2021 Vol. 42, No. 12
2021, 42(12): 1-5.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20211202
Abstract:
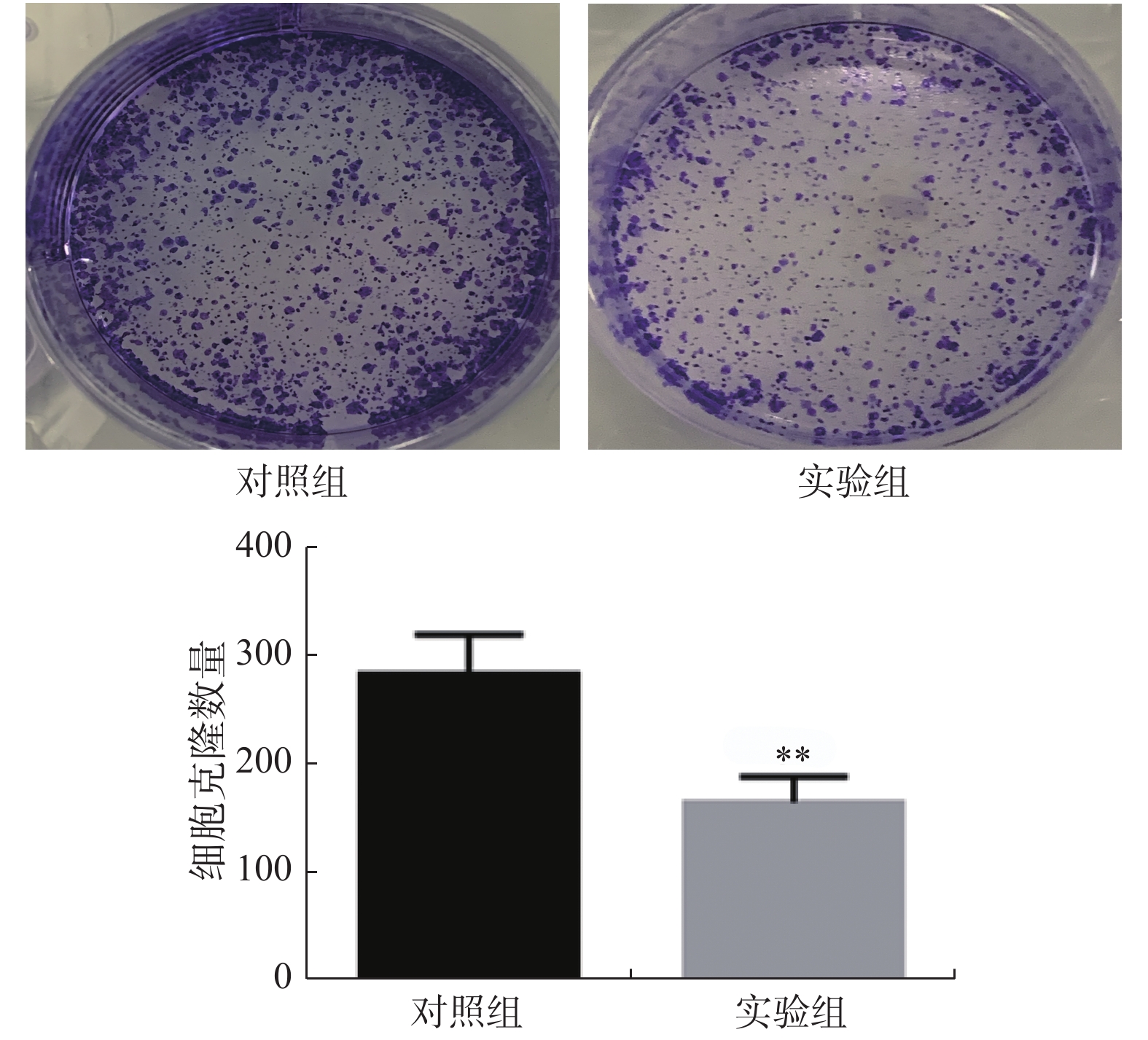
Objective To investigate the effects of sevoflurane on proliferation, migration, invasion and malignant behavior of Xuanwei lung cancer cells XWLC-05, and to further explore its potential mechanism. Method XWLC-05 cells were treated with sevoflurane, and the changes of proliferation, apoptosis, migration and invasion of XWLC-05 cells were detected in vitro; the tumorigenicity of XWLC-05 cells was detected in vivo, and the expressions of PI3K/AKT and MMP-2 / MMP-9 were analyzed by Western blot. Result The number of clones in control group (287.5±23.1) was higher than that in experimental group (174.1±16.3) (P < 0.05); the apoptosis rate in the control group (1.60±0.38) was significantly lower than that in the experimental group (31.48±5.81) (P < 0.01), and the number of migrating cells in the control group (87.8±10.2) was significantly higher than that in the experimental group (35.2±4.4) (P < 0.05). The number of invasive cells in the control group(93.6±7.3) was significantly higher than that in the experimental group (30.7±3.2) (P < 0.01). Sevoflurane treatment significantly decreased the expression levels of PI3K, p-Akt and MMP-2, MMP-9 (P < 0.05). Conclusion By inhibiting PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, sevoflurane decreased the proliferation ability of XWLC-05, induced apoptosis, and weakened the migration, invasion and tumorigenesis ability of XWLC-05 cells. Sevoflurane may be a new treatment option for Xuanwei lung cancer.
2021, 42(12): 6-10.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20211205
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the applicability of lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 (Lp-PLA2) as an indicator for effectiveness in patients with coronary heart disease taking statins. Methods Retrospective analysis and cohort design were used to study 58 patients with coronary heart disease who were admitted to Xinkunhua Hospital in Yunnan province. They were divided into two groups: 29 patients with coronary heart disease who were taking statins as the observation group; 29 patients with coronary heart disease who did not take statins were the control group. There were no significant differences between the observation group and the control group in gender, age, incidence of diabetes and smoking (P > 0.05). Lp-pla2 in the two groups was compared and analyzed, and the influence of related factors on LP-PLA2 was evaluated. Results The overall Lp-PLA2 [139.6 (94.0, 181.1) ng/mL] of the observation group is significantly lower than that of the control group [278.6 (207.0, 358.3) ng/mL] (P < 0.001). Conclusion Lp-PLA2 can be used as an effective indicator for monitoring the efficacy of statins of ASCVD.
2021, 42(12): 11-16.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20211210
Abstract:
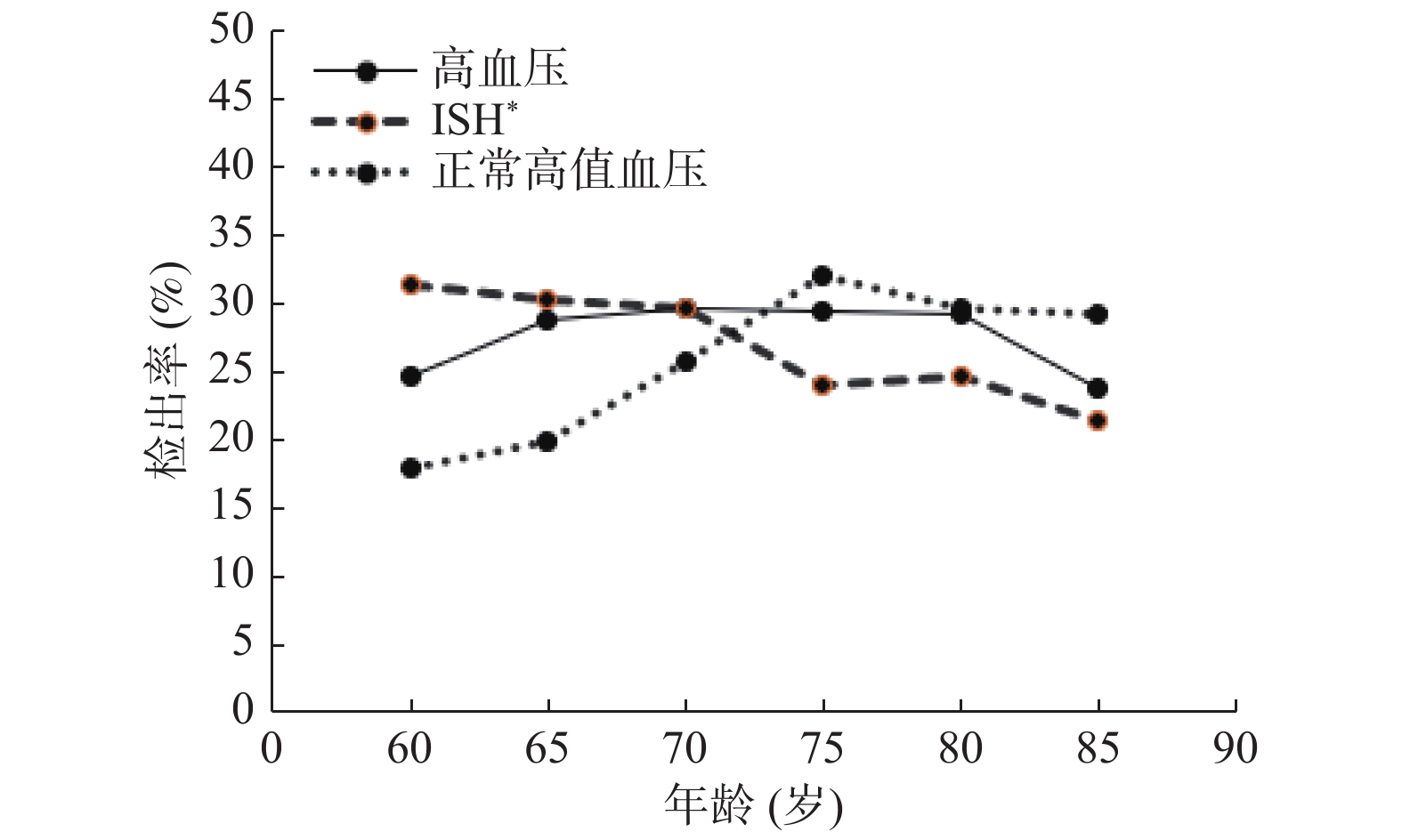
Objective To investigate the prevalence and determinants of hypertension in seniors in Anning city. Methods From September 2019 to January 2020, 9 709 people over 60 years old in Anning city were selected by multi-stage proportional stratified random sampling method. Questionnaires, physical and laboratory tests were used. Results A total of 9709 people aged 60-100 years (72.07±6.17) were investigated. The detection rate of hypertension was 28.82% (95%CI: 27.92%~29.72%), which was lower than the hypertension prevalence in people over 60 in China (49%, P < 0.05). The detection rate of hypertension in female was higher than that in male, but the detection rate of high normal and simple systolic hypertension (ISH) was lower than that in male population. The detection rate of hypertension varies in different areas ( P < 0.05). Logistic regression results showed that the senior with diabetes ( OR = 1.338), overweight (OR = 1.481), obesity (OR = 2.032), abnormal triglyceride (OR = 1.177), abnormal total cholesterol (OR = 1.361) were more likely to develop hypertension (P < 0.05). Conclusion The detection rate of hypertension in seniors in Anning city is lower than the national level. Diabetes, overweight, obesity, abnormal triglyceride and abnormal total cholesterol are the main risk factors.
