2021 Vol. 42, No. 6
2021, 42(6): 29-37.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210632
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the protective effect of metformin on the kidney in type II diabetes mellitus (T2DM) by regulating the activity of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP-1) and investigate the mechanism of this effect. Methods Wistar rats were divided into normal group (n = 12), DN group (n = 12), DN + DPQ group (n = 12), DN + metformin group (n = 12) and DN + metformin + DPQ group (n = 12). After model establishment, biochemical parameters such as fasting glucose content, urea nitrogen content, creatinine content, and urine protein concentration were measured in each group of rats.HE staining and TUNEL staining were used to observe the renal pathology, Western blot was applied to detect the protein expression of PARP-1, iNOS, NF-κB and caspase-3.The expression of inflammatory factors TNF-α and IL-1β was detected by ELISA, and the expression of 3-nitrotyrosine (3-NT)was determined by immunohistochemistry. Results (1)The biochemical indexes of rats in the three treatment groups decreased compared with those in the DN group, with the most obvious changes in the DN + metformin + DPQ group (P < 0.01) ; (2) The expression of PARP-1 in rats in the three treatment groups decreased compared to the DN group, with the most significant decrease in the DN + metformin + DPQ group ( P < 0.05); (3) The pathological changes of kidney tissue and apoptosis of kidney cells in the three treatment groups were alleviatedcompared with the DN group, with the most significant decrease in the expression of DN + metformin + DPQ group; (4) The expression of inflammatory factors as well as the expression of NF-kB, iNOS and 3-NT decreased in the three treatment groups compared with the DN group, with the most significant decrease in the DN + metformin + DPQ group ( P < 0.05). Conclusion Metformin plays a role in protecting the kidney under the high glucose environment caused by diabetes through regulating the expression of PARP-1, down-regulating the expression of NF-kB in the DN model, inhibiting NF-kB/iNOS/NO pathway, inhibiting oxidative damage, and reducing inflammation.
2021, 42(6): 50-55.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210625
Abstract:
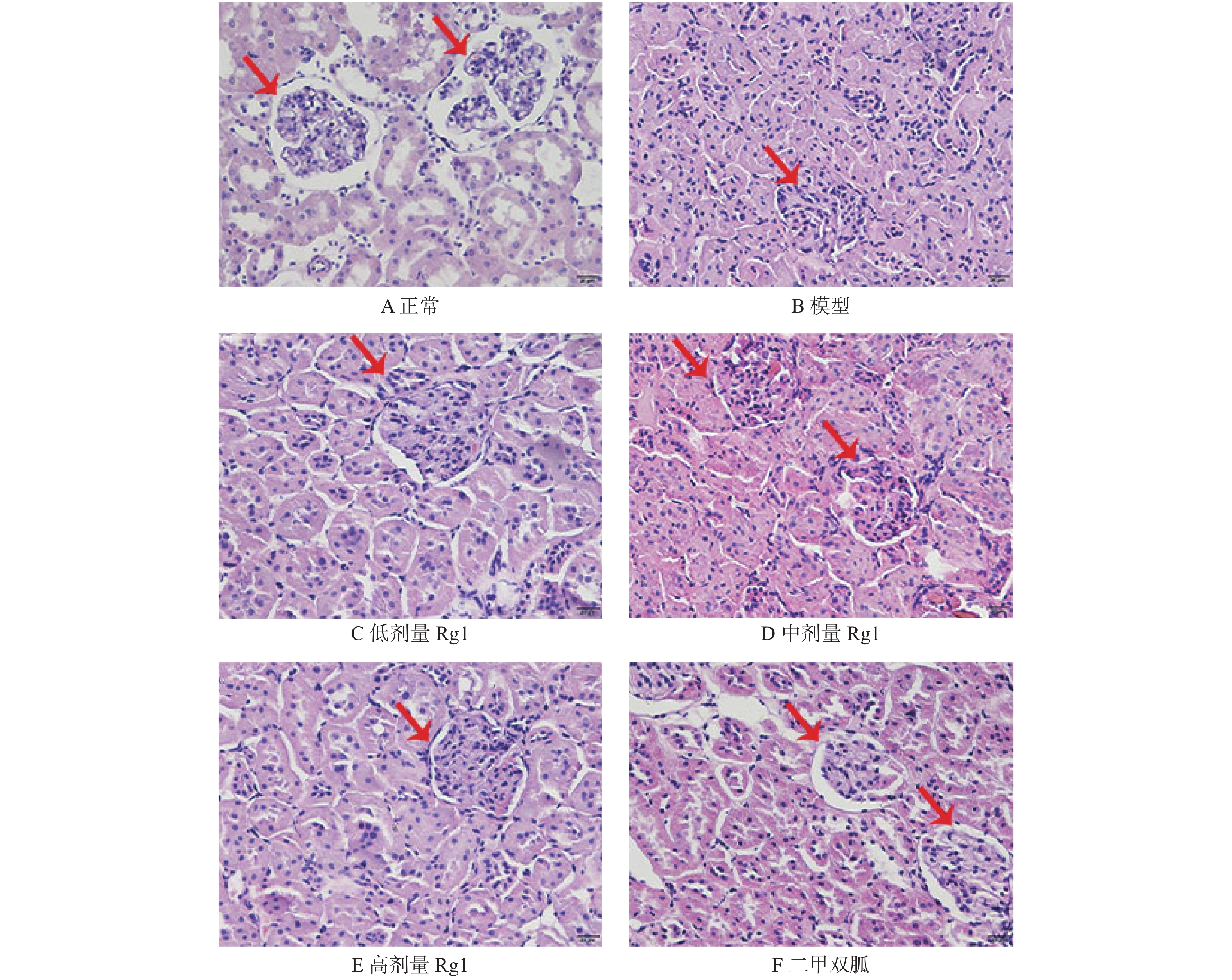
Objective To investigate the protective effect and mechanism of ginsenoside Rg1 on the kidneys of type 2 diabetic rats. Methods A high-sugar and high-fat diet + low-dose streptozotocin (STZ) was used to establish a type 2 diabetic rat model. Ginsenoside Rg1 was administered to the stomach for 4 weeks, and blood creatinine (Scr)、uric acid (UA) and urea nitrogen (BUN) were measured. Take kidney tissue sections for HE staining to observe the pathological changes of kidney tissue; Western blot was used to detect angiotensin Ⅱ type 1 receptor (AT1), transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) and metalloproteinase-9 in rat kidney tissue expression level. Results BUN of type 2 diabetic rats was significantly higher than that of the normal group, but Scr and UA were not statistically significant compared with the normal group. After different doses of ginsenoside Rg1, the BUN value decreased, and the BUN of the metformin group also decreased, but there was no statistical difference in the changes of Scr and UA (P > 0.05). The renal coefficient of diabetic rats was higher than that of the normal group, and the renal body ratio decreased after treatment with ginsenoside Rg1 and metformin ( P < 0.05). The expressions of AT1 and TGF-β1 in the kidneys of diabetic rats were higher than those in the normal group, and the expressions decreased after being given different doses of ginsenoside Rg1 and metformin treatment ( P < 0.05). The expression of MMP9 decreased in the kidneys of diabetic rats, but increased after treatment with ginsenoside Rg1 and metformin ( P < 0.05). Conclusions Ginsenoside Rg1 can protect the kidney from damage in rats. Its molecular mechanism may be through inhibiting the activation of the RAS system, inhibiting the expression of TGF-β1, promoting the hydrolysis of extracellular matrix, and reducing the degree of kidney damage.
