2022 Vol. 43, No. 8
2022, 43(8): 1-6.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220801
Abstract:
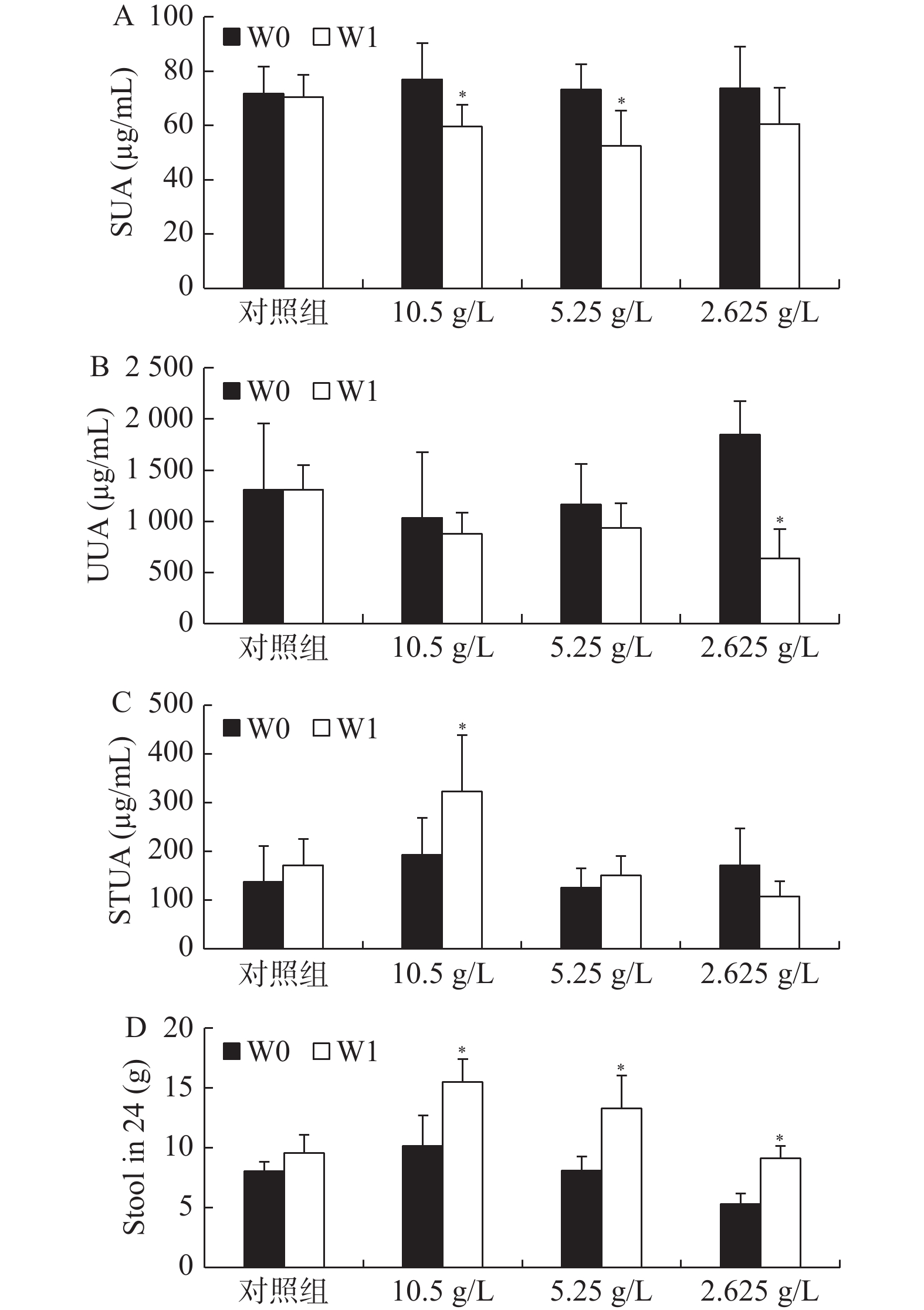
Objective To explore serum uric acid (SUA) lowering effect of polyethylene glycol 4000 (PEG4000) on male Kunming-DY rats (uricase-deficient rats). Methods A total of 24 45-day male Kunming-DY rats were selected and divided into control group (n = 6) and treatment group: high (10.5 g/L), medium (5.25 g/L) and low (2.625 g/L) PEG4000 dose groups with 6 rats in each group. The control group drank freely and the treatment group drank freely for 1 week. Before and after the experiment, the tail was cut and blood was collected, and the serum, urine and feces of the rats were collected for 24 hours. The food and water intake for 24 hours were recorded, and the main tissues and organs of the rats were harvested. The contents of uric acid, blood urea nitrogen and creatinine in serum samples, uric acid in excreta and uric acid in tissues and organs were tested, and the changes of indexes in control group and treatment group were compared. Results The blood uric acid in the control group was higher than 70 µg/mL, while PEG4000 (10.5 and 5.25 g/L) reduced it to 50-60 g/ml, and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). Compared with the control group, the fecal excretion of PEG4000 (10.5, 5.25, 2.625 g/L) groups increased significantly (P < 0.05). Compared with the control group, the blood urea nitrogen of PEG4000 (5.25 g/L) in the treatment group also decreased significantly, and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). Compared with the control group, PEG4000 (5.25 g/L) group decreased the uric acid content in tissues (heart, liver, spleen, lung, kidney and adrenal gland), and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05); PEG4000 (2.625 g/L) decreased the uric acid in tissues (liver, spleen, kidney and adrenal gland), and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). Conclusion Oral PEG4000 solution can reduce uric acid, which is related to the increase of defecation. Oral PEG4000 solution can reduce the burden of uric acid in kidney.
2022, 43(8): 7-16.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220802
Abstract:
Objective To investigate regulatory effect of the Lentivirus-mediated-GATA-3 RNAi (si-GATA-3)on the Th1/Th2 imbalance in a murine model of allergic rhinitis in vitro. Methods The lentiviral vector SI-GATA-3 with GATA-3 gene mediated by RNAi was developed and packaged, purified and titrated. BALB/C mice were randomly divided into AR group and normal control group. The allergic rhinitis model of BALB/C mice was developed by using ovalbumin (OVA). The peripheral blood of BALB/C mice was collected and their mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were isolated. The PBMCs were randomly divided into three groups, namely, si-GATA-3 group, si-NC group and AR group. si-GATA-3, si-NC and normal saline were used to intervene PBMCs in allergic rhinitis mice for 72 h, and normal saline was used to replace si-GATA-3 to intervene PBMCs in normal control mice. PBMCs and cell culture supernatant were separated after the intervention. The relative expression levels of GATA-3 mRNA, T-bet mRNA and GATA-3, T-bet protein in PBMCs were detected by fluorescence quantitative qPCR and Western bloting, respectively. The contents of IL-4 and IFN-γ in supernatant of cell culture were determined by ELISA. Results The RNAi mediated lentiviral vector si-GATA-3 with a titer of 5×108 TU/mL was successfully deeloped. The allergic rhinitis mice models were established successfully. The relative expression levels of GATA-3 mRNA and GATA-3 protein and the content of IL-4 in supernatant of PBMCs in si-GATA-3 group were significantly lower than those in AR group and si-NC group (P < 0.01), and the expression levels of GATA-3 in AR group and si-NC group were significantly higher than those in normal control group ( P < 0.01). There was no difference between AR group and si-NC group ( P > 0.05). The relative expression of T-bet mRNA and T-bet protein in si-GATA-3 group was significantly higher than that in AR group and si-NC group ( P < 0.01), and the expression of T-bet mRNA and T-bet protein in AR group and si-NC group was significantly lower than that in control group ( P < 0.01). There was no difference between AR group and si-NC group ( P > 0.05). However, the content of IFN-γ in cell culture supernatant of si-GATA-3 group was higher than that of normal control group ( P < 0.05), and the content of IFN-γ in AR and si-NC groups was significantly higher than that of normal control group and si-GATA-3 group ( P < 0.01). There was no significant difference in IFN-γ expression between AR group and si-NC group ( P > 0.05). Conclusions si-GATA-3 could down-regulate the relative expression of GATA-3 mRNA , GATA-3 protein and IL-4 level in Th2 cells, and up-regulate the relative expression of T-bet mRNA and T-bet protein in Th1 cells. Therefor, it can effectively correct the immune imbalance of Th2/Th1 in PBMCs in mouse AR model.
