2022 Vol. 43, No. 1
2022, 43(1): 1-7.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220121
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the expression changes of synaptic plasticity genes in chronic methamphetamine (MA) addicted mice. Methods C57BL/6J mice were selected to simulate the human drug addiction model, and the drugs were injected intraperitoneally with 5 mg/kg, 10 mg/kg or normal saline. The cerebral cortex and hippocampus of mice were selected, and the gene expression level of synaptic plasticity was detected by bisulfite treated genomic DNA and methylation specific PCR (MethylmionSpecificPCR, MSP). The sequencing results were compared and DNA methylation was analyzed by BiQ-Analyzer software. Results Compared to mice in the saline-treated group, MA addiction group mice showed increased methylation modification of the Egr2 (P = 0.064) gene promoter CpG site and decreased methylation modification of the Eln (P = 0.083) gene promoter in the cerebral cortex; in hippocampal tissue, methylation modification of the Arc (P = 0.025) and Egr2 (P = 0.034) genes was increased, while Eln (P = 0.063) gene methylation modifications were decreased. Conclusion Methylation of synaptic plasticity genes may be involved in the formation of MA addiction mechanism.
2022, 43(1): 8-13.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220120
Abstract:
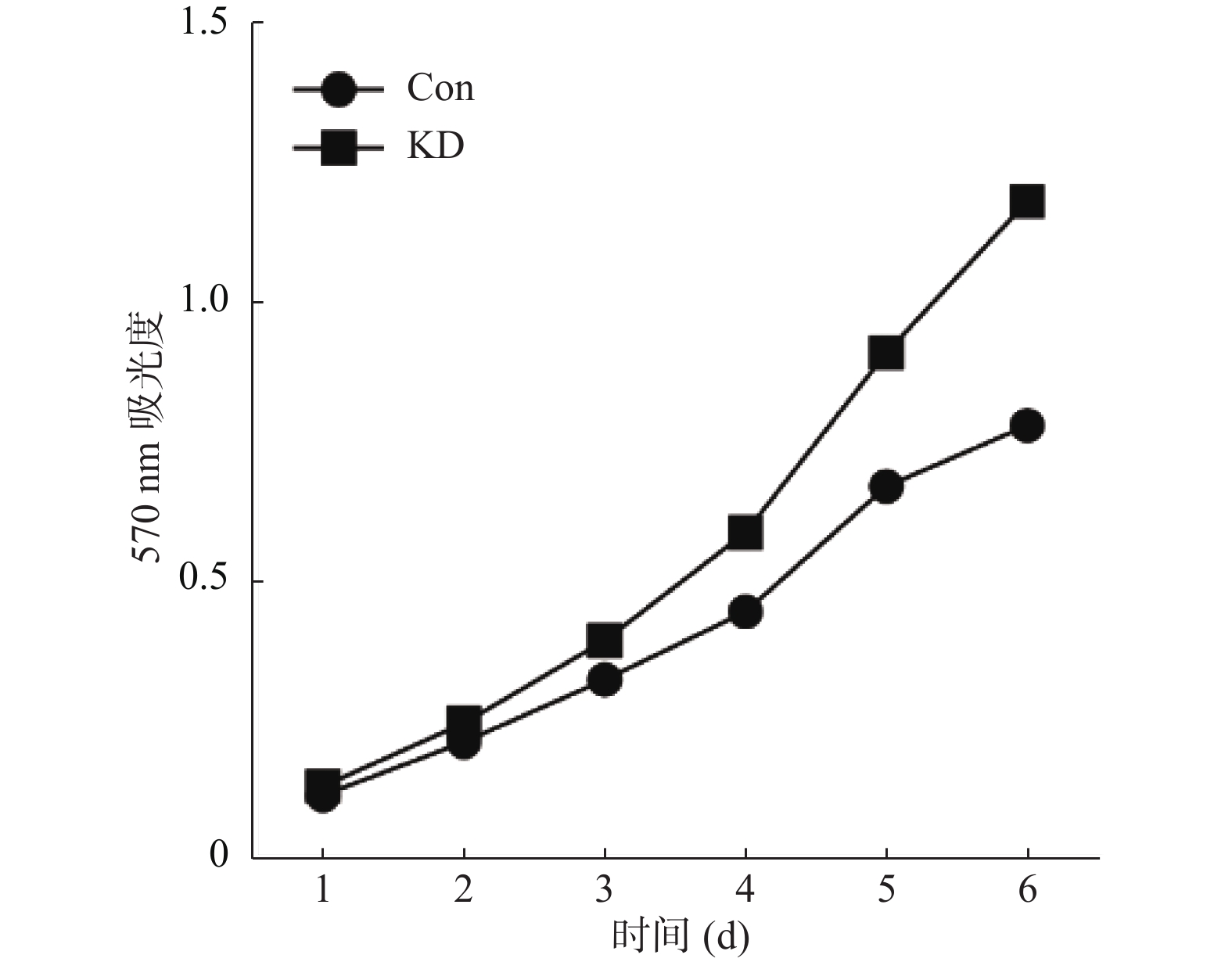
Objective To investigate the role of microRNA (miRNA, miR)-193b-5p in the process of iodine-125 particle radiotherapy for gastric cancer. Methods Gastric cancer cell line BGC-823 was used as the research object and iodine-125 seed in vitro irradiation model was established, and the expression profile of miRNA was detected by small molecule RNA sequencing. The expression of miR-193b-5p was analyzed by quantitative real time polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR). MiR-193b-5p knockdown cell and control cell lines (knockdown group and control group) were established in gastric cancer cell line BGC-823 by hsa-miR-193b-5p inhibitor and NC inhibitor. Cell proliferation was analyzed by methyl thiazolyl tetrazolium (MTT) assay in the two groups. Cell invasion was analyzed by Transwell. Result Compared with the expression level of miR-193b-5p in the non-irradiated group (0.173±0.045), the expression of miR-193b-5p in the iodine-125 irradiated group (0.853±0.180) was significantly increased (t = 6.371, P < 0.05). Compared with the expression of miR-193b-5p in the control group (12.219±2.464), the expression of miR-193b-5p in the knockdown group (1.264±0.311) was significantly decreased (t = -7.640, P < 0.05). Compared with the control group (0.424±0.246), the proliferation of knockdown group (0.574±0.382)was significantly increased (t = 3.927, P < 0.05). Compared with the control group (40±7), the number of cell invasion in the knockdown group (222+23) was significantly increased (t = -13.293, P < 0.05). Conclusion Iodine-125 seed suppresses the proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer cells by regulating the expression of miR-193b-5p in the process of radiotherapy for gastric cancer.