2021, 42(6): 56-61.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210608
Abstract:
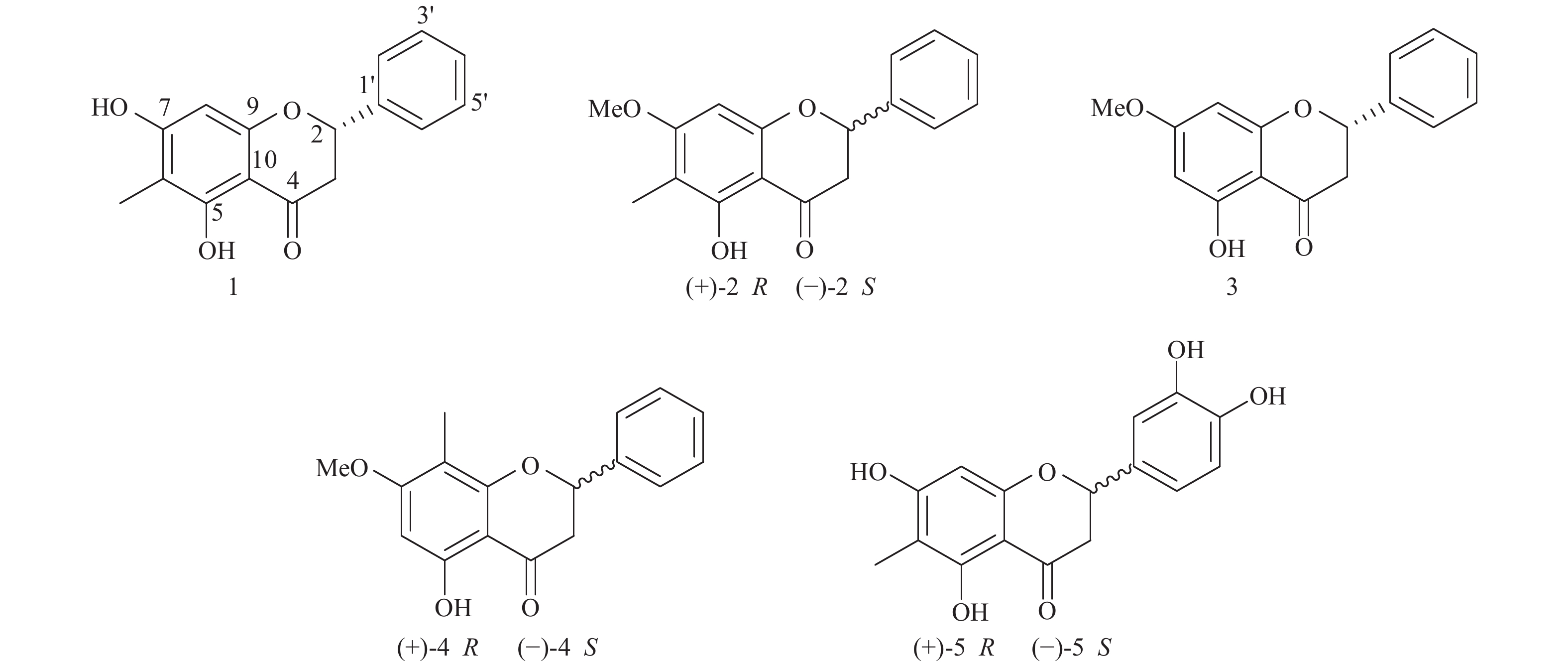
Objective To investigate the flavone constituents from Baeckeafrutescens and evaluate the cytotoxic effects of these isolates. Methods The chemical compositions were isolated by normal- and reverse-phase silica gel column chromatography, MCI gel column chromatography, Sephadex LH-20, and semi-preparative HPLC. Their structures and absolute configurations were established by comparison of their NMR and MS spectra with reported data in the literature, as well as optical rotatory dispersion (ORD) and electronic circular dichroism (ECD) calculations. Their cytotoxicity of flavones was evaluated against four human tumor cell lines by MTT method. Results Five dihydroflavone were obtained and identified as(2S)-5, 7-dihydroxy-6-methylflavanone ( 1 ), (±)-5-hydroxy-7-methoxy-6-methylflavanone ( 2 ), (2S)-pinostrobin ( 3 ), (±)-5-hydroxy-7-methoxy-8-methylflavanone ( 4 ), and (±)-6-methyl-eriodictyol ( 5 ). Conclusions Compound 1 , 3 , and 5 were isolated from this plant for the first time; The five dihydroflavones were determined to beoptical pure ( 1 and 3 ), racemic ( 4 ), and incoordinately enantiomeric ( 2 and 5 ) compounds, respectively. Compound 3 showed significant cytotoxicity against DU145 cells with an IC50 value of 4.56 μM.
2021, 42(6): 1-6.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210647
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the effects of pure and multiple cerebral concussion (MCC) on the changes of anxiety behaviors in rats. Methods There were 50 adult SD rats with single pendulum closed brain injury device to simulate pure concussion (PCC) and multiple concussion (MCC), and a normal control group (N) with 12 rats in each group. Open field test (OFT) and high plus maze (HPM) were performed on the 14th day after injury to assess changes in anxious behaviours. Results (1) In the OFT experiment: ① In the PCC group and the 3 MCC group, the walking number in the CA was (9.500 (6.50, 16.75), (5.00 (3.50, 9.00), and the N group was (10.00 (7.00, 17.88). The number of lattice walking and residence time in the central area in the injury group were both less than those in the control group, and the difference between the 3 MCC group and the N group and the PCC group was statistically significant (P < 0.05) (P = 0.024, P = 0.033). ② In the PCC group and the 3 MCC group, the walking number in the SA was (54.50 (26.88, 62.25)), (65.00 (28.50, 81.00)), and the N group was (33.00 (1.13, 51.50)). The number of surround areas (SA) and walking time in the injury group were all higher than those in the control group, and the difference between the 3 MCC group and the N group was statistically significant (P < 0.05, P = 0.015). ③ The frequency of combing hair in PCC group and 3 MCC group was (4.20±1.03) times, (2.44±0.73) times, and N group was (5.20±1.62) times.The number of grooming times in the injury group was less than that in the N group, and the difference between the 3 MCC group and the N group and the PCC group was statistically significant (P < 0.05, P = 0.013, P = 0.019). ④ in the open field experiment, the number of walking lattice, walking time and the number of grooming in the CA area of rats in each injury group showed a decreasing trend with the increase of the number of blows.In addition, with the increase of the number of strikes, the number of walking lattice and walking time in SA area of injured rats presented an increasing trend.(2) In the HMP experiment: ① The number of OA in the PCC group and the 3 MCC group was (1.00 (0.00, 1.00)) times, (0.50 (0.00, 1.00)) times, and the N group was (1.00 (0.00, 2.00)) times. The Times and time of entering open arms (OA) in each injury group were less than those in the normal group, but the differences between groups were not statistically significant, P > 0.05. ② the number of times of exploration in OA in the injury group was less than that in the N group, and the difference of 3 MCC group was statistically significant (P < 0.05, P = 0.032). ③ The number of EA in the PCC group and the 3 MCC group was (1.00 (1.00, 1.00))times, (0.00 (0.00, 1.00)) times, and the N group was (0.00 (0.00, 1.00)) times. The times and time of the lesion group entering the closed arm (EA) was higher than that of the N group, The number of EA entry was statistically significant between the 3 MCC group and the PCC group (P < 0.05, P = 0.015). At the time of EA, there was a statistically significant difference between the 3 MCC group, N group and PCC group (P < 0.05, P = 0.042, P = 0.027). ④ In the overhead cross maze experiment, the number of rats entering the OA arm, the time and the number of visits to the floor all decreased with the increase of the number of blows. In addition, with the increase of batting times, the residence time of injured rats in the EA arm increased. Conclusion The anxious behaviors of rats with PCC and MCC increased significantly on the 14th day after injury, and the anxious behaviors of rats with MCC are more serious than that with PCC.
2021, 42(6): 7-15.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210639
Abstract:
Objective To observe the therapeutic of PNS on wound healing and the expression of PDGF-BB, PDGFR-β in rats superficial second-degree burn model, and to explore the underlying mechanism of PNS on second-degree burn wound healing. Methods Rats with superficial second-degree burn were treated with PNS, applying HE staining to detect burn severity, and then biopsied biological tissue on days 0, 7, 14, 21 after administration, respectively. Moreover, Immunohistochemistry (IHC), Western blot and RT-PCR methods were used to detect protein and mRNA expression levels of PDGF-BB/PDGFR-β in skin tissues after treatment with PNS, respectively. Furthermore, the skin wound healing at different time points was monitored by macroscopic observation. Results HE staining suggested that the replication of rats second-degree burn model was successful. Macro monitoring data demonstrates that compared with model group, the removal time of scab and fur-growthing were shortened, and the wound healing rate was increased in the PNS high-dose group (P < 0.05). Combination of IHC, WB and RT-PCR showed that the expression levels of PDGF-BB/PDGFR-β increased sharply on day 7, maintaining a high level until day 14, approaching normal levels on day 21 after PNS treatment. However, the protein and mRNA expressions of PDGF-BB/PDGFR-β showed high values on day 21 in the model group, which was a slow process. Our results suggest that compared with model group, the peak expression of PDGF-BB/PDGFR-β are earlier, shortening of fur-growthing and decrustation time, and improvement of wound healing rate in rats superficial second-degree burn model. Conclusion PNS can significantly promote skin wound healing in rats superficial second-degree burn model, and its mechanism is closely related to the up-regulation of the expression levels of PDGF-BB/PDGFR-β in skin tissue.