2022, 43(8): 17-27.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220804
Abstract:
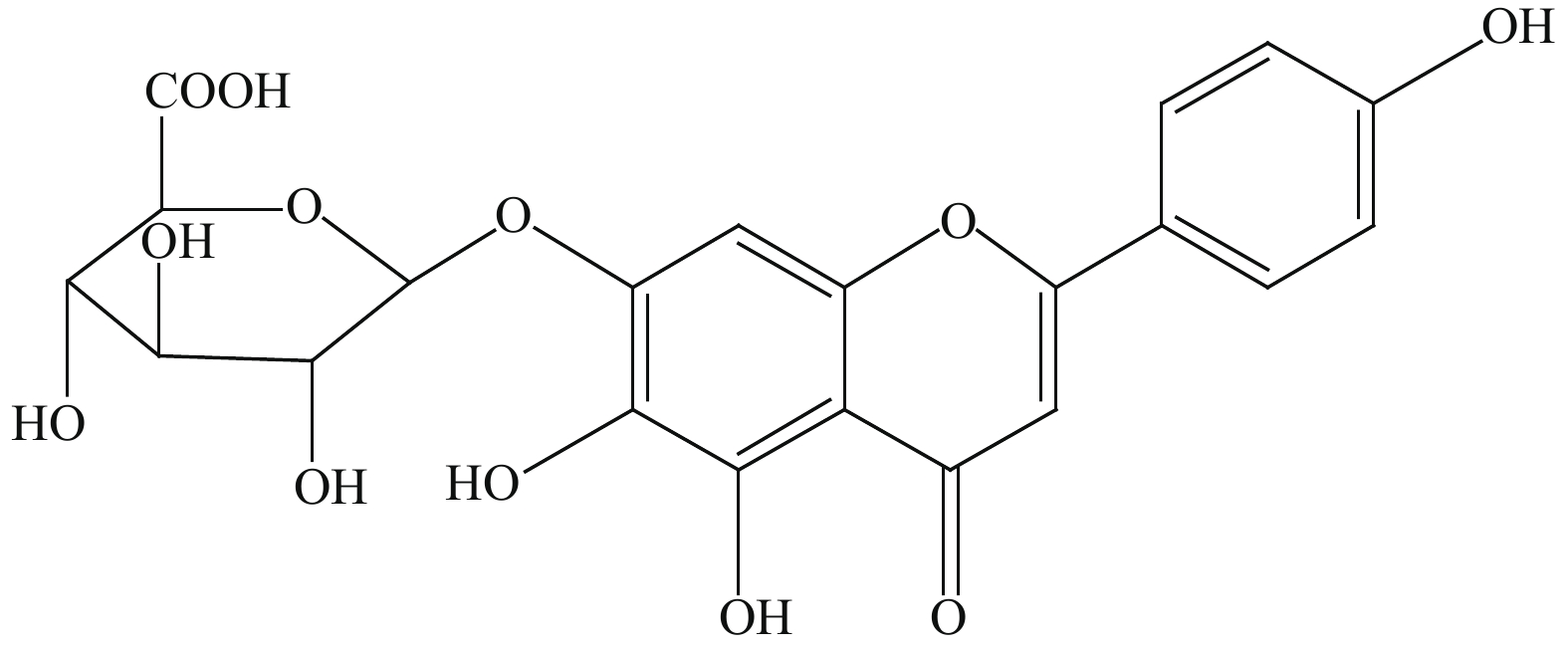
Objective To analyze the potential molecular biological mechanism of scutellarin for the treatment of atherosclerosis (AS) based on network pharmacology. Methods The PubChem database was used to predict the potential targets of scutellarin, and the Disgenet and CeneCards databases were used to predict and screen the genes related to atherosclerosis, and the Cytoscape 3.7.0 software was used to establish and construct the component-target-disease network visualization network. The GO and KECG pathways were analyzed using the David database. In addition, an APOE-/- mouse AS model was developed and treated with different concentrations of scutellarin, and the expression changes of the core targets were verified by RT-PCR. Results 1. Network pharmacological prediction results: the core targets of Scutellarin for AS treatment were tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), AKT serine/threonine kinase 1 (MAPK), low density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR), apolipoprotein E (APOE), among other targets, with 106 in total. The key targets of Scutellarin are PI3K/AKT signaling pathway (hsa04151), Ras signaling pathway (hsa04014) and MAPK signaling pathway (hsa04010) (P < 0.05), which are involved in cell proliferation, inflammatory response, oxidative stress and apoptosis, to treat AS. 2. Results of in vivo experiments: compared with the model group, the mRNA expression of PI3K, AKT, mTOR and Bcl-2 was down-regulated and the mRNA expression of Bax and Caspase-3 was up-regulated in the Scutellarin group. In addition, compared with model group, Scutellarin down-regulated the contents of TNF-α and IL-1β in serum concentration-dependent (P < 0.05). Conclusion Through network pharmacology screening and RT-PCR verification, Scutellarin inhibits the process of inflammatory response in a mouse model of AS by regulating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway.
2022, 43(8): 28-33.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220803
Abstract:
Objective To analyze the characteristics of katG and inhA genetic mutations associated with INH-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis in Yunnan Province. Methods The INH-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates were collected from drug-resistant monitoring sites in Yunnan Province, and the katG and inhA genes were amplified by PCR and then sequenced. Results Among the 88 MTB strains, the coincidence rate of INH-resistant genotype and phenotype was 82.95% (73/88). 75.00% (66/88) had katG mutations and 9.09% (8/88) had inhA mutations. katG315 (67.05%) and inhA-15 (7.95%) were the top two mutation sites, and a high prevalence of katG Ser315Thr mutations (59.09%, 52/88) was observed. The frequency of the katG mutation was significantly higher in MDR-TB compared to INH mono-resistant isolates (χ2 = 4.190, P = 0.041), while katG315, inhA and inhA-15T mutations did not differ significantly between these two groups (P > 0.05). Conclusion The most common mutation of INH-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis in Yunnan Province were katG315 and inhA-15, and katG mutation was higher among MDR isolates compared with INH mono-resistant strains. Molecular diagnostics based on gene mutations was a useful method for rapid detection of INH-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis in Yunnan Province.
2022, 43(8): 34-40.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220806
Abstract:
Objective To explore the specific effect of LL-37 on the destruction of the transmembrane barrier function of bladder urothelial cells and develop a cellular experimental model suitable for studying interstitial cystitis (IC) in vitro. Methods Human urothelial immortalized cells SV-HUC-1 were treated with LL-37 at different concentrations. The transepithelial electrical resistance (TEER) was measured by a transepithelial resistor, and the cell proliferative activity was detected by CCK-8 kit. Cell cycle and calcium ion concentration were detected by flow cytometry. The expression levels of heparan sulfate, a key component of glycosaminoglycan (GAGs), were detected by RT-qPCR and WB. Results In vitro measurement showed that 100 and 200 μg/mL of LL-37 significantly inhibited the TEER and destroyed the transmembrane barrier function of SV-HUC-1. The CCK-8 test and PI staining flow cytometry results showed that LL-37 above 100 μg/mL could significantly reduce the proliferation activity of SV-HUC-1 and increase the proportion of SV-HUC-1 in the G0/G1 phase (P < 0.05), suggesting that cell proliferation was significantly inhibited. Further flow cytometry analysis showed that the calcium ion concentration in SV-HUC-1treated with LL-37 was significantly increased (P < 0.05), and the increase was related to LL-37 concentration. RT-qPCR and WB assays confirmed significant up-regulation of heparan sulfate, a key GAGs component, in the LL-37-treated SV-HUC-1 (P < 0.05). Conclusion The cathelicidin LL-37 can inhibit the expression of GAGs and destroy the cell proliferation and transmembrane barrier function of SV-HUC-1.
2022, 43(8): 41-46.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220805
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the protective effect of interleukin-4 (IL-4) on acute lung injury (ALI). Methods ALI cell models were developed using lipopolysaccharide (LPS) to induce A549 cells. The model was treated with different concentrations of IL-4 (0.1 μg/mL, 1 μg/mL, 10 μg/mL) for different durations. Then the apoptosis rate of A549 cells was detected by flow cytometry, and the secretion of IL-1, IL-6, IL-10, TNF-α, TNF-γ of A549 cells was determined by ELISA. Results IL-4 reduced the apoptosis rate of A549 cells and inhibited the expression of Caspase3 in ALI model (P < 0.05). The effect was enhanced with the increase of IL-4 concentration and the extension of intervention time. IL-4 promoted the expression of Bcl-2 (P < 0.05), and the best effect was achieved when the concentration of IL-4 was 1 μg/mL for 12 h. Under the above conditions, IL-4 decreased IL-1, IL-6, TNF-α, TNF-γ and increased IL-10 in A549 cells in ALI model (P < 0.05). Conclusion IL-4 can positively regulate acute lung injury by improving cytokine secretion in ALI in vitro model.
2022, 43(8): 47-55.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220807
Abstract:
Objective To compare the differences in serum Val and Met concentrations in healthy people, patients with benign breast tumors and breast cancer patients, and explore the relationship between serum valine and methionine and the clinical characteristics and risk of breast cancer. Methods The serum Val and Met concentrations of 38 patients with benign breast tumors and 87 patients with breast cancer were determined by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry, and 91 healthy participants were selected as the control group. The Kruskal-Wallis H-test was used to compare the differences in serum Val and Met concentrations between different groups, and the effects of different chemotherapy regimens and surgical methods on serum Val and Met concentrations in breast cancer patients were analyzed. Binary Logistic regression analysis, calculation of odds ratio and 95% confidence interval (CI) were used to evaluate the relationship between serum Val, Met and breast cancer risk, and ROC curve was drawn to evaluate the diagnostic performance of serum Val and Met for breast cancer. Results Compared with healthy control group, the serum Val concentration in breast cancer (BC) group was higher than that in benign breast tumor (BE) group and healthy control group, and the Met level in BC and BE groups was higher than that in healthy control group, and the differences were statistically significant (P < 0.05). There were no significant differences in serum Val and Met concentrations among breast cancer patients with different TNM stages and chemotherapy regimens, but there were differences in serum Val concentrations among breast cancer patients with different molecular types. In addition, there was no significant relationship between serum Val concentration level and breast cancer risk, but serum Met significantly affected the occurrence of breast cancer ( P < 0.001). The higher serum Met concentration was, the higher the risk of breast cancer was; and for every one-unit increase in Met levels, the risk of breast cancer increased by 24 percent ( OR = 1.24 95%CI: 1.15-1.34). Serum Met (P < 0.001) was statistically significant in the diagnosis of breast cancer. The AUC was 0.83, the sensitivity and specificity were 69% and 90.1%, respectively, and the critical value was 19.76 μmol/L. Conclusion The serum Val concentration of breast cancer patients was higher than that of benign breast tumor patients and healthy population. Serum Met levels were also elevated in patients with breast cancer and benign breast tumors compared with healthy subjects. There was no significant correlation between serum Val concentration and breast cancer risk, but serum Met was negatively correlated with breast cancer risk, and serum Met had certain diagnostic efficacy for breast cancer diagnosis.
