2023 Vol. 44, No. 9
2023, 44(9): 1-6.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230925
Abstract:
Objective To research the analgesic effect of galanin on native rats, inflammatory rats and neuropathic rats in nucleus accumbens (NAc), and to explore its mechanism. Methods A inflammatory pain model was prepared by subcutaneous injection of carrageine into rat’s plantar, while the model of neuralgia was prepared by ligation of the left sciatic nerve. The hind-paw withdraw latency (HWL) induced by thermal stimulation and the hind-paw withdraw threshold (HWT) induced by mechanical stimulation were measured to reflect the pain threshold. The expression of galanin receptors (GalRs) in the nucleus accumbens of inflammatory and neuropathic rats were detected by western blot (WB). Results 1. The HWL of normal (Pleft < 0.05; Pright < 0.01), inflammatory (Pleft < 0.001; Pright < 0.001) and neuropathic (Pleft < 0.001; Pright < 0.001) rats were increased by injection of galanin into nucleus accumbens, and the HWT of normal (Pleft < 0.001; Pright < 0.01), inflammatory (Pleft < 0.001; Pright < 0.001) and neuropathic (Pleft < 0.001; Pright < 0.001) rats also were increased. 2. The antinociception of galanin on the rats with inflammatory (HWL: Pleft < 0.05, Pright < 0.05; HWT: Pleft < 0.01, Pright < 0.05) or neuropathic pain (HWL: Pleft < 0.05, Pright < 0.05; HWT: Pleft < 0.001, Pright < 0.001) was stronger than that of the native rats. However, the antinociception of galanin on the rats with the inflammatory pain and neuropathic pain was not significantly different (P > 0.05). 3. The expressions of GalR1 were increased in rats after 3 hours of subcutaneous injection of carrageine (P < 0.001) and 14 days of sciatic nerve ligation (P < 0.001), and the expressions of GalR2 also were increased in rats after 3 hours of subcutaneous injection of carrageine (P < 0.05) and 14 days of sciatic nerve ligation (P < 0.05). Conclusion Intra-NAc injection of galanin has the antinociceptive effects on native, inflammatory and neuralgia rats and the antinociceptive effect of galanin in rats is induced by the activation of GalRs.
2023, 44(9): 7-14.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230926
Abstract:
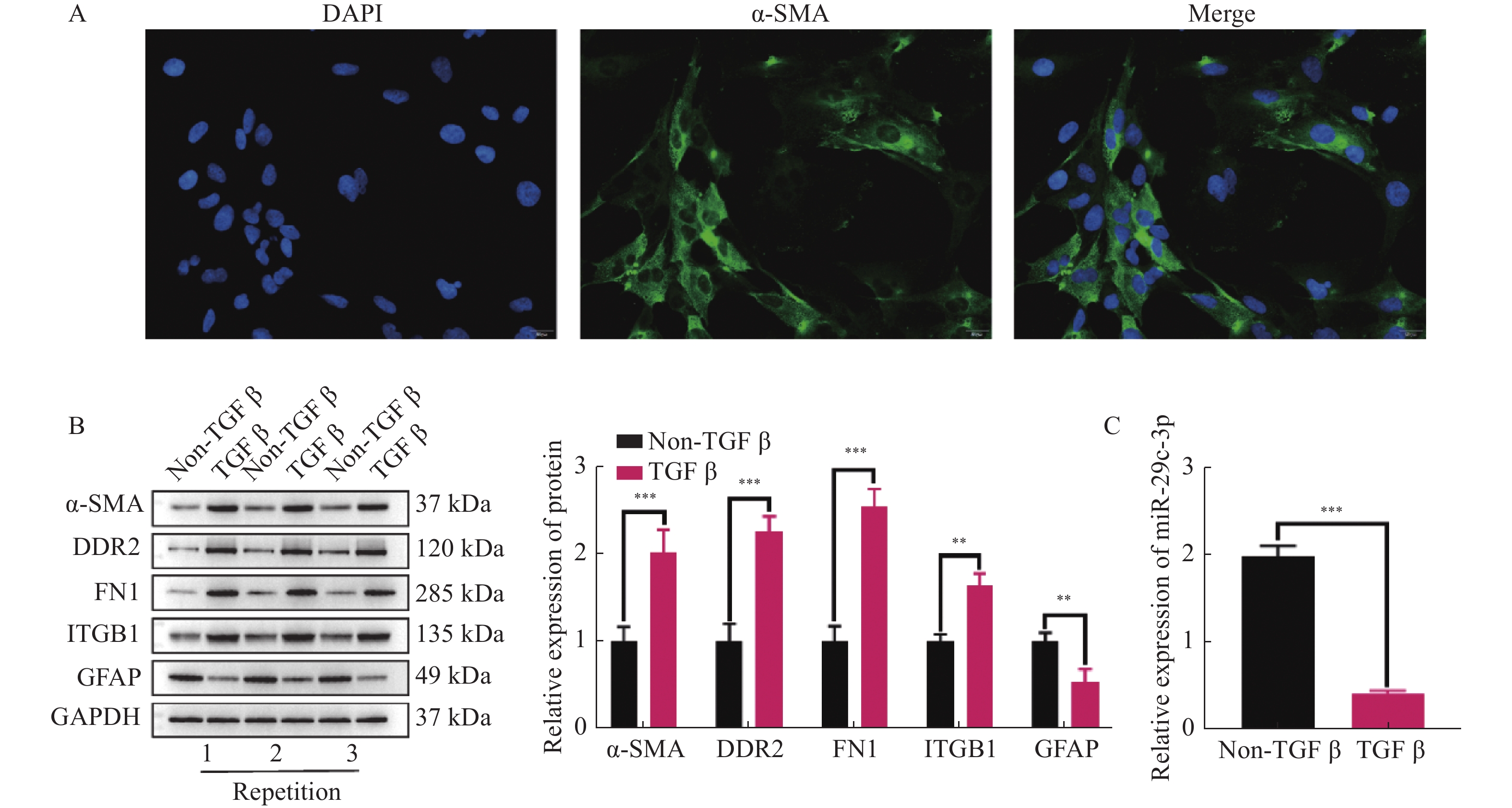
Objective To investigate the effects of miR-29c-3p on the activation, proliferation and apoptosis of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) via IGF-1. Methods Primary mouse HSCs were cultured and the expression of HSCs marker ɑ-SMA was detected by immunofluorescence. By dual-luciferase reporter gene assay was conducted to Validate the Targeting Relationship between miR-29c-3p and IGF-1. After TGF-β activation of HSCs and exogenous regulation of miR-29c-3p and IGF-1 expression, the expression of activation-related proteins (ɑ-SMA, DDR2, FN1, ITGB1 and GFAP), proliferation, colony-forming number and apoptosis in activated HSCs were detected by Western bolt, CCK-8, colony-forming unit assays and flow cytometry, respectively. Results Positive expression of ɑ-SMA indicated that the successful isolation of mouse HSCs. miR-29c-3p significantly reduced the luciferase activity of wild-type IGF-1, but had no effect on mutant IGF-1. Over-expression of miR-29c-3p and hypo-expression of IGF-1 significantly decreased ɑ-SMA, DDR2, FN1 and ITGB1 expression, increased GFAP expression, and decreased proliferation viability and colony-forming number of HSCs and upregulated their apoptotic ratio. Conclusion miR-29c-3p inhibits the activation and proliferation of HSCs and promotes their apoptosis by targeting IGF-1 expression.
2023, 44(9): 15-24.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230907
Abstract:
Objective To systematically analyse and describe the overall stillbirth rate in different regions of the Chinese mainland from 1994 to 2020 so as to provide the basis for further reducing the stillbirth rate and formulating perinatal management strategies suitable for different regions. Methods Databases including PubMed, Cochrane library, Web of Science, EMBASE, SinoMed, CNKI, VIP and WanFang Data were electronically searched to collect the cohort and cross-sectional studies on the stillbirth rate among the pregnant females in the Chinese mainland from building date to April30, 2022. Results A total of 200 literatures were included, with a total sample size of 22, 455, 289 cases in the study. Results of meta-analysis showed that the overall stillbirth rate among the pregnant females in the Chinese mainland was 6‰[95%CI (6‰, 7‰)]. Subgroup analysis showed that there were differences in the stillbirth rates between the different regions (χ2 = 392.00, P < 0.001), and that stillbirth rate among the pregnant females in western China was the highest 9‰[95% CI (8‰, 9‰)], followed by the central region with 8‰[95%CI (6‰, 9‰)], and the eastern and northeastern regions with 6‰[95%CI (6‰, 6‰), (5‰, 7‰)]. There were differences in the stillbirth rate in the first 10 years (1994-2005) , the second 10 years (2006-2016) and the past three years (2017-2020) in the Chinese mainland (χ2 = 113.00, P < 0.001). The stillbirth rate in 1994-2005 was 8‰ [95% CI (7‰, 8‰)], which was higher than that in 2006-2016 (6‰, [95%CI (5‰, 6‰)]). The stillbirth rate in the last three years (2017-2020) was the lowest 5‰, [95%CI (4‰, 6‰)]). Conclusion The stillbirth rate of the pregnant women in China’s mainland is 6‰ while the rate in western China is higher at 9‰. The stillbirth rate is on the decline between 1994 and 2020.