2021, 42(6): 16-21.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210633
Abstract:
Objective To study the effect of norathyriol on uric acid excretion indicators in hyperuricemic nephropathy (HN) rats induced by adenine and potassium oxazinate. Method Sixty male SD rats were randomly divided into normal group, model group, norathyriol 1.0, 2.0, 4.0 mg/kg group, positive control benzbromarone 12.5 mg/kg group, each group of 10, according to 20 mL/kg volume were given respectively adenine (0.1 g/kg) and potassium oxonate (1.5 g/kg) suspension after 1 hour, and according to 10 ml/kg volume were given the test drug was administered once a day for 28 days. The gain weight of the rats was monitored weekly, and the urine was collected for 24 hours in themetabolic cage at 7, 14, 21 and 28 days after the administration. The urine volume, urine uric acid and urine creatinine were measured. At the end of the experiment, blood uric acid, serum creatinine and organ weight were measured. Uric acid excretion indicators were calculated: The fractional excretion of uric acid (FEUA), the amount of 24 h uric acid excretion (24 h UUA), creatinine clearance (CCr), uric acid clearance (Cur), glomerular load of uric acid (FLur), excretion of uric acid per volume of glomerular filtration (EurGF) and ratio of urinary uric acid to creatinine. Results Norathyriol groups significantly reduced the level of serum uric acid in rats with hyperuricemic nephropathy. After 7 days of administration of 2.0 mg/kg norathyriol, 24 h UUA significantly increased (P < 0.05). After 14 days and 28 days of administration of 2.0 mg/kg norathyriol, FEUA and Cur significantly increased (P < 0.05, P < 0.01). Conclusion Norathyriol could affect FEUA and Cur, the sensitive indicators of uric acid excretion of rats with hyperuricemic nephropathy.
2021, 42(6): 22-28.
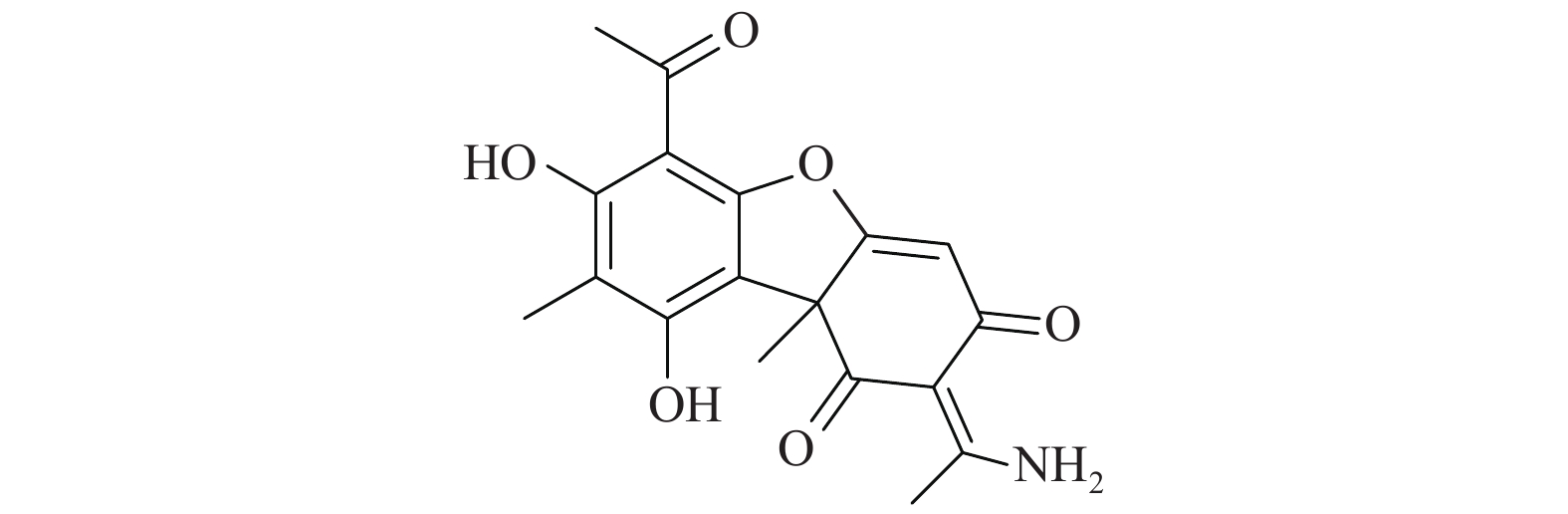
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210642
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the natural active compound Usenamine [C18H17NO6, 6-acetyl-2-(1-amino-ethylene)-7, 9-dihydroxy-8, 9b-dimethyl-9bH- diphenylfuran -1, 3-dione] is safe to use. Methods SPF mice were selected for oral toxicity test, in vivo and in vitro chromosomal aberration test, bone marrow micronucleus test, sperm abnormality test and 30-day feeding test. Results Under the research conditions, the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) of the test substance for acute oral toxicity was more than 15000 mg/kg; both in vivo and in vitro chromosomal aberration tests were negative (P > 0.05); bone marrow micronucleus test results were negative (P > 0.05) The result of sperm deformity test was negative (P > 0.05); no obvious signs of poisoning were found in the 30-day feeding test, and all the indicators were normal. Conclusion Usenamine is safe and has no acute or subacute toxic effects, and genetic toxicity.
2021, 42(6): 38-44.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210606
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the interaction among RANTES gene promoter region rs2280788 C/G polymorphism, CCR5 gene promoter region rs1799987 G/A polymorphism and environmental factors in the development of Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in the Han ethnic group in Kunming. Methods The general data and peripheral venous blood of 92 Han people with normal blood glucose and 97 Han T2DM patients in Kunming area were collected. Polymorphisms of RANTES gene rs2280788 and CCR5 gene rs1799987 were detected by TaqMan real-time quantitative PCR. Multifactor dimensionality reduction (MDR) was used to analyze the interaction among the gene polymorphisms of RANTES and its receptor and environmental factors in the occurrence of T2DM in Han nationality in Kunming. Results There was an interaction between CCR5 rs1799987 and RANTES rs2280788 (the testing balance accuracy was 0.5314, the training balance accuracy was 0.5820, and the cross validation consistency was 10/10, P < 0.05, OR: 2.0465, 95%CI: 1.1118-3.7672); There was an interaction between hypertension and central obesity (the testing balance accuracy was 0.7031, the training balance accuracy was 0.7031, the cross validation consistency was 10/10, P < 0.001, OR: 8.1640, 95%CI: 3.8745-17.2026); No interaction between CCR5 rs1799987 and environmental factors, as well as RANTES rs2280788 and environmental factors was found (P > 0.05). Conclusions There are interactions between the RANTES gene promoter region -28 (rs2280788) and the CCR5 gene promoter region 59029 (rs1799987) SNP, as well as between hypertension and central obesity, the co-existence of interacting factors will increase the risk of T2DM in Han nationality in Kunming.
2021, 42(6): 45-49.
