2021 Vol. 42, No. 5
2021, 42(5): 54-58.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210510
Abstract:
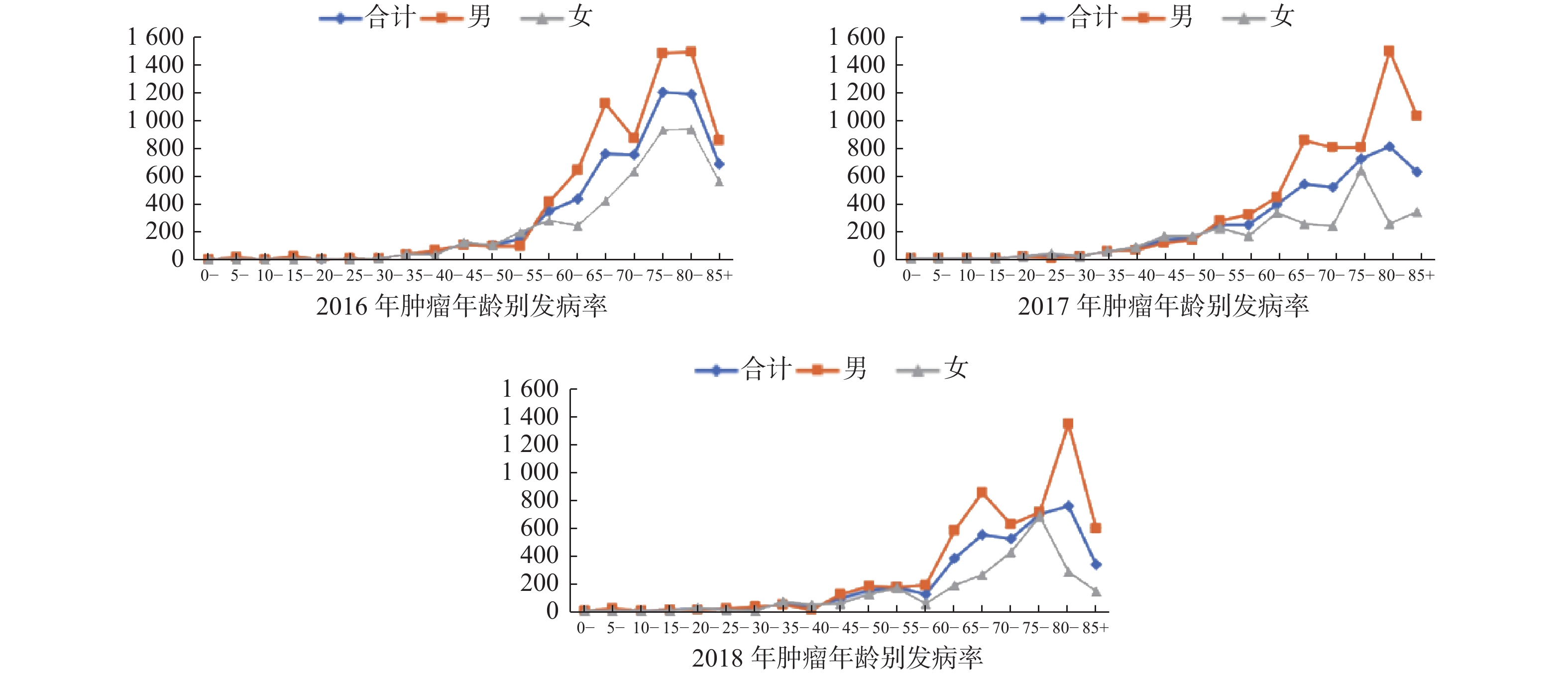
Objective To analyze the incidence rate and epidemiological trend of tumor in Shilin county, Kunming city from 2016 to 2018. Methods The data of tumor and demographics were collected form Shilin county surveillance system from 2016 to 2018. The crude rate, age-standardized rate, and cumulative rate (0-74 years) were calculated respectively. The age-standardized rate was evaluated by using the standard population in China in 2010 and the Segi’ s world standard population. Results From 2016 to 2018, there were 1202 cases of tumors in Shilin county. In the three years, the crude incidence rate (1/105), the age-standardized rate according to the standard population in Chinese (1/105), the age-standardized rate according to the standard population in world (1/105) and cumulative rates (0-74 years old), the incidence of tumors were 168.13, 175.03 and 133.10 respectively. The age-standardized rates according to the standard population in Chinese were 158.66, 159.31, 117.81 respectively; the age-standardized rates according to the standard population in world were 121.02, 122.78, 92.99 respectively; Cumulative rate (0-74 years old) 14.10, 13.65, 10.65; The incidence of tumor in the past three years was relatively stable. In Shilin county, the incidence of tumor in people over 40 years old accounts for over 95.9%, and over 60 years old accounts for over 78.9%. The incidence of tumor in elderly people accounts for a large proportion. The incidence of cancer was higher in males than in females for three years. Primary tumors of the respiratory system and digestive system such as lung, liver and stomach accounted for over 48.4% of the tumor incidence in Shilin county. Conclusion From 2016 to 2018, the incidence trend of tumors among the residents in Shilin county is basically stable. Therefore, it is necessary to strengthen the health examination of middle-aged and elderly people and tumor prevention and treatment intervention measures to improve the residents’ living habits and improve the quality of life of middle-aged and elderly people.
2021, 42(5): 1-5.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210501
Abstract:
Objective Coronarin E, a diterpenoid was utilized to synthesize bioactive derivatives. Method Coronarin E underwent SeO2 oxidation, acylation and photosensitized oxidation, two butenolide derivatives were obtained, which were subjected to antimicrobial and cytotoxic bioassays. Results Two butenolide derivatives were obtained, one showed good antimicrobial activities and the other showed good cytotoxic activities against five cancer cell lines. Conclusion It’ s worth to synthetize bioactive derivatives from Zingiberceae diterpenoids.
2021, 42(5): 6-11.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210502
Abstract:
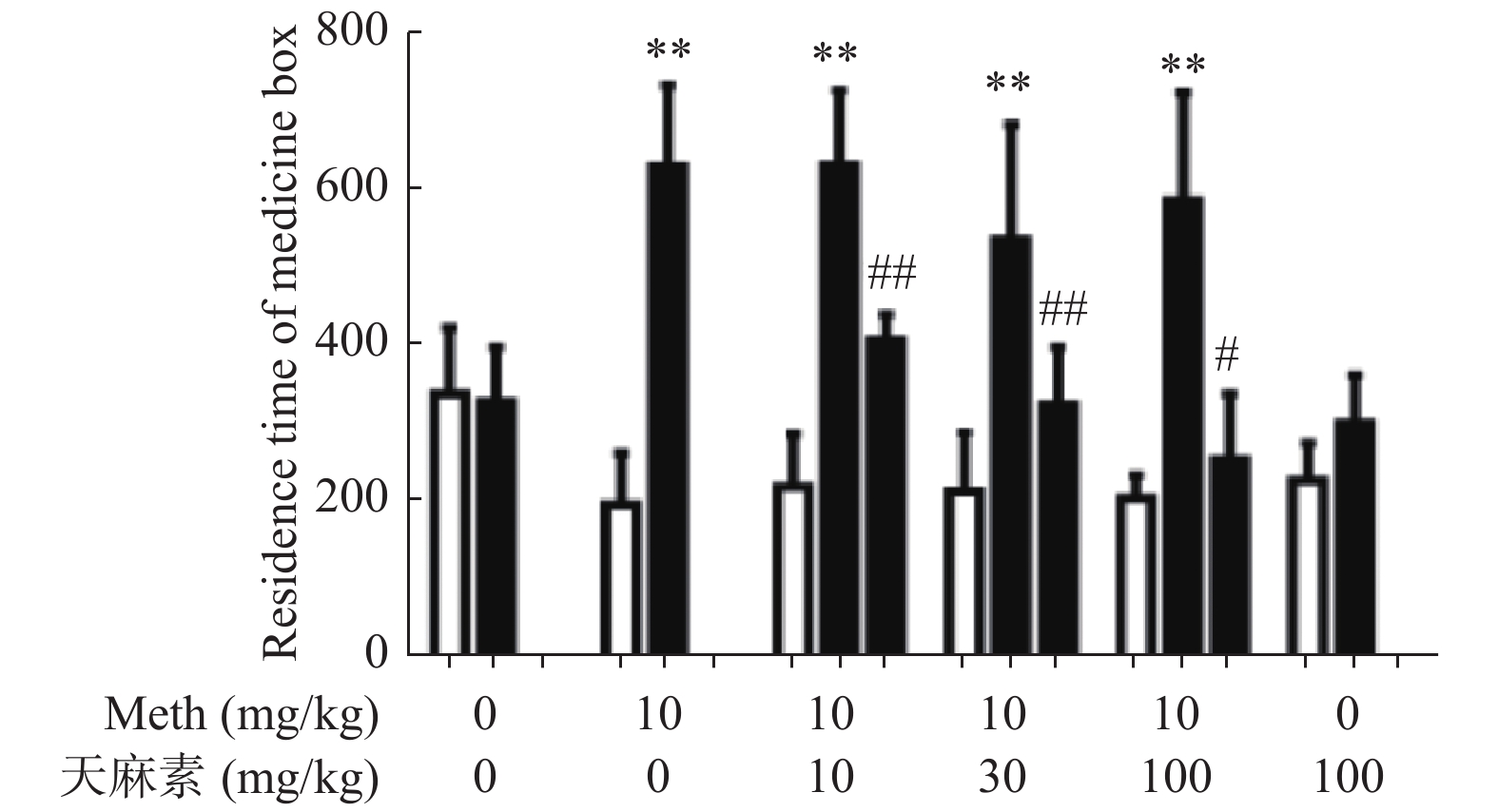
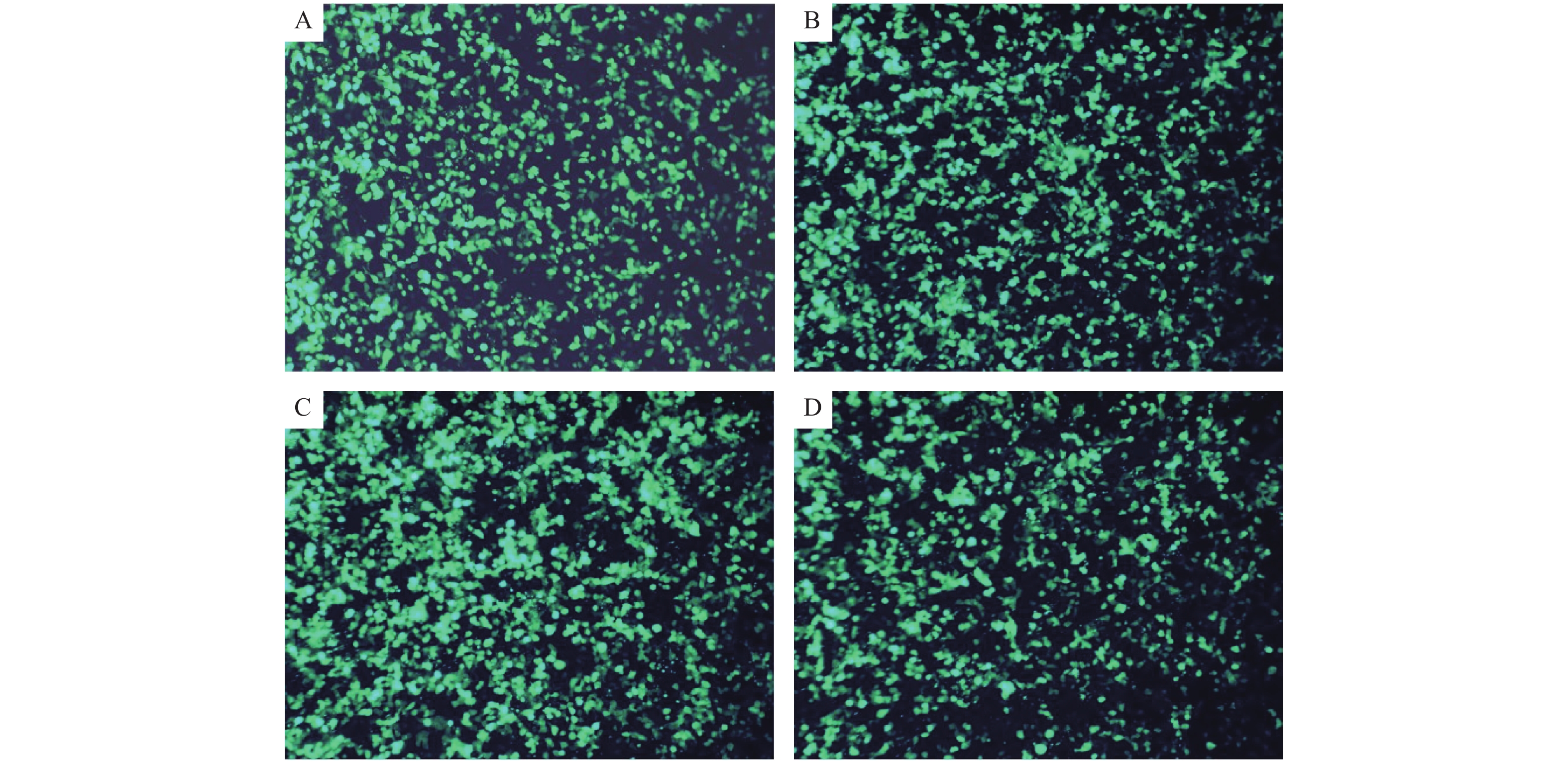
Objective To study the effects of different dosages of gastrodin on conditioned place preference and hippocampal microglia activation in methamphetamine (Meth)-dependent rats. Methods Meth dependent CPP model was established by intraperitoneal injection of meth (10 mg/kg, QD, 14 d) and then gastrodin (10 mg/kg, 30 mg/kg, 100 mg/kg) was used for 14 d to determine the effect of gastrodin on CPP in meth dependent rats. After that, the immunofluorescence technique was used to detect the effect of different doses of gastrodin on the activation of microglia in hippocampus. Results The Meth-dependent rat CPP model was successfully established. Gastrodin treatment could shorten the time of the rats stayed in the drug-paired chamber. Compared with the saline group, the CPP effect of the Meth group was significantly enhanced, and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). Compared with Meth group, 10 mg/kg, 30 mg/kg, and 100 mg/kg gastrodin treated groups showed a dose-dependent