2023, 44(9): 25-31.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230916
Abstract:
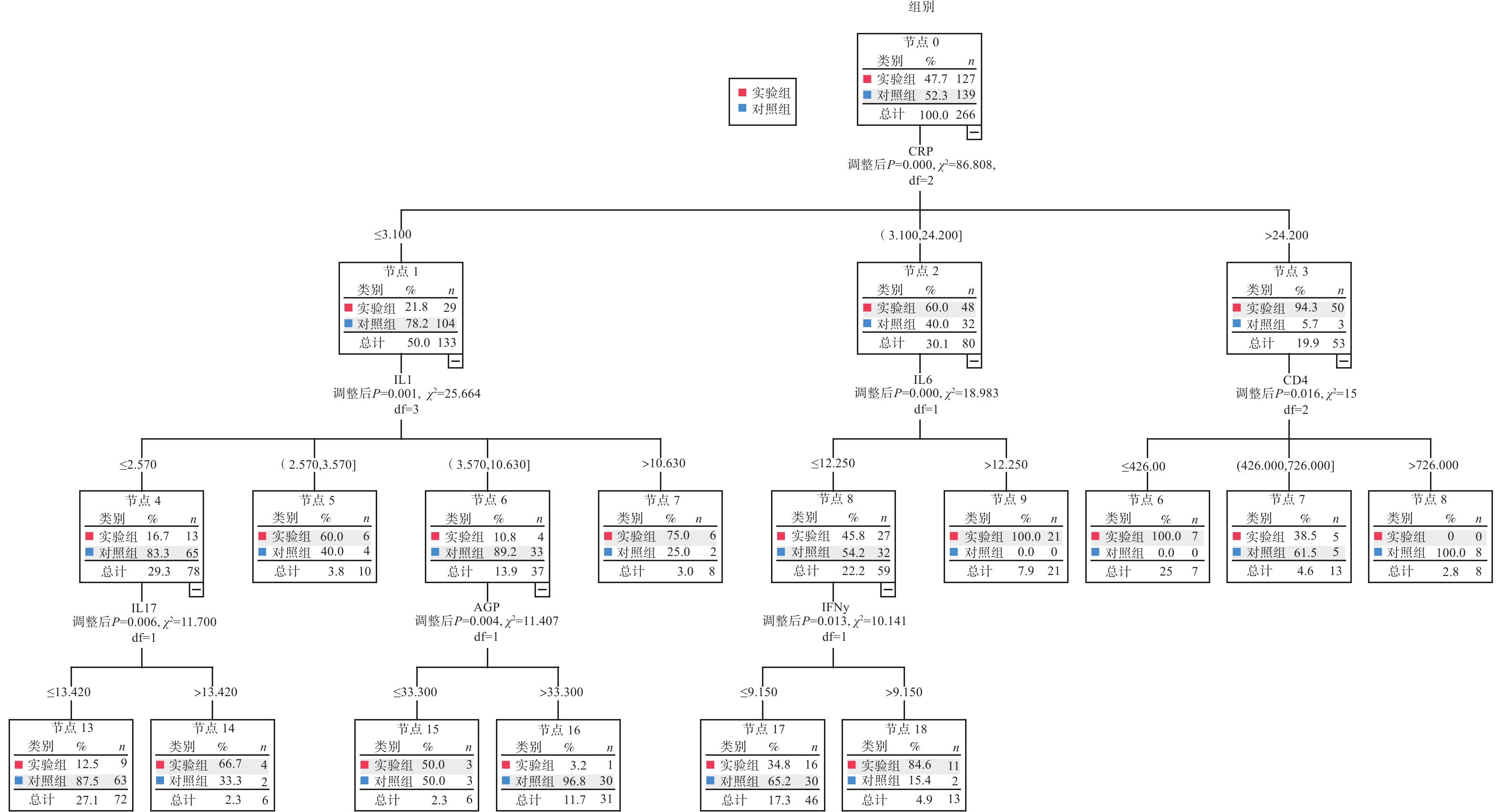
Objective To analyze the influence factors of active tuberculosis(ATB) using logistic regression model and decision tree model, and to provide a reference point for ATB prevention and control. Methods The experimental group consisted of 200 active pulmonary tuberculosis patients admitted to the Third People’s Hospital of Kunming from March 2021 to March 2023, and the control group consisted of 200 healthy individuals who underwent physical examination during the same period Logistic regression. Decision tree ATB risk prediction models were established, and the decision tree analysis models(Decision Tree 1 and Decision Tree 2) were set up under the condition of whether they were based on the results of Logistic regression or not, and the decision tree analysis models(Decision Tree 1 and Decision Tree 2) were set up. The prediction effect of the three models was evaluated using the subjects' work curves. Results The results of Logistic regression showed that AAT, IL-4, IL-6, IL-17 and IFN-γ were the risk factors for ATB with CD+4 as the protective factor. The results of Decision Tree 1 showed that CRP was the root node, followed by IL-1, IL-6, CD+4, IL-17, AGP, and IFN-γ as the sub-nodes, respectively. Decision Tree 2 showed that IL-6 was the root node, followed by AAT, IL-4, IL-17 as sub-nodes. The established risk prediction models showed an AUC of 0.887 for logistic regression and 0.900(Decision Tree 1) and 0.857(Decision Tree 2) for the decision tree model. The AUC comparison results of the three models showed that the AUC of Decision Tree 1 was better than that of Decision Tree 2(95% CI: 0.0019-0.0841, P < 0.05), but the difference with Logistic regression model was not statistically significant(95% CI: 0.0265-0.0522, P = 0.526). Conclusion Both Logistic model and Decision Tree 1 model have certain application value in predicting the risk factors of ATB, and it is recommended to combine the two models so as to provide the better reference value for the laboratory prediction of ATB.
2023, 44(9): 32-38.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230910
Abstract:
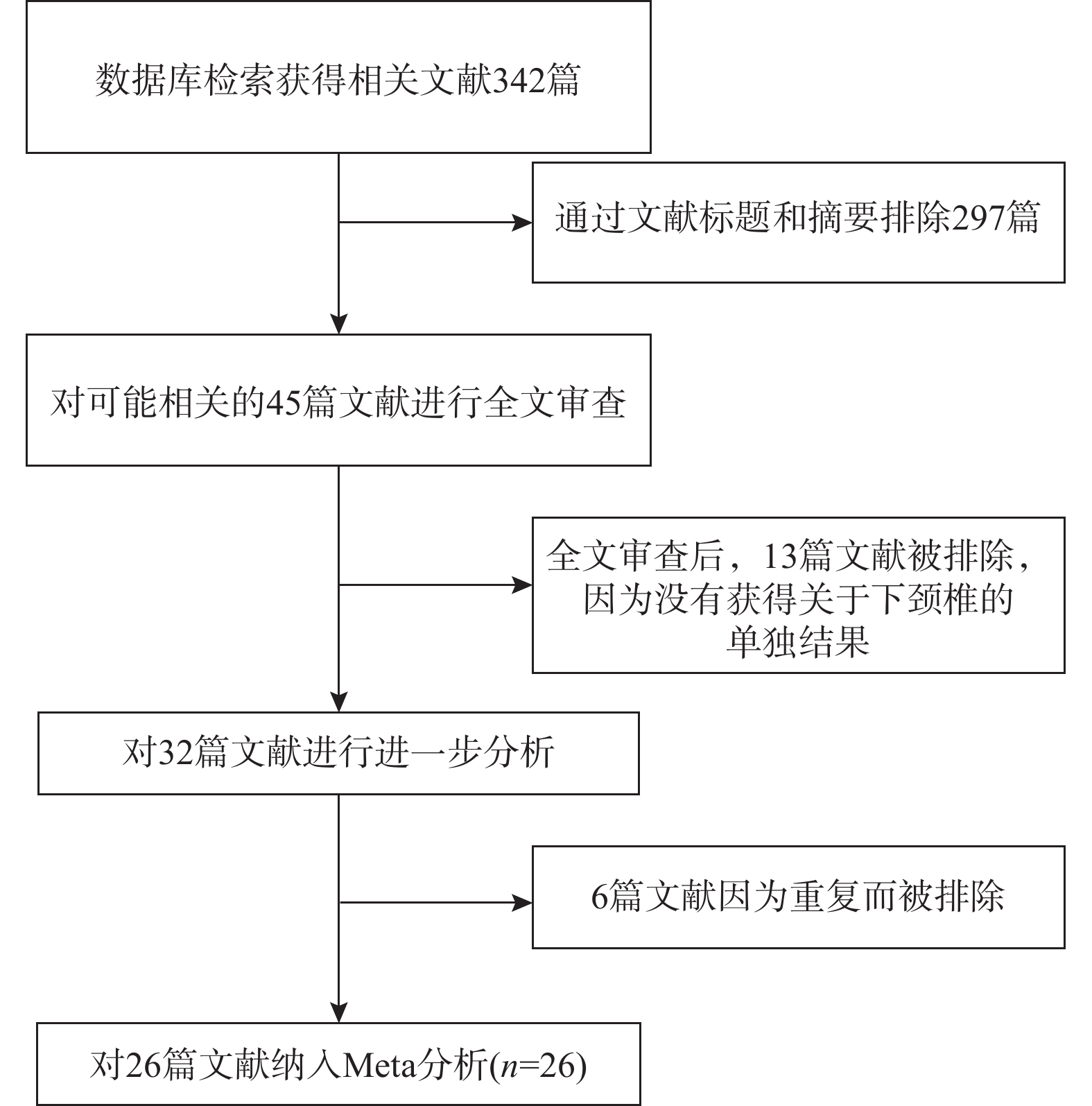
Objective To systematically compare the accuracy, direction of pedicle screw perforation, and screw-related complications of sub-axial cervical pedicle screw (sCPS) placement with and without assistant techniques. Methods A total of 26 studies involving 1697 patients and 6654 screws were included. Medline, Embase, and Cochrane databases were searched to collect the high-quality English literature on the accuracy of cervical pedicle screw (CPS) placement using different screw placement techniques from 2010.1 to 2022.12. Literature was screened according to the inclusion criteria, data was extracted, and a meta-analysis was performed using RevMan 5.4. Results The meta-analysis showed that assistant techniques had a higher accuracy rate for sCPS placement. Perforation of the lateral wall of the pedicle was more common than the medial wall, and free-hand screw placement was more common in the superior wall than the inferior wall. There was no statistically significant difference in the perforation rate between the superior and inferior walls with assistant techniques. Conclusion 1. Assistant techniques has a higher accuracy rate for sCPS placement than free-hand techniques. 2. Perforation of the lateral and inferior walls of the pedicle is more common than perforation of the medial and superior walls. 3. A unified evaluation standard is needed for assessing the accuracy of sCPS placement. 4. Different assistant screw placement techniques have their own advantages and disadvantages, and should be selected according to the actual conditions.