2021, 42(12): 17-22.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20211213
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the effect of probiotics combined with early enteral nutrition in the treatment of severe brain injury patients with VAP and the effect of intestinal mucosal barrier function. Methods A total of 84 patients with severe brain injury admitted to the Neurosurgery Department of Suzhou Hospital affiliated to Nanjing Medical University from September 2016 to November 2020 were randomly divided into observation group and control group. Both groups received early enteral nutrition with nasal feeding, and the observation group received additional probiotics on this basis. The incidence of ventilator-associated pneumonia, intestinal mucosal barrier function and gastrointestinal complications were compared between the two groups before and after treatment. Results Compared with the control group, the incidence of VAP in the observation group is lower, the levels of hypersensitive C-reactive protein and procalcitonin were significantly lower at 7th and 21st days after enteral nutrition, plasma D-lactic acid and diamine oxidase concentrations were significantly lower at 7th day after enteral nutrition. Gastrointestinal complications during treatment were significantly lower than those in the control group. And the differences were statistically significant (P < 0.05). Conclusion Probiotics combined with early enteral nutrition can reduce the incidence of VAP, reduce the release of inflammatory factors, protect the intestinal mucosal barrier function, and reduce gastrointestinal complications.
2021, 42(12): 23-27.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20211214
Abstract:
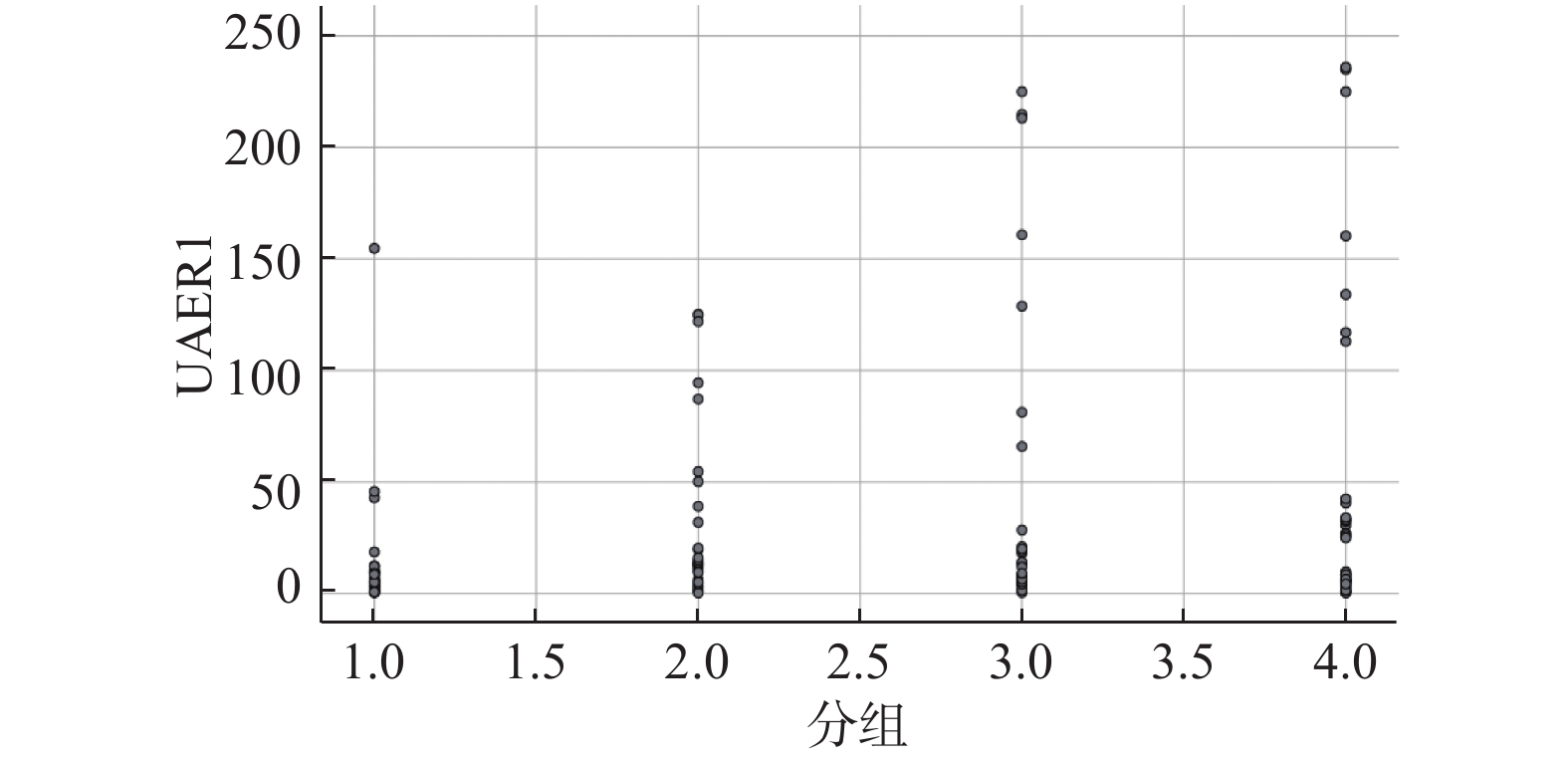
Objective To explore the correlation between time in range (TIR) and diabetic albuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes. Methods 120 patients aged 30 to 65 years and diagnosed with type 2 diabetes within 10 years were enrolled. Continuous Sugar Monitoring System (CGMS) was used to observe TIR of the patients. With TIR 30%, 50% and 70% as cut-off points, 120 patients were divided into 4 groups with 30 cases in each group: Study group 1: TIR > 70%, Study group 2: 50% < TIR≤70%, Study group 3: 30% < TIR≤50%, study group 4: TIR≤30%. The general characteristics, laboratory data, blood glucose monitoring data and the correlation between TIR and diabetic proteinuria of the 4 groups were analyzed. Results There were differences in LDL-C, HbA1c, UAER, and urine microalbumin among the 4 groups (P < 0.05), while there were no significant differences in age, gender, BMI, blood pressure, blood lipids, and renal function among the 4 groups. TIR was found to be an independent risk factor for diabetic proteinuria after adjusting for general information such as age and blood pressure, using Logistic regression analysis. Conclusion TIR is closely related to the occurrence and degree of diabetic albuminuria.
2021, 42(12): 28-35.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20211215
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the relationship between thyroid function and cardiovascular disease-related indicators, and explore feasibility of thyroid function in the risk assessment of cardiovascular disease and death in T2DM patients in the next 10 years. Methods A retrospective study was performed on 527 inpatients who met the diagnostic criteria for type 2 diabetes in the Department of Endocrinology, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University from January 2018 to December 2020. Among them, 100 patients with type 2 diabetes complicated with subclinical hypothyroidism without previous history of valvular heart disease or myocardial infarction were enrolled as case group (DM+SCH group); 100 patients with normal thyroid function without previous history of valvular heart disease or myocardial infarction were stratified and randomly selected from the 527 patients with type 2 diabetes as control group (DM group). Data of basic characteristics, blood chemistry and imaging of all patients were collected, and comparison between groups was conducted. Pearson correlation analysis was used to analyze the levels of thyroid stimulating hormone and blood lipids such as total cholesterol (TC) and Triacyl triglycerol (TG), respectively. Cardiac function indicators include left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), cardiac output (CO), cardiac index (Cardiac index). CI) and ratio of early and late mitral valve diastolic filling speed (E/A ratio) were collected to evaluate the correlation between thyroid function and cardiovascular disease related indicators. Results There were 100 patients with subclinical hypothyroidism among all the patients in this study, the prevalence rate is 18.98%.The female cases in DM+SCH group were significantly higher than DM group, the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). Compared with DM group, TSH level in DM+SCH group was significantly higher, TT3, FT3, TT4, FT4 and RT3 levels were decreased, and TG-AB level was significantly higher, with statistical significance (P < 0.05, P < 0.01). The serum levels of TC, LDL-C and LDL-C/HDL-C in DM+SCH group were higher than those in DM group, and the differences were statistically significant (P < 0.01). In DM+SCH group, CO, LVEF, E peak, E/A ratio decreased, and vascular resistance increased, with statistically significant difference(P < 0.05, P < 0.01). Pearson correlation analysis showed that TC and LDL-C levels were positively correlated with TSH levels (P < 0.05, P < 0.01). CO, LVEF, E peak and E/A were negatively correlated with TSH level (P < 0.05, P < 0.01), while vascular resistance was positively correlated with TSH level (P < 0.05). Conclusions 1. TSH is associated with lipid profile and partial cardiac function in type 2 diabetes mellitus with subclinical hypothyroidism. 2. Thyroid function should be included in the assessment of the occurrence and mortality risk of cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes over the next 10 years.
2021, 42(12): 36-40.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20211217
Abstract:
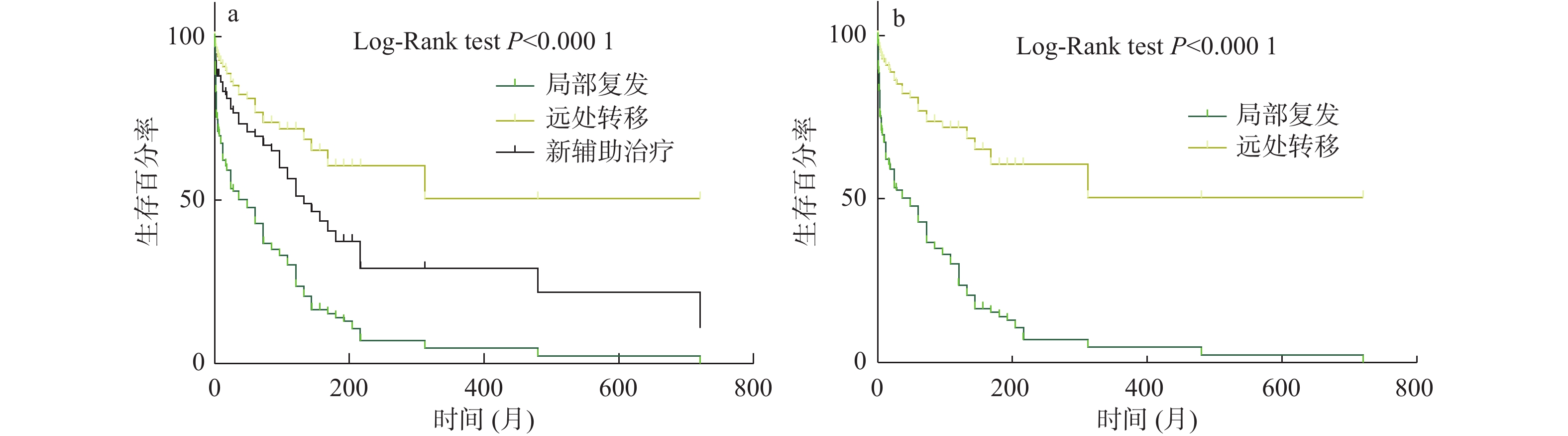
Objective To explore the correlation between preoperative clinical stage, carcinoembryonic antigen and postoperative prognosis in patients with rectal cancer. Methods 200 patients with rectal cancer from October 2013 to October 2015 were collected from The Central Hospital of Enshi Prefecture. Pathological T, N, AND M staging, preoperative CEA value, lesion location, length of involved bowel (measured by CT image), proportion of involved bowel, positive periintestinal lymph nodes, positive circumferential resection margin, distance from anus, and infiltration of extraneous vessels were collected retrospectively. The patients were followed up to observe whether the patients had recurrence, metastasis and death after surgery, and the time of recurrence, metastasis and death was recorded. Cox multivariate correlation analysis was used to analyze the correlation between the above indicators and postoperative recurrence and metastasis, and to find the factors that predicted postoperative recurrence and metastasis. Recurrence and metastasis were described by Kaplan-Meier curve and their differences were tested by Log-Rank. Results The factors related to postoperative metastasis were N stage, P = 0.001; HR = 11.22; 95%CI (2.55, 49.25), preoperative CEA value P < 0.001, HR = 1.00; 95%CI (1.002, 1.006); and these two factors were associated with distant metastasis after surgery. The factors associated with local recurrence were T stage (P = 0.036); HR = 1.726; 95%CI (1.03, 2.87), preoperative CEA value P = 0.034; HR = 1.00; 95%CI (0.99, 1.005). Conclusion T staging was significantly associated with postoperative local recurrence, and N staging was associated with postoperative distant metastasis. Preoperative T staging can predict postoperative local recurrence of rectal cancer. Preoperative N staging and CEA can predict postoperative distant metastasis of rectal cancer.