2022, 43(1): 14-19.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220142
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the effects of micafungin on the activity of Candida glabra in macrophages. Methods Macrophages were selected as the research object, and samples were isolated from the skin, vaginal secretion, pus, blood and body cavity fluid. Candida smooth strain and a standard strain ATCC2001 (purchased from the national strain collection center) were identified by biochemistry and molecular biology. Different concentrations of micafungin were used to treat Candida smooth. They were divided into the control group, model group, low concentration group, medium concentration group and high concentration group respectively. SOD activity, MDA content and no content were measured at the different times, and NF was measured- Κ B protein expression levels of p65, BKCa, NLRP3 and ATG5, IL-6, IL-10 and IL-1 β, TNF- α Level. Results Compared with the control group, the activity of SOD stimulated by macrophages in the modeling group was significantly decreased; Compared with the modeling group, the activity of SOD stimulated by macrophages in the low concentration group, medium concentration group and high concentration group was significantly increased, reaching the maximum value at 5 h, with the low concentration group > medium concentration group > high concentration group, and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). Compared with the control group, the secretion of MDA and NO by macrophages in the modeling group was significantly increased; Compared with the modeling group, the levels of MDA and NO in the low concentration group, medium concentration group and high concentration group were significantly increased, and the order of secretion content was as follows: medium concentration group > high concentration group > low concentration group, the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). The protein expressions of NF- κ B P65, BKca, NLRP3 and Atg5 were significantly increased in the modeling group compared with the control group, and the protein expressions of NF- κ B P65, BKca, NLRP3 and Atg5 were significantly increased in the low-concentration, medium-concentration and high-concentration groups compared with the modeling group. Low concentration group > medium concentration group > high concentration group, the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05).Compared with the control group, the level of serum inflammatory factors in macrophages in the model group was significantly increased; Compared with the modeling group, the levels of IL-6, IL-10, IL-1β and TNF-α in macrophages of low concentration group, medium concentration group and high concentration group were significantly increased, and the secretion of inflammatory factors was in the order of low concentration group > medium concentration group > high concentration group, the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). Conclusion Micafengin can effectively stimulate the stress response of macrophages, regulate the function of immune system, inhibit the activity of Candida glabra, and play a better antibacterial effect.
2022, 43(1): 20-25.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220131
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the effect of miR-181a on chemotherapy resistance of ovarian cancer and its regulatory mechanism. Methods Real-time PCR was used to detect the expression of miR-181a in A2780 and cisplatin resistant cell lines (A2780/DDP), and siltation/overexpression changed the expression of miR-181a in A2780 and A2780/DDP cells. MTT method was used to determine the sensitivity of cells to cisplatin before and after the transfection. Three MicroRNA target gene databases, TargetScan, miRDB and miRwalk, were used to predict the downstream targets of miR-181a, and the changes in protein expression of target genes were analyzed by Western blot. Results Compared with A2780 cells, the expression of miR-181a in A2780/DDP cells was significantly decreased (P < 0.05). After the transfection of A2780 cells with miR-181a inhibitor (interfering with Mir-181A expression), the sensitivity of A2780 cells to cisplatin decreased (P < 0.05), and after the transfection of A2780/DDP cells with miR-181a mimic (overexpressing miR-181a), The sensitivity of cells to cisplatin was increased (P < 0.05). It was predicted that PRKCD could be used as the downstream target gene of miR-181a by TargetScan, miRDB and miRwalk databases, and down-regulation of miR-181a expression could significantly enhance PRKCD protein expression (P < 0.05). On the contrary, up-regulation of miR-181a significantly inhibited PRKCD protein expression (P < 0.05). Conclusion miR-181a may inhibit cisplatin resistance of ovarian cancer cell A2780 by regulating PRKCD.
2022, 43(1): 26-32.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220126
Abstract:
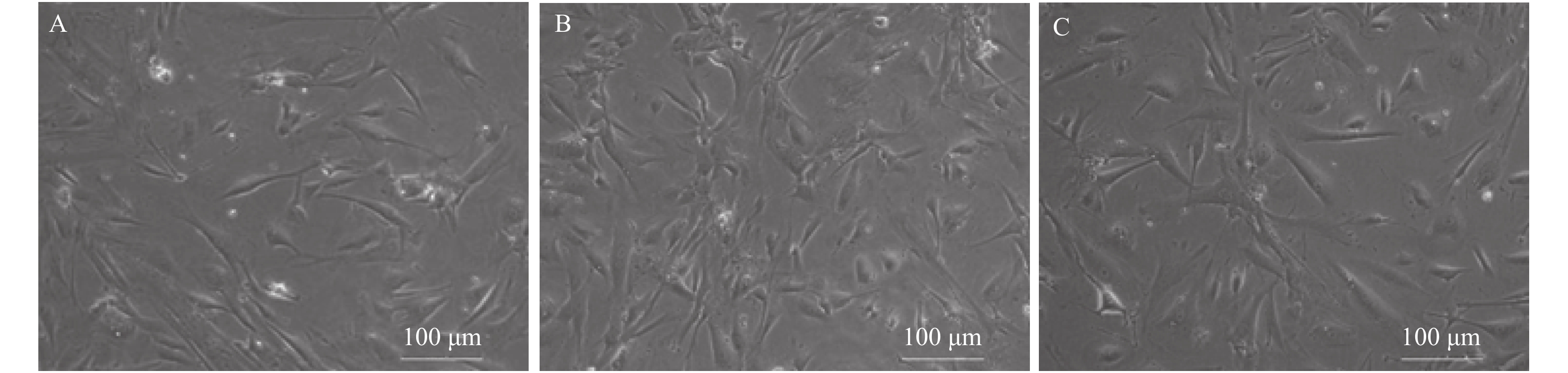
Objective To explore the mechanism of PRP promoting EnMSCs proliferation, and to provide a theoretical basis for the expansion and clinical application of EnMSCs. Methods EnMSCs were randomly divided into the control group, 2%PRP group and 2%PRP + LY294002 group. Cell proliferation was detected by CCK-8 method. Cell cycle was monitored by flow cytometry and protein expressions of p-PI3K, AKT, p-AKT, mTOR and p-mTOR were detected by Western Blot. Results (1) CCK-8 results: Compared with the control group, the proliferation level of EnMSCs in 2%PRP group was significantly higher (P < 0.05). Compared with the 2%PRP group, the proliferation level of EnMSCs in the 2%PRP+LY294002 group was significantly lower ( P < 0.05). (2) The results of cell cycle analysis by flow cytometry showed that the proportion of cells in G2/M phase in the 2% PRP group was significantly higher than that in the control group and 2% PRP+LY294002 group, and the proportion of cells in G0/G1 phase was significantly lower than that in the control group and 2% PRP+ LY294002 group. All of these had statistically significant differences ( P < 0.05). (3) The protein expressions of p-PI3K, AKT, p-AKT, mTOR and p-mTOR in EnMSCs in the 2%PRP group were significantly higher than those in the control group and the 2%PRP+LY294002 group, with statistical significance ( P < 0.05). Conclusion The proliferation of EnMSCs is regulated by the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. PRP activates this pathway by promoting the protein expression and phosphorylation of AKT and mTOR, thereby promoting the proliferation of EnMSCs.
