2023 Vol. 44, No. 10
2023, 44(10): 1-9.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231016
Abstract:
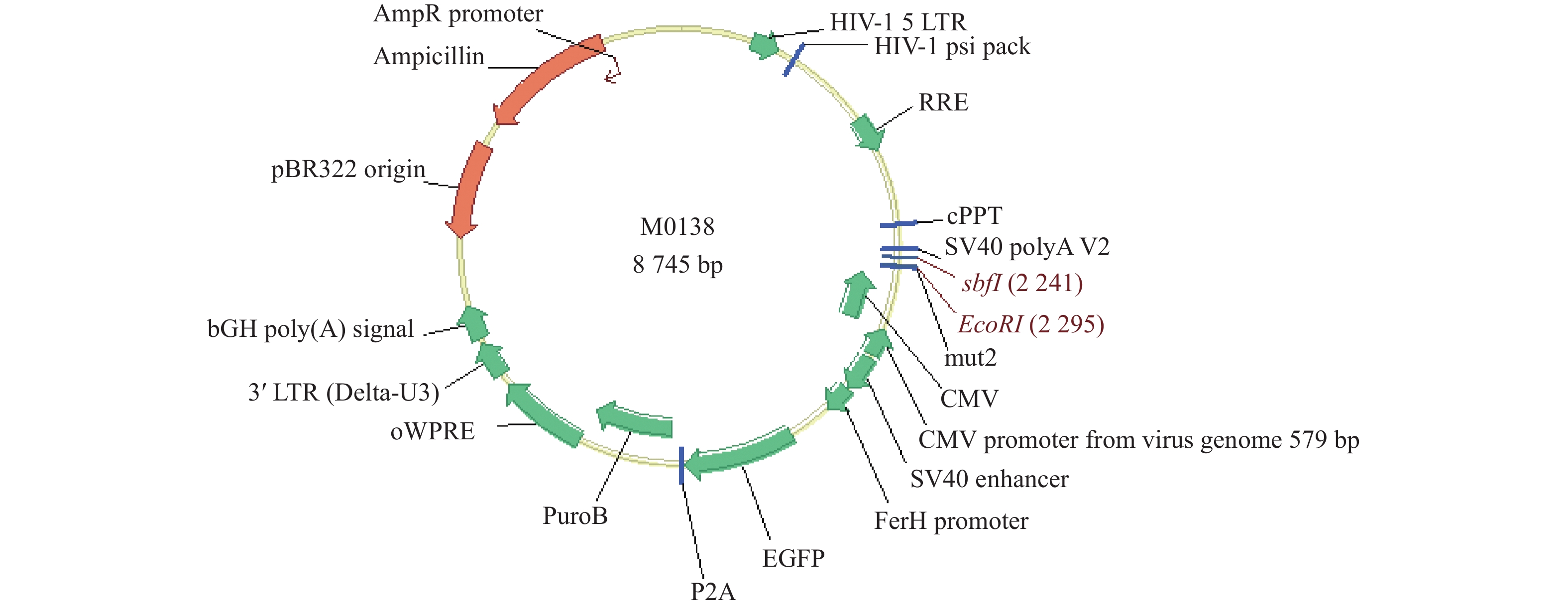
Objective To construct stable transfected cell lines of non-small cell lung cancer A549 with overexpression and knockdown LncRNA RP11-521C20.3. Methods According to lncRNA RP11-521C20.3 gene sequence, primers were designed and amplified. The target gene was then connected to a vector that had been cleaved with Sbf I and EcoRI enzymes to construct the recombinant plasmid pcSLenti-pA-RP11-521C20.3-CMV-SFH-EGFP-P2A-Puro-WPRE. This plasmid was transfected into 293T cells to package the Lentivirus containing the lncRNA RP11-521C20.3 plasmid. An shRNA (RP11-521C20.3) was constructed and connected to the pSLenti-U6-shRNA-CMV-EGFP-F2A-Puro-WPRE vector after being modified with AgeI and EcoRI enzymes. This vector was then transfected into 293T cells after verification. Recombinant plasmids pcSLenti-pA-RP11-521C20.3-CMV-SFH-EGFP-P2A-Puro-WPRE and pSLenti-U6-shRNA (RP11-521C20.3)-CMV-EGFP-F2A-Puro-WPRE were then constructed using the lentivirus-mediated method and introduced into A549 cells. Finally, RT-qPCR technology was used to detect the expression of lncRNA RP11-521C20.3 at the gene level. Results The expression level of lncRNA RP11-521C20.3 mRNA in the OV-lncRNA RP11-521C20.3 group (overexpression group) was higher than that in the NC-lncRNA RP11-521C20.3 group (overexpression control group) (P < 0.001), with a fold change of (20.43±0.69). The expression level of lncRNA RP11-521C20.3 mRNA in the sh-lncRNA RP11-521C20.3 group (knockdown group) was lower than that in the sh-NC group (knockdown control group) (P < 0.001), with a fold change of (0.21±0.08). Conclusion In this study, a stable cell line with overexpression and knockdown of lncRNA RP11-521C20.3 was successfully constructed, which laid an important foundation for the subsequent study of the role of lncRNA RP11-521C20.3 in the pathogenesis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
2023, 44(10): 10-17.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231021
Abstract:
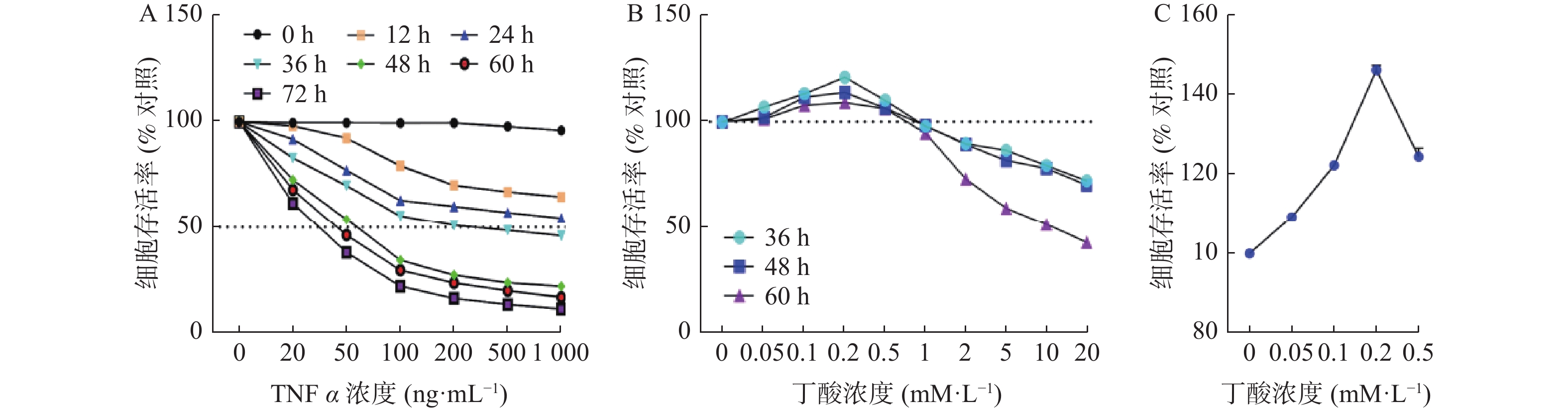
Objective To explore the protective effect of butyric acid on intestinal epithelial barrier damage induced by TNF α. Methods CCK-8 cell viability assay was used to determine the optimal concentration and time of TNFα in exerting damaged effects on Caco2 damage, and based on this, the protective effect of butyric acid on Caco2 cells was explored around the optimal time when TNFα exerted damage. Subsequently, the optimal time and concentration of TNFα and butyric acid acting on Caco2 cells were explored, and the FITC-dextran permeability of the Caco2 cell monolayer epithelial barrier, the mRNA expression of ZO-1 and Occludin, and the growth of cells after TNFα and butyric acid co-treatment were detected, as well as the expression and distribution of ZO-1 and Occludin in Caco2 cells were observed by immunofluorescence. Results TNFα, at a concentration of 100 ng/mL significantly decreased the cell viability of Caco2 after 48 hours of stimulation (P < 0.0001); butyrate at a concentration of 0.2mM/L significantly increased the cell viability of Caco2 after 48 hours of treatment (P < 0.0001). When TNFα and butyrate were co-administered, compared with the TNFα intervention group, butyrate significantly decreased the FITC-dextran permeability of the intestinal epithelial monolayer barrier caused by TNFα (P < 0.0001), and increased the expression of ZO-1 (P < 0.01) and Occludin (P < 0.01), and stabilized their distribution in Caco2 cells. Conclusion Butyrate can alleviate TNFα-induced damage to intestinal epithelial barrier, providing experimental basis for further elucidating the mechanism of butyrate in the treatment of ulcerative colitis.
2023, 44(10): 18-25.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231019
Abstract:
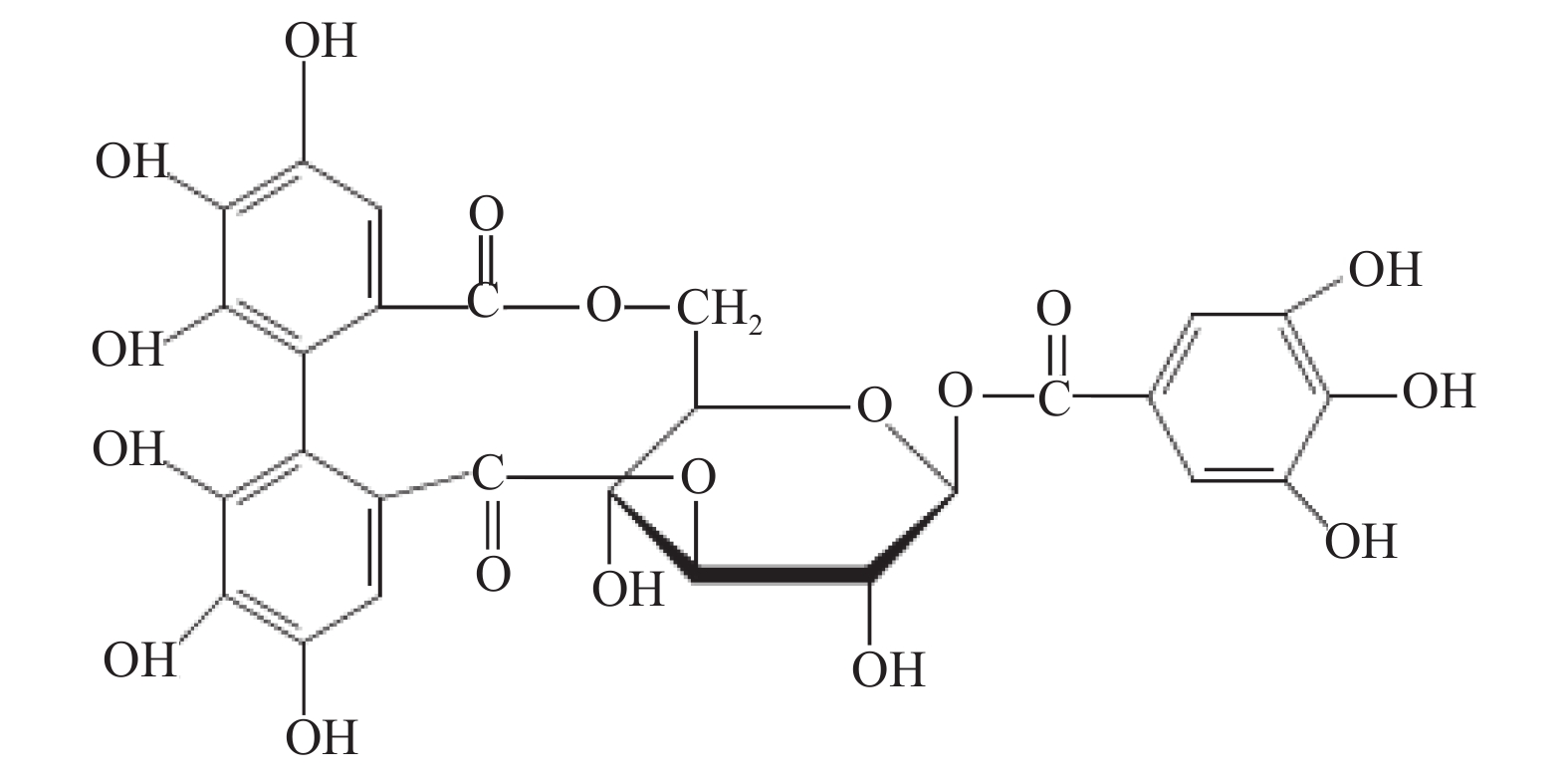
Objective To investigate the protective effects of different concentrations and durations of corilagin treatment on oxidative low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL)-induced damage in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs), as well as its effects on the expression regulation of the MyD88 signaling pathway. Methods In vitro cultured HUVECs were used to replicate the ox-LDL-induced damage model. Morphological and immunological methods were employed to identify HUVECs cells. The MTT assay was used to determine the optimal conditions for replicating the ox-LDL-induced damage model in HUVECs. Cells were divided into different groups based on different treatments: normal group, model group, Corilagin (3.125, 6.25, 12.5, 25, 50 µmol/L) group, and positive control (VE 10 µmol/L, Simvastatin 1 µmol/L) group. The protective effect of corilagin on ox-LDL-induced damage in HUVECs was observed. Western blot and RT-qPCR methods were used to detect the expression changes of MyD88, P65, TNF-α, and MCP-1 in HUVECs cells. Results The cultured cells were confirmed as HUVECs by using morphological and immunological methods. The best condition for replicating ox-LDL-induced damage to HUVECs was 12 hours of treatment with 70 mg/L of ox-LDL. MTT results showed that compared with the ox-LDL group, the corilagin group had a significantly higher cell viability (P < 0.01). RT-qPCR and Western blot results showed that compared with the control group, the mRNA and protein expression of MyD88, P65, TNF-α, and MCP-1 were increased in the ox-LDL group (P < 0.01). Compared with the ox-LDL group, the mRNA and protein expression of MyD88, P65, TNF-α, and MCP-1 were decreased (P < 0.01) in the corilagin group and positive control group, and the corilagin group showed a dose-dependent downregulation of the mRNA and protein expression of MyD88, P65, TNF-α, and MCP-1. Conclusion With the increase of time and concentration, corilagin can significantly improve the cell viability of HUVECs induced by ox-LDL damage, and its protective effect is associated with the inhibition of the MyD88 signaling pathway.