2023, 44(9): 39-48.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230905
Abstract:
Objective Maxillary sinus floor elevation is an effective way to increase the vertical bone mass of maxillary posterior region, and its success is closely related to the formation of new bone. In this study, a systematic review and meta-analysis was used to evaluate the correlation between bone window dimension and postoperative outcomes after maxillary sinus floor elevation. Methods An electronic search strategy was performed on Medline, Pubmed, Embase, Cochrane Library database, Chinese Biology Medicine disc (CBMdisc), China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), and National Library of Medicine (NLM) up to November 2022. Clinical and animal studies that analyzed the effect of bone window dimension and postoperative outcomes using lateral window elevation were included. Clinical studies with at least ten patients, and a minimum follow-up period of 6 months were included. According to the inclusion and exclusion criteria, three evaluators independently screened related studies, extracted data, and evaluated risk bias. Meta-analysis was performed by Revman 5.3 software. Results A total of 14 studies were included for the systematic review after the full text reading. 6 studies with low risk of bias, 2 studies with moderate risk of bias and 1 study with high risk of bias were controlled clinical studies. Both of the two bone window dimensions achieved ideal maxillary sinus bone regeneration and similar biological outcomes. The Meta-analysis results showed that mineralized bone% was negatively correlated with the bone window dimension (P < 0.01). There was no significant difference in the new bone%, residual graft material% between the small bone window and the large bone window groups. Conclusion Negative correlation has been observed between the mineralized bone%and the dimension of bone window. Therefore, the lateral wall should be preserved as much as possible during the maxillary sinus floor elevation. Reducing the bone window has a positive effect on the maturity and mineralization of new bone.
2023, 44(9): 49-54.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230918
Abstract:
Objective To study the drug resistance of CRE infection in children in the intensive care unit and the risk factors of nosocomial infection of CRE, and to provide the reference for the treatment of CRE infection in children and the formulation of infection prevention and control strategies in hospitals. Methods Clinical data of children admitted to the intensive care unit of a 3A Children’s Hospital in Yunnan Province from January 2019 to December 2022 were retrospectively analyzed. 92 cases with nocometary infection of carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae bacteria (CRE) were included in the case group, and 92 cases with carbapenem-sensitive enterobacteriaceae (CSE) infection were randomly selected at 1∶1. According to the group, strain identification and drug sensitivity test were carried out to analyze the infection strains and drug resistance. Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analysis was conducted for children with CRE infection by SPSS 26.0, to explore the risk factors related to CRE infection in severely ill children. Results Klebsiellapneumoniae was detected in 81 cases (88.04%), followed by Escherichiacoli in 5 cases (5.43%). The drug resistance rates of levofloxacin, amoxicillin/clavulanic acid, ceftazidime, imipenem, cefepime, ceftriaxoneand amikacin in CRE group were higher than those in CSE group, and the differences were statistically significant (P < 0.05).Univariate analysis showed that indwelling gastric tube, central venous catheterization, mechanical ventilation, history of using carbapenems, glycopeptides and polymyxin antibiotics, types of antibiotics used ≥3, time of using antibiotics, time of using carbapenems, time of staying in ICU and total hospital stay were all risk factors of CRE infection, showing statistically significant differences (P < 0.05).Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that carbapenem antibiotic use history and use time and antibacterial use time (P < 0.05) were independent risk factors for CRE infection in severely ill children. Conclusion Combined with the risk factors of severe children’s CRE infection, we should minimize invasive operations such as puncture and intubation, standardize the use and management of antibiotics in the treatment of severe children, especially carbapenem antibiotics, shorten the length of stay in ICU and the total length of stay as much as possible, strengthen the active screening of severe children’s CRE, formulate reasonable and effective infection prevention and control strategies, and reduce the occurrence of nosocomial infection of severe children’s CRE.
2023, 44(9): 55-61.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230917
Abstract:
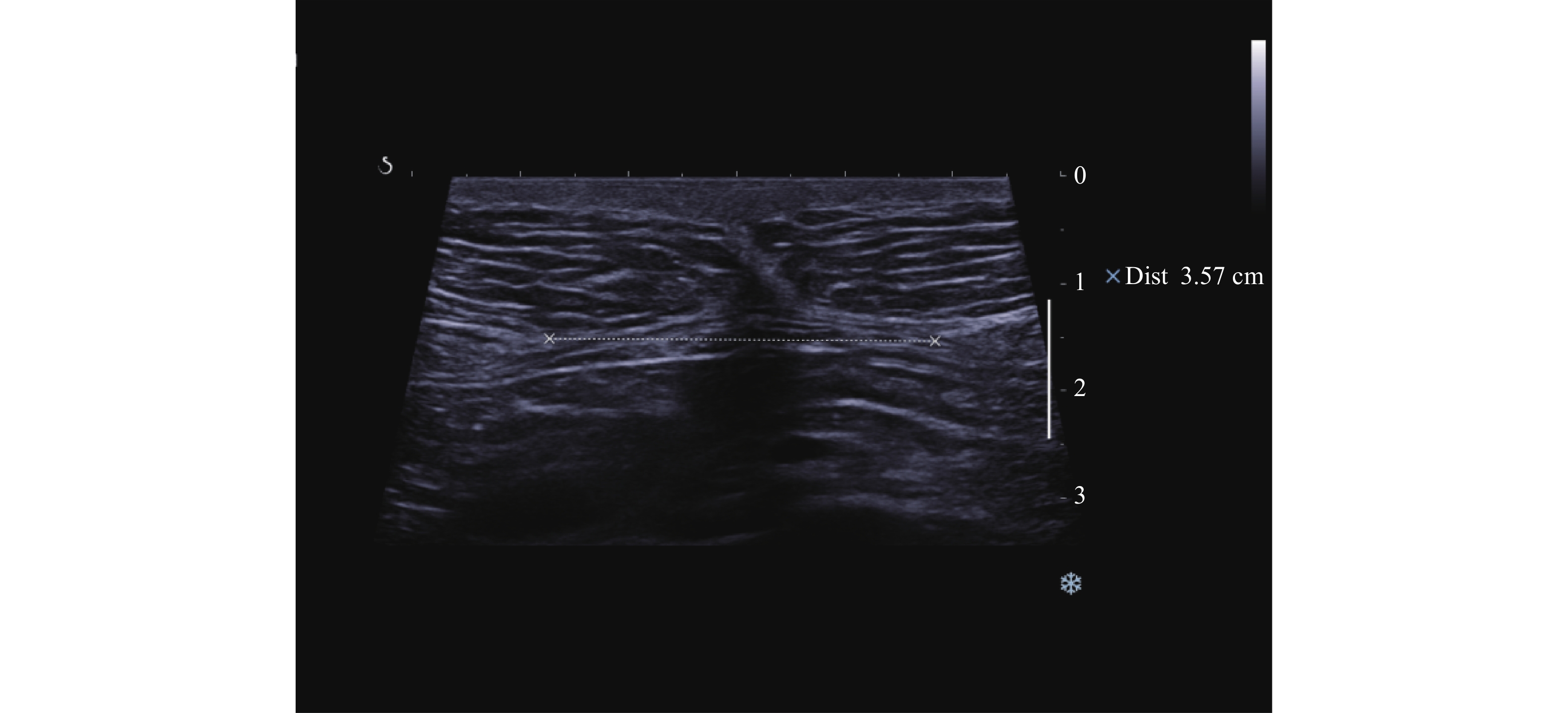
Objective To evaluate the distance between rectus abdominis muscle (IRD)and the hardness of primipara during the pregnancy and early postpartum by using two-dimensional ultrasound combined with shear wave elastography (SWE), and to explore the correlation between IRD and the hardness of primipara. Methods From October 2021 to August 2022, a total of 250 primipara who received the regular birth check-up in the Affiliated Hospital of Yunnan University and delivered at full term were selected. During the pregnancy, they were divided into the early pregnancy group, the middle pregnancy group and late pregnancy group based on the gestational age.After the birth, they were then were divided into the natural birth group and the cesarean section group based on the delivery mode. Another 50 healthy non-pregnant women were selected as the control group. The mean elastic modulus of rectus abdominis (Emean) was measured by two-dimensional ultrasound and SWE. The differences of IRD and the rectus abdominis hardness during the pregnancy and postpartum were compared, and the correlation between them was analyzed. Results IRD and the hardness increased with the gestational age and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.01). IRD of the cesarean section group was higher than that of the vaginal delivery group, and the hardness was lower than that of the vaginal delivery group. BMI during the pregnancy IRD was positively correlated with IRD and the hardness of rectus abdominis muscle (rp = 0.515, 0.641, 0.564, 0.483, 0.513, 0.462, P < 0.01) and IRD was positively correlated with the hardness of rectus abdominis muscle (rp = 0.559, 0.580, 0.425, P < 0.01). Postpartum BMI had no correlation with the hardness of rectus abdominis muscle (rp = −0.113, −0.071, −0.043, −0.005, −0.086, −0.045, P > 0.05), and IRD was negatively correlated with the hardness at 3cm below the umbilical cord (rp = −0.227, P = 0.023). Conclusion It is feasible to evaluate IRD and the rectus abdominis hardness by 2D ultrasound combined with SWE, which can provide more intuitive clinical basis for the diagnosis and treatment of postpartum rectus abdominis separation.