2022, 43(1): 33-39.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220103
Abstract:
Objective To explore the cognition, mood, sleep status and alcohol dependence degree of patients with alcohol dependence and its influencing factors. Methods In a cross-sectional study, alcohol dependent patients hospitalized in the psychiatric department of three hospitals in Yunnan Province from September 2020 to June 2021 were selected as the alcohol dependence group, and ordinary residents matched with age and years of education were recruited in the community as the control group. The demographic information, drinking status, cognition, emotion and sleep status of patients were collected through the questionnaire survey and compared. The data were analyzed by univariate and multiple linear regression analyses to determine the independent risk factors affecting the degree of alcohol dependence in patients. Results A total of 220 questionnaires were distributed, 110 for each group. A total of 192 valid questionnaires were collected, including 97 from the alcohol dependent group and 95 from the control group. The effective questionnaire recovery was 87.27%. The degrees of anxiety and depression in alcohol-dependent group were higher than those in the control group, and the sleep quality and cognition level were lower than those in the control group (P < 0.001). Multiple linear regression analysis showed that the drinking frequency, daily alcohol consumption and GAD-7 score were independent risk factors affecting the degree of alcohol dependence in patients with alcohol dependence (P < 0.05). Conclusion Alcohol-dependent patients have the symptoms of anxiety and depression, cognitive impairment and sleep problems, and the three kinds of problems interact with each other. The degree of alcohol dependence would increase along with the increase of drinking frequency, drinking amount and anxiety level.
2022, 43(1): 40-47.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220105
Abstract:
Objective To analyze the distribution and characteristics of multi-drug-resistant bacteria isolated from the clinic in a children’ s hospital, providing the clinical evidence for the prevention and treatment of multi-drug-resistant bacteria in the hospital. Methods A retrospective analysis method was used to collect the data of the top five multi-drug-resistant bacteria of clinically isolated pathogens from inpatients in a children’ s hospital from January 2018 to December 2020, to understand the age, sex, and department distribution in children of multi-drug resistance bacteria, and analyze the drug resistance. Results 1451 strains of multi-drug resistant bacteria were clinically isolated in three years, and the top five were ESBLs-producing Escherichia coli, MRSA, ESBLs-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae, CRAB, and CRKP. The detection rates of ESBLs-producing Escherichia coli, MRSA, and ESBLs-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae were not statistically different in each year (P = 0.163, P = 0.125, P = 0.174), and the detection rate of CRAB first increased and then decreased ( P < 0.001), the detection rate of CRKP was decreasing year by year (P = 0.001). The majority of children with multi-drug-resistant bacteria were boys (55.4%) and infants (43.6%). The department with the highest detection rate was neurosurgery, with 9.18%, followed by burn plastic surgery, with a detection rate of 4.32%; specimen types had the highest positive rate of secretion, which was 7.06%. The main type of specimens was sputum (52.3%). The drug sensitivity results showed that the resistance rates of ESBLs-producing Escherichia coli to penicillins, cefazolin and ceftriaxone were greater than 99%. The resistance rate of MRSA to penicillins was 100%, and the resistance rates to vancomycin, linezolid, tigecycline were all 0.0%. The resistance rates of ESBLs-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae to penicillins, cefazolin and ceftriaxone were 100.0%. In 2018, the resistance rate of Acinetobacter baumannii to meropenem was 16.7%, and the resistance rates to the other 13 antibacterial drugs were all 100.0%. In 2019 and 2020, The resistance rates of Acinetobacter baumannii to nitrofurantoin, cefazolin, ampicillin were 100.0%, and the resistance rates to other antibiotics were lower than those in 2018. The resistance rates of CRKP to penicillins, cephalosporins and carbapenem antibiotics were above 90.0%. Conclusion In recent years, the situation of multi-drug resistant bacteria in children’ s hospitals has been severe. The management of the rational use of clinical antimicrobials should be strengthened to reduce the occurrence of drug-resistant bacteria.
