2021 Vol. 42, No. 2
2021, 42(2): 18-22.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210216
Abstract:
Objective To explore a method for the synthesis of alkaloid-likes from Genipin by reductive amination is reported. Methods The reduction of Genipin and amines in the presence of sodium cyanoborohydride: after the methanol solution of Genipin and arylethylamine was mixed, excessive sodium cyanoborohydride was added and the reaction was kept at room temperature for 3 days. The product was eluted and separated on silica gel by petroleum ether-isopropyl alcohol-diethylamine and petroleum ether-ethyl acetate. Results Nine alkaloid-likes were synthesized. Some alkaloid-likes were screened for inhibition activity of PTP1B enzyme for Ⅱ diabetes treatment. Conclusions All of the tested compounds have a certain inhibitory effect on PTP1B. The acquisition of a series of active derivatives has laid a foundation for the study of the structure-activity relationship between the compounds and their bioactivities, so as to facilitate the search for more active PTP1B inhibitors.
2021, 42(2): 1-5.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210202
Abstract:
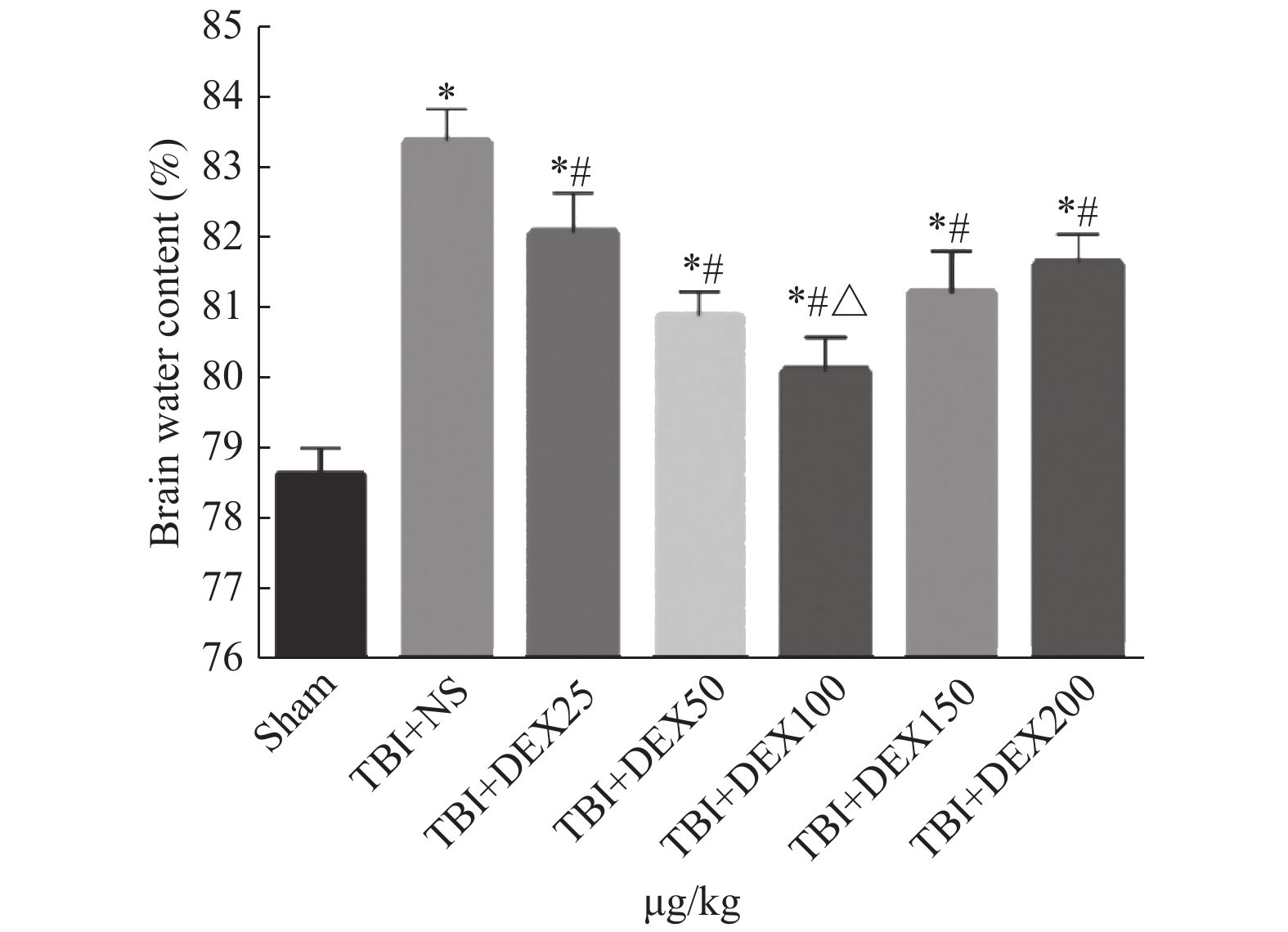
Objective To discuss whether the neuroprotective effect of dexmedetomidine (DEX) against traumatic brain injury (TBI) is related to the inhibition of neuronal apoptosis and whether it is involved in SIRT1 signaling pathway. Methods SD rats were randomly divided into 4 groups: Sham group, TBI + NS group, TBI + DEX group and TBI + DEX + EX527 group. The water content of brain tissue after traumatic brain injury was evaluated by dry/wet weight method; the neurological function was evaluated by neurological severity score; the expression of Bcl-2 and Bax proteins in rat cortex were detected by Western blot. Results DEX decreased the expression of apoptosis-promoting regulatory protein Bax (P < 0.05), increased the expression of apoptosis-inhibiting regulatory protein Bcl-2 (P < 0.05), alleviated brain edema (P < 0.05) and improvedthe neurological function after traumatic brain injury (P < 0.05). The changes of the above indexes were reversed by SIRT1 inhibitor EX527. Conclusions DEX can reduce the secondary damage after traumatic brain injury by inhibiting the apoptosis of nerve cells. There may be a certain correlation between the neuroprotective effect and SIRT1 signaling pathway.
2021, 42(2): 6-12.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210222
Abstract:
Objective To explore the application value of Ultrasound Targeted Microbubble Destruction (UTMD) with IL-6 monoclonal antibody combined with different ultrasonic irradiation intensity in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury (MI/RI). Methods Ninety rabbits were randomly divided into 3 groups, including 15 rabbits in the thoracotomy control group (group A), 15 rabbits in the thoracotomy control group (group B), and 60 rabbits in the R/I group (group C, divided into T1-T4 periods, reperfusion for 30 min, 60 min, 120 min, and 180 min). Each group was further divided into group U0 (without ultrasonic irradiation), group U1 (0.5 w/cm2 intensity), group U2 (0.75 w/cm2 intensity). An animal model of MI/RI was obtained by blocking the left anterior descending branch of the coronary artery for 30 min and then releasing it from reperfusion. The targeted contrast agent containing IL-6 was injected through ear vein, and then ultrasound irradiation was performed. QLAB10.5 software to analyze the video intensity of myocardium in reperfusion injury area before and after irradiation, and the ultrasonic video intensity difference (VID) was calculated. The content of IL-6 in the myocardium of each group before and after irradiation was detected by ELISA. Results The VID value of U2 group was higher than that of U1 group during T1-T4 (P < 0.05). The values of U2 and U1 VID in theT1-T4 period were compared in pairs within the group, the difference was not statistically significant (P > 0.05). ELISA analysis of rabbit myocardial tissue showed that the content of IL-6 in U2 group was lower than that in U1 group during T1-T4 period after ultrasonic irradiation (P < 0.05). The difference of IL-6 content between U1 group and U2group during T1-T4 was compared in pairs within the group, the difference was not statistically significant (P > 0.05). The difference of IL-6 content in myocardial tissue was positively correlated with the mean difference of ultrasonic video intensity (rU1 = 0.745, rU2 = 0.734). Conclusion IL-6 monoclonal antibody microbubbles combined with UTMD can effectively alleviate MI/RI inflammatory response, in addition, under the premise of no damage to the myocardium, the earlier the intervention, the stronger the radiation intensity, the better the effect of reducing the inflammatory response.
