2022 Vol. 43, No. 3
2022, 43(3): 1-6.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220303
Abstract:
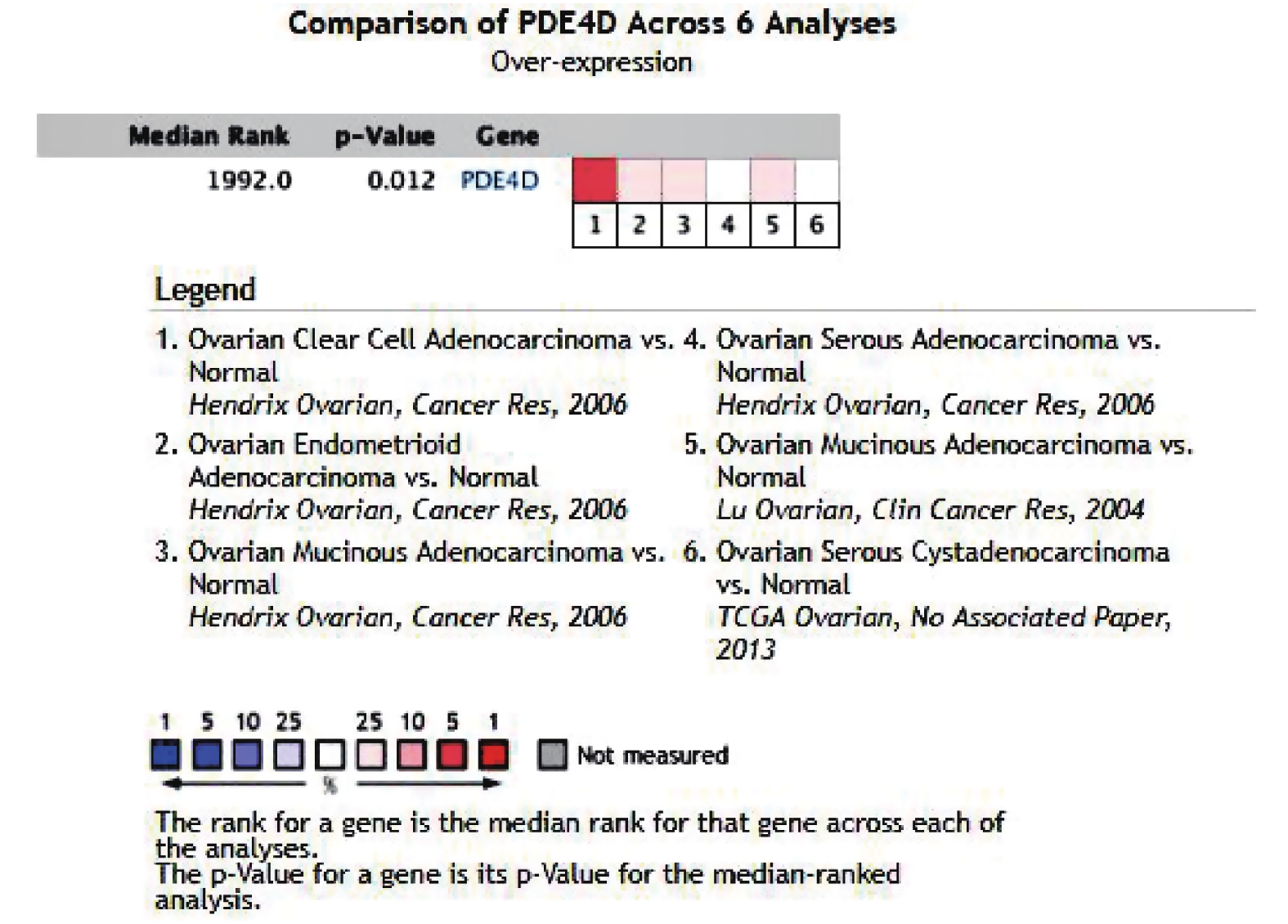
Objective To investigate the expression and clinical significance of PDE4D in ovarian cancer by excavating gene information in Oncomine and explore the effect of sanguinarine on PDE4D by cells experiment. Methods PharmMapper was used to find the targets matched with the pharmacodynamic groups of sanguinarine. The gene information about PDE4D in ovarian cancer research was collected in Oncomine, and the expression level was analyzed. The A2780 and SKOV3 ovarian carcinoma cells were divided into control group and sanguinarine group. CCK8 and RT-qPCR were used to detect the effects of sanguinarine on the proliferation and PDE4D mRNA expression of A2780 and SKOV3 cells. Results PDE4D was the target matched with the pharmacodynamic group of sanguinarine. There were 6 studies referred to PDE4D in ovarian cancer and normal sample collected in the Oncomine. The expression of PDE4D in tumor tissues was significantly higher than that in normal (P < 0.05). The cell experiments showed that compared with the control group, the proliferation of A2780 and SKOV3 cells was significantly inhibited and the expression of PDE4D mRNA was decreased in the sanguinarine group, with statistical significance (P < 0.05). Conclusions PDE4D gene may play a role in the occurrence and development of ovarian cancer, and sanguinarine can inhibit the growth of ovarian cancer cells, which may be related to the down-regulation of PDE4D expression.
2022, 43(3): 7-12.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220327
Abstract:
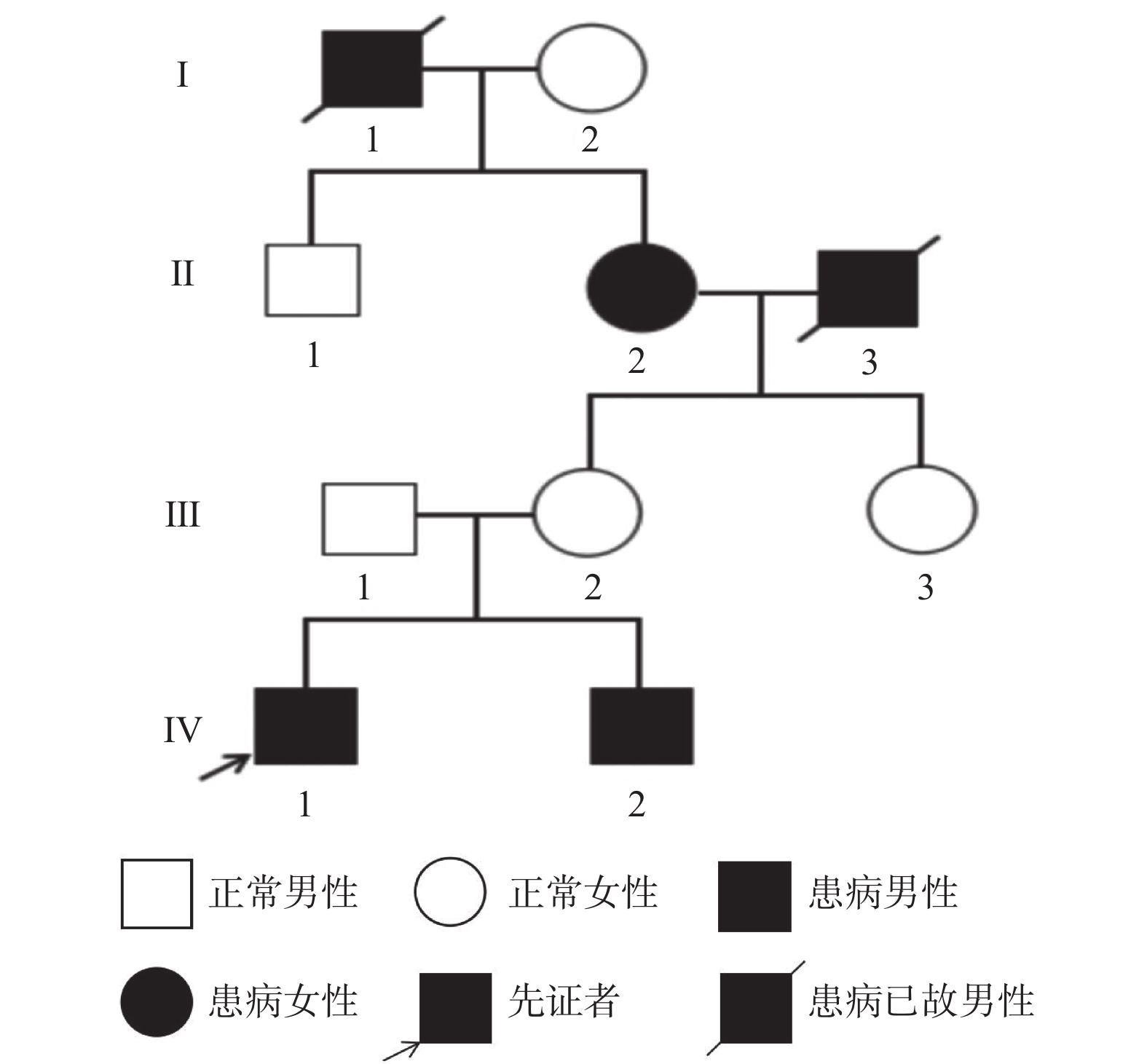
Objective To screen the pathogenic mutations in the four generations of a proband with atrial septal defect, so as to analyze the relationship between genotype and phenotype by whole exon sequencing and Sanger sequencing. Methods Retrospectic analysis of the clinical data on a child with atrial septal defects treated in the Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, the First People’ s Hospital of Yunnan Province was conducted in tandem with genetic tests for the sick child, his younger brother and mother by means of whole-exome sequencing to find out the genetic causes of the family in combination with bioinformatics analysis. Meanwhile, sporadic ASD patients and healthy people were screened for the Caudal Homebox Gene 4 (CDX4) mutation found in the family. Results The cardiac ultrasound results of the sick child and the intraoperative findings conformed with ASD diagnosis. The genetic tests suggested that CDX4 gene c.C233T homozygous mutation occurred to the child, his mother carries heterozygous mutation of the gene and his younger brother homozygous mutation of it. Codon 233 of exon 1 of CDX4 gene mutated from C to T (c.C233T), leading to conversion of amino acid 78 from proline to leucine (p.P78L). Multi-species comparison showed that the locus was highly conserved. The three software programs PROVEAN, Mutation Taster and Mutation Assessor suggested that the mutation was harmful. Of the 198 patients with sporadic atrial septal defects, 5 suffered this gene mutation, but that was not found in the 265 healthy people. According to the Fischer’s Exact Test, CDX4 gene c.C233T homozygous mutation was associated with congenital heart diseases (P = 0.014). Conclusion CDX4 gene c.C233T (p.P78L) homozygous mutation is the highly likely the pathogenic mutation of the family.