2022, 43(1): 48-52.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220140
Abstract:
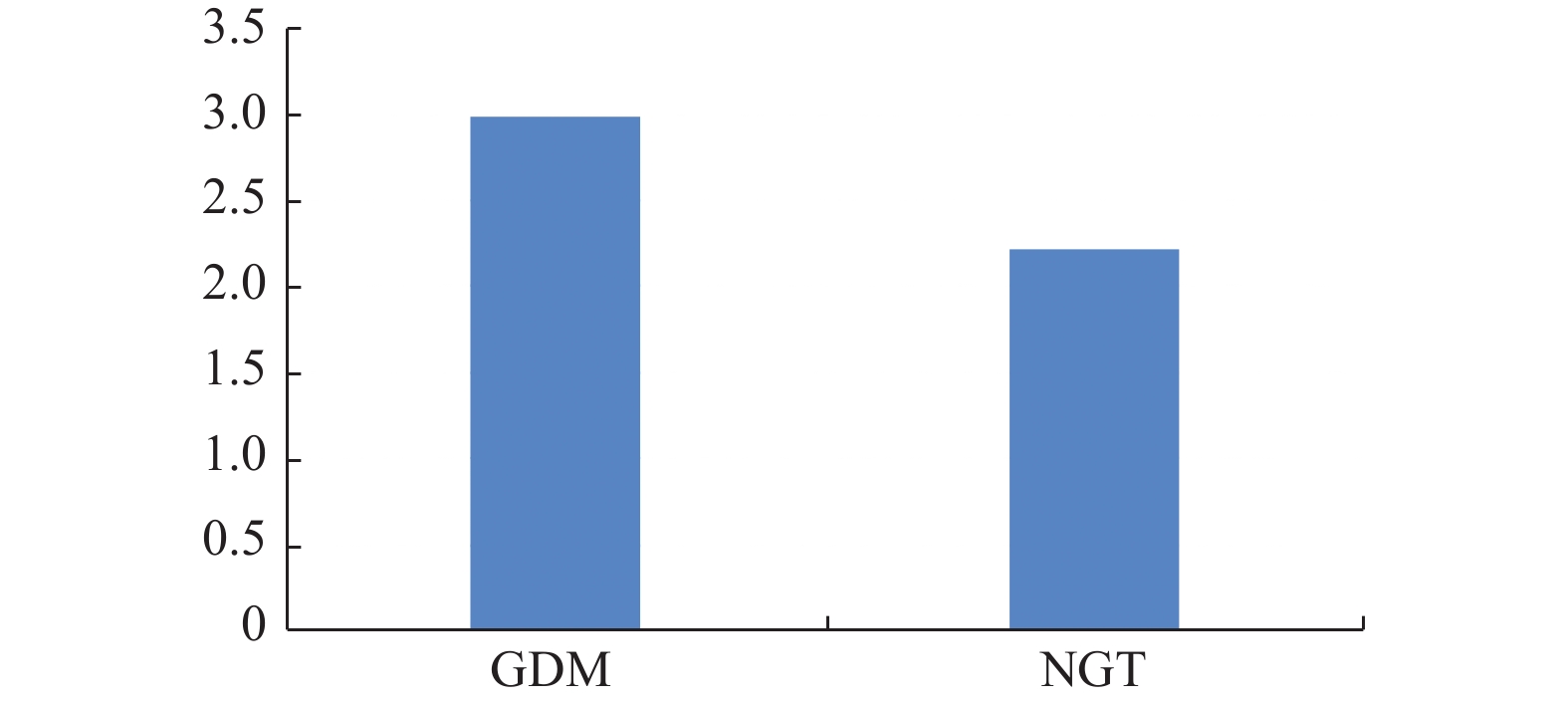
Objective To investigate the relationship between chemerin and insulin resistance in GDM by detecting the expression of insulin receptor substrate-1 and tyrosine phosphorylation in omental adipose tissue. Methods Subjects were divided into the GDM group 24 and the normal control group with 22 NGT. Two grams of omental adipocytes were collected during the cesarean section. The expression of chemerin and IRS-1 in placental tissues was detected with Western blot and qPCR, and the tyrosine phosphorylation of IRS-1 was detected with the immunoprecipitation. Results The expression of chemerin protein in retinal adipocytes in GDM group was significantly increased (2.99 (0.04, 7.90) vs 2.21 (0.02, 13.30), P = 0.010). The protein expression of IRS-1 (3.52(2.51, 4.49) vs 5.47 (4.04, 8.98), P = 0.024) was significantly decreased in GDM group. The phosphorylation of IRS-1 tyrosine was significantly decreased in GDM group (0.60(0.01, 1.74) vs 4.06 (0.06, 54.41), P = 0.012). Correlation analysis showed that chemerin protein expression was closely related to OGTT2h glucose. Chemerin mRNA was closely correlated with prenatal BMI. Chemerin protein expression was positively correlated with IRS-1 protein. IRS-1 tyrosine phosphorylation was negatively correlated with OGTT 0 h PG and OGTT 2 h PG. Conclusion The expression of chemerin in omental adipose tissue is closely related to IRS-1 signaling, which is one of the factors causing insulin resistance in GDM.
2022, 43(1): 53-58.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220109
Abstract:
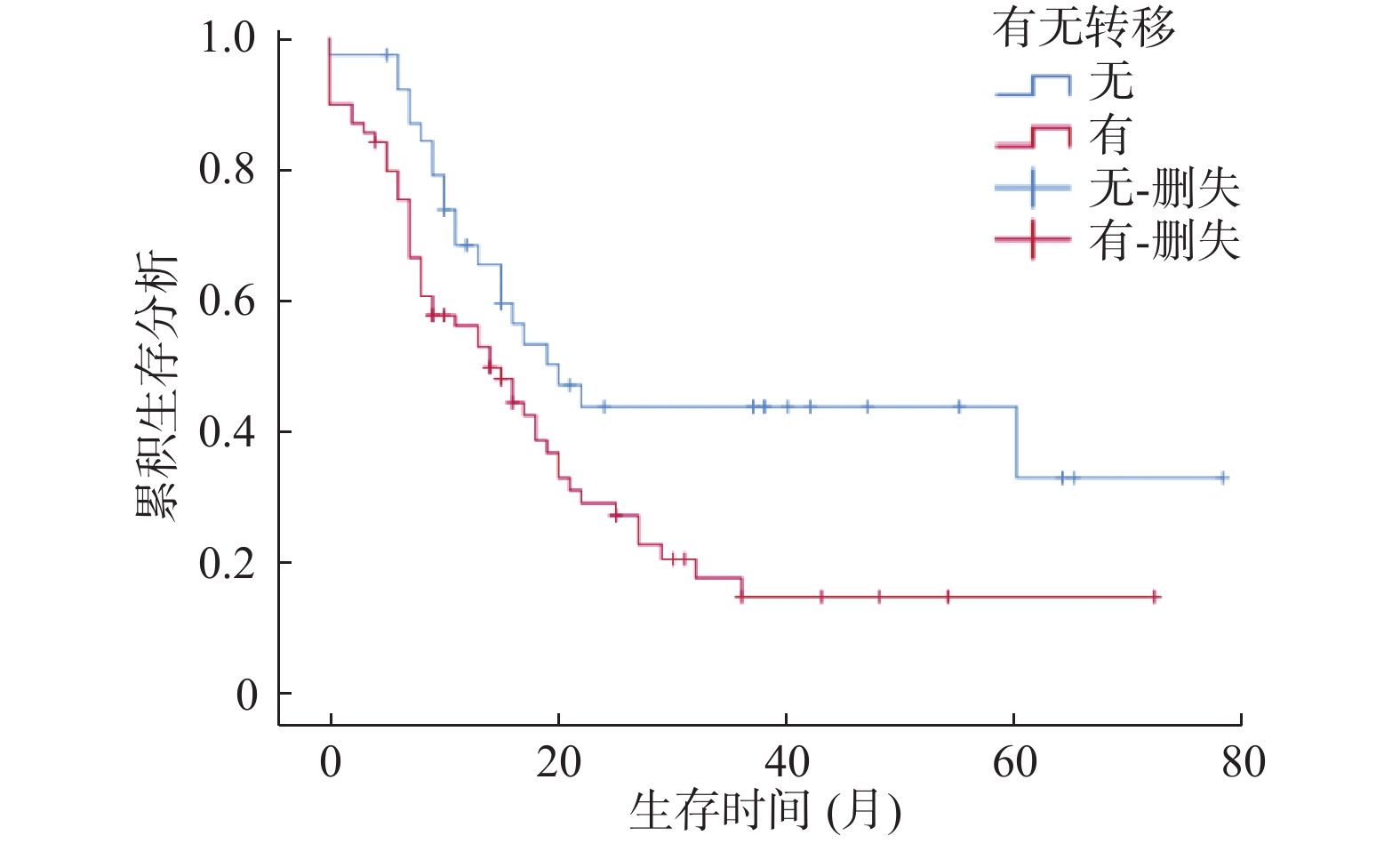
Objective To analyze the clinical characteristics and related prognostic factors of patients with duodenal adenocarcinoma. Methods 88 patients with duodenal adenocarcinoma who were pathologically diagnosed and admitted to Yunnan Cancer Hospital from January 2010 to December 2019 were studied retrospectively. The Kaplan-Meier method was used to evaluate the survival status of patients, the Log-rank test was used for univariate analysis, and the Cox proportional hazard regression model was used for multivariate analysis to screen out the relevant risk factors affecting the prognosis of patients with duodenal adenocarcinoma. Results The age range of 88 patients with duodenal adenocarcinoma: 23-79 years old, with an average age of 54.83 years old, male to female ratio: 1.44∶1. Survival analysis showed that the median survival time of patients with and without metastasis of duodenal adenocarcinoma was 14 months and 19 months respectively, the prognosis of patients with metastasis was worse than those without metastasis (P < 0.05). Univariate analysis showed that the presence or absence of metastasis, primary tumor diameter, clinical stage, chemotherapy regimens, types of chemotherapy drugs, surgical methods, Hp infection, CEA, CA199, AST/ALT, NKC, PLT, LMR were related to the prognosis of duodenal adenocarcinoma patients (P < 0.05). Cox multivariate analysis suggested that metastasis, Hp (+), CA199 > 27 U/mL were the independent risk factors affecting the prognosis of patients with duodenal adenocarcinoma (P < 0.05), and radical surgery was the duodenal Beneficial factors for the prognosis of patients with adenocarcinoma (P < 0.05). Conclusion The prognosis of duodenal adenocarcinoma with metastasis is extremely poor, and early close monitoring is needed. Clinically, the prognosis of patients can be predicted by four indicators of metastasis, surgical method, Hp infection, and CA199.
2022, 43(1): 59-62.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220136
Abstract:
Objective To explore the protective effect of breviscapine on graft vein grafting in the patients who underwent Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG). Methods According to the inclusion criteria and exclusion criteria, 64 patients entered the study and were randomly divided into two groups (n = 32). Group A was the control group, in which patients took oral routine drugs including aspirin, clopidogrel and atorvastatin; Group B was the treatment group, in which patients took oral routine drugs + breviscapine. The rate of graft stenosis was examined by Multi-slics Computed Tomography Angiography (MSCTA) 3 months and 6 months after CABG. Results The rate of graft stenosis in the treatment group was significantly lower than that in the control group 3 and 6 months after CABG (P < 0.05). Conclusion Breviscapine has a protective effect on graft veins in patients who underwent CABG.