2022, 43(8): 56-60.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220808
Abstract:
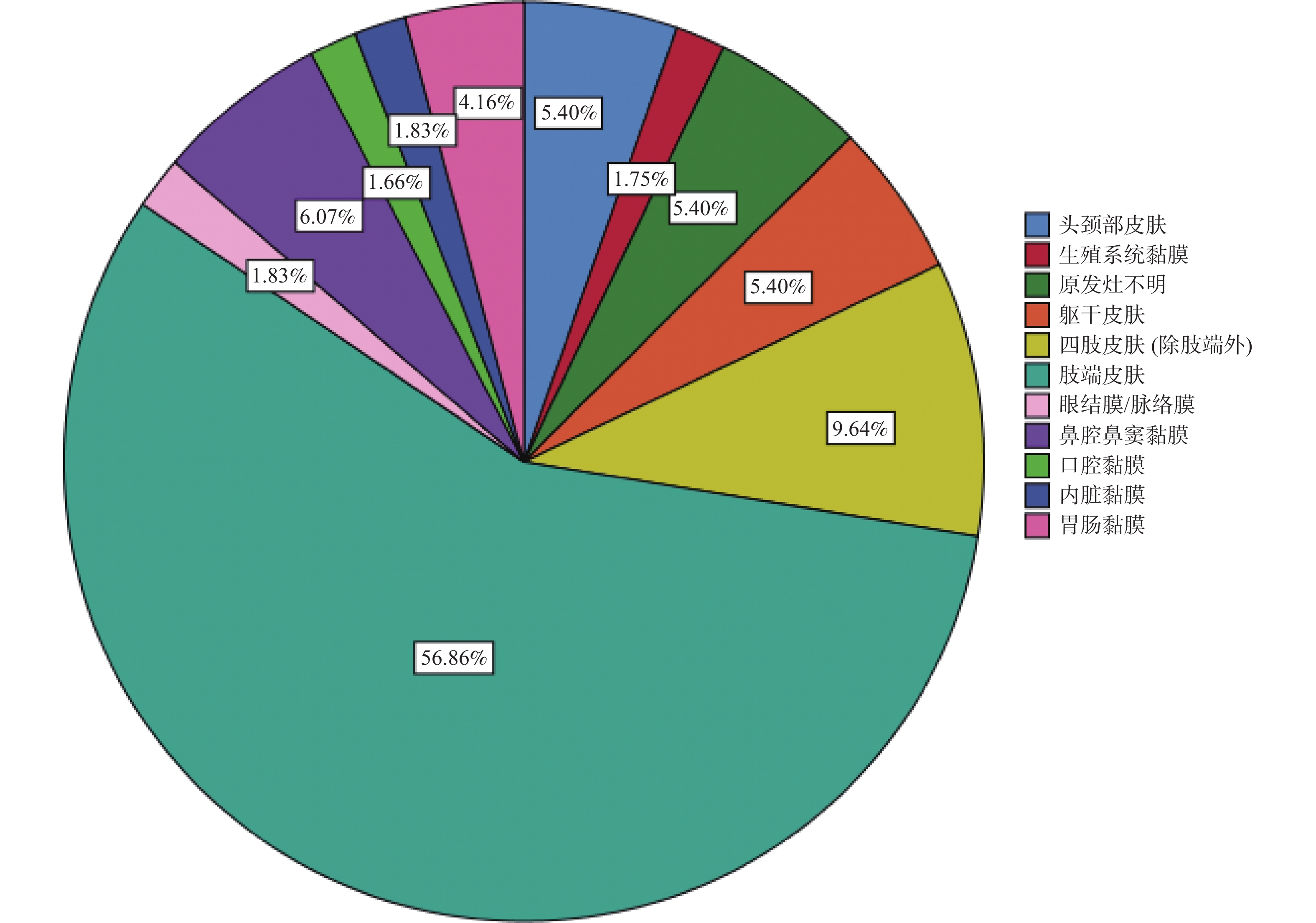
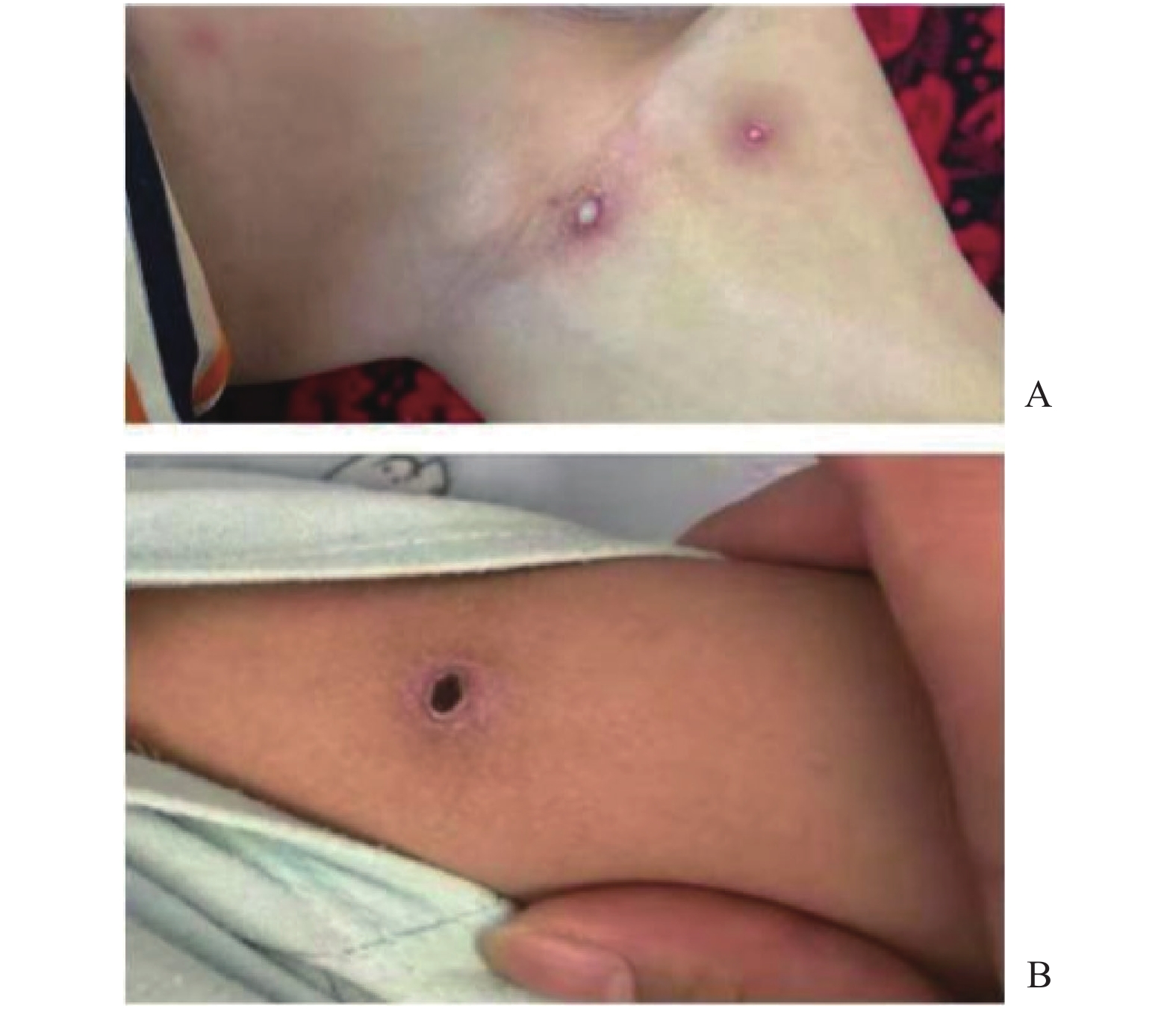
Objective To explore the clinical characteristics of melanoma in our hospital, and provide a reference for the prevention and treatment of melanoma. Methods The clinical data of melanoma patients diagnosed in the Third Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University/Yunnan Provincial Cancer Hospital from January 2007 to December 2021 was collected, and data on gender, age, lesion location, and incidence trends were analyzed. Results Of the 1203 melanoma patients, 77.3% had primary cutaneous melanoma and 17.3% had primary mucosal melanoma. The age of patients ranged from 11 to 90, with the highest prevalence (82.8%) in the age group of 31-70 years. Acral lentiginous melanoma is more common in men; genital mucosal melanoma is most commonly seen in women (P < 0.05). Head and neck mucosal melanoma accounted for 55.3% of the total body mucosal melanoma, and the proportion of head and neck mucosal melanoma was 5.58 times higher than that of other parts of the body. Conclusion The melanoma diagnosis rate in Yunnan Cancer Hospital is on the rise. The focus of prevention and treatment in Yunnan Cancer Hospital is melanoma of the limbs and head and neck, especially mucosal melanoma of the head and neck.
2022, 43(8): 61-65.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220809
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the efficacy of blood transfusion combined with radiotherapy and chemotherapy in patients with colorectal cancer and its effects on tumor markers and T lymphocyte levels. Methods A retrospective analysis was performed on 68 patients with colorectal cancer who received treatment in Yunnan Cancer Hospital from January 2018 to February 2020. These patients were divided into 2 groups based on their conditions and treatment plans. The control group (34 cases) received radiotherapy and chemotherapy, and the study group (34 cases) received blood transfusion combined with radiotherapy and chemotherapy. The clinical therapeutic effect, T lymphocyte level and tumor marker level were compared between the two groups. Results The clinical effective rate of the study group was siginificantly higher than that of the control group (P < 0.05). Before treatment, there was no statistically significant difference in the levels of T lymphocyte cytokines between the two groups (P > 0.05). After treatment, the levels of CD8+ in the study group were lower than those in the control group, while the levels of CD3+, CD4+ and CD4+/CD8+ were higher than those in the control group, with statistically significant differences (P > 0.05). Before treatment, there were no statistically significant differences in the levels of CA19-9, TK1, CEA and AFP between 2 groups (P > 0.05). After treatment, the levels of CA19-9, TK1, CEA and AFP in the study group were significantly lower than those in the control group (P < 0.05). Conclusion Blood transfusion combined with radiotherapy and chemotherapy can improve the therapeutic effect, improve the level of tumor markers and enhance the immunity of colorectal cancer patients.
2022, 43(8): 66-71.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220810
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the influence of butylphthalide on National Institute of Health stroke Scale (NIHSS) and hemorheology in patients with acute cerebral infarction. Methods A total of 66 patients with acute cerebral infarction admitted to the Department of Neurology of Kunming Second People’s Hospital from March 2020 to April 2021 were selected and divided into study group and control group by numerical random table method. The control group received routine treatment, and the research group was treated with butylphthalide on the basis of routine treatment as in the control group. Hemorheology, efficacy of the two groups before and after treatment, neurological deficit score and adverse reactions of daily living ability were detected and compared. Results After treatment, the total effective rate of the study group was higher than that of the control group, and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). After treatment, the NHISS score of the study group was lower than that of the control group, and the Barthel index was higher than that of the control group, with statistical significance ( P < 0.05). After treatment, the hemorheology indexes (whole blood specific viscosity, plasma specific viscosity, hematocrit and platelet aggregation rate)in the study group were lower than those in the control group, and the differences were statistically significant ( P < 0.05). There was no significant difference in the adverse reaction rate between the study group and the control group ( P > 0.05). Conclusion The use of butylphthalide for the treatment of acute cerebral infarction patients is effective, with improvement in patients’ neurological functions and hemorheology indicators. It is safe and worthy of application and promotion.
