2024 Vol. 45, No. 3
2024, 45(3): 1-6.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240301
Abstract:
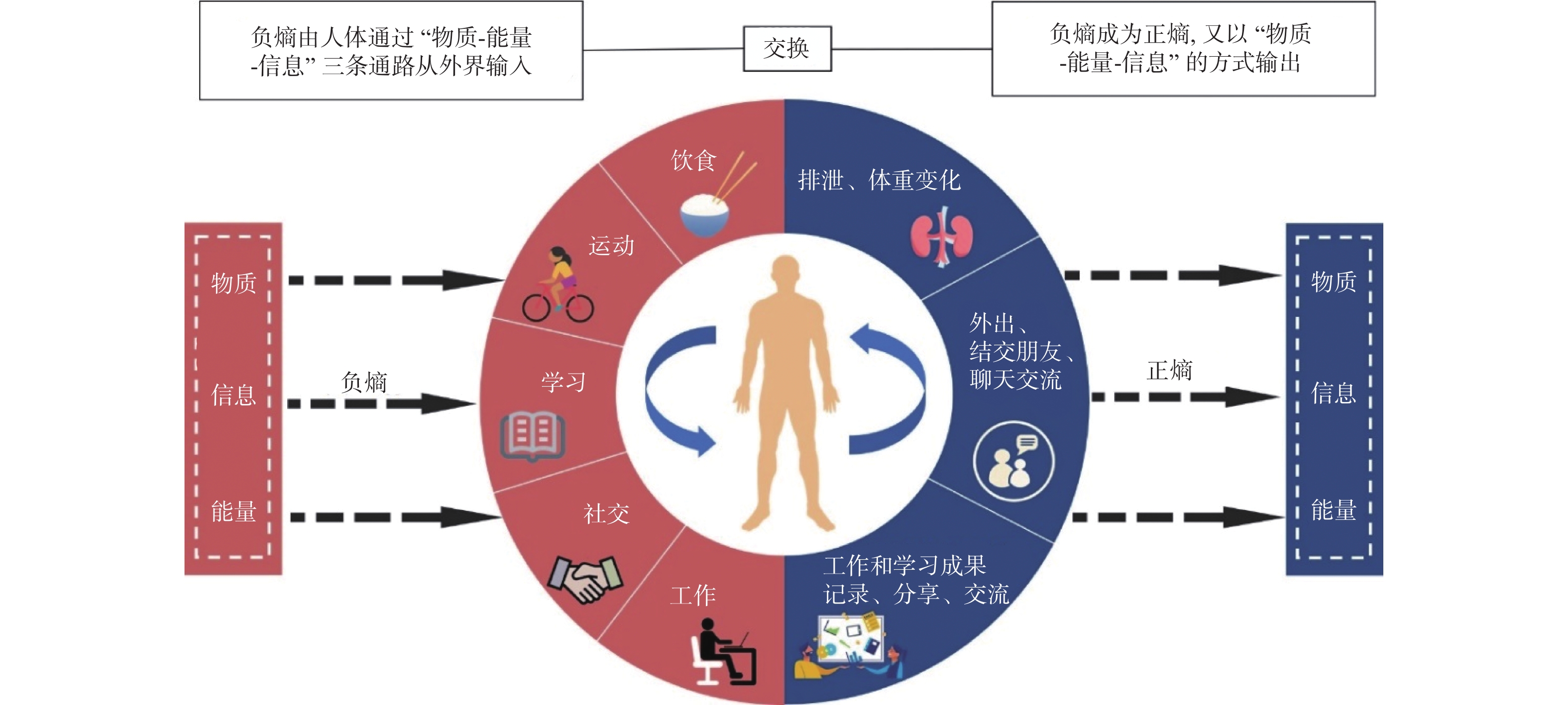
Dissipative structure refers to a self-organized and orderly structure that exists far from equilibrium. The human body, considered a classical example, generates negative entropy through the exchange of matter, energy, and information with the environment to counteract the increase in entropy. In this paper, we organized theories and related research on dissipative structure and entropy, discussing their significance in regulating various aspects such as the human body, cancer, aging, and more. By selecting the special population of pregnant women, focusing on the information dimension, developing the corresponding information exchange scale (Cronbach's α > 0.9), and proposing the information exchange index, we preliminarily explored the influence of the dissipative structure's information dimension on pregnancy health. The results showed a negative correlation between the information exchange index and anxiety scores during pregnancy (r = -0.35, P < 0.001), with an OR value of 0.26 (95%CI: 0.08~0.80), preliminarily confirming the feasibility of conducting empirical research based on dissipative structure theory. If further relevant empirical studies are conducted, it is expected that new disease prevention strategies will be developed and new theories and methods will be provided for the field of public health.
