkage group(106 cases). According to the development time of blastocyst, the experimental group was divided into five groups: shrinkage D5 group, shrinkage D6 group, non shrinkage D5 group and non shrinkage D6 group. Then according to the score of cell mass and trophoblast layer in blastocyst, the experimental group was divided into three groups: shrinkage D5 group, shrinkage D6 group, non shrinkage D5 group and non shrinkage D6 group. The clinical outcomes of cryothaw transfer of single blastocysts with different developmental time and different grades were compared among the three groups. Results Compared with the single blastocyst and with the same development time, the abortion rate of D5 group with laser shrinkage was higher than that of D5 group without shrinkage, and the difference was statistically significant(P < 0.05). There were no statistically significant differences in the other outcome indicators between the wrinkled group and the non-wrinkled group(P > 0.05). Compared with the single blastocysts of the same grade, the pregnancy rate of the wrink-led embryo group was significantly higher than that of the other groups(P > 0.05). Conclusion Laser shrinkage can improve the clinical pregnancy rate of high quality single blastocyst transplantation but it can also increase the risk of D5 single blastocyst abortion rate.
2021, 42(1): 157-160.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210107
Abstract:
Objective To explore the relationship between serum homocysteine(Hcy)and blood lipid in physical examination population and provide the evidence for the mechanism research between Hcy and lipid level. Methods 234 health examinees who came to the health management center of a grade A hospital in Yunnan Province from January 2019 to November 2019 were randomly selected as the subjects. General information, smoking, drinking and diabetes histories of the cases were collected. Plasma homocysteine, blood lipid were measured. Statistical analysis software SPSS 17.0 was used to analyze the level of Hcy and its influencing factors on blood lipid. Results (1)The value of Hcy Md(QR)for males was 12.36(9.90)μmol/L, for females was 7.73(6.40)μmol/L. There was a significant difference between males and females.(2)Smoking history(KW = 15.335, P < 0.001), drinking history(KW = 18.937, P < 0.001), LDL-C(r = 0.304, P = 0.002)、TC(r = 0.294, P = 0.003)were all correlated with blood Hcy level. Conclusion Total serum cholesterol(TC), low density lipoprotein(LDL-C)are all correlated with blood Hcy level. And smoking, drinking and men are also related to the increase of Hcy level. It is necessary to strengthen the monitoring of the level of Hcy in the risky population and do more research about the relationship between Hcy and blood lipid.
2021, 42(1): 161-166.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210131
Abstract:
Drug dependence is considered as a serious chronic recurrent encephalopathy. Long-term use of addictive substances will lead to the occurrence and development of related comorbidities including the central nervous system, respiratory system, circulatory system and digestive system. Due to its special anatomical position and physiological function, the intestinal barrier plays an important role in preventing “foreign enemy invasion” and maintaining body homeostasis. This article focuses on the composition and function of the intestinal barrier, and studies on intestinal barrier damage caused by addictive substances (amfetamines, opioids, alcohol, etc.), and provides theories for further elucidating the mechanism of intestinal barrier damage caused by addictive substances and the later researches.
Drug dependence is considered as a serious chronic recurrent encephalopathy. Long-term use of addictive substances will lead to the occurrence and development of related comorbidities including the central nervous system, respiratory system, circulatory system and digestive system. Due to its special anatomical position and physiological function, the intestinal barrier plays an important role in preventing “foreign enemy invasion” and maintaining body homeostasis. This article focuses on the composition and function of the intestinal barrier, and studies on intestinal barrier damage caused by addictive substances (amfetamines, opioids, alcohol, etc.), and provides theories for further elucidating the mechanism of intestinal barrier damage caused by addictive substances and the later researches.
2021, 42(1): 167-172.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210108
Abstract:
Objective To study the construction, the prevention and treatment effect of the intensive nursing plan of oral mucositis caused by chemotherapy in acute leukemia. Methods 100 patients newly diagnosed as acute leukemia chemotherapy in the Dept. of Hematology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University were selected from October 2019 to October 2020 to carry out this study. According to the random number table method, they were divided into the observation group and the control group, with 50 cases in each.The control group was given routine preventive care, and the observation group was given intensive care on the basis of the control group. After the nursing intervention, the general data(before the intervention), the incidence of oral inflammation infection, the OMDQ score, the psychological state score and the nursing satisfaction of the two groups were evaluated and compared. Results There was no significant difference between the two groups(P > 0.05). After the nursing intervention, the infection rate of oral mucosa in the observation group was 32.00%(16/50), which was lower than that in the control group 52.00%(26/50). The difference between the two groups was statistically significant(P < 0.05). After the nursing intervention, the scores of OMDQ, SAS and SDS in the observation group were lower than those in the control group(P < 0.05). The nursing satisfaction of the observation group was 90.00%(45/50), which was higher than that of the control group 74.00%(37/50). There was significant difference between the two groups(P < 0.05). Conclusion Through the construction of cluster nursing intervention program, the effect of nursing intervention on the oral mucositis caused by chemotherapy of acute leukemia is good, which can reduce the incidence of patients with oral inflammation infection, improve the patients' quality of life score, bad psychological state, and improve the patients' nursing satisfaction. It is worthy of clinical recommendation.
2021, 42(1): 173-176.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210116
Abstract:
Objective To analyze the risk factors and countermeasures of PICC catheter-related infection in cancer patients. Methods From May 2019 to August 2020, 180 patients over 18 years old with PICC were enrolled and divided into non infection group(162 cases)and infection group(18 cases). The differences in gender, age, single catheterization puncture number, PICC retention time, catheter movement, chemotherapy times and diabetes mellitus were compared between the two groups. Results There were no significant differences in age and gender between the infection group and non infection group(P > 0.05), but there were significant differences in single catheterization puncture number, PICC retention time, catheter movement, chemotherapy times and diabetes mellitus between the two groups(P < 0.05); the basic diseases such as catheter movement(or = 2.421), chemotherapy times(or = 6.475), and diabetes mellitus(or = 3.271)were CR I risk factors. Conclusion There are many risk factors for catheter-related infection in cancer patients after PICC catheterization, mainly including catheter movement, chemotherapy frequency and diabetes mellitus. In clinical practice, symptomatic nursing strategies for related risk factors can prevent and reduce the probability of catheter-related infection to the greatest extent.


 Email
Email RSS
RSS