2022, 43(3): 13-20.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220317
Abstract:
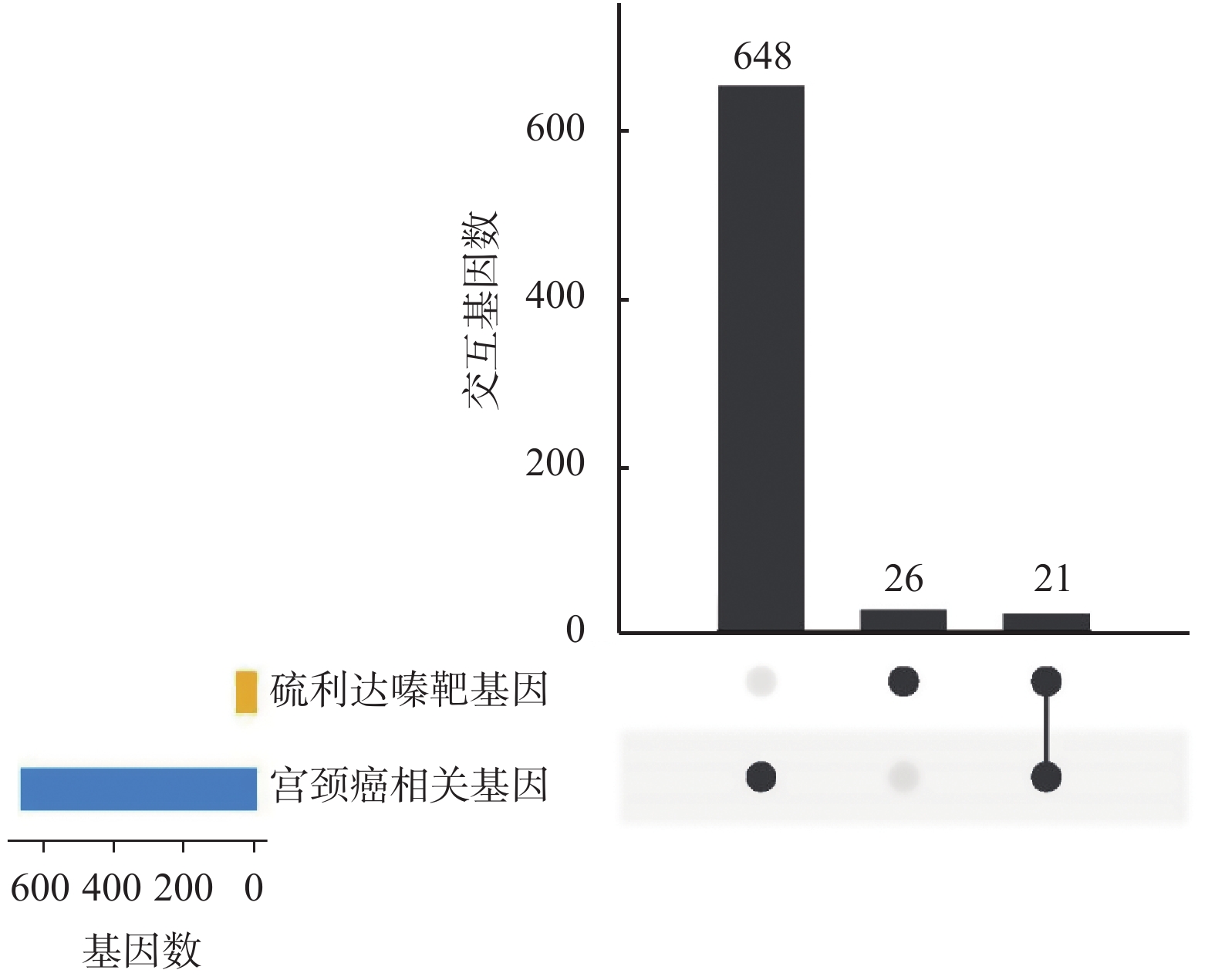
Objective To explore the potential mechanism of thioridazine in the treatment of cervical cancer by bioinformatics analysis. Methods The target genes that can interact with thioridazine was predicted by PharmMapper, and then conducted pathway and tissue expression enrichment analysis by STRING online tool. The cervical cancer related genes were screened through GeneCards and DisGeNET databases, and cross the target genes of thioridazine to obtain the interaction genes that thioridazine may act on cervical cancer. The protein-protein interaction(PPI) network was constructed using STRING, and the core targets were speculated and evaluated their importance.The GO and KEGG enrichment analysis were conducted using clusterProfiler package. Results A total of 47 target genes were predicted by PharmMapper, which were enriched in tumor-related pathways and cervical cancer cells. Intersection with 669 cervical cancer genes, 21 common genes were obtained, of which 10 key genes were EGFR, PPARG, AR, NOS3, ALB, ESR1, MAPK1, MAPK14, ANXA5 and MAPK8. These key genes were important in the cervical cancer PPI network. The biological processes involved in interactive genes mainly include positive regulation of anion transport, peptidyl-serine phosphorylation, steroid metabolic process, blood coagulation, and cellular response to chemical stress. Enriched KEGG pathways include pathways in cancer, relaxin signaling pathway, endocrine resistance, proteoglycans in cancer, cellular senescence, GnRH signaling pathway, and VEGF signaling pathway. Conclusion Thioridazine has potential anti-tumor effects and may play a role in the treatment of cervical cancer through multiple targets and multiple signaling pathways.
2022, 43(3): 21-26.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220320
Abstract:
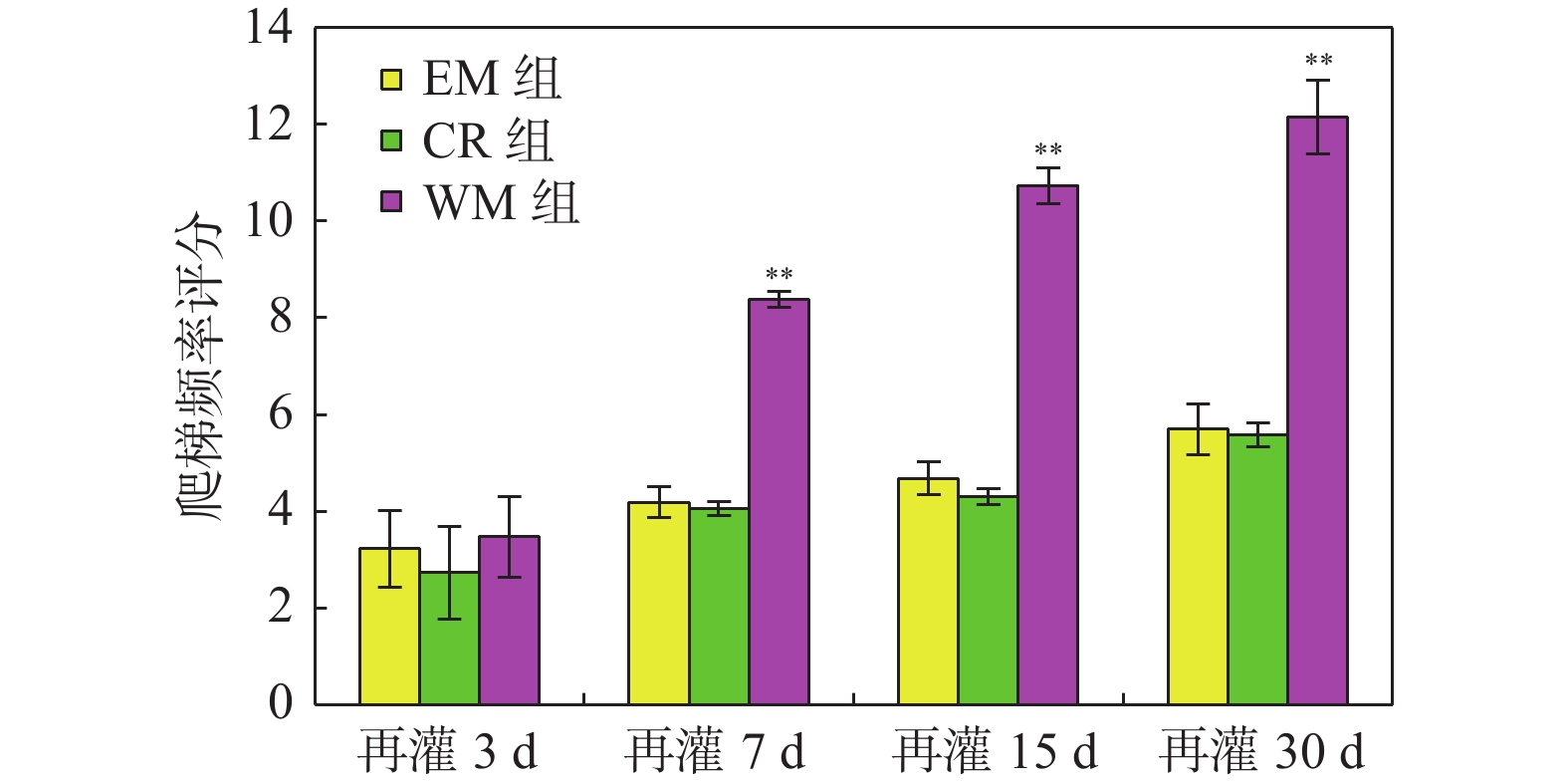
Objective To explore effect of the Willed movement on behaviours of rats with focal cerebral ischemia and the expression of GluA2 and N-cadherin in the brain tissue around ischemia. Methods We selected clean-level healthy male SD rats, and prepared 144 middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) models by thread occlusion method, and randomly divided them into model (MCAO) group, environment modification (EM) group, control rehabilitstion (CR) group and Willed movement (WM) group, each group was divided into four subgroups of 7, 15, and 30 days according to the postoperative time. The behavioral changes of rats in each group were dynamically observed, and the expression changes of GluA2 and N-cadherin protein in the brain tissue around the ischemic area were observed by immunohistochemical staining. Results On 7, 15, and 30 days after reperfusion, the climbing frequency of rats which were treated by willed movement was obviously higher than EM and CR group (P < 0.01). After 30 days of reperfusion, the neurological deficits score of the intentional exercise intervention group was lower than MCAO rats (P < 0.05). Compare with MCAO rats, the expression levels of GLUA2 and N-cadherin were higher in ischemic penumbra (P < 0.05). Conclusions Willed movement can promote the recovery of damaged nerve function after focal cerebral ischemia, which may be related to up-regulating the expression of GLUA2 and N-cadherin in the brain tissue around the ischemic focus and enhancing synaptic plasticity.
Genetics Analysis in a Congenital Cataract Pedigree Associated with a Missense Mutation in GJA8 gene
2022, 43(3): 27-31.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220305
Abstract:
Objective To analyze the clinical manifestations in a congenital cataract pedigree and the genetic etiology was identified using exon sequencing. Methods A family with congenital cataract admitted to the Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University in June 2020. A comprehensive ophthalmological examination and physical examination was conducted with the family members. Peripheral blood from proband and 6 relatives were collected, and genomic DNA was extracted. The potential pathogenic genes were screened by whole exome sequencing, pathogenicity analysis of suspected gene mutations was performed using bioinformatics tools, and the mutations were identified using Sanger sequencing in all pedigree members. Results A missense mutation c.593G > A,p.R198Q was identified in GJA8 gene by Exon sequencing and bioinformatics analysis. The GJA8 gene is one of gene family encoding gap junction protein. The amino acids affected by this mutations site are highly conserved between species and the mutation was considered pathogenic according to the Guidelines of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG). Sanger sequencing results in all in the family showed that the proband and other patients with congenital cataract all carried the mutation, while the mutation was not detected in healthy people in the family, and the mutation was co-separated with the disease phenotype, presenting autosomal dominant inheritance. Conclusions Our study shows that missense mutation c.593G > A,p.R198Q located in the GJA8 gene is the genetic cause of congenital cataract in this family, and the inheritance mode is autosomal dominant inheritance.