2021, 42(2): 13-17.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210225
Abstract:
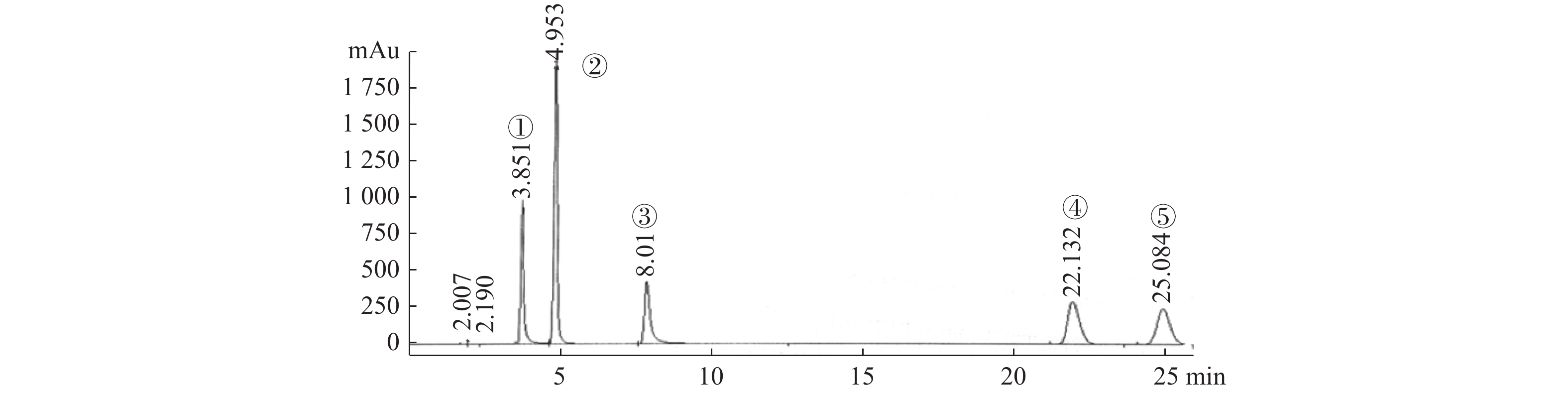
Objective To determine the content of five nucleosides in Periplaneta Americana L. extract by HPLC. Methods We did degreasing the Periplaneta Americana L.powder with petroleum ether, ultrasonic extraction of 65% ethanol as solvent, acetonitrile dissolution formulated into the American dating test solution, The Agilent alkyl silica gel column (9.4 mm × 250 mm, 5 μm) was applied in HPLC determination with water and acetonitrile mixture (95∶5) as the mobilephase at the flow rate of 0.5 mL·min−1. Detection wavelength was set at 254 nm, 10 μL sample was injected for analysis. Results The determination of five nucleosides in Periplaneta Americana L. extract by HPLC with high sensitivity, special properties, could be used for the content determination of this product. The concentration of 5 kinds of nucleoside in a certain range and peak area showed a good linear relationship (R2 > 0.9941), high precision, good repeatability, good stability, plus sample recovery rate is between 97.58% to 103.26%. Conclusion The experimental process of this method is simple, the results are reliable and stable, and it can be used as a method for determining the content of nucleoside components in Periplaneta Americana L.
2021, 42(2): 23-28.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210206
Abstract:
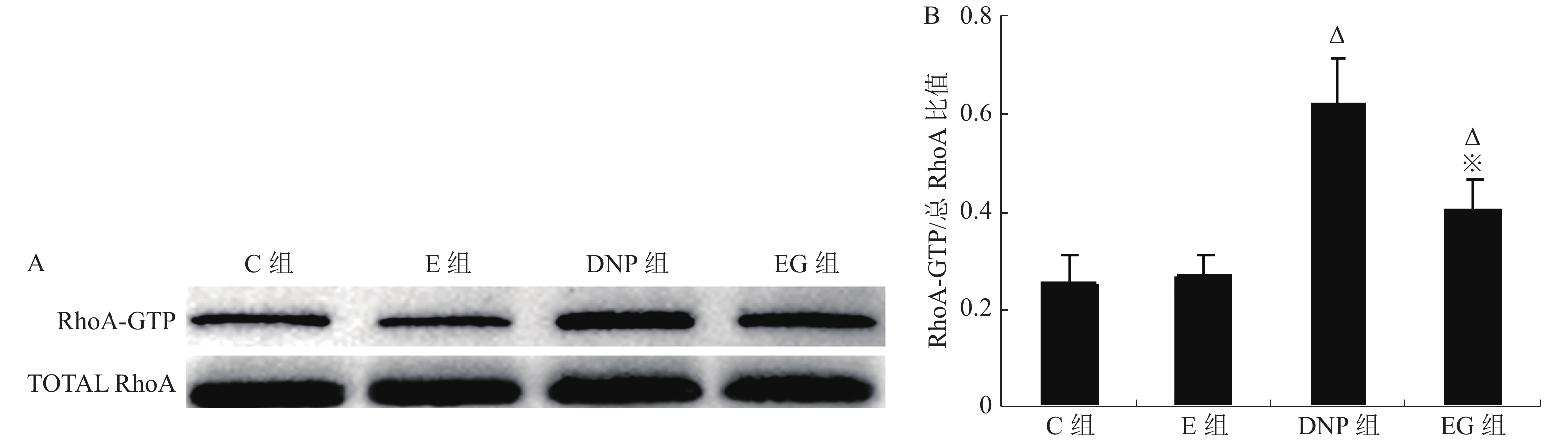
Objective To elucidate the pathogenic role of phospholipase C epsilon 1 (PLCE1) in neuropathic pain of rats with type 1 diabetes by observing the effect of intrathecal injection of exoenzyme C3 (a RhoA inhibitor) on the activity of PLCE1 and inflammatory response in the spinal cord. Methods Twenty-four 8-week-old healthy male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were randomly allocated to healthy rats plus vehicle group (Group C), healthy rats plus exoenzyme C3 group (Group E), type 1 diabetic neuropathic pain rats induced by streptozotocin (STZ) plus vehicle group (Group DNP) and type 1 diabetic neuropathic pain rats plus exoenzyme C3 group (Group EG). The diabetic neuropathic pain model of STZ -induced type 1 diabetes in rats was established by a single intravenous injection of STZ (65 mg/kg). In Group E and Group EG, 10 µL exoenzyme C3 (1 pg/µL ) was injected intrathecally once a day for 7 consecutive days, whereas vehicle was injected intrathecally in Group C and Group DNP. Accu-Chek Compact Plus glucose meter was used to measure fasting blood glucose concentration (mmol/L) in the tail vein once weekly. Western blot was used to detect the expressions of total RhoA and PLCE1 in the spinal cord in rats, while the RhoA activity detection kit was used to measure the expression of RhoA-GTP protein. The expression of PLCE1 protein and the ratio of RhoA-GTP/ total RhoA were used to estimate the activities of PLCE1 and RhoA, respectively. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was used to measure the contents of TNF-α and IL-6 in spinal cord to evaluate proinfammatory cytokines- induced the inflammation. The severity of DNP was evaluated by thermal withdrawal latency (TWL) and mechanical withdrawal threshold (MWT). Results No significant difference was detected between group C and group E. Rats with DNP had a decreased pain threshold (P < 0.05), up-regulated activities of RhoA and PLCE1 (P < 0.05) and increased production of TNF-α and IL-6 in spinal cord (P < 0.05) as compared to the group C and group E. Intrathecal injection of exoenzyme C3 rather than vehicle decreased the activity of RhoA in spinal cord (P < 0.05) of type 1 DNP rats, accompanied by a down-regulation of PLCE1 activity and proinflammatory mediators (P < 0.05) and a relief of DNP (P < 0.05). Conclusion PLCE1 plays an important role in type 1 diabetic neuropathic pain by promoting spinal cord inflammation, and its activity is regulated by RhoA.
2021, 42(2): 29-32.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210232
Abstract:
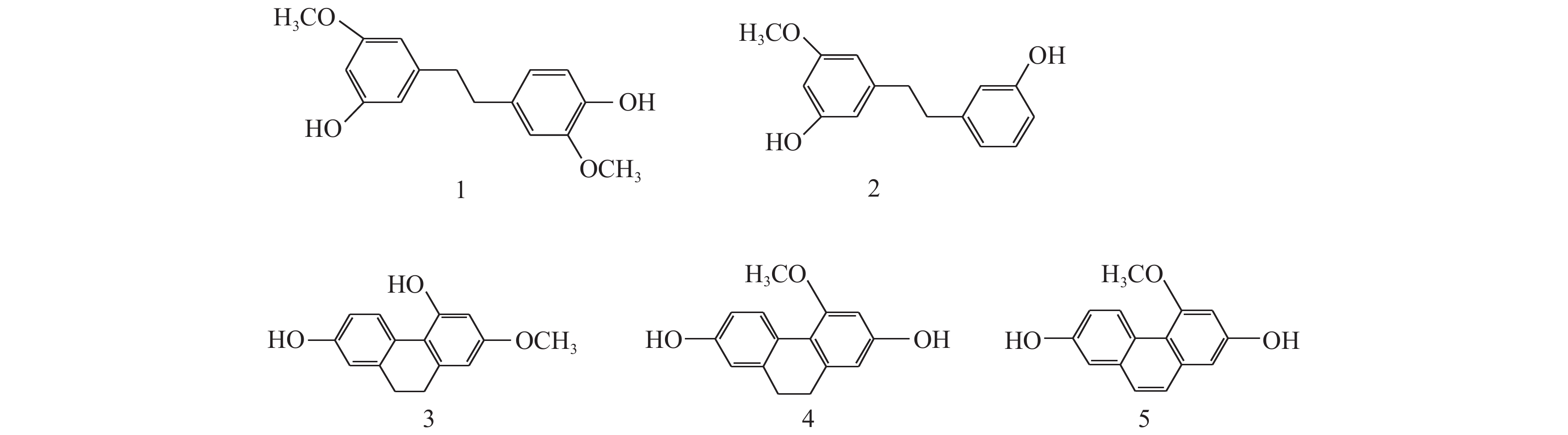
Objective Study the chemical compounds from the plants of P. yunnanensis and find its bioactive constituents. Methods The compounds were extracted by ethyl acetate and isolated by column chromatography on silica gel and Sephadex LH-20. 1H NMR, 13CNMR and EI-MS were used to elucidate their structure. Results Five compounds including gigantol (1), batatasin III (2), 2-methoxy-4,7-dihydroxy-9,10-dihydrophenanthrene (3), 2,7-dihydroxy-4-methoxy-9,10-dihydro-phenanthrene (4), 2,7-dihydroxy-4-methoxyphenanthrene (5) were obtained. Conclusion Compound 5 was isolated from the plant for the first time.