2023, 44(10): 26-32.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231004
Abstract:
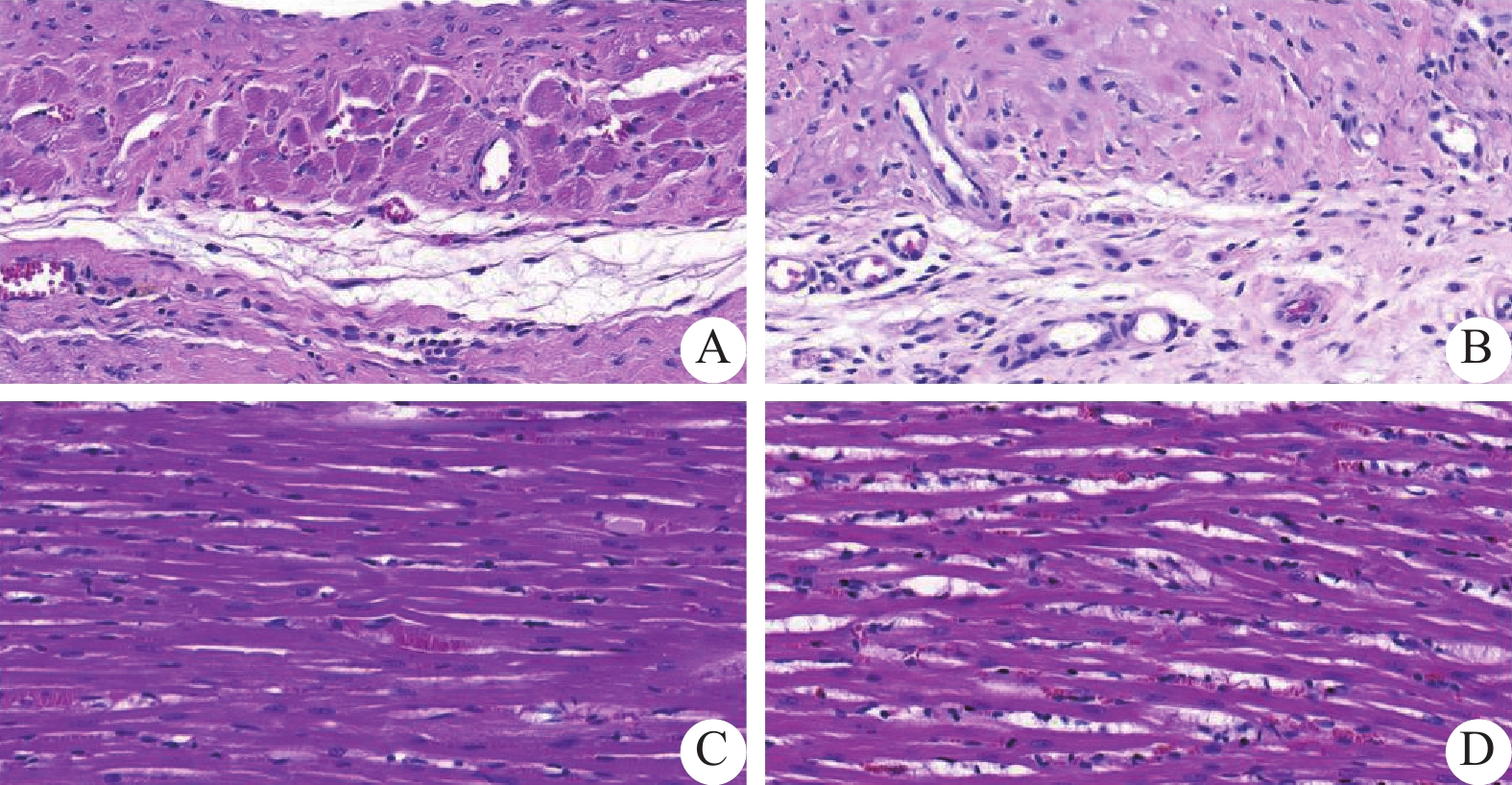
Objective To explore the effect of exercise rehabilitation on cardiac fibrosis and function in rats with myocardial infarction. Methods Twenty-four male SD rats were randomly divided into four groups: MI-E group, MI-Sed group, Sham-E group and Sham-Sed group, with five to seven rats in each group. A myocardial infarction model was prepared using ligation of the left anterior descending coronary artery (LAD), while the sham surgery group underwent needle insertion without ligation. One week after surgery, exercise training was initiated, including one week of adaptive exercise and four weeks of formal exercise. The non-exercise group did not participate in any exercise training throughout the study. After completion of the exercise regimen, echocardiography, HE staining, Masson staining, Tenel staining, and transmission electron microscopy were performed for evaluation. Results Compared with sham group, left ventricular wall thinning and systolic function were decreased in MI groups, especially in MI-Sed group (P < 0.05), while LVESD, LVEF and FS were improved in MI-E group compared with MI-Sed group (P < 0.05); there was no significant difference between Sham-E group and Sham-Sed group (P > 0.05). Compared with the sham group, HE staining showed that cardiomyocyte exhibited different degrees of lysis with inflammatory cell infiltration and fibroblast proliferation in the MI group while the damage was milder in the MI-E group. Masson staining showed that cardiomyocyte was disorganized and myocardial fibrosis was significantly increased in the MI group compared with the sham group, while collagen volume fraction (CVF%) was decreased in the MI-E group compared with the MI-Sed group and the Sham-E group compared with the Sham-Sed group (P < 0.05). Tunel staining showed that compared with the Sham group, the MI group had increased myocardial cell apoptosis, while the MI-E group had a lower myocardial cell apoptosis index compared to the MI-Sed group, Sham-E group, and Sham-Sed group (P < 0.05). Transmission electron microscopy showed that compared with the Sham group, the MI group had severe damage to myocardial cells and mitochondria, as well as loose and disordered muscle fibers, while the MI-E group had milder myocardial cell injury, more intact mitochondrial structure, and more formation of autophagosomes. Conclusion Exercise rehabilitation can reduce cardiomyocyte damage and apoptosis, reduce myocardial infarct area, improve myocardial fibrosis and cardiac function in MI rats. Exercise can moderately induce autophagy level to play a cardioprotective role.
2023, 44(10): 33-38.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231009
Abstract:
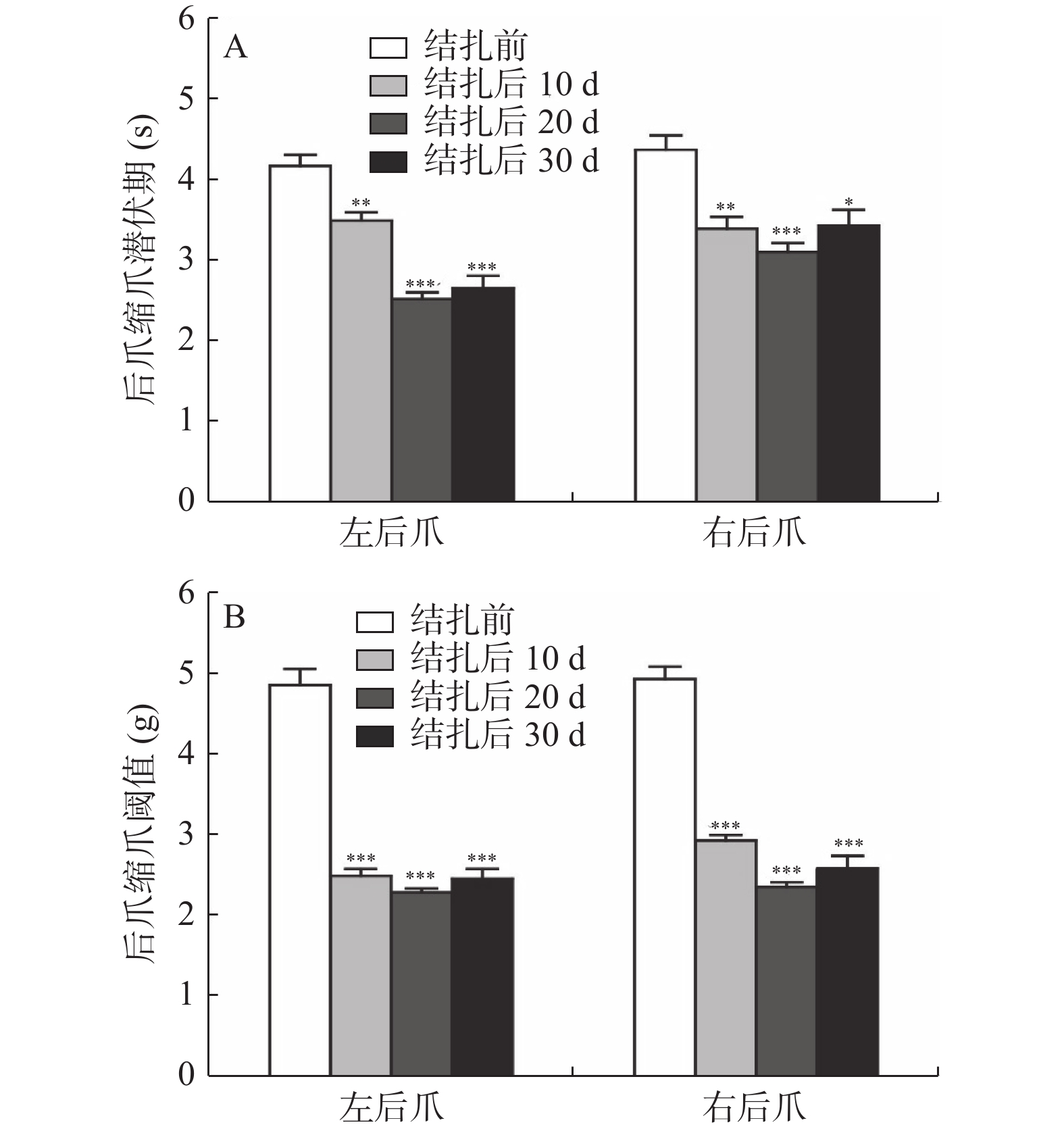
Objective To explore the antinociception of acupotomology in rats with sciatic nerve ligation, so as to provide experimental basis for the clinical application and promotion of needle-knife therapy on neuralgia. Methods The hot-plate test was used to measure the hindpaw withdrawal latency (HWL) induced by thermal stimuli, and the Randall-Selitto test was used to measure the hindpaw withdrawal threshold (HWT) induced by pressure stimuli as indicators of pain threshold. The chronic constriction injury (CCI) model was established by partial ligation of the left sciatic nerve to create neuropathic pain in rats. The CCI rats were randomly divided into a model group, a control group, and a needle-knife treatment group, and the pain thresholds of each group of rats were measured. The CCI rats were further randomly divided into a morphine group (subcutaneous injection of morphine 10 mg/kg) and a needle-knife treatment group (needle-knife intervention), and the pain thresholds in each group of rats were observed. Results Compared with before ligation, bilateral HWL and HWT of rats decreased after left sciatic nerve ligation at 10 d (HWL: Pleft < 0.01, Pright < 0.01; HWT: Pleft < 0.001, Pright < 0.001), 20 d (HWL: Pleft < 0.001, Pright < 0.001; HWT: Pleft < 0.001, Pright < 0.001) and 30 d (HWL: Pleft < 0.001, Pright < 0.05; HWT: Pleft < 0.001, Pright < 0.001). Compared with the control group, the HWL (left: P < 0.001; right: P < 0.001) and HWT (left: P < 0.001; right: P < 0.001) of rats in the needle-knife group were significantly prolonged; compared with the model group, the HWL (left: P < 0.001; right: P < 0.001) and HWT (left: P < 0.001; right: P < 0.001) of rats in the needle-knife group were also significantly prolonged. However, there was no significant difference between the model group and the control group (P > 0.05). Compared with the morphine group, the analgesic effect of the needle-knife group on neuropathic pain was stable and lasted longer, while the subcutaneous injection of morphine had a significant analgesic effect at 20-180 min after injection, but its analgesic effect weakened or even disappeared with the prolongation of time. Conclusion Needle-knife therapy has an analgesic effect on CCI rats. Compared with morphine, the analgesic effect of needle- knife therapy is more stable and lasting.
2023, 44(10): 39-46.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231018
Abstract:
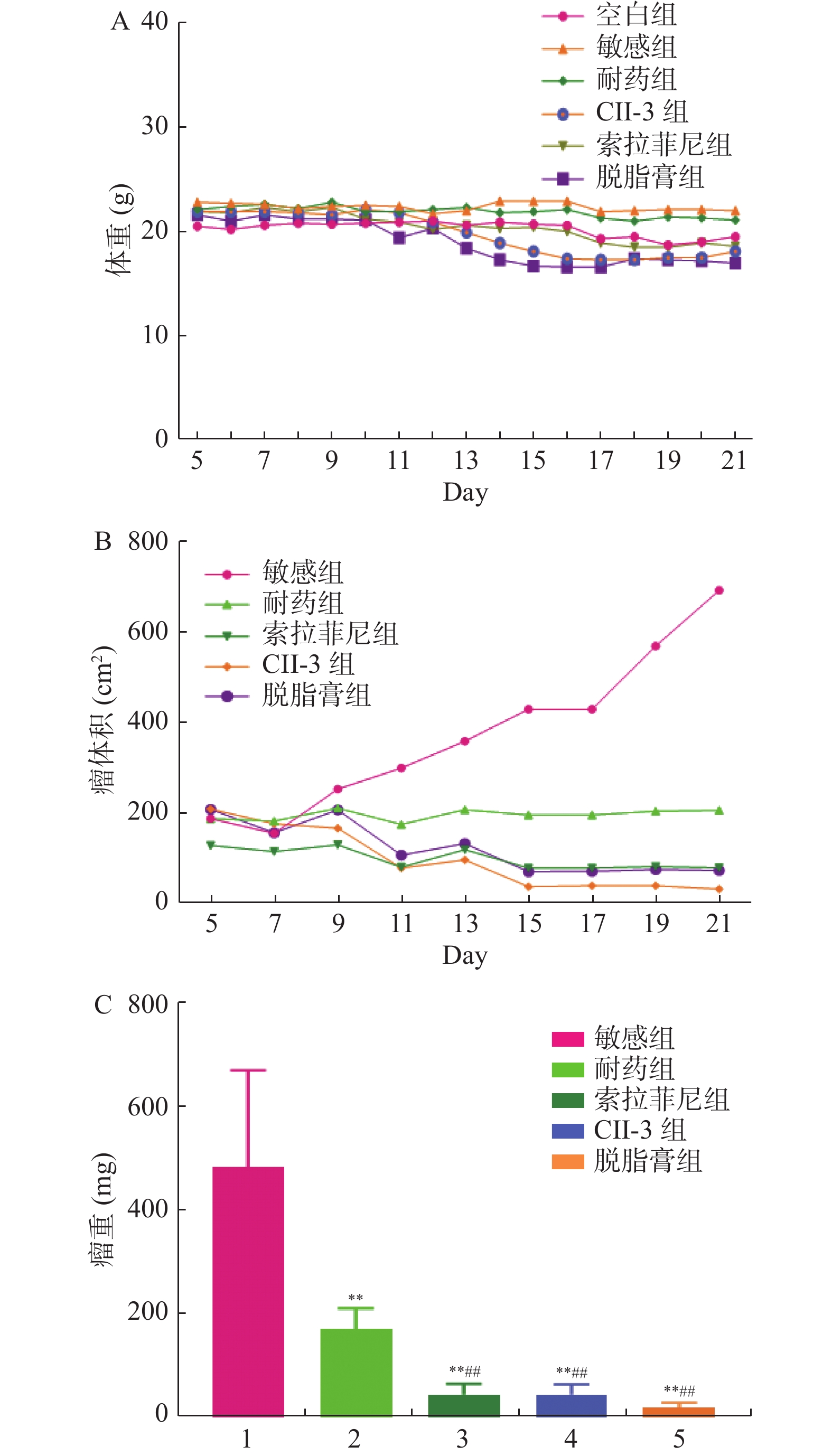
Objective To investigate the effects and preliminary mechanisms of the extract CII-3 and defatted ointment of Periplaneta americana on autophagy, invasion and metastasis of drug-resistant hepatocellular carcinoma cell line BEL-7402/5-FU. Methods The transplantation tumors of liver cancer-sensitive cells BEL-7402 and liver cancer-resistant cells BEL-7402/5-FU were treated with Sorafenib, CII-3, and defatted ointment drugs. Then, the serum biochemical indicators of the nude mice, changes in tumor size, and changes in organ indices such as heart, liver, kidney, and spleen were observed after drug administration. The histopathological changes in the liver and tumor were also observed, along with changes in autophagy-related factors and invasion and metastasis-related factors in tumor tissue cells. Results CII-3 and the deffated cream reduced the body weight of nude mice and inhibited tumor growth, significantly reducing tumor weight (P < 0.01). CII-3 increased the spleen index and heart index (P < 0.05); compared to the drug-resistant group, the CII-3 group showed an upward trend in serum CR (P < 0.05). Sorafenib and CII-3 treatment induced tumor tissue necrosis, with better effects than the deffatede ointment group; compared to the drug-resistant group, both the CII-3 and deffatede ointment groups significantly inhibited autophagy and invasion-related factors, except for AKT (P < 0.05). Conclusion Periplaneta americana extract CII-3 and deffatede ointment can inhibit the autophagy, invasion and metastasis of drug-resistant hepatocellular carcinoma cells, and also have a good anti-tumor effect. Further observation is needed for its liver and kidney damage on nude mice with hepatocellular carcinoma transplanted tumors.