2021, 42(12): 41-46.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20211218
Abstract:
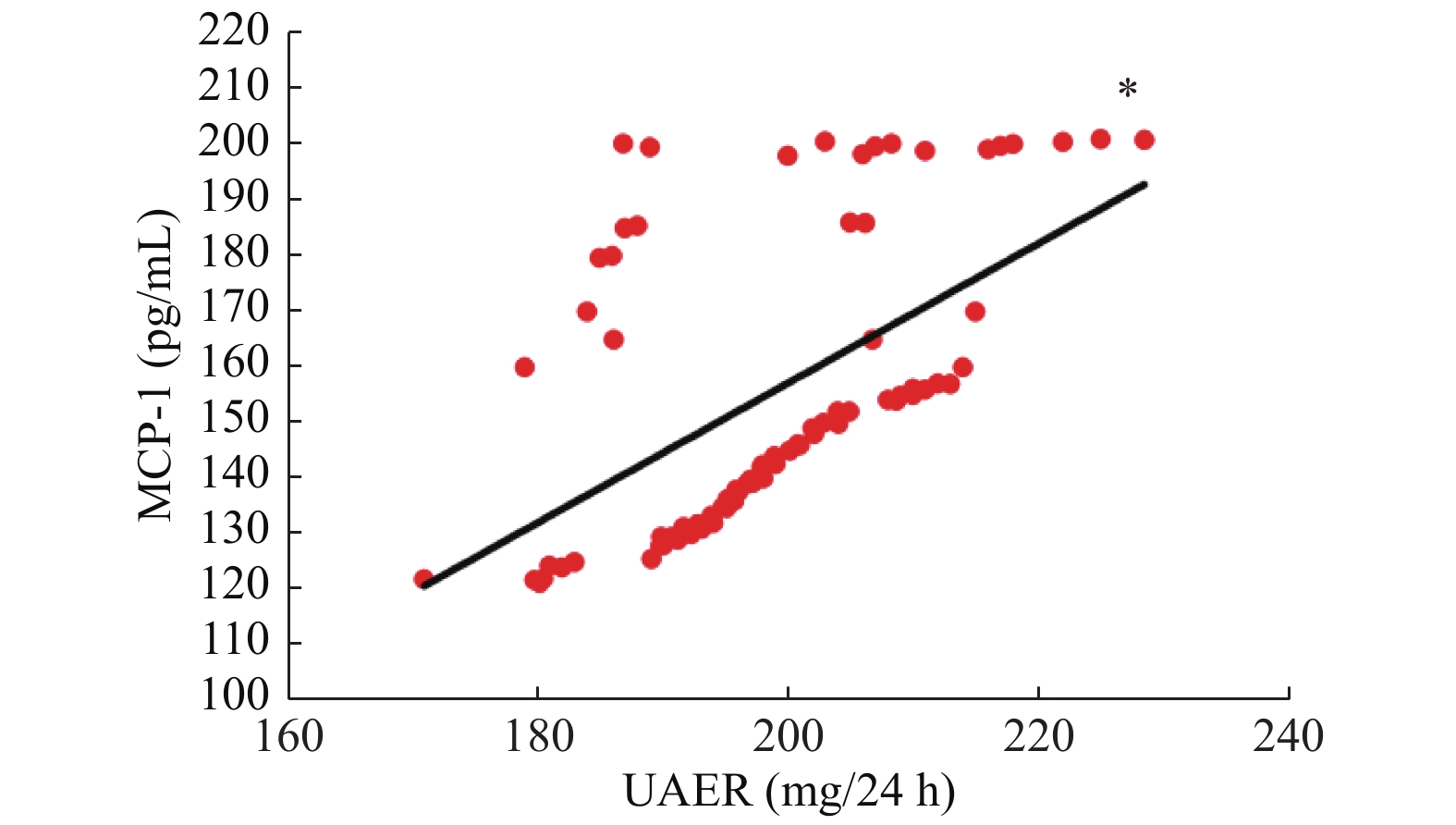
Objective To investigate the effect of Dapagliflozin in the treatment of early diabetic nephropathy and its effect on serum MCP-1 and IL-6. Methods 78 cases of patients with early diabetic nephropathy treated in our hospital from January 2019 to January 2020 were randomly divided into observation group and control group, with 39 cases in each group. Both groups received irbesartan and other conventional treatment. In addition, patients in the control group were treated with metformin, and patients in the observation group were treated with dagaglidine for 12 weeks. The changes of serum creatinine, fasting blood glucose (FBG), 2 h postprandial blood glucose (2 h PG), glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), urinary albumin excretion rate (UAER) and serum McP-1 and IL-6 levels in 2 groups were compared before and after treatment. Results After treatment, FBG, 2hPG and HbA1c in the two groups were significantly decreased, and the observation group was significantly lower than the control group (P < 0.05). After treatment, UAER in both groups was significantly lower than before treatment, and the observation group was lower than the control group, the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). There was no significant change in serum creatinine level in 2 groups before and after treatment (P > 0.05). After treatment, the serum LEVELS of McP-1 and IL-6 in 2 groups were significantly decreased compared with before treatment, and the observation group was significantly lower than the control group, the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). Pearson correlation analysis showed that UAER was positively correlated with serum MCP-1 and IL-6 in early diabetic nephropathy patients (P < 0.05). Conclusion The application of Dapagliflozin in the treatment of early diabetic kidney disease can not only effectively control the blood glucose, but also reduce the serum MCP-1 and IL-6, reduce the leakage of urine protein, and then protect the renal function.
2021, 42(12): 47-50.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20211219
Abstract:
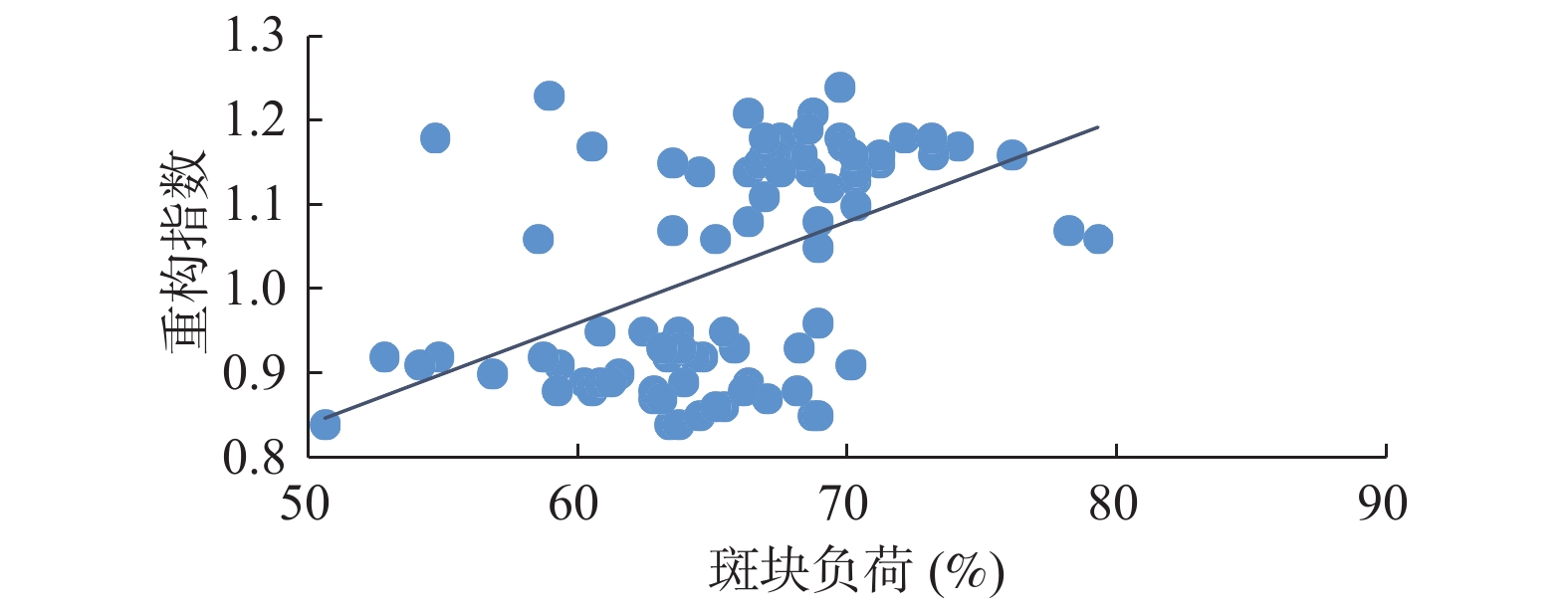
Objective To investigate the role of plasma miR-30a and coronary intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) in the early assessment of coronary artery disease in patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS). Methods 88 ACS patients were randomly selected, including stable angina group (SA group, 42 cases) and ACS group (46 cases). Plaque load and remodeling index (RI) were detected by IVUS, and plasma miR-30a was detected by real-time PCR. The changes of plaque load, RI and plasma miR-30a in ACS group were studied. The relationship between plaque load, plasma miR-30a and RI was analyzed by Pearson correlation. Plaque load and remodeling index (RI) were detected by IVUS, and plasma miR-30a was detected by real-time PCR. The changes of plaque load, RI and plasma miR-30a in ACS group were studied. The relationship between plaque load, plasma miR-30a and RI was analyzed by Pearson correlation. Results Compared with SA group, plaque load in ACS group was increased [ (62.82±4.40)% vs (68.32±4.59)%]; RI increased from (0.90±0.03) to (1.15±0.05); plasma miR-30a[ (8.10±1.09)2-ΔΔct*104 vs (11.66±1.19)2-ΔΔct*104] increased. RI was positively correlated with plaque load (r = 0.482, P = 0.000) and plasma miR-30a level (r = 0.817, P = 0.000). Conclusion Patients with ACS have early coronary artery positive remodeling, and plasma miR-30a can be used as an evaluation indicator of early ACS coronary artery disease.