2022, 43(1): 63-66.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220114
Abstract:
Objective To understand the serum levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25 (OH) D] and vitamin A in infants with asthmatic pneumonia during the onset of pneumonia, so as to analyze their correlation with lung function and serum Ig E and to further discover vitamin A and D relationship with infantile asthmatic pneumonia. Methods Fifty-six infants and 50 matched healthy infants and young children who met the diagnostic criteria for asthmatic pneumonia from June to 3 in the Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University from 2020 to 2021 were investigated, and enzyme-linked immunoassay was used to check serum 25 (OH) D and Ig E concentration. A pulmonary function meter was used to detect the tidal volume、respiratory rate, Inspiratory time, up to the peak volume of infants with asthmatic infants and young children. The differences in serum 25 (OH) D and vitamin A levels between the two groups of children were analyzed, and the correlation between serum 25 (OH) D and vitamin A levels in children with asthmatic pneumonia and the severity of acute attacks was analyzed. Results The serum 25 (OH) D and vitamin A concentrations of infants and young children in the asthmatic pneumonia group were (18.26±6.64) ng/ml and (0.20±0.09) ng/ml, respectively, which were significantly lower than those of the control group (25.28±3.48) ng/ml, (0.58±0.12) ng/ml, the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.01). Serum 25 (OH) D levels were positively correlated with the tidal volume, respiratory rate, Inspiratory time , up to the peak volume in infants with onset (r = 0.364, 0.341, 0.369 and 0.548), and negatively correlated with Ig E (r = -0.549). Conclusion Children in the asthmatic pneumonia group had vitamin A and D deficiency, and serum vitamin A, 25 (OH) D asthmatic pneumonia episodes were associated.
2022, 43(1): 67-72.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220132
Abstract:
Objectives To investigate the dosimetric differences between TOMO and Monaco planning systems in preoperative radiotherapy for rectal cancer and the comparison of Gamma pass rate, so as to provide a reference for the selection of clinical treatment. Methods A total of 20 patients with preoperative radiotherapy for rectal cancer admitted from December 2019 to January 2021 were selected, TOMO and Monaco planning were performed for these 20 patients respectively. The dose-volume histogram was used to evaluate the dose distribution of the target area and the radiation dose of the organs at risk. The differences between the two planning systems in the dosimetry of the planned target area and endangering organs were analyzed and compared, and the gamma pass rates of the two schemes were compared. Results Both TOMO and Monaco plans could meet the prescription dose requirement of target area. The HI and CI of PGTV target of Tomo plan were better than those of Monaco planning system, and the CI of PCTV target area was also superior to that of Monaco plan system (P < 0.001). In terms of organs at risk, compared with Monaco planning system, the mean values of Dmean, V50, V40, V30 of bladder, Dmean, V30, V20, V15 of bilateral femoral head, and pelvic V50 indicators in TOMO plan were lower (P < 0.05). The execution time of Tomo’ s planning machine was 4.3 times that of Monaco’ s, and the execution time of Tomo’ s planning machine was 1.31 times that of Monaco’ s (P < 0.05). The mean Gamma pass rate of Tomo plan was higher than that of Monaco plan (P < 0.05). Conclusion The TOMO plan system design for preoperative radiotherapy of rectal cancer patients can significantly improve the target uniformity and conformal degree, and can also reduce the dose of normal tissues. The plan Gamma has a higher pass rate, but the treatment time is longer. The treatment time of Monaco planning system is significantly shortened.