2023, 44(10): 47-54.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231028
Abstract:
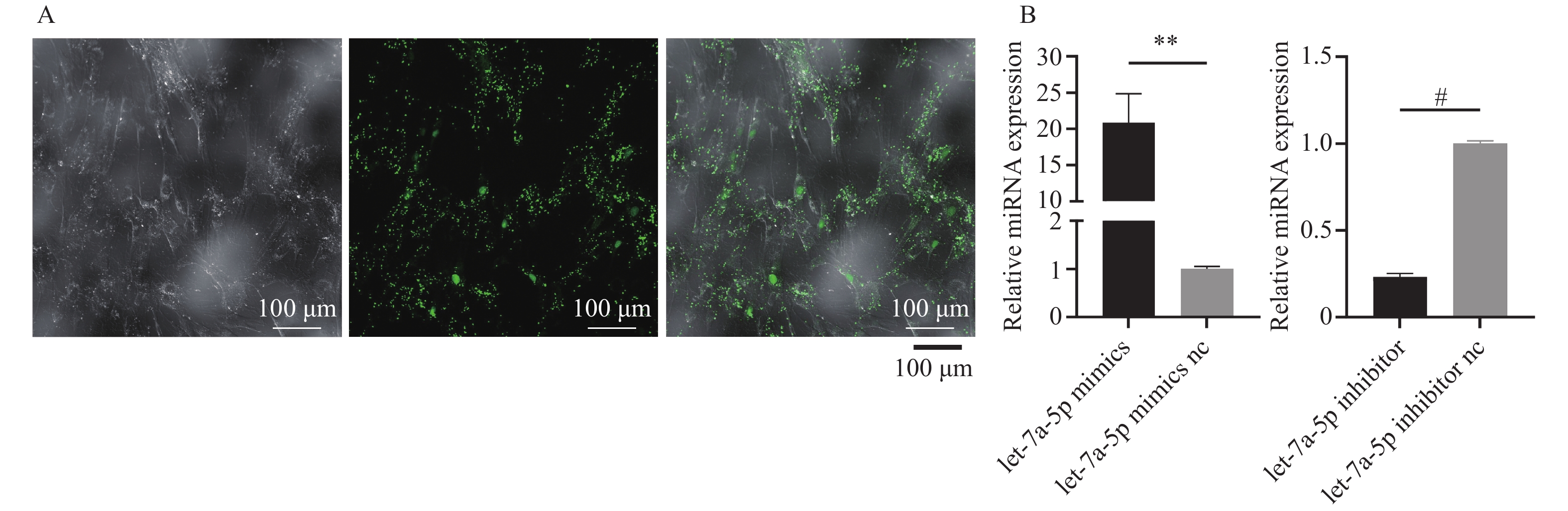
Objective To investigate the effect of hsa-let-7a-5p on the proliferation and apoptosis of periodontal ligament stem cells (PDLSCs). Methods let-7a-5p mimics, mimics nc, let-7a-5p inhibitor, and inhibitor nc were transfected into PDLSCs, and transfection efficiency was measured by RT-qPCR. The effects of let-7a-5p on PDLSCs proliferation were evaluated by CCK-8, cell cycle, and EdU experiments, while the apoptosis rate of PDLSCs was detected by apoptosis experiments. Results let-7a-5p was successfully transfected into PDLSCs. let-7a-5p mimics inhibited cell proliferation (P < 0.05) and promoted cell apoptosis of PDLSCs (P < 0.01). let-7a-5p inhibitor promoted cell proliferation (P < 0.05) and inhibited cell apoptosis of PDLSCs (P < 0.01). Conclusion hsa-let-7a-5p can inhibit the proliferation of PDLSCs and promote the apoptosis of PDLSCs.
2023, 44(10): 55-59.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231010
Abstract:
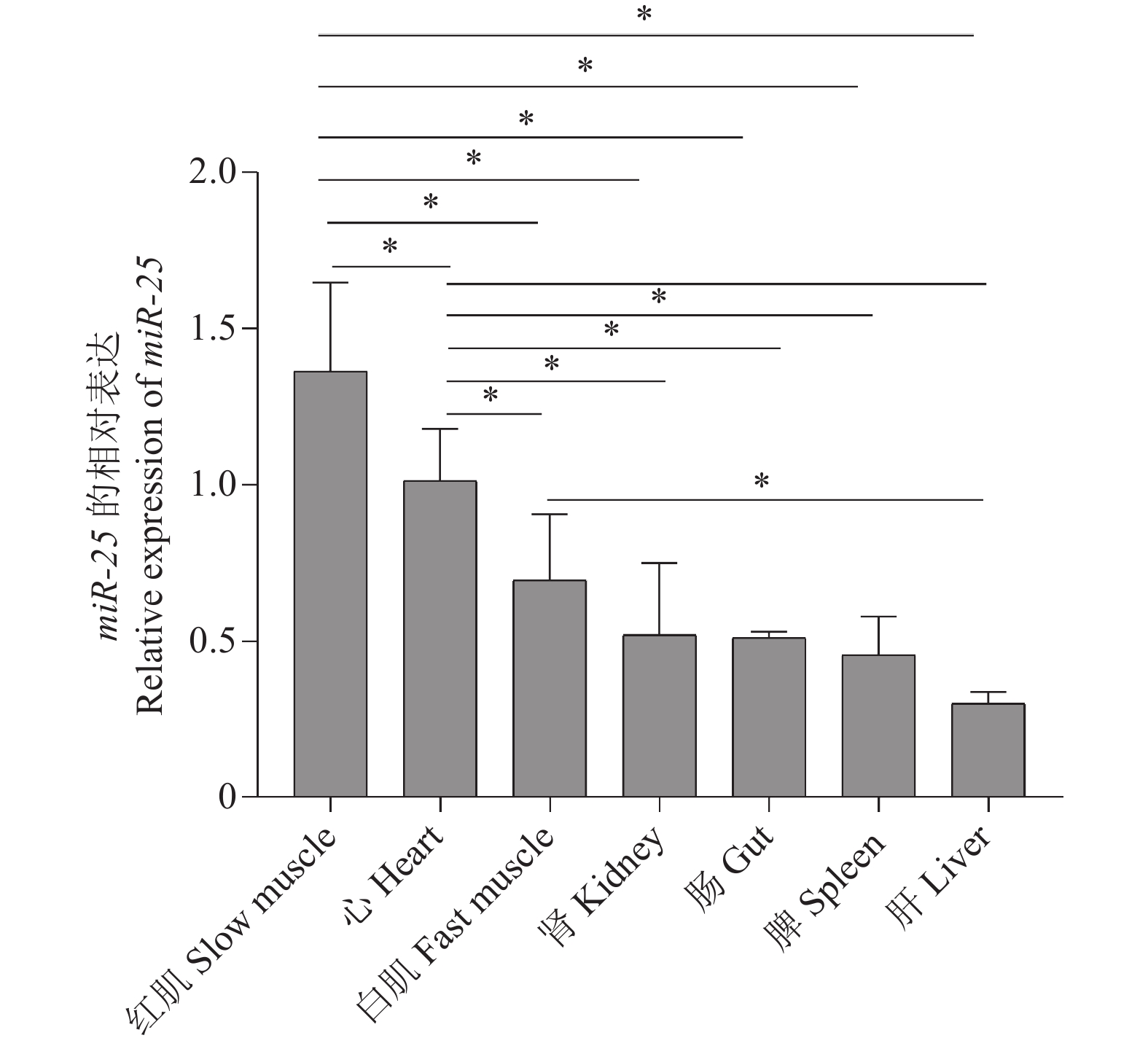
Objective To study the spatiotemporal expression profiles of miR-25 in the Chinese perch(Siniperca chuatsi), to predict its targeting core Circadian clock genes, and to explore its possible biological significance. Methods Real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR was used to analyze the expression characteristics of miR-25 in various tissues and embryos at different stages of Siniperca chuatsi, and TargetScan was used to predict its targeted core clock genes. Results The expression level of miR-25 was higher in the red muscle and heart (P < 0.05), while it was lower in the spleen, kidney, intestine, and liver of the Chinese perch. However, the expression level difference in these four tissues was not statistically significant (P > 0.05). The expression level of miR-25 was higher in the phase 2 of cell cycle in embryos (P < 0.05), and it gradually decreased as the embryos developed. Target gene prediction results showed that the 3’UTR region of the rhythmic genes Arntl2 and Nr1d2b mRNA contained target sites for miR-25. Conclusion miR-25 exhibited maternal expression during embryonic development and may have important regulatory significance in the red muscle and heart of Chinese perch. Additionally, miR-25 may regulate the circadian rhythm by targeting the expression of Arntl2 and Nr1d2b, providing a reference for further research on the physiological effects of miR-25 and the regulation of circadian rhythm to prevent related diseases.
2023, 44(10): 60-66.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231026
Abstract:
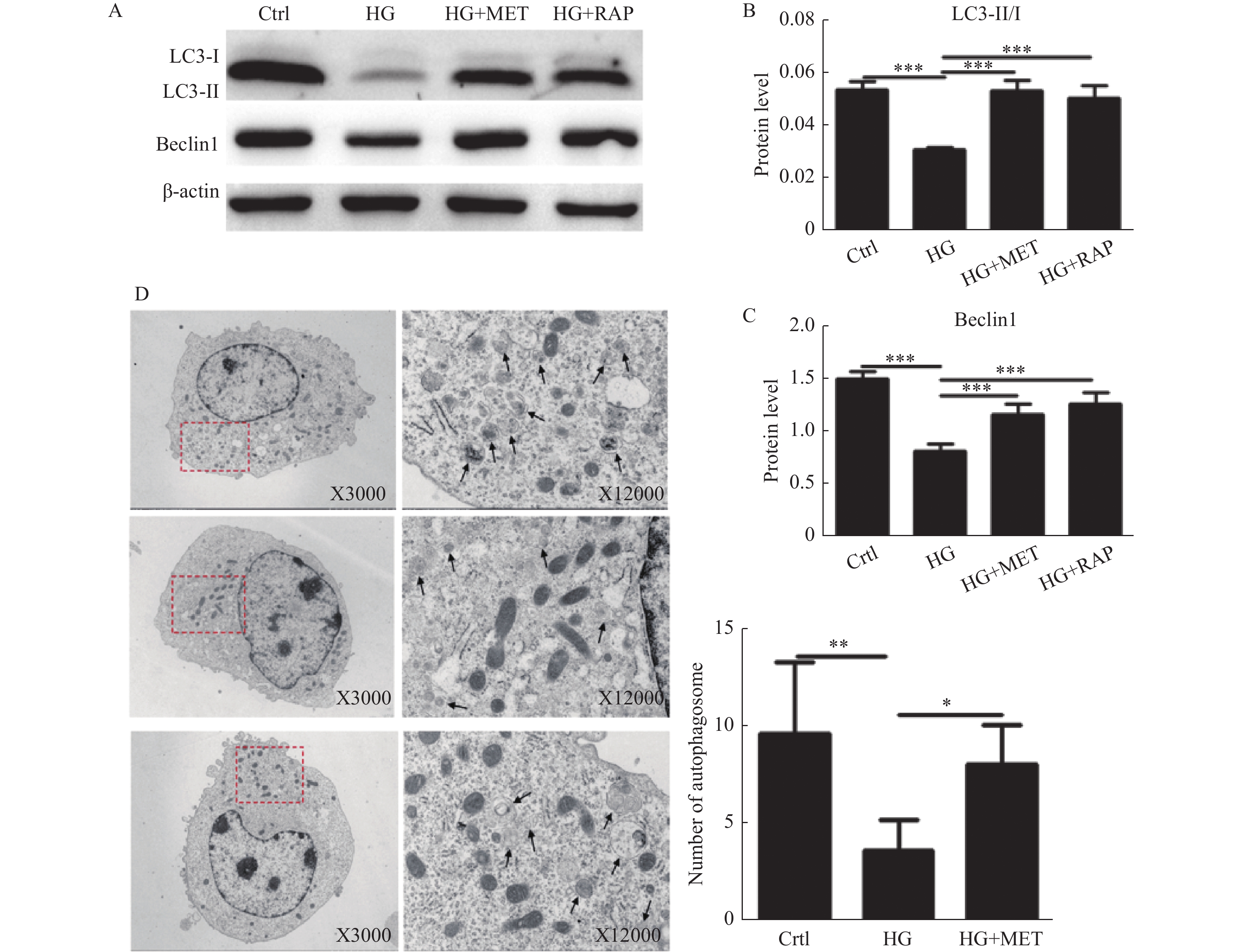
Objective To investigate the effect and regulatory mechanism of metformin on autophagy and cell proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) cultured in high glucose in mice aortic. Methods Western blot was used to detect the changes in microtubule-associated protein light chain 3-II (LC3-II) and Beclin-1 protein levels in different treatment groups. Transmission electron microscope was used to observe the the level of autophagosomes in VSMCs of each treatment group. Western blot was used to detect the expression levels of p-AMPK/AMPK and PPAR-γ proteins in different treatment groups. The EDU method was used to detect the proliferation of VSMCs in different treatment groups. Results Metformin and rapamycin reversed the inhibitory effect of high glucose on VSMC autophagy (P < 0.001). Compound C and GW9662 enhanced the inhibitory effect of high glucose on VSMC autophagy (P < 0.05). Metformin reversed the negative regulation of high glucose on the AMPK/PPAR-γ pathway (P < 0.01). Metformin and rapamycin inhibited high glucose-induced VSMC proliferation (P < 0.001), and Compound C and GW9662 reversed the inhibitory effect of metformin on high glucose-induced VSMC proliferation (P < 0.05). Conclusion High glucose promotes the proliferation of VSMCs, which may be regulated by autophagy. Metformin can upregulate autophagy levels in VSMCs by activating the AMPK/PPAR-γ pathway, thereby inhibiting the abnormal proliferation of VSMCs induced by high sugar.