2022, 43(8): 72-80.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220814
Abstract:
Objective To analyze the clinical manifestations of scrub typhus in children , and the risk factors that may progress to critical cases were discussed, so as to provide a basis for clinicians to diagnose and identify critical patients as soon as possible. Methods The data of scrub typhus patients diagnosed in Kunming Children’s Hospital from 2017 to 2021 were retrospectively analyzed. The subjects were divided into non-critical group and critical group, and the symptoms, signs, laboratory data, treatment and outcome of each group were compared. The indexes with statistically significant differences in univariate analysis were included in multivariate Logistic regression analysis, and the receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) for identifying severe cases was drawn for the indexes that were significant in regression analysis. Results Among the enrolled 175 cases, 145 cases (82.9%) were in the non-critical group and 30 cases (17.1%) in the critical group. There was 2 patients died and other 173 patients were improved or cured after treatment. All the children had fever (100%), eschar or ulcer were common (85.7%), followed by hepatomegaly and lymphadenopathy. Compared with the non-severe group, the incidence of cough, edema and hepatomegaly was higher in critical group, and the differences were statistically significant (P < 0.05). Laboratory tests of all enrolled cases demonstrated that the levels of eosinophils (EOS), platelet counts (PLT) and albumin (ALB) significantly decreased, and the levels of alanine transaminase (ALT), aspertate aminotransferase (AST), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) , C reactive protein (CRP), procalcitonin (PCT) increased. Compared with non-critical group, PLT, EOS, ALB and FIBRinogen (FIB) in critical group were decreased (ALL P < 0.05), ALT, AST, LDH, CRP and PCT in critical group were increased (P < 0.05), prothrombin time (PT) and partial prothrombin time (APTT) were prolonged (P < 0.05). Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that PLT (OR:0.980, 95%CI 0.966~0.994, P < 0.05) and LDH (OR: 1.002, 95%CI 1.000~1.004, P < 0.05) were risk factors for scrub typhus to develop into critical cases. The sensitivity and specificity of PLT and LDH were 89.7% and 76.6% respectively. Conclusion During the epidemic season, clinical manifestations including fever, with or without eschar or ulceration, hepatomegaly, lymphadenopathy and laboratory findings including decresesd EOS, PLT and elevation of ALT, AST and LDH can help the diagnosis of scrub typhus. Decreased PLT and increased LDH are risk factors for the development for critical scrub typhus in children.
2022, 43(8): 81-86.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220811
Abstract:
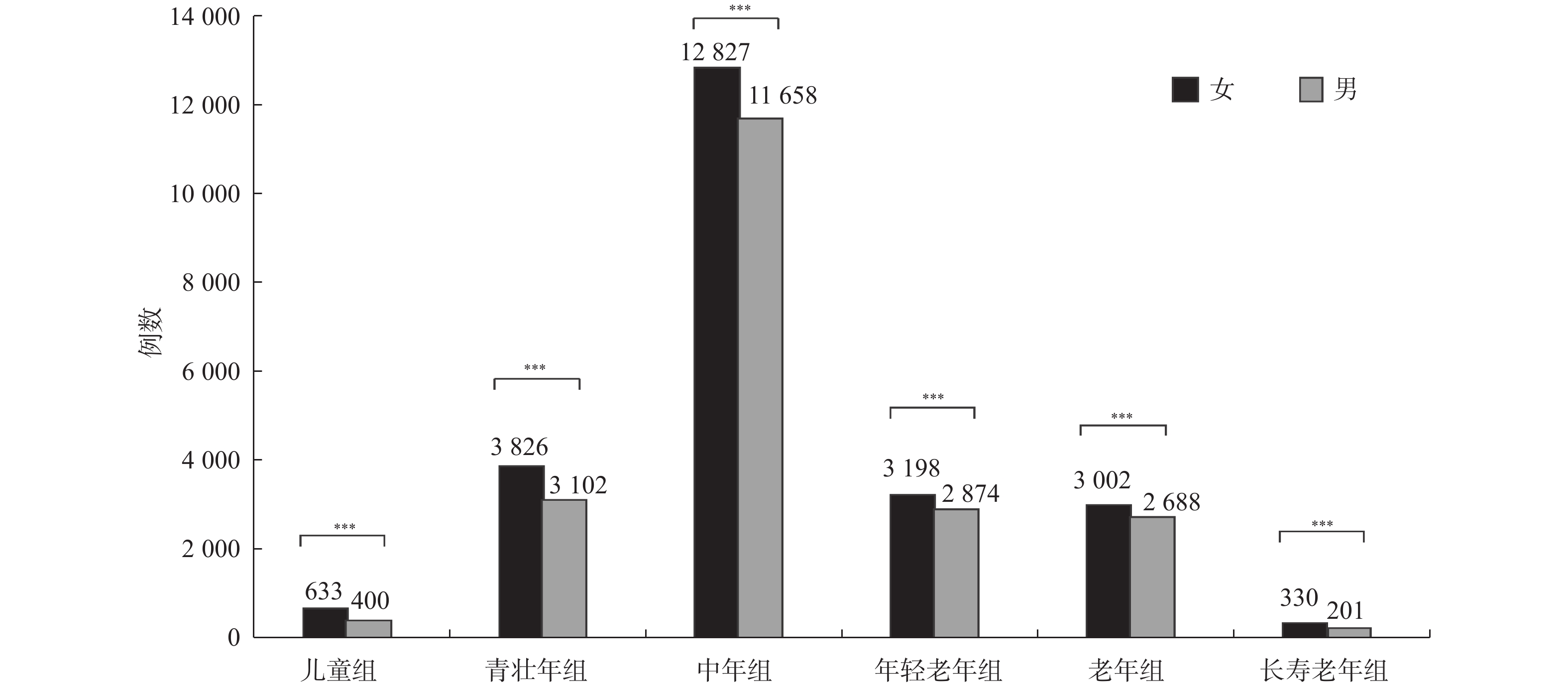
Objective To study the epidemiological characteristics of patients triaged in the emergency department during COVID-19 pandemic in our hospital in 2020 to provide a reference basis for further optimizing the diagnosis and treatment services, response measures, and management strategies in the emergency department. Methods The triage registration records of 44, 739 emergency patients who visited the First People’s Hospital of Yunnan Province from January 1 to December 31, 2020, were retrospectively collected, and a database was established. Epidemiological characteristics were analyzed based on age, sex, visiting season, disease grading, and way of visiting the hospital. Results Among the 44, 739 emergency patients, 20, 923 (47%) were male and 23, 816 (53%) were female. The age ranged from 0.2 to 110 years old, with 25, 828 cases (58%) mainly among 45 to 59 years old. The maximum number of patients visited in summer was 12, 449 (28%), followed by 11, 558 (26%) in autumn; the peak hours of visits were mainly from 9:00 am to 12:00 am and from 3:00 to 9:00 pm; 77% of the patients came to the clinic by taxi and by foot, and 12% by ambulance; The proportion of patients with disease grading was grade I (12%), grade II (10%), grade III (58%), and grade IV (21%). Conclusion A comprehensive tertiary hospital in Kunming has more female than male emergency patients, and their ages are mainly between 45 and 59 years old; the summer is the peak season for consultation, and the daily consultation peaks are mainly on 9:00-12:00 a.m and 15:00-21:00 p.m.The emergency department should combine the current COVID-19 epidemic control requirements with reasonable allocation of emergency medical resources.
2022, 43(8): 87-92.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220812
Abstract:
Objective To explore the health literacy management and related influencing factors of type-Ⅱ diabetes mellitus patients and thus provide a basis for improving the health literacy management of diabetic inpatients in community hospitals in Kunming. Methods The convenience sampling method was used to select 185 inpatients with type-Ⅱ diabetes mellitus from two community hospitals in Chenggong, Kunming. The self-designed diabetes basic knowledge questionnaire, health literacy management scale (HeLMS), and patient health questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9) were used in this study. Results In the four dimensions of HeMLS, the scores of desire for financial support was 30 points lower than the total scores of other three dimensions for diabetic patients (P < 0.05), which indicates a strong desire for financial support in diabetic patients. Gender, education level, monthly income, duration of diabetes and physical exercise were the influencing factors for patient’s basic knowledge of diabetes score ( P < 0.05). The patients with low-income and long-term adherence to exercise are positively related to adequate basic knowledge of diabetes and the ability to manage health literacy. Conclusion The health literacy of knowledge score influence factors including gender, education level, low income, long-term diabetes and adherence to exercise . They are the main obstacles in improving health literacy management. In response to this situation, community hospitals should make efforts for effective intervention.
2022, 43(8): 93-99.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220813
Abstract:
Objective To explore the effect of integrating palliative care to reduce the pain and anxiety symptoms of liver cancer patients. Methods 60 patients with hepatitis related liver cancer in Kunming Third People’s Hospital were divided into standard treatment group (control group) (n = 30) and palliative interventional treatment group (n = 30) (study group). The control group received interventional treatment, and the study group received interventional treatment plus palliative treatment. Patients in the two groups were evaluated by pain scale and anxiety scale respectively after interventional treatment. After 12 weeks, the two groups were evaluated again with the scales mentioned above, and the pain and anxiety scores of the two groups were compared before and after 12 weeks, to analyze the factors influencing the pain and depression in patients with hepatitis related liver cancer, and to analyze the correlation between the related factors in the pain and anxiety scores of the two groups. Results There was no statistical significance in age, sex, education level, smoking history, alcoholism history, medical insurance type, liver function grade and hepatitis type between the two treatment groups (P > 0.05). There were statistically significant differences in family background, pain history, tumor stage, ECOG score, NRS score before treatment, NRS score after treatment, anxiety score before treatment and anxiety score after treatment between the 2 treatment groups ( P < 0.05). After 12 weeks of treatment, the pain and anxiety scores of the patients in the control group were significantly higher than those in the research group ( P < 0.05). Conclusion Palliative care combined with standard treatment has significant effects on alleviating pain and anxiety, and the earlier the palliative care program is entered, the better the improvement of patients’ pain and anxiety. Therefore, palliative care is not limited to patients with advanced liver cancer.