2021, 42(12): 51-58.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20211220
Abstract:
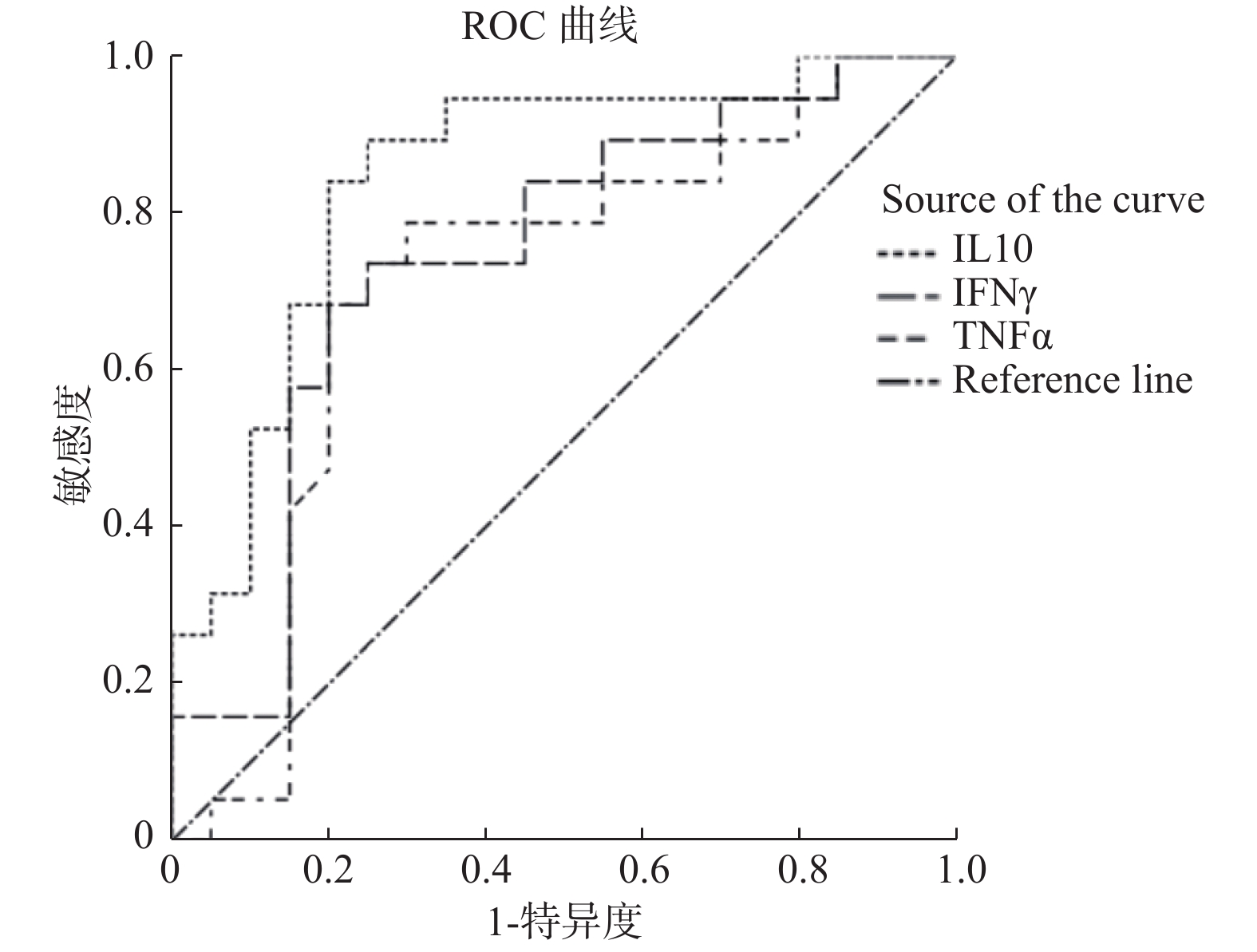
Objective To analyze the clinical features of adult hemophagocytic syndrome (HPS) and the correlation between the levels of various cytokines and prognosis. Methods The data of 19 adult patients with hemophagocytic syndrome were collected, and the clinical features and laboratory tests were analyzed. The blood samples were collected for 12 cytokine levels detection, and the correlation between the levels and prognosis was analyzed. Results The levels of cytokines IL-1β, IL-2, IL-4, IL-8, IL-10, IL-6, IFN-γand TNF-α in HPS patients were higher than those in non-HPS non-infected patients (P < 0.05). The levels of IL-4, IL-5, IL-10, IFN-γ and TNF-α in HPS patients were higher than those in non-HPS patients (P < 0.05), the ROC curve of IL-10, IFN-γ and TNF-α showed that the AUC of IL-10, IFN-γ and TNF-α was between 0.7 and 0.9, indicating accuracy in the diagnosis of HPS. Fib was significantly lower than that in the survival group (P < 0.05), while there were no significant differences in age, sex, clinical features (fever, liver, spleen, lymphadenopathy) and laboratory tests (ALT, AST, TBIL, ALB, Fer, TG, ACN, HGB, PLT) between the HPS death group and the survival group (P > 0.05), and the levels of IL-1β, IL-8 and TNF-α in HPS death group were significantly higher than those in survival group (P < 0.05). Conclusion HPS may present increased levels of various cytokines, among which IL-10, IFN-γ and TNF-α may be significant for the diagnosis of HPS. The significant decrease of Fib and the significant increase of IL-1β, IL-8 and TNF-α may indicate a poor prognosis.
2021, 42(12): 59-66.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20211221
Abstract:
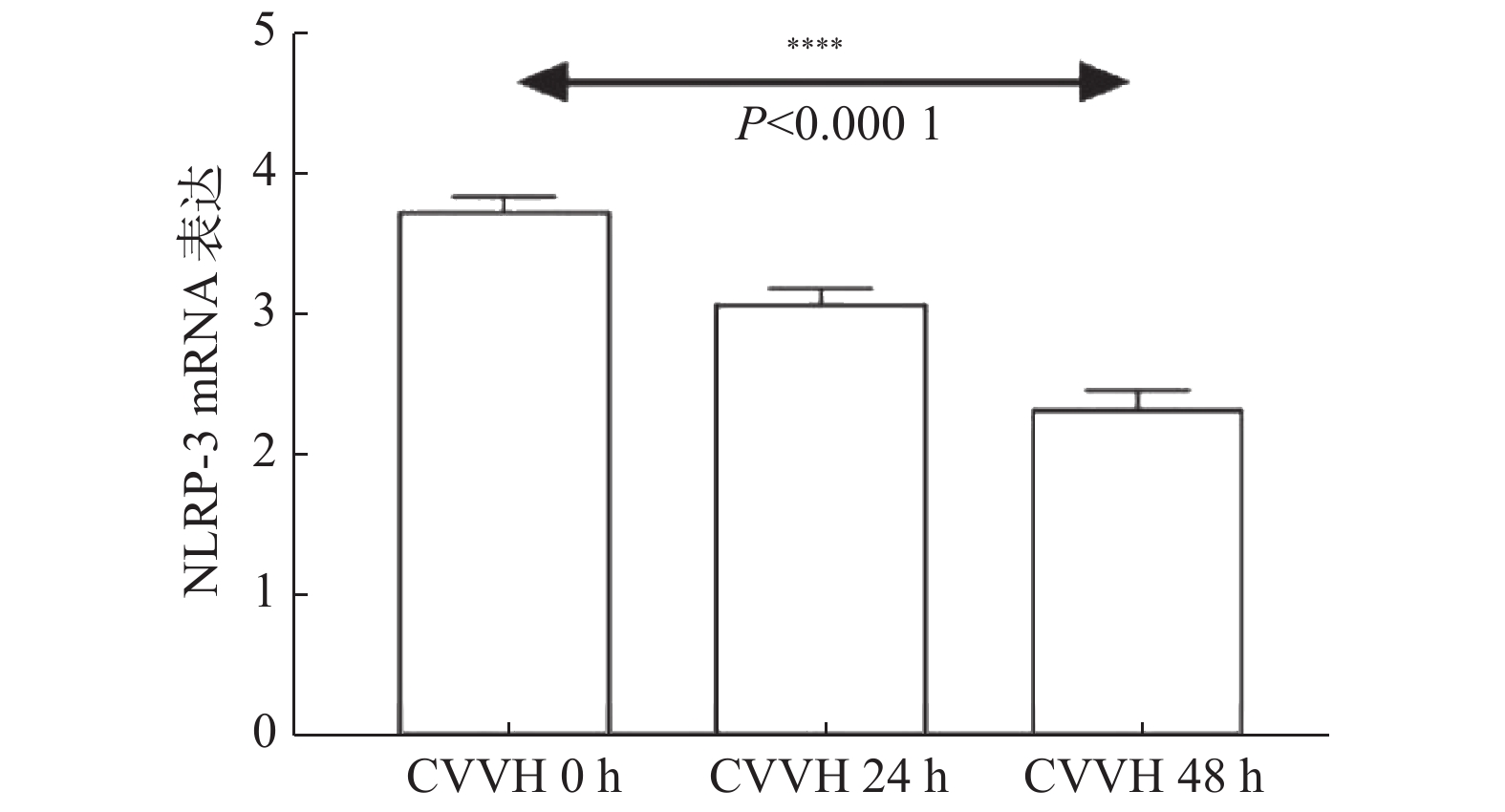
Objectives To explore the effects of regional citric acid anticoagulation on the expression of NLRP3 and its downstream inflammatory pathway in patients with acute kidney injury (AKI) after cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB). Methods A total of 37 patients with acute kidney injury who received open-heart surgery assisted by cardiopulmonary bypass from April 2019 to April 2021 in The Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, Yan’an Hospital Affiliated to Kunming Medical University were selected, including 31 patients in the AKI group requiring CRRT after cardiac surgery. 32 patients without AKI after cardiac surgery were randomly selected as the control group. Cardiac ultrasound, cardiopulmonary bypass auxiliary time, liver and kidney function, myocardial enzymology and other baseline data were measured in each group. The mRNA relative expression levels of NLRP-3 and apoptotic pathway caspase-1 were determined by qRT-PCR, and the expression levels of downstream cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, IL-18) were determined by ELISA. The correlation between NLRP-3 and the above indicators was analyzed. Results Compared with the control group, the auxiliary time of cardiopulmonary bypass (cardiopulmonary bypass time, blocking time, stop time and parallel circulation time) in AKI group was significantly longer (P < 0.05). qRT-PCR results showed that in AKI group, the mRNA expressions of NLRP-3 and Caspase-1 decreased after 24 h and 48 h CVVH treatment compared with before treatment (P < 0.05), and further decreased with the prolonged treatment time (P < 0.05). In the control group, the mRNA expressions of NLRP-3 and Caspase-1 increased at all postoperative time points compared with those before surgery (P < 0.05), and began to decrease at 48h after surgery (P < 0.05). ELISA results showed that in AKI group, the expression of downstream cytokines IL-1β, IL-6 and IL-18 decreased after 24h and 48h CVVH treatment compared with before treatment (P < 0.05). In the control group, the expressions of downstream cytokines Il-1 β, Il-6 and Il-18 at all postoperative time points were increased compared with those before surgery (P < 0.05), and began to decrease 48h after surgery (P < 0.05). Spearman correlation analysis indicated that nlRP-3 expression was positively correlated with blocking time and stopping time after regional citric acid anticoagulant CVVH treatment (R = 0.514, P = 0.003; R = 0.401, P = 0.025). Conclusions The expression of NLRP-3 and downstream inflammatory factors increased in patients with AKI after cardiopulmonary bypass. Regional citric acid anticoagulation can effectively reduce the expression of NLRP-3 and downstream inflammatory factors. NLRP-3 expression after CVVH treatment was positively correlated with blocking time and stopping time.