2023, 44(9): 62-68.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230901
Abstract:
Objective To analyze the platelet antibody detection results and the influence factors of 937 patients in our hospital, explore the impact of platelet antibodies on clinical transfusion effects, provide basis for the application value of platelet antibody detection, and ensure that platelet transfusion is more effective and safe. Methods From June 2019 to April 2021, samples from 937 patients were randomly collected from inpatients who applied for blood preparation or blood transfusion, and platelet antibodies were detected. The patients’ general clinical data were collected through the electronic medical record system and LIS system. Results 1. The positive rate of platelet antibody in patients with multiple transfusions was 13.23% , and the positive rate of platelet antibody correlated with the number of transfusions with statistically significant differences; 2. The positive rate of platelet antibody test was higher in women than in men (15.95% vs 10.57%, P < 0.05); 3. The positive rate of platelet antibody test was higher in medical patient than in surgical patient (16.31% vs 3.88%, P < 0.05), among which the top three department of medicine with positive platelet antibody test rates were the hematology department, the emergency department, and ICU (19.07% vs 18.42% vs 16.95%); 4. For patients in the hematology department, the number of chemotherapy, the combined use of more than 2 types of chemotherapy drugs, and the number of previous transfusion of platelets were significantly correlated with the detection rate of platelet antibodies (P < 0.05); 5. The positive rate of antibodies in the effective and ineffective groups of platelet transfusion was statistically different (P < 0.05); 6. The detection rate of HLA antibodies among platelet antibodies in non-hemolytic febrile reactions was as high as 67.85% (19/28). Conclusion 1. The production of platelet antibody is positively correlated with the number of blood transfusion, and the factors affecting the positive rate of platelet antibodies included: the number of platelet transfusions, female maternal history, the number of chemotherapy treatments in chemotherapy patients, and the use of chemotherapy drugs; 2. The investigation and study of platelet antibody detection has the enormous application value in the ineffectiveness of platelet transfusion, the assessment of transfusion efficacy in patients with hematologic diseases and chemotherapy, the establishment of transfusion strategy, and the diagnosis of non-hemolytic febrile transfusion adverse reactions; 3. The effect of Platelet transfusion can be significantly improved by coordinating platelets transfusion, and can effectively reduce the occurrence of ineffective platelets transfusion.
2023, 44(9): 69-74.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230921
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the effect of OCT after the stent implantation in patients with the Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS). Methods 172 patients with the ACS admitted to Yan’an Hospital Affiliated to Kunming Medical University from June 2019 to August 2022 were included in this study. They were treated with PPCI and accepted the assessment of OCT after the stent implantation. According to the result of OCT, they were treated with different methods. These 172 patients were matched with other 172 patients guided by CAG alone from PPCI patient database in order of 1∶1 by propensity score.The effects of the two strategies on the following treatment methods, the incidence of no-reflow phenomenon (NRP) and 6-month clinical follow-up results were compared and evaluated. Results 56 patients in the OCT guidance group had the incomplete stent expansion, 78 patients had the poor stent adhesion, and 18 patients had the stent edge dissection. The number of balloon dilation and placement of the second stent in the OCT guided group was significantly higher than that in the CAG guided group (P < 0.05), and the incidence of no reflow phenomenon in the OCT guided group was significantly lower than that in the CAG guided group (P < 0.05). The incidence of recurrent acute myocardial infarction and retarget vessel revascularization in the OCT guided group was lower than that in the CAG guided group (P < 0.05). Conclusion OCT examination can accurately identify whether ACS patients have the poor stent adhesion, incomplete stent expansion, and presence or absence of the stent edge dissection immediately after the stent placement. Based on the evaluation results, different follow-up treatment strategies are formulated, significantly reducing the possibility of recent adverse events related to the stent placement in ACS patients after PPCI surgery, and achieving personalized and precise treatment of ACS patients’ PPCI.
2023, 44(9): 75-79.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230923
Abstract:
Objective To explore the use of digital technology to intervene in the precise force stimuli for labial high positioned maxillary canines before the orthodontic treatment so as to improve alveolar crest absorption. Methods 54 maxillary labial low canine teeth from 43 adult orthodontic patients were included and divided into an intervention group and a non-intervention group. The distance between cemento-enamel bone junction and alveolar crest (CEJ-AC) before and after the treatment and other relevant data were statistically analyzed. Results 1. There was no statistical difference of CEJ-AC between the intervention group and the non-intervention group before the treatment; After the treatment, the CEJ-AC in the intervention group was lower than that before the treatment (P < 0.05), and there was no statistical difference of the CEJ-AC in the non-intervention group . 2. Before and after the treatment, there was no statistical difference in the changes of CEJ-AC in patients with thin gingival biotype, but decreased in patients with thick gingival biotype in the intervention group (P < 0.05). 3. The CEJ-AC decreased after the fixed orthodontic therapy intervention group (P < 0.05), and the difference between CEJ-AC before and after the treatment was greater than that in the conventional correction group (P < 0.05), while the reduction value of CEJ-AC of the invisible intervention group after the orthodontic therapy was greater than that in the conventional correction group (P < 0.05). Conclusion Pre-treatment intervention appliance with digitally designed for labial high maxillary canines can improve alveolar crest absorption after the orthodontic treatment in patients with thick gingival biotype. However, there are no significant effects on thin gingival biotype. Interventions prior to fixed or invisible correction are both effective.
2023, 44(9): 80-85.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230903
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the effect of different concentrations of atropine on myopia prevention and control in adolescents. Methods A prospective double-blind randomized controlled trial was conducted. A total of 86 adolescent myopia patients admitted to the Department of Ophthalmology, Yuxi People’s Hospital from October 2021 to October 2022 were selected and divided into three groups by random number table method. Among them, 26 cases only wore the proper framework of single focal lens. Study group 1 (n = 30) and study group 2 (n = 30) were treated with 0.01% and 0.05% atropine eye drops while wearing fully corrected monocular frames, respectively. The axial length (AL), uncorrected visual acuity (UCVA), and refractive index of three groups before and after the treatment, and the clinical treatment effectiveness and adverse reaction rates of study 1 and study 2 groups were recorded respectively. Results Before the treatment, there were no statistically significant differences in ocular axial length, naked eye sight, diopter index comparison among the three groups(P > 0.05); After the treatment, the axial length of study group 1 and study group 2 was shorter than that of the control group, the uncorrected visual acuity was higher than that of the control group, and the diopter was lower than that of the control group. There were statistically significant differences (P < 0.05). The axial length of study group 1 and study group 2 was shorter than that of the control group, and the naked eye vision was higher than that of the control group. The diopter was lower than that of the control group, and there was a statistically significant difference (P < 0.05); The treatment effectiveness rate of 96.67% (29/30) in study group 2 was higher than that of 73.33% (22/30) in study group 1, with a statistically significant difference (P < 0.05); In terms of the incidence of adverse reactions, study group 1 was 13.33% (4/30), and study group 2 was 6.67% (2/30), with no statistically significant difference (P > 0.05). Conclusion Compared with those only wearing the whole framework of single focal lens correction, the application of 0.01% and 0.05% atropine eye drops in juvenile myopia prevention and control of all have a certain therapeutic effect. Among them, 0.05% atropine application is more effective and it can effectively shorten the ocular axial length and improve the naked eye sight so as to reduce the diopter and incidence of adverse reactions and effectively improve the clinical treatment.