2022, 43(8): 100-105.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220815
Abstract:
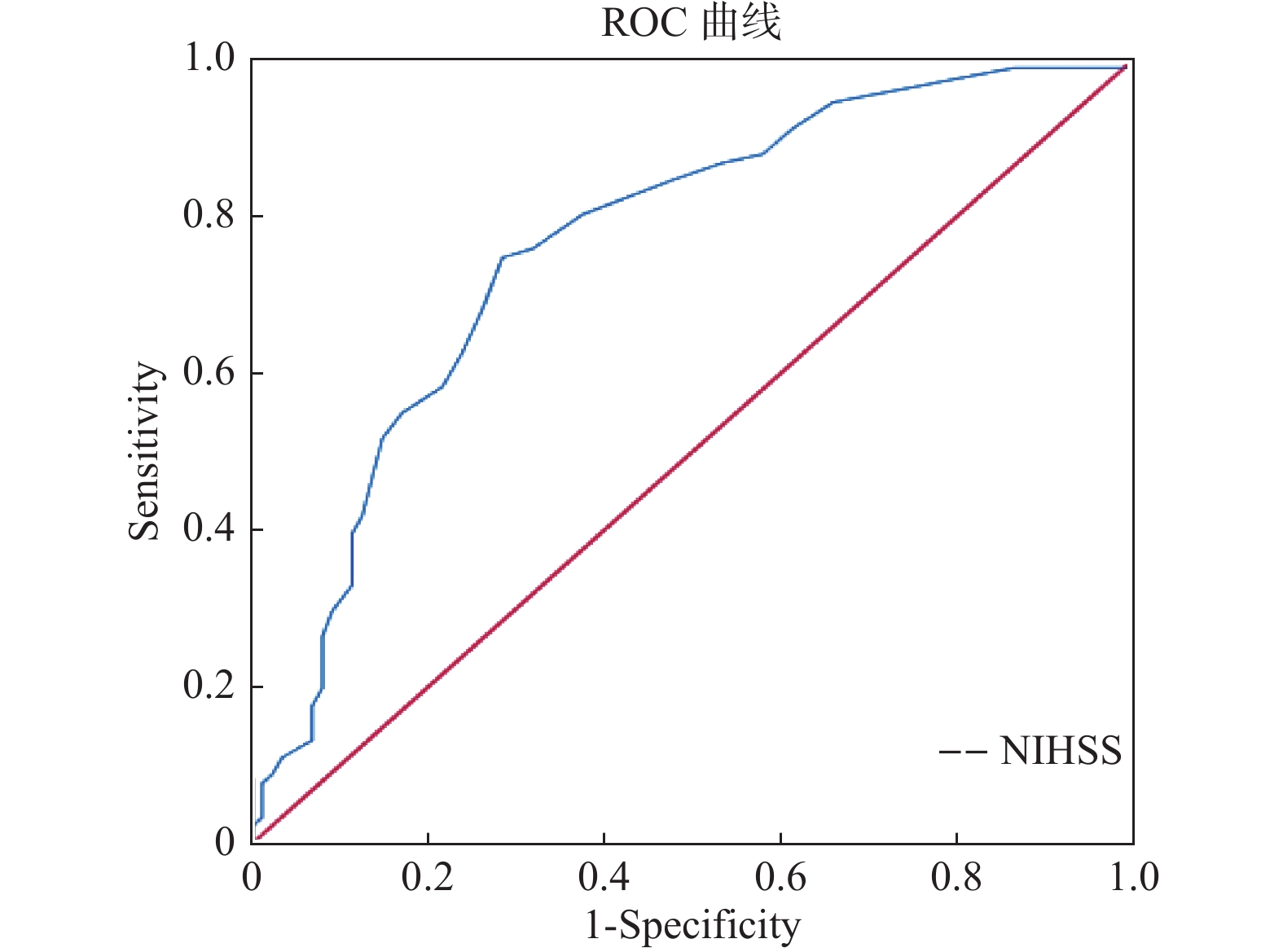
Objective To study the influencing factors of poor prognosis before and after revascularization of acute ischemic stroke, so as to provide more biomarkers for prognosis prediction. Methods A total of 179 patients with acute ischemic stroke who received revascularization therapy (including intravenous thrombolysis, mechanical thrombectomy, or both) admitted to the Department of Neurology and The Department of Neurointervention of Qujing Hospital Affiliated to Kunming Medical University from December 2020 to October 2021 were collected. According to mRS score after 3 months, the patients were divided into good prognosis group (mRS < 3) and poor prognosis group (mRS≥3). General data, clinical test indicators, NLR value and NIHSS score before and after revascularization were compared between the two groups, and independent risk factors of patients with poor prognosis were further analyzed. Results There are siginificant differences in triglyceride, total cholesterol, c-reactive protein, NIHSS score, the number of neutrophils and percentage of the hospital, lymphocyte count and percentage, NLR value and reascularization 8 hours after the number of white blood cells, neutrophils and percentage, lymphocyte count and percentage, NLR value between the two groups (P < 0.05). Multivariate Logistic regression analysis showed that admission NIHSS score (OR=1.123, 95%CI 1.065-1.184, P < 0.05) was an independent risk factor for poor prognosis 3 months after revascularization in AIS patients, with a clinical diagnostic cut-off value of 11. The NLR values of the poor prognosis group before and after revascularization were higher than those of the good prognosis group, the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). The NLR values of AIS patients after revascularization were higher than those before revascularization, the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). Conclusion NIHSS score at admission is an independent risk factor for poor prognosis at 3 months in patients with AIS revascularization. Changes in NLR in AIS patients before and after revascularization showed an upward trend, and NLR in the poor prognosis group was higher than that in the good prognosis group before and after revascularization, but it was not an independent risk factor for poor prognosis in AIS patients 3 months after revascularization.
2022, 43(8): 106-112.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220816
Abstract:
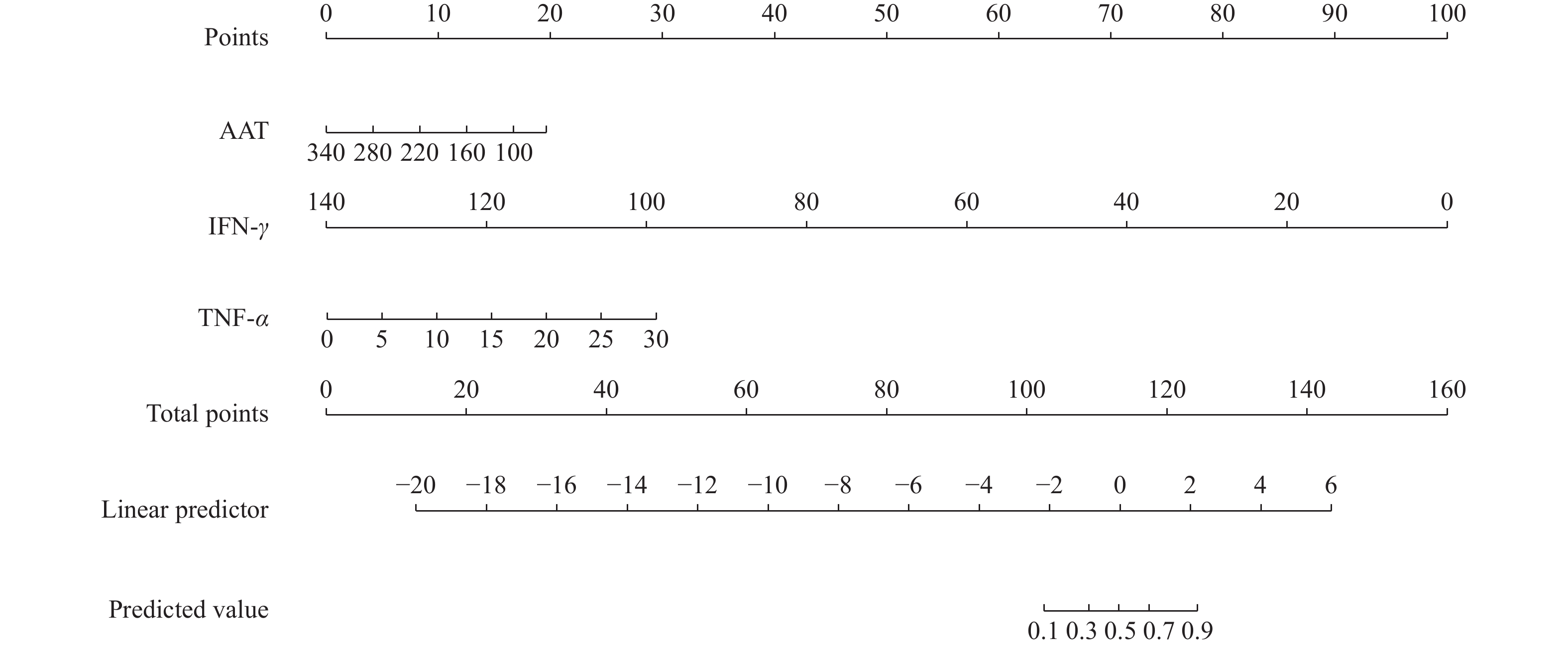
Objective To construct a predictive model of AAT and cytokines in the diagnosis of active pulmonary tuberculosis. Methods A total of 96 patients with active pulmonary tuberculosis admitted to the Third People’s Hospital of Kunming from March 2020 to March 2021 were collected as the experimental group, and 82 healthy subjects during the same period were selected as the control group. HAP, CRP, AAT and cytokines were compared between the two groups. Based on the results of Logistic regression analysis, a Nomogram prediction model was constructed, and the model was verified and evaluated. Results Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that AAT (OR = 0.983, 95% CI = 0.968-0.999, P = 0.039), IFN-γ (OR = 0.783, 95% CI = 0.659-0.931, P = 0.006), TNF-α (OR = 1.495, 95% CI = 1.106-2.020, P = 0.009) are predictors of active pulmonary tuberculosis (P < 0.05). Conclusion The fit of the model and the area under the ROC curve were good, which confirmed that the model had a high prediction accuracy. The Nomogram model established based on the above predictors has good predictive performance and can provide a certain reference value for the laboratory diagnosis of active pulmonary tuberculosis.