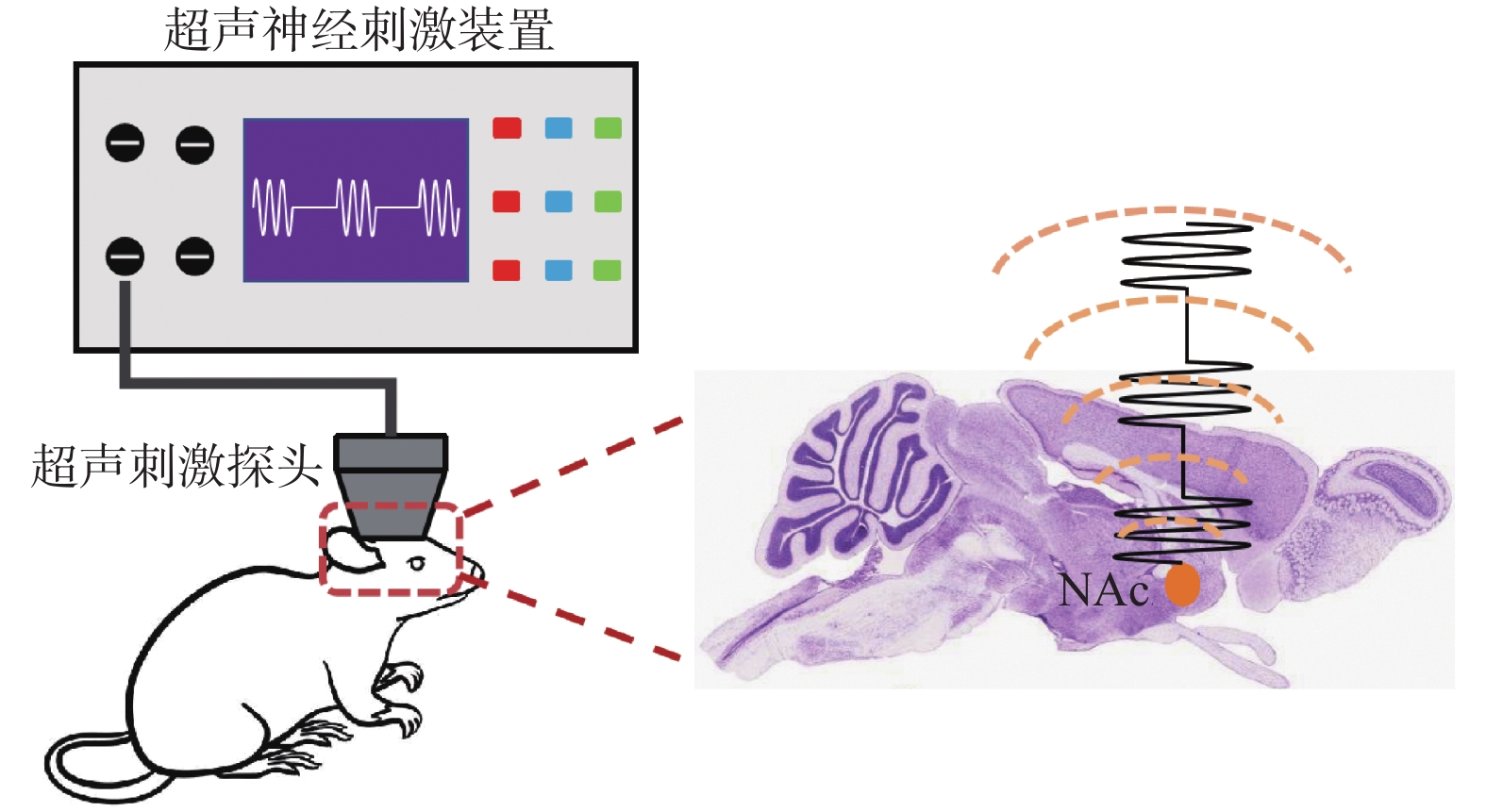
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210645
Abstract:
Objective To observe the neuronal activation and structural changes after the stimulation of the nucleus accumbens (NAc) in mice by detecting c-Fos protein and structural plasticity, and to preliminally explore the mechanism of neural regulation by ultrasound. Methods C57 BL/6 mice were randomly divided into ultrasonic stimulation group (n = 12) and sham stimulation group (n = 6). In the ultrasound stimulation group, low intensity focused ultrasound was used to stimulate the NAc region of mice with fixed parameters. After 7 days of continuous stimulation, the expression of c-Fos protein in the NAC region was determined by immunohistochemistry, and the changes of neuronal plasticity were observed by electron microscopy. The sham stimulation group was also irradiated with ultrasonic stimulation probe, and no output power was obtained without turning on the machine. Results All mice successfully completed the whole process of ultrasonic stimulation. The expression ratio of c-fos in NAC neurons was significantly increased after ultrasound stimulation (P < 0.001). Under electron microscope, it was found that the distribution of dendritic spines in the ultrasonic stimulation group was sparse, the number of dendritic spines was significantly reduced, and the morphology was mushroom-like or dwarf stump-like. Compared with the sham stimulation group, the density of dendritic spines was significantly reduced (P < 0.0001), and the length of dendrites was significantly shortened (P < 0.0001). Conclusion Low intensity focused ultrasound can significantly activate neurons in NAc brain region, and inhibit and regulate the structural plasticity of neurons, which proves that ultrasound stimulation has the potential to intervene and treat brain diseases.
2021, 42(6): 62-66.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210624
Abstract:
Objective To study the dental caries and periodontal status, and to investigate the factors that affect the dental caries of the undergraduate students. Methods A sample of undergraduate students was selected using a multi-stage sampling method. Four calibrated dental students examined the participants. Dental caries and periodontal status were accessed according to the DMFT, gingival bleeding scores and pocket scores, respectively. A self-completed questionnaire was used to study the student’ s oral health-related behaviors and knowledge. A logistic regression analysis was used to explore the risk factors for the dental caries. Results A total of 616 undergraduate students joined the study. 52% of them had caries experience (DMFT > 0), and their mean DMFT score was 1.5±2.0. 66% students had gingival bleeding. Periodontal pockets were found among 14% students. Ethnic minority students with higher oral health-related knowledge and visiting a dentist within the last year had higher caries risk (P < 0.05). Conclusions Dental caries status is moderate among the undergraduate students in Kunming but their periodontal status is unsatisfactory. Their caries prevalence is related to ethnicity, dental knowledge and dental visit habits.
2021, 42(6): 76-81.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210603
Abstract:
Objective To analyze the effects of homocysteine (Hcy) on blood pressure, blood glucose and blood lipid in a longitudinal cohort study, so as to provide basis knowledge for the prevention and treatment of related chronic diseases. Methods 987 physical examination personnel with complete data in the annual physical examination survey during the two-year period after the 2017 baseline survey were selected as study subjects to construct a longitudinal study cohort. We collected demographic characteristics, homocysteine, blood pressure, blood glucose and blood lipid, and based on the homocysteine change, divided them into three groups: the non-change group (normal-normal; abnormal-abnormal), normal-abnormal group, abnormal-normal group. Generalized linear regression model was used to analyze the relationship between homocysteine change and the changes in blood pressure, blood glucose and blood lipid. Results The average age of participants in baseline survey was (43.63±11.4) years with a range of 23 to 85 years. During the three-year period, there were 50.25%(496), 14.39%(142), 35.36%(349) people with non-change group (normal-normal;Abnormal-abnormal), normal-abnormal group, abnormal-normal group, The Hcy change was taken as the dependent variable for analysis. Univariate analysis showed that, compared with the non-changed group, systolic blood pressure in the abnormally normal group was significantly reduced (P < 0.05), and there were no statistical differences in other indicators. Based on generalized linear model, after adjustment for age, gender, baseline BMI, drinking, smoking, results show that when compared with the non-change group, the systolic blood pressure, total cholesterol, blood sugar of anomaly-normal group were significantly decrease ( P < 0.05), and the drop-out value were 2.132, 0.203, 0.182 respectively. There was no significant difference in the change of diastolic blood pressure, triglyceride, High-density lipoprotein and low-density lipoprotein. Conclusion The change of Hcy is related to the change of systolic blood pressure, total cholesterol and blood glucose, and the decrease of Hcy is conductive to the improvement of blood glucose, blood pressure and lipid levels.
2021, 42(6): 82-87.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210607
Abstract:
Objective To determine the effect of the Neuregulin-1 and its receptor ErbB4(NRG1-ErbB4) polymorphisms on focal epilepsy. Methods Three single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of NRG1 gene and three single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of ErbB4 gene in 70 patients with focal epilepsy and 64 healthy persons were analyzed by the PCR-SnapShot genotyping methods.The samples were all from the First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University from March to July, 2020. Results It was found that focal epilepsy was correlated with polymorphism of NRG1 (SNP rs35753505, T > C), the distribution of genotype ( P = 0.007) and allele (P = 0.005) of NRG1 (SNP rs35753505, T > C) was statistically significant ( P < 0.005). Meanwhile, ErbB4 gene polymorphisms of NRG1 downstream receptors was analyzed firstly, and two SNPs was found to be associated with focal epilepsy, ErbB4 SNP(rs839523, P = 0.026) and its allele (P = 0.013), ErbB4 SNP(rs707284, P = 0.038) and its allele (P = 0.018). However, no statistically significant association was found between NRG1(rs6994992, rs62510682), ErbB4(rs7598440) polymorphisms and focal epilepsy. Conlusions The susceptibility of focal epilepsy carrying NRG1(SNP, rs35753505) and ErbB4(rs839523, rs707284) mutation homozygous has increased. NRG1-ErbB4 polymorphisms might play an important role together in the susceptibility to partial epilepsy.