2021, 42(2): 33-37.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210226
Abstract:
Objective To analyze the status of malnutrition for Dulong residents aged 6-80 years in Gongshan county of Yunnan in 2006 and to study it's influencing factors. Methods By using a stratified cluster sampling method, 460 Dulong nationality residents aged 6-80 years were selected from Gongshan county in Yunnan Province. The questionnaire survey including questionnaire, and dietary survey such as body height and weight were used respectively for the survey. The status of nutrition was determined by Dulong residents' body mass index(BMI). The prevalence of malnutrition was calculated by statistics software. Multiple factors analysis were finished by non condition logistic regression in software. Results In 2016, of all Dulong children and adolescents aged 6-17 years, the prevalence of stunting was 16.1% and that of waisting was 1.8% in Gongshan county of Yunnan Province. Of all Dulong residents aged 18-80 years, the prevalence of underweight was 5.9%. Removing other variables, the result indicated: For the Dulong minority residents aged from 6 to 80, eaten fish(grass carp)(β: -1.116, OR = 0.328, 95%CI: 0.142-0.755)and tea(β: -0.899, OR = 0.407, 95%CI: 0.184-0.902)in the past 12 months were less possible to get malnutrition than those residents who were not. However, eaten liquid milk(low fat)(β: 1.973, OR = 7.192, 95%CI: 1.392-37.179)in the past 12 months decreased the possibility to get malnutrition. Conclusions The malnutrition of Dulong residents can not be ignored. The main influencing factors of malnutrition in Dulong minority are milk, fish and tea.
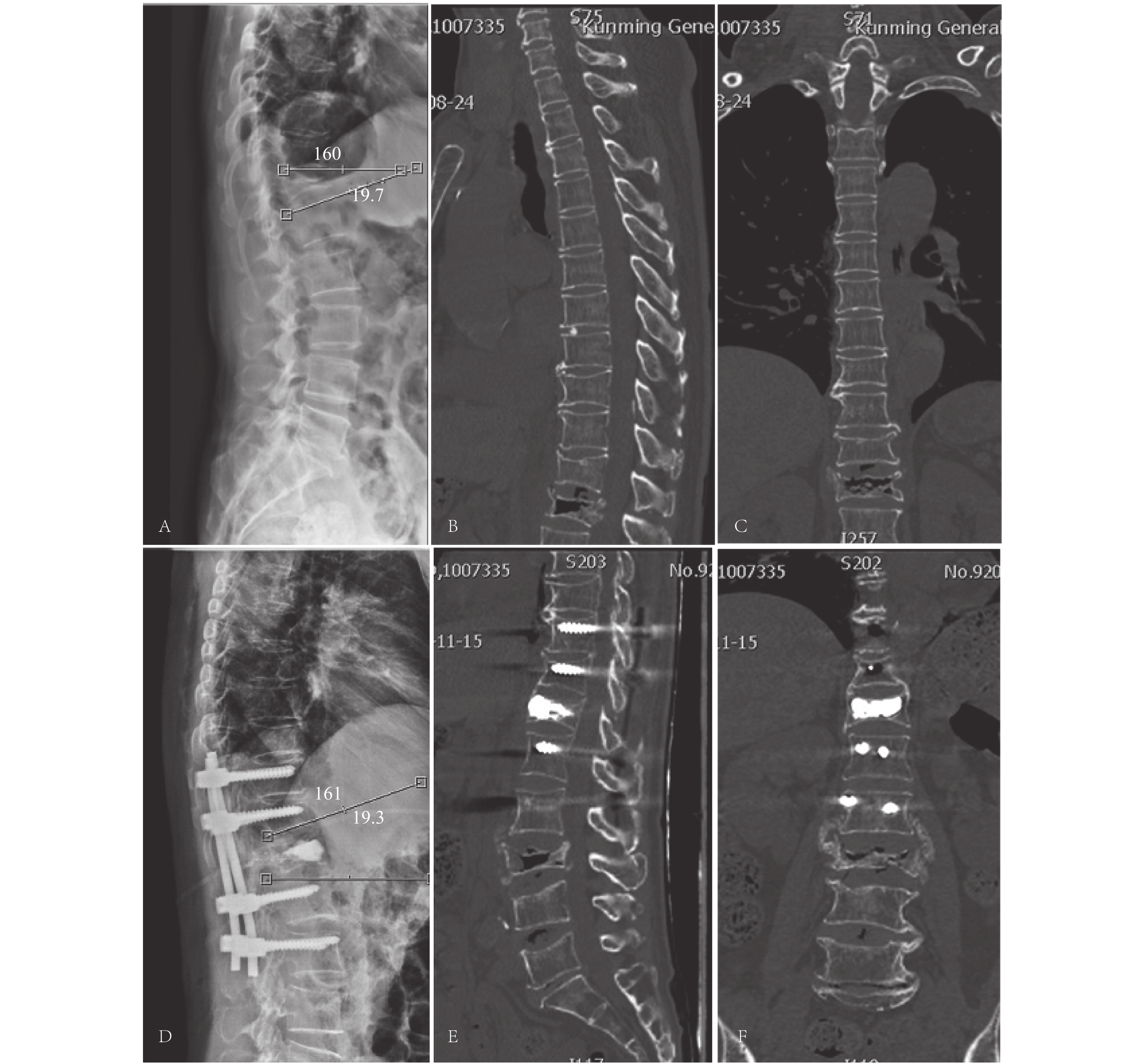
2021, 42(2): 75-80.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210230
Abstract:
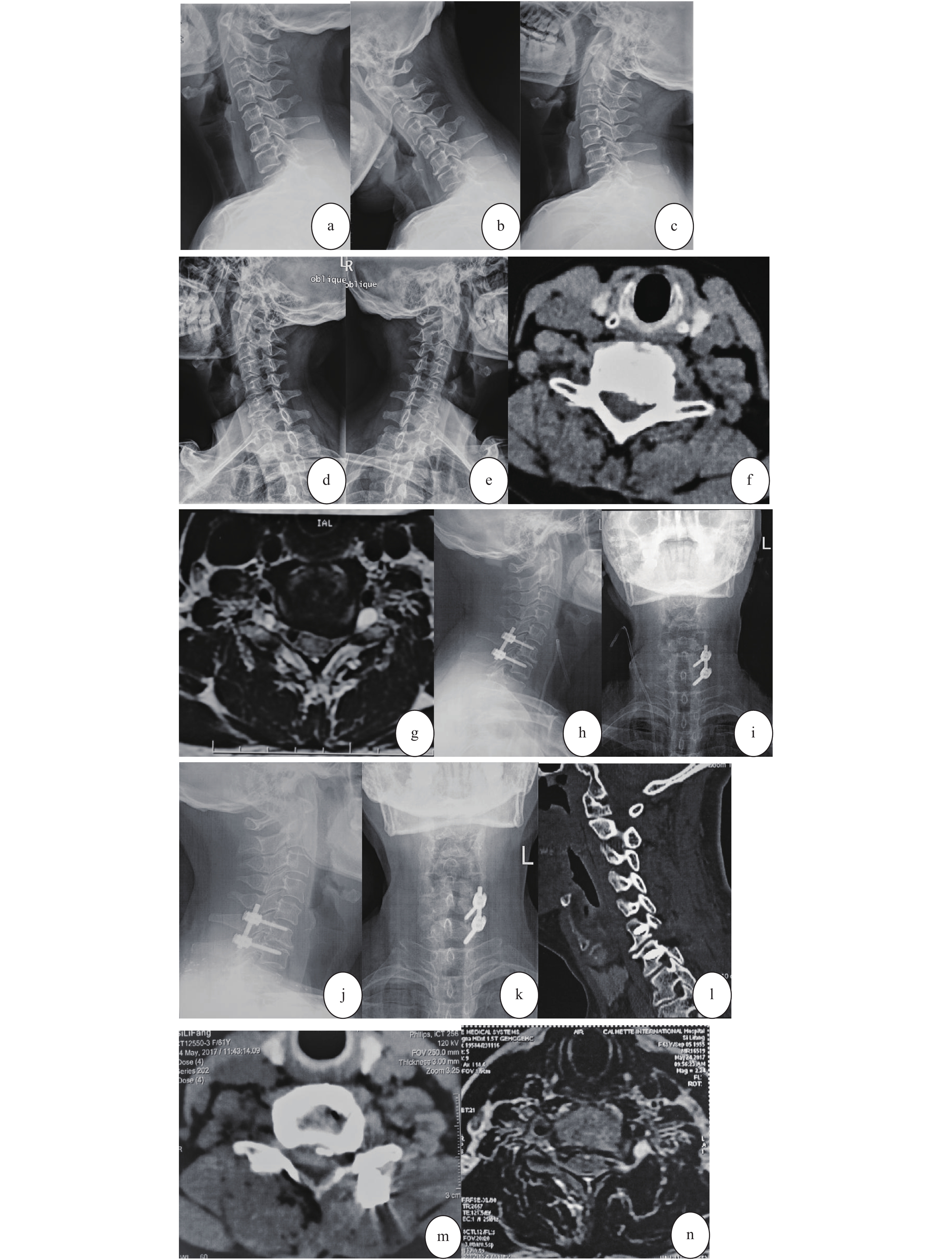
Objective To explore the initial clinical effect of posterior unilateral decompression and fixation for single-segment cervical spondylosis. Methods We retrospectively analyzed the clinical data of 26 patients with cervical spondylotic radiculopathy treated by unilateral decompression and fixation by posterior approach from January 2016 to December 2018. Among them, there were 16 males and 10 females, aged 39-62 years old, with an average age of 50.5 years. The surgical segment included 7 cases in C6/7, 12 cases in C5/6, and 7 cases in C4/5. Then we evaluated the operation time, intraoperative blood loss, visual analogue (VAS) score of cervical radiculopathy before operation and last follow-up, cervical spine functional disability index (NDI) score before operation and last follow-up, and Odom rating of postoperative cervical spondylopathy, 2 days after operation and at the last follow-up, the height of the cervical intervertebral space (DH), surgical complications, and the improvement of postoperative imaging examination of nerve compression. Results All 26 patients were followed up for 16-25 months, with an average of (18.1±4.8) months. The average operation time was (76.9±12.8) min; intraoperative blood loss was (87.3±14.3) mL; average preoperative radicular pain VAS score was (6.9±0.8) points, average postoperative radicular pain VAS score was (1.4±0.6). There were significant differences in radicular pain VAS scores between the preoperation and postoperation (P < 0.05); the preoperative NDI score was (32.4±4.3) points, and (16.3±6.7) points at the last follow-up. After operation 2 days, the DH average was (5.8±0.6) mm, and (5.7±0.4) mm at the last follow-up. There was no statistically significant difference between the two groups ( P > 0.05). The postoperative cervical spondylosis efficacy Odom rating was excellent in 8 cases (30.8%), 14 cases were good (53.8%), 4 cases were fair (15.4%), and the excellent and good rate was 84.6%. There were no complications such as infection, internal fixation loose, and vertebral artery injury. Conclusions The posterior unilateral decompression and fixation has a good initial effect in the treatment of single-segment cervical spondylotic radiculopathy. For cervical radiculopathy with lateral disc herniation and nerve root canal stenosis, it can be used as an alternative excluding the anterior surgery.