2023, 44(10): 67-76.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231017
Abstract:
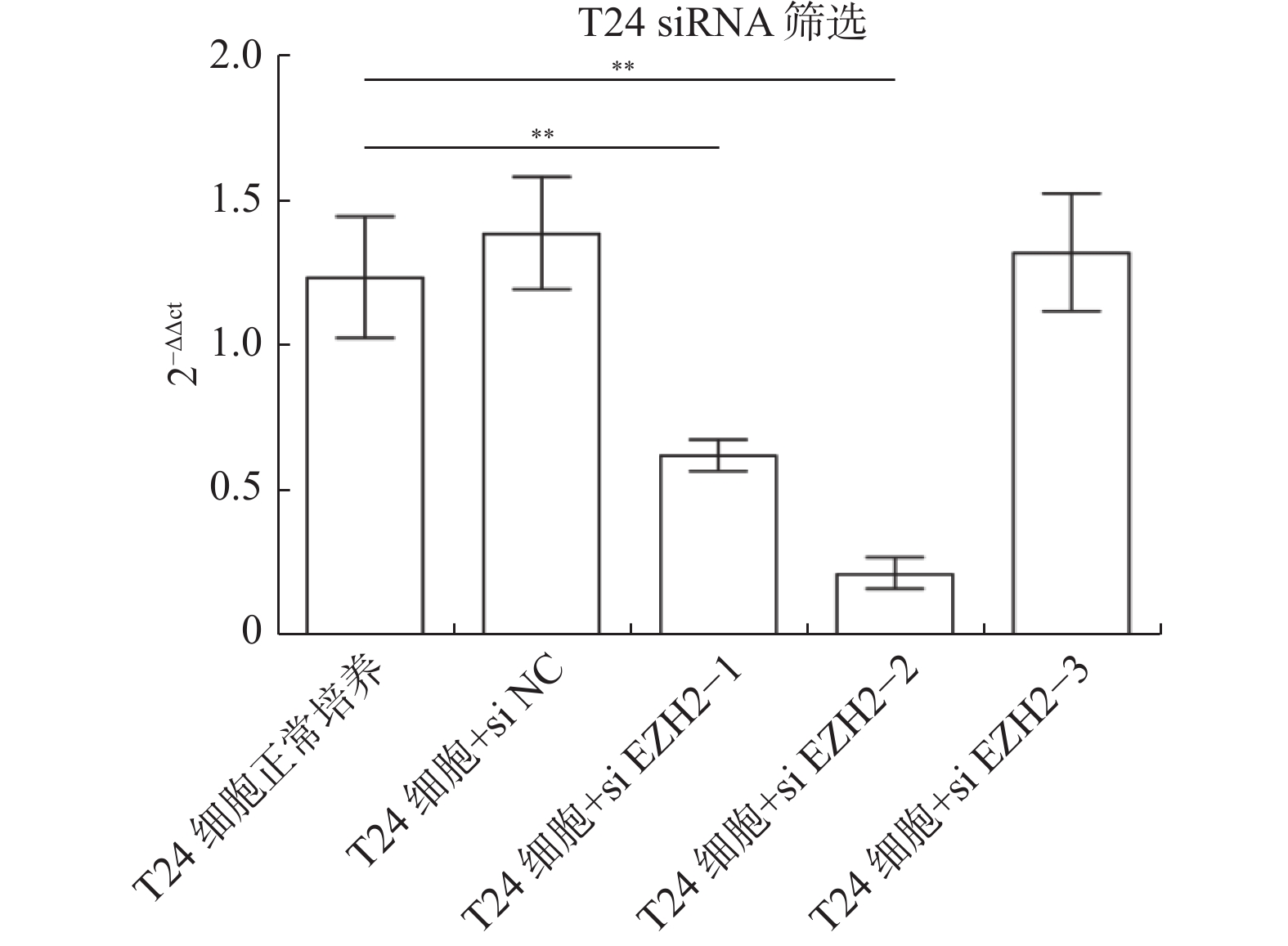
Objective To explore the synergizing effect of histone methyltransferase enhancer of Zeke 2 (EZH2) inhibitors on Gemcitabine and Cisplatin (GC) chemotherapy regimen in bladder cancer treatment. Methods Firstly, EZH2 siRNA knockdown lines were constructed, and then the expression level of siRNA in bladder cancer UCC cells was verified using qPCR and WB. According to different treatments, these cells were divided into control group (bladder cancer T24 cells cultured normally), GC chemotherapy group (T24 cells + GC), siEZH2 transfection group (T24 cells + siEZH2 transfection + GC), GSK126 inhibitor group (T24 cells + GSK126 5 μM + GC), UNC1999 inhibitor group (T24 cells + UNC1999 5 μM + GC), EI1 inhibitor group (T24 cells + EI1 5 μM + GC), DZNep1 inhibitor group (T24 cells + DZNep1 5 μM + GC), and EPZ005687 inhibitor group (T24 cells + EPZ005687 5 μM + GC). CCK-8, plate clone formation, Annexin/PI, and other experiments were used to detect the proliferation rate, apoptosis rate, and the effect on the cell cycle of the eight groups of cells respectively. Then, 30 female BALB/C nude mice were randomly divided into control group (bladder cancer T24 cells cultured normally), T24 cells + EZH2 inhibitor solvent buffer group, T24 cells + GC chemotherapy group, T24 cells + UNC1999 EZH2 inhibitor group, and T24 cells + UNC1999 EZH2 inhibitor + GC chemotherapy group, with 6 mice in each group. Tumor formation experiment in nude mice was used to detect the growth of transplanted tumors in each group after transfection, immunohistochemistry was used to observe the expression of Ki67 and EZH2 in the transplanted tumor tissues, and blood routine examination was used to detect the number of white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets and the degree of bone marrow suppression in nude mice. Results In T24 cells transfected with siRNA plasmids, siEZH2-1 and siEZH2-2 showed statistically significant differences in siRNA and protein expression levels compared to the control group (P < 0.01). Compared to the control group, the above experimental groups found that EZH2 inhibitors can inhibit the proliferation, migration, and invasion ability of T24 cells, and increase the proportion of early apoptotic cells through CCK-8, plate cloning, and Annexin V/PI double staining, and Pi single staining experiments ( P < 0.01). Among them, in the plate cloning experiment, the difference in the number of cell clones between the experimental group T24 cells+EPZ005687 5 μM+GC chemotherapy drug group and the control group was statistically significant ( P < 0.05). In vivo experiments in mice showed that the tumor weight of nude mice treated with GC chemotherapy drugs or EZH2 inhibitors decreased compared to the control group ( P < 0.05), and the blood cell content also increased in the blood routine examination. Conclusion EZH2 inhibitors can enhance the sensitivity of bladder cancer GC chemotherapy regimen, thereby reducing the proliferation, migration, and growth of bladder cancer cells in nude mice xenografts. Additionally, combination therapy can significantly reduce bone marrow suppression. These findings suggest that combination therapy plays a role in sensitizing bladder cancer chemotherapy.
2023, 44(10): 77-82.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231022
Abstract:
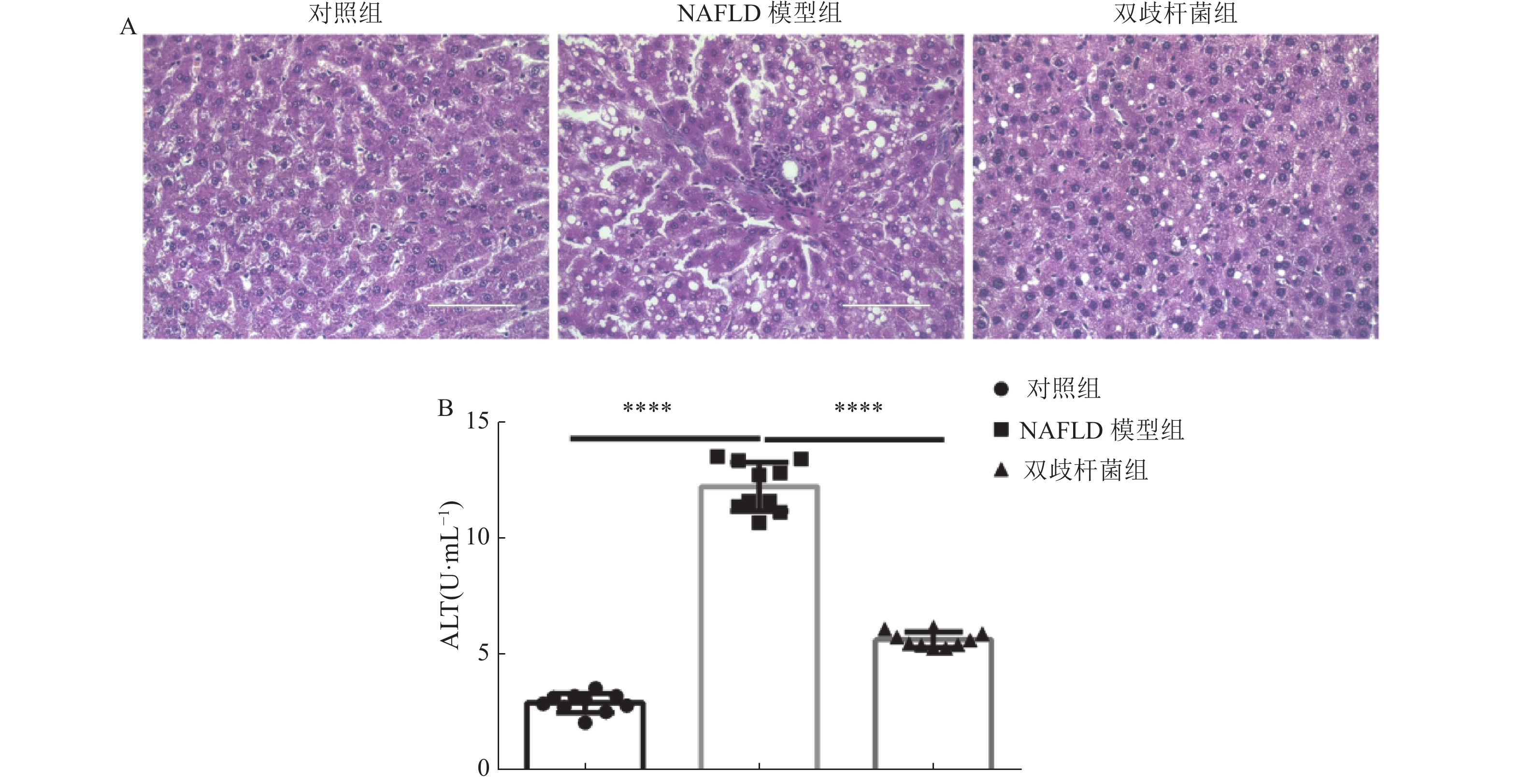
Objective To investigate the therapeutic effects of probiotics containing Bifidobacterium on a mouse model of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and its impact on the gut microbiota. Methods C57BL/6J mice were divided into three experimental groups. The control group (n = 10) of mice was fed a normal diet, the NAFLD model group (n = 10) was fed a high-fat diet, and the probiotics group (n = 10) was given Bifidobacteriumtrisporus treatment while using NAFLD model mice. HE staining was performed on paraffin sections of mouse liver from different groups at the end of the experiment to observe pathological changes. The 16S rRNA gene sequencing technique was used to detect the gut microbiota in each group of mice, followed by bioinformatics analysis. Results Compared with the control group, NAFLD mice showed increased accumulation of liver fat, increased number of lipid droplets, enlarged cells, and increased levels of serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT)(P < 0.0001). After treatment with Bifidobacteriumtrisporus, the accumulation of liver fat in NAFLD mice decreased and serum ALT levels decreased (P < 0.0001). Microbiota analysis of the intestinal tract identified 348 common species of microorganisms in the three groups. Functional analysis of the microbiota showed that the metabolic function of the intestinal microbiota in the Bifidobacterium group was intermediate between the control group and the NAFLD group; Bifidobacterium treatment was able to alter the abundance of specific intestinal microorganisms in the NAFLD model, and these intestinal microorganisms may be involved in the regulation of metabolic function pathways such as glutathione metabolism, purine metabolism, and sphingolipid metabolism in the body. Conclusion Bifidobacterium may improve NAFLD by regulating the function of the intestinal microbiota in a mouse model, and it has the potential to improve disordered lipid metabolism in the body.
2023, 44(10): 83-91.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231023
Abstract:
Objective To explore the mechanisms of miR-196b affecting the progression of lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD). Methods The expression level of miR-196b in LUAD tissues was analyzed through TCGA database. TargetScan was used to predict its downstream target genes, and dual-luciferase assay was performed to validate the predictions. qRT-PCR was used to detect the expression of miR-196b and ETS-related gene (ERG) in LUAD cell lines. MTT, scratch healing, and Transwell assays were used to respectively assess the changes in proliferation, migration, and invasion abilities of LUAD cells after different treatments. Results miR-196b was highly expressed in LUAD (P = 3.50e-17) and negatively regulated ERG. Overexpression of miR-196b promoted proliferation, migration, and invasion of LUAD cells (P < 0.05). Rescue experiments confirmed that miR-196b/ERG regulatory axis can affect the proliferation, migration, and invasion of LUAD cells ( P < 0.05). Conclusion The molecular mechanism of miR-196b targeting ERG in promoting the progression of LUAD has potential significance for the development of new clinical treatment methods for LUAD.
2023, 44(10): 92-99.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231024
Abstract:
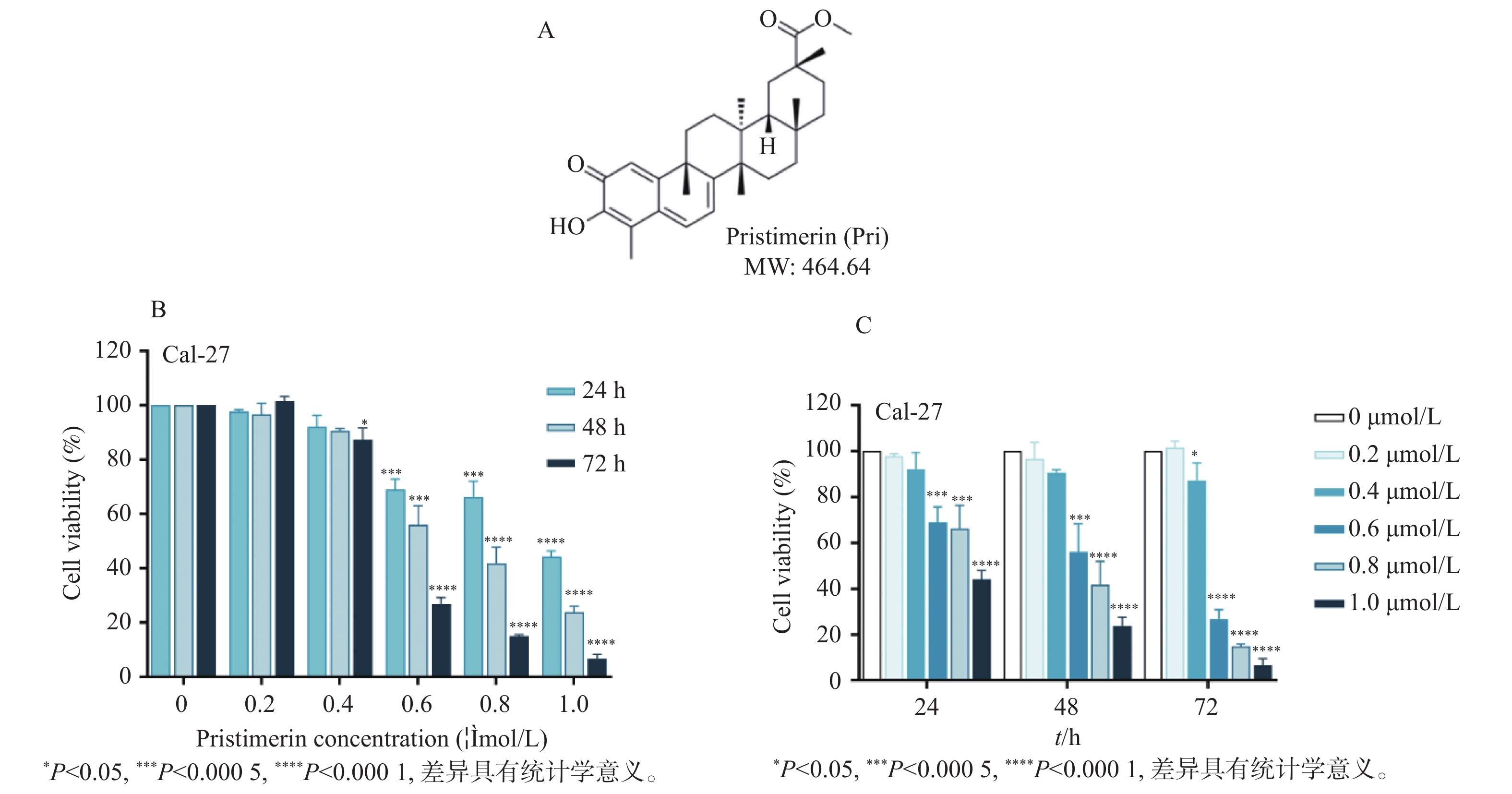
Objective To investigate the effect of pristimerin on the proliferation ability of human oral squamous cell carcinoma cells CAL-27 and its related mechanisms. Methods CCK-8 assay was performed to determine the proliferative bioactivity of CAL-27 cells treated with different concentrations of pristimerin, and the IC50 was calculated for different time periods. Colony formation assay was used to detect the cloning ability of CAL-27 cells. Western blotting was used to detect the protein expression levels of the proliferation marker PCNA and the autophagy flux markers BECLIN1, LC3B-II, and LC3B-I. CAL-27 cells were treated with pristimerin in combination with the autophagy inducer rapamycin (RAPA), and Western blotting was used to detect the protein expression levels of PCNA and the autophagy flux markers BECLIN1, LC3B-II, and LC3B-I. Results Compared with the blank group, the pristimerin at various concentration gradients can inhibit the viability of CAL-27 cells (P < 0.05), and it exhibits concentration-time dependence. Compared with the blank group, the expression levels of PCNA, BECLIN1 and LC3B-II/LC3B-I proteins in cells were significantly upregulated after treatment with the pristimerin (P < 0.05). Compared with the group treated with only the pristimerin, the combined treatment of the pristimerin with the autophagy activator rapamycin (RAPA) enhanced the cell activity of CAL-27 cells (P < 0.05), and the expression levels of PCNA, BECLIN1, and LC3B-II/LC3B-I proteins were significantly upregulated (P < 0.05). Conclusion Pristimerin significantly inhibits the proliferation of CAL-27 oral squamous carcinoma cells in vitro, which may be associated with downregulation of autophagy-related genes BECLIN1, LC3B-II, and LC3B-I.