2022, 43(8): 113-121.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220817
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the application value of Silva typing pattern in prognosis of HPV-associated endocervicalnadenocarcinoma (HPVA). Methods A total of 95 cases of invasive HPVA diagnosed by pathology department in the Third Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University from February 2013 to December 2018 were collected and reclassified by Silva classification criteria. Clinicopathological features. According to the case data and follow-up, the survival rate was estimated and the influencing factors were analyzed. Results (1) Compared with SilvaA subtypes, SilvaB and C subtypes had larger tumor diameter, deeper myometrial invasion, poor differentiation, later FIGO stage, higher risk classification, and a higher proportion of pelvic and abdominal lymph node metastasis and nerve invasion. , postoperative adjuvant therapy was also more active (P < 0.05), but there was no significant difference in age and lymphovascular invasion (P > 0.05); (2) The 5-year overall survival rate and 5-year disease-free survival rate of SilvaA and SilvaB were higher than 90%, while those of SilvaC were significantly lower than 50% (P < 0.05). (3) COX proportional hazards model multivariate analysis: pelvic and abdominal lymph node metastasis (HR = 12.602, 95%CI: 2.722-58.333) was the influence Independent factors of OS in patients with invasive HPVA (P = 0.001); FIGO stage was an independent factor affecting DFS of patients with invasive HPVA (P < 0.05). The 95%CI were 5.319 (1.597-17.716), 53.365 (5.458-521.734), and 25.982 (2.169-311.299). Conclusion Silva classification pattern is closely related to tumor diameter, degree of differentiation, depth of muscle invasion, FIGO stage, pelvic and abdominal lymph node metastasis, nerve invasion, risk classification, postoperative adjuvant therapy, but not age, lymphovascular invasion . Pelvic and abdominal lymph node metastasis and FIGO stage are risk factors affecting the prognosis of cervical invasive HPVA.
2022, 43(8): 122-126.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220821
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the characteristics and significance of immune function in patients with active and non-active pulmonary tuberculosis. Methods A total of 78 patients with active tuberculosis treated in Kunming Third People’s Hospital from January 2020 to January 2021 were enrolled as the control group, and 28 patients with non-active tuberculosis were enrolled as the observation group. The expression levels of antibodies and cytokines and immune cell production in the two groups were analyzed. Results Compared with the control group, the levels of IFN-γ and IL-6 in observation group were decreased, and the differences were statistically significant (P < 0.05). There was no significant difference in the levels of IgG, IgA, IgM and other 10 cytokines including IL-1, IL-2, IL-4, IL-5, IL-8 ( P > 0.05); CD3 +T, CD4+T, CD8+T cells and CD4+/CD8+ increased, the absolute numbers of lymphocytes and NK cells decreased, and the differences were statistically significant (P < 0.05), while the absolute numbers of B cells showed no significant difference ( P > 0.05). Conclusion Cytokines IFN-γ, IL-6 and lymphocyte subsets can be used as reference indicators of immune function in patients with inactive pulmonary tuberculosis, and have certain guiding significance for active relapse of tuberculosis.
2022, 43(8): 127-131.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220820
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the clinical characteristics of varicella-zoster virus (VZV) infection in immunocompromised population. Methods From January 2020 to December 2021 in the Third People’s Hospital of Kunming, 38 cases of VZV infection in immunosuppressed population were selected as the observation group, and 40 cases of VZV infection in the general population were selected as the control group. The clinical data were retrospectively analyzed, and the indexes of cardiac enzymes, liver function, kidney function and other organs function evaluation in the two groups were observed. And IL-6, IL-8, CD+4 T lymphocytes and other indicators’s data were analyzed to evaluate the body’s immunity. Results The GGT/AST/ALT and LDH/CK of the observation group were significantly higher than those of the control group (P < 0.05). There was no statistical significance in CREA between the two groups ( P > 0.05). IL-6 and IL-8 in the observation group were significantly higher than those in the control group ( P < 0.05). The number of CD4+T lymphocytes in the observation group was significantly lower than that in the control group ( P < 0.05). Conclusion Immunocompromised population with VZV infection are more likely to induce cytokine storm, and are more often complicated with organ dysfunction or even organ failure. The disease progresses faster and is more severe. Early identification and treatment can improve the prognosis.
2022, 43(8): 132-137.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220822
Abstract:
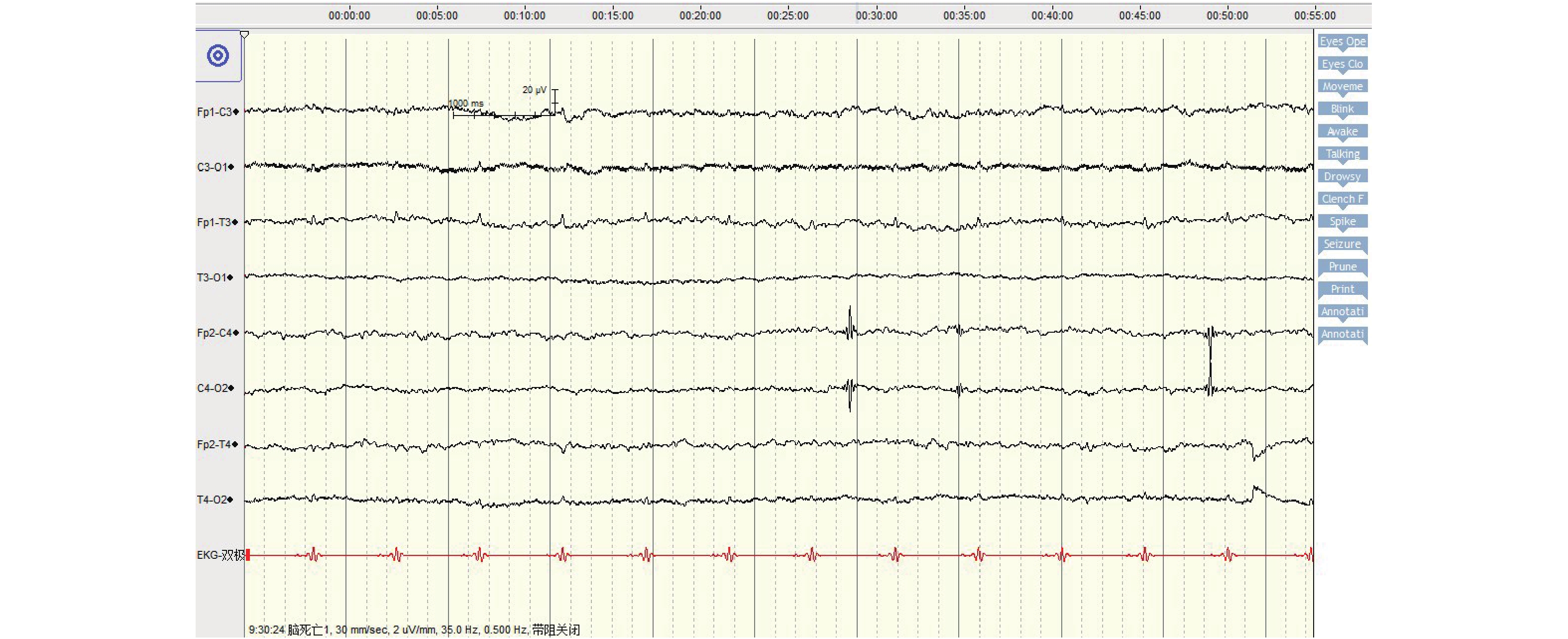
Objective To explore the value and application of electroencephalogram, short latency somatosensory evoked potential and transcranial Doppler ultrasound in the determination of brain death. Methods 31 patients with brain death in our hospital were enrolled. Each patient was tested twice by electroencephalogram, short latency somatosensory evoked potential and transcranial Doppler ultrasound. According to the experimental standard of brain death confirmation, they were divided into brain death positive group and brain death negative group. The sensitivity, specificity and accuracy of the three tests were compared. Results The sensitivity, specificity and accuracy of EEG were higher than those of short latency somatosensory evoked potentials and transcranial Doppler, with sensitivity of 100%, specificity of 75% and accuracy of 93.55%. The number of positive EEG and short latency somatosensory evoked potential in brain death group was significantly higher than that in non-brain death group, the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). Conclusion ROC curve analysis showed that electroencephalogram was effective in diagnosing brain death.