2022, 43(1): 77-83.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220128
Abstract:
Objectives To investigate the correlation between the thyroid function and renal function in patients with the differentiated thyroid cancer in the short-term hypothyroid state after the discontinuation of prior radioiodine therapy. Methods A total of 122 patients with the differentiated thyroid cancer and operated on and suitable for radioiodine therapy were included. The data of thyroid function level and renal function level before and after the withdrawal of levothyroxine in enrolled patients were collected. The changes in renal function measures before versus after the discontinuation were compared and the thyroid function and associated factors on renal function were analyzed. Results The levels of uric acid, creatinine, and eGFR in patients with DTC increased after the treatment discontinuation compared with those before the treatment discontinuation; In the hypothyroid state after the drug withdrawal, male patients had the higher levels of creatinine and uric acid than female patients. The level of creatinine in TSH > 60 miu/l group was higher than that in TSH ≤ 60 miu/l group, and the level of EGFR in TSH > 60 miu/l group was lower than that in TSH ≤ 60 miu/l group. There was no significant difference in biochemical indexes of renal function between cervical lymph node metastasis group and non cervical lymph node metastasis group, total thyroidectomy group and subtotal thyroidectomy group (P > 0.05); The levels of FT4, TT3 and TT4 were positively correlated with the level of EGFR (r value was 0.267, 0.249 and 0.330, P < 0.05), age was negatively correlated with the level of EGFR (r value was -0.213, P < 0.05), and TT4 was negatively correlated with the level of creatinine (r value was -0.232, P < 0.05); Multiple linear regression showed that TT4 level, age and gender were independently correlated with EGFR level. Conclusion For DTC patients in hypothyroidism after the withdrawal before the radioactive iodine treatment, the levels of uric acid and creatinine increase and the level of eGFR decreases; the reduced TT4 level, old age and male are the independent influencing factors for the decrease of eGFR level.
2022, 43(1): 84-88.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220104
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the feasibility and clinical effect of total hip replacement with the biologically lengthened stem in the treatment of subtrochanteric fractures combined with the necrosis of femoral head. Methods A total of 88 patients admitted from January 2016 to January 2020 were analyzed retrospectively. Among them, 30 cases of subtrochanteric fractures with the avascular necrosis of the femoral head underwent stage I biotype long-stem joint replacement (experimental group), 20 cases of simple subtrochanteric fracture group underwent PFNA internal fixation (PFNA group), and 32 cases of simple avascular necrosis of the femoral head underwent the artificial joint replacement (joint replacement group). The operation time, perioperative blood loss and postoperative hospitalization were compared among the three groupsand the fracture healing time between the experimental group and the PFNA group was compared so as to compare the hip Harris scores of the experimental group and the joint replacement group 1, 3, 6 months after the surgery and the last follow-up. Results The operation time of the experimental group was higher than those of the PFNA group and the joint replacement group, and the difference was statistically significant; The three groups had the statistically significant differences in perioperative blood loss, time of postoperative activities and the length of hospital stay; There was no significant difference in fracture healing time between the experimental group and the PFNA group and there was no statistically significant difference in the Harris score of the hip joint between the experimental group and the joint replacement group. Conclusion The total hip arthroplasty for the treatment of subtrochanteric fractures with the necrosis of femoral head can achieve good clinical results. There is no significant difference between fracture healing time and PFNA surgery.
2022, 43(1): 89-95.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220107
Abstract:
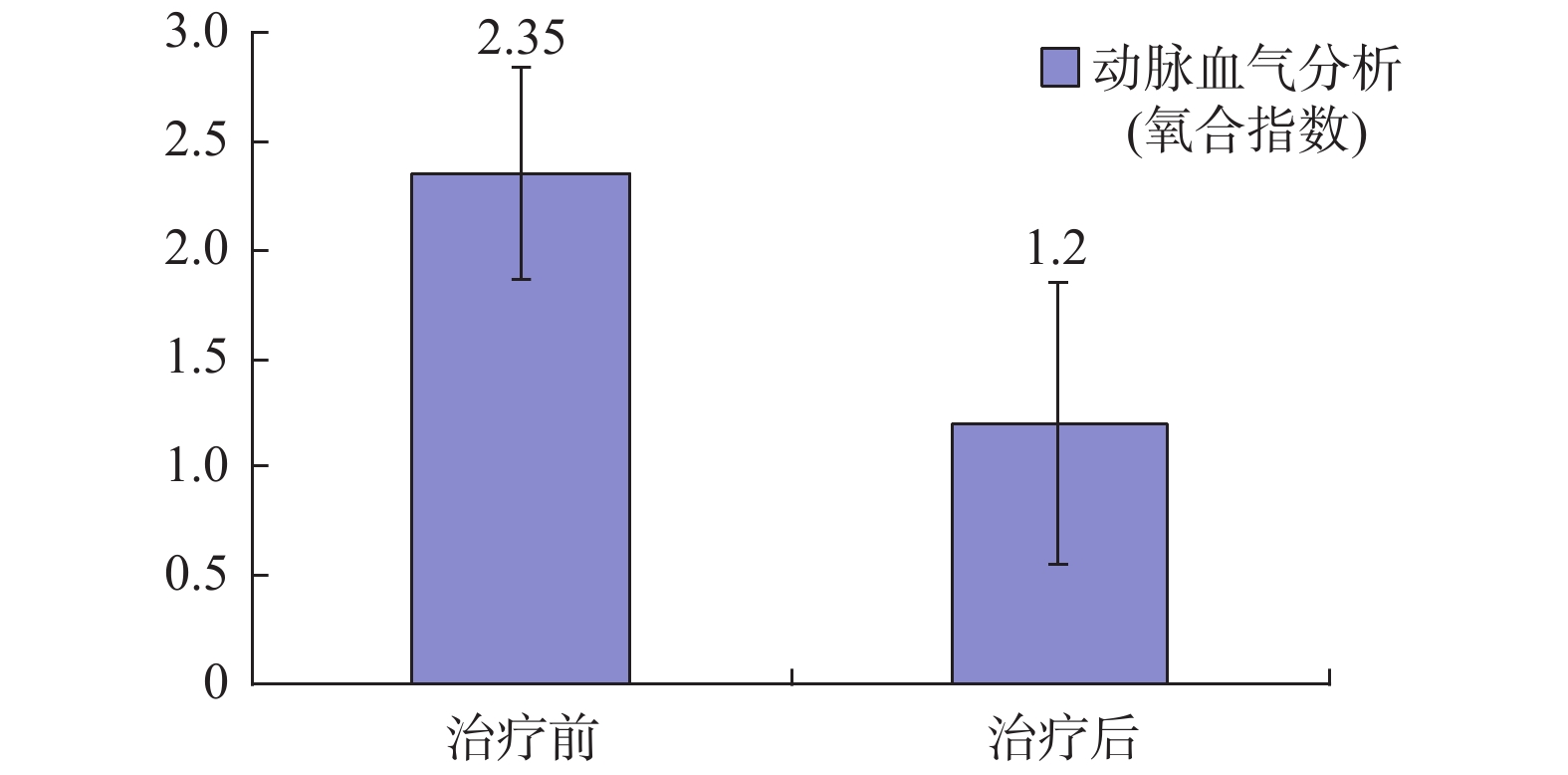