2021, 42(6): 88-93.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210644
Abstract:
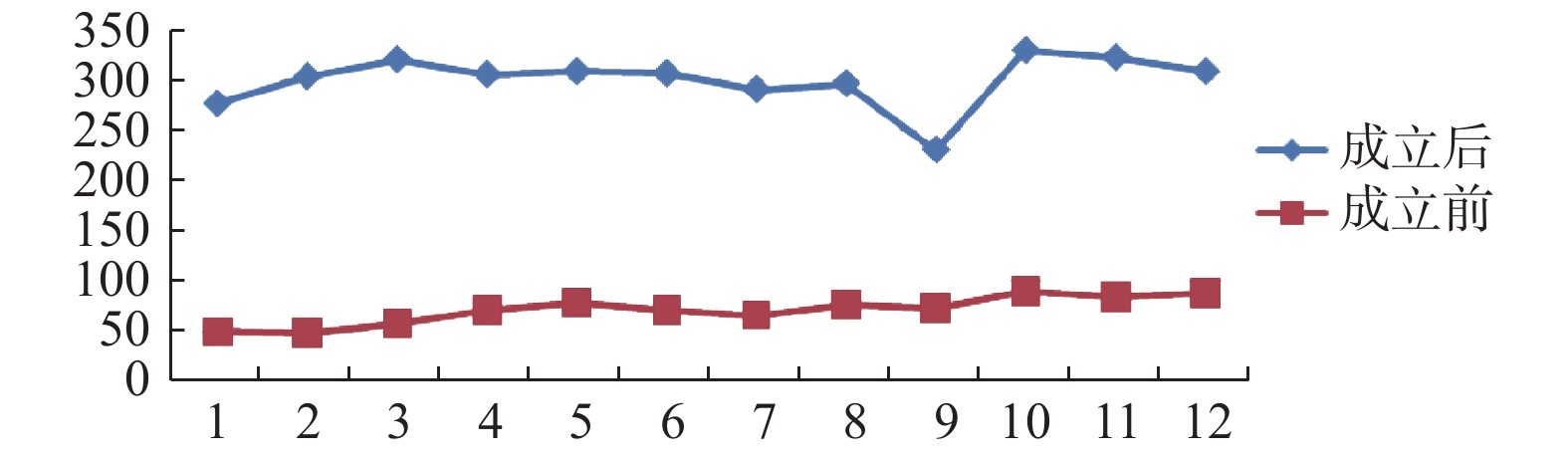
Objective To provide scientific basis for improving the treatment efficiency of chest pain center for patients with acute myocardial infarction, comparing and analyzing the epidemiological characteristics of hospitalized patients with acute myocardial infarction before and after the establishment of chest pain center in a Grade III Level A hospital. Methods A retrospective investigation was conducted on 4445 cases of acute myocardial infarction admitted to the chest pain center of the hospital before and after the establishment of the center in 10 years. Study subjects were divided into the pre-establishment group (852 cases) and the post-establishment group (3593 cases), and the relevant data on the first page of the medical records were statistically analyzed. Results After the establishment of chest pain center, the number of AMI patients admitted to the hospital increased by more than 3 times. There were significant increases in three important variables: the number of patients admitted through emergency care got significantly larger (P < 0.001); the proportion of surgical cases, especially PCI cases, significantly increased ( P < 0.001), and 66.5% of patients were implanted with one or more stents ( P < 0.001); the proportion of patients who used national medical insurance increased significantly ( P < 0.001). There were significant increases in three important variables: the mortality rate among admitted patients decreased significantly ( P < 0.001); the length of hospital stay before operation reduced significantly ( P < 0.05); the cost of hospitalization has dropped significantly ( P < 0.05). Conclusions The construction of Chest Pain Center has greatly improved the efficiency and quality for AMI patients. In the treatment of AMI patients, preventive and control measures should be taken according to its epidemiological characteristics.
2021, 42(6): 103-109.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210618
Abstract:
Objective To evaluate the causes and influencing factors of re-hospitalization of patients with coronary heart disease by coronary angiography, so as to guide clinical diagnosis and treatment decisions and reduce re-hospitalization. Methods From January 2013 to December 2019, a total of 316 patients who were hospitalized twice with coronary angiography and/or percutaneous coronary intervention were analyzed retrospectively, including 235 males and 81 females, with a male to female ratio of 2.9∶1. According to the times of hospitalization, they were divided into the first hospitalization group and the second hospitalization group, with an average age of 59.45 ±10.09 years and 60.47±10.16 years. The average time interval between the two hospitalizations was 14.30±11.67 months. Among them, 265 patients were diagnosed with coronary heart disease for the first time and percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), accounting for 83%. Results After two hospitalizations, there were significant differences in LDL-C, TG, diabetes history smoking history, drinking history, first-time clinical diagnosis, severity of lesion (Gensini score) of each blood vessel (LAD, RCA, LCX), and stent placement of each blood vessel between the two groups (P < 0.05). The number of diabetic patients increased during the second hospitalization, with significant difference ( P < 0.05) Multivariate Logistic regression analysis showed that LDL-C control was not up to standard, and the low rate of reaching the standard (13.3%, 31.0%) was an independent risk factor affecting the second hospitalization of patients with coronary heart disease (OR = 1.985, 95%CI 1.506~2.617). RCA, LAD and LCX were the protective factors for the second hospitalization of patients with coronary heart disease [(OR = 0.304, 95%CI 0.144~0.642), (OR = 0.184, 95%CI 0.099~0.343), (OR = 0.228, 95%CI 0.123~0.424)] Compared with those who were diagnosed as ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) for the first time, active revascularization treatment was a protective factor for re-hospitalization of patients who were diagnosed as stable angina pectoris (SAP), unstable angina pectoris (UAP) and non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) again [(OR = 0.071, 95%CI 0.031~0.163), OR = 0.323, 95%CI 0.117~0.743, P < 0.05]. However, there was no significant difference in age, TC, HDL-C, Cre, BUN, UA, FPG, hypertension and vascular diseases of various coronary arteries ( P > 0.05). Conclusion Strict control of LDL-C level in patients with coronary heart disease can effectively prevent and control the progress of diabetes, and actively carry out effective revascularization on seriously diseased coronary vessels during the first hospitalization can reduce the occurrence of second hospitalization.
2021, 42(6): 67-71.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210615
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the efficacy of 0.01% atropine eye drops combined with visual function training in patients with mild myopia and its influence on visual acuity. Methods A total of 86 patients with mild myopia treated in Yuxi People’ s Hospital from October 2019 to October 2020 were selected and randomly divided into two groups.The control group was treated with 0.01% atropine eye drops, and the research group was treated with 0.01% atropine eye drops combined with visual function training.The changes of pupil diameter, naked visual acuity, axial length, diopter, intraocular pressure and ocular adjustment sensitivity were compared between the two groups. Results The pupil diameter and naked eye vision of the study group were higher than those of the control group, and the diopter was lower than that of the control group (P < 0.05). There was no significant difference in IOP between the two groups before treatment, at 1 month, 3 months and 6 months after treatment (P > 0.05). There was no significant difference in the incidence of complications between the two groups at 1 month, 3 months and 6 months after treatment (P > 0.05). The sensitivity of eye regulation in the study group was higher than that in the control group at 3 months and 6 months (P < 0.05). Conclusions mild myopia patients treated with 0.01% atropine eye drops combined visual function training, can obviously regulate eye sensitivity adjustment, control diopter, axial length growth, improve eyesight, compared with 0.01% atropine eye drops alone did not significantly increase the incidence of complications, intraocular pressure does not appear drastically changes obviously, more effective for myopia prevention and control, improve eye adjustment function, treatment effect is more ideal, is worth further clinical application.
2021, 42(6): 72-75.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210617
Abstract:
Objective To evaluate the association between neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and renal damage in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Methods A total of 410 patients with SLE from the Department of Rheumatology and Immunology of the First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University were selected. According to whether accompanied by renal involvement, patients with SLE were divided into non-lupus nephritis group (non-LN group) and lupus nephritis group (LN group). The differences in NLR between the two groups were compared, and the correlation between NLR and renal damage was analyzed. Results The NLR of LN group was significantly higher than that of SLE patients in non-LN group, and the difference wsa statistically significant (P < 0.05). The NLR of SLE patients were positively correlated with leukocyte count, neutrophils count, serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen, ESR, CRP, PCT and 24-hour urine protein, and negatively correlated with lymphocyte count, total protein, albumin and globulin, respectively. Conclusion NLR can be used as an auxiliary index to evaluate renal damage in SLE patients.
2021, 42(6): 94-97.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210637
Abstract:
Objective To study the pharmacokinetics of etomidate in patients with varying degrees of burns. Methods 45 burn patients who underwent escharetomy and skin grafting, and they were divided into A.B.C three groups according to light, mooderate and severe burns. Anesthesia induction: All the 45 patients were given target controlled infusion of sufentanil (target blood concentration 0.4 ng/ml). Intravenous infusion of etomidate began after 15 minutes (Tt15), the dosage of etomidate was 0.4 mg/kg, and the pump infusion was set at the end of 2 minutes, and supplemented by rocuroniumto, dexmedetomidine and sevoflurane maintaining the BIS at 40~60. Before anesthesia (basis), starting TCI sufentanil 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 90 min and stopping TCI sufentanil (Stop) and stopping TCI sufentanil 1, 3, 5, 8, 10, 20, 30 min.arterial blood were collected.Plasma concentration of etomidate was determined. Finally, the pharmacokinetic parameters of each group were calculated. Results Pharmacokinetic parameters of etomidate K31, CL1 and CL3 in group C were smaller than those in group A and group B, (P < 0.05). V3, T1/2r r of group C were greater than those of group A and B (P < 0.05). There was no significant difference between group A and group B in V3, K31. T1/2r, CL1 and CL3. (P > 0.05). Conclusion In patients with severe burns, when etomidate was used intraoperatively, K31 became smaller, V3 increased, CL1 and CL3 decreased, T1/2r was significantly prolonged, and pharmacological effects were enhanced, In clinical work, dosage can be appropriately reduced.