2022, 43(8): 138-144.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220823
Abstract:
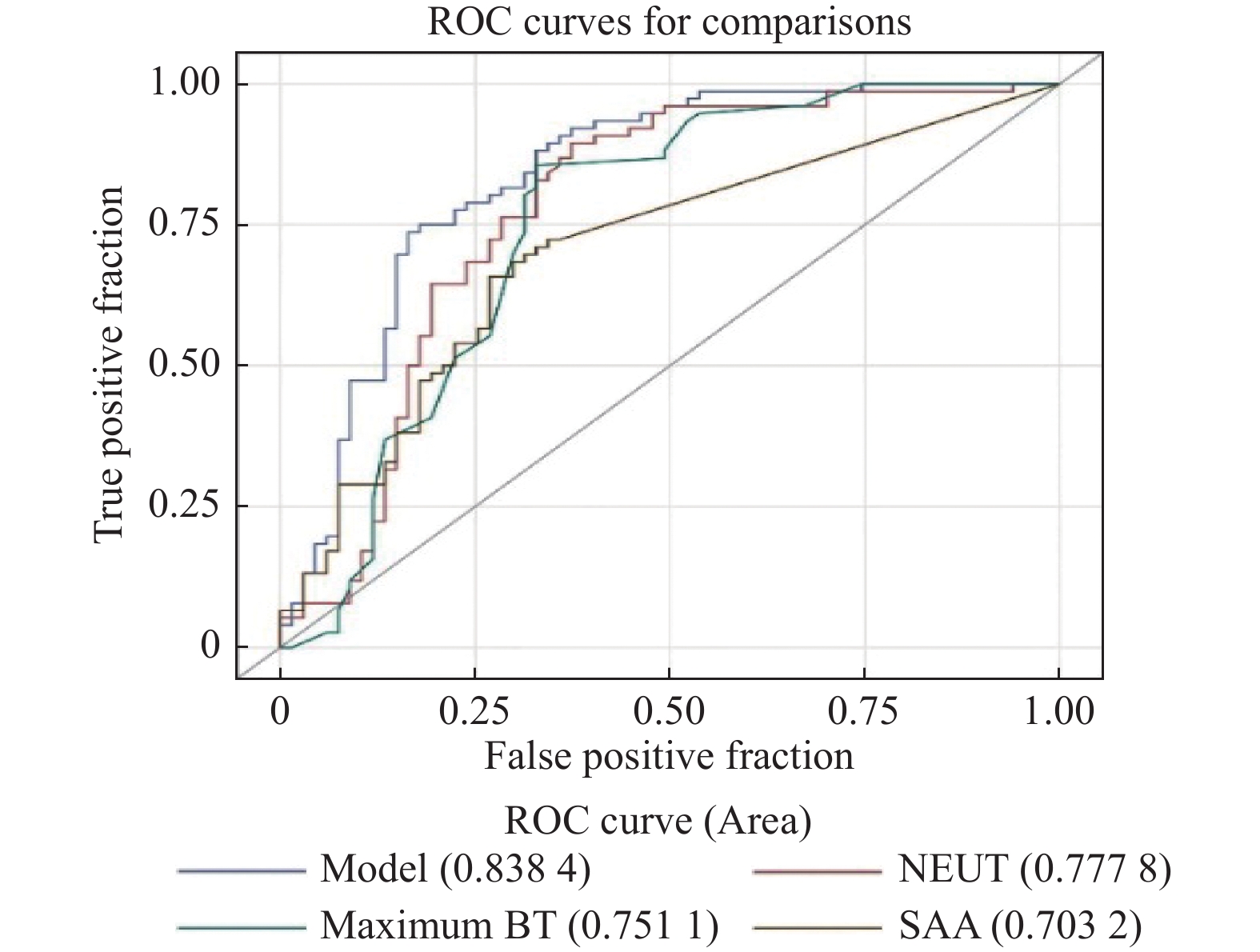
Objective To investigate the changes in serum PCT, IL-6, SAA levels and clinical characteristics of pediatric rotavirus (RV) and norovirus (NV) enteritis, and to analyze the factors for distinguishing the two. Methods In a prospective observational study, we selected children with watery diarrhea and diagnosed viral enteritis who were admitted to the Department of Infectious Diseases of Kunming Children’s Hospital from November 2019 to January 2021 as the research objects. Stool and venous blood samples were collected within 24 hours after admission for detection of fecal rotavirus and norovirus and determination of blood cells, serum procalcitonin (PCT), interleukin-6 (IL-6) and serum amyloid A (SAA). The gender, age, the most vomiting and diarrhea times within 24 h, complications, maximum BT, Vesikari score and other clinical characteristics of the children were analyzed by multivariate logistic regression and the accuracy of the model was assessed by ROC. Results 143 children were eligible, among which 76 were RV and 67 were NV. The maximum BT, the highest number of diarrhea within 24 hours, Vesikari score, neutrophil count (NEUT), SAA, and the number of patients with body temperature > 38 ℃ were significantly higher in the RV group than those in the NV group ( P < 0.05); There were no statistically significant differences in gender, age, the maximum number of vomiting at 24 h, complications, the number of people with Vesikari score ≥11, white blood cell count (WBC), PCT, CRP, and IL-6 levels ( P > 0.05). Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that maximum BT, NEUT, and SAA were independent factors that distinguished the two. ROC was used to assess the accuracy of the model, and its AUC was 0.838 (95%CI: 0.770-0.907, P < 0.001), maximum approximate den index (J = 0.573), sensitivity was 83.6%, specificity was 73.7%. Conclusion RV enteritis causes more patients with higher fever ( > 38 ℃), and there are more frequent diarrhea within 24 hours, which is more serious than NV enteritis. A model containing maximum BT, NEUT and SAA can assist pediatricians in differential diagnosis of infection by unknown pathogens.
2022, 43(8): 145-149.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220824
Abstract:
Objective To analyze the distribution, epidemiological characteristics, clinical symptoms and high-risk factors of pertussis in Yunnan Province, and to explore the epidemiology, clinical characteristics and high-risk factors of pertussis. Methods Data of 148 children with pertussis who were admitted to Kunming Children’s Hospital from January 2020 to December 2021 in Yunnan province were collected and retrospectively analyzed based on regional distribution, age, clinical manifestation, laboratory test results and severity of disease. Results Among the 148 children, 96 cases (64.86%) were male and 52 cases (35.14%) were female; 123 cases (83.11%) were common type, 25 (16.89%) were severe pertussis. Children aged under 3 months accounted for 27.03%, children aged 3 months to 6 months accounted for 33.11%, children aged from 6 months to 3 years accounted for 23.65%, children aged ≥ 3 years accounted for 16.22%. 94 cases (63.51%) were not immunized at the time of infection. 51 cases (34.46%) had chicken crowing during cough, and 26 cases (17.57%) had cyanosis during cough. There were 128 cases (86.49%) complicated with pneumonia, 93 cases (62.84%) with past history. There were 85 cases (57.43%) with WBC (10 ~ 30) × 109/L and 12 cases (8.11%) with WBC ≥ 30 ×109/L. There are 9 cases (6.08%) with increased CRP. The median length of hospital stay was 9 days, and 6 children used ventilator. Compared with the moderate cases , the proportion of severe patients with < 3 months old (χ2 = 29.480, P < 0.001), non immunization (χ2 = 7.783, P = 0.005), cyanosis during cough (χ2 = 21.850, P < 0.001) and past history (χ2 = 8.156, P < 0.001) was higher, and the difference was statistically significant. The length of hospital stay of severe pertussis was significantly higher than that of moderate cases (Z = -6.712, P < 0.001). Multivariate logistic regression analysis of pertussis showed that cyanosis during cough (OR = 0.275, P < 0.001) , previous history (OR = 0.188, P = 0.008) and use of ventilators (OR = 0.141, P < 0.001). Conclusion As cyanosis during cough, previous history and use of ventilator are the risk factors of severe pertussis, it is recommended that infants with past history should be vaccinated against pertussis as soon as possible if there are no contraindications. After the diagnosis of pertussis in children under 3 months , especially those who need mechanical ventilation, respiratory tract management and observation of symptoms and signs should be strengthened to avoid developing into severe pertussis.
2022, 43(8): 150-155.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220825
Abstract:
Objective To understand the recent infection status and influencing factors of HIV-1 infected men who have sex with men (MSM) newly reported by non-governmental organizations (NGO) in Kunming city from January 2018 to December 2020, and to provide guidance for AIDS prevention and treatment for this population. Methods The limiting-antigen avidity enzyme immunoassay (LAg-Avidity EIA) combined with CD4+ T lymphocyte count was used to determine the recent infections among HIV-1 antibody positive MSM in Kunming city from January 2018 to December 2020. The influencing factors of recent infections were analyzed by Logistic regression. Results A total of 389 HIV-1 antibody positive samples were collected, and the proportion of HIV-1 recent infections was 48.1% (90/187), 51.6% (49/95) and 30.8% (33/107) from January 2018 to December 2020. There was no statistical difference in the proportion of recent infections between 2018 and 2019 (P > 0.05) . The proportion of recent infections in 2020 was lower than those in 2018 and 2019 (P < 0.05). Multivariate Logistic regression analysis showed that students (P = 0.017, OR = 2.989, 95%CI: 1.221~7.318) had a high proportion of recent infections. Conclusion The proportion of HIV-1 recent infection among MSM in Kunming showed a decreasing trend, and the proportion of recent infection was relatively higher in the certain population. The targeted measures should be taken, including strengthening the monitoring of recent infections among MSM, improving access to intervention services and promoting HIV testing through NGO.
2022, 43(8): 156-160.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220831
Abstract:
COVID-19 virus is the pathogen of the new type of corona virus disease 2019, a global infectious disease that began to spread at the end of 2019. It has caused damage to multiple organs particularly human respiratory tract. Oral lesions is considered to be a common manifestation of this disease. This article summarized the characteristics and possible mechanisms of COVID-19 related oral damage in novel coronavirus infections and oral manifestations from publications between December 2019 and November 2021. It showed that the oral manifestations of the reported cases were mainly gustatory dysfunction, xerostomia and ulcerative lesions. The mechanism of oral lesions is not yet fully understood, but 2019-nCoV enters the cell receptor ACE2 widely in oral epithelial cells. Virus replication and possible tissue inflammation and destruction could be its possible pathogenic mechanisms.
COVID-19 virus is the pathogen of the new type of corona virus disease 2019, a global infectious disease that began to spread at the end of 2019. It has caused damage to multiple organs particularly human respiratory tract. Oral lesions is considered to be a common manifestation of this disease. This article summarized the characteristics and possible mechanisms of COVID-19 related oral damage in novel coronavirus infections and oral manifestations from publications between December 2019 and November 2021. It showed that the oral manifestations of the reported cases were mainly gustatory dysfunction, xerostomia and ulcerative lesions. The mechanism of oral lesions is not yet fully understood, but 2019-nCoV enters the cell receptor ACE2 widely in oral epithelial cells. Virus replication and possible tissue inflammation and destruction could be its possible pathogenic mechanisms.
2022, 43(8): 161-165.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220826
Abstract:
Smad4 protein binds to the TGF-β type I receptor(TβR I) on transforming growth factor-β(TGF-β) and activates it. The TGF-β/Smads signaling pathway is known to play a key role in the maturation, function, and precise connectivity of vomeronasal sensory neurons(VSNs). Mutations in Smad4 lead to abnormal formation of the posterior paraolfactory bulb, resulting in abnormal olfactory conduction. Smad4 is a recognized tumor suppressor gene, and its expression in malignant tumors is significantly different from normal tissues. TGF-β transmits biological signals from the cell membrane to the nucleus through its signal transduction pathway and its substrate Smads protein to activate transcription of nucleic acid; consequently, to regulate cell differentiation, proliferation, adhesion, migration, apoptosis, angiogenesis, and immune response.