2023, 44(10): 100-106.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231011
Abstract:
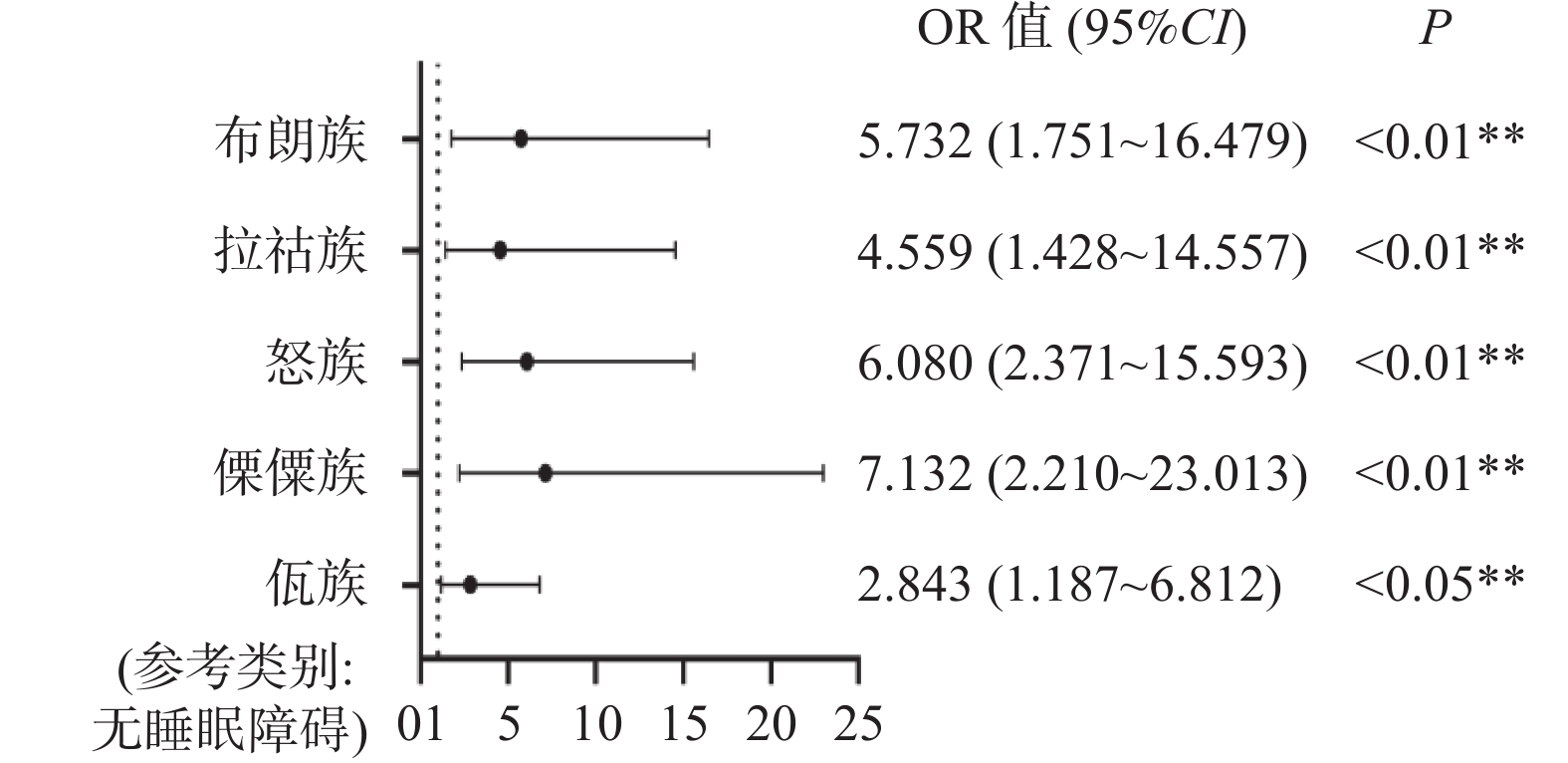
Objective To understand the occurrence of depression symptoms and its influencing factors among youth in eight indigenous ethnic minority groups in Yunnan Province, in order to provide a basis for promoting the psychological health of different ethnic youth groups. Methods By stratified random sampling, 9 patient health questionnaires were used to investigate 15~44 years old young people from eight ethnic minorities in three prefectures (cities) of Yunnan Province. Results Among the 1145 minority youth included in the analysis, the detection rate of depressive symptoms was 17.29%. After gender standardization, the Wa (14.18%) and Nu (11.04%) ethnic groups had higher rates of depressive symptoms. Sleep disorder was a common risk factor for depressive symptoms among five ethnic groups (P < 0.05). The likelihood of depressive symptoms in female Jinuo individuals was 9.245 times higher than in males (95% CI: 1.062-54.002). Patients with chronic diseases in the Lisu ethnic groups were 5.796 times (95% CI: 1.684~19.944)(P < 0.01) more likely to have depressive symptoms than those without the disease. Conclusion The occurrence and influencing factors of depression symptoms among the youth of eight indigenous minority groups in Yunnan Province vary among ethnic groups, and targeted policies should be implemented according to the unique situations of different ethnic groups.
2023, 44(10): 107-113.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231003
Abstract:
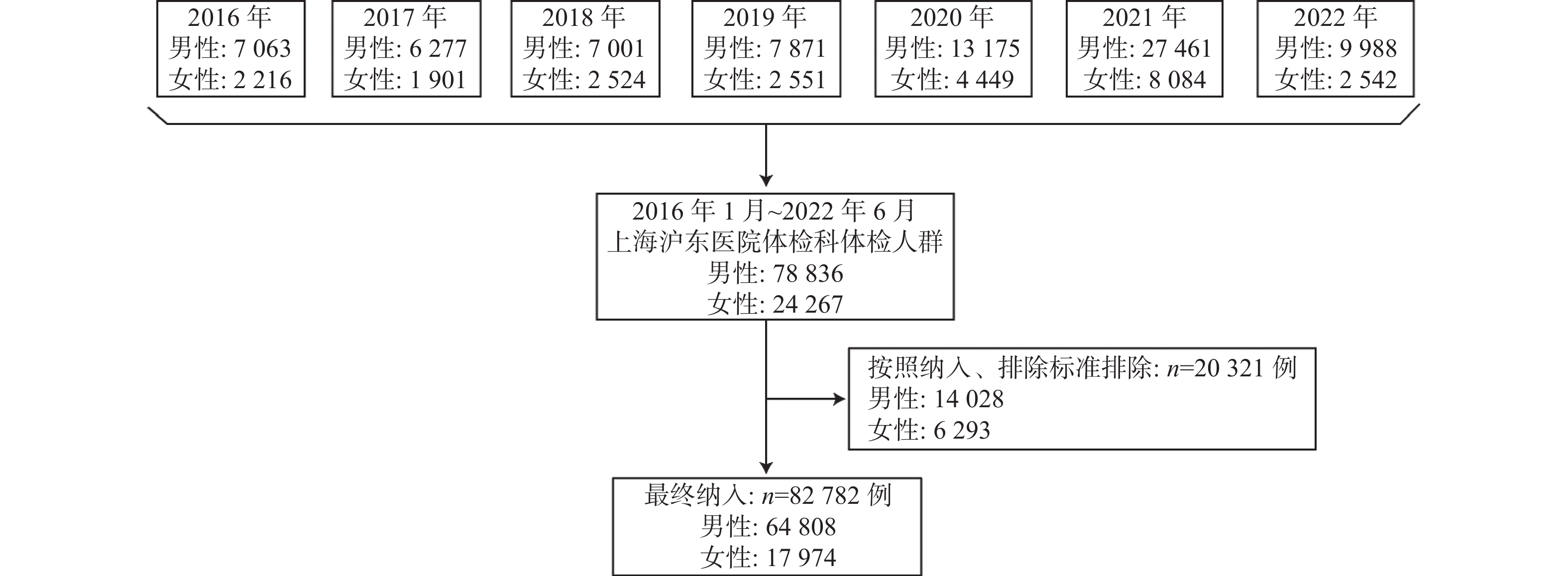
Objective To investigate the correlations of age, diseases and blood pression (BP). Methods A retrospective study was conducted to include 82 782 patients who underwent physical examination in the physical examination department of Hudong Hospital in Shanghai from January 2016 to June 2022 and met relevant criteria. Grouping according to age stages, with each stage representing 10 years, the groups are divided into ≤20 years, 21-30 years, 31-40 years, 41-50 years, 51-60 years, 61-70 years, 71-80 years, and ≥81 years. Pearson bivariate correlation method was used to analyze the correlation between BMI and systolic and diastolic blood pressure. The data were screened again and classified according to the physical examination results. The physical examination population was divided into control group and disease group, and the correlation between hypertension and disease factors was analyzed by Logistic analysis. Results Systolic blood pressure tended to increase with age, and the level of systolic blood pressure in the group aged 61-70 was consistently higher than in the younger age groups (P < 0.01). Diastolic blood pressure also showed an increasing trend with age, with the highest levels observed between the ages of 51 and 60, followed by a significant decrease. Logistic analysis results indicated that after adjusting for age and BMI factors, metabolic syndrome had a statistically significant impact on isolated systolic blood pressure (OR = 1.068, P = 0.042). Furthermore, metabolic syndrome had a statistically significant effect on both systolic and diastolic blood pressure elevation in hypertension (OR = 1.032, P = 0.038). Conclusion Blood pressure changes have age specificity, with systolic blood pressure showing a continuous increase with aging. Diastolic blood pressure reaches its highest value between the ages of 51 and 60, and then gradually decreases. Metabolic syndrome is associated with the occurrence of hypertension.
2023, 44(10): 114-121.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231005
Abstract:
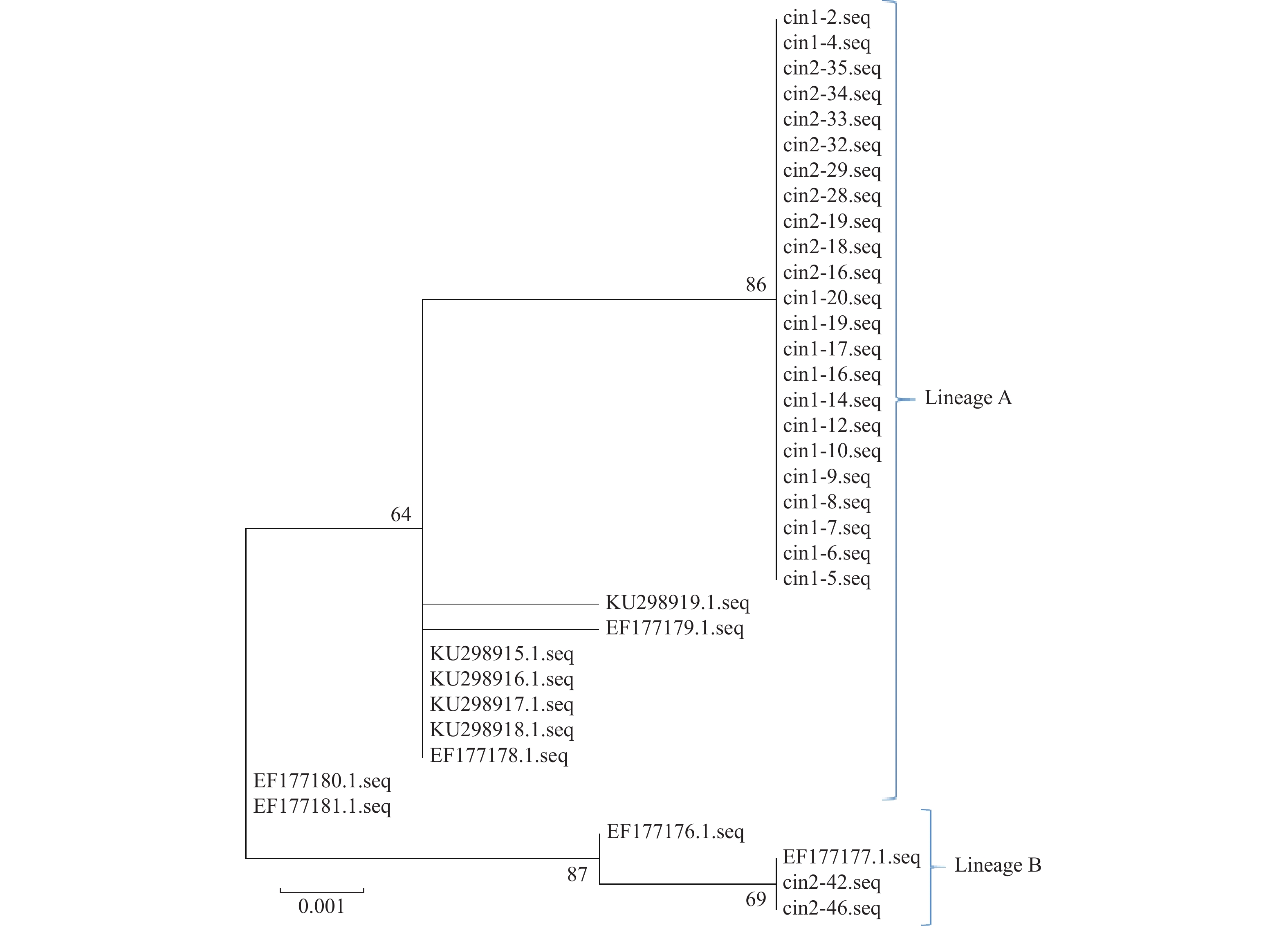
Objective To study the genetic variation characteristics of HPV56 E6, E7 and L1 in patients with precancerous lesions infected with HPV56, and to obtain the molecular epidemiological data of HPV56 in patients with precancerous lesions of cervical cancer in Yunnan. Methods A total of 300 cervical intraepithelial neoplasia patients were enrolled and HPV genotyping kit was used to detect the types of HPV infection in the patients. The HPV E6, E7, and L1 genes in patients infected with HPV 56 were sequenced. Finally, the lineage distribution of HPV 56 and the genetic variations of HPV 56 E6, E7, and L1 genes in the study subjects were analyzed. Results In this study, the HPV56 virus infected by the study subjects mainly belonged to the A lineage, with more than 90% belonged to the A lineage, and about 10% belonged to the B lineage. There were 13 mutation loci in the E6, E7 and L1 genes of HPV56, including 6 in the E6 gene, 4 in the E7 gene and 3 in the L1 gene. Among the 6 mutation sites of HPV56 E6 gene, 2 were synonymous mutations (T158C (S19S), G437A (P112P)), and 4 were non-synonymous mutations (A141C (S14R), A241G (N47S), A263C (K54N), G279A (D60N)). The four mutation sites of HPV56 E7 gene were all non-synonymous mutations (C601A (D10E), G605A (V12I), G770C (E67Q), G802C (Q77H)). Among the three mutation sites of HPV56 L1 gene, two were synonymous mutations (G6454T (P321P), A6868C (I459I)), and one was non-synonymous mutation (A5867G (N126D)). Conclusion This study obtained preliminary data on the genetic variations of HPV 56 E6, E7, and L1 genes in CIN patients in Yunnan area, and obtained the molecular epidemiological characteristics of HPV 56 E6, E7, and L1 genes. It provides necessary data for further analysis of the molecular epidemiological characteristics of HPV 56 E6, E7, and L1 genes in CIN patients in Yunnan area.