2021, 42(12): 67-73.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20211222
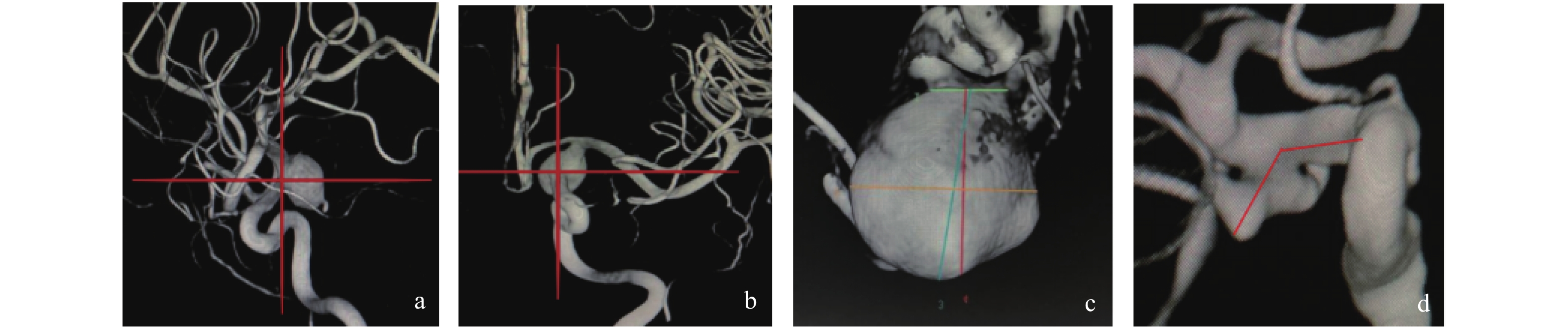
Abstract:
Objective To analyze the clinical features and morphological risk factors of rupture and hemorrhage of posterior communicating artery aneurysm in the brain, in order to provide decision-making basis for the clinical diagnosis and treatment of posterior communicating artery aneurysm. Methods The clinical data of 72 patients diagnosed with posterior communicating aneurysm from January 2016 to December 2020 in the Second Department of Neurosurgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University were retrospectively analyzed. The clinical data and aneurysm morphological parameters of the patients were collected. According to whether subarachnoid hemorrhage was complicated, they were divided into ruptured group and unruptured group. SPSS software was used for statistical analysis to analyze the risk factors related to the rupture of posterior communicating aneurysm. Results There was no statistically significant difference (P > 0.05) between the two groups in the comparison of basic characteristics such as gender, age, and smoking history, while there was a statistically significant difference (P < 0.05) in the comparison of hypertension, maximum diameter of the aneurysm less than 5 mm, Inflow angle more than 90°, daughter sacs and bleb, whether the morphology was regular or not, and the orientation of the apex of the aneurysm. Multifactorial analysis showed that hypertension (OR: 5.82, 95% CI : 1.23-27.51), Inflow angle > 90° (OR: 7.88, 95% CI: 1.27-48.59), and daughter sacs and bleb (OR: 11.92, 95% CI: 2.06-68.76) were independent risk factors for posterior communicating aneurysm rupture. Conclusion A history of hypertension, a maximum diameter smaller than 5 mm, an Inflow angle greater than 90°, daughter sacs and bleb ,dome of the aneurysm directed to posterior-outer-inferior were risk factors for posterior communicating aneurysm rupture. Conclusion A history of hypertension, a maximum diameter smaller than 5 mm, an Inflow angle greater than 90°, daughter sacs and bleb ,dome of the aneurysm directed to posterior-outer-inferior were risk factors for posterior communicating aneurysm rupture.
2021, 42(12): 74-82.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20211223
Abstract:
Objective To compare the torque control of upper teeth with 3 appliances (Damon double wings bracket, Tip-Edge Plus bracket and Damon self-ligating bracket) in the extraction cases, and to provide the reference basis for the comprehensive consideration of the patient’s condition and the selection of the best appliance and correction technique. Methods A total of 40 patients were selected from the Orthodontics Department of Stomatology Hospital affiliated to Nanjing University School of Medicine and The Stomatology Department of Kunming Yan’an Hospital from January 2016 to December 2019. The patients were moderate dentition congestion with Angle type I malocclusion requiring extraction of the first maxillary premolars. Among them, 10 patients were treated with Ormaco traditional double-wing straight wire arch bracket orthodontic device, 10 patients with TIP-EDGE Plus differential dynamic straight wire arch bracket orthodontic device and 20 patients with Damon passive self-locking orthodontic device with standard torque. Twenty measurement items reflecting cranio-maxillofacial relationship and soft tissue morphology were compared before and after treatment. Results In the three groups, the anterior protrusion of the anterior teeth was presented before the treatment, and the side appearance was in the protrusive state. After treatment of three kinds of orthodontic techniques, the anterior teeth protrusion improved, ∠U1-L1 increased than before treatment, while ∠U1-NA decreased.In the soft tissue, the three groups of UL-EP and LL-EP reduced, and the Z angle increased, which was close to the normal value, suggesting that the side front process was also improved. There was no significant difference among the three groups in the 4 aspects of sagittal, vertical, anterior dental protrusion and soft tissue before and after correction (P > 0.05). Conclusion The results of this study showed that Damon double wings bracket, Tip-Edge Plus bracket and Damon self-ligating bracket have a certain effect on improving anterior teeth protrusion. After treatment, the measured values were closed to normal numerical value. The standard torque Damon self-ligating bracket and Tip-Edg plus bracket as well as Damon double wings bracket can effectively control the anterior teeth torque in the extraction cases. Three kinds of brackets have no obvious difference in the control torque.
2021, 42(12): 83-88.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20211224
Abstract:
Objective To analyze the clinical effect of arthroscopy combined with open-wedge high Tibial osteotomy (OWHTO) and open-tibial high osteotomy alone in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis. Methods The clinical data of 34 patients (39 knees) who received surgery for osteoarthritis of the knee in our department from January 2018 to January 2020 were retrospectively analyzed. They were divided into two groups according to the surgical methods. Group A consisted of 17 patients who received arthroscopy combined with OWHTO surgery, and group B consisted of 22 patients who received OWHTO surgery alone. The clinical efficacy of the two groups was compared. Results (1) There were no significant differences in preoperative HSS score, VAS visual simulation score, knee range of motion and Lysholm knee score between the two groups, which makes the two groups comparable. (2) There were significant differences in HSS, VAS and Lysholm knee score between 2 groups 3 days and 1 month after surgery, and group A was higher than group B, with statistical significance (P < 0.05); however, there were no significant differences in HSS, VAS score, Lysholm knee score at 3 months, 6 months and 12 months postoperatively between the two groups. There was no significant difference in knee joint range of motion between the two groups 3 days, 1 month, 3 months, 6 months and 12 months after operation. Conclusion Arthroscopy combined with open tibial high osteotomy is more effective than open tibial high osteotomy alone in the treatment of early knee osteoarthritis in terms of pain relief, and there is no significant difference in the long-term clinical efficacy.
2021, 42(12): 89-94.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20211225
Abstract:
Objective To evaluate the efficacy of myocardial ischemic preconditioning in paclitaxel eluting PTCA balloon catheter. Methods A total of 210 patients who underwent paclitaxel eluting PTCA balloon catheter were randomly divided into 3 groups. The control group received percutaneous paclitaxel eluting coronary balloon dilatation coronary angioplasty was performed according to the routine operation; The second group, half minute ischemic preconditioning group, received non compliant balloon dilation twice for 30 seconds interval 3 minutes. The third group, minute ischemic preconditioning group, received non compliant balloon dilation was applied twice for 60 seconds interval 3 minutes. Coronary SYNTAX II scores were recorded for all patients, percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA), the values of creatine kinase (CK), creatine kinase isoenzyme (CK-MB) and cardiac troponin I (cTnI) were recorded before and 24 hours after operation. All patients were followed up for MACE events (including cardiac death, myocardial infarction, heart failure, cardiac readmission, target vessel re-vascularization) and improvement of clinical symptoms within 180 days after surgery. Results (1) There was no significant difference in myocardial injury markers before PTCA, occurrence of angina pectoris, tachyarrhythmia and bradyarrhythmia during PTCA among the three groups (P>0.05), but the myocardial injury markers 24 hours after PTCA in 1 minute ischemic preconditioning group was significantly lower than that in the control group and half minute preconditioning group (P < 0.05); (2) The incidence of MACE events and the improvement of clinical symptoms within 180 days after PTCA in 1 minute ischemic preconditioning group were significantly better than those in the control group and half minute preconditioning group (P < 0.05). Conclusion (1) Myocardial ischemic preconditioning in paclitaxel eluting coronary balloon catheter can reduce myocardial injury; (2) Myocardial ischemic preconditioning in paclitaxel eluting coronary balloon catheter can improve the prognosis and clinical symptoms of PTCA.
2021, 42(12): 95-100.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20211226
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the efficacy of ultrasound-guided percutaneous transhepatic cholecystectomy combined with elective laparoscopic cholecystectomy in the treatment of cholecystolithiasis complicated with acute onset of chronic cholecystitis. Methods 61 patients with cholecystolithiasis complicated with acute onset of chronic cholecystitis admitted to The 2nd Heptatopancreatobiliary Surgery Department of The Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University and The General Surgery Department of Xishuangbanna Dai Autonomous Prefecture People’ s Hospital from January 2018 to September 2021 were retrospectively analyzed. All patients received PTGD in the acute stage, and 40 of them received elective LC after readmission. The clinical manifestations, laboratory examinations and imaging differences between patients before PTGD and before LC were compared, and PTGD and LC related complications and postoperative conditions were analyzed. Results 40 patients returned to the hospital again for elective LC. Compared with before PTGD, the clinical manifestations of the patients, such as abdominal pain and fever, were improved or disappeared. WBC count decreased, alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase decreased, and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). Abdominal ultrasound showed that the gallbladder wall thickness was thinner and the longest diameter of the gallbladder was shortened, with statistical significance (P < 0.05). All the 40 patients who received LC were operated under laparoscope without conversion to laparotomy, biliary tract injury or complications, and all were cured and discharged from hospital. Conclusion PTGD combined with elective LC is effective in the treatment of cholecystolithiasis with acute attack of chronic cholecystitis, which can avoid biliary tract injury and reduce the conversion of LC to laparotomy.