2022, 43(3): 32-36.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220307
Abstract:
Objective To screen out the best method of PEG6000 modified liposomes for influenza vaccine and evaluate its stability. Methods After 7 d of immunization, the optimal molar percentage of PEG6000 and the optimal preparation method were assumed by MTT method. The PEG-modified influenza vaccine liposomes were prepared by freeze-thaw freeze-drying method. The samples were stored at different temperatures (4 ℃, 25±2 ℃, 37±2 ℃), and the encapsulation rate and thymus index and antibody titer were measured at a fixed time. So the physical and biological stability of the samples were investigated. Results The MTT experiment showed that PEG6000 was the best dosage when the molar percentage of phospholipid was 4% (P < 0.01), and the best process was post-modification method.The entrapment rate of PEG6000 modified liposome for influenza vaccine was still higher than 80% when stocked at 37±2 ℃ for 6 months.At 25±2 ℃ for 3 months, the antibody titer was more than 4, indicating that the antibody still had nice immune effection. Conclusions PEG6000 best dosage of phospholipid when the molar percentage of PEG6000 is 4%, and post-modification method is the best preparation process. PEG6000 liposome has nice physical stability and biological stability.
2022, 43(3): 37-43.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220310
Abstract:
Objective To develop a special module of PRO-IBD for patients with inflammatory bowel disease in China , so as to construct a complete digestive system scale. Methods The interview and questionnaire data of 32 gastroenterologists and 69 IBD patients were statistically analyzed by six methods: critical ratio method, linear correlation coefficient method, Cronbach coefficient A method, discrete trend method, factor analysis method and doctor importance score. Finally, experts were organized to discuss and determine the final items. Results The critical ratio method shows that the average number of each item is different between the high group and the low group (P < 0.05) The SD of items 5 and 8 in the discrete trend method is less than 0.8, which should be deleted; The results of linear correlation coefficient method show that the correlation coefficient between each item and the total score is greater than 0.5, and no item will be deleted; In Cronbach coefficient α method, items 14 and 15 are deleted respectively, and the Cronbach coefficient α < 0.890 is calculated and deleted; Among the 15 items, the average score of doctors' importance is between 3.57 and 4.36 (> 3.5), and the full score ratio is between 19.0% and 61.9%, which shows that experts have a high degree of concentration on the operability of items, and the items screened by experts and patients are consistent. Conclusion The 15 items selected according to the above steps have good reliability, validity and representativeness, which can further evaluate the popularization of the scale and test its clinical application value in future research.
2022, 43(3): 44-49.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220319
Abstract:
Objective To study the correlation between attention and motor function in children with spastic hemiplegia. Methods A small sample cross-sectional observational study was conducted. Spearman correlation analysis was used to statistically analyze the correlation between children’ s attention and motor function. Results The three functional areas of gross motor function B, C, and D of children were positively correlated with the correct rate of children’ s attention network; the four functional areas of gross motor function B, C, D, and E of children had negative correlation with the rate of missing attention network of children; B and C functional areas were negatively correlated with error rate; D(rs = −0.344, P = 0.052) and E(rs = −0.300, P = 0.100) functional areas were correlated with children’s error rate, there was no statistical difference. However, in children with spastic hemiplegia, there was no statistically significant correlation between the three sub-components of the network. Conclusions There is a correlation between attention and motor function in children with spastic hemiplegia. In the rehabilitation of motor function in children, it is suggested that attention should be included as a focus.
2022, 43(3): 50-54.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220313
Abstract:
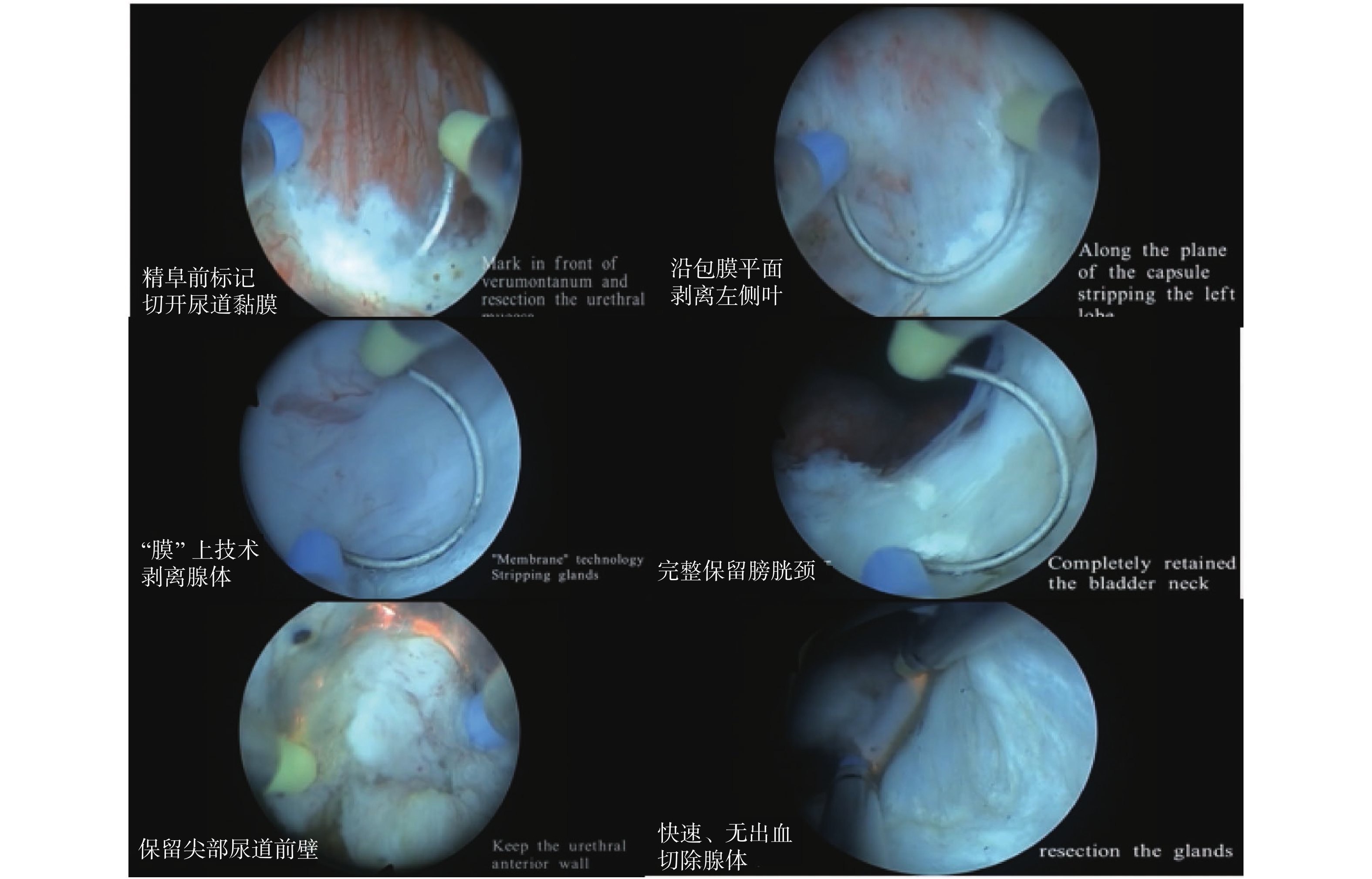
Objective To explore the feasibility of short-term indwelling urete in patients aftert PKEP (transurethral plasmamakinetic enucleation surgery). Methods We performed a retrospective analysis of the clinical data of 89 patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and treated with PKEP in Yan'an Hospital Affiliated to Kunming Medical University from February 2019 to December 2019. These patients was divided into control group and observation group. The control group was given indwelling with the urine after PKEP, and the observation group left the urete after PKEP short-termly. Compared to the operation time, intraoperative blood volume, resection of gland weight, and other related indicators. Results The surgical time of the control group and the observation group was [(58.40 ± 29.80) min vs (67.40 ± 29.80) min], the weight of the gland was [(54.90 ± 16.60) g vs (61.20 ± 21.50) g], the volume of intraoperative bleeding was [(35.50 ± 13.20) mL vs (35.50 ± 19.20) mL], the difference was not statistically significant (P > 0.05). However, the observation group was hospitalized [(10.80 ± 3.90) D], hospitalization cost [(1.06 ± 0.49) D VS. (1.38 ± 0.53) d] was significantly lower than that in the control group (P < 0.05) . There was no significant difference between the two groups (P > 0.05) in the incidence of urinary retention, urinary tract infection, urinary incontinence complications. Conclusions After the operator strictly abides by the PKEP operating standard, postoperative short-term indwelling urete can shorten the hospitalization time and reduce the hospitalization cost without increasing the incidence of postoperative complications. It not only achieves a good therapeutic effect, but also reduces the economic burden of patients. These findings verifies the feasibility of this method.
2022, 43(3): 55-59.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220318
Abstract:
Objective To explore the risk factors of lymph node metastasis in patients with gallbladder cancer, and to provide references for comprehensive treatment and prognosis evaluation of gallbladder cancer. Methods We retrospectively analyzed the clinical and pathological data of patients with gallbladder cancer confirmed by postoperative pathological examination who underwent radical resection of gallbladder cancer in the Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University from January 1, 2013 to September 30, 2020. The patients were divided into Lymph node metastasis group and non-lymph node metastasis group, univariate and multivariate analysis was used to determine the relevant risk factors of gallbladder cancer lymph node metastasis. Results A total of 101 patients were finally included, of which 41 patients had lymph node metastasis and 60 patients had no lymph node metastasis. The univariate analysis showed that T stage, histological grade, liver invasion, preoperative CA19-9≥100 U/mL and preoperative CA19-9+CEA+CA125 combination were risk factors for lymph node metastasis of gallbladder adenocarcinoma(P < 0.05). The results of multivariate analysis showed that T stage, histological grade, and preoperative CA19-9+CEA+CA125 combination were independent risk factors for lymph node metastasis of gallbladder adenocarcinoma(P < 0.05). Conclusions Patients with gallbladder adenocarcinoma with CA19-9≥100 U/mL or CEA≥20 ng/mL or CA125≥50 U/mL should consider expanding the scope of lymph node dissection. For patients with gallbladder adenocarcinoma with T3-T4 staging, histological grade G3-G4 and preoperative CA19-9≥100 U/mL or CEA≥20 ng/mL or CA125≥50 U/mL, comprehensive postoperative treatment and close follow up should be considered.
