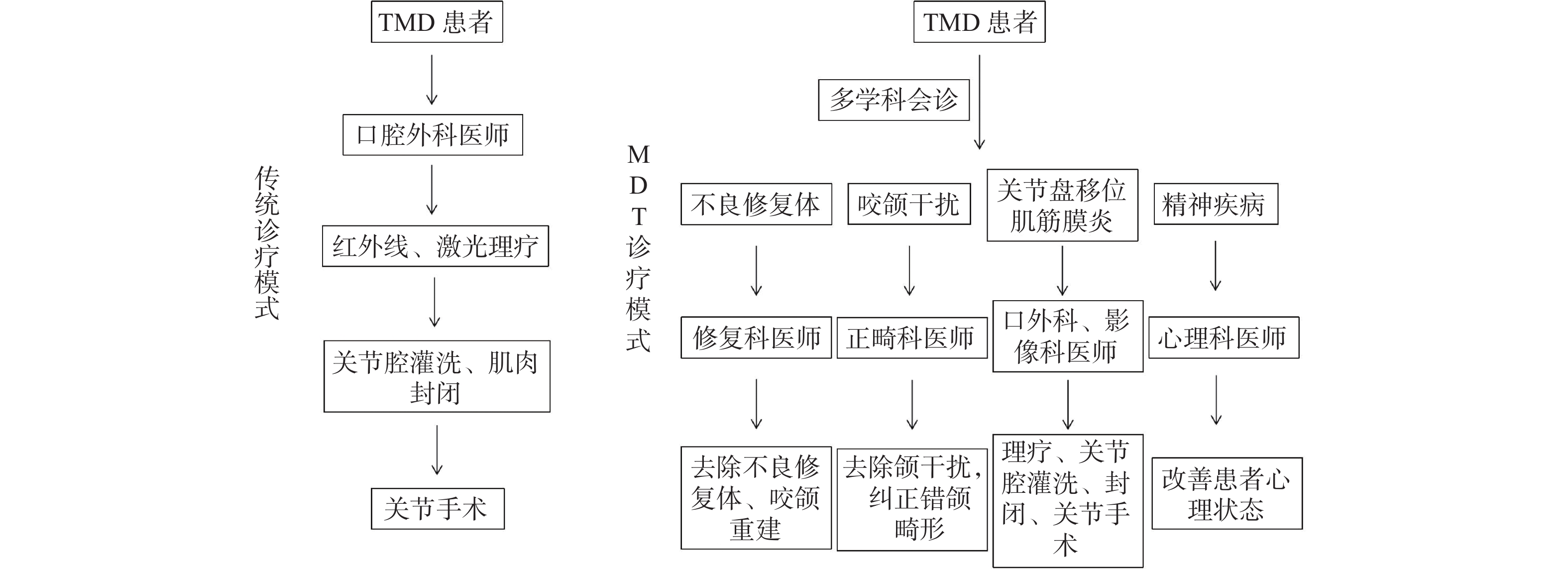
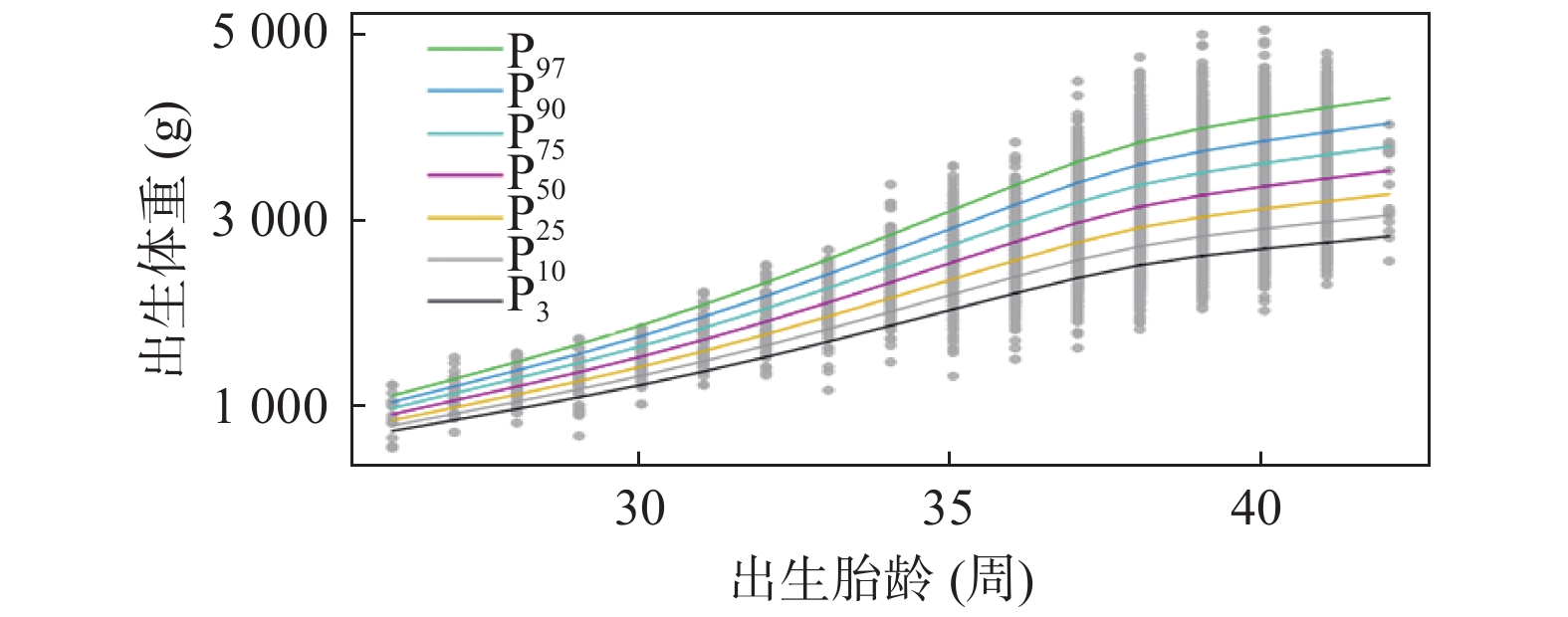
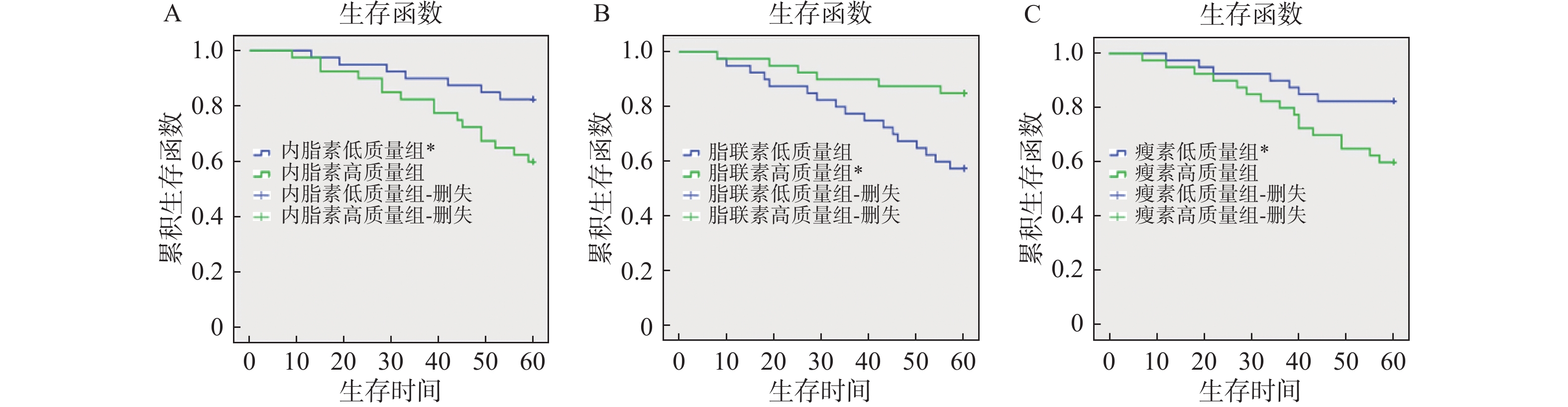
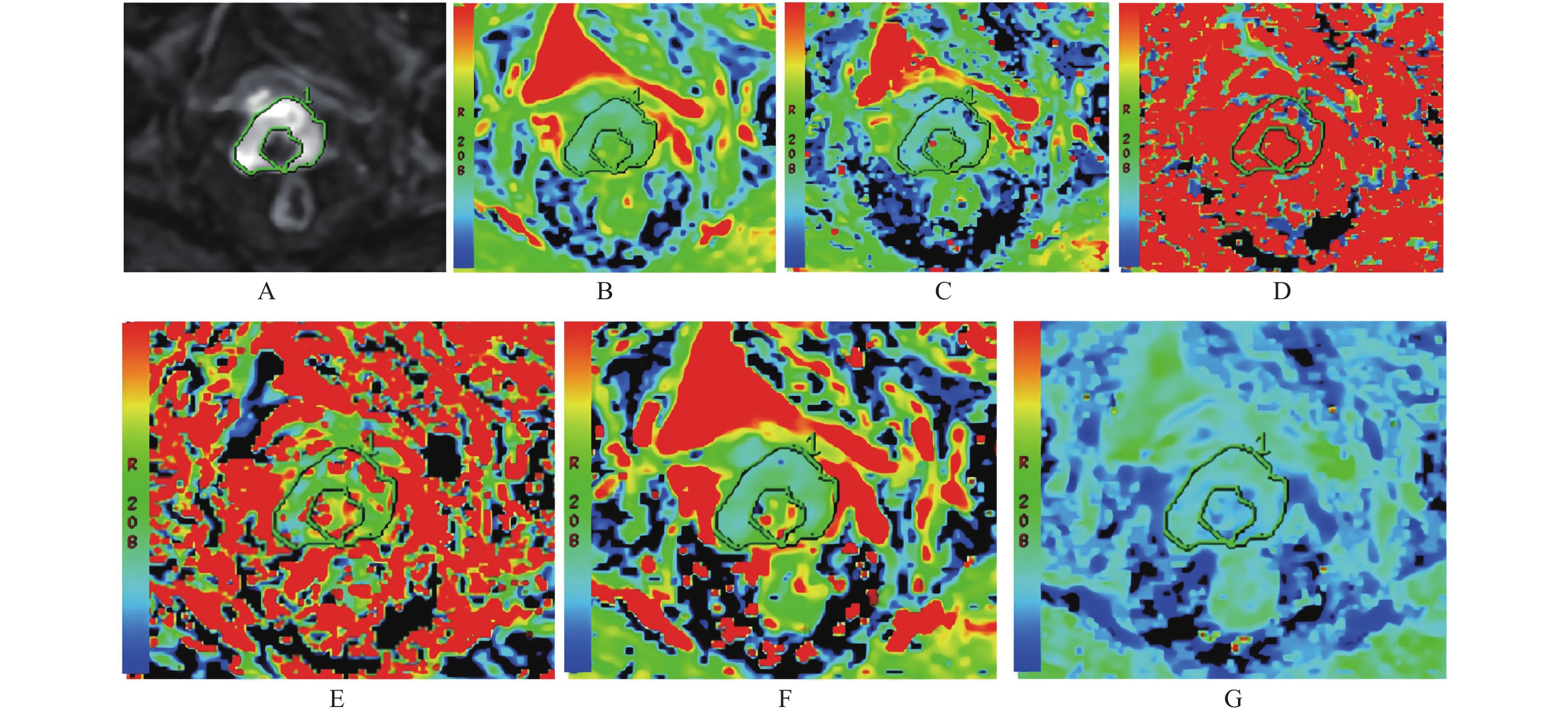
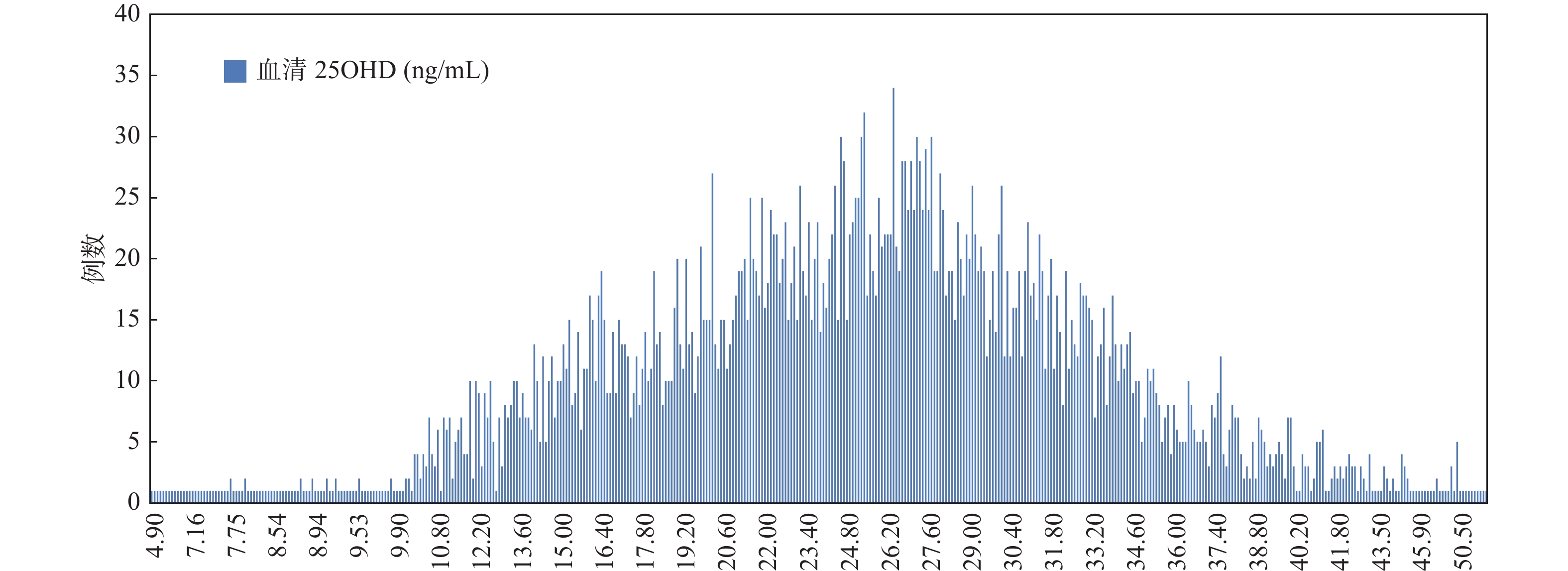
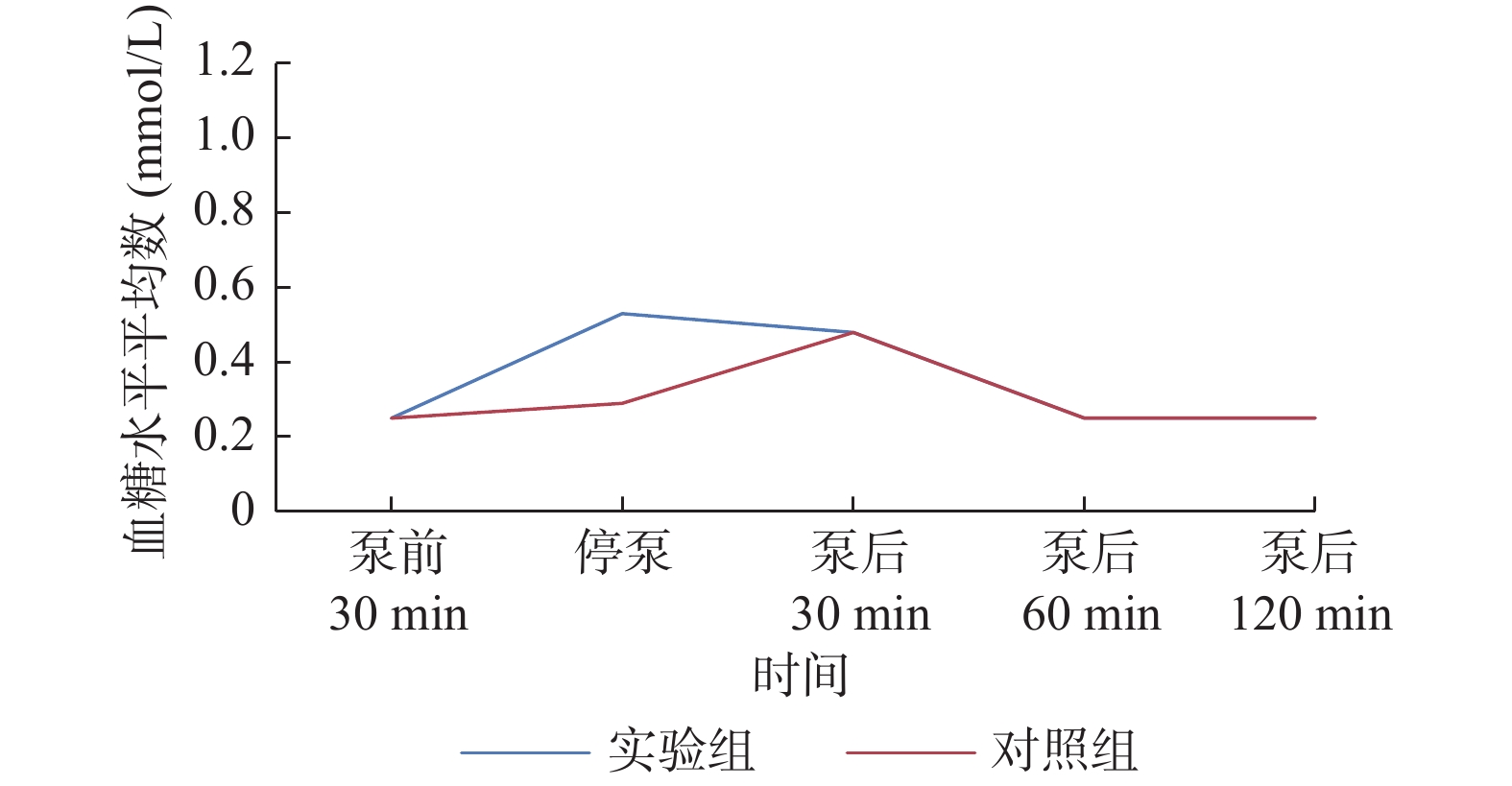
2022 Vol. 43, No. 4
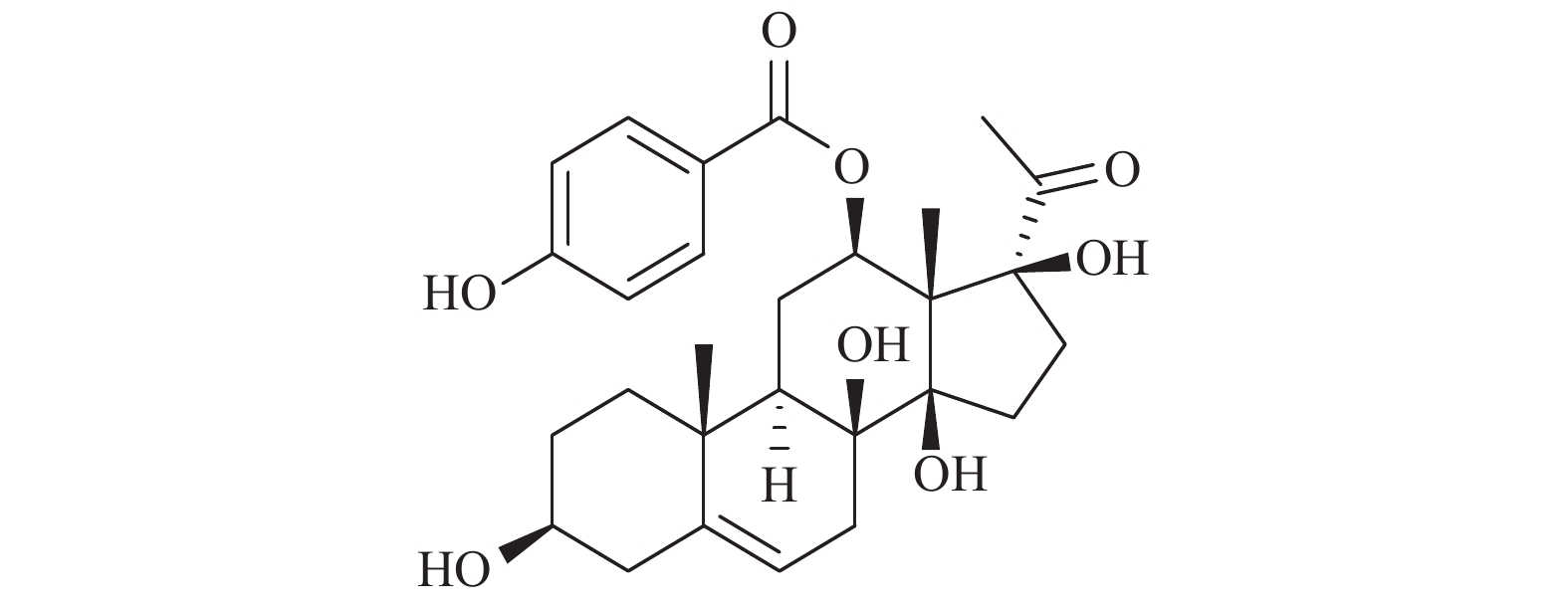
Scutellarin, chemically named 4, 5, 6-trihydroxyflavone-7-glucosidic acid, is the main active ingredient of the traditional