2021, 42(12): 101-105.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20211227
Abstract:
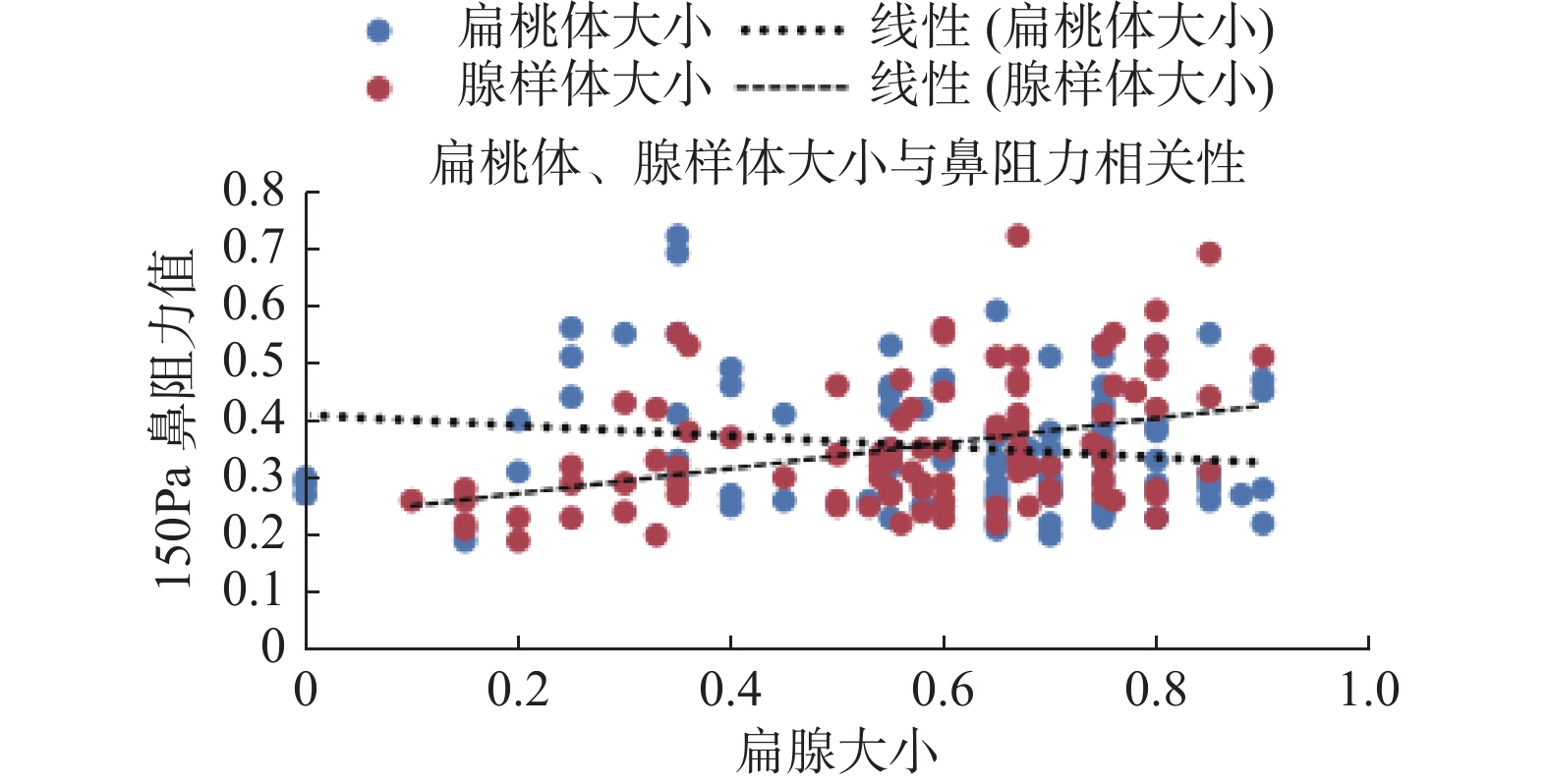
Objective To analyze the efficacy of nasal resistance measurement in the diagnosis and treatment of OSA in children by measuring the data of nasal resistance measurement in children with OSA. Methods A total of 100 OSA children admitted to our hospital from July 2019 to July 2020 were included as the experimental group. All the children were diagnosed by polysomnograph (PSG), and 20 healthy children without sleep disorders were randomly selected as the control group. The children in the experimental group and the control group were tested for nasal resistance. According to the results of PSG, the study group was divided into three groups: mild OSA, moderate OSA and severe OSA. According to the size of tonsils and adenoids, the experimental group was further divided into three subgroups: adenoid hypertrophy group, tonsil hypertrophy group, and adenotonsillar hypertrophy group. In the experimental group, hypertrophy tonsils and/or adenoids were removed by low-temperature plasma knife, and nasal resistance was measured again after 1 month follow-up. Results The mean nasal resistance value of experimental group was significantly higher than that of control group (P < 0.05), but there was no statistical difference in the mean nasal resistance of mild OSA group, moderate OSA group and severe OSA group ( P > 0.05). Adenoid hypertrophy group and adenotonsillar hypertrophy group were significantly higher than tonsil hypertrophy group and control group ( P < 0.05). There was no statistical difference in mean nasal resistance value between tonsil hypertrophy group and control group ( P > 0.05), and there was no statistical difference between adenoid hypertrophy group and adenotonsillar hypertrophy group ( P > 0.05). The nasal resistance value of the study group was lower after surgery than before ( P < 0.05). Nasal resistance value was positively correlated with adenoid hypertrophy ( ρ = 0.38, P < 0.001), but not with OAHI value and tonsil hypertrophy ( ρ = 0.09, ρ= -0.16, P > 0.05). Conclusion The nasal resistance value is significantly increased in OSA children, which reflects the degree of OSA adenoidal hypertrophy in children, and can be used to evaluate the effect of postoperative improvement of upper airway resistance to a certain extent.
2021, 42(12): 106-111.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20211228
Abstract:
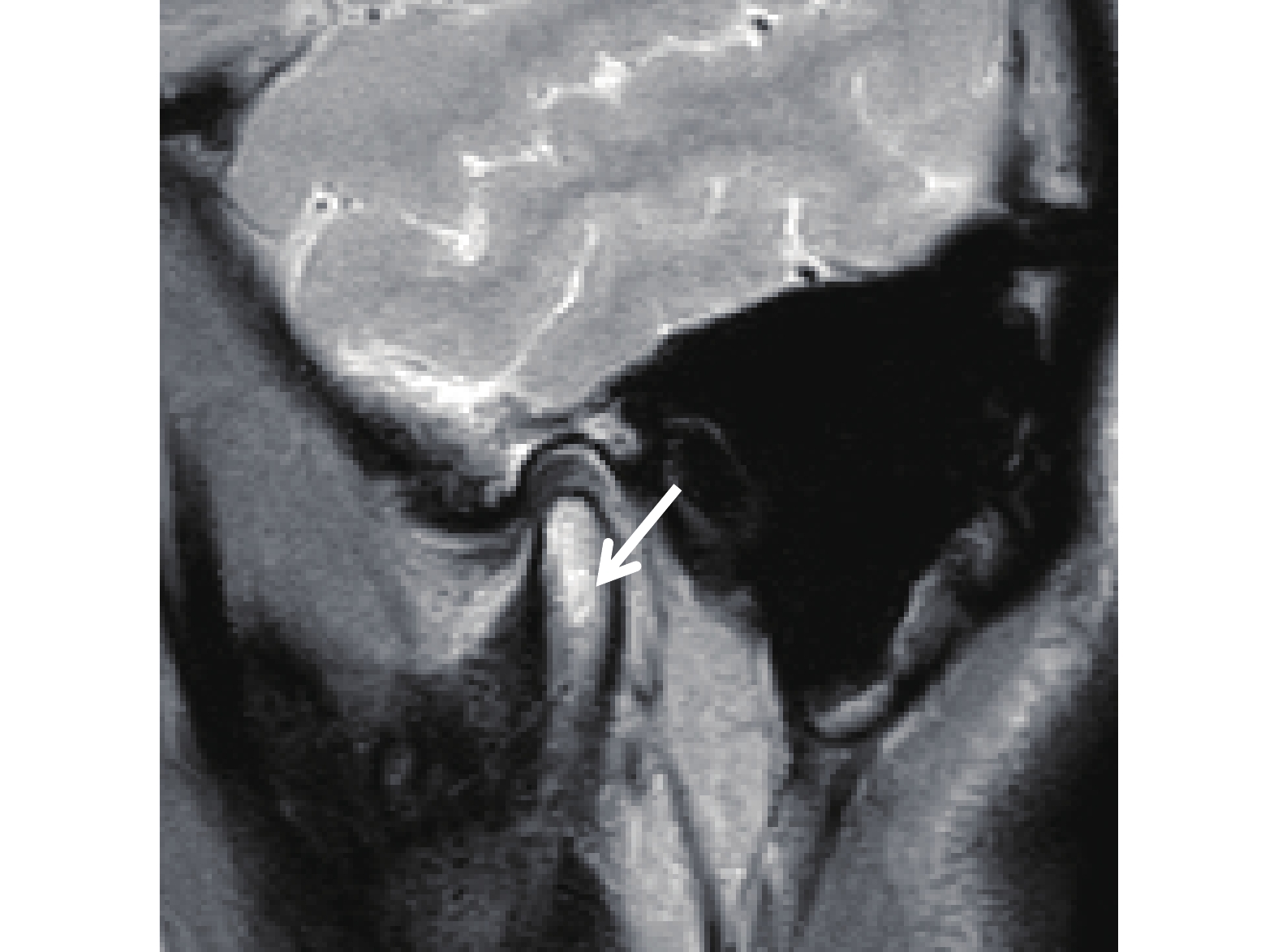
Objective To investigate the diagnostic value of MRI in immediate injury of temporomandibular joint without condylar fracture. Methods 36 patients with temporomandibular joint injury without condylar fracture treated in the Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery of the Affiliated Hospital of Yunnan University from June 2018 to March 2021 were selected, with a total of 72 joints included in the study. Cone beam CT results of all patients showed that there was no fracture of condyle and articular fossa, and the bone on the surface of condyle was “complete” after injury. All patients had no history of joint diseases. After injury, they had varying degrees of joint pain, limited opening and popping. Among them, 24 cases were complicated with fractures of face and other parts. The included patients were examined by MRI, and the results were statistically analyzed. Results MRI showed that 48 joints had different degrees of injury, and the incidence was 66.7%. The injury types included 12 joints with bone marrow edema (25%), 27 joints with posterior disc tear (56.25%), 33 joints with disc displacement (68.75%), and 36 joints with joint cavity hematocele and effusion (75%). The incidence of posterior disc disruption, disc displacement, and intraarticular blood accumulation (bone effusion) were significantly higher than those of bone marrow edema( P <0.05). Conclusion MRI can clearly show the location and type of injury of joint soft tissue after immediate injury of temporomandibular joint without condylar fracture. In addition, in these injuries, the incidence of posterior disc tear, disc displacement, joint cavity hematocele (effusion) was significantly higher than that of bone marrow edema. MRI is an important examination and evaluation method after immediate injury of temporomandibular joint without condylar fracture.
2021, 42(12): 112-116.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20211229
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the factors causing abnormal insertion of umbilical cord placenta during pregnancy, and to analyze the influence of abnormal insertion of umbilical cord placenta on pregnancy outcome. Methods A total of 15,771 pregnant women who were examined in the Ultrasound Department of The Second People’s Hospital of Yunnan Province from January 1, 2016 to January 31, 2021 were included in the observation. 879 cases of abnormal insertion ports were pathologically confirmed after delivery and were selected as the study group, and 1000 cases of normal insertion ports were randomly selected as the control group. Results Logistic regression analysis suggested multiple pregnancy history (OR = 3.34, P < 0.001), scarred uterus (OR = 3.54, P < = 0.003), twin pregnancy (OR = 5.25, P < 0.001), abnormal placental position (OR = 3.47, P < 0.001), abnormal placental morphology (OR = 8.52, P = 0.007), in vitro embryo transfer (OR = 5.06, P < 0.001), uterine fibroids (OR = 4.86, P < 0.001) were the risk factors for abnormal umbilical cord insertion. In terms of pregnancy outcomes, there was no significant difference between normal umbilical insertion and marginal umbilical insertion( P >0.05), but there was significant difference between normal umbilical insertion and velamentous umbilical insertion (P < 0.001). Conclusion Multiple pregnancy history, scar uterus, twin pregnancy, abnormal placenta position, abnormal placenta morphology, in vitro embryo transfer, uterine fibroids are the high risk factors for abnormal umbilical cord insertion. For pregnancy with high-risk factors, doctors should be alert to the insertion location during prenatal ultrasound, so as to improve the prenatal diagnosis rate of abnormal insertion of the insertion mouth, especially the velamentous-like umbilical cord insertion, and improve clinical pregnancy and perinatal outcomes.