2023, 44(9): 86-92.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230902
Abstract:
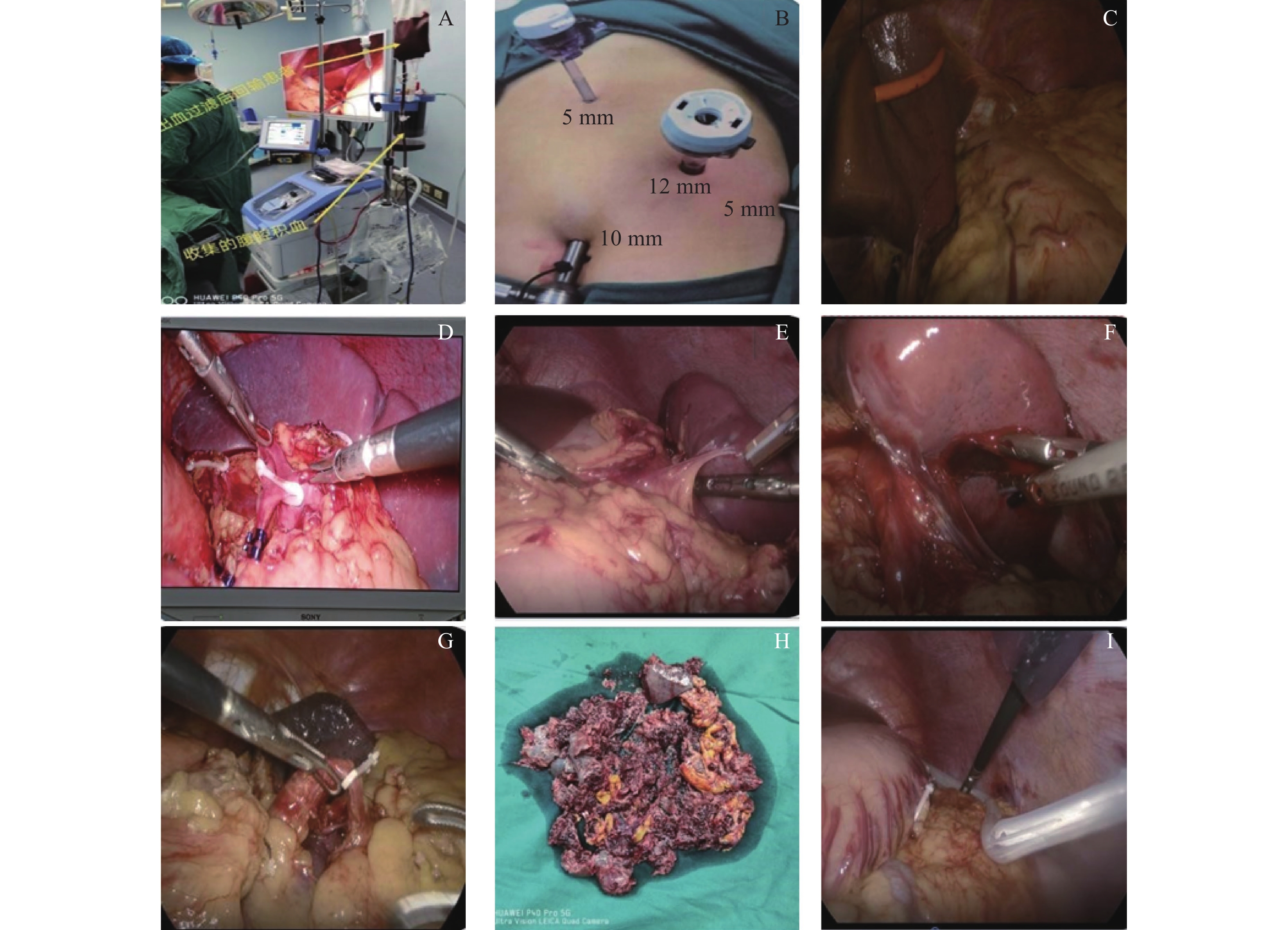
Objective To investigate the advantages and disadvantages of laparoscopic splenectomy in patients with splenic rupture, which is very common in surgical practice. Methods The data of 61 patients with traumatic splenic rupture admitted to the Second People’s Hospital of Baoshan from May 2012 to October 2022 were retrospectively analyzed. Among the collected data, 25 patients underwent laparoscopic splenectomy and were included in the observation group. Thirty-six patients underwent open surgery (OS) and were included in the control group. The orientation score was matched in 1∶1 ratio, and finally LS and OS were included in 25 cases each. In the observation group (LS group), there were 16 males and 9 females, aged (43.92±21.24) years old, ranging from 16 to 75 years old. In the control group (OS group), there were 19 male patients and 6 female patients, aged (35.20±16.28) years old, ranging from 14 to 65 years old. The indexes (blood loss, postoperative analgesic time, operation time, etc.), hospitalization cost and postoperative complications were compared between the two groups during the whole operation period. Results The baseline data of the two groups met the requirement of comparability after the propensity bisection. The operation time of LS group was (157.16±43.47) min, abdominal fluid was 98.00 (50.00, 100.00) mL, intraoperative blood loss was 800.00 (500.00, 1000.00) mL, intraoperative blood transfusion was 450.00 (400.00, 601.25) mL. The first postoperative exhaust was (40.32±13.36) h. The first time of getting out of bed after the operation was 48.00 (48.00, 72.00) h, drainage tube removal time was (72.96±21.33) h, and the postoperative analgesia time was 24.00 (24.00, 48.00) h. The hospital stay was 12.00 (10.00, 14.00) d, which was better than the operating time (184.20±63.14) min, with the effusion volume being 100.00 (100.00, 200.00) mL, intraoperative bleeding volume being 1000.00 (800.00, 1750.00) mL, intraoperative blood transfusion beting 1200.00 (461.00, 1200.00) mL. The first postoperative exhaust (58.56±18.43) h, first postoperative time of getting out of bed 72.00 (48.00, 120.00) h, drainage tube removal time was (102.72±43.00) h , the postoperative analgesia time was 48.00 (36.00, 96.00) h, and the hospital stay time 14 (11.50, 17.00) d was statistically significant (all P < 0.05). The hospitalization cost of LS group was 21800 yuan (1.68, 25800 yuan), slightly higher than that of OS groupof 17 700 yuan (15 100, 21 800 yuan), but the overall difference was not significant. Conclusion LS has the advantages over OS in terms of operation time, intraoperative blood loss control, intraoperative blood transfusion amount, postoperative exhaust, postoperative getting out of bed time, analgesic drug use time, abdominal effusion, postoperative complications, etc. It is more conducive to the recovery of patients and the improvement of the prognosis and survival quality, and more in line with the development of modern medicine.
2023, 44(9): 93-99.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230911
Abstract:
Objective To compare and analyze the effects of three different frozen-thawed embryo transfer(FET) protocols natural cycle(NC), hormone replacement cycle(HRT) and gonadotropin releasing hormone agonist-hormone replacement cycle(GnRH-a-HRT) on endometrial thickness on the day of endometrial transformation, endometrial blood flow and the pregnancy outcome of FET in patients with endometrial tuberculosis. Methods Patients with endometrial tuberculosis who underwent FET in the Reproductive Medicine Department of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University from January 1st, 2017 to January 1st, 2021 were collected. According to the FET endometrial preparation protocol, the patients were divided into NC group, HRT group and GnRH-a-HRT group respectively. After the comparation and analysis to the endometrial thickness, endometrial blood flow and embryo transfer outcomes were compared among the three groups; Results The embryo implantation rate, clinical pregnancy rate, continuing pregnancy rate and live birth rate in GnRH-a HRT group were higher than those in HRT group(P < 0.05). The embryo implantation rate, clinical pregnancy rate, ongoing pregnancy rate and live birth rate in HRT group were higher than those in NC group, and the differences were statistically(P < 0.05). The endometrial thickness and endometrial blood flow of the three groups, it was found that the endometrial thickness and PSV value of the endometrial blood flow in the GnRH-a HRT group were higher than those in the HRT group and NC group, while the RI value and PI value of the endometrial blood flow were lower than those in the HRT group and NC group(P < 0.05). The endometrial thickness and PSV of the HRT group were higher than those of the NC group, while the RI and PI of the endometrial blood flow were lower than those of the NC group, and the differences were statistically(P < 0.05); Conclusion GnRH-a-HRT can improve the endometrial thickness and PSV value of endometrial blood flow on the day of endometrial transformation, reduce the RI and PI value of endometrial blood flow, and finally improve the pregnancy outcome of FET for patients with endometrial tuberculosis.
2023, 44(9): 100-103.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230909
Abstract:
Objective To observe the expression of peripheral blood IL-1β, IL-2, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6 levels in patients with gestational hypertension and explore the importance of peripheral blood cytokines in HDCP and their relations to the severity of the disease. Methods Multiple microsphere flow immunofluorescence assay was used to measure the levels of IL-1β, IL-2, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6 (27 patients with gestational hypertension, 18 patients with preeclampsia, 15 patients with severe preeclampsia)and 20 normal pregnant women were measured in 60 HDCP patients . Results The serum levels of IL-1β, IL-2, IL-4, IL-5 and IL-6 in HDCP group were(12.53±1.32) pg/mL, (10.69±1.40) pg/mL, (1.02± 6.77) pg/mL, (4.41±1.29) pg/mL, (23.32±4.58) pg/mL, respectively. Normal pregnant women were(10.25±1.42) pg/mL, (4.41±1.32) pg/mL, (6.86±4.62) pg/mL, (5.31±1.31) pg/mL, and(6.82±1.02) pg/mL, respectively, The difference in IL-2、IL-4、IL-6 was statistically significant( P < 0.05) , while the difference in IL-1β and IL-5 was not statistically significant ( P > 0.05) . The levels of IL-2 and IL-6 were significantly different in the classificationof HDCP( P < 0.05). However, there was no significant difference in serum levels of IL-4( P > 0.05) . Conclusion Patients with gestational hypertension have significantly increased levels of IL-2 and IL-6 in their peripheral blood, which increase with the severity of the condition. IL-4 levels are significantly reduced but not related to the severity of the disease. Abnormal expression levels of IL-2, IL-6, and IL-4 in peripheral blood may induce the endothelial cell damage, abnormal immune activation, and promote the occurrence and development of pregnancy-induced hypertension.