2021, 42(2): 118-123.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210207
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the status of insomnia and the related influencing factors among patients with chronic pain in department of pain. Methods A total of 431 patients were recruited from department of pain and a questionnaire survey was performed between January and June 2019, the general information were collected, the assessment of anxiety, depression, insomnia and the measurement of pain level and were conducted by self-rating anxiety scale(SAS), self-rating depression scale(SDS), athens insomnia scale(AIS)and visual analogue scale(VAS)and NIPRO painvision respectively, the rates of insomnia were statistically analyzed. Results Among 431 patients, there were 226 patients experienced insomnia(52.44%, 95%CI: 47.72%~57.15%). Data from the multiple logistic regression analysis indicated that males were 1.832 times more likely to suffer from insomnia than females, those more than 60 years' age were 1.832 times more likely to suffer from insomnia than those 18-30 years' age, patients with mild, moderate and severe depression were 4.181, 19.381 and 21.688 times more likely to suffer from insomnia than those than those without depression respectively, patients with severe pain had a 13.954 times higher risk of insomnia than those with mild pain, patients with more than one site of pain had a 3.762 times higher risk of insomnia than patients with only 1 site of pain, patients with type 2/3/4/5 pain were 2.150, 2.670, 25.067 and 38.052 times more likely to suffer from insomnia than patients with type 1 pain, while patients with pain duration of 1 year and 3 years while no likely suffer insomnia. Conclusion The chronic pain patients are always concomitant with depressive and anxiety symptoms and suffer from insomnia, meanwhile, it is urgently needed to pay close attention and mentality guidance to patients easily suffer from insomnia, relief and control pain timely to avoid insomnia.
2021, 42(2): 137-139.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210205
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the effects of MHI on diaphragm movement and BI Index in stroke patients. Methods From 2017 to 2018, 40 patients with stroke were randomly assigned into treatment group and control group equally. The control group received routine rehabilitation training, while the treatment group received MHI and Chest physiotherapy training in addition. All the patients were assessed with diaphragmatic motion, and Bathel Index(BI)before, four weeks and eight weeks after treatment. Results After eight weeks treatment, the scores of diaphragmatic motion, and BI improved more in the treatment group than in the control group(P < 0.001). Conclusion MHI combined with routine rehabilitation training can improve the diaphragm motion amplitude and ADL ability of hemiplegic patients.
2021, 42(2): 38-42.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210212
Abstract:
Objective To exlpore the application value of Color Doppler Flow Imaging (CDFI) and superb microvascular imaging (SMI) combined with self-defined scoring in the evaluation of renal perfusion in chronic kidney disease (CKD). Methods CDFI and SMI were used to observe the renal perfusion conditions of the case group and the control group, the blood perfusion scores were obtained by using the self-defined scoring criteria. The case group was 158 patients with CKD diagnosed, and was divided into CKD1-5 stages according to the diagnostic criteria of GFR. The control group was 200 patients with normal bilateral kidneys. Results CDFI and SMI scores were compared within the group, the control group, CKD1, CKD5 were not statistically significant (P > 0.05), CKD2, CKD3, CKD4 were statistically significant (P < 0.05). There was no significant difference in CDFI scores between the control group and CKD1, CKD1 and CKD2, CKD4 and CKD5 (P > 0.05), but there were significant differences in the other groups (P < 0.05). There was no significant difference in SMI scores between the control group and CKD1, CKD4 and CKD5 (P > 0.05), but there were significant differences in the other groups (P < 0.05). Conclusion The self-defined scoring method can be used for semi-quantitative evaluation of renal blood perfusion. SMI can identify the blood perfusion of early CKD lesions. The combination of the two methods is helpful to evaluate the degree of CKD lesions and the therapeutic effect.
2021, 42(2): 43-48.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210221
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the impact of propofol combined with Dexmedetomidine (Dex) or midazolam on the clinical effect, postoperative cognitive function and adverse reactions in elderly's painless gastrointestinal endoscopy. Methods Three hundreds and forty elderly patients who underwent joint painless gastroscopy from September 2018 to April 2019 were selected. Two hundreds and fifty patients were randomly divided into five groups (n = 50), Dex group (D1, D2, D3 group) was given intravenous injection of dexmedetomidine 0.25 μg / kg, 0.5 μg / kg, 0.75 μg / kg respectively (within 15 minutes). In the midazolam group (group M), 0.03 mg / kg was injected intravenously 15 minutes before surgery. The control group (group C) was given an equivalent volume of 0.9% sodium chloride solution. The rest of the anesthesia protocol is same. We recorded vital signs and adverse reactions during the operation and got the best Dex dose. The rest 90 patients were randomly divided into 3 groups (n = 30), Dex group (D group), midazolam group (M2), and control group (C2). Montreal Cognitive Assessment Scale (MOCA) was used to evaluate cognitive function at preoperative (T0), and 5min (T1), 30min (T2), 1h (T3), 2 h (T4), 6 h (T5) after awakening. Results Group C had the largest amount of propofol (P < 0.05). The recovery time of D3 and M groups was longer than that of D1, D2 and C (P < 0.05). The incidence of respiratory depression was the highest in group C, followed by group M (P < 0.05). The incidence of bradycardia in group D3 was the highest, followed by group D2 (P < 0.05); group C had the most body movements, and group D3 had the least (P < 0.05); the incidence of Postoperative cognitive dysfunction (POCD) in group M2 was higher than that in group D (P < 0.05). Conclusion Propofol combined with 0.5 ug/kg dexmedetomidine can reduce the occurrence of adverse reactions and early POCD in elderly's painless gastrointestinal endoscopy.
2021, 42(2): 49-53.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210214
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the clinical application value of anti-dsDNA antibody, complement C3 and other laboratory indicators in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) with renal injury. Methods The clinical data of 296 SLE patients were retrospectively analyzed. The differences of autoantibodies and other laboratory indicators between SLE with renal injury group and without renal injury group were compared, and the immunological indicators of SLE renal injury were found. Results The positive rates of serum anti-dsDNA, anti-nucleosome and anti-histone antibodies in SLE with renal injury group were significantly higher than those in without renal injury group, serum renal function indexes such as urea, creatinine and uric acid, electrolytes such as potassium, chlorine and calcium ion were significantly higher than those in without renal injury group, and the levels of immunoglobulin IgG, IgA and complement C3 were significantly lower than those in without renal injury group (P < 0.05). Conclusion Anti-dsDNA, anti-nucleosome, anti-histone autoantibodies, complement C3 and other laboratory indicators may be associated with renal injury in SLE patients.
2021, 42(2): 54-63.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210211
Abstract:
Objective To study the metabolomic differences of serum and feces between patients with type 2 diabetes and healthy people, and analyze the correlation between different metabolites and type 2 diabetes. Methods From January 2018 to March 2019, 53 patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus and 30 healthy controls were enrolled in the Department of Endocrinology, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University. The serum metabolites of the two groups and the fecal metabolites of 30 diabetic patients and the control group were detected by ultra performance liquid chromatography quadrupole time of flight mass spectrometry (UPLC-QTOF/MS) To carry out non targeted and targeted metabolomics studies. Spearman correlation analysis method was used to analyze the correlation between the differential metabolites in serum and stool and related indicators of type 2 diabetes. Results Fifteen differential metabolites were identified in serum samples of type 2 diabetes group and healthy control group, and 6 differential metabolites were identified in stool samples. The levels of glutamine, azelaic acid, sebacic acid, 3-hydroxysebacic acid and other dicarboxylic acid hydroxylated derivatives in patients with diabetes were significantly lower than those in healthy controls (P < 0.01), while the levels of succinylacetoacetate, valine, leucine, glucose and lactic acid in patients with diabetes were significantly higher than those in healthy controls (P < 0.01). In the fecal metabolites, deoxycholic acid, chenodeoxycholic acid and other bile acids also had a certain positive correlation with the blood glucose concentration of the subjects, and univariate analysis results showed that compared with the healthy control group, the blood glucose concentration of the subjects was significantly higher in the two groups The serum levels of deoxycholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid were significantly increased in patients with uropathy. Conclusions There are obvious differences in serum metabolomics between patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and healthy people, and these metabolites are closely related to the occurrence and development of diabetes mellitus. In fecal metabonomics, the level of bile acid in diabetic patients is closely related to the change of blood glucose concentration.