2022, 43(3): 60-66.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220312
Abstract:
Objective To evaluate the reliability, validity and responsiveness of Patient Reported Outcome Instruments System for Chronic Disease-Hypertension, PROISCD-HY (V1.0), a scale for measuring reported outcomes in patients with hypertension. Methods During May 2020 to October 2020, 111 community hypertension patients with initial hypertension were enrolled in PRO scale two surveys (before and after antihypertensive drug treatment), and the reliability, validity and responsiveness were evaluated based on scale scores. Results The Cronbach’ α of the total table was 0.894 and the split - half reliability coefficient was 0.783. The Cronbach’ α of spiritual/belief health was 0.434, respectively, and 0.725 or above in other fields. The fractional reliability coefficients of physical health and spiritual/belief health were 0.585 and 0.489, respectively, and 0.678 and above in other fields. The scale was developed according to the PRO scale development and application guidelines issued by FDA, and has good content validity. Factor analysis of common modules extracted 11 common factors, and the cumulative variance contribution rate was 79.275%. Factor analysis of specific modules extracted 4 common factors, and the cumulative variance contribution rate was 64.554%. The scale has good structural validity. The ES value ranged from 0.129 to 0.594, the CR value ranged from -8.911% to -1.796%, and the SRM value ranged from 0.103 to 0.516, indicating that the scale had a good response degree in the same population at different times. Conclusion PROISCD-HY (V1.0), a clinical outcome measurement scale reported by patients with hypertension, has good reliability, validity and reactivity, and can be used to measure the clinical outcome reported by patients with hypertension.
2022, 43(3): 67-73.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220306
Abstract:
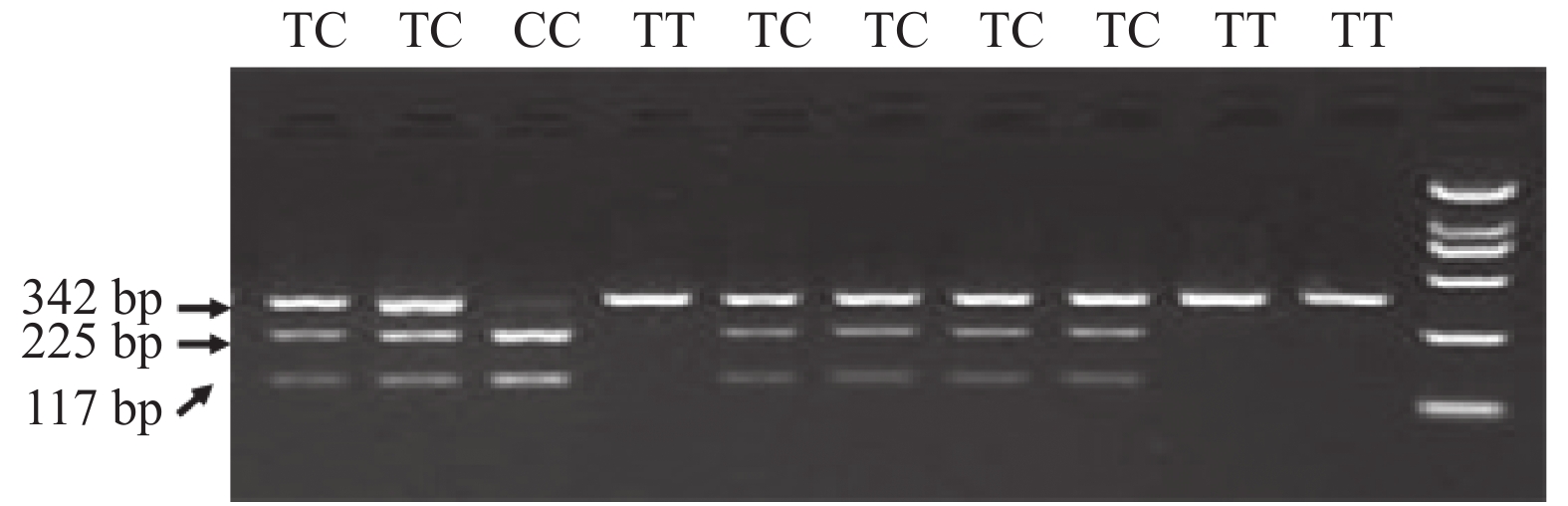
Objective To investigate the relationship between T950C polymorphism in the promoter region of osteoprotegerin (OPG) gene and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) complicated with osteoporosis, and to understand the genetically related susceptibility genes of T2DM complicated with osteoporosis. Methods (1) Using polymerase chain reaction technology, the T2DM without osteoporosis group (group A), the T2DM with osteopenia group (B group), the T2DM with osteoporosis group (C group), the OPG gene T950C group were detected. Genotype, the OPG gene T950C polymorphism in the three groups was analyzed respectively; (2) Gender, body mass index, age, blood pressure, weight, glycated hemoglobin, height, blood lipids, fasting blood glucose, testosterone, estrogen, vitamin D were compared among the three groups. (3) The differences in bone mineral density was compared between different parts of the OPG gene T950C genotype; (4) The independent risk factors of T2DM patients with osteoporosis was learned through logistic regression analysis. Results (1) TC type was the main genotype of OPG gene T950C in T2DM and T2DM patients with osteoporosis; (2) There was no significant difference in the genotype frequency and allele frequency of OPG gene T950C among the three groups (P > 0.05); (3) The weight, age, height, BMI, and BMI of the three groups of patients were compared, the difference was statistically significant ( P < 0.05), and the differences among the groups were statistically significant ( P < 0.05); ( 4) Comparison of the three genotypes of the OPG gene T950C, there was no difference in the bone mineral density of each part ( P > 0.05); (5) Regression analysis showed that age and smoking entered the regression equation, but the genotype of the OPGOPG gene T950C did not enter regression equation. Conclusions (1) TC type is the main genotype of OPG gene T950C in T2DM and T2DM patients with osteoporosis; (2) The genotype of OPG gene T950C may not be a susceptibility gene for T2DM and T2DM combined with osteoporosis; (3) Smoking and age are independent risk factors of T2DM combined with osteoporosis.
2022, 43(3): 74-79.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220322
Abstract:
Objective To explore the value of VI-RADS scoring system in predicting preoperative for invasive bladder cancer. Methods The MRI data of 320 cases of bladder cancer were retrospectively analyzed by the VI-RADS scoring system, T2WI, DWI and DCE-MRI were scored separately, and finally VI-RADS score was obtained, the samples were divided into NMIBC group and MIBC group according to the pathological results, and the VI-RADS scores were analyzed for correlation with pathological stages and different groups. Results There were 187 cases of muscular invasive bladder cancer and 133 cases of invasive bladder cancer. There was a positive correlation between VI-RADS score and pathological results(r = 0.841, P < 0.001). The sensitivity and specificity of VI-RADS > 3.5 for muscle invasion of bladder cancer were 88.4% and 97.1%, respectively. Conclusion The VI-RADS scoring system has better sensitivity and specificity in predicting the degree of bladder cancer invasion, and has a good value in guiding clinical treatment.
2022, 43(3): 80-85.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220311
Abstract:
Objective To observe the clinical efficacy of external radiative shock wave combined with sodium hyaluronate injection in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis (KOA). Methods Sixty-two patients with KOA be divided into observation group and control group randomly, with 31 cases in each group. The observation group included 13 males and 18 females, the mean age was (62.35±9.70) years old, and the course of disease was (3.06±1.49) years. There were 16 males and 15 females in the control group, the mean age was (60.87±1.56) years old, and the course of disease was (2.74±1.53) years. The Extracorporeal Shockwave therapy (ESWT) was given firstly , then the Intra-articular injection of hyaluronic acid (HA) was injected 2 days later in the observation group. The control group was treated with HA only 1 week. Both of the groups were treated once a week for 5 weeks. The Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) and Western Ontario and McMaster University Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) were used to evaluate the difference in efficacy between the two groups, at the time of before the treatment, 1 week after the treatment and 3 months after that.KOA patients were divided into observation group Ⅱ and control group Ⅱ according to Kellgren-Lawrence grading (Ⅱ, Ⅲ). VAS score and WOMAC score of observation group Ⅲ and control group Ⅲ were compared before and after treatment, respectively. Results The VAS score and WOMAC score in both group were significantly lower than those before at the time of 1 week and 3 months after treatment (P < 0.05), while 1 week after treatment and 3 months after treatment the VAS and WOMAC scores in the observation group were lower than those in the control group (P < 0.05). The WOMAC score of the observation group was further decreased after 3 months than 1 week after treatment (P < 0.05). In kellgren-Lawrence class Ⅱ and Ⅲ patients, the scores of observation group and control group decreased after treatment compared with before treatment (P < 0.05), VAS of observation group decreased 1 week after treatment in class Ⅱ group, but the difference was not statistically significant, WOMAC score decreased (P < 0.05). VAS and WOMAC scores of kellgren-Lawrence grade Ⅲ patients were lower than those of control group 3 months after treatment (P < 0.05), VAS and WOMAC scores of Kellgren-Lawrence grade Ⅲ patients were lower than those of control group 1 week and 3 months after treatment (P < 0.05). Conclusion The ESWT combined with HA can significantly reduce the joint pain and improve knee joint mobility more effectively than HA alone in the treatment of KOA.