Smad4 protein binds to the TGF-β type I receptor(TβR I) on transforming growth factor-β(TGF-β) and activates it. The TGF-β/Smads signaling pathway is known to play a key role in the maturation, function, and precise connectivity of vomeronasal sensory neurons(VSNs). Mutations in Smad4 lead to abnormal formation of the posterior paraolfactory bulb, resulting in abnormal olfactory conduction. Smad4 is a recognized tumor suppressor gene, and its expression in malignant tumors is significantly different from normal tissues. TGF-β transmits biological signals from the cell membrane to the nucleus through its signal transduction pathway and its substrate Smads protein to activate transcription of nucleic acid; consequently, to regulate cell differentiation, proliferation, adhesion, migration, apoptosis, angiogenesis, and immune response.
2022, 43(8): 166-172.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220827
Abstract:
Objective To explore the application effect of PBL and evidence-based teaching method in clinical teaching of nursing students in emergency department. Method A total of 100 nursing students who practiced in the emergency department of a level A tertiary hospital in Yunnan Province from December 2020 to December 2021 were selected as the research subjects. The odd-numbered students were included in the control group, and the even-numbered students were included in the intervention group, with 50 students in each group. The control group received traditional training, and the intervention group received PBL+ evidence-based nursing training , which consisted of four progressive steps: evidence-based nursing theory teaching, PBL group discussion, nursing round report and teacher guidance. After intervention, critical thinking ability scale, teaching effect self-assessment questionnaire and theory test were used to evaluate. Results The scores of critical thinking ability, teaching effect self-assessment questionnaire and theoretical score of nursing students in the intervention group were better than those in the control group (P < 0.05). Conclusion PBL teaching method and evidence-based teaching method combined with the characteristics of the department in the clinical teaching of emergency department is helpful to improve the critical thinking ability and theoretical performance of nursing students and improve the evaluation results of teaching effect.
2022, 43(8): 173-177.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220828
Abstract:
Objective To analyze the training effect of the mixed curriculum construction of clinical four handed dentistry skills for stomatological students under the background of public health emergencies, so as to provide basis for stomatological undergraduates to expand four handed dentistry teaching. Methods Medical students who practiced in Yunnan Stomatological Hospital from 2020 to 2021 were selected as the research subjects. 30 students who practiced in 2020 were selected as the control group, and 30 students who practiced in 2021 were selected as the experimental group. The control group received traditional chair-side teaching following the clinical practice syllabus, while the experimental group received mixed teaching on the basis of chair-side teaching (online theoretical training → offline situational simulation practical training). After the training, the two groups’ theory and skill assessment results, occupational exposure and teaching satisfaction were analyzed. Results The examination results of six core skills and teaching satisfaction in the experimental group were better than those in the control group, and the difference between the two groups was statistically significant(P < 0.05). The duration of diagnosis and treatment of six core skills in the experimental group was less than that in the control group, and the difference between the two groups was statistically significant (P < 0.05); The incidence of occupational exposure in the experimental group decreased by 23.3% compared with the control group (P < 0.05). Conclusion Under the background of COVID-19, the online and offline teaching mode can improve the clinical competency and diagnosis and treatment efficiency of stomatological students, meet the requirements of infection control, and reduce the occupational exposure risk. It has high application value and clinical significance for training comprehensive and practical stomatological talents.
2022, 43(8): 178-183.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220829
Abstract:
Objective To qualitatively analyze the needs of health education for dysphagia in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients undergoing radiotherapy by using KANO model, and provide the basis for optimizing the health education. Methods Based on the KANO model, a questionnaire was designed to investigate the knowledge needs of nasopharyngeal carcinoma radiotherapy patients on dysphagia. Cluster sampling method was used to investigate 160 patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma treated in radiotherapy department of a third-class cancer hospital from September 2021 to December 2021. Results Among the 23 items of health education needs of nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients with dysphagia after radiotherapy, 6 items are necessary (26.08%), 9 items are expected (39.13%), 7 items are attractive (30.43%) and 1 item is undifferentiated (4.34%).In the importance-satisfaction matrix, 2 items (8.67%) are located in the area for improvement, and 5 items (21.73%) are located in the area for minor improvement. Conclusion The KANO model can be used in the neeeds assessment of health education of patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma radiotherapy demand investigation, which helps us to fully and comprehensively understand the needs of patients and to improve the satisfaction of patients with health education.
2022, 43(8): 184-190.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20220830
Abstract:
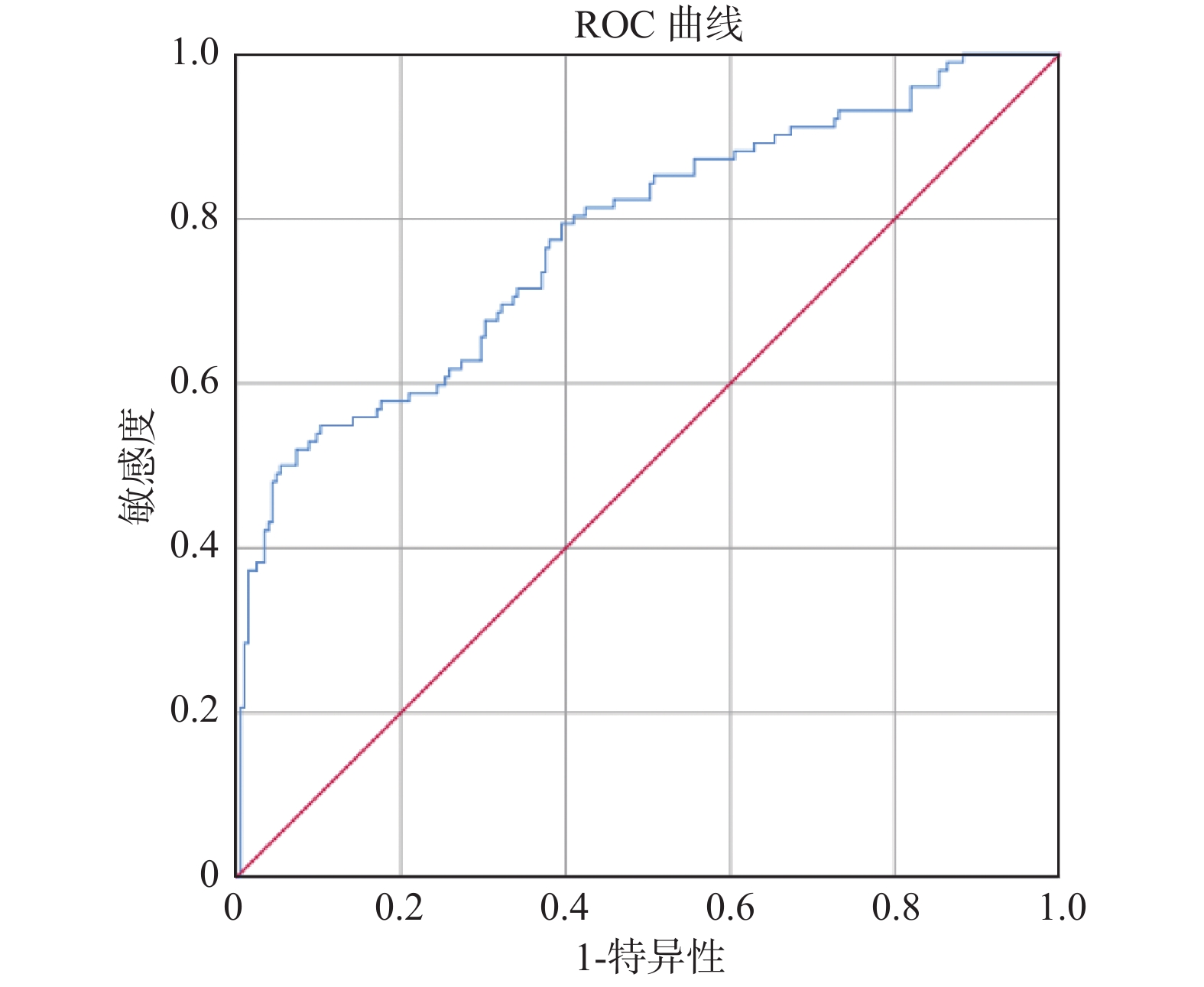
Objective To explore the risk factors of readmission in patients with AECOPD and develop a disease risk prediction model, aiming to provide an evaluation tool for early identification and screening of patients at high risk of readmission with AECOPD. Methods A total of 414 patients diagnosed with AECOPD in a tertiary hospital in Yunnan Province from January 1, 2016 to January 1, 2021 and met the criteria for inclusion and exclusion were selected as the study subjects. 70% (307) of these patients were included as the modeling group and the remaining 30% (107) patients were included as the validation group. According to whether patients have readmission as an outcome indicator, the risk factors for readmission of patients with AECOPD are analyzed and a disease risk prediction model is constructed. Results Age (OR = 0.958), nebulized inhaled hormone (OR = 1.893), predicted value of FEF75 (OR = 0.583), actual value of FEV1 (OR = 1.947) and combined respiratory failure (OR = 0.501) were included. Prediction model formula: P = 1/{1 + exp [− (3.361 + (−0.043)×age + 0.638×type of inhaled nebulized hormone + (−0.539)×predicted value of FEF75 + 0.666 × actual value of FEV1 + (−0.691)×respiratory failure)]}. The area under ROC curve (AUC) of the modeling group was 0.777, and the sensitivity and specificity were 0.898 and 0.549, respectively. The area under ROC curve (AUC) of the verification group was 0.821, and the sensitivity and specificity were 0.857 and 0.7, respectively. Conclusion The risk prediction model for readmission of AECOPD patients established in this study has good predictive efficacy, providing an evaluation tool for early identification and screening of high-risk patients with AECOPD readmission, and provides a reference for medical staff to adjust the treatment and care of high-risk patients.


 Email
Email RSS
RSS