2021, 42(12): 117-122.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20211230
Abstract:
Objective To analyze perioperative psychological needs of parents of cleft lip and palate patients. Methods Using the family function assessment scale, a questionnaire survey was conducted on the parents of 65 patients with cleft lip and palate who were randomly selected during hospitalization from January 2017 to December 2018. The survey involved the psychological needs of the parents of children with cleft lip and palate, including the degree of worry about surgery, the degree of understanding of cleft lip and palate disease knowledge, the level of family education, how to encourage children, how to enhance children’s resilience and how to improve children’s mental health. Results Among the six psychological needs of parents of patients with cleft lip and palate, more than half of the parents of children are generally worried about cleft lip and palate surgery (50.77%); the education level of children’s families is mainly junior middle school or below (53.85%), and nearly half of the parents’ knowledge of cleft lip and palate disease is mainly expressed as general knowledge (44.62%). As for how to increase the understanding degree of children’s stress resistance, how to encourage the understanding degree of children’s advantages and how to improve the understanding degree of children’s mental health, most of the parents of children showed little understanding (40.00%, 47.69% and 46.15%, respectively).The correlation analysis showed that among the six psychological needs of parents of patients with cleft lip and palate, parents’ understanding of disease knowledge, how to encourage their children and how to enhance their children’s resistance were significantly positively correlated with how to improve their children’s mental health (P < 0.01); there was a significant positive correlation among the three (P < 0.01). There was also a significant positive correlation between family education level and the three (P < 0.01). There was a significant positive correlation between parents’ knowledge of cleft lip and palate disease and family education level (r = 0.361), how to encourage children with advantages (r = 0.534) and how to enhance children’s stress resistance (r = 0.696) (P < 0.01). Conclusion It is of great significance to carry out psychological intervention for parents of children with cleft lip and palate during the perioperative period to improve their understanding of the disease knowledge, to help parents in the perioperative period to encourage their children’s advantages, and to guide parents to cultivate their children’s ability to cope with adversity, so as to improve the clinical psychological treatment level of parents and children with cleft lip and palate.
2021, 42(12): 123-128.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20211231
Abstract:
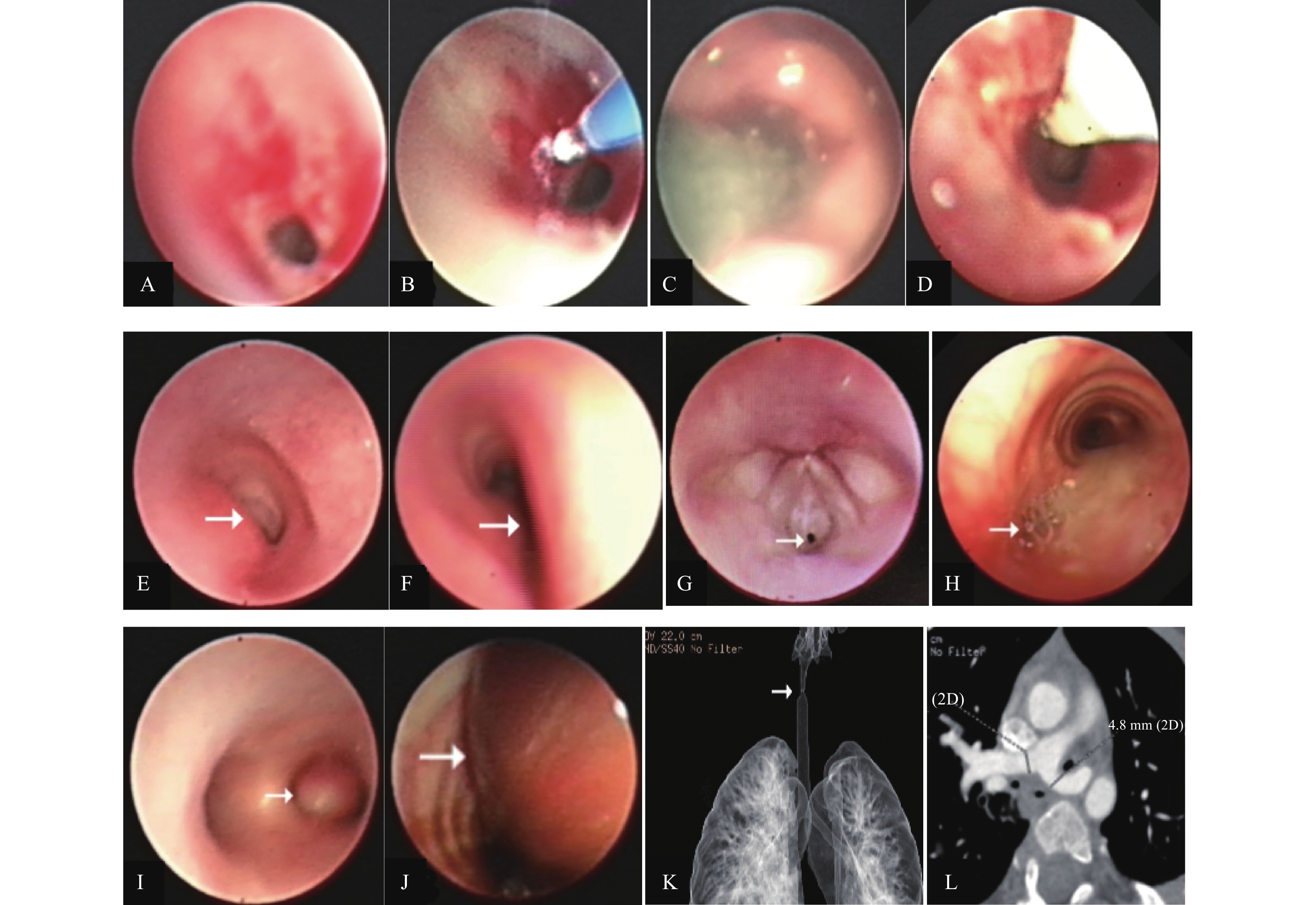
Objective To analyze the etiology and morphological classification of children with central airway stenosis, and to explore the diagnosis and treatment methods. Methods Clinical data of 84 children with central airway stenosis hospitalized from August 2017 to August 2020 were retrospectively collected, including 54 males and 30 females; aged 20d to 14 years, and there are 64 infants (76%, 64/84). Through CT and electronic bronchoscopy, the etiology and morphological characteristics of the children's central airway stenosis were determined, and the treatment based on electronic bronchoscopy was developed. Results (1) Majority of them were structural stenosis (88.1%, 74/84), and a few were dynamic stenosis (11.9%, 10/84). (2) The most common stenosis was left and right main bronchial stenosis (54.8%, 46/84), followed by subglottic stenosis (23.8%, 20/84), and carina stenosis (2.4%, 2/84) (3) 76% to 90% stenosis of was the most common (54.8%, 46/84). (4) Stenosis of 1-3cm was the most common (57.1%, 48/84). 16 of the 84 cases received follow-up observation without intervention treatment, and their conditions were stable during follow-up observation. 50 patients received electronic bronchoscope intervention therapy, the treatment was effective. Conclusion Central airway stenosis can be reported in children of all ages, and its etiology and morphological classification can be basically determined by CT and electronic bronchoscopy examination. The central airway stenosis in children was mainly structural and benign. Interventional therapy via electronic bronchoscope is the main treatment for central airway stenosis in children.
Correlation Analysis of Chest Imaging and Laboratory Indicators in Patients with 2019-nCoV Infection
2021, 42(12): 129-134.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20211232
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the correlation between chest CT scan and laboratory indicators in 2019-nCoV infected patients, and to provide reference for early diagnosis and treatment. Methods Retrospective analysis was performed on 2019-nCoV infected patients admitted to the Third People’s Hospital of Kunming from February to March 2020. Patients were divided into abnormal chest CT group and normal chest CT group. Correlation analysis was conducted on CT data and laboratory related indicators. Results The age of 9 patients with 2019-nCoV infection was positively correlated with the size of whole lung consolidation shadow and ground glass density shadow (r = 0.34, r = 0.48, P < 0.05), and age was positively correlated with the size of whole lung lesion (r = 0.40, P < 0.05). Pneumonia accounted for 64.1%, among which double lung disease accounted for 80.00%, unilateral disease accounted for 20.00%; There were differences in eosinophil count, CRP, CD8+ count and R-glutamylaminotransferase increase in lung CT with or without abnormality (P < 0.05). The size of lung lesion was negatively correlated with lymphocyte count, eosinophil count, CD8+ and CD3+ count, and positively correlated with CRP and GGT. Conclusion In 2019-nCoV patients, bilateral lung lesions are common. The older the age, the more lung lesions; The lower the number of lymphocytes, the higher the number of CD8+ and CD3+, the higher the CRP and GGT, the more lung lesions, which can be used as an early warning indicator of pneumonia and severe disease.
2021, 42(12): 135-139.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20211233
Abstract:
Objective To explore the correlation between depression and health status of the elderly with chronic disease and the intervention outcomes. Methods A total of 119 geriatric inpatients from The Second People’s Hospital of Kunming were recruited in the cross-sectional study from June 2017 to December 2019. We gathered general information, and evaluated depressive state by Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale-Depression Subscale (HADS-D), activities of daily living (ADL) by Barthel index, cognitive function by mini-mental state examination (MMSE), nutrition risk by Nutrition risk screening (NRS2002). According to the HADS-D scores, 119 geriatric inpatients were divided into a depressive state group (n = 26, HADS-D≥11) and a non-depressive state group (n = 93, HADS-S < 11). Follow-up and record the curative effect of the depressive group after intervention. Chronic diseases, comorbidities, activities of daily living and nutritional status were compared between two groups by using. Results Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, stroke, comorbidities increase the risk of depression. The depressive state is negatively related to the ADL (r = - 0.447, P < 0.001), and positively related to the nutrition risk (r = 0.197, P < 0.05).With effective interventions for depressive state, nutrition risk and ADL can be improved. (t = 7.5340, P < 0.001) (t = 13.5695, P < 0.001. Conclusions Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, stroke and comorbidities increase the risk of depressive state. The elderly with depression have poor daily living ability and higher nutrition risk. After effective intervention in depressive state, the daily living ability can be partially recovered and the nutrition risk can be improved.
2021, 42(12): 140-144.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20211034
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the clinical efficacy of non-biological artificial liver in patients with liver failure. Methods A retrospective analysis of 112 cases of liver failure patients treated with non-biological artificial liver in our hospital from January 2017 to December 2020, to observe the clinical efficacy and influencing factors. Results 112 patients with liver failure had significantly increased ALB, ALT, AST, CHE, TBIL, DBIL, IBIL, and PLT after treatment with non-biological artificial liver. The difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). According to non-biological artificial liver treatment, the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). Liver treatment results, 112 patients were divided into improved group (61 cases), no improvement group (51 cases), in terms of the overall efficacy of non-biological artificial liver in the treatment of liver failure, AST, TBIL, DBIL, IBIL, PT, INR The MELD value decreased significantly, and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). Conclusion Non-biological artificial liver can effectively improve the liver function and coagulation function of patients with liver failure, reduce bilirubin, and reduce the mortality of patients. MELD value can be used to guide non-biological artificial liver treatment after evaluating the condition of patients with liver failure.
2021, 42(12): 145-150.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20211234
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the incidence and influencing factors of potentially inappropriate medication (PIM) among hospitalized elderly patients, and provide reference for promoting rational drug use among elderly patients. Methods The incidence of PIM in elderly patients discharged from Kunming Second People’s Hospital from January to December 2019 was retrospectively investigated using Beers criteria (2019 edition) of American Geriatrics Society. The basic information and concomitant diseases of patients were collected, and the influencing factors of PIM were analyzed by Logistic regression method. Results According to the assessment of 2019 AGS Beers criteria, among 3577 elderly patients, the incidence of PIM was 58.51%, involving a total of 45 drugs and 3198 times. The top three drugs were gastrointestinal system drugs (48.23%), diuretic drugs (39.47%) and central nervous system drugs (25.0%). Logistic regression analysis showed that age ≥ 75 years, hospitalization ≥ 25 days, medication ≥ 10 kinds, heart failure, atrial fibrillation, cerebrovascular disease, gastrointestinal disease, insomnia, osteoporosis, hyperuricemia and pain were risk factors for PIM (P < 0.05). Conclusion PIM was present in more than 50% of elderly inpatients in Kunming Second People’s Hospital. Advanced age, long hospital stay, heart failure, atrial fibrillation, cerebrovascular disease, gastrointestinal disease, insomnia, osteoporosis, hyperuricemia and pain were all independent risk factors for PIM.