2023, 44(10): 122-128.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231012
Abstract:
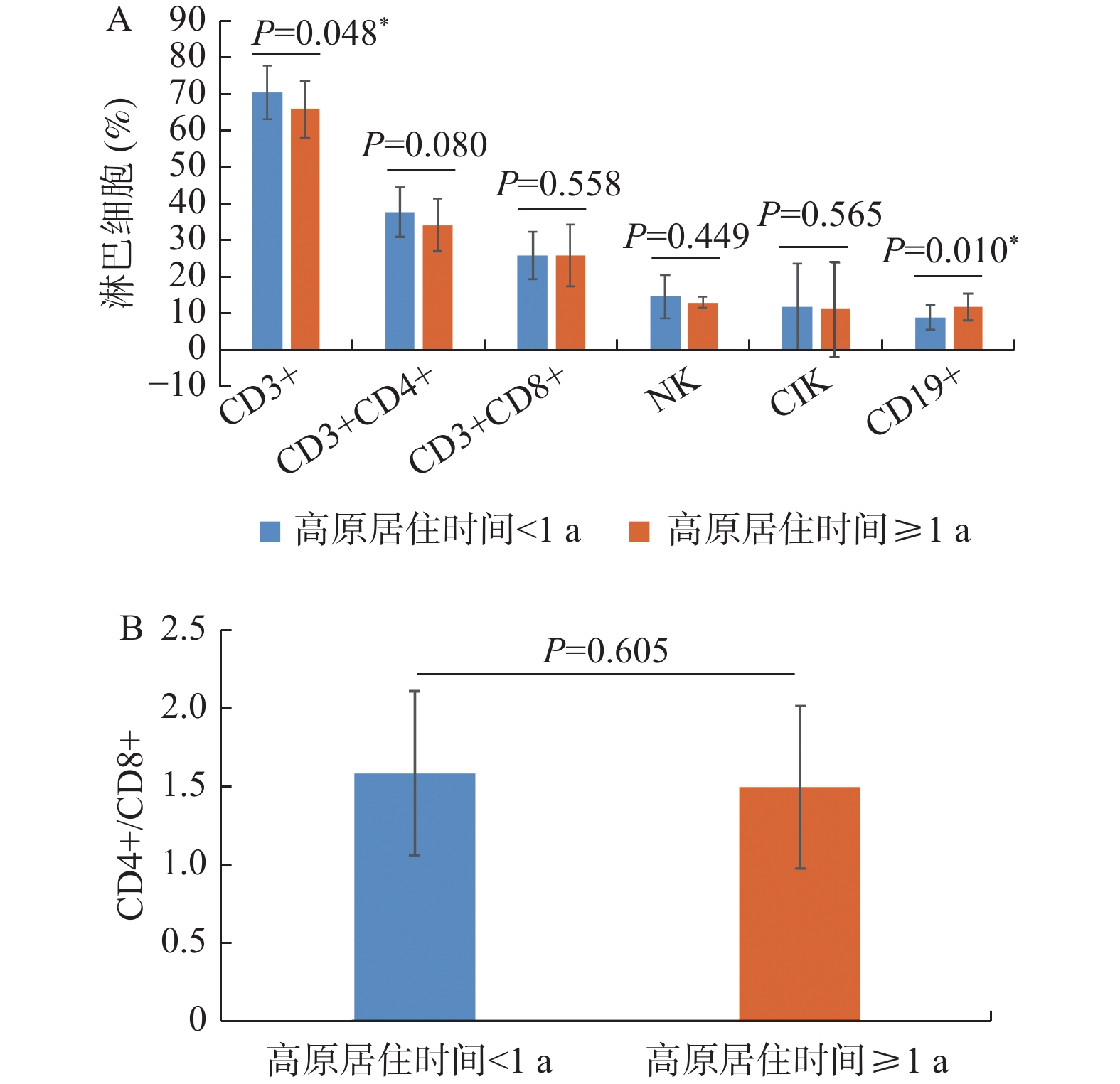
Objective To understand the changes in peripheral blood lymphocyte subsets in individuals who have migrated to high-altitude low-oxygen environments and returned to lower altitude areas, and to explore the impact of high-altitude deadaptation on the immune function of healthy individuals. Methods The changes of peripheral blood lymphocyte subsets in 47 migrants within 15 days de-adaptated from high altitude were measured by flow cytometry. Results People with a residence time of ≥1 year in high-altitude areas had lower CD3+ T cell levels and higher B cell levels on the first day of returning to low-altitude regions compared to those with a residence time of < 1 year (P < 0.05). On the 15th day of returning to low-altitude regions, people with a residence time of ≥1 year in high-altitude areas had higher B lymphocyte levels compared to those with a residence time of < 1 year (P < 0.01). In the peripheral blood T lymphocyte subgroups of high-altitude residents returning to low-altitude regions after 15 days, the percentage of CD8+ T cells increased (P < 0.05), the ratio of CD4+ T cells to CD8+ T cells decreased (P < 0.05), the percentage of natural killer (NK) cells increased (P < 0.05), and the percentage of cytokine-induced killer (CIK) cells increased (P < 0.01). There was no statistically significant difference in CD3+ T cells, CD4+ T cells, and B cells (P > 0.05). Conclusions Analysis of peripheral blood lymphocyte subgroups in populations adapted to high altitudes suggests that the duration of residence at high altitudes affects cellular and humoral immunity during the de-adaptation period. The percentage of CD8+ T lymphocytes, NK cells, and CIK cells in the peripheral blood of individuals during the de-adaptation period at high altitudes increases, indicating that the main effect of high-altitude de-adaptation is to affect the immune function of the body through cellular immunity and non-specific immune processes.
2023, 44(10): 129-133.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231001
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the basic status of refractive development in children aged 6~36 months and analyze the related influencing factors. Methods A total of 562 children aged 6~36 months were selected to detect the diopter of both eyes without ciliary paralysis using a hand-held automatic vision screening instrument. The diopter and the prevalence rate of abnormal refraction in different age groups were obtained and compared . Logistic regression was used to analyze the influencing factors of refractive development. Results The mean SE was 0.38 (0, 0.63)D, DS was 0.75 (0.5, 1.13)D, and DC was 0.75 (0.5, 1.28)D. There was no statistical significance in SE, DS and DC between boys and girls (P > 0.05); there was statistical significance in DS and DC between left and right eyes (P < 0.05), but there was no statistical significance in SE between right and right eyes (P > 0.05). Hyperopia was the main refractive state in children aged 6~36 months, of which 38.97% were normal refractive, 61.03% were abnormal refractive (42.70% were premyopia, 20.64% astigmatism, 3.91% were hypertropia, 1.25% were myopia). There were no significant differences in refractive power and refractive abnormality rate among different age groups (P > 0.05). Logistic regression analysis showed that preterm birth was a risk factor for refractive abnormalities (P = 0.012, OR = 2.68, 95%CI: 1.24~5.79), and outdoor activity was a protective factor against refractive abnormalities (P = 0.008, OR = 0.83, 95%CI: 0.72~0.95). Other factors do not contribute to the influence of diopter (P > 0.05). Conclusion Hypermetropia is the dominant refractive state in children aged 6 to 36 months, and astigmatism is the main type of refractive abnormalities. The refractive status of children aged 6~36 months is mainly farsightedness, astigmatism is the main type of refractive abnormalities, preterm birth and outdoor activities are the influencing factors of refractive development, and the overall influence of genetic and environmental factors is small. People in the early stage of myopia should be vigilant about the occurrence of myopia young age.
2023, 44(10): 134-139.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231027
Abstract:
Objective To establish a convolutional neural network model for ultrasound diagnosis of ovarian tumors and explore its value in distinguishing between benign and malignant ovarian tumors. Methods A total of 400 ovarian tumor ultrasound images, including 200 benign and 200 malignant tumors, were collected from June 2015 to September 2022 at the Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University. These images were confirmed by cytology or histopathology. The images were divided into a training set and a validation set in a 1∶3 ratio. Two diagnostic models, VGG16 and MobileNet-V2 were constructed based on convolutional neural networks for training and validation. A senior and a junior sonographers were selected to diagnose the ultrasound images in the training set. The performance of the two diagnostic models and the ultrasound doctors in distinguishing between benign and malignant ovarian tumors was evaluated using the pathological results as the gold standard. Results The sensitivity, specificity and accuracy of VGG16 model in diagnosing the benign and malignant nature of ovarian tumors were 80.67%, 79.33% and 80.00% respectively. The sensitivity, specificity and accuracy of MobileNet-V2 were 89.33%, 93.33% and 91.33% respectively. The MobileNet-V2 model had the best diagnostic performance, and both the MobileNet-V2 and VGG16 models had better diagnostic performance than ultrasound doctors (P < 0.05). Conclusion The convolutional neural network ovarian tumor diagnostic model has good diagnostic value, with the MobileNet-V2 model accurately determining the benign or malignant nature of ovarian tumor ultrasound images.
2023, 44(10): 140-148.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231006
Abstract:
Objective To explore the differences of maternal placental microbiota DNA between gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) and normal full-term infants, and provide reference data for further research. Methods A total of 30 cases of full-term infants’ placental tissue were collected from February to September 2018 at the First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University. The cases were divided into two groups: the gestational diabetes group (Group A) and the normal full-term infants group (Group B), based on the presence or absence of gestational diabetes. The bacterial DNA in the placental tissue was sequenced using the Illumina MiSeq sequencing system, and the differences in placental microbiota DNA between the two groups were compared. Results The DNA of microbial communities in the placental tissue was mainly composed of phyla such as Proteobacteria, Actinobacteria, Firmicutes, and Bacteroidetes. LEfSe analysis showed no statistically significant differences in the microbial communities at the phylum and class levels between the two groups (P > 0.05). However, at the genus level, the relative abundance of Propionibacterium, Thermus, Collinsella, Clostridium IV, Alistipes and Anaerostipes was significantly higher in the gestational diabetes group (LDA > 2). Conclusion The results of our study indicates that there are a rich microbiome DNA in the maternal placenta and that the composition and abundance of microbiome DNA are different between GDM and normal full-term infants, which may affect the occurrence and prognosis of GDM and deserves further study.
2023, 44(10): 149-154.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231025
Abstract:
Objective To evaluate the accuracy of digital models obtained using the iTero Element 1 intraoral scanner and traditional plaster models for measurements in mild to moderate crowding. Methods 37 patients who sought treatment at the Qinxing Road Clinic of Kunming Medical University Affiliated Stomatological Hospital were selected. The iTero Element 1 intraoral scanner was used to obtain digital models, while alginate impression was used to obtain traditional plaster models. The differences in digtal measurements and manual measurements of the traditional plaster models of tooth crown width, dental arch width, and coverage were compared. Results The ICC value of the three repeated measurements for both digital and plaster models were all above 0.9, indicating good repeatability. There were statistically significant differences in the arch width of 14~24 in mild and moderate crowded group, crown width (11、16、21、31、36、41、43、46) and 22 overjet in mild crowded group, and crown width of (11、23、16、31)and 11、12 overjet in moderate crowded group. Conclusion There are some differences between the data from iTero digital models and the manually measured plaster models in cases of mild to moderate crowding. This may be due to misalignment of teeth, leading to measurement errors. However, the differences in measurement data are small and do not affect the clinical application of iTero digital models.
2023, 44(10): 155-160.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231015
Abstract:
Objective To explore the gene variation profile of Gilbert syndrome in Kunming, and to provide basic data for the mechanisms of Gilbert syndrome. Methods 357 children with Gilbert syndrome in Kunming were analyzed by high-throughput sequencing and bio-information analysis. Results Among 357 children with Gilbert syndrome, 82 cases were found to have homozygous variations in the UGT1A1 gene, with c.211G > A homozygous variation accounting for 93.9% of the cases; c.1091C > T homozygous variation accounting for 3.7% of the cases; and c.1198A > C homozygous variation accounting for 2.4% of the cases. 275 cases were found to have heterozygous variations in the UGT1A1 gene, with c.211G > A heterozygous variation accounting for 69.1% of the cases; c.1091C > T heterozygous variation accounting for 17.8% of the cases;c.1456T > G heterozygous variation accounting for 5.5% of the cases; c.1198A > C heterozygous variation accounting for 2.5% of the cases; c.1352C > T accounting for 1.1% of the cases; c.596C > G heterozygous variation accounting for 1.1% of the cases; c.1423C > T heterozygous variation accounting for 0.7% of the cases; and c.1100G > A, c.1389G > C, c.610A > G, c.163C > T, c.715C > T, c.1021C > T heterozygous variations each accounting for 0.4% of the cases. Conclusion The top three gene variants associated with Gilbert's syndrome in the Kunming region were c.211G > A, c.1091C > T, c.1456T > G, which were different from those found in the border areas of Yunnan. This provides important reference data for the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia in the Kunming region, and also lays the foundation for further exploration of the pathogenesis of unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia.