reduction of Meth-induced CPP effect, and 100 mg/kg of gastrodin could basically eliminate the CPP effect induced by Meth. The results of immunofluorescence showed that, compared with the normal saline group, the hippocampal microglia of the Meth group was significantly activated. After the treatment with 10 mg/kg, 30 mg/kg, or 100 mg/kg gastrodin, the microglia cell activation was inhibited by gastrodin, and the performance was more obvious after the treatment with 30 mg/kg and 100 mg/kg gastrodin. Conclusion Gastrodin can reduce the CPP effect of Meth-dependent rat in a dose-dependent manner; gastrodin has a potential effect on methamphetamine dependence. Gastrodin can inhibit the activation of hippocampal microglia in hippocampus region of Meth-dependent rat.
2021, 42(5): 12-17.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210503
Abstract:
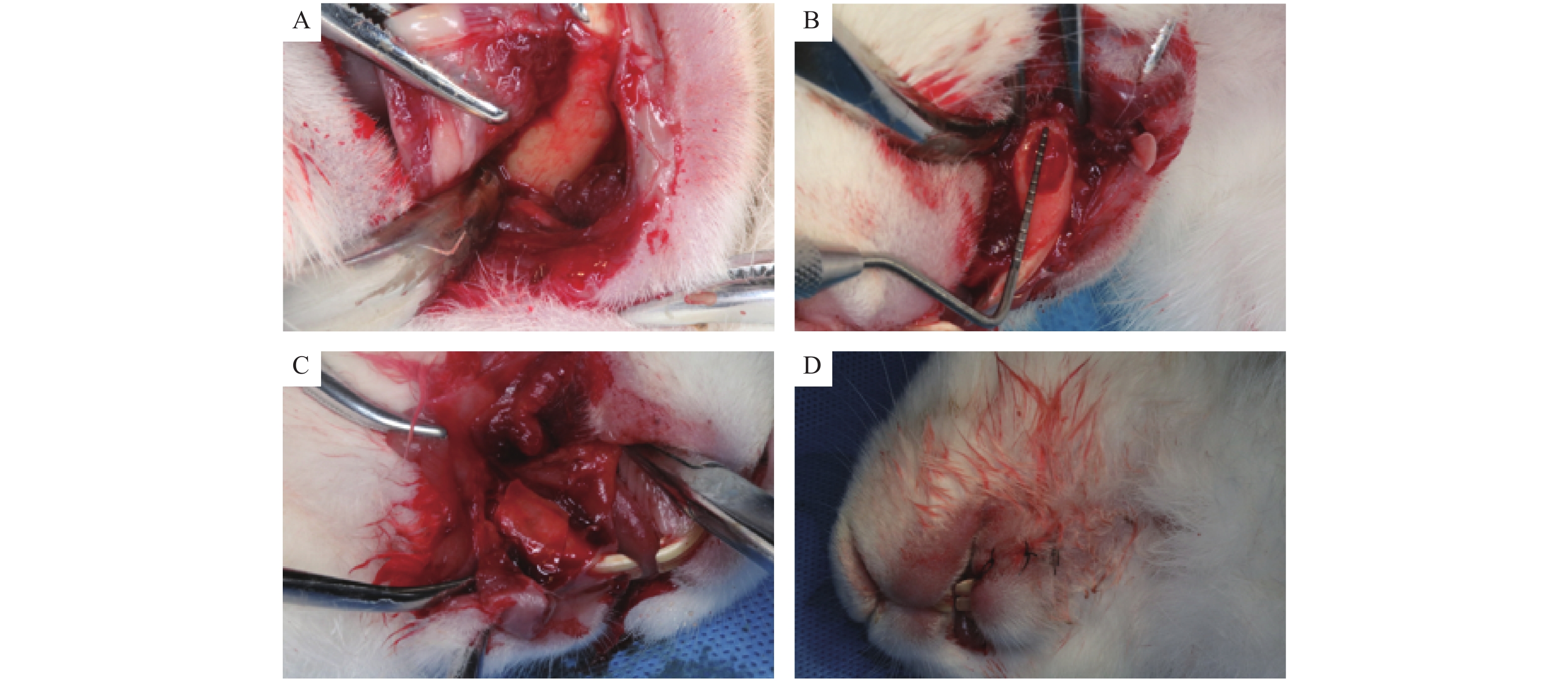
Objective It is planned to build a New Zealand rabbit periodontal defect model and determine the biological safety of hPDLSCs-BMP-2-PSH membrane and its in vivo osteogenic repair effect. Methods After confirming that the BMP-2-PSH membrane was not cytotoxic, the cultured hPDLSCs cell membrane was compounded to the BMP-2-PSH membrane. Respectively, HPDLSCs/PSH composite membrane was implanted into the alveolar bone defect of mandibular left incisor in each New Zealand rabbit as the experimental group, and the controlled porous fiber membrane material was implanted into alveolar bone defect of the right central incisor as the control group (or not implanted any material was used as a control), then the whole flap was reset and sutured. Imaging (CT) examination was performed immediately after the surgery and every 3 weeks (observed continuously for 12 weeks) to observe the healing of bone defects; meanwhile, the absorbance of PDLSCs/BMP-2 double membrane materials, the amount of new bone formation and new bone morphology of samples in each group were observed at 4, 8 and 12 weeks after the surgery. Results Different concentrations of PSH membrane and BMP-2-PSH membrane extracts were not cytotoxic to hPDLSCs cells, hPDLSCs cells could be successfully compounded to BMP-2-PSH membranes; The analysis of CBCT and histomorphology showed that hPDLSCs/PSH composite membranes can effectively promote the repair and regeneration of alveolar bone defects. Conclusion The hPDLSCs/PSH composite membrane has the good biological safety and is beneficial to repair periodontal defects of New Zealand rabbits.
2021, 42(5): 18-23.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210504
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the influence of the silence of UBE2C gene on the gastric cancer AGS cells proliferation and migration of human. Methods Using RNA interference technology, the expression vector of UBE2C silenced lentivirus was transfered into 293T cell line with packaging plasmids to produce the lentiviral particles. Lentivirus was used to infect human gastric cancer AGS cells, and the cells with stably expressing UBE2C were obtained by puromycin screening. The experiment was divided into the interference group and the interference control group. The expression levels of UBE2C mRNA in human gastric cancer AGS cells were detected by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). The capacity of AGS cell proliferation and migration was determined with real-time label free cell analyzer (RTCA). Meanwhile, Cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) was used to further confirm the effect of UBE2C expression level on the proliferation of human gastric cancer AGS cells. Results Compared with the interference control group, UBE2C shRNA transfected human gastric cancer AGS cells significantly decreased the expression of UBE2C mRNA (P < 0.05); the cellular proliferation and migration ability were obviously decreased. Conclusion Targeted silencing of UBE2C gene expression can inhibit the malignant biological behavior of human gastric cancer AGS cells.