2021, 42(2): 64-69.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210201
Abstract:
Objective To analyse the clinical features of Rhupus syndrome. Methods The medical records of 21 Rhupus syndrome patients who were admitted to the Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University from 2015 to 2019 were analysed retrospectively. One hundred and twenty RA patients and 45 SLE patients from our Unit were randomly selected as the controls. The data of patients in the three groups were compared. Results Twenty-one patients with Rhupus syndrome were female, 61.9% patients were initiallypresented with RA. The age of onset was significantly younger than that of RA (P < 0.05), but similar to that of SLE. Rhupus patients had longer diseaseduration than control groups.As compared with RA patients, Rhupus patients had higher incidence of bone erosion, joint defornlity and rheumatoid nodules, lower anti-CCP, AKA and APF antibodies positivity (P < 0.05). There were no significant differences in the incidence of hand arthritis, polyarthritis, symmetrical arthritis and RF positivity (P > 0.05). As compared with SLE patients, Rhupus patients had less malar erythema while no differences were observed in serositis, kidney, hematological involvement and ANA, anti-dsDNA antibody positivity (P > 0.05). Conclusions Most of the Rhupus patients are firstly presented with RA and with severe arthritis. The positivity of ANA, anti-CCP and RF arehigh, are helpful to the diagnosis.
2021, 42(2): 70-74.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210229
Abstract:
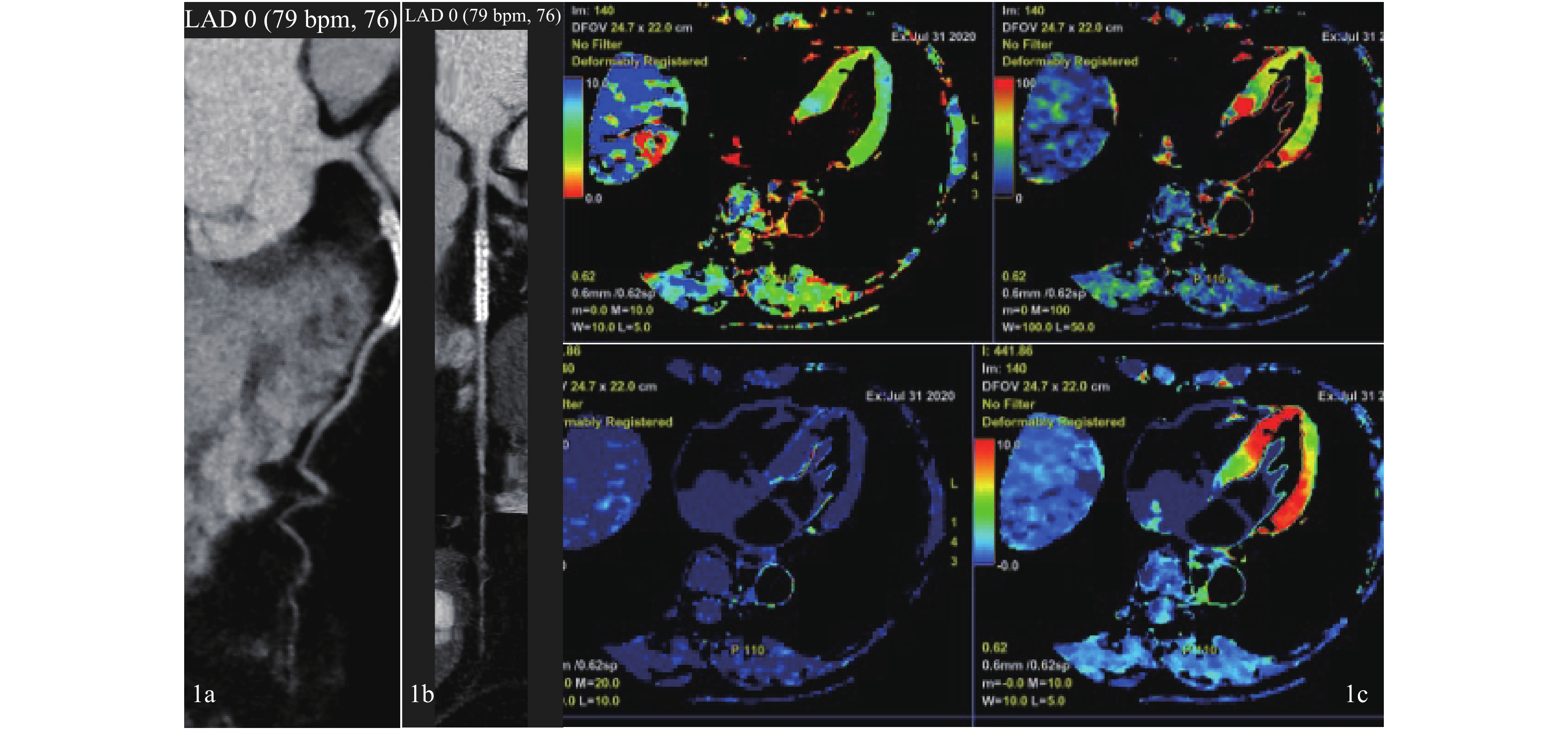
Objective To analyze the diagnostic value of Coronary Computed tomography angiography (CCTA)combined with rest CT myocardial perfusion (CT-MPI) in patients after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). Methods Twenty-two patients after PCI were selected to receive CCTA combined with resting PCT to evaluate the patency and myocardial perfusion to evaluate the effect of CCTA combined with resting CTMP on myocardial ischemia after PCI. Results CCTA showed restenosis in 4 of 25 stents, combined examination showed that 10 cases had abnormal myocardial perfusion and 12 cases had no abnormal myocardial perfusion, the same as that of echocardiography; the accuracy of CTMPI and combined examination was 90% and 100%, combined examination can improve the detection of myocardial ischemia and evaluate the stenosis in the stent. Conclusion CCTA combined with CTMPI is more effective in the diagnosis of mysocardial ischemia after PCI. We can get the data of stent and myocardial perfusion, which improves the diagnostic value of patients after PCI.
2021, 42(2): 81-85.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210217
Abstract:
Objective To observe the clinical effect of swallowing dysfunction training on neonates with swallowing disorder. Methods We selected 140 cases of pediatric NICU ward in March 2018 to July 2018, randomly divided them into intervention group and control group, each group had totally 70 cases, there were 44 male cases, 26 female cases, 17 full term cases, 53 premature cases in the intervention group, and there were 41 male cases, 29 female cases, 14 full term cases, 56 premature cases in the control group, from start until discharged into the group, the intervention group accepted the basis of conventional treatment, and received swallowing function training by rehabilitative therapist at the same time, Weight gain (g), total milk volume amount of increase, oral feeding volume amount of increase (mL), indwelling gastric tube time (d), and total hospital stay time (d)were observed. Results For patients in the intervention group and control group respectively, the weight were (1 990±632) g and (1 879±581) g in the begining, the weight of the two groups after treatment, respectively were (2 538±521) g and (2 496±394) g, there was no statistically significant difference (P > 0.05), while the intervention group's total milk supply growth were (23.41±8.67) mL, feeding by mouth growth were (17.18±4.63) mL, were significantly higher than control group in total growth in milk production (19.58±8.85) mL, feeding by mouth growth for (15.11±4.79) mL, in the same way, The duration of gastric tube indwentment were (8.45±10.69) d and the total length of hospital stay were (18.75±12.75) d in the intervention group were shorter than those in the control group (14.18±15.65) d and the total length of hospital stay (23.97±13.57) d, and the differences were statistically significant (P < 0.05). Conclusion Deglutition training for newborns with dysphagia can increase milk volume, shorten the duration of indwelling gastric tube and hospital stay, but has no obvious effect on weight gain.
2021, 42(2): 86-90.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210215
Abstract:
Objective To inverstigate the association between methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR)677C > T gene polymorphism and pregnancy induced hypertension in pregnant women. Methods Ninety HDCP patients who underwent prenatal examination in Yan'an Hospital of Kunming City from October 2016 to September 2017 were selected as the experimental group, and 2386 pregnant women without HDCP were selected as the control group. The correlation between the polymorphism of MTHFR 677C > T gene and the experimental group and the control group was analyzed by digital fluorescence molecular hybridization(DFMH). Results The genotype frequencies of MTHFR 677C > T CT were 52.22% in the experimental group and 44.38% in the control group. There was no significant difference between the two groups(P > 0.05). The frequency of mutant T allele was 37.22% in the experimental group and 37.07% in the control group. There was no significant difference between the two groups(P > 0.0). Conclusion The 677C > T polymorphism of MTHFR gene may not be a risk factor for HDCP, and may not be associated with the occurrence of HDCP, but it may also result from the limitation of retrospective study
2021, 42(2): 91-95.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210224
Abstract:
Objective To evaluate the clinical effect of flexible ureteroscope lithotripsy on solitary and non-solitary renal calculi. Methods We collected 20 cases of solitary renal calculi and 48 cases of non-solitary renal calculi in the second affiliated hospital of kunming medical university between January 2018 and April 2019. In 20 patients with solitary renal calculi, there were 14 male cases, 6 female cases, the average age was (51.05±9.49) years, the calculi was 0.7~2.0 cm in diameter, an average of 1.34 cm, there were 9 cases of right kidney stones, 11 cases of left kidney stones. In 48 patients with non-solitary renal calculi, there were 30 male cases of male and 18 female cases, aged 23~64, the average (51.75±7.68) years of age, the Calculi was in 0.7~2.0 cm in diameter, an average of 1.46 cm, there were 27 cases of right kidney stones and 21 cases of left kidney stones. All patients received general anesthesia, Under the guidance of super smooth black guide wire, the sheath was put in first and then the flexible ureteroscope was put in. Among them, 6 cases failed to put in the flexible ureteral sheath and entered along the guide wire to find the renal pelvis stones and smash them. Then we observed the operation time, hospitalization days, stone clearance rate (after 1 month of therapy), and the postoperative complications in the two groups. Results In the solitary renal calculi group, the average operation time was (72.10±8.20) min, average hospitalization days was (3.40±1.04) d, SFR after 1 month of therapy was 80% (16/20), the incidence of complications was 20.00% (4/20), in the non-solitary renal calculi group, the average operation time was (71.93±10.00) min, average hospitalization days was (3.35±1.06) d, SFR after 1 month of therapy was 75% (36/48), the incidence of complications was 14.58% (7/48). There were no statistically significant differences between the two groups in terms of operation time, length of stay, SFR(after 1 month) and complications (P > 0.05). The renal function of the solitary renal calculi group one month after surgery was statistically significant compared with that before surgery (P < 0.05), and the renal function of the non-solitary renal calculi group was not significantly different from that before surgery (P > 0.05). Conclusion Flexible ureteroscope lithotripsy has the advantages of feasibility, relative safety, high stone clearance rate and low infection rate in the treatment of isolated kidney stones and non-isolated kidney stones.