2022, 43(3): 86-93.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220301
Abstract:
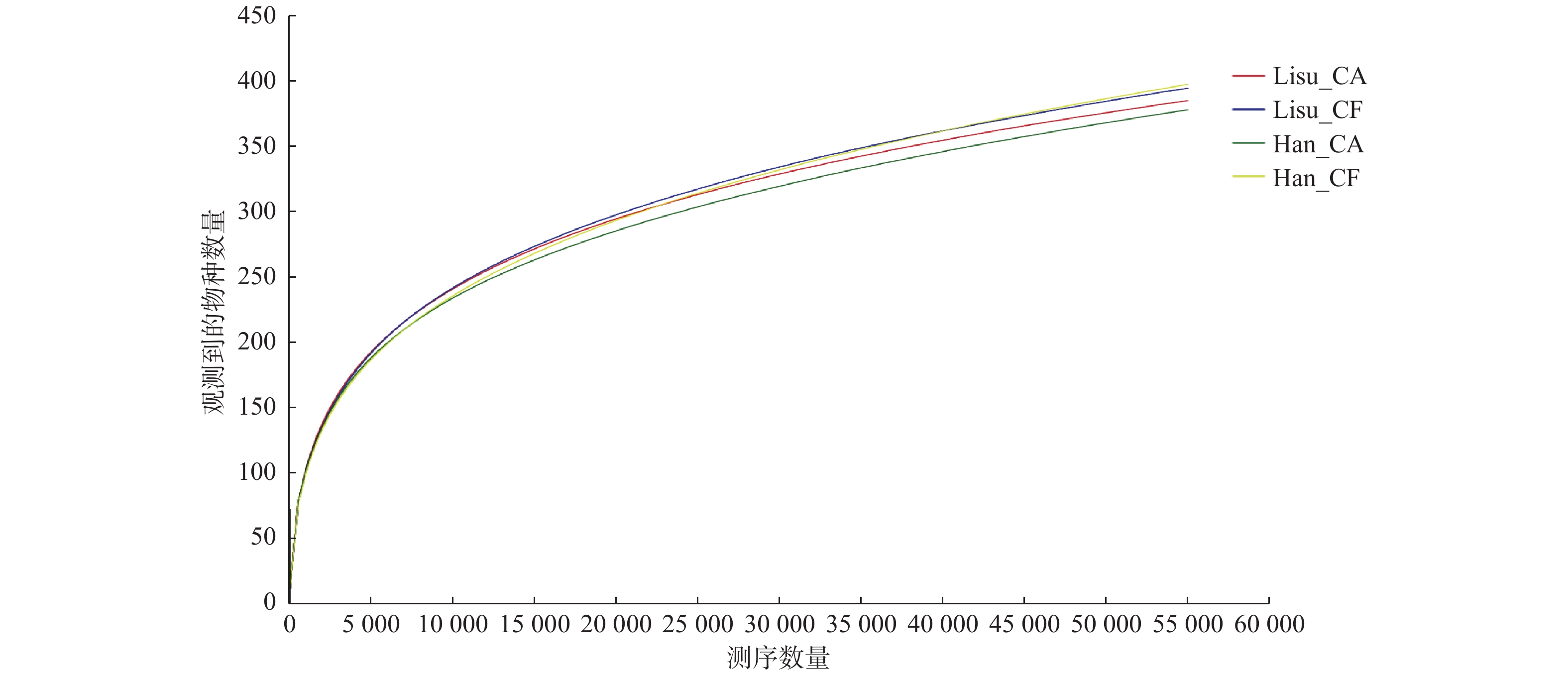
Objective To study the salivary predominant bacteria in 5-year-old Lisu children with and without dental caries in Yunnan Province and to analyze the differences with local Han children. Methods 20 Lisu children with high caries (dmfs≥6) and 20 children without caries (dmfs = 0)were selected from Nujiang Prefecture of Yunnan Province. Local Han children were also selected with the same inclusion criteria as comparison. Saliva samples were collected. The 16SrRNA V4 hyper variable region was sequenced using illumina Hisequencing platform. The community structure and diversity of microorganisms were analyzed using Mothur software. Results A total of 3965 oral microbial species annotations (Operational taxonomic unit , OTU) were obtained based on 97% similarity clustering in Lisu and Han Chinese children with and without dental caries, belonging to 16 phyla, 23 classes, 57 orders, 102 families and 202 genera. The differences in Alpha diversity and richness indices among the four groups were not statistically significant (P > 0.05), and the differences in principal co-ordinates analysis (PCoA analysis) among the four groups were not statistically significant ( P > 0.05). The abundance of Streptococcus in the Lisu caries-active group is higher than that of the caries-free group, while the abundance of Haemophilus, Escherichia-Shigella, Fusobacterium, Capnocytophaga, Megasphaera is lower than that of the caries-free group. For caries-active children, the abundance of Gemella was higher in Lisu than in Han, and the abundance of Escherichia-Shigella was lower in Lisu than in Han. Conclusions The diversity, richness and composition of salivary microbial communities were similar among the Lisu and Han children with and without dental caries in Yunnan. However, the dental caries bio-markers of the two ethnic minority were different. The reasons underline the findings need further invesitigation.
2022, 43(3): 94-97.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220326
Abstract:
Objective To analyze the detection of human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) DNA in different types of samples from pregnant women and infants. Methods From May 2021 to October, a total of 2403 clinical samples were collected. Fluorescence quantitative PCR to test the HCMV-DNA, and we analyzed positive rate of HCMV-DNA in different samples sources and types retrospectively. Results Among different types of samples, the positive rate of HCMV-DNA in maternal milk was 31.70%, and that in urine was 0.85%. The positive rate of maternal milk and urine samples increased with the increase of age, and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.001). Among 221 urine samples from infants as well as their maternal milk samples, the positive rate of maternal milk samples was higher than that of urine or serum. When the maternal milk samples were negative, 0.58% of the children’ s urine samples were positive; When the maternal milk samples were positive, the children’ s urine were negative. Conclusions The positive rate of HCMV-DNA in maternal milk samples is significantly higher than that in other types of samples. Therefore, for pregnant women or infants with suspected infected HCMV, it’ s recommended to collect milk samples for the test. However, HCMV-DNA detected in maternal milk can’ t fully reflect the detection of infant body fluid samples. As age goes on, the positive rate of infant urine will increase. It is necessary to collect fluid samples at different periods for the test, and analyze comprehensively the test results.
2022, 43(3): 98-102.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220308
Abstract:
Objective To compare the effects of hydromorphone and sufentanil on early postoperative cognitive function in patients with colorectal cancer. Methods Eighty-five patients with selective radical resection of colorectal cancerr (including laparoscopic surgery or open surgery) were randomly divided into hydromorphone group of 44 (H group) and sufentanil group of 41 (S group) by random number table method. Postoperative H group was treated with hydromorphone for intravenous analgesia. Group S was treated with sufentanil for intravenous analgesia. Visual analogue score (VAS) was recorded at 6, 12, 24, 48 h after surgery. The adverse reactions such as nausea, vomiting, skin itching, respiratory inhibition, hypotension and dizziness occurred within 48 hours after the operation were observed. Ramsay sedation score was recorded 24 hours after surgery. Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) scores were recorded at 1, 2, 3 d after the operation were recorded. Results There was no significant difference in postoperative VAS scores between the two groups (P > 0.05). There was no statistically significant difference in the incidence of adverse reactions between the two groups within 48 hours after surgery (P > 0.05). There was no statistically significant difference in Ramsay sedation score at 24h after surgery between the two groups (P > 0.05). There was a statistical difference in the postoperative MMSE score between the two groups (P < 0.05). The incidence of postoperative cognitive dysfunction (POCD) in group H was 15.9% (7/44), and group S 39% (16/41). There was a statistical difference in the incidence of POCD between the two groups (P < 0.05). The grouping factor was an independent one affecting the occurrence of POCD (OR = 3.307, P < 0.05). Conclusions Hydromorphone and sufentanil are both safe and effective for intravenous controlled analgesia in patients after radical resection of colorectal cancer with no difference in analgesia. Compared with sufentanil, hydromorphone can significantly improve the cognitive impairment of patients after radical colon cancer.
2022, 43(3): 103-107.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220323
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the effect of parent administered physical therapy in the preterm period on motor performance in infants. Methods This study included 153 infants, 97 preterm infants and 56 term infants (term control group). The preterm infants were born at gestational age 32- < 37 weeks and randomized to an intervention (n = 47) or a preterm control (n = 50) group. Parents, supervised by a physical therapist, conducted the intervention for 3 months. The control group received usual care. Results At the age of 1 year, children in the preterm intervention group had significantly higher gross motor and fine motor scores than those in the preterm control group [Gross motor, preterm intervention group (91.9±9.4), preterm control group (86.6±9.6); Fine motor, preterm intervention group (87.9±9.3), preterm control group (83.9±10.0); P < 0.05]. Conclusion It is feasible for parents to conduct early physical intervention in the family and effective for the motor development of premature infants at the age of one year.
2022, 43(3): 108-112.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220325
Abstract:
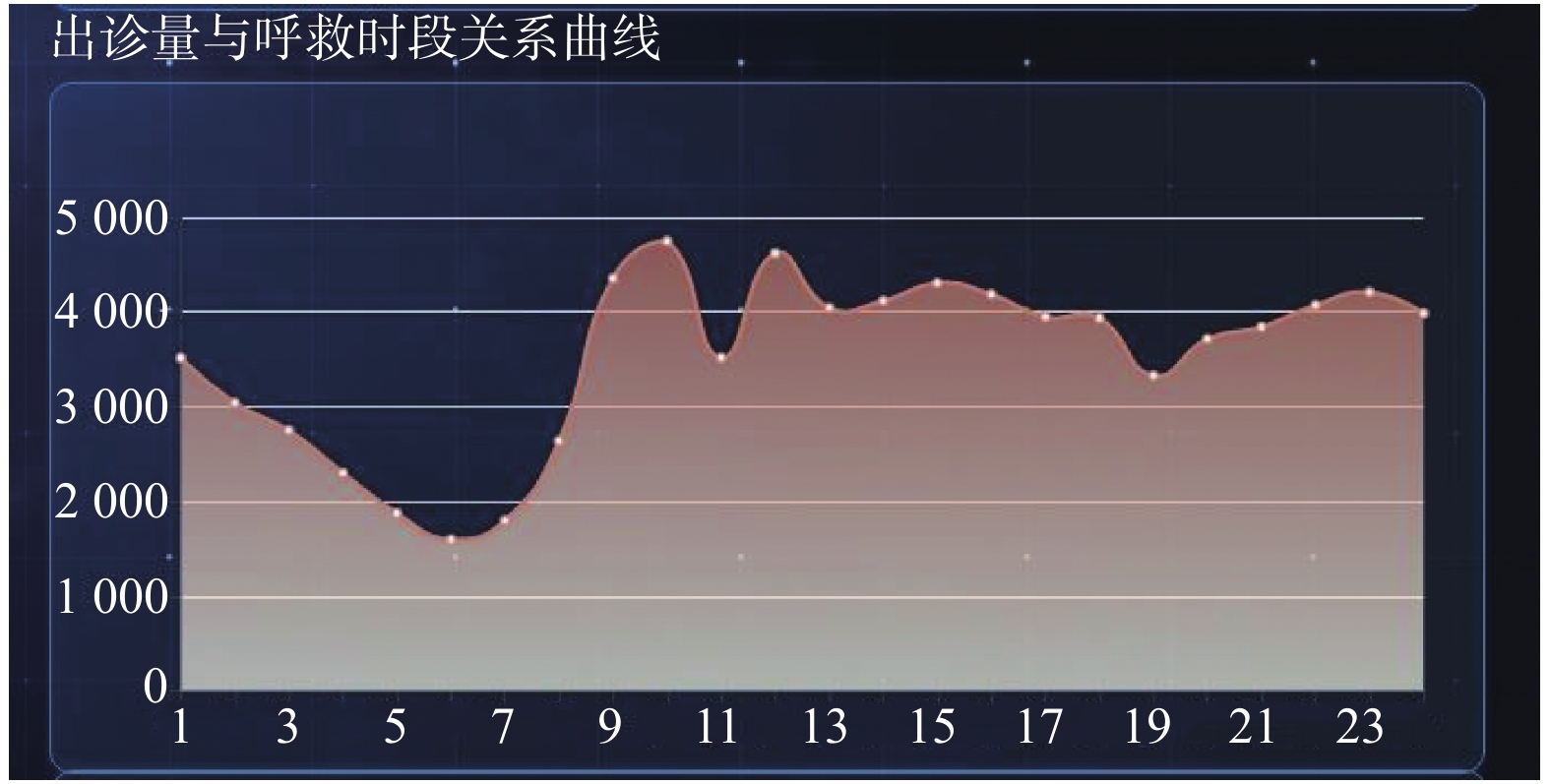
Objective To understand and analyze the epidemiological characteristics of pre-hospital emergency patients in Kunming, so as to provide basis for optimizing the allocation of pre-hospital emergency resources. Methods Data of patients in Yunnan Emergency Center from January to December 2020 were collected, and an investigation was conducted. Results Among 80169 pre-hospital emergency patients, 47723 (59.5%) were male and 32446 (40.5%) were female. The age distribution ranged from 0.2 to 110 years, and most of them were 14 to 44 years, accounting for 28313 cases (35.3%). The top three disease spectrums were injury and poisoning diseases (28786 cases, 35.9%), symptoms and signs diseases (25, 618 cases, 32.0%) and circulatory system diseases (8129 cases, 10.1%). The subgroup analysis of diseases with symptoms and signs showed that the top five diseases were neurological symptoms, fever and fatigue symptoms that could not be classified, death symptoms, digestive system and respiratory system symptoms. The number of patients was 22, 571 in autumn (28.2%), followed by 21, 129 in summer (26.4%), and 17, 747 in spring (22.1%). In a day, most calls were made from 9:00 to11:00 and 12:00 to13:00, and the high incidence of different diseases was different in different months. Conclusions In Kunming, there were more males than females in pre-hospital emergency patients, and the ages of patients were mainly 14-44 years old. The disease spectrum mainly includes injury and poisoning diseases, symptoms and signs diseases and circulatory system diseases. Autumn is the peak season of outpatient visits, and the peak of daily outpatient visits mainly concentrates on 9:00-11:00 a.m. and 12:00-13:00 noon.