2021, 42(5): 24-28.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210505
Abstract:
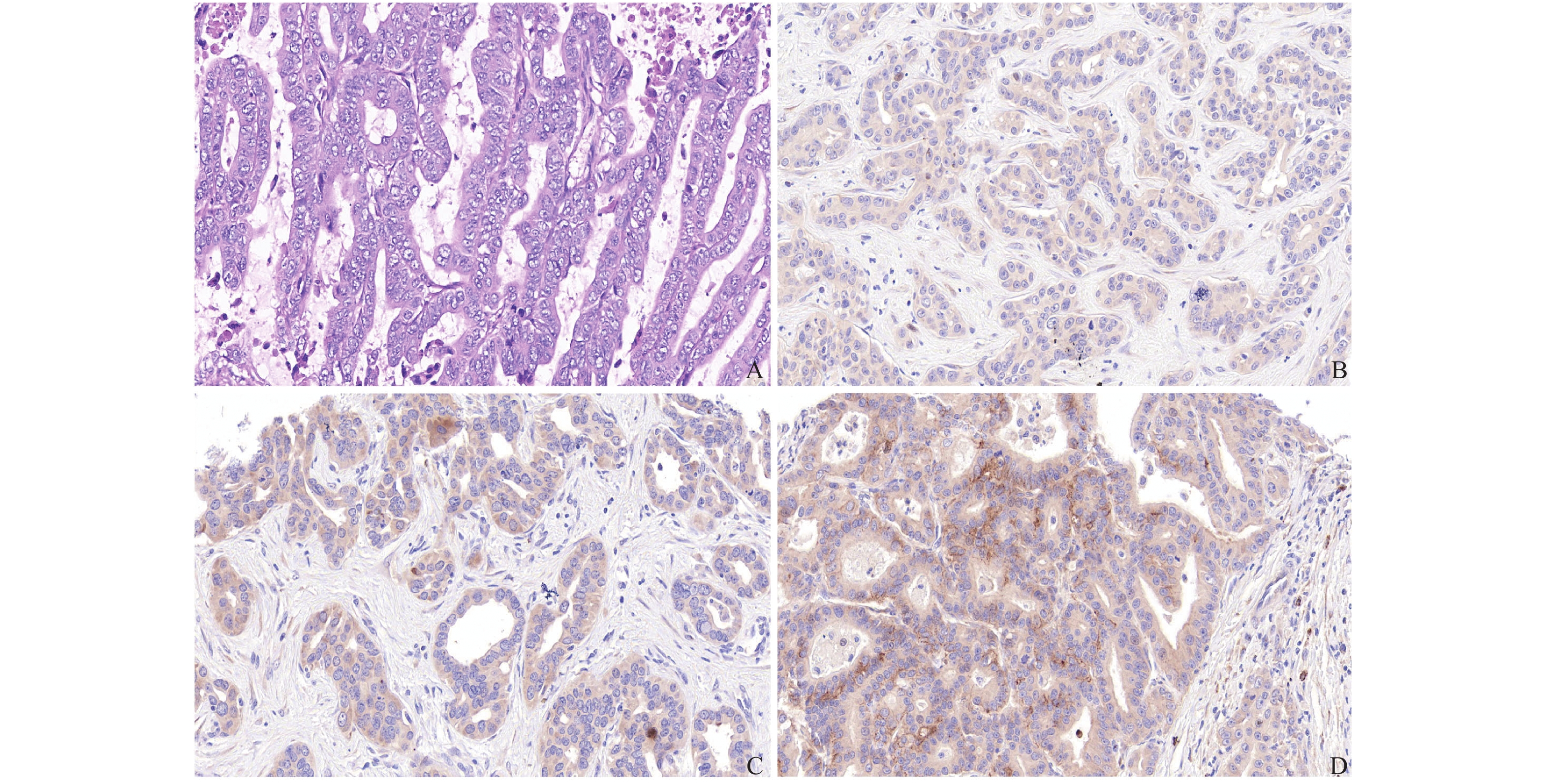
Objective To study the expression of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A2 (eIF5A2) in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and its correlation with nerve invasion and peripheral adipose tissue infiltration. Methods Paraffin sections from 156 patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma were collected from October 2013 to October 2020 in the Department of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Surgery, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, and the normal liver tissues from 30 cases of hepatic hemangioma undergoing partial hepatectomy were collected during the same period. In the control group, the immunohistochemical methods were used to detect the expression level of eIF5A2, and pathological data were collected to analyze the correlation between eIF5A2 and nerve invasion and peripheral adipose tissue infiltration. Results In 156 cases of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma tissue sections, 95 cases (60.9%) had high expression of eIF5A2. The high expression rate of eIF5A2 in normal liver tissue bile duct epithelium was 13.3%. The expression of eIF5A2 was significantly related to nerve invasion and peripheral adipose tissue infiltration (P < 0.05). Conclusion eIF5A2 is highly expressed in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and is significantly related to nerve invasion and surrounding adipose tissue infiltration.
2021, 42(5): 29-34.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210506
Abstract:
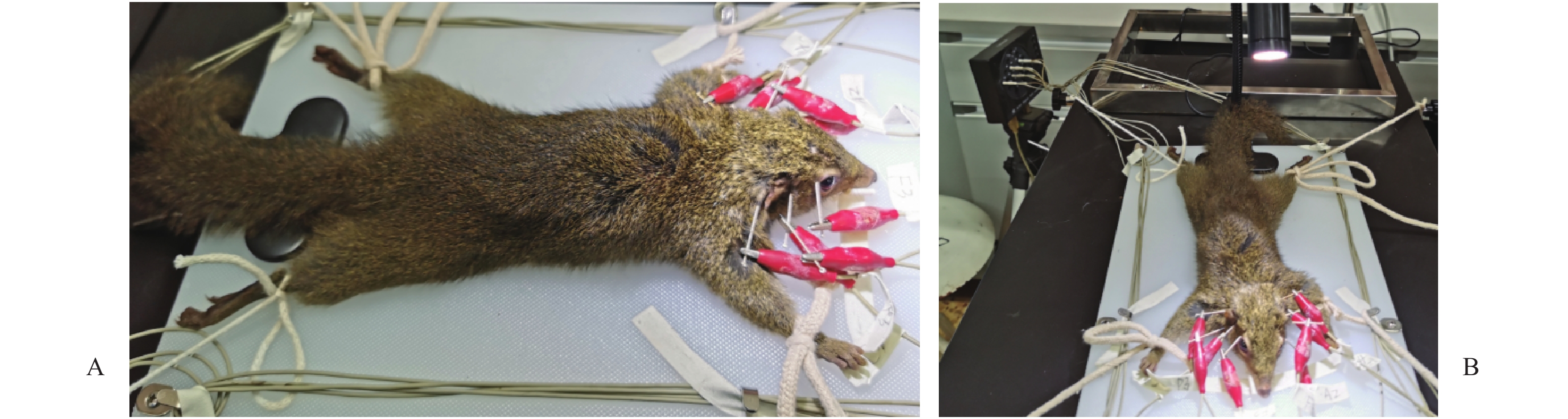
Objective To study the characteristics of cortical electroencephalogram (EEG), power spectrum and mapping in tree shrew model for Parkinson’ s disease (PD). Methods Ten common-level Burmese adult tree shrews were selected and randomly divided into a model group (n = 5) and a control group (n = 5). A PD model of tree shrew was produced by intramuscular injection of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP), with a MPTP dose of 2 mg/kg. The control group was injected with an equal volume of 0.9% sodium chloride solution continuously for 15 days. One month after the drug withdrawal, EEG technology was used to perform the cortical EEG tracing, power spectrum and topographic analysis of the tree shrew PD model. Results The MPTP-Induced Tree Shrew Model for PD was established successfully. In the normal control group, there was no significant difference and specificity in frequency, amplitude, waveform and phase of EEG in the frontal, parietal and occipital parts of the cerebral hemisphere,α wave was dominant in the waves recorded in each part of the tree shrews brain and amplitude difference was less than 30%, with δ and θ waves being scattered; The histogram of EEG power spectrum was basically symmetrical on both sides; The power value of each frequency band was distributed symmetrically in the two hemispheres and the bilateral six bands in the EEG mapping was low power and its power value was less than 100 μv2/Hz. In the tree shrew PD model group, spikes, sharp waves and other abnormal waves were recorded, showing rhythmic emission. The mainly manifested α wave was asymmetry, the abnormal waveforms were mainly in the frontal and parietal areas, and the high amplitude slow waves δ、θ also appeared in some areas; The main features of EEG power spectrum were as follows: α wave phase was not synchronous, and the histogram distribution of power spectrum in each frequency band was asymmetric; The δ frequency band in the EEG mapping was low frequency and high power and the average power was more than 1 000 μv2/Hz. Compared with the control group, the frequency band power values of δ、θ、α1and α2 were significantly higher than those of the control group. Conclusion Compared with the normal control group, the EEG waveforms, EEG spectrum histogram and EEG mapping in the tree shrew PD model all show the significant characteristics, proving that they can provide references for the study of neuroelectrophysiology in PD model.