2023, 44(9): 104-109.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230919
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the effects of different methods of complete mesocolectomy (CME) on the platelet activation, complication rate and tumor recurrence in patients with colon cancer. Methods 80 patients with colon cancer in The 2nd People's Hospital of Kunming from January 2020 to January 2022 were selected and divided into 2 groups according to the treatment plan, with 40 cases in each group. The control group underwent open CME, and the observation group underwent laparoscopic CME to compare the perioperative situation, number of lymph node dissection, incidence of postoperative complications, as well as serum inflammatory [interleukin-6 (IL-6), C-reactive protein (CRP)] and platelet activation indicators [platelet neutrophil aggregates (PNA), platelet lymphocytic aggregation (PlyA), platelet leukocyte aggregation (PMA), platelet leukocyte aggregates (PLA)] before and after surgery and the tumor recurrence rate between the two groups. Results The intraoperative blood loss and postoperative drainage volume in the observation group were less than those in the control group, and the anal defecation time, anal exhaust time and hospitalization days were shorter than those in the control group (P < 0.05). The number of stage III, positive and left and right hemicolic lymph nodes dissection in the observation group was higher than that in the control group, and the incidence of postoperative complications was lower than that in the control group (P < 0.05). Serum IL-6 and CRP in the observation group were lower than those in the control group 1 day after the operation (P < 0.05). PLA, PlyA, PMA and PNA in the observation group were lower than those in the control group 1 day after the operation (P < 0.05). The one-year recurrence rate of the observation group was lower than that of the control group, and the survival time without recurrence was longer than that of the control group (P < 0.05). Conclusion The operative time of laparoscopic CME for colon cancer is similar to that of open CME, but it can reduce the intraoperative bleeding, reduce the inflammatory response, improve the platelet activation, promote the disease recovery, improve the lymph node clearance, reduce the recurrence risk, prolong survival, and reduce complications.
2023, 44(9): 110-120.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230912
Abstract:
Objective To systematically evaluate the efficacy and safety of different bronchoscopic intervention methods combined with the conventional anti-tuberculosis regimen in the treatment of tracheobronchial tuberculosis (TBTB), and to provide the evidence-based reference for clinical practice. Methods Computer search PubMed, Web of Science, EMBase, CNKI, Wanfang Database, VIP database, randomized controlled trials (RCTS) of different bronchoscopic interventions (local administration, cryotherapy, and atomization) combined with conventional anti-tuberculosis therapy were collected. After the data extraction and quality evaluation, network meta-analysis was performed using Stata 16.0 software. Results A total of 38 RCTS were included, involving a total of 3114 patients and three interventions (conventional + local administration, conventional+ cryotherapy, conventional + local administration + atomization). Compared with the conventional treatment, conventional+ cryotherapy, conventional + local administration, conventional + local administration + atomization could significantly improve the total clinical response rate (P < 0.05). The results of mesh Meta ranking were conventional + local administration + atomization > conventional + local administration > conventional + cryotherapy > conventional. Compared with the conventional treatment, conventional + cryotherapy, conventional + local administration, conventional + local administration + atomization could significantly improve the effective rate of fiberoptic bronchoscopy (P < 0.05). The results of mesh Meta ranking were conventional + local administration > conventional + local administration + atomization > conventional + cryotherapy > conventional. Compared with the conventional treatment, conventional + local administration, conventional + local administration + atomization could significantly improve the sputum negative conversion rate at the end of 8 weeks after the treatment (P < 0.05). Compared with conventional + cryotherapy, conventional + local administration could significantly improve the sputum negative conversion rate at the end of 8 weeks after treatment (P < 0.05). The results of mesh Meta ranking were conventional + local administration > conventional + local administration + atomization > conventional + cryotherapy > conventional. Compared with the conventional treatment, conventional + local administration could significantly improve the sputum negative conversion rate at the end of 24 weeks after treatment (P < 0.05). The results of mesh Meta ranking were conventional + local administration > conventional + local administration + atomization > conventional + cryotherapy > conventional. There was no statistically significant difference in the incidence of adverse reactions among all groups (P > 0.05). Conclusion The conventional + local administration + atomization scheme has the most significant improvement effect, while the conventional + local administration scheme has the best effect in improving the effective rate under bronchoscopy. In TBTB patients, the conventional + local administration + atomization regimen can accelerate the sputum to negative in the early stage, but the conventional + local administration regimen can accelerate the conversion of sputum to negative in the long-term treatment. Bronchoscopic intervention on the basis of conventional anti-tuberculosis therapy does not increase adverse reactions and has the good safety. However, this study needs to be further verified by including more high-quality, double-blind RCTS.
2023, 44(9): 121-125.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230924
Abstract:
Objective To explore the effect of multidisciplinary team building in hospice care on patients with end-stage diseases. Methods 200 end-stage patients who were hospitalized in our hospital from January 2020 to December 2021 were selected and divided into the control group and the observation group by random number table method, with 100 patients in each group. The control group received the routine clinical intervention, while the observation group received the intervention through a multidisciplinary team of hospice care. Quality of life (QOL), Pain Assessment Form, Edmonton Symptom Assessment System (ESAS), Nutritional Risk Screening (NRS-2002), Palliative Performance Scale (PPS) were used to evaluate the quality of life, symptoms, pain, nutritional status andbehavior function. Results After the intervention, QOL score and normal rate of action state in the observation group were higher than those in the control group, and pain, nutritional status and symtom scores were lower than those in the control group (P < 0.05). Conclusion The establishment of a multidisciplinary team of hospice care and intervention to end-stage patients can effectively improve their quality of life.
2023, 44(9): 126-135.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230927
Abstract:
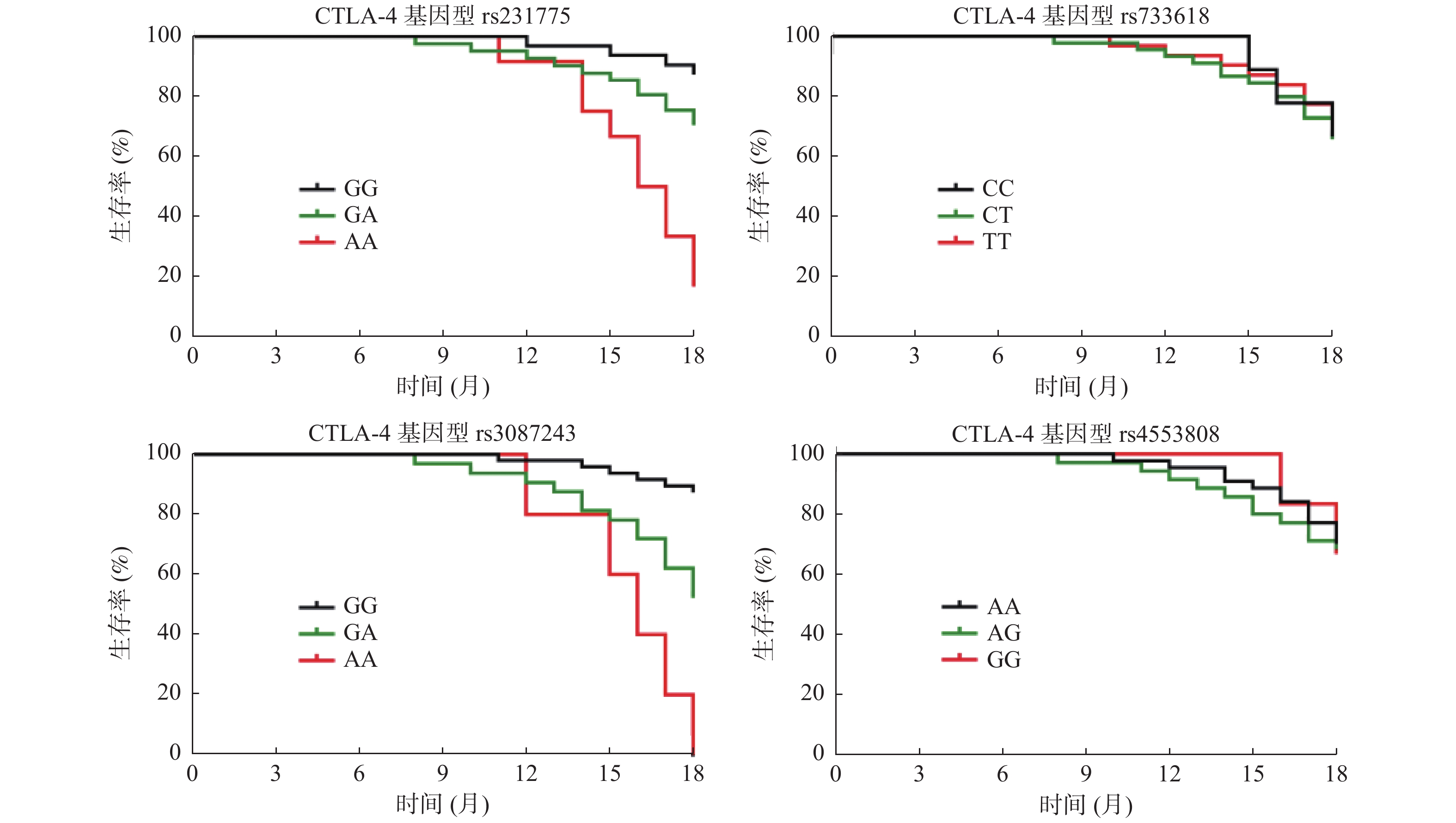
Objective To investigate the correlation between gene polymorphisms of B and T lymphocyte attenuator (BTLA) and cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4 (CTLA-4) and the efficacy and prognosis of targeted therapy combined with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) for liver cancer. Methods Eighty-five new hepatocellular carcinoma patients admitted to the Department of Interventional Radiology of Nantong University Hospital between 2021-01-01 and 2021-12-31 were selected for the study, and all of them were treated with TACE combined with targeted therapy. According to the RECIST solid tumor efficacy evaluation criteria, the patients were divided into the effective treatment group (n = 58) and the disease progression group (n = 27). The clinical data, BTLA, CTLA-4 gene polymorphisms between the 2 groups were compared and the correlation between BTLA, CTLA-4 gene polymorphisms and efficacy were analyzed, And follow-up survival status by phone at 18 months after the treatment was conducted to compare the survival status of patients with different genotypes, and analyze their correlation with survival prognosis. Results CTLA-4 rs231775, rs733618, rs3087243, rs4553808, BTLA and the genotypes of rs2171513, rs3112270, rs1982809 and rs16859629 all conformed to Hardy-Weinberg law of genetic balance. The BTLA rs3112270 AG, GG genotype ratio, rs1982809 GA, AA ratio, rs16859629 CC genotype, CTLA-4 rs231775 AA genotype ratio, rs3087243 GA, AA genotype ratio in the treatment effective group were all lower than those in the disease progression group, while the proportion of AA genotype at BTLA rs3112270, GG genotype at rs1982809, TT genotype at rs16859629, GG genotype at CTLA-4 rs231775, and GG genotype at rs3087243 were all higher than those in the disease progression group (P < 0.05); Univariate and multivariate analysis showed that BTLA rs3112270 A > G, rs1982809 G > A, rs16859629 T > C, CTLA-4 rs231775 A > G, rs3087243 G > A were all associated with the efficacy (P < 0.05); The 18 month survival rate of BTLA rs3112270 AA and AG genotype patients was higher than that of GG genotype patients, rs1982809 GG and GA genotype patients were higher than that of AA genotype patients, and rs16859629 TT genotype patients are higher than those of TC and CC genotype patients (P < 0.05); The 18 month survival rate of patients with CTLA-4 rs231775 GG and GA genotypes was higher than that of patients with AA genotypes, and the 18 month survival rate of GG genotype at rs3087243 was higher than that of patients with GA and AA genotypes (P < 0.05); Univariate and multivariate analysis showed that BTLA rs3112270 A > G, rs1982809 G > A, rs16859629 T > C, CTLA-4 rs231775 A > G, rs3087243 G > A were all associated with the survival prognosis (P < 0.05). Conclusion The polymorphisms of BTLA gene rs3112270, rs1982809, rs16859629, CTLA-4 gene rs231775, rs3087243 are closely related to the efficacy and prognosis of TACE combined with the targeted therapy for liver cancer and these will provide the reference for predicting TACE treatment.
2023, 44(9): 136-142.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230928
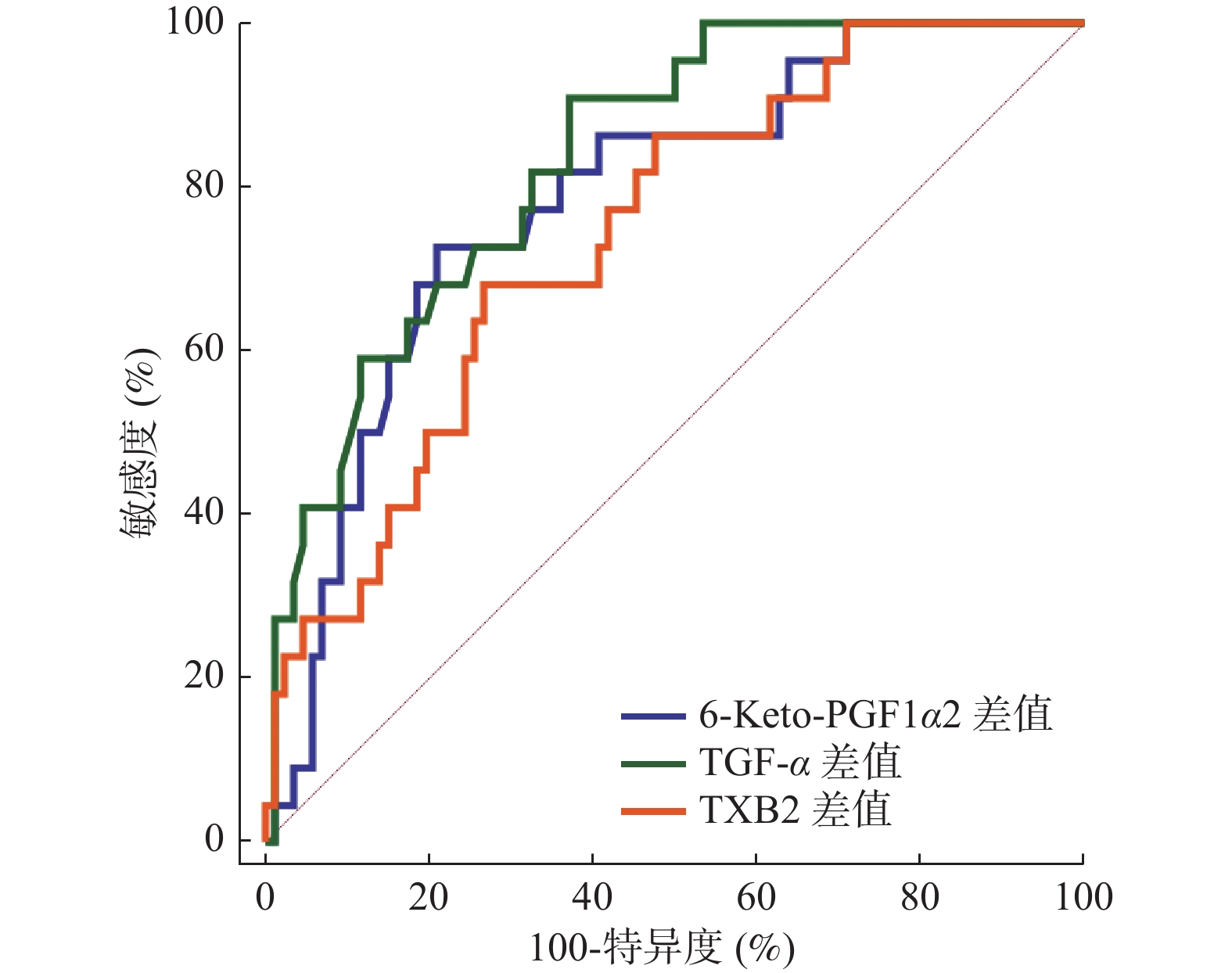
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the changes of serum levels of 6-Keto-PGF1α, transforming growth factor α (TGF-α) and thromboxane B2 (TXB2) during the treatment of peptic ulcer in children, and to analyze their prognostic value. Methods 108 children with peptic ulcer from January 2019 to June 2022 were selected as the study subjects. According to the therapeutic effect of omeprazole triple therapy, they were divided into the good prognosis group (86 cases) and the poor prognosis group (22 cases). The clinical data and serum levels of 6-Keto-PGF1α, TGF-α and TXB2 during the treatment were compared between the two groups to analyze the influence and prognostic value of each serum index on the treatment and prognosis. Results After 6 weeks of the treatment, the serum levels of 6-Keto-PGF1α and TGF-α in the poor prognosis group were higher than those in the good prognosis group, and the level of TXB2 was lower than that in the good prognosis group, and the difference of serum indexes before and after the treatment was smaller than that in the good prognosis group (P < 0.05). The difference of serum 6-Keto-PGF1α, TGF-α and TXB2 were independently correlated with the prognosis, and the risk of adverse prognosis in positive patients was 5.804, 4.014 and 3.241 times that of negative patients respectively (P < 0.05). The combined prediction AUC of the difference of serum indexes was greater than that of the single indexes (P < 0.05). Conclusion The serum levels of 6-Keto-PGF1α and TGF-α increased during the treatment of peptic ulcer in children, while the levels of TXB2 decreased. The changes of serum indexes before and after treatment are closely related to poor prognosis, and the combined detection of their changes has certain predictive value for poor prognosis.