Objective To investigate the effect of bronchoscopic alveolar lavage on the maintenance of borderline donor lung in brain death. Methods The brain death patients meeting the inclusion criteria and admitted to Ganmei Hospital of Kunming Medical University from September 2017 to December 2019 were randomly divided into the fiberoptic bronchoscopy alveolar lavage group (experimental group) and the control group on the basis of routine maintenance. Statistical analysis was carried out through the comparison of chest film, arterial blood gas (oxygenation index), fiberoptic bronchoscopy and other indexes between the two groups. Result The scores of oxygenation index, chest radiograph and fiberbronchoscope performance of the two groups after the experiment were all lower than those before the experiment the differences were statistically significant (P < 0.05), and there was statistically significant difference in effective rate between the two groups (P < 0.05). The effective rate of the experimental group was higher than that of the control group. Conclusion Fiberbronchoscope alveolar lavage can be used as an effective technique to maintain the donor lung and has a wide application prospect.
2022, 43(1): 96-101.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220112
Abstract:
Objective To explor the clinical characteristics and detoxification rules of the patients with COVID-19 nucleic acid positive by analyzing their clinical manifestations of throat swabs and fecal, so as to provide the evidence for the clinical diagnosis and treatment. Methods The clinical symptoms, laboratory indexes, and the detoxification of throat swab and faecal in 59 patients with COVID-19 infection admitted to Kunming Third People’s Hospital from February 2020 to December were retrospectively analyzed. Result Fecal positive group: In 7 cases of latent infection, the first pharyngeal swab nucleic acid was positive to symptomatic for 3~8 days (median 4 days), 5 cases were continuously positive and 2 cases were repeatedly positive; The stool was positive 1~28 days after the pharyngeal swab was positive (median 6 days). 5 cases were asymptomatic, 2 cases were continuously positive and 2 cases were repeatedly positive; The stool was positive 4~21 days after the pharyngeal swab was positive (median 6 days). 21 symptomatic patients were positive for pharyngeal swab for 1~21 days (median 5 days), 8 cases were continuously positive for 4~20 days, and 10 cases were repeatedly positive for 8~26 days; The stool was positive 4~29 days after the pharyngeal swab was positive (median 15 days). Fecal negative group: In 6 cases of latent infection, pharyngeal swabs were positive to symptomatic for 4~10 days (median 5 days), 2 cases were continuously positive and 2 cases were repeatedly positive; In 4 asymptomatic patients, pharyngeal swabs were continuously positive in 1 case and repeatedly positive in 1 case; In 16 symptomatic patients, the pharyngeal swab was positive for 1~16 days (median 5.5 days), 3 cases were continuously positive and 10 cases were repeatedly positive. There was significant difference in the continuous positive time of the pharyngeal swab nucleic acid between the two groups (P < 0.05), and there was no significant difference in the repeated positive time (P > 0.05); There was significant difference in CT findings between the two groups (P < 0.05); There was no significant difference in clinical manifestations, liver function, renal function, myocardial enzymes, blood routine, CRP and T lymphocytes between the two groups (P > 0.05). Conclusion There is no difference in symptoms and signs, organ function injury and inflammatory indexes between the two groups. The regularity of virus detoxification is not strong, but those who detoxify with pharyngeal swabs and feces last longer than those who detoxify only with pharyngeal swabs, and pneumonia is more common.
2022, 43(1): 112-117.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220115
Abstract:
Objective This study was to analyze the prognosis between soluble growth stimulation expressed gene 2 protein ( sST2 ) and the severity of coronary heart disease. Methods 400 patients who needed coronary angiography and stent implantation were selected and divided into low concentration group (< 35 μg/mL), medium concentration group (35 μg/mL-70 μg/mL)and high concentration group (> 70 μg/mL)according to the concentration of sST2. SYNTAX II score of coronary artery was used in patients and mace events (including cardiac death, myocardial infarction, heart failure, readmission of cardiac causes, target vessel revascularization) were followed up within 360 days after PCI. Results (1) High concentration group had significantly higher SYNTAX II scores than low concentration group and medium concentration group (P < 0.05). (2) High concentration group had significantly higher mace events than low concentration group and medium concentration after 360 days of PCI (P < 0.05). Conclusion (1)There is a significant correlation between Serum sST2 Level and SYNTAX II score of coronary artery; (2)There is a significant correlation between Serum sST2 Level and the mace events after 360 days of PCI.