2021, 42(6): 98-102.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210626
Abstract:
Objective To observe the effect of Kan Fu Xin combined with Montmorillonite on the prevention and treatment of radiation-induced oral mucositis in patients with Head and Neck Cancer. Methods In this trial, we included 138 patients with head and neck cancer who underwent radiotherapy from the First People’ s Hospital of Yunnan Province from April 2018 to February 2019, which were randomly divided into the experimental group (69 cases) and the control group (69 cases). The control group received routine care and symptomatic treatment. The experimental group gave Kan Fu Xin combined with Montmorillonite protection on the basis of routine care, and adjusted 1 bag of Montmorillonite and appropriate amount of Kan Fu Xin fluid into a paste. Then contained in the mouth for 5 minutes before each radiotherapy and before going to bed. We observed the degree of radiation-induced oral mucositis damage, the degree of oral radiation pain, the completion time of radiotherapy and recovery, etc. Results We found that the experimental group had a late onset of radiation-induced oral mucositis and a shorter recovery time than the control group (P < 0.05). At the 3rd and 4th week of radiotherapy, the RTOM of the experimental group was mainly mild to moderate, and the control group was mainly moderate and severe. At the 5th and 6th week, the RTOM of the experimental group was mainly moderate, and the control group was mainly severe. At the 3rd to 6th week, there was a statistically significant difference in the incidence of RTOM between the two groups (P < 0.01). The average radiotherapy time of the experimental group was less than that of the control group, and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). Conclusion Kan Fun Xin combined Montmorillonite can significantly reduce the symptoms of patients with radioactive oral mucositis, ensure that radiotherapy is completed on time, and can be widely used in clinical.
2021, 42(6): 110-114.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210614
Abstract:
Objective To provide reference for clinical rational use of vancomycin through analyzing the monitoring results of vancomycin plasma concentration in patients with intracranial infection or/and pulmonary infection after neurosurgery in our hospital. Methods We collected the related information of 119 neurosurgical patients with intracranial infection and/or pulmonary infection, and the monitoring results of vancomycin blood concentration and the influencing factors were analyzed. Results With the dosage of vancomycin 1g, IVGTT, q12h, only 26.1% of the patients were within the reference range (10-20 mg/L)and 68.1% were lower than the reference range. Multiple linear regression analysis showed that only creatinine clearance rate had significant effect on the trough concentration of vancomycin. Conclusion When patients with postoperative infection in neurosurgery are treated with vancomycin, the dosage of 1g, IVGTT, q12h may not reach the effective blood concentration, so the initial dosage should be selected according to the creatinine clearance rate of patients, and the blood concentration of vancomycin should be closely monitored, and the dosage regimen should be adjusted according to the situation of patients and the detection results timely.
2021, 42(6): 115-118.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210629
Abstract:
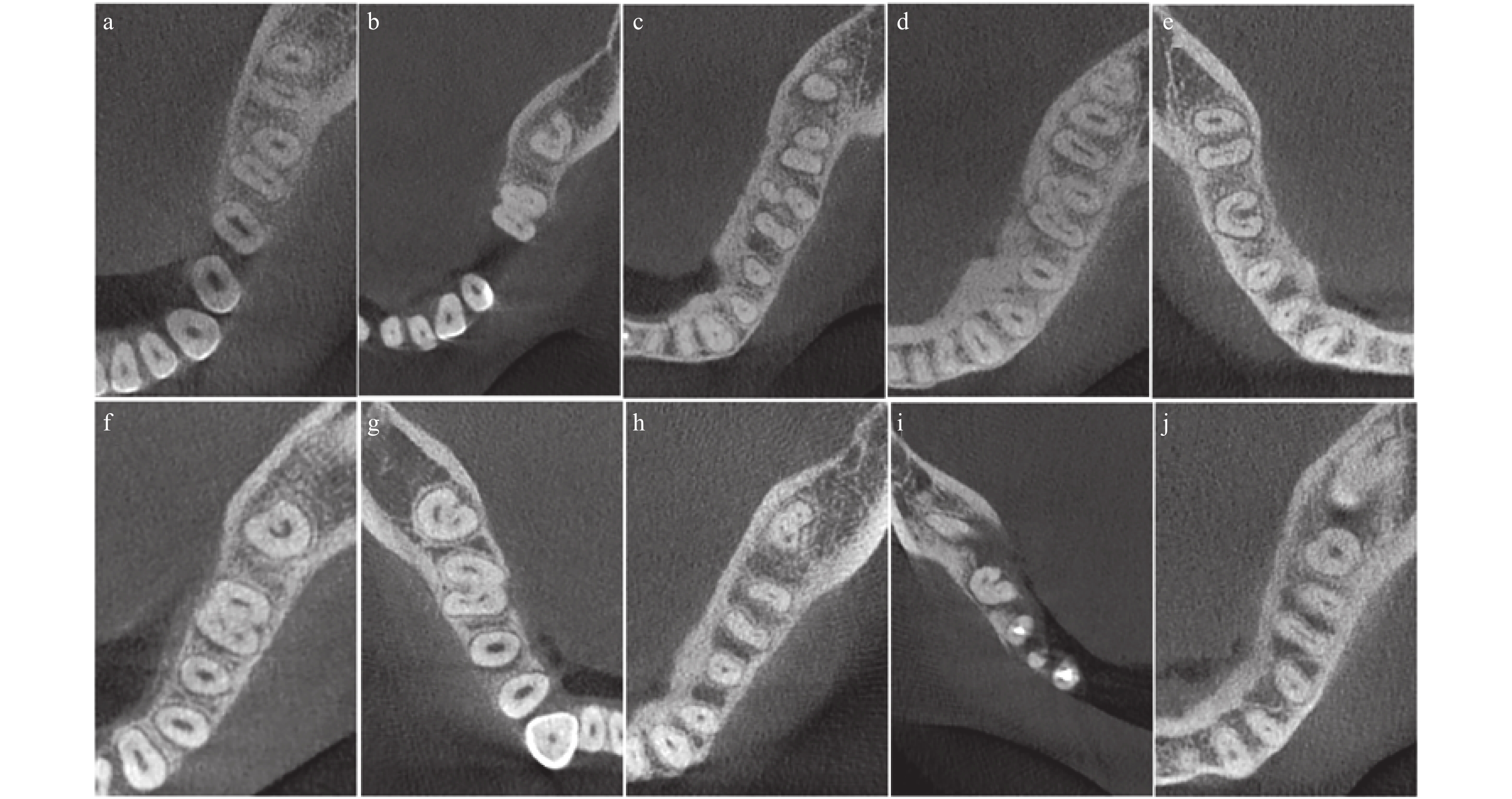
Objective To investigate the characteristics of root canal system of mandibular first and second molars ina Kunming population with cone-beam computed tomography technology. Methods CBCT dada of 1229 mandibular first and second molar from 358 patients were collected. The root canal number, classification and incidence of radix entomolaris and C-shaped canalswere calculated to conclude their characteristics. Results The majority of mandibular first molars (73.96%) showed 4 canals, 19.73% with 3 canals, 4.48% with 5 canals, 0.33% with 2 canals. The incidence of radix entomolaris was 14.43%. The incidence of C-shaped canals in mandibular second molars was 30.83%.There was a significant difference of incidence in female than that in male (34.95% > 26.81%, P < 0.05). The incidence of C-shaped canals in group 1 and 2 was higher than that in group 3 and 4 (P < 0.05). Most of the C-shaped canals were C1 and C2 type at the level of orifice (81.35%), 70.47% being C2 and C3 type at the level of middle and 83.42% being C3 and C4 type at the level of apical 3mm. Conclusion More attention must be paid when treating mandibular first and second molars in Kunming population bucause there is a high incidence of radix entomolaris and C-shaped canal.