2023, 44(10): 161-167.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231014
Abstract:
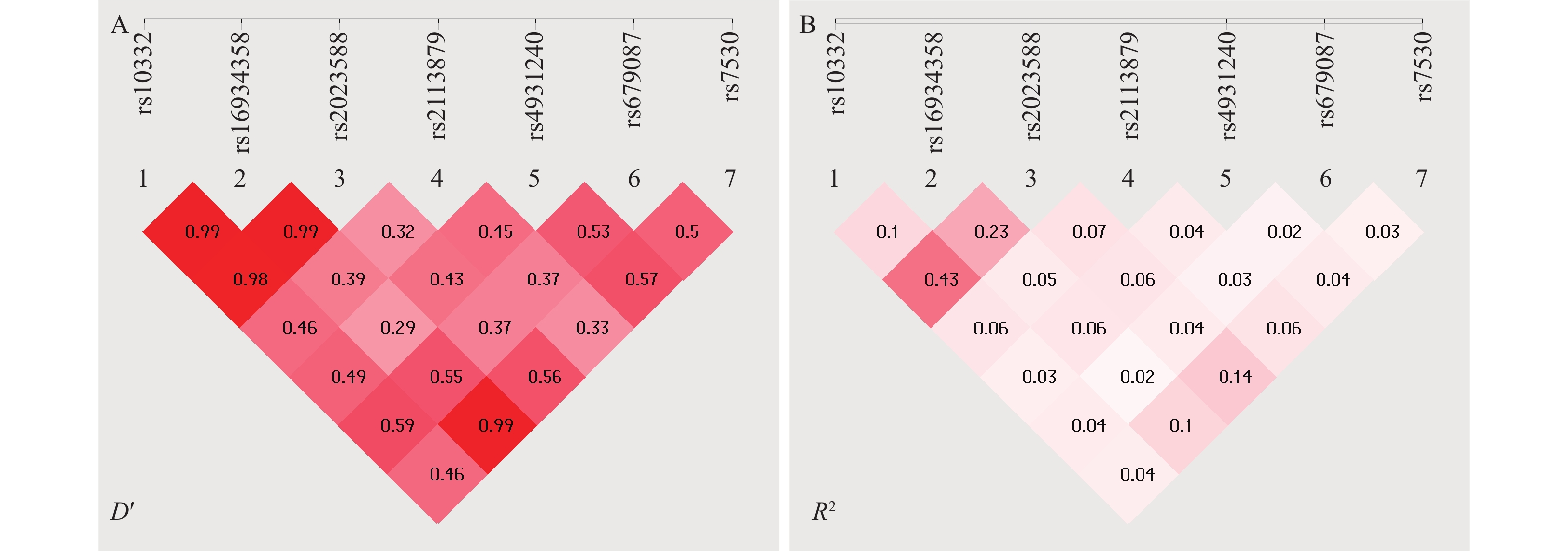
Objective To explore the association between single nucleotide polymorphisms of TMTC1 gene and schizophrenia. Methods A total of 207 patients with schizophrenia and 186 healthy controls were included in the study. SNPscanTM multiplex SNP genotyping technology was used to perform genetic typing of 7 SNP loci in the TMTC1 gene. Differences in allele frequencies, genotypes, and haplotypes were compared, and the correlation between SNP loci and susceptibility to schizophrenia was analyzed under different genetic models. Results The genotype distribution of the 7 SNP sites loci is consistent with Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. There was no statistically significant difference in the allele and genotype frequency distribution of the 7 loci between the two groups (P > 0.05). The polymorphisms of the 7 SNP loci under different genetic models are not associated with the risk of schizophrenia (P > 0.05). However, there is a high degree of linkage disequilibrium (LD) between rs10332 and rs16934358, rs10332 and rs2023588, rs16934358 and rs2023588, rs16934358 and rs7503. Conclusion The polymorphisms of the TMTC1 gene at rs7503, rs10332, rs2023588, rs16934358, rs2113879, rs679087, and rs4931240 sites are not associated with schizophrenia. Further analysis is needed by increasing the sample size and screening for new SNP loci.
2023, 44(10): 168-179.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231007
Abstract:
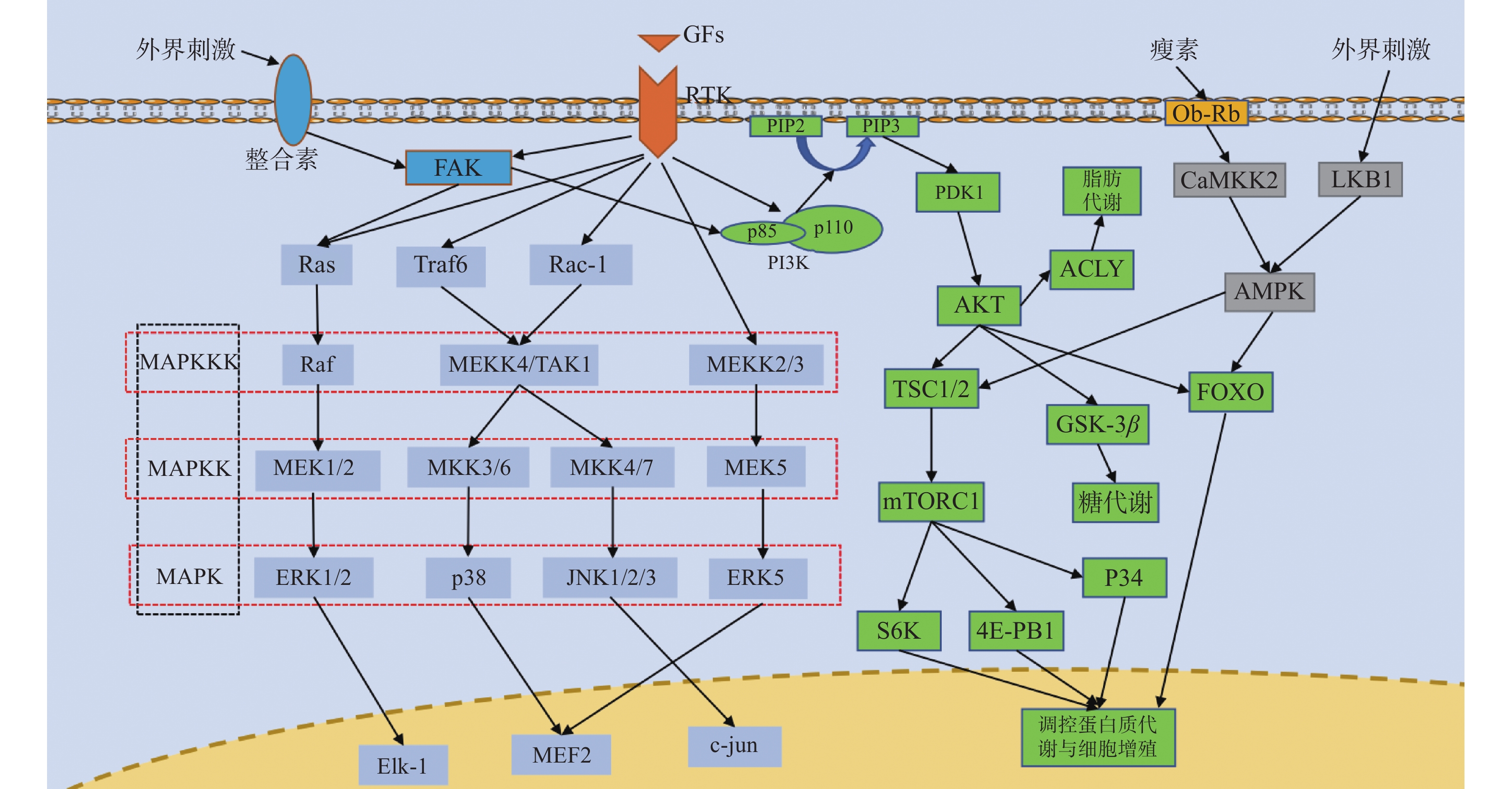
Signal pathways including MAPK, PI3K/AKT, AMPK, TGF-β superfamily, Wnt, Hippo, NF-κB, Notch, JAK/STAT, Hedgehog, integrin, OPG/RANKL/RANK, HIF, etc. are all related to osteogenic differentiation and play a certain regulatory role in the process of bone regeneration promoted by bone repair materials. Bone repair materials such as metal materials, inorganic materials, organic polymer materials and composite materials can promote bone tissue regeneration by activating one or more signaling pathways related osteogenic. Further understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying the promotion of osteogenesis by bone repair materials will help to broaden their application in bone tissue engineering and clinical practice. However, the specific molecular mechanisms by which bone repair materials promote osteogenesis have not yet been fully elucidated, and further research is still needed. This article briefly introduces the signal pathways related to osteogenic differentiation, summarizes the research on bone repair materials in various signal pathways, and provides a reference for the in-depth study of the mechanism of bone repair materials in promoting osteogenesis.
Signal pathways including MAPK, PI3K/AKT, AMPK, TGF-β superfamily, Wnt, Hippo, NF-κB, Notch, JAK/STAT, Hedgehog, integrin, OPG/RANKL/RANK, HIF, etc. are all related to osteogenic differentiation and play a certain regulatory role in the process of bone regeneration promoted by bone repair materials. Bone repair materials such as metal materials, inorganic materials, organic polymer materials and composite materials can promote bone tissue regeneration by activating one or more signaling pathways related osteogenic. Further understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying the promotion of osteogenesis by bone repair materials will help to broaden their application in bone tissue engineering and clinical practice. However, the specific molecular mechanisms by which bone repair materials promote osteogenesis have not yet been fully elucidated, and further research is still needed. This article briefly introduces the signal pathways related to osteogenic differentiation, summarizes the research on bone repair materials in various signal pathways, and provides a reference for the in-depth study of the mechanism of bone repair materials in promoting osteogenesis.
2023, 44(10): 180-188.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231020
Abstract:
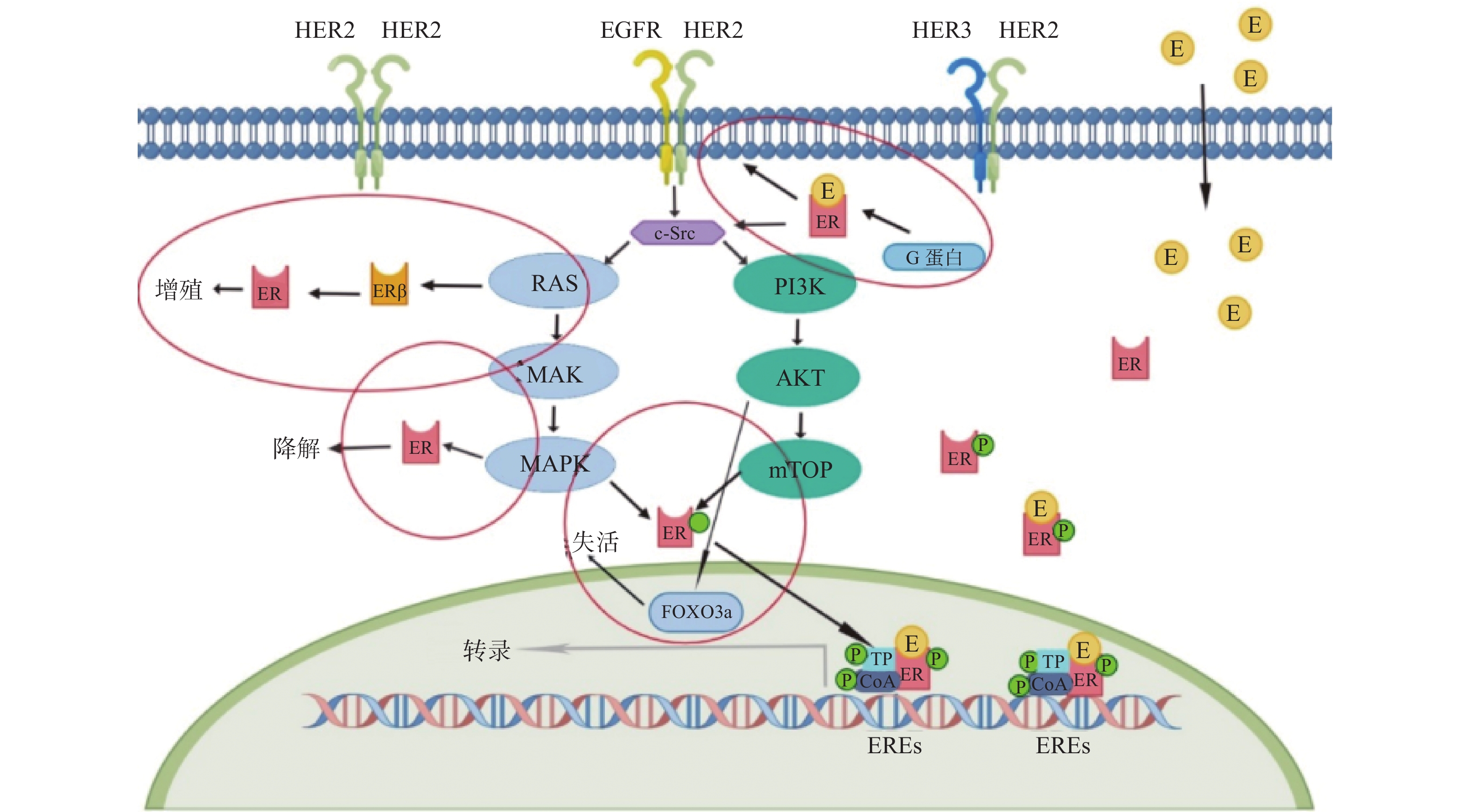
Triple-positive breast cancer (TPBC) is a special type of breast cancer characterized by the co-expression of hormone receptors (HR+) and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2+). Due to the regulation of the HR signaling pathway and the HER2 signaling pathway, the treatment strategy for TPBC has been a hot topic of clinical attention. There is currently a lack of systematic theoretical support for the selection of intensive adjuvant therapy for TPBC patients, including sequential or combination therapy, endocrine therapy, and targeted therapy. This review article examines 11 randomized controlled trials on TPBC treatment in recent years, obtained from database such as PUBMED, ClinicalTrials.gov, and CNKI, in order to provide clinical reference for the selection of neoadjuvant therapy strategies for TPBC.
Triple-positive breast cancer (TPBC) is a special type of breast cancer characterized by the co-expression of hormone receptors (HR+) and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2+). Due to the regulation of the HR signaling pathway and the HER2 signaling pathway, the treatment strategy for TPBC has been a hot topic of clinical attention. There is currently a lack of systematic theoretical support for the selection of intensive adjuvant therapy for TPBC patients, including sequential or combination therapy, endocrine therapy, and targeted therapy. This review article examines 11 randomized controlled trials on TPBC treatment in recent years, obtained from database such as PUBMED, ClinicalTrials.gov, and CNKI, in order to provide clinical reference for the selection of neoadjuvant therapy strategies for TPBC.