Chinese medicine Breviscapus. Clinically, it has been used in the treatment of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases because of its extremely wide biological activities. In recent years, cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases characterized by high morbidity and mortality have become common and frequently-occurring diseases among middle-aged and elderly people. With the change of people’ s diet, unhealthy life style, the onset of the disease has a trend of younger age. Studies have shown that oxidative stress is an extremely important factor in the occurrence and development of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. Scutellarin has a better therapeutic effect on the treatment of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. Therefore, it is not difficult to find that scutellarin has a certain inhibitory effect on oxidative stress. This article reviews the mechanism of scutellarin and oxidative stress, and to explore the clinical application of scutellarin to inhibit oxidative stress, so as to provide a certain evidence for the treatment of clinical diseases in the future.
The incidence of human cancers attributable to infectious agents has been estimated to be 15%. Hepatitis B virus(HBV) infects hepatocytes causing hepatocellular carcinoma. It can also infect extrahepatic cells and cause chronic inflammation, which is associated with a variety of extrahepatic cancers. Female reproductive organs communicate with the external environment through vagina. Viral nucleic acid can be detected in the vaginal secretions and ovarian tissues of HBV carriers. Epidemiological studies suggested HBV infection may be a risk factor for gynecologic malignancies, and related to poor prognosis of patients. Cervical cancer, endometrial cancer and ovarian cancer are most common gynecologic malignancies. This paper reviews the recent studies on the association between HBV infection and gynecologic malignancies, and analyzes the potential mechanism of HBV infection in the occurrence and development of cancer and prospects the future research direction.


 Email
Email RSS
RSS