2021, 42(2): 96-102.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210218
Abstract:
Objectives To observe the effect of renal sympathetic denervation on acute ventricular remodeling in SHR. Methods This experiment enrolled 50 male rats of SHR, the average weight was (265±12) g. According to the difference of intervention way, they were randomly divided into operation intervention group(M) and blank control group(B). The group M were divided into groups of Left, Right, Dual and Sham-operation randomly again. Five rats of WKY were enrolled as negative control group. The blood pressure, weight and the activity of plasma renin were measured for all rats. The mode of Renal Sympathetic Denervation was made by operation. After operation, they were executed and and their hearts and kidney tissues were collected. The index of weight of body and heart, HW/BW, thickness of ventricular tissue and its histopathology were collected and analyzed, while, the level of RAAS factors were dectected in circulation and tissue. Results There were statistically significant differences among group B and S with group M(P < 0.05), including HW/BW, cardiac muscle cell hypertrophy, interstitial edema and fibrosis under the microscope. The concentration of factors, including AngⅠ, AngⅡ, ALD and NA, were down regulated in circulation and tissue, and there were statistically significant differences between operation with control group respectively. Conclusions Renal sympathetic denervation has significant alleviation effect on acute ventricular remodeling in SHR. These effect maybe come from decreasing the level of factor related with RAAS.
2021, 42(2): 103-107.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210219
Abstract:
Objective To explore the clinical value of B-lynch suture combined with intrauterine gauze packing in the treatment of refractory postpartum hemorrhage in hospitals in underdeveloped areas. Methods A comparative study was conducted on 108 cases of refractory postpartum hemorrhage admitted by the first people's hospital of zhaotong city from May 2015 to October 2017. The treatment regimen was used as a basis for grouping, 108 cases were divided into: (A) 58 cases of B-lynch suture plus intrauterine gauze packing, and (B) 50 cases of other treatment groups. The operation time, blood loss, amount of blood transfusion, length of hospital stay, hemostatic effect, uterine retention and complications were compared. Results The intraoperative blood loss and blood transfusion amount in group A were significantly lower than that in group B, and the operation time was longer than that in group B, and the difference between the two groups was statistically significant (P < 0.05). All the 58 cases in group A were effective in hemostasis, accounting for 100%, without hysterectomy and serious postoperative complications. In group B, 43 patients were effective in hemostasis, accounting for 86%, and 7 patients were treated with hysterectomy for secondary uterine weakness and bleeding again, accounting for 14%, without serious postoperative complications. Hemostasis in both group A and group B was significantly effective. The effective hemostasis rate of group A was higher than that of group B, while the uterine excision rate was lower than that of group B. There was significant difference between the two groups (P < 0.05), showing statistical significance. Conclusions B-lynch suture plus intrauterine gauze packing is not only simple and effective in operation, quick and effective in hemostasis, but also can keep the uterus as far as possible. It is an effective measure to treat refractory postpartum hemorrhage in hospitals in underdeveloped areas, and is worthy of popularization and application.
2021, 42(2): 108-112.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210223
Abstract:
Objective To evaluate the effect of continuous infusions of dexmedetomidine on the pediatric anesthesia emergence delirium (PAED)after general anesthesia in pediatric patients undergoing hip surgery. Methods Seventy children, ASA class I-II, aged 3~6 years scheduled for elective hip surgery under general anesthesia. The patients were randomly assigned to two groups. The dexmedetomidine group (group D, n = 35), which received dexmedetomidine infusion at a rate of 0.3 μg/(kg·h) after induction of anesthesia until to 30 minutes before the end of surgery and the control group (group C, n = 35), which received a volume-matched normal saline infusion as a placebo at the same time. All children were sent to the PACU after extubation. The primary outcome was the incidence of paedED and pain within 30 minutes after extubation. The scale of pain and paedED were recorded at 10, 20, 30, 60 minutes and 24h after extubation. In addition, the extubation time, the incidence of requiring rescue analgesic and the satisfaction scale of nurse were recorded as well. Results Compared with the Group C, the incidence of pain and the paediatric emergence delirium (PaedED)were significantly decreased respectively in group D (48.6% vs 22.9%; P < 0.01; 62.9% vs 37.1% P < 0.05), but extubation time was prolonged ( P < 0.05). The satisfaction scale of nurse was significantly higher and the incidence of requiring rescue analgesic was significantly lower in Group D than it was in Group C during PACU ( P < 0.05, respectively). There was no statistically significant difference between the pain score and the PAED score at 24 hours after surgery. Conclusion Continuous infusions of dexmedetomidine 0.3 μg/(kg·h)can reduce the incidence of paedED after general anesthesia in pediatric patients undergoing hip surgery.
2021, 42(2): 113-117.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210231
Abstract:
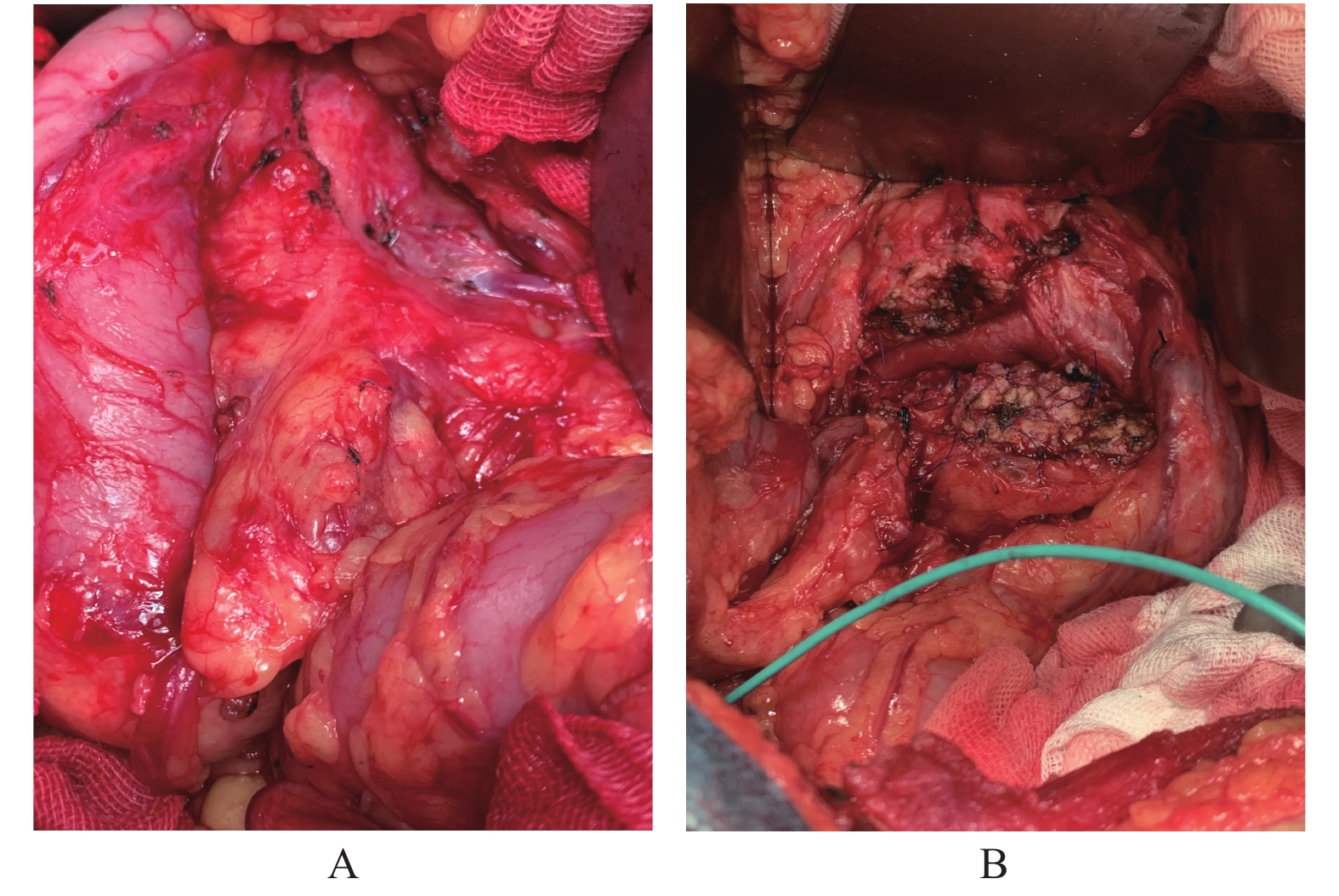
Objective To investigate the clinical application value of modified Beger operation. Methods The clinical data of 59 patients with chronic pancreatitis, benign and low-grade malignant tumor of pancreatic head treated by surgery from January 2014 to January 2020 were retrospectively analyzed, Among them, there were 49 cases of mass type chronic pancreatitis in the head of pancreas, 3 cases of cyst with pancreatic duct stones, 2 cases of solid pseudopapillary tumor, 2 cases of intraductal papillary mucinous tumor, 2 cases of serous cystadenoma and 1 case of mucinous cystadenoma. They were randomly divided into modified beger operation group and pancreatoduodenectomy (PD) group. Among them, 31 cases underwent modified beger operation and 28 cases underwent pancreaticoduodenectomy (PD). Results For patients in the modified beger operation group and PD group, the operation time, intraoperative bleeding, postoperative hospital stay, incidence of postoperative complications and pain relief efficiency were(231.4 ± 42.3/268.1 ± 52.5)min, (405.5 ± 64.1 / 449.9 ± 61.2)mL, (17.1 ± 3.4 / 28.5 ± 4.1)d, (12.9 / 42.9)% and (89.7 / 88.9)%, respectively. 56 cases (29 cases in Beger group and 27 cases in PD group) were followed up for 6 months to 5 years without recurrence of tumor or stone. Conclusion The modified Beger operation has the advantages of less pancreatic tissue resection, less surgical trauma, safer operation, faster recovery, more accurate relief of intractable abdominal pain, and significant improvement of postoperative quality of life and nutritional status of patients.