2022, 43(1): 138-143.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220133
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the infection, immunity, and drug resistance of newly-treated HIV cases in Kunming. The clinical characteristics and virological characteristics were jointly analyzed, so as to provide a basis to determine the ease of treatment and individualized solutions for antiviral precision treatment. Method The HIV-RNA , HCV-RNA, HBV-DNA, CD4 cell count, ALT, AST, Hb, PLT, ALB, HIV typing and resistance testing in 200 cases of newly-treated cases of HIV were detected before the therapy. Result The mainly infection route of newly-treated cases of HIV in Kunming was the heterosexual transmission, accounting for 80.5%, and MSM people also occupied a certain proportion (6.5%). Youth and seniors accounted for 25%. CD4 level was negatively correlated with viral load in newly-treated cases of HIV in Kunming (r = -0.58, P < 0.05), and 83 cases of them suffered from the opportunistic concurrent infection. HIV subtype had the highest proportion with CRF08_BC subtype in newly-treated cases of HIV in Kunming (27.5%). A total of 7 infected persons were detected resistance mutation sites in 200 newly-treated cases of HIV in Kunming. Primary resistance rate was 3.5%. Conclusion New features of HIV spreading in Kunming have emerged. The route of transmission has changed from intravenous drug use to heterosexual transmission. Increasing proportion of MSM population, adolescents and the Elderly. HIV subtypes have unique distribution characteristics in Kunming. The overall immune status is low. Primary resistance rate is 3.5%.
2022, 43(1): 144-149.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220135
Abstract:
Due to its complicated mechanism, the occurrence and development of hepatocellular carcinoma have not been fully revealed yet. As the largest transcription factor family in the human genome, zinc finger proteins have been confirmed to play a key role in many cancers, including liver cancer. The mechanism of action is reviewed in this article.
Due to its complicated mechanism, the occurrence and development of hepatocellular carcinoma have not been fully revealed yet. As the largest transcription factor family in the human genome, zinc finger proteins have been confirmed to play a key role in many cancers, including liver cancer. The mechanism of action is reviewed in this article.
2022, 43(1): 150-156.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220110
Abstract:
Bladder cancer is one of the most common urinary tumors with the high morbidity and recurrence rate. It is of great clinical value to develop a non-invasive detection technique with the high sensitivity and specificity in vitro for the diagnosis and treatment of bladder cancer. Exosomes are extracellular vesicles secreted by many cells and play a key role in intercellular communication by delivering intracellular signaling substances (such as proteins, nucleic acids, non-coding RNAs, etc.). More and more studies have shown that exosomes-derived long non-coding RNA plays an important regulatory role in the development and progression of bladder cancer and can effectively reflect the progression and prognosis of tumors, which is expected to become a new tumor marker. Therefore, this paper reviews the research progress of exosomes-derived long non-coding RNA in the development and diagnosis of bladder cancer.
Bladder cancer is one of the most common urinary tumors with the high morbidity and recurrence rate. It is of great clinical value to develop a non-invasive detection technique with the high sensitivity and specificity in vitro for the diagnosis and treatment of bladder cancer. Exosomes are extracellular vesicles secreted by many cells and play a key role in intercellular communication by delivering intracellular signaling substances (such as proteins, nucleic acids, non-coding RNAs, etc.). More and more studies have shown that exosomes-derived long non-coding RNA plays an important regulatory role in the development and progression of bladder cancer and can effectively reflect the progression and prognosis of tumors, which is expected to become a new tumor marker. Therefore, this paper reviews the research progress of exosomes-derived long non-coding RNA in the development and diagnosis of bladder cancer.
2022, 43(1): 157-162.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220143
Abstract:
The intestinal microbiota plays a vital role in regulating host immunity and energy metabolism, and is related to the occurrence of obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. At present, various animal models and human studies have proved that Akkermansia muciniphila (Akkermansia muciniphila/A. muciniphila) levels are negatively correlated with the occurrence of metabolic diseases such as obesity, diabetes, obese liver disease, and atherosclerosis. A. muciniphila has broad prospects in the treatment of metabolic disorders by increasing the thickness of the intestinal mucus layer, reducing systemic inflammation, improving glucose tolerance and insulin resistance, and is considered to be a new generation of therapeutic drugs. This article systematically reviews the basic mechanism of the interaction between A. muciniphila and metabolic diseases and hosts.
The intestinal microbiota plays a vital role in regulating host immunity and energy metabolism, and is related to the occurrence of obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. At present, various animal models and human studies have proved that Akkermansia muciniphila (Akkermansia muciniphila/A. muciniphila) levels are negatively correlated with the occurrence of metabolic diseases such as obesity, diabetes, obese liver disease, and atherosclerosis. A. muciniphila has broad prospects in the treatment of metabolic disorders by increasing the thickness of the intestinal mucus layer, reducing systemic inflammation, improving glucose tolerance and insulin resistance, and is considered to be a new generation of therapeutic drugs. This article systematically reviews the basic mechanism of the interaction between A. muciniphila and metabolic diseases and hosts.
2022, 43(1): 163-166.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220102
Abstract:
Objective To explore the application and research of 3D animation and traditional teaching in neurotomy. Methods 240 first-year undergraduates of clinical medicine at our college were enrolled as the research objects, and the teaching period was from December 2018. The students were randomly divided into the study group (115 subjects) and the control group (125 subjects). The study group were taught with the 3D animation multimedia teaching, while the control group were taught with the traditional teaching. The satisfaction of the two teaching modes was investigated, and the assessment results of the two groups of undergraduates were compared. Results The scores of students’ basic theory of neuroanatomy, the score of viewing pictures and the score of questionnaire(learning initiative, learning interest, knowledge understanding and memory, knowledge mastery and spatial thinking ability) of the study group were higher than those of the control group, the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). Conclusion 3D animation technology has a good effect in the teaching of neuroanatomy, which can not only improve students’ basic theoretical knowledge, but also cultivate their spatial thinking, understanding and reasoning abilities in the learning process.
2022, 43(1): 167-172.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220146
Abstract:
Objective To construct and apply the health education model for in vitro fertilization-embryo transfer (IVF-ET) assisted patient node based on health information needs, and to evaluate its effect. Method Cases studied were divided into the control group and the experimental group and class experimental research method was adopted. The control group used the conventional health education mode, and the experimental group used the nodes-oriented health education mode oriented by health information needs. The scores of anxiety and depression, the recognition of IVF-ET knowledge and the satisfaction were compared between the two groups. Results After the intervention, the scores of anxiety and depression in the experimental group ([1(0, 2)], [1(0, 2)]) were significantly lower than those in the control group ([2(0, 4)], [2(0, 4)])(P < 0.001). The recognition score of the experimental group was significantly higher than that of the control group (76.63±9.67 VS 70.19±11.92)(P < 0.001). The satisfaction of the experimental group was higher than that of the control group of routine health education, and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). Conclusion Node health education model oriented by patients’ health information needs can improve patients’ knowledge awareness and satisfaction, and relieve patients’ anxiety and depression. It is worthy of clinical reference and promotion.


 Email
Email RSS
RSS