2022, 43(3): 113-122.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220321
Abstract:
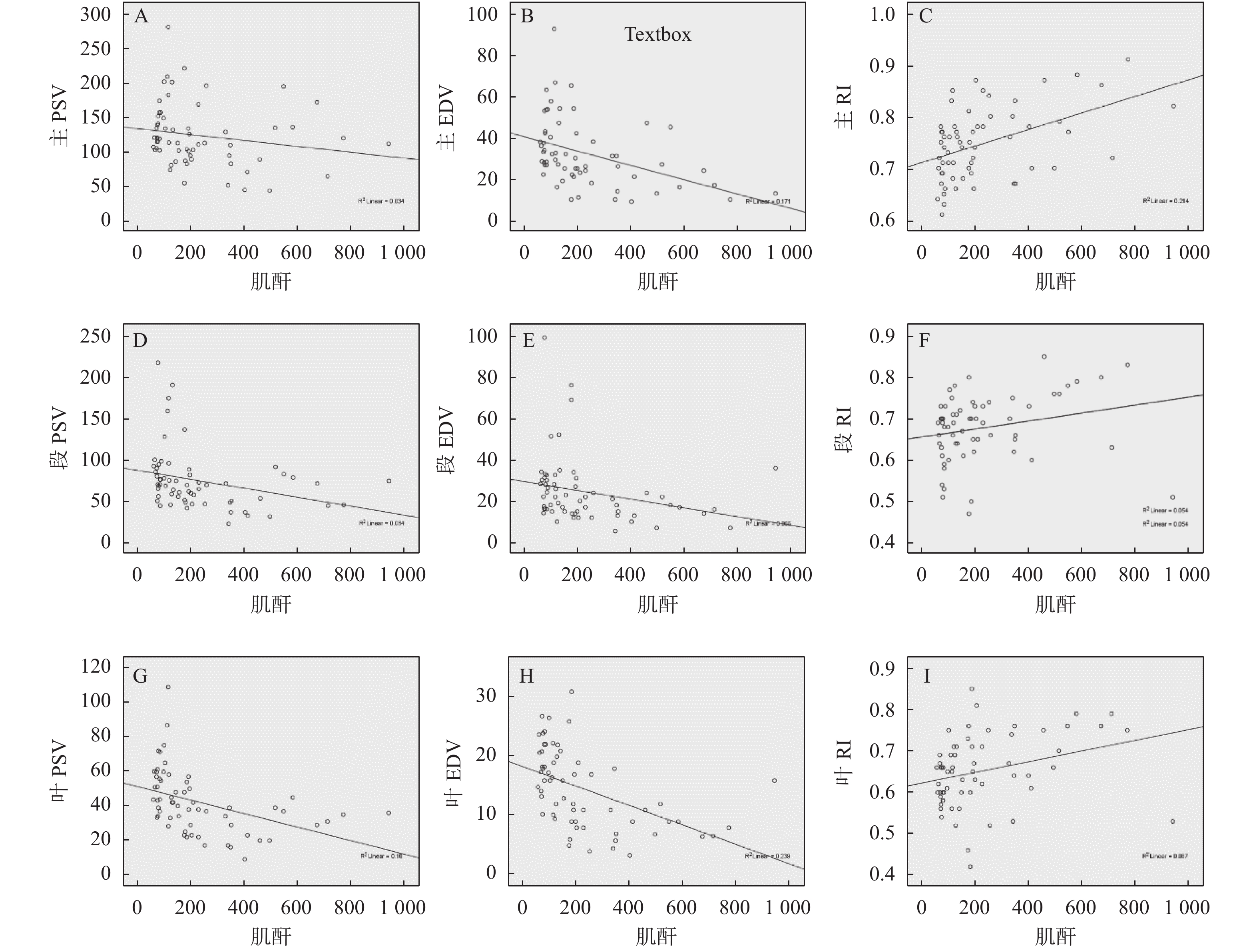
Objective To evaluate the value of multimodal ultrasound in monitoring renal function and postoperative complications of DBD transplantation. Methods 67 cases of brain dead organ donor kidney transplantation (DBD) in Ganmei Hospital Affiliated to Kunming Medical University from July 2019 to June 2021 were selected to evaluate the transplanted kidney by multimodal ultrasound. The transplanted kidneys were divided into normal function group and abnormal group according to blood creatinine. The abnormal group was divided into acute rejection group, chronic rejection group, viral nephropathy group, fibrosis group and drug injury group according to puncture pathology. The correlation between arterial peak velocity (PSV), diastolic velocity (EDV), resistance index (RI) and serum creatinine was analyzed. To compare the diagnostic efficacy of contrast-enhanced ultrasound with pathology or DSA in renal transplantation complications, and to analyze the correlation between contrast-enhanced ultrasound parameters and renal transplantation function. Rank sum test was used to compare the young’ s modulus between abnormal group and normal group. The ROC curve was drawn, and the young’ s modulus at the highest yoden index was used as the cut-off value to distinguish normal and abnormal transplanted kidneys, and the corresponding sensitivity and specificity were calculated. Results The correlation between blood flow parameters of transplanted kidney and serum creatinine was general, and the correlation coefficients were less than 0.5. The arrival time and peak time of chronic rejection group (8 cases) were significantly longer than those of normal group (10 cases), and the difference was statistically significant. Two cases of pseudoaneurysm, two cases of graft ischemia and one case of graft venous thrombosis were diagnosed by contrast-enhanced ultrasonography, which were confirmed by pathology or DSA. According to the serum creatinine value, 62 cases of transplanted kidney were divided into 22 cases in the normal group and 40 cases in the abnormal group (5 cases in the acute rejection group, 11 cases in the chronic rejection group, 10 cases in the viral nephropathy group, 10 cases in the fibrosis group and 4 cases in the drug injury group). The RI of renal aorta in acute rejection group was higher than that in normal group, the RI of interlobar artery in chronic rejection group was higher than that in normal group, the EDV of main and interlobar artery was lower than that in normal group, the PSV of interlobar artery was lower than that in normal group, and the main PSV of fibrosis group was lower than that in normal group. The above differences were statistically significant (P < 0.05); There was no significant difference in parameters between viral nephropathy, drug injury group and normal group (P > 0.05). The young’ s modulus of ste in abnormal group and normal group were 22.550 (17.1, 28.1) and 13.370 (11.8, 15.9) kPa, respectively (P < 0.01). When the cut-off value = 17.31 kpa, the sensitivity and specificity of shear wave elastography in the diagnosis of renal allograft lesions were 75% and 91%. The young’ s modulus of STQ in abnormal group and normal group were 21.760 (16.4, 33.4) and 13.870 (10.5, 16.8) kPa, respectively, with significant difference (P < 0.01). When the cut-off value = 18.16 kpa, the sensitivity and specificity of shear wave elastography in the diagnosis of renal allograft lesions were 70% and 91%. The young’ s modulus of ste in acute rejection group, chronic rejection group, viral nephropathy group, fibrosis group and drug injury group were 13.370 (11.8, 15.9), 15.550 (13.4, 16.6), 26.870 (21.6, 38.6), 26.660 (19.5, 34.2), 16.310 (13.2, 23.1) and 27.690 (24.6, 29.2) respectively; The young’ s modulus values of STQ were 13.870 (10.5, 16.8), 16.330 (15.5, 17.4), 23.780 (19.2, 40.7), 22.760 (19.9, 36.0), 16.540 (14.5, 26.0) and 33.355 (29.1, 35.4) respectively. There was significant difference among the groups (P < 0.05). The chronic rejection group, viral nephropathy group and drug injury group were significantly higher than those in the normal group (P < 0.05), but there was no significant difference between the acute rejection group, fibrosis group and the normal group (P > 0.05). The elastic value of viral nephropathy was higher than that of acute rejection, ste: 26.660 (19.5, 34.2) vs 15 550 (13.4, 16.6)kPa (P<0.01), STQ: 22.760 (19.9, 36.0)vs16. 330 (15.5, 17.4) kPa (P < 0.01), the difference was statistically significant. Conclusions The blood flow parameters of transplanted kidney can early evaluate the function of transplanted kidney, and have guiding significance for the differentiation of normal, acute and chronic rejection and viral nephropathy. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound has guiding significance in the differentiation of renal transplant complications. Elastography can noninvasively evaluate the hardness of transplanted kidney, and has a certain clinical value in the timely detection of transplanted kidney complications and differential diagnosis.
2022, 43(3): 123-127.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220309
Abstract:
Objective To analyze the changes of intestinal flora in children with functional constipation (FC) and the clinical significance of non-pharmacological basic treatment. Methods A total of 30 children with FC were selected from the outpatient department of the Children's Hospital affiliated to Kunming Medical University between September 2019-October 2021, and 30 health children were selected as control group. The children with FC were given basic treatment that including dietary structure adjustment, regular defecation training and appropriate exercise.The fecal samples were collected respectively in the pre-treatment group and post-treatment group from the children with FC and from the healthy children. The contents of intestinal flora in the stools of children in each group were measured by the MiNi8 plus fluorescence quantitative PCR instrument from the Kunming Hehe Medical Laboratory. In addition, the relief of constipation symptoms after basic treatment in children with FC was observed. Results The content of lactobacillus and bifidobacterium in children with FC was significantly lower than that in control group , and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.01). The content of lactobacillus in the post-treatment group was significantly higher than that in the pre-treatment group, and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.01). The scores of constipation symptoms in children with FC after basic treatment were lower than those in pre-treatment group, and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.01). Conclusions The children with FC will have intestinal flora disorder. After basic treatment such as dietary structure adjustment and lifestyle improvement, the intestinal flora disorder and constipation symptoms can be improved.