2021, 42(5): 35-40.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210507
Abstract:
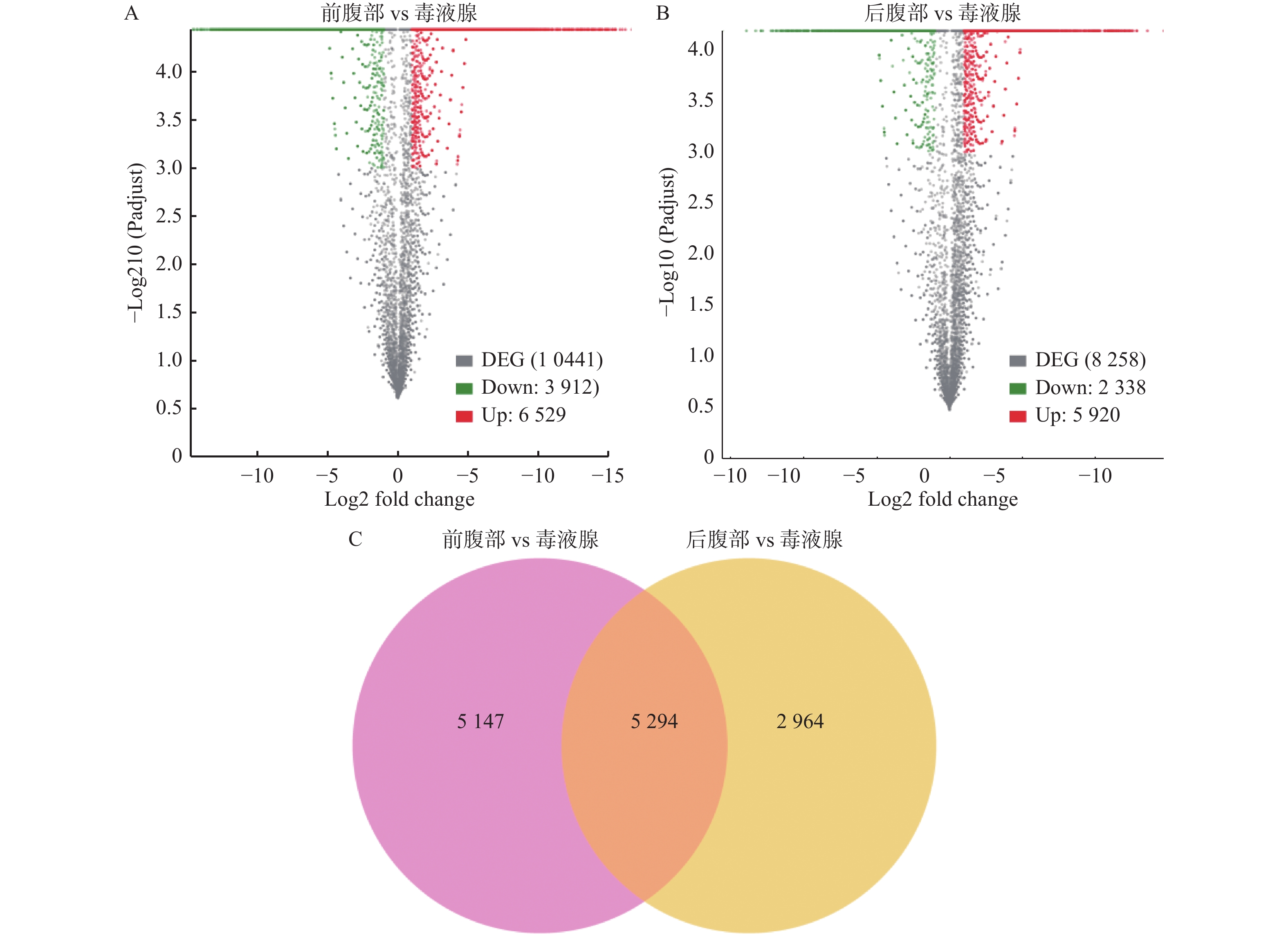
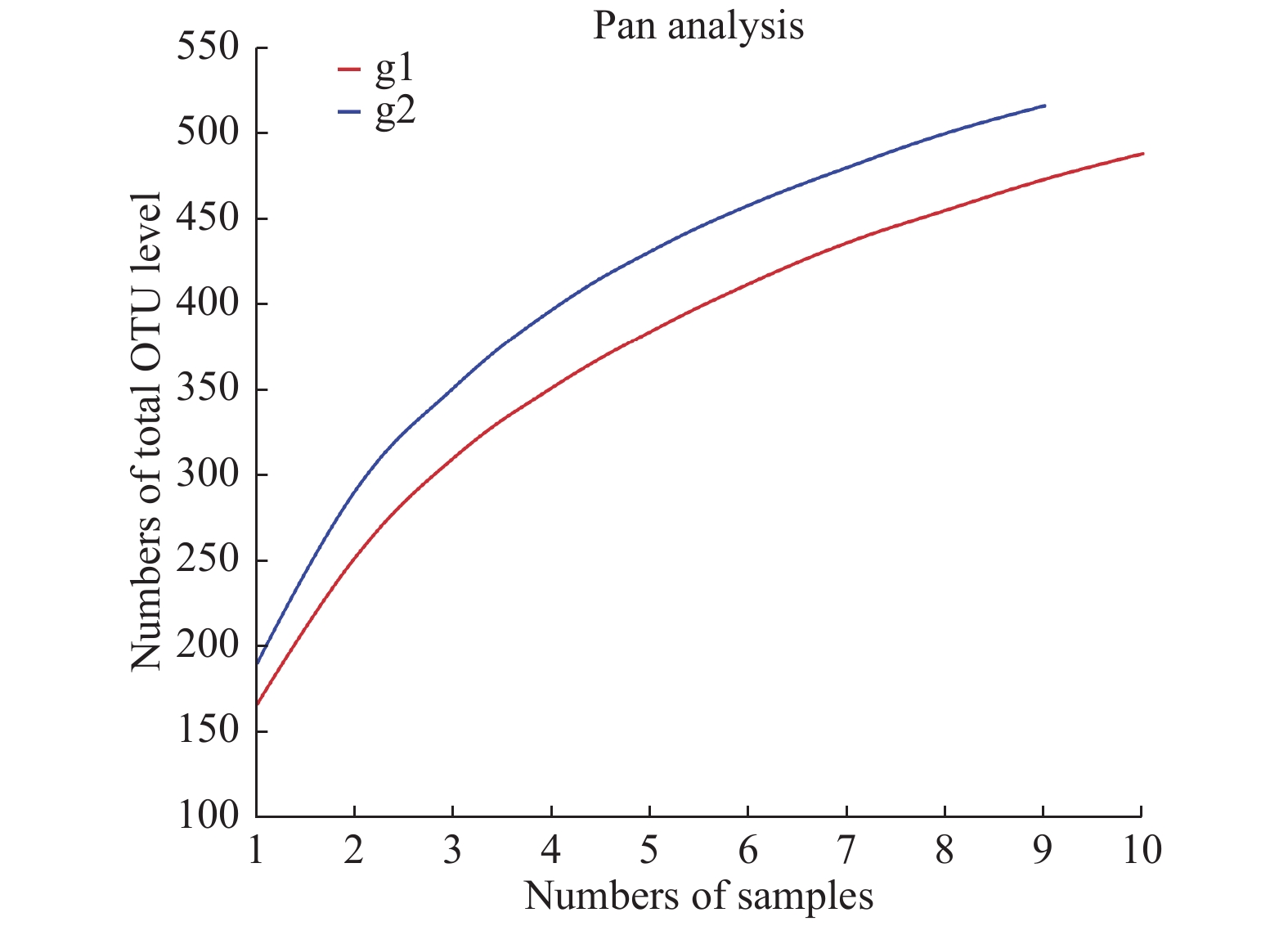
Objective To obtain the transcriptome dataset of Buthus martensii. Methods Taking the characteristic Buthus martensii in Linyi area of Shandong Province as the research object, the second-generation high-throughput sequencing platform Illumina HiSeq 4000 150PE was used to sequence the transcriptome of the anterior abdomen, posterior abdomen and venom gland of Buthus martensii. The venom gland genes were compared with the preabdomen and the postabdomen gene sets, and then the intersection of the two comparison was analyzed. The screening differential gene sets were analyzed by GO and KO. Results There were 60 major categories of GO functional classification, containing 23 biological pathways, 13 cellular components, and 24 molecular functions. Among the first 20 KEGG pathways that were most significantly enriched, the calcium ion signaling pathway and phospholipase signaling pathway were closely related to toxins. Conclusion In this study, we have constructed the transcriptome sequence database of B. martensii by nonparticipating transcriptome sequencing, which provids the sequence basis for the future research on the gene mining function of Buthus martensii and the research basis for the biosynthesis of metabolites.
2021, 42(5): 41-47.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210508
Abstract:
Objective To investigate and evaluate the quality of life and its influencing factors in Han nationality patients with PCOS. Methods Convenient sampling methods were used.163 Han patients with PCOS who were diagnosed in gynaecological out-patient clinics and 194 healthy women were recruitedingrade Ⅲ-A hospitals of Yunnan Province. Sociodemographic characteristics questionnaire, clinical characteristics questionnaire and WHOQOL-BREF scale were used in the research. Results There were significant differences in the physiological and psychological fields between PCOS patients and healthy women in quality of life, and the PCOS group was lower with the healthy control group (P < 0.05). The quality oflife score of PCOS patients were between 5.50 to 23.25, the average value was (14.82±2.84), the score of each dimension from low to high was in order psychological, environmental, social relationship and physiological field. Multiple linear regression analysis showed that the quality of life and its dimension of PCOS patients were influenced by different factors, and the negative life events were the important factors influencing the quality of life as well as physiological and psychological fields (P < 0.05). Conclusion The quality of life in PCOS patients was decreasing, which is mainly manifested in the decrease of mental health status. Therefore, attention should be paid to the mental health of PCOS patients and the personalized and targeted measures should be taken according to their social demography and clinical characteristics so as to improve their quality of life.
2021, 42(5): 48-53.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210509
Abstract:
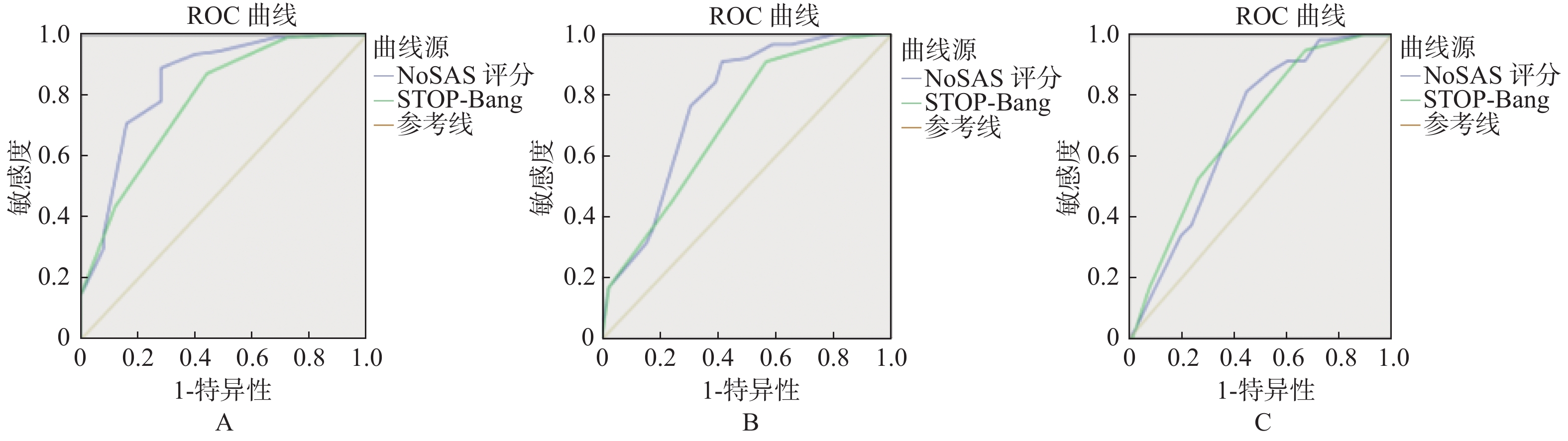
Objective To compare the predictive value of NoSAS score and STOP-Bang questionnaire score, and evaluate the feasibility of NoSAS score screening for OSAHS in physical examination population. Methods Retrospective analysis of the polysomnography (PSG) monitoring results of 135 patients with suspected OSAHS in our health management center was made from January 2018 to August 2019, including the NOSAS score and the Stop Bang Questionnaire and patient information. Grouped by apnea-hypopnea index (AHI), the sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value and negative predictive value of NOSAS score and Stop-Bang questionnaire score were calculated, and ROC curves were drawn so as to compare the effectiveness of two scores which screened OSAHS. Result Of the 135 patients, 75.6% were male and 24.4% were female. Using AHI ≥ 5 events/h, AHI ≥ 15 events/h and AHI ≥ 30 events/h as the diagnostic criteria, the sensitivity and specificity of NOSAS scores were: 0.891 and 0.720, 0.910 and 0.587, 0.814, and 0.553; The sensitivity and specificity of STOP-Bang questionnaire were 0.873 and 0.560, 0.910 and 0.435, 0.949 and 0.329, respectively. When AHI ≥ 5 events/h, AHI ≥ 15 events/h and AHI ≥ 30 events / h were used as diagnostic criteria, the areas under ROC curveofthe NoSAS score were 0.847, 0.773 and 0.693, the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.001); the areas under the ROC curve of the STOP-Bang questionnaire were 0.784, 0.711, 0.694 and the differences were statistically significant (P < 0.001). When AHI is 5 events/h, 15 events/h and 30 events/h as the critical points, the area under the NOSAS score ROC curve is greater than or equal to the STOP-Bang questionnaire score. The NOSAS score has good predictive value. Conclusion As a simple and effective initial screening tool, the NOSAS score can effectively help physicians quickly screen OSAHS patients in physical examination population.