2021, 42(6): 119-123.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210631
Abstract:
Objective To detect the serum levels of the inflammatory factors TNF-α and IL-6 in patients with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH) and further study their clinical significance in CTEPH. Methods A retrospective analysis was performed on 59 cases of CTEPH patients admitted to our hospital from January 2015 to January 2020. According to the echocardiography, the patients were divided into the group with normal right heart function (observation group 1) and the group with injured right heart function (observation group 2). A total of 30 patients with no PH who met the standards were selected as the control group.Serum levels of inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-6 and NT-proBNP were detected. Pulmonary artery systolic pressure (PASP) was measured by echocardiography. Results The serum concentrations of TNF-α, IL-6 and NT-proBNP in the control group, observation group 1 and observation group 2 increased successively. The concentrations of TNF-αwere (13.54±6.37) pg/mL, (25.20±11.87) pg/mL and (40.75±1.74) pg/mL, and the concentrations of IL-6 were (6.04±2.89)pg/mL, (8.56±4.25)pg/mL and(4.95±5.24)pg/mL, respectively.The concentrations of NT-proBNP were (265.07±132.47)pg/mL, (719.52±345.23)pg/mL and (1250.00±421.22) pg/mL respectively. There were significant differences in TNF-α, IL-6 and NT-proBNP between groups (P < 0.05). PASP was also increased successively, which were (32.07±6.15)mmHg, (57.04±11.26)mmHg, and (73.22±11.79) mmHg, respectively. Correlation analysis showed that the levels of TNF-α, lL-6 were significantly correlated with NT-proBNP and PASP (P < 0.05). Conclusion In patients with CTEPH hypertension, there are high expressions of inflammatory cytokines TNF- and IL-6, and their expression levels can reflect right heart function and pulmonary artery pressure.
2021, 42(6): 124-128.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210643
Abstract:
Objective The correlation between pulmonary artery diameter measured by high resolution computedtomography (HRCT) and pulmonary artery pressure measured by echocardiography in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) was investigated to find a new method to assess pulmonary artery pressure and to add a new method to the clinical assessment of the disease. Methods Seventy-seven patients with stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease who were seen in Kunming First People’ s Hospital from May 2018 to May 2020 were set as the test group, and 50 healthy individuals who underwent health checkups in same period were selected as the control group, all of whom underwent chest HRCT to measure right pulmonary artery diameter, left pulmonary artery diameter, and main pulmonary artery diameter, and also underwent cardiac ultrasound to measure right ventricular diameter, pulmonary artery pressure, and main pulmonary artery diameter. The data collected were analyzed for correlation. Results The data of left and right pulmonary artery diameter and main pulmonary artery diameter measured by HRCT in the COPD group were larger than those in the normal group (P < 0.05), and there were differences in the data of right pulmonary artery diameter and main pulmonary artery diameter between the COPD groups (P < 0.05), but not in the left pulmonary artery diameter (P > 0.05); the right intraventricular diameter and pulmonary artery pressure measured by echocardiography were different between the COPD groups (P < 0.05). The right intraventricular diameter, pulmonary artery pressure, and main pulmonary artery diameter were significantly correlated with the left and right pulmonary artery diameters and main pulmonary artery diameter by Pearson linear correlation analysis (P < 0.05), and all were positively correlated. Conclusio There is a significant correlation between the values of pulmonary artery pressure and the values of pulmonary artery diameter in patients with COPD. HRCT measurement of pulmonary artery trunk diameter and right pulmonary artery diameter can be used as a method to assess pulmonary artery pressure.
2021, 42(6): 129-133.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210611
Abstract:
Objective To observe the influence of mirror therapy combined with occupational therapy on upper limb motor function and ADL in hemiplegia after stroke. Methods Totally 72 patients with hemiplegia after stroke were randomly assigned to the mirror therapy group and the control group, with 36 cases in each group. Both groups accepted occupational therapy. Additionally, the mirror therapy group accepted mirror therapy to train the non-paretic upper limb. The motor function of upper limb and activities of daily living were evaluated by FMA-UE, MSS, Brunnstrom Stage, Modified Ashworth and MBI at baseline, after 2-weeks and 4-weeks training. Results Before training, there were no significant difference between groups in all indexes mentioned above (P > 0.05). FMA-UE and MBI scores of the upper limb in the mirror therapy group were improved at 2 week and 4 weeks after treatment compared with that of pre-treatment (P < 0.05); MSS score and Brunnstrom score of mirror therapy group were significantly improved at 4 weeks after treatment compared with that of pre-treatment (P < 0.05) ; After treatment, all indexes mentioned above in the control group had no significant difference compared with pre-treatment (P > 0.05); Compared with the control group at the same period, the FMA-UE 、MSS and MBI scores of the mirror therapy group at 4 weeks of treatment was higher than that of the control group (P < 0.05). Conclusion Mirror therapy combined with occupational therapy is helpful for the recovery of upper limb motor function and ADL of hemiplegia patients after stroke, and can be used as an adjuvant treatment for motor function of upper limb after stroke.
2021, 42(6): 134-138.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210616
Abstract:
Objective To observe the effect of MHI (Manual Hyperinflation) on diaphragmatic movement and pulmonary function in stroke patients. Methods 67 stroke patients were randomly divided into treatment group (n = 35) and control group (n = 32). The treatment group received MHI combined with conventional rehabilitation therapy, and the control group received conventional rehabilitation therapy for 8 weeks. All the patients were assessed with diaphragmatic motion with ultrasound, lung function (FEV1, FVC) and Barthel Index (BI) before, four weeks and eight weeks after treatment. Results Intra-group comparison of FVC (L), FEV1 (L), phrenic motion amplitude and Barthel index: Indicators in the treatment group were continuously improved from before intervention, 4 weeks after intervention, to 8 weeks after intervention (P < 0.05). comparison among groups: After intervention for 8 weeks, all indexes in the treatment group were better than those in the control group (P < 0.05). Conclusion MH technique can improve the activity of diaphragm, lung function and daily living ability of stroke patients.
2021, 42(6): 139-145.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210622
Abstract:
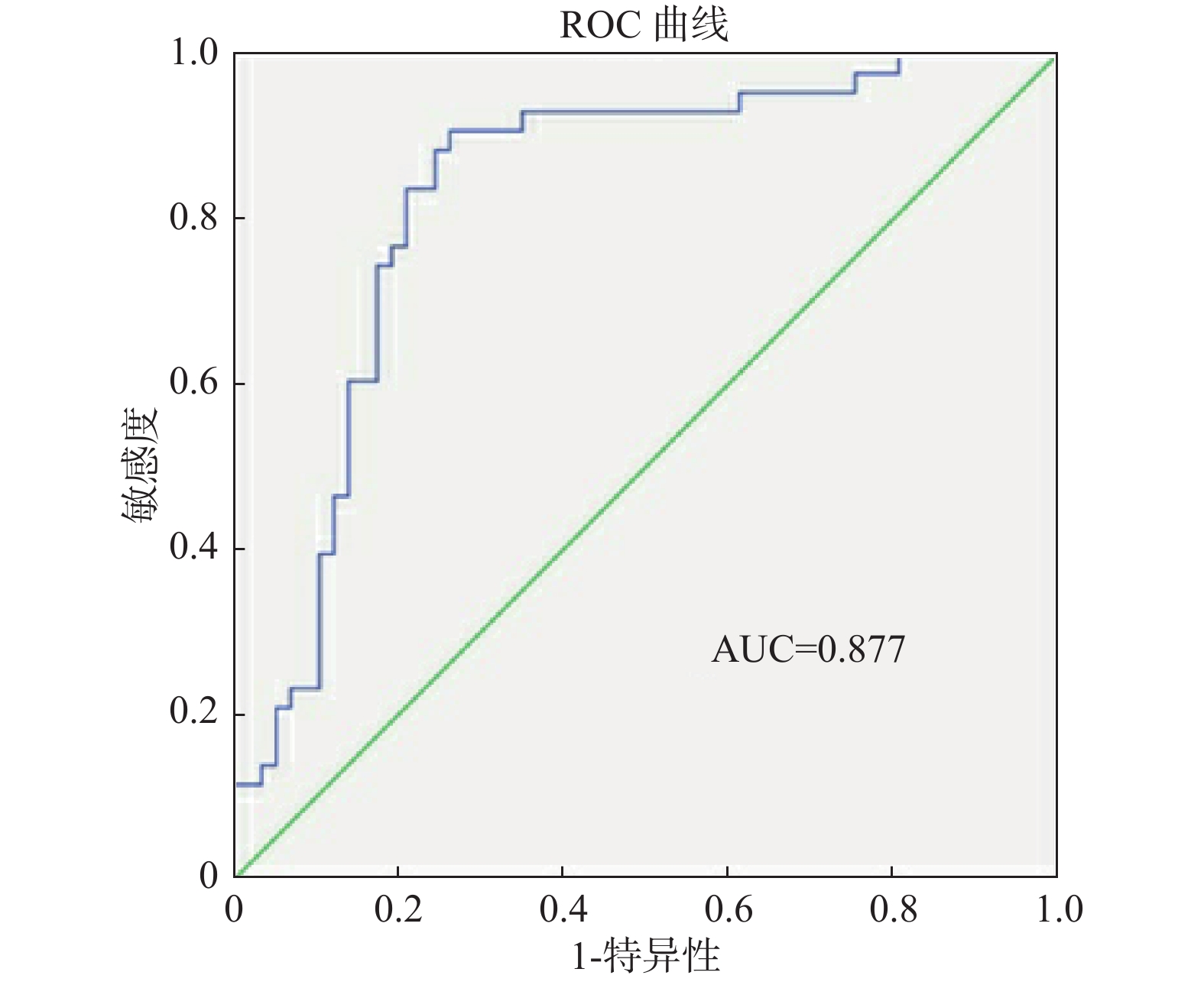
Objective To analyze the safety of cefoperazone Sodium and Sulbactam Sodiumfor injection in Kunming medical institutions, explore the influencing factors of adverse reactions (ADR) and the correlation between the factors, so as to construct the prediction model of adverse reactions, and provide reference for the rational application ofcefoperazone Sodium and Sulbactam Sodium in clinical practice. Methods From January 2015 to June 2020, 222 adverse reaction reports of cefoperazone sodium and sulbactam sodium for injection in the Kunming City Adverse Drug Reaction Report Monitoring Database were extracted as the observation group. During the same period, no adverse reaction occurred when using cefoperazone sodium and sulbactam sodium for injection, The 250 responding cases were used as the control group. The clinical data of the two groups of patients were collected, and the relationship between the factors was analyzed through correlation; the related factors of adverse reactions were analyzed by multivariate logistic regression, and the prediction of adverse reactions was constructed according to the results Model. Evaluate the effectiveness of predictive models through receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves. Results Correlation analysis showed that age was positively correlated with the number of primary diseases (Kendall’ s tau-b = 0.764, P < 0.05). There was a negative correlation between medication time and hospital stay (r = -0.124, P < 0.05). Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that retirees, patients with liver and kidney dysfunction, and medication time (11-15) days were related factors for the adverse reactions of cefoperazone sodium and sulbactam sodium. The prediction model is logit (P)= 1.357 + 1.739 × retirees + 3.485 × liver and kidney damage + 2.681 × days of medication (11-15). The area under the ROC curve of this model is 0.877, and the sensitivity and specificity are 91.8% and 77.4%, respectively. Conclusion Liver and kidney dysfunction patients, medication time (11~15) d are the related factors of adverse reactions of Cefoperazone Sodium and Sulbactam Sodiumand the prediction model has high clinical value.