2022, 43(3): 128-134.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220316
Abstract:
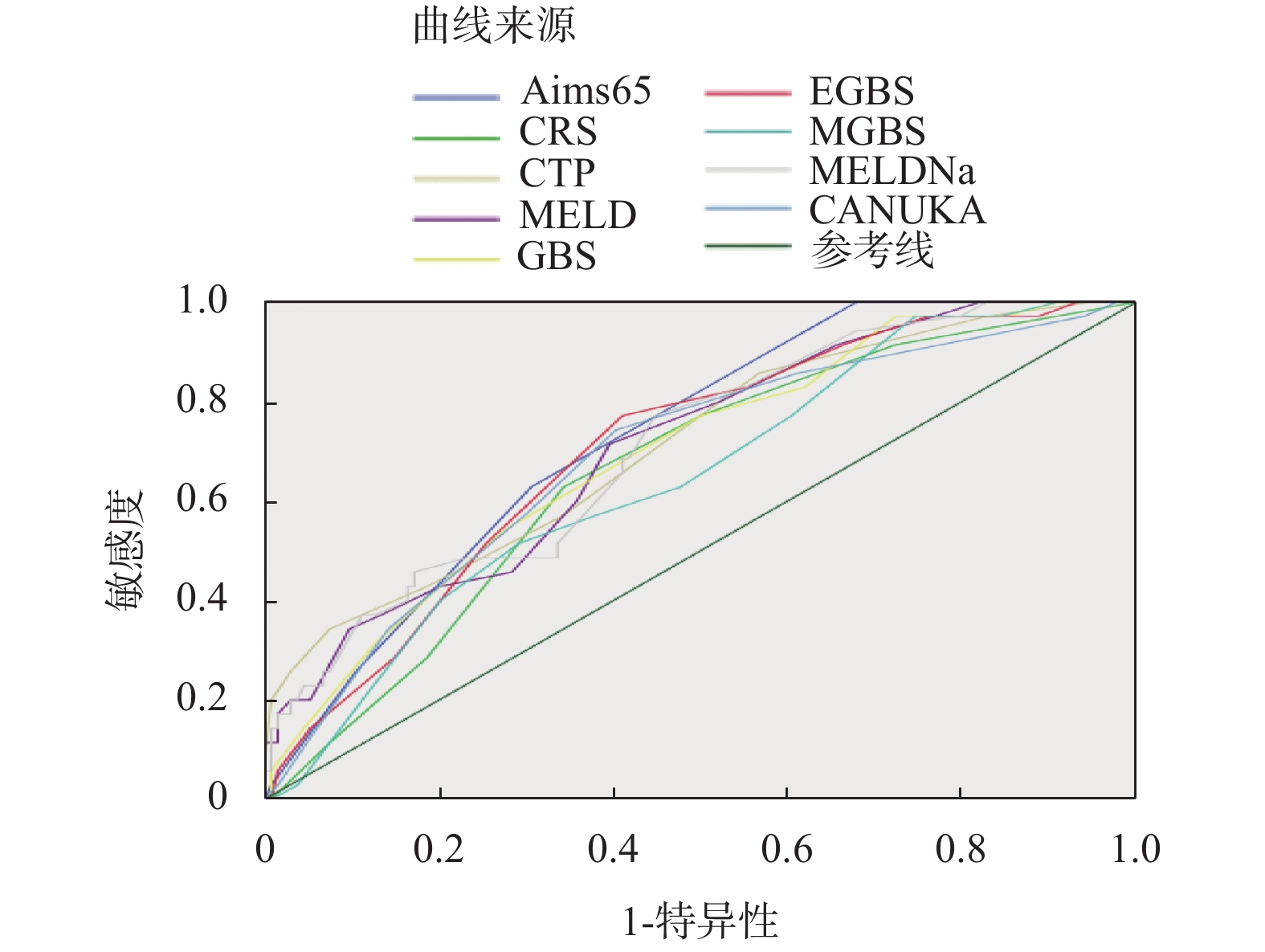
Objective To compare the values of AIMS65, GBS, MGBS, EGBS, CRS, CANUKA, Child-Turcotte-Pugh (CTP), MELD, and MELD-Na scoring systems in the evaluation of the prognosis of patients with liver cirrhosis and EGVB, and explore the factors affecting the poor prognosis of patients with liver cirrhosis and EGVB. Methods A total of 169 patients diagnosed with liver cirrhosis and EGVB were divided into a good prognosis group and a poor prognosis group according to whether the patients had rebleeding or death in the hospital. The scores of each model at the time of admission of each patient were calculated, and the clinical characteristics of the two groups of patients were compared. Results There were 35 cases in the poor prognosis group and 134 cases in the good prognosis group. The scores of the poor prognosis group were higher than those of the good prognosis group. The AIMS65 score was the best in predicting whether the patient had a poor prognosis, and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). The HB and ALB in the good prognosis group were higher than those in the poor prognosis group, and the PT and INR were lower than those in the poor prognosis group. The difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). Multivariate logistic regression analysis suggested that ALB may be an independent protection factor for poor prognosis in patients with liver cirrhosis and EDVB. Conclusion AIMS65 is the best scoring system for prognostic evaluation of patients with liver cirrhosis and esophageal varices bleeding; ALB may be an independent protective factor for the poor prognosis of patients with liver cirrhosis and esophageal and gastric varices bleeding.
2022, 43(3): 135-141.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220304
Abstract:
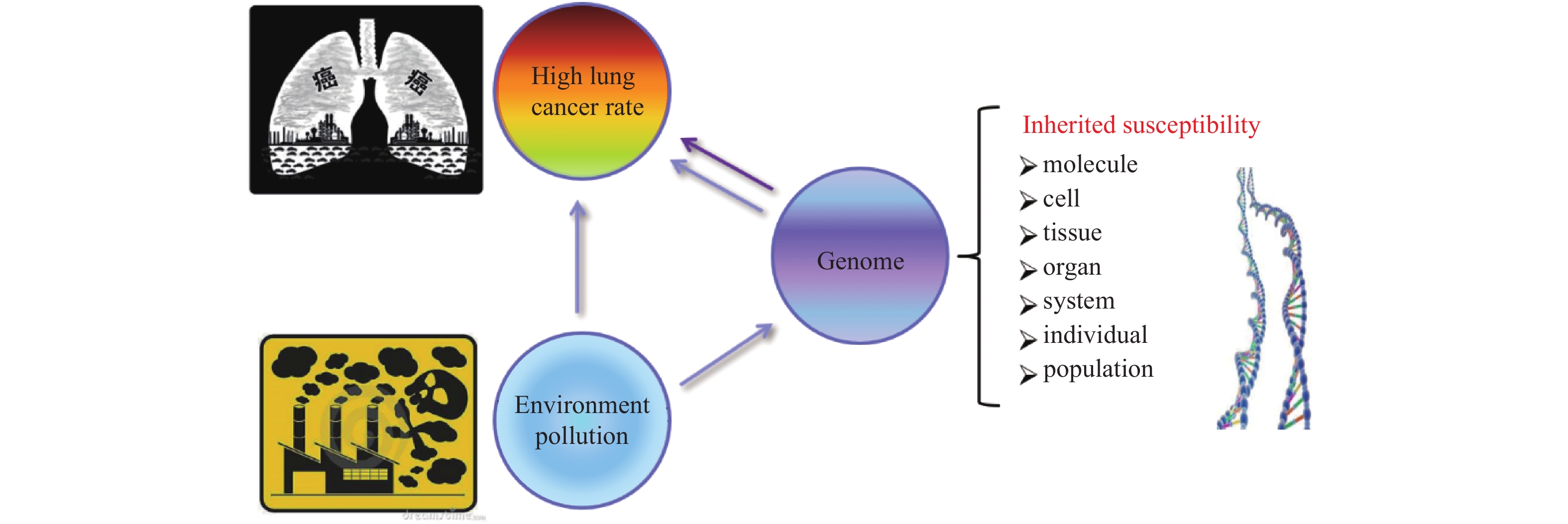
The incidence of lung cancer in Xuanwei area of Yunnan Province ranks first in China, which is a typical air pollution related lung cancer. In recent years, Xuanwei lung cancer incidence rate continues to grow rapidly, showing a clear phenomenon of family aggregation. The incidence of lung cancer in the Xuanwei area is earlier than that of adenocarcinoma and multiple primary lung cancer. Hypertension, diabetes and other cancers are common. The gene mutation spectrum and genetic background of family lung cancer patients are unique. Xuanwei family lung cancer is an ideal object to study the environment, genetics and occurrence of lung cancer. This paper reviews the research progress of family lung cancer in Xuanwei area of Yunnan Province.
The incidence of lung cancer in Xuanwei area of Yunnan Province ranks first in China, which is a typical air pollution related lung cancer. In recent years, Xuanwei lung cancer incidence rate continues to grow rapidly, showing a clear phenomenon of family aggregation. The incidence of lung cancer in the Xuanwei area is earlier than that of adenocarcinoma and multiple primary lung cancer. Hypertension, diabetes and other cancers are common. The gene mutation spectrum and genetic background of family lung cancer patients are unique. Xuanwei family lung cancer is an ideal object to study the environment, genetics and occurrence of lung cancer. This paper reviews the research progress of family lung cancer in Xuanwei area of Yunnan Province.
2022, 43(3): 142-147.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220324
Abstract:
With the development of medical diagnostic technology, the detection rate of adrenal tumor is increasing year by year. As a new technology, radiomics can mine, predict and analyze the deep-seated data which is difficult for human eyes to recognize. It has been widely concerned in the field of oncology. This article mainly introduces the research progress of radiomics in the diagnosis and treatment of adrenal tumors, including the adrenal tumor diagnosis and differential diagnosis, clinical decision-making and risk assessment, prognosis prediction and forecasting tumor biological behavior and so on. Finally, the problems existing in radiomics at the present stage are summarized and the future development direction is prospected, in order to provide reference for clinical diagnosis and treatment.
With the development of medical diagnostic technology, the detection rate of adrenal tumor is increasing year by year. As a new technology, radiomics can mine, predict and analyze the deep-seated data which is difficult for human eyes to recognize. It has been widely concerned in the field of oncology. This article mainly introduces the research progress of radiomics in the diagnosis and treatment of adrenal tumors, including the adrenal tumor diagnosis and differential diagnosis, clinical decision-making and risk assessment, prognosis prediction and forecasting tumor biological behavior and so on. Finally, the problems existing in radiomics at the present stage are summarized and the future development direction is prospected, in order to provide reference for clinical diagnosis and treatment.