2021, 42(5): 59-63.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210511
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the oral health status of the elderly over 60 years old in rural areas of Yunnan province, investigate the quality of life of the elderly, and analyze the relationship between the oral health and quality of life. Methods A stratified sampling method was used to record caries, attachment loss and dentition defect according to the World Health Organization standard. The quality of life (QoL) survey was performed with SF-36 scale. Oral health status and quality of life scores were analyzed by SPSS 25.0 statistical software. Results A total of 2263 people were investigated in this study. The prevalence of caries and loss of attachment > 3 mm were 95.6%, 73.4% respectively. There were 91.2% subjects with dention defects. Patients with caries, loss of attachment > 3 mm and dentition defects had a lower quality of life (P < 0.05). Conclusion The oral health status of the elderly over 60 years old in rural areas of Yunnan province is not optimistic, and oral diseases can affect the quality of life of the elderly.
2021, 42(5): 64-69.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210512
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the poor vision and ametropia of primary school students in Xundian County, Yunnan Province in 2019. Methods From November 2018 to November 2019, a total of 3, 764 students in 30 classes from grade one to grade five in six primary schools were selected in Xingdian county by using a stratified random sampling method.The rate of poor vision and the composition of ametropia were analyzed, and the differences of the total and each ametropia in gender and grade were compared by rank sum test. Results 1392 children with poor vision were detected, with an average rate of 36.98%. The proportion of myopia in girls (15.25%) was higher than that in boys (12.65%), the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.01). The proportion of myopia in the total number of students gradually increased from 14.23% (grade 1) to 44.61% (Grade 5), the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.01). The proportion of myopia in girls in grade 3 and 5 (17.19%, 24.66%) was higher than that in boys in the same grade (10.73%, 19.95%), the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.01). The proportion of hyperopia decreased rapidly in grade 3 (10.41%), and the difference was statistically significant compared with grade 1 and grade 2 (P < 0.01). The proportion of astigmatism was the highest in grade 5 (17.43%), and the difference was statistically significant compared with grade 1, 2 and 4 (P < 0.01). Conclusion In the six primary schools in Xundian County, myopia is the main factor of poor eyesight and the main reason for its change.Among various types of refractive errors and female students have more problems than male students.
2021, 42(5): 81-86.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210515
Abstract:
Objective The rate of gastric cancer in young patients has increased over the past few decades. The aim of this study was to analyze the clinical characteristics of young patients with gastric cancer, and investigate the possible risk factors that may be related to the survival rate of young patients. Methods From January 2005 to December 2015 a series of 535 consecutive patients were admitted to our hospitals because of a gastric cancer. We carried out a retrospective cohort study in 81 patients younger than 40 years old and in 454 patients aged 40 years older. The comparison was involved in the evaluation of patient and tumor characteristics. Results The proportion of the female in the young group was higher than that in the middle-aged and old group. The young patients had significantly more preoperative abdominal pain, while the elder had more weight loss as well as upper gastrointestinal bleeding and abdominal pain. There was no significance in duration of symptoms before the diagnosis between the two groups; In terms of lesion, pathological change occurred at the antrum or full stomach was seen more often in young patients, while elderly patients often had lesions at the upper part of corpus or the fundus. Helicobacter pylori infection and diffuse histological type were significantly associated with younger age. There was also statistically significant difference regarding overall and cancer-related 5-year survival; advanced cancer stage and diffuse histological type were the independent negative prognostic factors influencing cancer-related survival. Conclusion In our study, the proportion of the female in young patiants was higher than that in the middle-aged and old patiants and had more Helicobacter pylori infection, as well as the diffuse histological type of gastric cancer along with poor cancer-related 5-year survival rate, but we do not have sufficient evidence to consider gastric cancer in female patients as a different clinical entity. Further studies are needed to understand carcinogenesis in younger patients, especially females.
2021, 42(5): 92-95.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210517
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the effect of "|" shaped incision on concha plasty. Methods 68 cases with chronic suppurative otitis media and middle ear cholesteatoma were randomly divided into two groups, with 39 cases in the "|" shaped incision group and 29 cases in the "Y" shaped incision group. Results The patients were followed up for 1 year. There was no significant difference in the incidence of postoperative vertigo, tinnitus, granulation and scab in the operation cavity between the two groups (all P > 0.05). But there were statistically significant differences in dry ear time, epithelialization time and postoperative auricular perichondritis ( P < 0.05). Conclusion Compared with Y-shaped incision, concha plasty with "|" incision is more simple and easy to operate, which improves the curative effect of operation, and is worthy of promotion and application.
2021, 42(5): 101-106.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210519
Abstract:
Objective To provide the certain guidance for the accurate treatment of patients with abdominal infection by observing the changes of the difference between HCT and ALB in the treatment of patients with abdominal infection. Methods A total of 106 patients with various abdominal infection treated in the First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University from January 2018 to December 2018 were selected and divided into 7 groups (n = 106) according to the operation time: preoperative, postoperative 12 h, postoperative 1 day, postoperative 2 days, postoperative 7 days, postoperative 14 days and postoperative 21 days. Gender and age of patients were recorded. The hematocrit and plasma albumin of patients at each time point above were collected, and the HCT-ALB difference was calculated. According to the clinical outcome, they were divided into the postoperative improvement group and the death group. The difference of HCT, ALB and HCT-ALB in each group was compared. Results Compared with those before the surgery, HCT and ALB decreased and HCT-ALB increased 12 h, 1 day, 2 days and 7 days after the surgery (P < 0.05). Compared with those before the operation, HCT and ALB decreased 14 days after the operation ( P < 0.05), but there was no significant difference in HCT-ALB ( P > 0.05). Compared with the improved group, the age of patients in the death group increased ( P < 0.05), and the preoperative HCT-ALB increased ( P < 0.05). Conclusion Capillary leakage is aggravated in patients with celiac infection after the surgical treatment, and the pathological process lasts for more than 7 days, and the capillaries of the dead are more leaky.
2021, 42(5): 126-130.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210523
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the effect of different doses of Solina xin combined with Xingpi Yanger granule on primary nocturnal enuresis (PNE) in children. Methods From March 2018 to January 2020, 120 PNE children admitted to Pediatric Internal Medical Department in The Third People’ s Hospital of Hubei province Yichang city were selected as the study subjects. The patients were divided into Group A (40 cases, low-dose Solina Xinlianxingpi Yanger granule), group B (40 cases, medium-dose Solina Xinlianxingpi Yanger granule), and group C (40 cases, high-dose Solina Xinlianxingpi Yanger granule) by using the random number table method. The clinical efficacy of the three groups was compared. Bladder volume and bladder volume wall thickness index (BVWI) before and after the treatment were compared among the 3 groups. The relapses of the 3 groups were compared. The occurrence of adverse reactions during the treatment was compared among the 3 groups. Results There was no significant difference in the total effective rate among the 3 groups (P > 0.05). There were no statistically significant differences in bladder volume and BVWI among the 3 groups before the treatment ( P > 0.05). Bladder volume was significantly increased after the treatment compared with that before the treatment in the 3 groups ( P < 0.05), and BVWI was significantly decreased after the treatment compared with that before the treatment ( P < 0.05). There were no statistically significant differences in bladder volume and BVWI among the 3 groups after the treatment ( P > 0.05). There was no statistically significant difference in the recurrence rate after 3 months and 6 months of treatment among the 3 groups ( P > 0.05). The incidence of adverse reactions in group C was higher than that in group A and group B ( P < 0.05), and the incidence of adverse reactions in group B was higher than that in group A ( P > 0.05). Conclusion Low, medium and high doses of Solinaxin combined with Xingpi Yanger Granule have similar effects on the treatment of PNE in children, both of which can improve the bladder function of children, and have little influence on the recurrence rate. However, high dose solinazine can significantly increase the occurrence of adverse reactions, so it is recommended to select low dose solinazine clinically for safety reasons.
2021, 42(5): 70-75.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210513
Abstract:
Objective To explore the clinical effects of ankle arthroscopic microfracture used in different MRI classifications of osteochondral lesions of the talus. Methods 48 cases with osteochondral lesions of the talus and treated with microfracture under the ankle arthroscopy were divided into 4 groups according to MRI classification. The functional recovery and pain relief of ankle joint were observed after the follow-up, and the curative effects of each group were compared. Results The average follow-up of 48 cases was 23.7 months. For MRI grade Ⅱ° , Ⅲ° , Ⅳ° , Ⅴ° injury patients, microfracture could bring good functional results (P < 0.05). The total excellent and good rate of postoperative AOFAS function score was 40 cases (83.33%), of which Ⅱ° 13 (100%) and Ⅲ° 16(100%) were much higher than Ⅳ° 7(63.64%), Ⅴ° 4(50%). There was no significant difference in the improvement of AOFAS score among the four groups (P > 0.05). And the improvement of VAS score in patients with Ⅱ° and Ⅲ° injuries was significantly better than that in patients with Ⅳ° and Ⅴ° injuries (P < 0.05). Conclusion The clinical effects of ankle arthroscopic microfracture are different in different MRI classifications of osteochondral lesions of the talus. Pain relief and postoperative function in patients with Ⅱor Ⅲ grade are significantly better than those with Ⅳ or Ⅴ grade.