2021, 42(6): 152-155.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210601
Abstract:
Periodontitis is a common chronic infectious disease. It is one of the main causes of tooth loss in adults and seriously affects the quality of life of patients. With the development of laser technology, laser therapies are gradually used in various fields of medicine. As a clinical treatment technology, laser therapy can be used alone or combined with other treatment methods for the treatment of periodontal diseases. This article summarized the types, characteristics and clinical application of lasers in periodontal treatment.
Periodontitis is a common chronic infectious disease. It is one of the main causes of tooth loss in adults and seriously affects the quality of life of patients. With the development of laser technology, laser therapies are gradually used in various fields of medicine. As a clinical treatment technology, laser therapy can be used alone or combined with other treatment methods for the treatment of periodontal diseases. This article summarized the types, characteristics and clinical application of lasers in periodontal treatment.
2021, 42(6): 146-151.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210630
Abstract:
Laser is generally used in in all kinds of oral treatment, for its convenience, safety and comfort. Researches of Neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet laser as well as erbium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet laser in the scientific and clinical research are becoming common. However, there are only a few of studies evaluating combined Er: YAG and Nd: YAG laser therapy in the treatment of stomatology. This review will focus on the application of Er: YAG laser combined with Nd: YAG laser in clinical stomatology.
Laser is generally used in in all kinds of oral treatment, for its convenience, safety and comfort. Researches of Neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet laser as well as erbium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet laser in the scientific and clinical research are becoming common. However, there are only a few of studies evaluating combined Er: YAG and Nd: YAG laser therapy in the treatment of stomatology. This review will focus on the application of Er: YAG laser combined with Nd: YAG laser in clinical stomatology.
2021, 42(6): 156-160.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210613
Abstract:
Objective To explore the application of PBL teaching based on microlecture as a carrier in standardized training of residents. Methods Forty-five trainees of standardized training of clinical residents in 2019 were taken as the research objects and randomly divided into two groups; 22 of them used PBL teaching as the control group; the other 23 used the PBL teaching model with microlecture as the carrier as the research group. The assessment results of the two groups after training were compared. Results Clinical thinking, practical ability and initiative of the study group after training were better than the control group (P < 0.05). Conclusion The PBL teaching model with microlecture as the carrier plays a good role in the standardized training and teaching of resident doctors, and its teaching effect is better than that of the PBL teaching method alone.
2021, 42(6): 161-165.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210605
Abstract:
Objective To improve the quality of life of patients, we use systematic intervention with standardized management model to intervene ankylosing spondylitis (AS) to improve the disease awareness and living quality. Methods This study selected 100 patients with ankylosing spondylitis who were hospitalized from September 2018 to February 2019 as the research objects, and they were divided into the control group (50 cases) and the experimental group (50 cases) according to the random grouping principle. During 10 months, the patients in the control group were given routine nursing management, and the patients in the experimental group were given systematic intervention with standardized management model. After 10 months, the two groups were compared. Results The control group had no significant difference in knowledge of disease and quality of life between before and after intervention (P < 0.485). The cognitive status of disease knowledge and quality of life of the experimental group were significantly higher than those in the control group (P < 0.05). Conclusion Systematic intervention with standardized management model can significantly improve the disease awareness and the quality of life of AS patients, and promote their early return to family and society.
2021, 42(6): 166-169.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210646
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the effect of intermittent prone position ventilation in neonatal respiratory distress syndrome (NRDS) in rats. Methods 120 cases of NRDS children undergoing mechanical ventilation from January 2020 to December 2020 in the pediatric neonatal intensive care unit of the Third People’ s Hospital of Yunnan Province, It was divided into experimental group and control group, 60 cases each, The experimental group was given intermittent prone position, that is, prone 2 h-left position 1 h- prone position 2 h-right position 1 h alternately change the position of the child, apply for 16 hours per day, of prone position daily The control group took routine supine nursing, collect and analyze blood and gas analysis indexes, hospitalization days, Mechanical ventilation duration between experimental and control children. Results Percutaneous oxygen saturation (SpO2), arterial oxygen partial pressure (PaO2), arterial carbon dioxide partial pressure (PaCO2) and oxygenation index (PaO2/FiO2) were significantly different between the two groups after treatment (P < 0.05); There was no significant difference in the PaO2、PaCO2、PaO2/FiO2 of 2 h after treatment and the SpO2 of 24 h after treatment (P > 0.05). The experimental group was significantly lower than the control group in ventilator treatment time and hospitalization days, difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). Conclusion Intermittent prone position can effectively improve the ventilation / ventilation function of newborns with respiratory distress, relieve their respiratory distress symptoms, and shorten the ventilator-assisted ventilation time of children.
2021, 42(6): 170-174.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210636
Abstract:
Objective To explore the application effect of integrated intervention with multiple follow-up methods on high-risk discharged patients with venous thromboembolism. Methods A total of 192 patients in the Second Department of General Surgery of Yan’ an Hospital in Kunming were selected as the research objects. They were randomly divided into the experimental group of 96 cases and the control group of 96 cases. In the experimental group, on the basis of the control group, the follow-up management team carried out a 3-month integrated intervention of multiple follow-up methods to observe the compliance of the two groups of patients’ out-of-hospital prevention behaviors, the effectiveness of health education, satisfaction, Whether there is a difference in the incidence of VTE. Results The experimental group and the control group were in compliance with prevention behavior (t = -14.91, P < 0.001), effectiveness of health education (χ2 = 71.31, P < 0.001), satisfaction (t = -12.27, P < 0.001). There are significant differences in these aspects, and the experimental group is significantly higher than the control group. The final incidence of VTE in the experimental group was significantly lower than that in the control group (χ2 = 5.13, P < 0.05). Conclusion The integrated intervention of multiple follow-up methods can effectively reduce the incidence of VTE, improve the quality of life of patients, and expand the coverage of VTE disease prevention, which can be applied and promoted.


 Email
Email RSS
RSS