2023, 44(10): 189-195.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231013
Abstract:
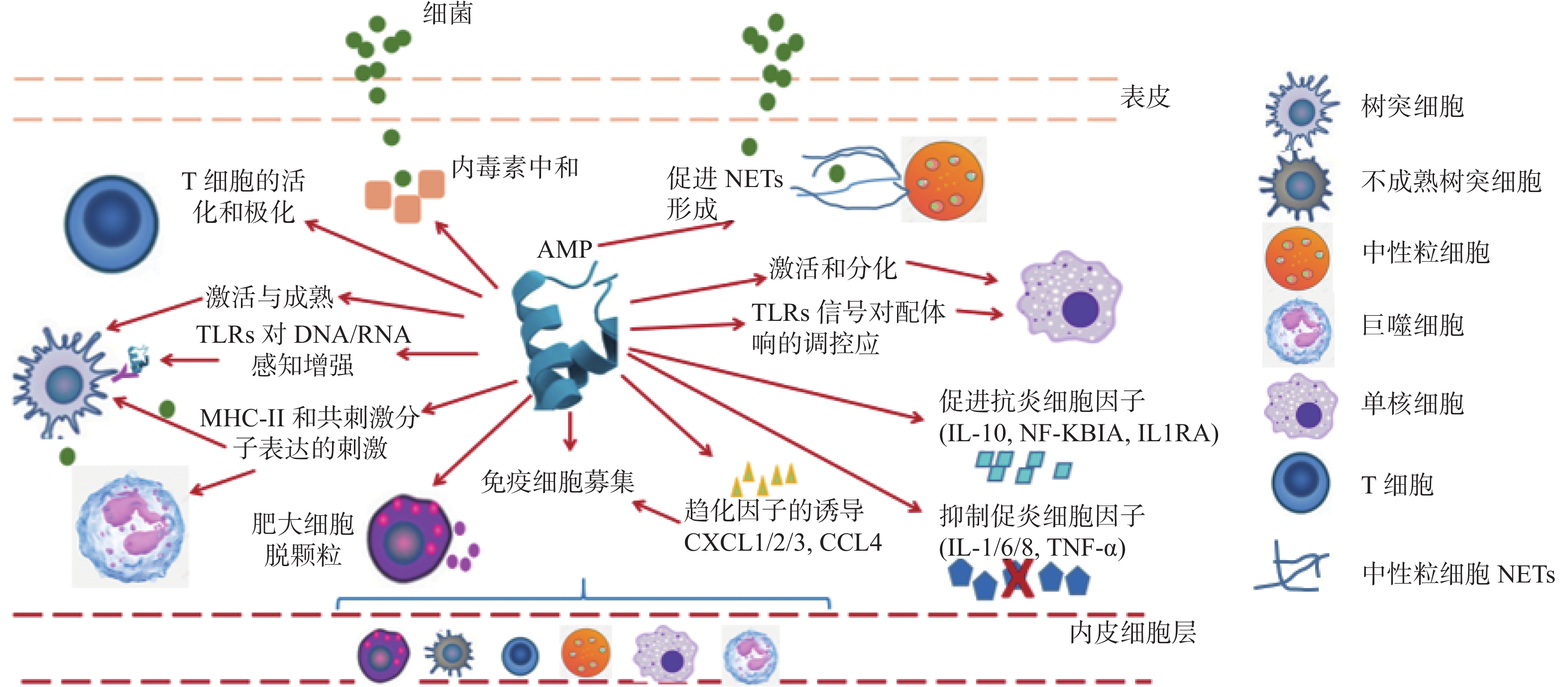
Since penicillin was used to treat bacterial infectious diseases in 1928, antibiotics have saved countless patients’ lives. However, with the increase of bacterial drug resistance, the clinical treatment of bacterial infectious diseases has become increasingly difficult. Antimicrobial peptides is considered as an ideal substitute for traditional antibiotics because of its wide range of functions and low toxicity. Among them, some antimicrobial peptides with immune regulation function can regulate the innate immunity and acquired immune response of the body, directly target the immune system of the body rather than pathogenic microorganisms, thus avoiding the selection pressure on pathogenic microorganisms, and are not easily resistant to antibiotics. They have broad application value in infection treatment. This article reviews the immunomodulatory activity of antimicrobial peptides, its potential application in clinical treatment, and its limitations, so as to provide a new perspective for the development and utilization of new antibiotics.
Since penicillin was used to treat bacterial infectious diseases in 1928, antibiotics have saved countless patients’ lives. However, with the increase of bacterial drug resistance, the clinical treatment of bacterial infectious diseases has become increasingly difficult. Antimicrobial peptides is considered as an ideal substitute for traditional antibiotics because of its wide range of functions and low toxicity. Among them, some antimicrobial peptides with immune regulation function can regulate the innate immunity and acquired immune response of the body, directly target the immune system of the body rather than pathogenic microorganisms, thus avoiding the selection pressure on pathogenic microorganisms, and are not easily resistant to antibiotics. They have broad application value in infection treatment. This article reviews the immunomodulatory activity of antimicrobial peptides, its potential application in clinical treatment, and its limitations, so as to provide a new perspective for the development and utilization of new antibiotics.
2023, 44(10): 196-201.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231008
Abstract:
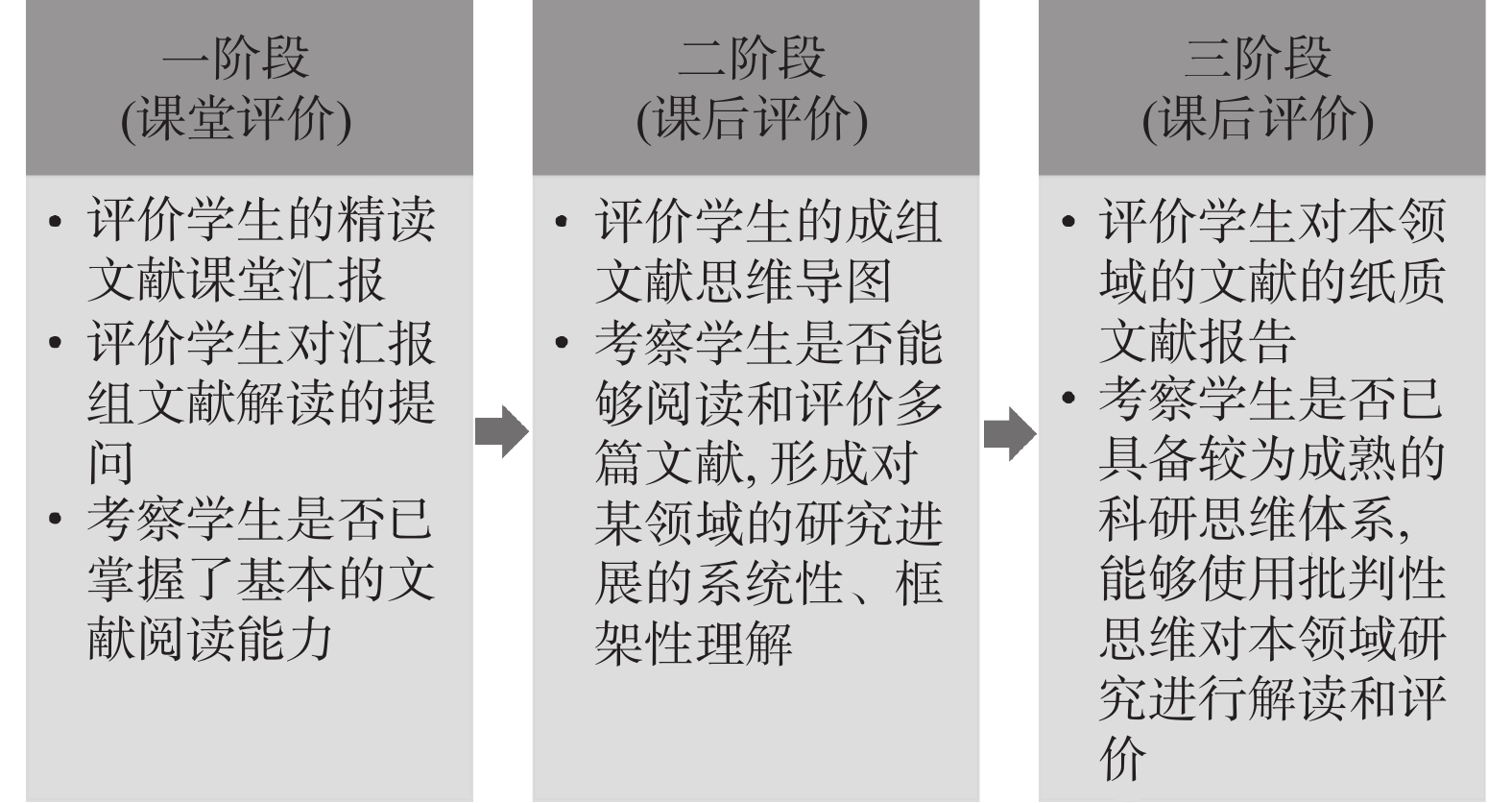
Objective To evaluate the impact of research-based learning (RBL), a new teaching method, on the critical thinking ability of medical postgraduates in order to enhance their critical thinking skills. Methods A total of 330 postgraduate students majoring in medicine participated in this study. Among them, the experimental group (n = 165) completed the course of “Cultivation of Basic Quality of Scientific Research” using RBL teaching method, while the students in the control group (n = 165) did not participate in this course. Subsequently, a critical thinking ability questionnaire was used to assess the differences in critical thinking ability between the two groups. Results The experimental group had a higher total score in critical thinking ability compared to the control group (P < 0.001). The experimental group also scored higher than the control group in five dimensions: seeking truth, analytical ability, confidence in critical thinking, curiosity, and cognitive maturity (P < 0.05). Conclusion The RBL teaching method can improve the critical thinking ability of medical postgraduate students.
2023, 44(10): 202-206.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231002
Abstract:
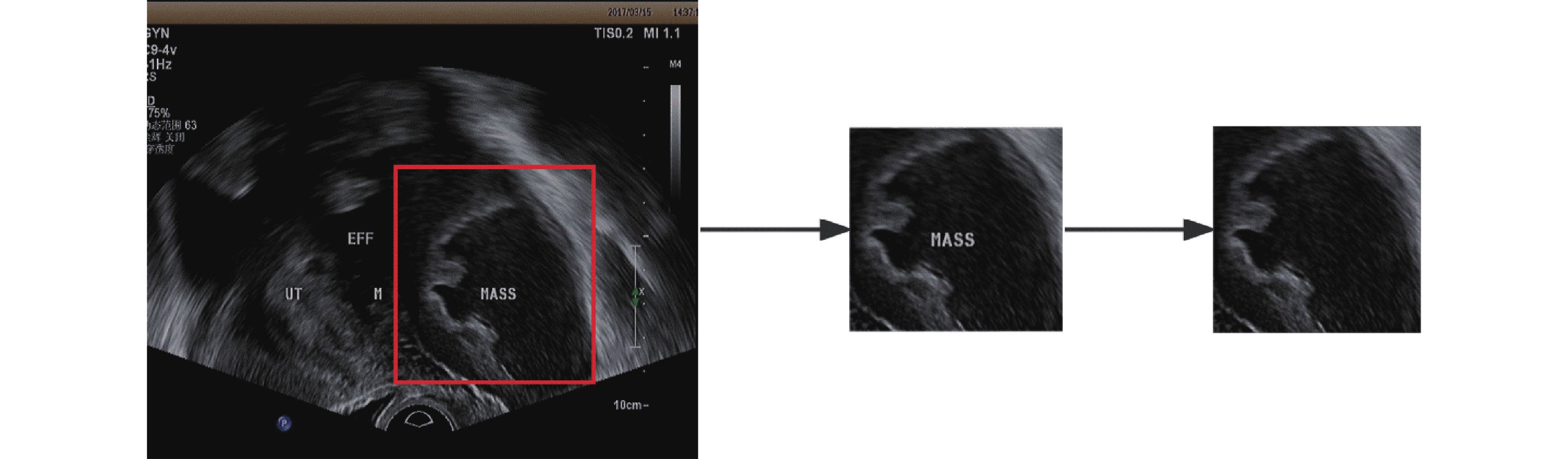
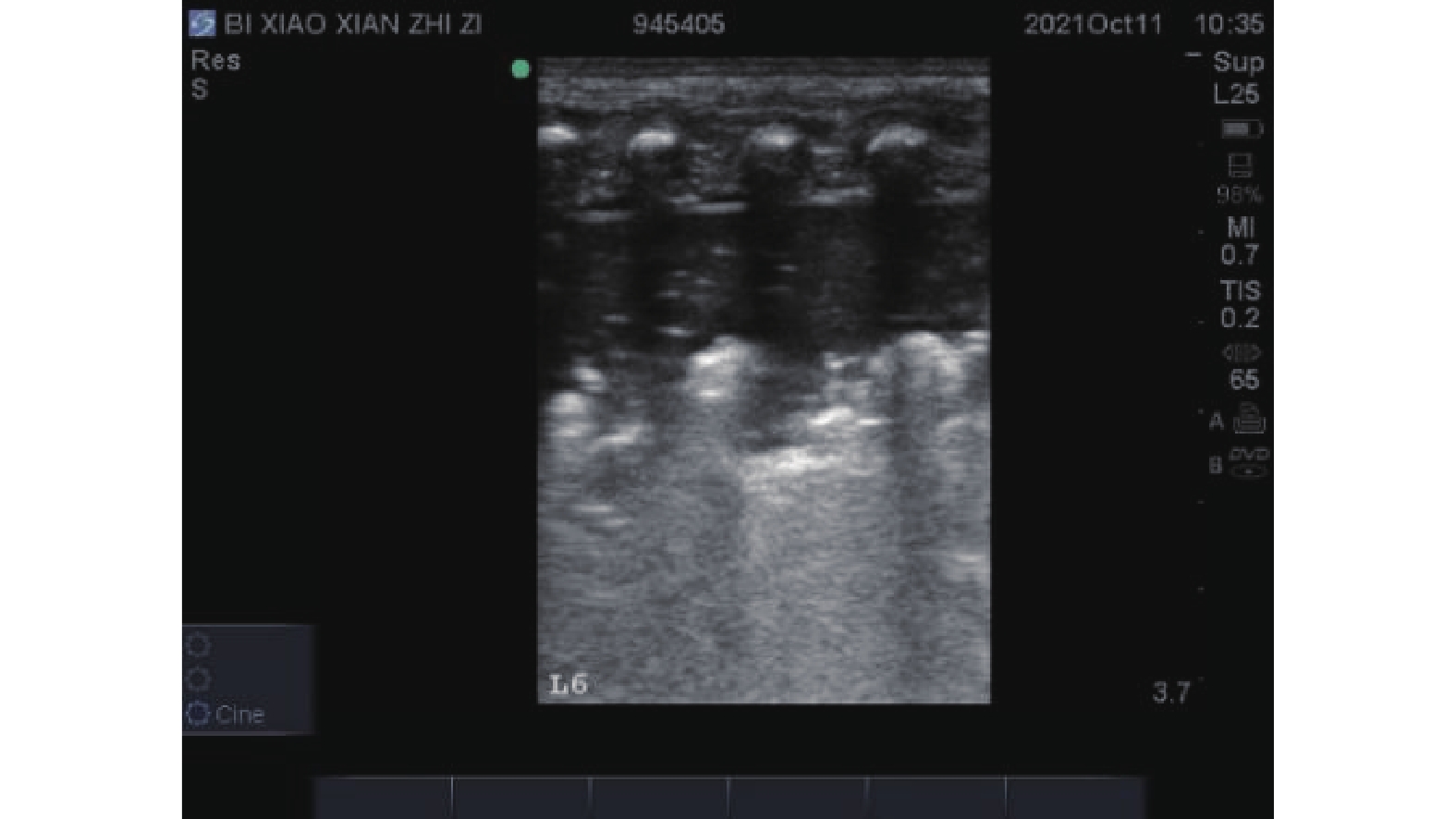
Objective To explore the application effect of dynamic monitoring of lung ultrasound in precision nursing care of severe neonatal pneumonia with pulmonary consolidation. Methods 60 newborns diagnosed with severe pneumonia in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU) of Kunming Children’s Hospital were selected for the study. They were randomly divided into a control group and an experimental group, with 30 cases in each group. The control group received routine nursing for newborns, while the experimental group received dynamic monitoring of bedside ultrasound in addition to routine nursing. Precise nursing measures were implemented based on the ultrasound findings of lung consolidation. The time for clinical respiratory symptoms to disappear, the time for extubation in critically ill cases, and the average length of hospital stay were analyzed in both groups. Results In the lung consolidation patients who received precise nursing measures based on dynamic monitoring of bedside ultrasound, the time for respiratory symptoms to disappear, the average length of hospital stay, and the time for extubation in critically ill cases were all shorter than those in the control group (P < 0.05). Conclusion Lung ultrasound dynamic monitoring can provide real-time information about the nature, size, location, and severity of lung lesions. After implementing precise nursing measures for lung lesions, it is possible to timely assess the intervention effect and guide the next nursing measures, thus effectively improving the treatment outcomes. Lung ultrasound is easy to operate and worth promoting.


 Email
Email RSS
RSS