2021, 42(5): 76-80.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210514
Abstract:
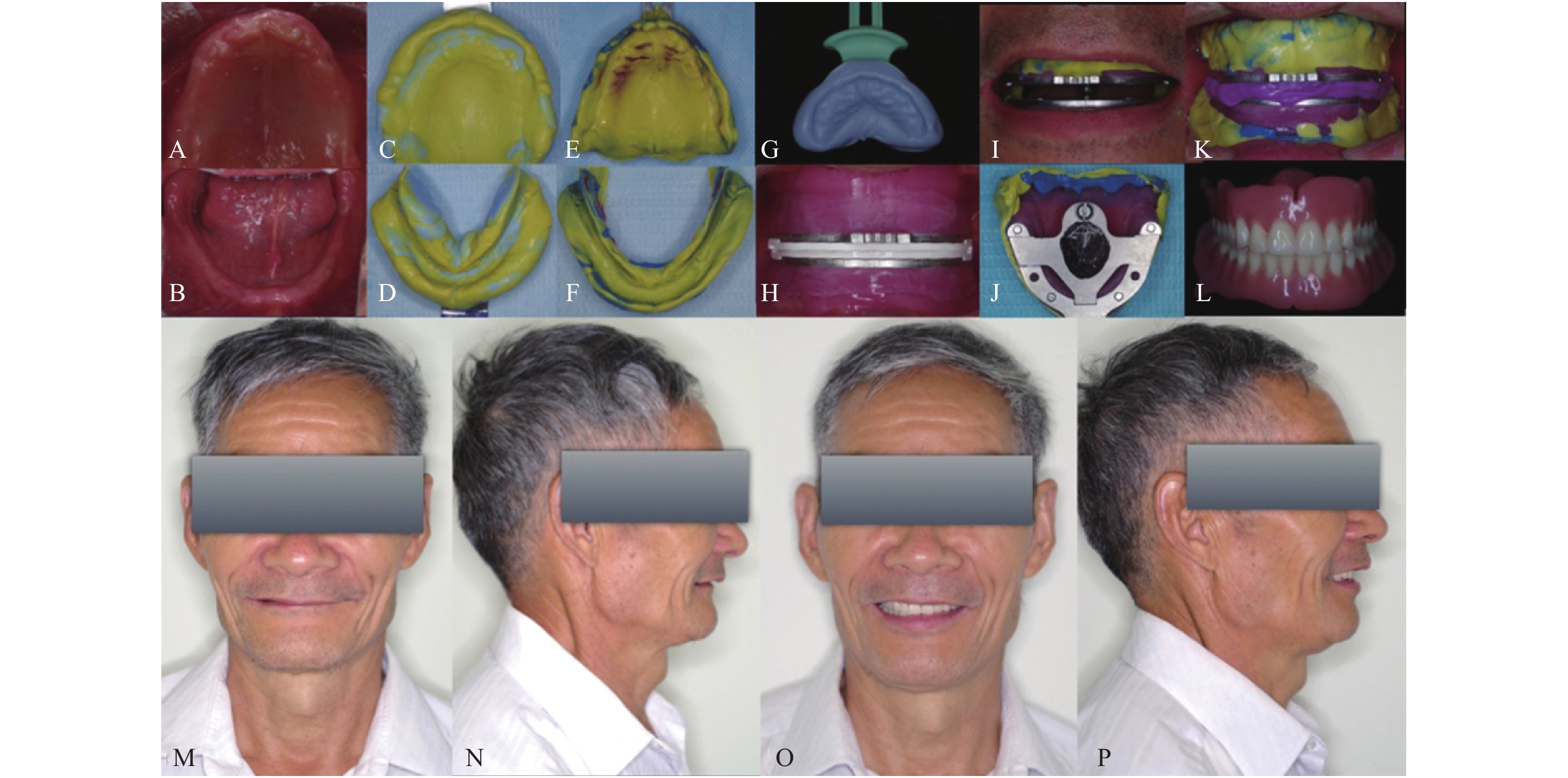
Objective To evaluate the efficacy and satisfaction of the edentulous patients with the simplified biofunctional prosthetic denture (SBPD). Methods 26 patients with complete denture restoration were randomly divided into two groups: conventional complete denture (CCD) group (n = 13) andSBPD group (n = 13). The satisfaction degree was investigated by filling in the visual analoguescale (VAS) at baseline, 1 month and 3 months following the denture delivery. Results In terms of masticatory function, comfort and retention, the VAS score on SBPD group was higher than that of CCD group, (P < 0.05). Conclusion The SBPD method has the good precision and it is worthy of clinical promotion.
2021, 42(5): 87-91.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210516
Abstract:
Objective To explore the changing characteristics of fecal bacteria in patients with malignant obstructive jaundice. Methods From January 2019 to May 2019, 87 cases with malignant obstructive jaundice were taken as case bank and screened by inclusion and exclusion criteria. After that, 10 patients and 10 healthy relatives of patients were selected, age, sex and BMI were recorded, and faeces were sent for 16srDNA copy number. Results (1)The fecal bacteria abundance and diversity index of the experimental group were lower than that of the control group, but there was no statistical significance (P < 0.05). However, when the data of fecal bacteria abundance were presented in the Heatmap, the intuitive difference was more obvious. (2) The data of the two groups were subdivided by bacteria genus, and it was found that the composition of fecal bacteria genus in the experimental group changed fundamentally compared with that in the control group (P < 0.05). Among them, Escherichia-Shigella, Streptococcus, Veillonella, Enterococcus, Akkermansia increased significantly, while the bacteria genera of wiesia and clostridium declined significantly. Whether the intestinal flora can be rebalanced may affect the therapeutic effect. Conclusion The fecal flora structure of patients with malignant obstructive jaundice is significantly different from that of normal control group, and the dominant flora genus has been fundamentally changed.
2021, 42(5): 96-100.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210518
Abstract:
Objective Our aim was to investigate the expression and significance of coagulation markers in patients with early colorectal cancer. Methods This study was conducted by the case-control study to collect data from patients with early colorectal cancer confirmed by pathological examination at the First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University from January 1, 2010 to December 31, 2018, and the difference of coagulation-related indexes was compared between the early cancer group and the control group. Results Compared with the control group, PT, PTR, FIB, TT, APTT, PLT, MPV in the early cancer group were lower than those in the control group, and the values of PT, PTR, TT, APTT, MPV were higher than those in the control group (P < 0.05), showing that FIB and MPV were independent risk factors for early colorectal cancer. Conclusion Abnormalities in the coagulation system are also present in patients with early colorectal cancer. It seems that patients with early colorectal cancer need prophylactic antiplatelet and anticoagulant therapy, but the time of anti-platelet therapy and anti-coagulant therapy, as well as the types and methods of medication, need to be further studied.
2021, 42(5): 107-113.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210520
Abstract:
Objective To explore the effect of individualized cardiac rehabilitation exercise program extended in stages on cardiac function and daily living ability in patients with hypertension and heart failure. Methods Sixty patients with heart failure were randomly divided into the control group and the intervention group, with 30 cases in each group. The control group was given the routine anti-heart failure treatment and routine care. The intervention group carried out personalized cardiac rehabilitation based on the control group exercise before the intervention and 6 months after the intervention to evaluate the cardiac function, daily life ability and rehospitalization rate of the two groups of patients. Results After 6 months of the intervention, the 6MWT distance of patients in the intervention group was significantly higher than that of the control group, the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05); Before the intervention, the intervention group was significantly lower than the control group, the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05); the intervention group within 6 months was significantly lower than the control group, the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). Conclusion The personalized cardiac rehabilitation exercise program extended in stages can significantly improve the cardiac function and exercise tolerance of patients with heart failure and hypertension and improve the daily life ability of patients. Thus it can improve the quality of life, reduce the rate of rehospitalization and promote the rehabilitation of patients.
2021, 42(5): 114-119.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210521
Abstract:
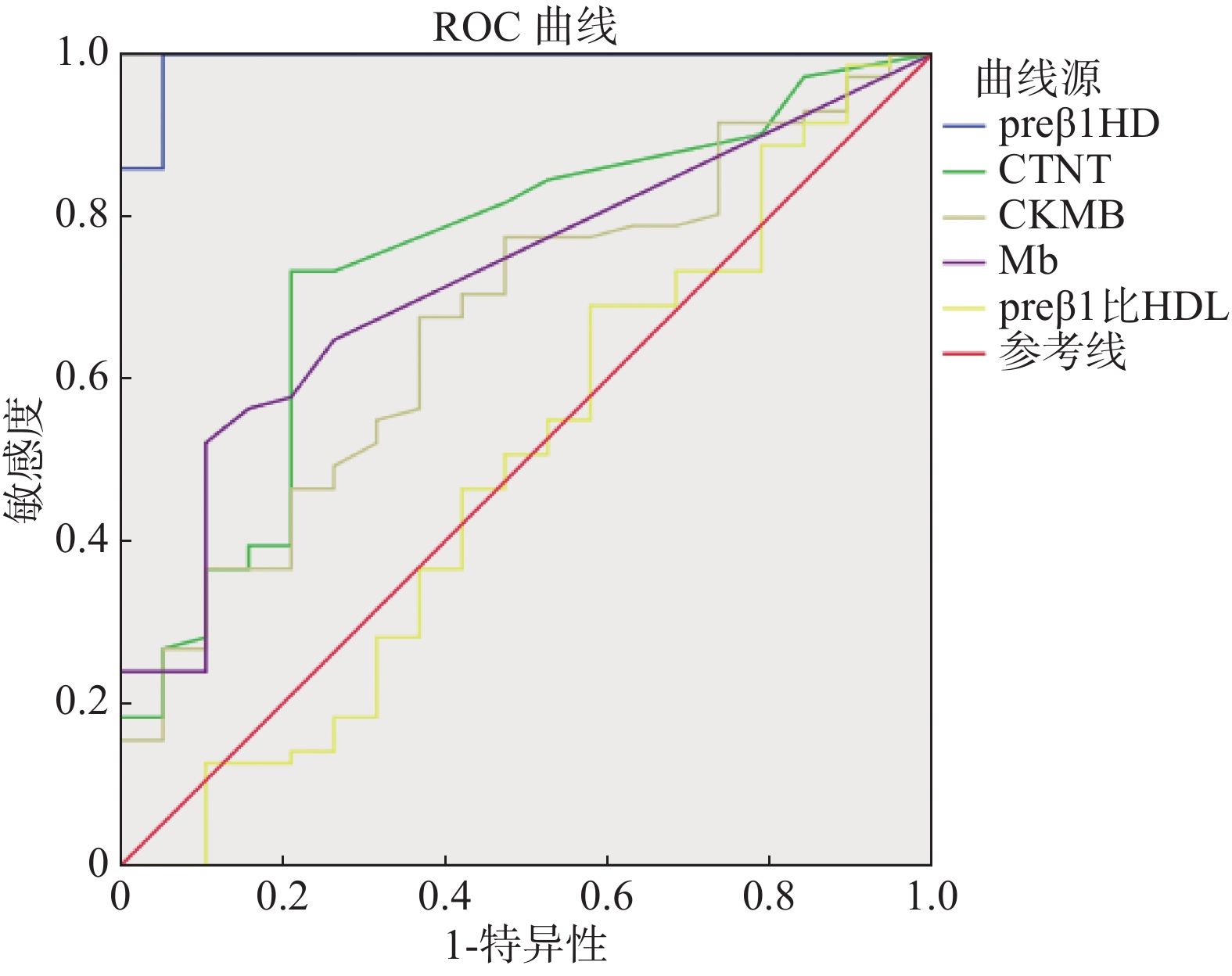
Objective To investigate the correlation between Pre β1-HDL and the predictive value of coronary artery disease severity in patients with coronary heart disease. Methods In this study, 90 patients undergoing coronary intervention diagnosis and/or treatment in our hospital were enrolled sequentially. Among them, there were 70 patients with coronary artery disease (including 15 patients with single coronary artery disease, 55 patients with multiple coronary artery disease)and 20 patients with normal coronary artery disease. Clinical baseline data of each group were collected. Blood preβ1-HDL concentration was determined by ELISA. SPSS was used for statistical analysis. Results The results of this study showed that blood pre β1-HDL levels in patients with different severity of coronary artery disease had the statistically significant differences (P < 0.05). Preβ1-HDL concentration was positively correlated with coronary Gensini score (P < 0.000), and the correlation was (r = 0.782). Preβ1-HDL concentration was positively correlated with cTnT (P < 0.000), and the correlation was (r = 0.421). The area under ROC curve(AUC) of blood Pre β1-HDL was 0.993, the diagnostic threshold was 3.66, and the sensitivity and specificity were 100% and 94.7%, respectively. Conclusion Blood Pre β1-HDL concentration has been found to be a new indicator to predict the severity of coronary artery disease.