2021, 42(2): 124-129.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210203
Abstract:
Objective To explore the effective treatment for osteoporotic delayed vertebral collapse. Methods Between March 2013 and March 2018, a total of 46 patients with osteoporotic delayed vertebral fracture with no or mild neurological symptoms were enrolled in our hospitals. 24 patients underwent posterior fixation with vertebroplasty(PFV group), and 22 patients underwent percutaneous balloon kyphoplasty(PKP group). The clinical results, imaging parameters and long-term complications were compared between the two groups. Results Postoperative PFV group had significantly higher vertebrae height and local Cobb angle recovery than PKP group(P < 0.001). The VAS score and ODI score in the PKP group were better than those in the PFV group(P = 0.03). There was no significant difference between the two groups at the last follow-up(P = 0.28). In the PFV group, 3 cases(12.5%)had adjacent vertebral fractures, 3 cases(16.7%)had internal fixation loosening, and 1 case(4.5%)had revision surgery. In the PKP group, 4 cases had severe kyphosis, 2 cases had neurological symptoms, and 2 cases underwent revision surgery. Conclusions Both PFV and PKP for delayed osteoporosis vertebral collapse can achieve satisfactory clinical results. PFVB is indicated for patients with a significant change in the sagittal position of the spine, whereas PKP is suitable for a single vertebral body and no significant changes in the sagittal plane of the spine.
2021, 42(2): 130-136.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210204
Abstract:
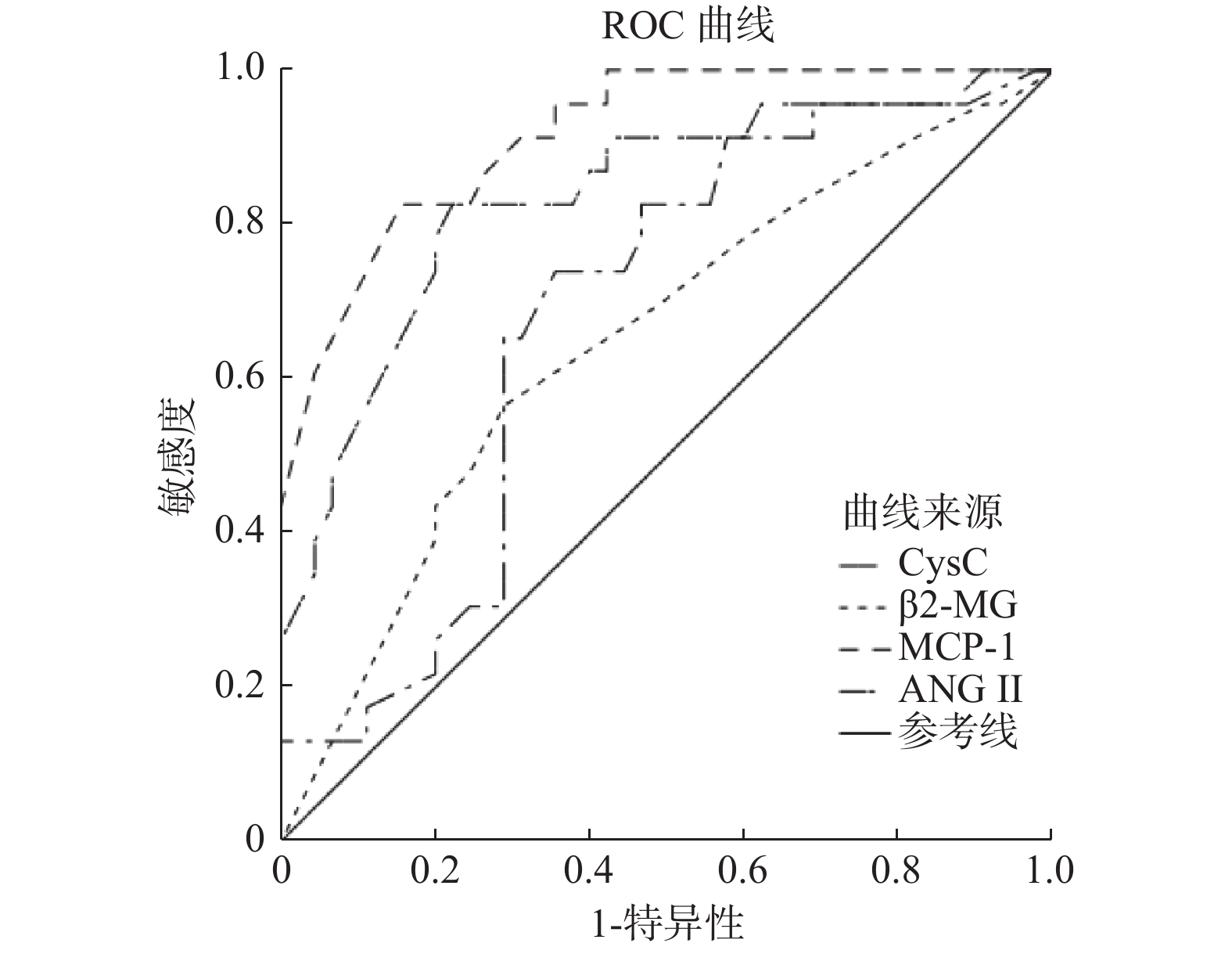
Objective To investigate the changes of serum cystatin C(Cys C), β 2-microglobulin(β 2-MG), monocyte chemoattractant protein-1(MCP-1)and angiotension Ⅱ(ANG Ⅱ)levels in patients with chronic renal failure(CRF), and analyze the relationship between them and the prognosis of CRF patients. Methods From January 2017 to January 2019, 68 CRF patients(CRF group)and 50 healthy people(control group)were selected from the nephrology department of our hospital. The levels of Cys C, β 2-MG, MCP-1 and ANG Ⅱ in serum were measured, and the differences between the two groups were compared. The end point was all-cause death, the relationship between Cys C, β 2-MG, MCP-1, ANG Ⅱ and the prognosis of CRF patients was analyzed. Results The median follow-up time was 18(13-25)months, 23 cases died(death group), 50 cases survived(survival group). The serum levels of CysC, β 2-MG, MCP-1 and ANG Ⅱ in the death group were higher than those in the survival group and the control group(P < 0.05). The levels of CysC, β 2-MG, MCP-1 and ANG Ⅱ in CRF patients increased with the increase of CKD grading(P < 0.05). Serum CysC, β 2-MG, MCP-1, ANG Ⅱwere negatively correlated with estimated glomerular filtration rate(EGFR)(r = -0.435, -0.406, -0.621, -0.594, P < 0.05), and positively correlated with urinary albumin / creatinine ratio(ACR)(r = 0.406, 0.435, 0.562, 0.503, P < 0.05). ROC analysis showed that AUC of CysC, β 2-MG, MCP-1 and ANG Ⅱ were 0.681(95% CI: 0.551-0.811), 0.649(95% CI: 0.510-0.789), 0.917(95% CI: 0.852-0.981)and 0.838(95% CI: 0.733-0.942), respectively. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis showed that the survival time of high level CysC, β 2-MG, MCP-1, ANG Ⅱ group was shorter than that of low level CysC, β 2-MG, MCP-1, ANG Ⅱ group(P < 0.05). Multivariate Cox regression analysis showed high levels of CysC, β 2-MG, MCP-1 and ANG Ⅱ were independent risk factors for all-cause death of CRF(P < 0.001). Conclusion The serum levels of CysC, β 2-MG, MCP-1 and ANG Ⅱ are closely related to the degree of renal injury and poor prognosis in CRF patients, which can be used as an auxiliary index for the prognosis evaluation of CRF.
2021, 42(2): 140-146.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210220
Abstract:
Atopic dermatitis(AD)also known as atopic eczema, Besnier prurigo diathesique or hereditary allergic eczema, is a skin disease characterized by eczema-like skin lesions, severe itching and obvious "atopy" in oneself or his family. In recent years, the theory of AD pathogenesis tends to be abnormal in immune barrier function. At present, it has been found that the method of Jianpi Yangxue Qufeng Decoction has definite curative effect in treating AD with Xuexu Fengzao type, which can effectively control skin lesions, reduce recurrence rate and regulate the immune barrier function of AD. This article reviews the mechanism of regulating the immune barrier function of AD by the method of Jianpi Yangxue Qufeng Decoction.