2023, 44(9): 143-147.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230922
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the effect of butylphthalide on cognitive dysfunction after the stroke caused by cerebral small vessel disease and its effect on cerebral blood perfusion. Methods 84 patients with the cognitive impairment after the stroke caused by small vessel disease were retrospectively selected from the Neurology Department of Shijiazhuang People’s Hospital from March 2019 to March 2021. According to the different treatment methods, they were divided into the control group (basic treatment) and the study group (basic treatment+butylphthalide treatment), with 42 patients in each group. Cognitive function, daily living ability, neurological function deficits, and changes in cerebral blood flow perfusion were observed. Results After 3 months of treatment, MMSE and Barthel index scores increased and NIHSS scores decreased in the two groups (P < 0.05). After the treatment, MMSE and Barthel index scores in the study group were higher than those in the control group (P < 0.05). The mean passage time of patients in the two groups decreased, and the CEREBRAL blood flow and blood flow velocity increased. In comparison with the results between the two groups, the mean passage time of patients in the study group was lower than that of the control group after the treatment, while the cerebral blood flow and blood flow velocity were significantly higher than that of the control group (P < 0.05). Conclusion Butylphthalide can improve the cerebral blood flow perfusion and promote the recovery of patients’ cognitive function and daily living ability in the treatment of cognitive dysfunction after the stroke caused by cerebral small vascular disease.
2023, 44(9): 148-154.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230920
Abstract:
Diabetic kidney disease(DKD) has become a major cause of chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease. A better understanding of the characteristics and molecular mechanisms of the early changes in DKD will contribute to the development of new strategies to prevent this chronic disease. The research on the damage mechanism and therapeutic targets of early DKD has shifted from glomerular damage to diabetic tubulopathy(DT). This article summarizes the mechanism and therapeutic targets of blood glucose, complement, biomarkers and mitochondria in DT, with the purpose to provide a new direction for the diagnosis and treatment of early DKD.
Diabetic kidney disease(DKD) has become a major cause of chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease. A better understanding of the characteristics and molecular mechanisms of the early changes in DKD will contribute to the development of new strategies to prevent this chronic disease. The research on the damage mechanism and therapeutic targets of early DKD has shifted from glomerular damage to diabetic tubulopathy(DT). This article summarizes the mechanism and therapeutic targets of blood glucose, complement, biomarkers and mitochondria in DT, with the purpose to provide a new direction for the diagnosis and treatment of early DKD.
2023, 44(9): 155-160.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230913
Abstract:
Cerebral ischemic stoke is a disease in which oxidative stress, activation of inflammatory storms, interference, induction of apoptosis, and blood reperfusion aggravate the tissue and cell damage due to ischemia and hypoxia. Mesenchymal stem cells(MSCs) induce the angiogenesis and can be used to treat the ischemia-reperfusion injury, anti-apoptosis and anti-inflammatory. Preclinical studies have confirmed that targeted delivery of mesenchymal-derived exosomes to recipient cells exerts the effects of inducing angiogenesis, anti-apoptosis, and anti-inflammatory, while avoiding the shortcomings of mesenchymal stem cell therapy. The purpose of this study is to summarize the mechanism of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of stroke so as to provide new opportunities for treating ischemic cerebrovascular disease clinically.
Cerebral ischemic stoke is a disease in which oxidative stress, activation of inflammatory storms, interference, induction of apoptosis, and blood reperfusion aggravate the tissue and cell damage due to ischemia and hypoxia. Mesenchymal stem cells(MSCs) induce the angiogenesis and can be used to treat the ischemia-reperfusion injury, anti-apoptosis and anti-inflammatory. Preclinical studies have confirmed that targeted delivery of mesenchymal-derived exosomes to recipient cells exerts the effects of inducing angiogenesis, anti-apoptosis, and anti-inflammatory, while avoiding the shortcomings of mesenchymal stem cell therapy. The purpose of this study is to summarize the mechanism of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of stroke so as to provide new opportunities for treating ischemic cerebrovascular disease clinically.
2023, 44(9): 161-165.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230908
Abstract:
Objective To explore the effect of routine teaching mode and PBL case base teaching method on the teaching effectiveness of thoracic nursing interns in Yunnan Cancer Hospital. Methods 157 nursing interns in the Thoracic Surgery Department of Yunnan Cancer Hospital from January 1, 2021 to December 31, 2022 were selected as the research objects and divided into the control group and the experimental group. The conventional teaching mode was used in the control group while the PBL case library teaching method was used in the experimental group and the teaching effect of the two groups was compared. Results The scores of autonomous learning ability evaluation and post competency of the experimental group were higher than those of the control group, the differences were statistically significant (P < 0.05), while the scores of CD-RISC-10 scale between the control group and the experimental group were not statistically significant ( P > 0.05). Conclusion Compared with the conventional teaching mode, PBL case base teaching method can effectively improve the independent learning ability and post competency of nursing students, and can help standardize the clinical practice teaching activities. However, this teaching method does not improve the psychological resilience level of nursing students.
2023, 44(9): 166-170.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230914
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the effect of navigation nurses on children with allergic asthma under the nursing-led model. Methods A total of 110 children with the allergic asthma who were admitted to the Respiratory Department of Shanghai Children’s Hospital from March 1, 2021 to March 1, 2022 were selected as the research subjects and randomly divided into the control-group and the observation-group with 55 cases in each group. The control-group was treated with routine nursing care, and the observation-group was treated with improved Allergic Asthma Navigational Nursing (AANN) model on this basis. The clinical efficacy, vital capacity (FVC), peak expiratory flow rate (PEF), forced expiratory volume per second (FEV1/FVC), serum total immunoglobulin E (IgE), eosinophil (EOS) level, Asthma Control Test (ACT) score and job satisfaction were compared between the two groups. Results After 4 weeks of the treatment, the effect on the observation-group was higher than that on the control-group (P < 0.05); FCV, FEV1/FVC and PEF in the two groups were higher than those before the treatment, and those in the observation-group were higher than those in the control-group (P < 0.05); The levels of IgE and EOS in the two groups were lower than those before the treatment, and those in the observation-group were lower than those in the control-group (P < 0.05); The ACT score of the two groups was higher than that before the treatment, and the ACT score of the observation-group was higher than that of the control-group (P < 0.05). All nursing contents and total satisfaction scores in the observation-group were higher than those in the control-group (P < 0.05). Conclusion The navigation nursing mode can improve the treatment effect on children with allergic asthma, promote their early recovery, improve parents’ satisfaction, and improve the quality of medical services, which is worth promoting.
2023, 44(9): 171-175.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230906
Abstract:
Objective To explore the relationship between the caregiver burden and life meaning of patients with the early stage lung cancer, and to provide the reference for later intervention of patients with the early stage lung cancer. Methods The Life Meaning Scale (C-MLQ) was used to investigate 197 patients with the lung cancer at the early stage of diagnosis (≤6 months) by convenience sampling method. The Zarit Caregiver Burden Interview (ZBI) was used to investigate the caregivers of patients, and the impact of caregiver burden on patients’ life meaning was finally analyzed. Results The total caregiver burden was 47.93±3.23; The total meaning of life score was 33.64±4.63. Caregiver burden was negatively correlated with the total score of life meaning and scores of all dimensions (all P < 0.05). Conclusion The caregiver burden of patients is at a moderate level, the life meaning of patients is at a low level, and the caregiver burden negatively affects the life meaning of patients. Medical staff should pay attention to the mental health of patients, formulate appropriate intervention programs, improve patients’ sense of life meaning, and reduce the psychological burden of caregivers.
2023, 44(9): 176-182.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230915
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the current status of PROMIS informational support among ostomy patients and analyze the factors influencing it. Methods A total of 159 ostomy patients from a tertiary hospital in Yunnan Province, China, were surveyed using the Chinese version of the PROMIS Informational Support Scale. Results The total score for self-reported information support among ostomy patients was (28.00±7.92). The univariate analysis was showed that ostomy systerm changing, the major caregiver number of ostomy surgery, the number of health information support had a statistical significance (P < 0.05). Pearson correlation analysis results showed that the total scores of everyday health information literacy and social support scores, the dimension of health information consciousness, application ablity, and objective social support, the usage of it, had a difference in ostomy patients (P < 0.05). The results of a multiple regression analysis indicated that the main factors affecting self-reported information support for ostomy patients included age, the way to the hospital, ostomy systerm changing, the major caregiver number of ostomy surgery, the number of health information support channels, health information application ability, and utilization of social support. It could expain 35.5% variance of the total scores for ostomy patients’ self reported information support. Conclusion Self-reported information support among ostomy patients is found to be at a moderately low level. Healthcare professionals should diversify health information support channels, enhance patients' health information application ability, and strengthen the diversified information support so as to improve the self-reported information support among ostomy patients.
2023, 44(9): 183-188.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230904
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the status quo of parents’ readiness for discharge of high-risk neonates and analyze its influence factors, so as to provide the reference for formulating and implementing corresponding nursing measures. Methods From February to June, 2023, the parents of 158 high-risk neonates in the Department of Pediatrics of the Third People’s Hospital of Yunnan Province were investigated by using the general information questionnaire and the Chinese version of the discharge readiness scale-parents version, and the influence factors of the discharge readiness of parents of high-risk neonates were analyzed. Results The total score of the discharge readiness scale was 194.82±25.261, which was above the average. The results of multiple regression analysis showed that the birth type, education level, relationship with children, current employment status, and average monthly income of families were the independent influence factors on the discharge readiness score of parents of high risk neonates (P < 0.05). Conclusion Parents of high risk neonates are generally prepared for discharge, and clinical medical staff can formulate targeted discharge education programs to ensure the discharge quality of high-risk infants and reduce their readmission rate.


 Email
Email RSS
RSS