2022, 43(3): 148-153.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220314
Abstract:
Objective To evaluate the effect of PBL teaching method on the critical thinking ability of surgical interns majoring in clinical medicine, so as to improve the critical thinking ability of undergraduates majoring in clinical medicine. Methods A total of 190 clinical medicine undergraduate interns who participated in the laboratory practice from March to December 2020 were included in this study. They were randomly divided into control group and experiment pilot. The experimental group received PBL teaching mode, while the control group received traditional teaching mode. Critical thinking ability questionnaire was used to evaluate the change of critical thinking ability before and after intervention. Results After intervention, the total score of critical thinking in the experimental group was higher than that in the control group (P < 0.001), and the experimental group was better than the control group in the four dimensions of analytical ability, critical thinking confidence, curiosity and cognitive maturity ( P < 0.05). After intervention, the surgical operation score of experimental group (91.04±3.51) was significantly higher than that of control group (85.72±3.94) ( P < 0.05). After intervention, the quantitative indexes of course satisfaction of the experimental group were significantly higher than that of the control group ( P < 0.05). Conclusion PBL teaching method can significantly improve the critical thinking ability of clinical general surgery interns
2022, 43(3): 154-159.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220328
Abstract:
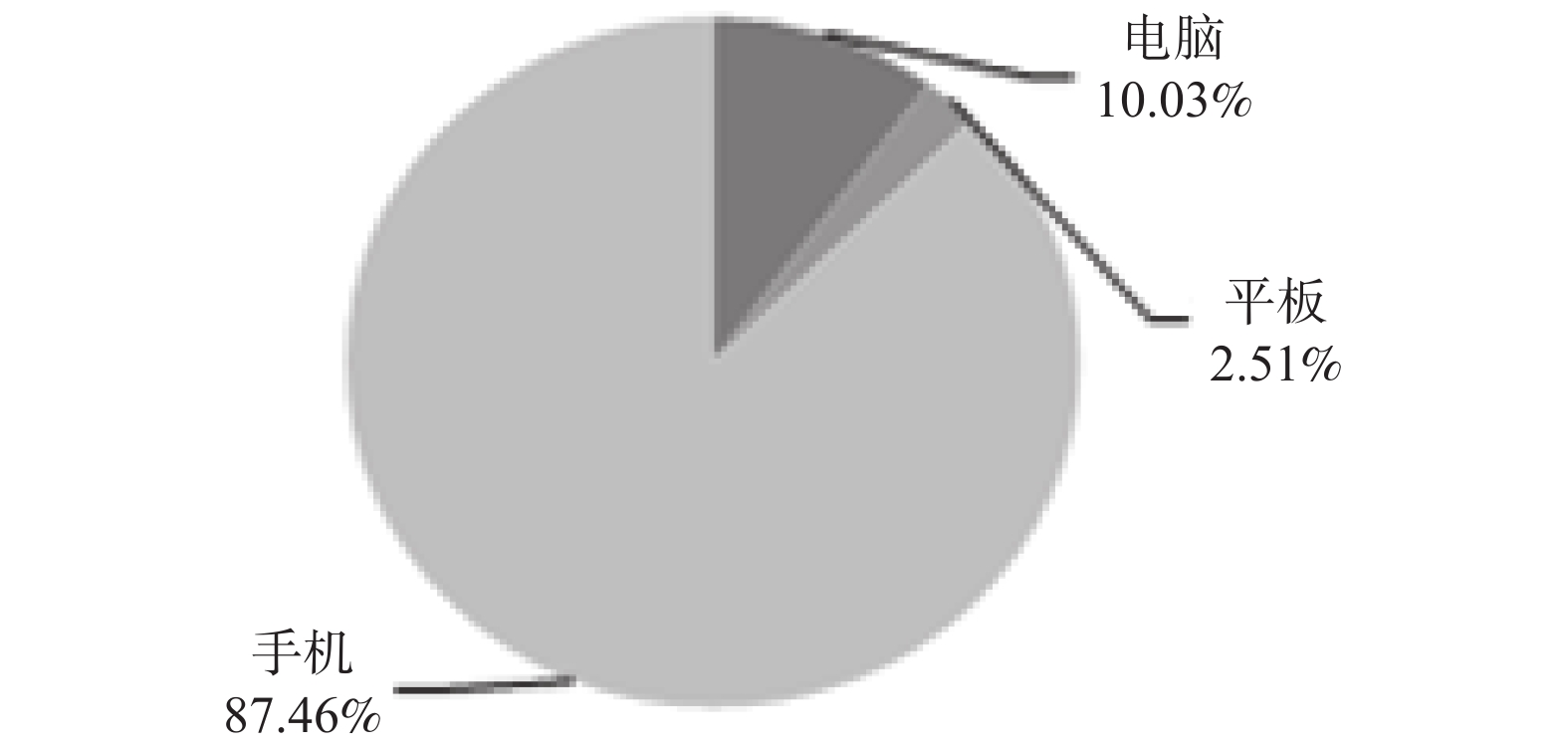
Objective To explore outcome of online learning during the period of Covid-19 pandemic, and provide the theoretical basis for blended teaching methods of online and offline. Methods A total number of 917 undergraduates at a University in Kunming, were randomly selected to the survey. The survey was conducted by “Questionnaire Star”, and utilized multistage stratified cluster sampling method. Moreover, the survey was designed to investigate the factors that may influence the outcome of remote learning, including learning resources, teaching methods, and learning process. Results We found that participants preferred to use mobile phones for remote learning than any other electronic devices. Meanwhile, there was a significant difference between network connection status and learning efficiency (P < 0.05). However, learning efficiency was considered as “average” regardless of teaching methods. The degree of teacher’ s supervision was significantly correlated with learning status ( P < 0.05). Therefore, students’ self discipline, teaching methods, subjective interest, and teacher’ s degree of supervision were the four main factors which may influence virtual learning efficiency. Yet, comparing with the average scores of students on spring semester of 2019 and 2020, there was no significant difference ( P > 0.05). Conclusion It is necessary to consider multiple factors that may affect remote learning efficiency, which may imply that instructors would integrate various of online resources and strengthen the supervision of online teaching in order to improve learning outcomes. Since there was no significant difference between pre-and post pandemic period, it may suggest that intensive learning could help online learning efficiency.
2022, 43(3): 160-165.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220302
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the mental status of the patients in rheumatic immunology department, and evaluate the risk of depression and suicide, so as to identify the patients with depression and high risk of suicide, ensure the safety of the patients. Methods Patients in the Department of Rheumatology of the First Affiliated Hospital of the Wenzhou Medical University from October 2018 to September 2019 were included in the study. All the patients were investigated with the health questionnaire depression symptom cluster scale (PHQ-9) at the time of admission, the depression status and suicide risk were assessed. Results Data of 861 patients were collected. The prevalence of mood disorder, moderate depression and suicide risk were 24.62% , 7.43% and 3.72% respectively. The rate of suicide risk was 2.56% in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), ankylosing spondylitis (AS), sjogren’ s syndrome (SS), rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and metabolic arthritis (MA), and the rate of moderate to severe depression was 3.13%. The incidence of depression in patients with different diseases was significantly different (χ2 = 27.734, P < 0.0001). Fish analysis showed that there was significant difference in the proportion of patients with moderate depression or above (χ2 = 13.187, P < 0.05) . The prevalence of depression was significantly higher in SLE patients than in the other four groups, and the rates of moderate to severe depression and suicide were also higher than in the other groups. Conclusions The prevalence of depression and suicide risk is high in patients with rheumatic diseases, and the incidence of depression is positively correlated with the PHQ-9 score. The application of simple mental state screening by PHQ-9 score bank on admission of nursing staff is helpful to carry out nursing path intervention by grading and classification, might reduce the incidence of patient suicide and medical disputes.
2022, 43(3): 166-170.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220315
Abstract:
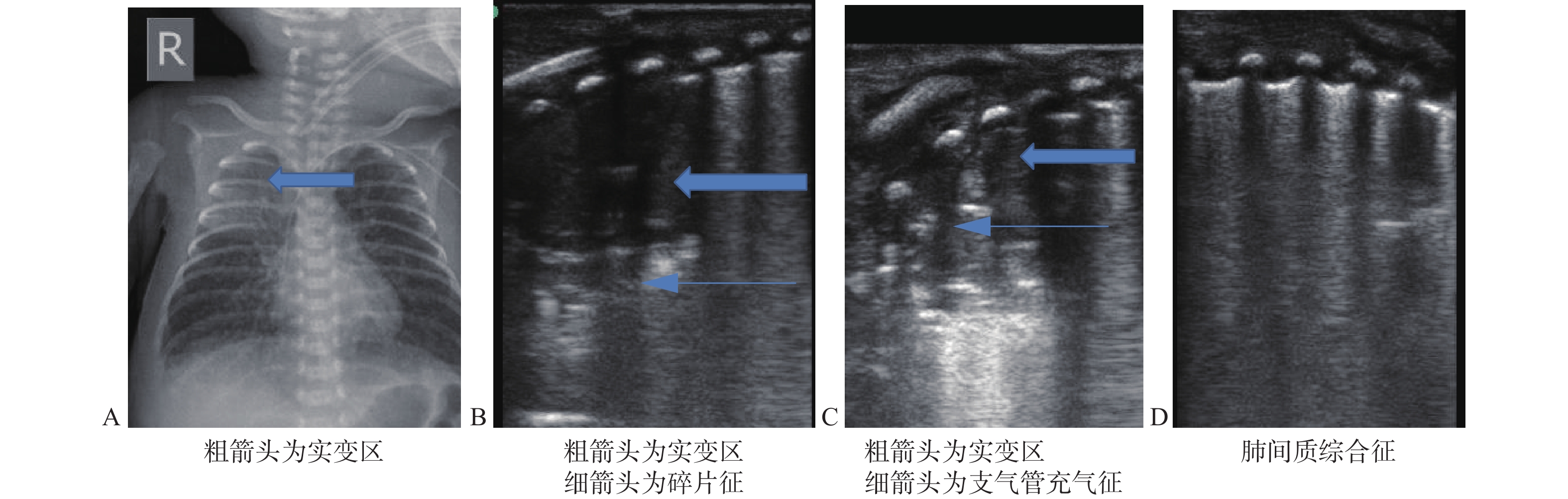
Objective To explore the effect of mechanical vibration of electric toothbrush on neonatal sputum excretion. Methods 120 children with neonatal infectious pneumonia were randomly divided into control group and experimental group. The control group received electric sputum suction nursing according to the conventional method, and the experimental group received electric sputum suction after mechanical vibration with electric toothbrush. The disappearance time of symptoms, the hospital stay and the changes of blood gas analysis indexes and lung ultrasound before and after treatment were compared between the two groups. Results The symptom disappearance time and hospitalization time of children in the electric toothbrush mechanical vibration assisted expectoration group were shorter than those in the control group (P < 0.05). After treatment, the results of blood gas analysis index PaO2 in the experimental group were higher than those in the control group, and PaCO2 was lower than those in the control group (P < 0.05). Dynamic observation of the changes of pulmonary ultrasound images of children in the two groups before and after treatment showed that the time of signs such as the gradual reduction of B line, the recovery of pleural line and a line, and the reduction of consolidation range in the experimental group were significantly less than those in the control group. Conclusion Mechanical vibration before sputum suction for neonatal infectious pneumonia can make sputum discharge more fully, so as to improve the treatment effect, and the operation is simple and is worthy of clinical application.


 Email
Email RSS
RSS