Atopic dermatitis(AD)also known as atopic eczema, Besnier prurigo diathesique or hereditary allergic eczema, is a skin disease characterized by eczema-like skin lesions, severe itching and obvious "atopy" in oneself or his family. In recent years, the theory of AD pathogenesis tends to be abnormal in immune barrier function. At present, it has been found that the method of Jianpi Yangxue Qufeng Decoction has definite curative effect in treating AD with Xuexu Fengzao type, which can effectively control skin lesions, reduce recurrence rate and regulate the immune barrier function of AD. This article reviews the mechanism of regulating the immune barrier function of AD by the method of Jianpi Yangxue Qufeng Decoction.
2021, 42(2): 147-152.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210208
Abstract:
The main components of cannabis with medicinal value are Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol(Δ9-THC)and cannabidiol(CBD), of which CBD cannot directly activate cannabinoid type 1 receptor(CB1R)and cannabinoid type 2 receptors. Body(CB2R)does not have psychoactive and drug dependence, and its safety is relatively high. CBD, as the main cannabinoid extract, has proven to have analgesic, sedative, anti-inflammatory, anti-convulsant, sleep-improving, anti-anxiety, anti-psychotic, anti-rheumatic, skin barrier, anti-apoptotic and neuroprotective effects. This review aims to summarize the application status of CBD in the treatment of clinical diseases, and provide new ideas for the future application of CBD-related drugs in the treatment of epilepsy, neuropathic pain, anxiety and depression, tumors, skin, and metabolism-related diseases.
The main components of cannabis with medicinal value are Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol(Δ9-THC)and cannabidiol(CBD), of which CBD cannot directly activate cannabinoid type 1 receptor(CB1R)and cannabinoid type 2 receptors. Body(CB2R)does not have psychoactive and drug dependence, and its safety is relatively high. CBD, as the main cannabinoid extract, has proven to have analgesic, sedative, anti-inflammatory, anti-convulsant, sleep-improving, anti-anxiety, anti-psychotic, anti-rheumatic, skin barrier, anti-apoptotic and neuroprotective effects. This review aims to summarize the application status of CBD in the treatment of clinical diseases, and provide new ideas for the future application of CBD-related drugs in the treatment of epilepsy, neuropathic pain, anxiety and depression, tumors, skin, and metabolism-related diseases.
2021, 42(2): 153-157.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210210
Abstract:
Methamphetamine is a serious threat to public health and safety of mental excitatory drugs. Long-term abuse of METH will cause obvious neuronal injury and neurotoxicity. Oxidative stress, mitochondrial metabolic damage and neuroinflammation play important roles in meth-induced neuronal injury. In this paper, we reviewed the mechanism of neuronal injury induced by METH and the neurotoxicity mechanism of METH. The neuroinflammatory effect of reactive glial cells is described in detail, and the neuroinflammatory drugs induced by targeted METH are summarized. This article aims to further explore the mechanism of meth-induced neurotoxicity and provide new ideas for inhibiting meth neurotoxicity and drug development.
Methamphetamine is a serious threat to public health and safety of mental excitatory drugs. Long-term abuse of METH will cause obvious neuronal injury and neurotoxicity. Oxidative stress, mitochondrial metabolic damage and neuroinflammation play important roles in meth-induced neuronal injury. In this paper, we reviewed the mechanism of neuronal injury induced by METH and the neurotoxicity mechanism of METH. The neuroinflammatory effect of reactive glial cells is described in detail, and the neuroinflammatory drugs induced by targeted METH are summarized. This article aims to further explore the mechanism of meth-induced neurotoxicity and provide new ideas for inhibiting meth neurotoxicity and drug development.
2021, 42(2): 158-161.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210213
Abstract:
Pathological pain refers to the pain caused by various diseases, which can be divided into inflammatory pain, neuropathic pain, cancer pain and so on. Due to the complexity of its pathogenesis and the specificity of clinical features, the analgesic effect of analgesics is not good and the side effects are obvious. Therefore, it is imperative to develop new drugs and tools that do not induce significant side effects. In recent years, studies have shown that small needle knife therapy plays an effective analgesic effect on pathological pain, and its side effects are small. However, the analgesic mechanism of small needle knife on the pathological pain remains unclear. This paper will review the role and mechanism of small needle knife on pathological pain.
Pathological pain refers to the pain caused by various diseases, which can be divided into inflammatory pain, neuropathic pain, cancer pain and so on. Due to the complexity of its pathogenesis and the specificity of clinical features, the analgesic effect of analgesics is not good and the side effects are obvious. Therefore, it is imperative to develop new drugs and tools that do not induce significant side effects. In recent years, studies have shown that small needle knife therapy plays an effective analgesic effect on pathological pain, and its side effects are small. However, the analgesic mechanism of small needle knife on the pathological pain remains unclear. This paper will review the role and mechanism of small needle knife on pathological pain.
2021, 42(2): 162-166.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210228
Abstract:
Objective To explore the standardization process of laparoscopy operation training in undergraduate teaching. Methods A total of 90 undergraduate interns from the First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University from January 01, 2017 to June 19, 2019 were selected. They were divided into 3training sessions, 30 people per session, 4 weeks of training and 30 hours of training per session. The training included laparoscopy basic theory learning, surgical video learning, in vitro simulation box basic skills operation training(picking beans, suture knotting, animal tissue suture)and laparoscopy virtual training system training. According to the feedback from trainees in each session, the next class schedule was adjusted. The theoretical assessment scores, performance skills assessment scores and trainee satisfaction of the trainees were compared in the 3 different classes. Results The results of all trainees in the 3 phases were all qualified, and the differences were not statistically significant(P > 0. 05). After the trainees completed the training, the time to complete the basic skills training(picking beans, suture knotting, animal tissue suture)was all shorter than that before the training, and the differences were statistically significant( P < 0. 05). After the trainees with more vitro simulation box basic skill operation training, laparoscopy surgery virtual training system training classes assigned completed the training in the second and third phases, the time to complete picking beans, suture knotting, animal tissue suture was all shorter than that in the first phase fewer classes assigned, and the differences were statistically significant( P < 0.05).The time that the trainees in the second and third phases completed picking beans, suturing and knotting and suturing animal tissues was completed, the differences were not statistically significant(all P > 0. 05).The feedback results after the training indicated that the trainees in the third phase had the highest degree of satisfaction and participation. Conclusion The scientific arrangement of training time and training methods can improve the laparoscopy minimally invasive skills of surgical postgraduates and it has the promotion value.
2021, 42(2): 167-172.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210227
Abstract:
Objective To explore the application of scenario simulation nutrition intervention to improve the cognitive level of children with diabetes of different ages. Methods From January 2018 to December 2019 120 school-age children with diabetes were divided into children group and adolescent group, each consisting of 60 cases. Scenario simulation nutrition intervention was carried out in three forms: physical simulation, video simulation and role simulation. And the effects of cognitive level of children with diabetes, blood glucose and three forms of scenario simulation were studied before and after the intervention. Results The two groups of children with diabetes had improved their knowledge of diabetes through scenario simulation nutrition intervention, and the difference was statistically significant(P < 0.05).Fasting blood glucose and 2-hour postprandial blood glucose were significantly lower at the time of discharge and 6 months after discharge than at the time of admission, and the difference was statistically significant(P < 0.05). Among the three forms of scenario simulation nutrition intervention, the two groups had little acceptance of the physical simulation form. There was no significant difference between the two groups(P > 0.05).The acceptance of video simulation intervention in the adolescent group was higher than that in the child group(P < 0.05).The role simulation intervention in the child group was higher than that in the young group(P < 0.05). Conclusions The situational nutritional intervention is helpful to improve the cognitive level of children with diabetes, effectively control blood glucose, and promote the development of self-management ability. In the process of implementing situational nutritional intervention, video demonstration intervention is more suitable for the youth group, while role simulation intervention is more suitable for the children group. Only by choosing the right way of nutritional intervention can we effectively improve the quality of life of children with diabetes.
2021, 42(2): 173-178.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210209
Abstract:
Objective To observe the incidence of complications in patients with ultrasound-guided PICC catheterization and explore the influencing factors. Methods The clinical data of 536 patients with ultrasound-guided PICC catheterization were retrospectively selected. Patients were divided into complication group(52 cases)and control group(484 cases) according to whether catheterization related complications occurred. Patients' baseline data, catheterization method, puncture vein selection, indwelling time and other information were collected, and multiple Logistic regression was used to analyze the risk factors of ultrasound-guided PICC catheterization related complications. Results The incidence of complications in this group was 9.70%(52/536), the incidence of catheter-related infection was the highest(4.66%), and the incidence of complications in oncology department was the highest(3.36%). Univariate analysis of age, BMI, education level, diabetes mellitus, puncture vein selection, catheterization distribution, catheterization method, venous thrombosis history, length of experience of PICC operation nurse, and out-hospital catheterization nursing method were all correlated with the occurrence of ultrasound-guided PICC catheterization complications(P < 0.05). Logistic regression analysis showed that complications of PICC catheterization were associated with diabetes mellitus, puncture vein selection, catheterization method, PICC operation nurse experience, and out-hospital catheter nursing mode(P < 0.05). Conclusion Combined diabetes mellitus, cephalic vein catheterization, badseddinger puncture, lack of experience in nurse operation and lack of hospital management may be the risk factors for complications of PICC catheterization.


 Email
Email RSS
RSS