2021, 42(5): 120-125.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210522
Abstract:
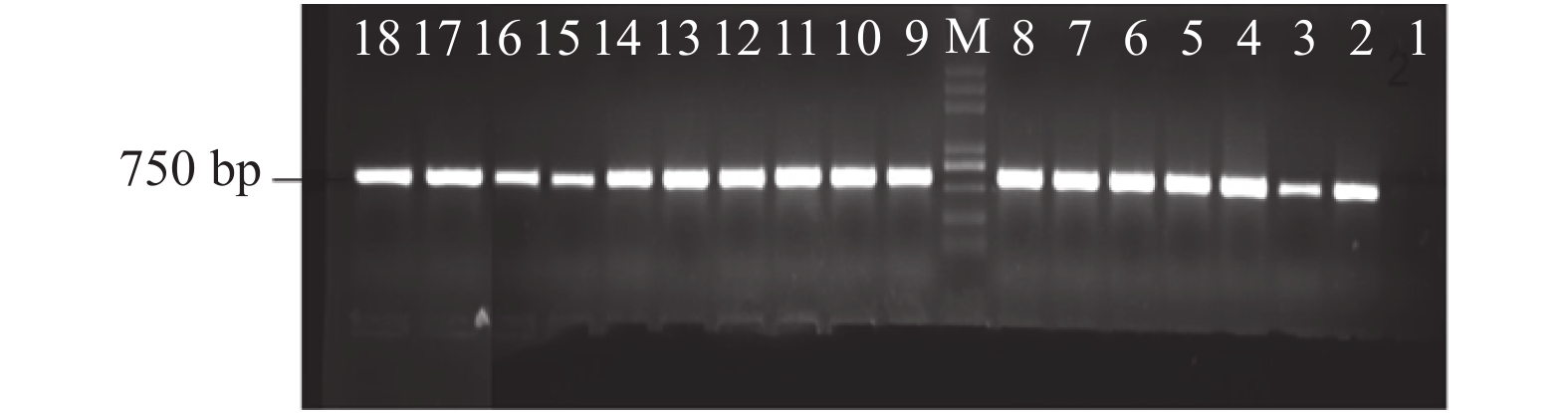
Objective To explore the value of 16SrRNA gene detection in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the early diagnosis of bacterial meningitis (BM) in children. Methods CSF specimens were collected from 40 patients with BM who were diagnosed of BM in Kunming Children’ s Hospital between January 2019 and June 2020. PCR was used to detect the 16SrRNA gene in the specimens. Then the 16SrRNA gene was sequenced for the positive samples by PCR, and the sequencing results sequence alignment and homology were analyzed by NCBI BLAST. At the same time, all the specimens were cultured simultaneously. Results Of the 40 children’ s CSF samples, 16 were positive for 16SrRNA gene PCR, with a positive rate of 40%; 7 cases were positive for bacterial culture, with a positive rate of 17.5%. The positive rate of PCR method was higher than that of the bacterial culture method (χ2 = 4.93, P < 0.05), with CSF as the “gold standard”, the sensitivity and specificity of PCR assay were 71.4% (5/7) and 66.7% (22/33); the results of 16SrRNA gene sequencing were consistent with the results of CSF culture, and five bacterias which were not detected by CSF culture; the time of CSF culture was (61.21±12.62) h, however, the PCR detection time required (7.09±0.45) h, and the difference of detection time between the two methods was statistically significant (P < 0.05). Conclusion The PCR detection method of 16SrRNA gene in CSF can improve the detection rate of CSF pathogenic bacteria in BM patients, and it can reduce the missed detection rate. It has the specific and rapid characteristics and can provide the reliable pathogenic basis for early diagnosis of clinical BM in time.
2021, 42(5): 131-137.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210524
Abstract:
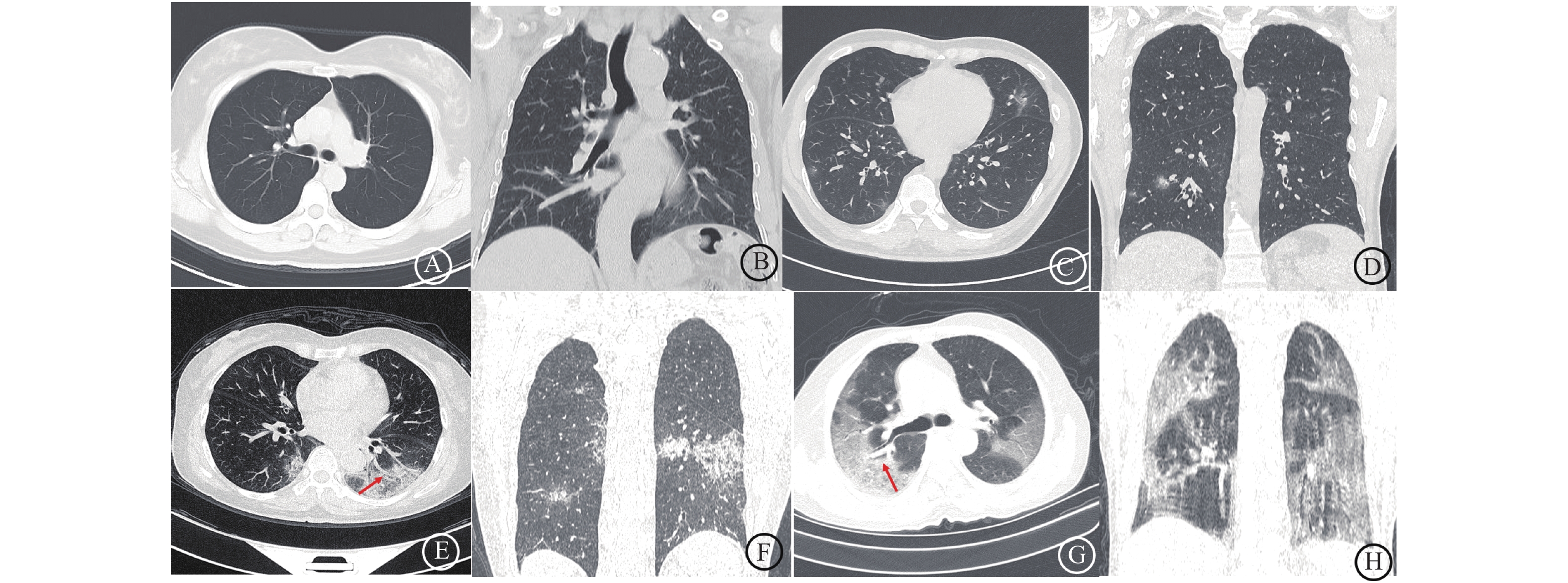
Objective To investigate the clinical and CT image characteristics of COVID-19 pneumonia, and the predictive value of CT in the early stage of different clinical types. Methods Chest CT and clinical data of confirmed 143 patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in January to February 2020 were enrolled. According to the diagnosis and treatment of COVID-19 pneumonia(trial version 7), all the patients were classified into the mild (n = 28), common (n = 92), severe (n = 36), and critical (n = 5) type, and their clinical findings and CT findings were analyzed. CT features included lesions' distribution, density, extension, shape, interior/ periphery features, vascular changes. Then the prediction performance of image features were analyzed. Results The main clinical manifestations were fever (60/143, 41.9%) and cough (57/143, 39.9%). High fever was more common seen in severe patients. Severe and critical types were more common in elderly patients. And the total number of lymphocytes reduced (0.6±0.2x10^9/L) in critical patients. Except for mild patients, there were 6 cases without the obvious abnormality in the first CT diagnosis. In the remaining 109 cases, the number of pulmonary segments involved in the first CT examination of severe patients was significantly higher than that of common patients (5.88 ± 6)(P < 0.001). Severe and critical COVID-19 showed wedge-shape (59/109, 54.1%) or Ficus crown sign (35/109, 32.1%) lesions more frequently than in common COVID-19 and the thickening of blood vessels (87/109, 79.8%) and vascular clustering signs (65/109, 59.6%) in / around the lesions were more likely to occur in severe and critical types (P < 0.05). There was no significant difference in the number of lesions, lesion density, lesion morphology (round, irregular) and internal/peripheral features of the lesion (crazy-paving sign, halo sign, bronchiectasis)(P > 0.05). Area under the curve (AUC) of the number of involved lung segments, wedge-shape and Ficus crown sign (AUC: 0.769, 0.759, 0.697, respectively) were higher compared with that of thickening of blood vessels and vascular clustering signs (AUC: 0.626, 0.667, respectively). Combined model resulted in a further increased diagnostic performance (AUC: 0.854). Conclusion Chest CT findings not only play an important role in the early diagnosis of COVID-19, but also can evaluate the severity and prognosis of patients.
The Association of Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase Gene Polymorphism with Coronary Heart Disease
2021, 42(5): 138-142.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210525
Abstract:
Objective To analyze the relationship between methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) gene polymorphism and severity of coronary heart disease. Methods A total of 400 patients who were to undergo coronary angiography and stent implantation when necessary were tested with folate metabolism 677 gene. And according to MTHFR C677T polymorphism, these patients were divided into three groups: C / C, C / T, T / T and Gensini score of coronary artery was used to evaluate the mace events (including cardiac death, myocardial infarction, heart failure, readmission for cardiac reasons and target vessel revascularization) within 180 days after PCI. Results (1) Patients with MTHFR C677T T/T genotype had significantly higher Gensini scores than those with C/T and C/C genotypes (P < 0.05). (2) Patients with MTHFR C677T T/T genotype had significantly higher mace events than those with C/T and C/C genotypes after 180 days of PCI (P < 0.05). Conclusion (1) There is a significant correlation between MTHFR gene polymorphism and severity of coronary heart disease; (2) There is a significant correlation between MTHFR gene polymorphism and the mace events after 180 days of PCI.