2021, 42(12): 151-155.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20211235
Abstract:
Objectives To explore the drug concentration in cerebrospinal fluid of isoniazid by one and two intrathecal injections after lumbar cisterna catheterization, and to analyze the correlation between concentration and curative effect. Methods Based on the inclusion criteria, 90 patients with tuberculous meningitis were selected and randomly divided into 3 groups with 30 patients in each group, including control group, intrathecal injection A1 group and A2 group, respectively. The 2 intrathecal injection groups received lumbar cistern catheterization. By observing the concentration of isoniazid in the cerebrospinal fluid of the two intrathecal injection groups at 0 h, 6 h and 12 h, the concentration of isoniazid in the cerebrospinal fluid of the one and two intrathecal injections was compared, and the efficacy of the two groups was compared. Result In the control group, the drug concentration in cerebrospinal fluid was lower at 0 h. After 6 h of intrathecal injection, the concentration of isoniazid in cerebrospinal fluid of group A2 was higher than that of group A1, the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). After 2 weeks of treatment, the effective rate of A2 (90.0%) was significantly higher than that of A1 group (66.7%). Conclusion Intrathecal injection of isoniazid is more effective than peripheral anti-tuberculosis treatment of tuberculous meningitis. Two intrathecal injections in one day can maintain the effective concentration of isoniazid in cerebrospinal fluid for a longer time than one intrathecal injection. It also provides a foundation for developing personalized treatment plan for patients of varying severity.
2021, 42(12): 156-160.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20211237
Abstract:
As a key enzyme in the process of gluconeogenesis, FBP1 controls the rate of gluconeogenesis and catalyzes the irreversible hydrolysis of fructose 1-6 diphosphate into fructose 6-phosphate and inorganic phosphate, thereby controlling the rate of gluconeogenesis and affecting cellular glycolysis. In recent years, its role in malignant tumors has attracted more and more attention. Studies have found that FBP1 is abnormally expressed in a variety of tumors and is closely related to tumor occurrence and prognosis. These results show a good prospect for tumor molecular markers, targeted drug research, and prognosis-related research.
As a key enzyme in the process of gluconeogenesis, FBP1 controls the rate of gluconeogenesis and catalyzes the irreversible hydrolysis of fructose 1-6 diphosphate into fructose 6-phosphate and inorganic phosphate, thereby controlling the rate of gluconeogenesis and affecting cellular glycolysis. In recent years, its role in malignant tumors has attracted more and more attention. Studies have found that FBP1 is abnormally expressed in a variety of tumors and is closely related to tumor occurrence and prognosis. These results show a good prospect for tumor molecular markers, targeted drug research, and prognosis-related research.
2021, 42(12): 161-164.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20211239
Abstract:
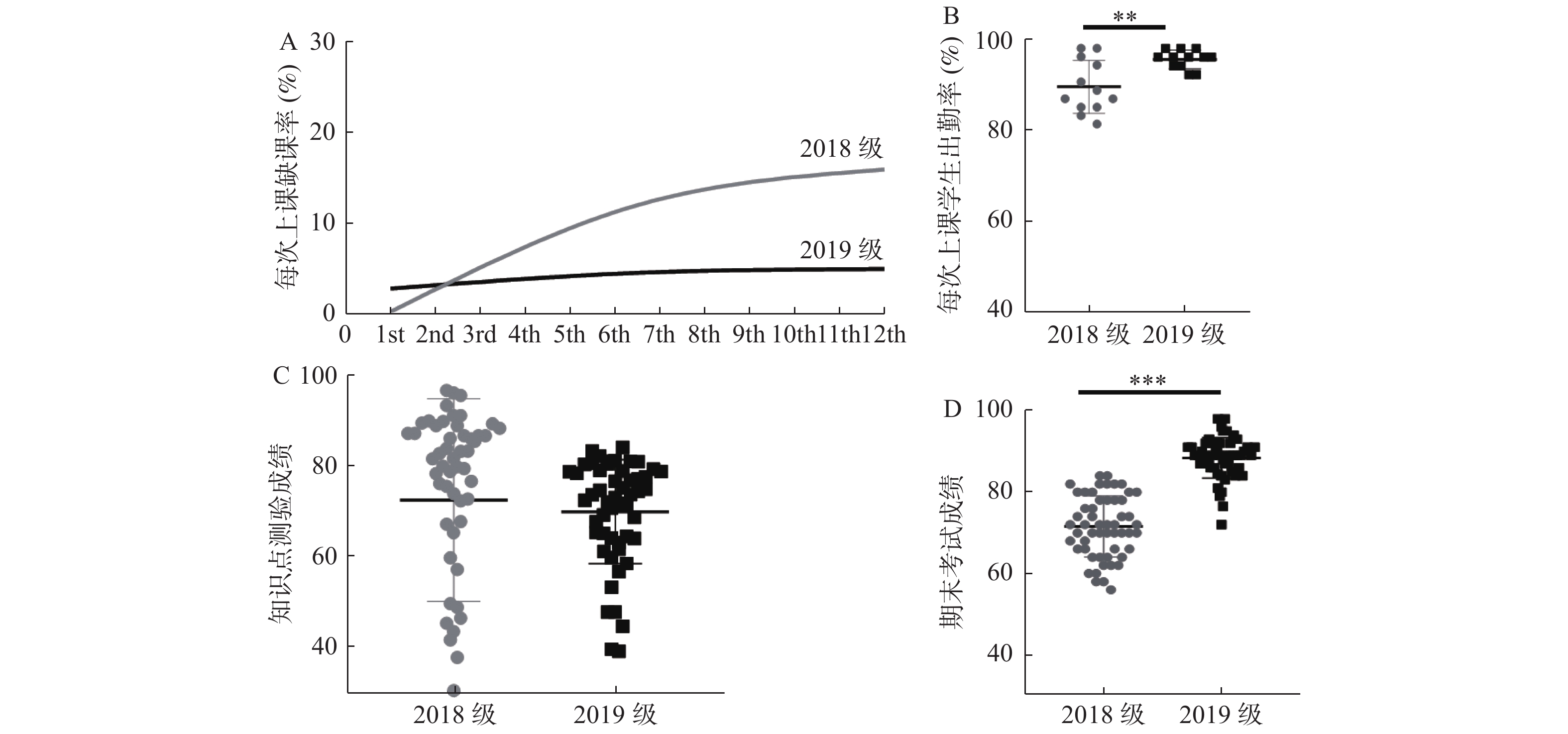
Objectives To explore a better online teaching model for MBBS international students under the impact of COVID-19. Methods The “PPT+ voice mode” based on rain classroom and the “live online mode” based on Dingding software were used for online teaching. The advantages and disadvantages of the two modes were evaluated by analyzing students’attendance rate and test scores. Questionnaire was used to explore students’acceptance of online teaching. Results The attendance rates of the batch 2018 "PPT + voice courseware" group and the batch 2019 "live online mode" group were (89.66±5.58)% and (95.67±1.94)%, respectively, and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.001). The results of knowledge content test were (72.49±22.12) and (69.94±11.34) respectively, and there was no significant difference between them ( P > 0.05). The final exam scores were (71.56±7.44) and (88.40±4.95) respectively, and the difference between the two groups was statistically significant ( P < 0.0001). The results of the questionnaire survey are that 7.14% of students prefer online teaching. 74.08% students have no preference for online teaching methods. Conclusion Compared with "PPT+ voice mode", "live online mode" based on Dingding software yielded higher attendance rate and better final exam results.
2021, 42(12): 165-168.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20211241
Abstract:
Objective To explore the effect of comfort care on patients with complications after gynecological laparoscopic CO2 pneumoperitoneum. Methods A total of 204 patients with CO2 pneumoperitoneum complications after laparoscopic surgery in The Department of Gynecology of the Third People’s Hospital of Yunnan Province from June 2019 to December 2020 were selected, and they were divided into control group and experimental group by non-random convenient sampling method, with 102 cases in each group. The control group was given routine nursing care, and the experimental group was given comfort care on the basis of routine nursing care. Results The scores of postoperative anxiety, comfort, postoperative pain and postoperative defecation time in the experimental group were better than those in the control group, and the differences were statistically significant. Conclusion Comfort care can reduce postoperative pain, accelerate postoperative defecation time, relieve abdominal distension, relieve anxiety and increase patient comfort, so it is widely applied in clinical practice.
2021, 42(12): 169-176.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20211242
Abstract:
Objective To explore the effect of family empowerment intervention program on patients with radiotherapy for lung cancer and family caregivers. Methods A total of 60 patients with lung cancer who were hospitalized for radiotherapy from June 2020 to June 2021 and their family caregivers were selected as the research objects. They were divided into control group and experimental group by drawing lots, with 30 patients in each group. The control group was given routine care in radiotherapy department. The experimental group received routine nursing in the department of Family empowerment intervention plus radiotherapy. The patients were evaluated by the medical coping style questionnaire and Psychological Resilience Scale, caregiver readiness scale and cancer patient family Quality of life scale, and the family care of the patients was evaluated. Results After intervention, there were statistically significant differences in the scores of medical coping style avoidance, confronting and yielding, total score of mental toughness and scores of tenacity, optimism and self-strengthening in the experimental group (P < 0.05). There were statistically significant differences in caregiver readiness score and quality of life score among family caregivers (P < 0.05). Conclusion Family empowerment intervention program can significantly improve the level of psychological resilience of lung cancer patients undergoing radiotherapy, help patients establish a more active medical coping style, and significantly improve the care ability and quality of life of family caregivers.
2021, 42(12): 177-182.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20211243
Abstract:
Objective To explore the effect of optimal care + volume self-management model on cardiac function and quality of life in patients with chronic heart failure. Method 72 patients with chronic heart failure were randomly divided into control group (n = 36) and observation group (n = 36). The control group was given routine health education and telephone follow-up, and the intervention group received the model of optimal nursing + volume self-management. Before intervention, 3 months after intervention and 6 months after intervention, the stage behavior changes of patients in the 2 groups were evaluated, the cardiac function and quality of life of patients in the 2 groups were evaluated, and the readmission rate within 30 days after discharge was compared between the 2 groups. Results At 3 and 6 months after intervention, 44.4% and 63.9% of the intervention group were in the stage of behavior change, and the number of the intervention group in the stage of action maintenance was significantly higher than that of the control group, the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). At 3 and 6 months after intervention, the 6MWT distance in the intervention group was higher than that in the control group, with statistical significance (P < 0.05). 6 months after intervention, there was a significant difference in time and interaction between the two groups (F = 5.928, P < 0.05). Compared with the control group, the 6MWT distance in the intervention group increased slowly with the extension of the intervention time. 6 months after intervention, the total score of quality of life, physical domain, emotional domain and other domains in the intervention group were higher than those in the control group, and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). The readmission rate within 30 days after discharge in the intervention group was significantly lower than that in the control group, with statistical significance (P < 0.05). Conclusion The optimal care + capacity self-management model can effectively improve the cardiac function and quality of life of patients with chronic heart failure, reduce the readmission rate, reduce the pressure of heart failure on the world health care system and social and economic environment, and truly achieve the goal of effective long-term self-management outside the hospital.


 Email
Email RSS
RSS