2021, 42(5): 143-146.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210526
Abstract:
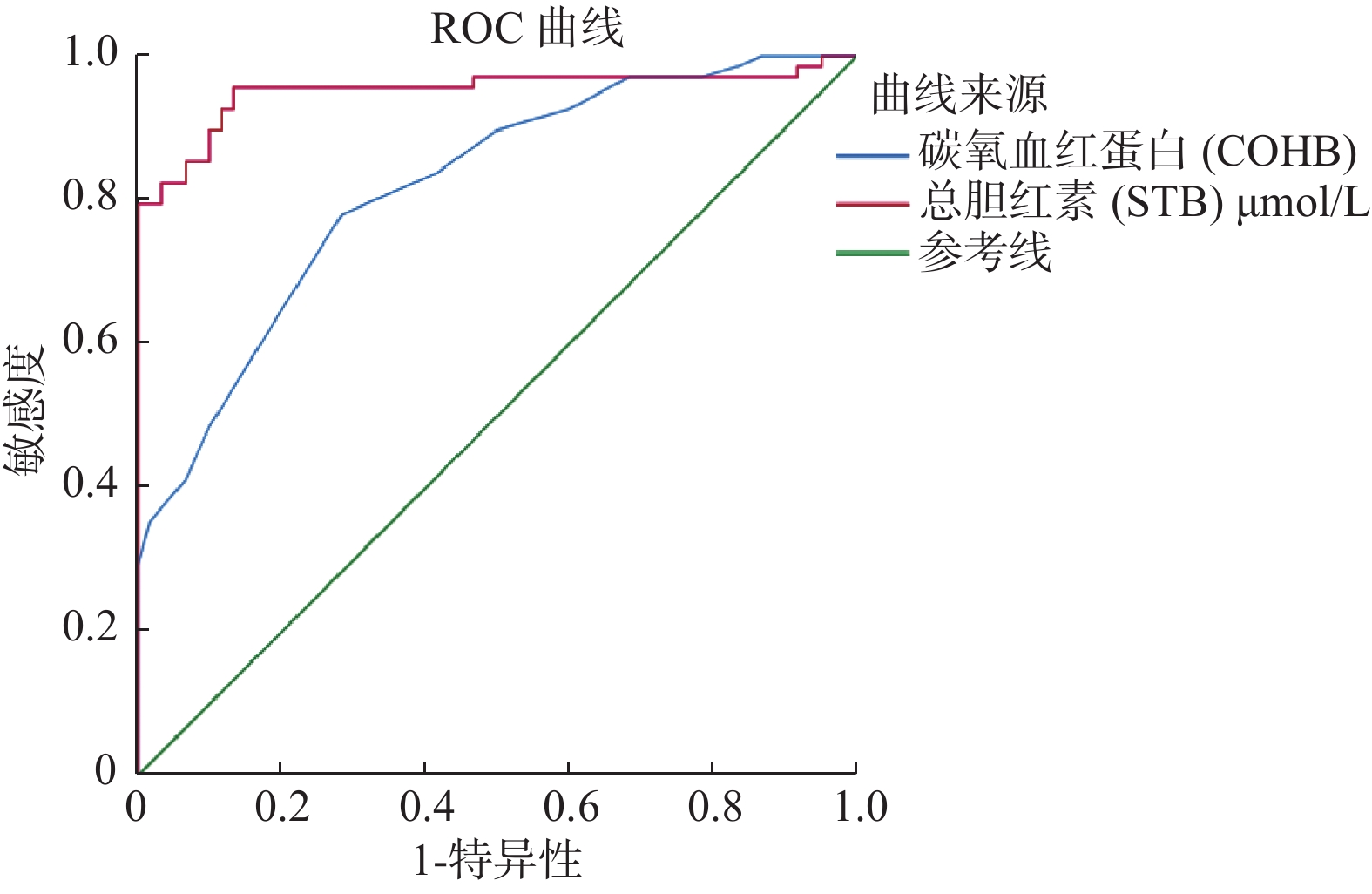
Objective To investigate the clinical significance of carboxyhemoglobin (COHb) in neonatal ABO hemolytic jaundice. Methods Retrospective analysis was conducted and from January 2019 to December 2019, 68 cases of ABO hemolysis were selected as the observation group and at the same time, 60 cases of non-hemolytic pathological jaundice were selected as the control group. The peak levels of c0hb and total bilirubin (STB) of the two groups were compared and analyzed. Results The observation group’ s COHb (1.39±0.36) and STB (270.10±63.73) were higher than the control group’ s COHb (0.93±0.34), STB (158.62±26.77), difference was statistically significant (P < 0.01); The area under the curve(AUC) of COHb diagnosis ABO hemolysis was 0.814, 78% sensitivity and the specificity was 72%. Conclusion COHb increases significantly in the early stage ABO neonatal hemolysis and it can be used as ABO early diagnosis reference index of hemolytic jaundice in newborns.
2021, 42(5): 170-175.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210531
Abstract:
Objective To explore the effect of clustered nursing program on oral mucositis and restricted mouth opening in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma undergoing radiotherapy. Methods In this study, 119 patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma admitted to the radiotherapy department of a tertiary A tumor hospital in Kunming from June 2019 to July 2020 were divided into the intervention group of 59 cases and the control group of 60 cases according to the length of stay. The control group adopted conventional nursing intervention, and the intervention group adopted a clustered nursing plan. The degree and incidence of oral mucositis and mouth opening restriction were compared between the two groups. Results The incidence of oral mucositis in the intervention group was lower than that in the control group at 16, 24, and 32 times of radiotherapy and 1 month after the radiotherapy. The difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). The incidence of the limited mouth opening was lower than that of the control group at 24, 32 times and 1 month after the radiotherapy and the difference was statistically significant ( P < 0.05). Conclusion The clustered nursing measures can effectively reduce the occurrence of oral mucositis and restricted mouth opening in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma radiotherapy, promote the recovery of patients, and improve the effect of nursing intervention.
2021, 42(5): 176-180.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210532
Abstract:
Objective To explore the application effect of narrative nursing in maintaining normal lactation state of parturients with mother infant separation during the hospitalization. Methods Parturients delivered in the Tenth People’ s Hospital Affiliated to Tongji University from January to December 2020 and transferred immediately after the delivery were randomly divided into the experimental group and the control group. The experimental group added narrative nursing mode under the routine nursing mode. The nursing related outcome indexes of the two groups were analyzed. Results The first time of milking, average times of milking during the hospitalization, start time of lactation phase II and postpartum depression score of the narrative nursing group were better than those of the control group (P < 0.01); Multiple linear regression analysis showed that the start time of lactation phase II was positively correlated with the postpartum depression, and the total variance explained was 67.00%. Conclusion Narrative nursing is beneficial to keep the normal lactation of parturients with mother infant separation during the hospitalization, and can improve the level of pure breast feeding.
2021, 42(5): 147-153.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210527
Abstract:
Cell therapy based on mesenchymal stem cells is one of the important strategies for the tissue regeneration and repair. Recent studies have shown that exosomes, as an important product secreted by mesenchymal stem cells, can play a role similar to parental mesenchymal stem cells. As an important way to transmit information between cells, exosomes participate in various physiological and pathological processes and play an important role in promoting tissue repair and regeneration, which provides a new idea for the tissue engineering.
Cell therapy based on mesenchymal stem cells is one of the important strategies for the tissue regeneration and repair. Recent studies have shown that exosomes, as an important product secreted by mesenchymal stem cells, can play a role similar to parental mesenchymal stem cells. As an important way to transmit information between cells, exosomes participate in various physiological and pathological processes and play an important role in promoting tissue repair and regeneration, which provides a new idea for the tissue engineering.
2021, 42(5): 154-158.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210528
Abstract:
Published reports have suggested that patients previously shunted for hydrocephalus or arachnoid cyst may appear slit ventricle syndrome presenting with intermittent headache and narrow ventricles. At present, the pathogenesis and treatment of slit ventricle syndrome have not been thoroughly studied, which is still a challenge for neurosurgeons. This paper aims to review its etiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis and treatment.
Published reports have suggested that patients previously shunted for hydrocephalus or arachnoid cyst may appear slit ventricle syndrome presenting with intermittent headache and narrow ventricles. At present, the pathogenesis and treatment of slit ventricle syndrome have not been thoroughly studied, which is still a challenge for neurosurgeons. This paper aims to review its etiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis and treatment.
2021, 42(5): 159-164.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210529
Abstract:
Hypersecretion of GH in acromegaly produces the insulin resistance and is prone to diabetes mellitus.The main mechanism is that the insulin receptor and its substrate phosphorylation level, phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase regulatory subunit P85 level, glucose transport level and 11β-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenaseactivity play a series of roles through the growth hormone receptor, resulting in glucose metabolism disorder.
Hypersecretion of GH in acromegaly produces the insulin resistance and is prone to diabetes mellitus.The main mechanism is that the insulin receptor and its substrate phosphorylation level, phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase regulatory subunit P85 level, glucose transport level and 11β-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenaseactivity play a series of roles through the growth hormone receptor, resulting in glucose metabolism disorder.
2021, 42(5): 165-169.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210530
Abstract:
In recent years, due to the increase of high-risk pregnancies in obstetrics and the improvement of diagnostic techniques, clinical attention to pregnancy complicated with venous thrombotic diseases is increasing from year to year. Although various risk factors that induce deep vein thrombosis have been identified, the mechanism of thrombosis is not yet completely clear. Studies have demonstrated that histones play a key role in venous thrombotic diseases, mediating the production of thrombus through inflammatory pathways or TLRs that activate inflammation.This article aims to provide an overview of histone-induced venous thrombotic diseases through TLRs to stimulate inflammation, and provide a new breakthrough point for the prevention and treatment of obstetric venous thrombotic diseases in the future.
In recent years, due to the increase of high-risk pregnancies in obstetrics and the improvement of diagnostic techniques, clinical attention to pregnancy complicated with venous thrombotic diseases is increasing from year to year. Although various risk factors that induce deep vein thrombosis have been identified, the mechanism of thrombosis is not yet completely clear. Studies have demonstrated that histones play a key role in venous thrombotic diseases, mediating the production of thrombus through inflammatory pathways or TLRs that activate inflammation.This article aims to provide an overview of histone-induced venous thrombotic diseases through TLRs to stimulate inflammation, and provide a new breakthrough point for the prevention and treatment of obstetric venous thrombotic diseases in the future.


 Email
Email RSS
RSS