Dissipative structure refers to a self-organized and orderly structure that exists far from equilibrium. The human body, considered a classical example, generates negative entropy through the exchange of matter, energy, and information with the environment to counteract the increase in entropy. In this paper, we organized theories and related research on dissipative structure and entropy, discussing their significance in regulating various aspects such as the human body, cancer, aging, and more. By selecting the special population of pregnant women, focusing on the information dimension, developing the corresponding information exchange scale (Cronbach's α > 0.9), and proposing the information exchange index, we preliminarily explored the influence of the dissipative structure's information dimension on pregnancy health. The results showed a negative correlation between the information exchange index and anxiety scores during pregnancy (r = -0.35, P < 0.001), with an OR value of 0.26 (95%CI: 0.08~0.80), preliminarily confirming the feasibility of conducting empirical research based on dissipative structure theory. If further relevant empirical studies are conducted, it is expected that new disease prevention strategies will be developed and new theories and methods will be provided for the field of public health.
2024, 45(3): 7-17.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240302
Abstract:
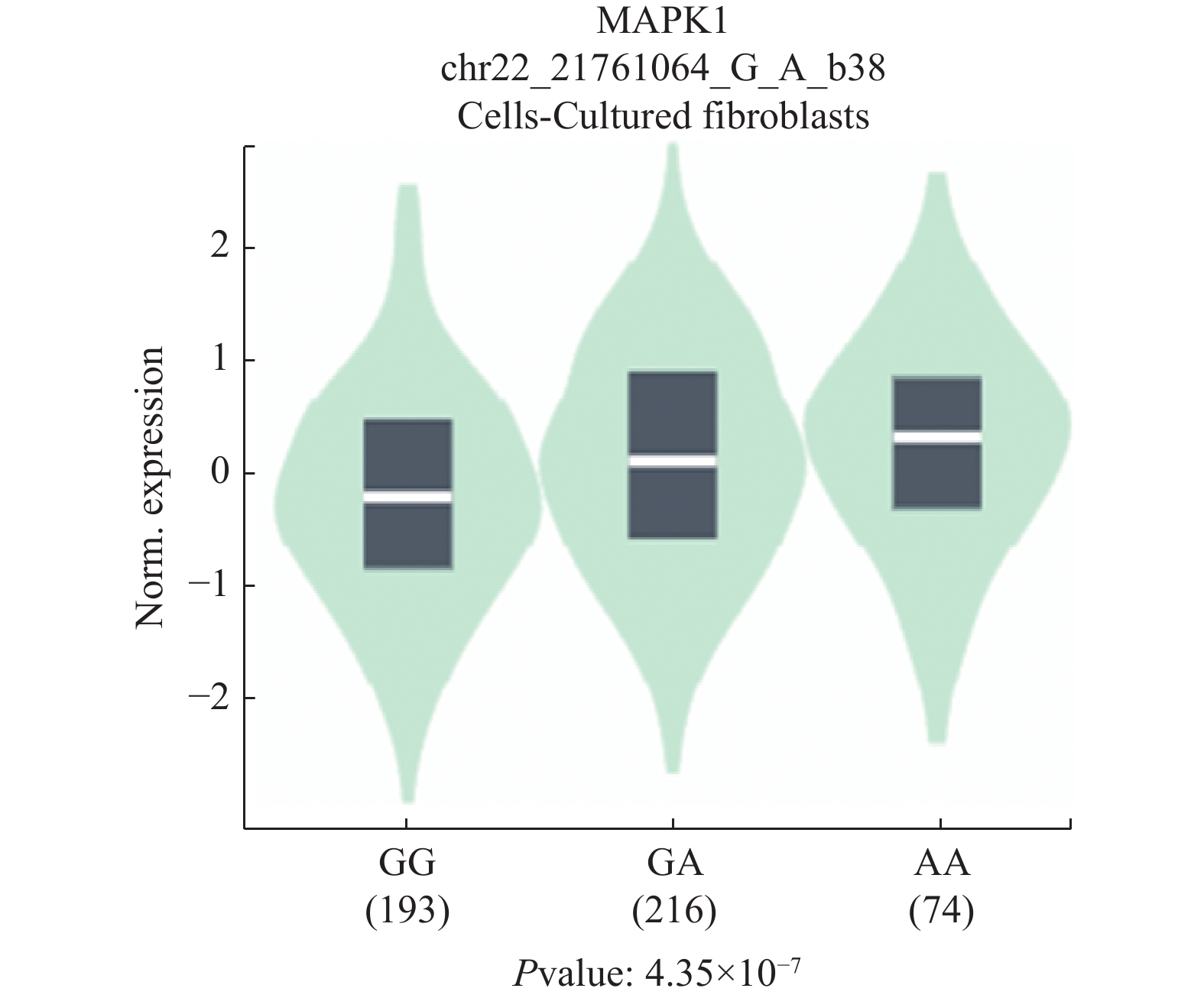
Objective To investigate the association between four single nucleotide polymorphisms(SNP)(rs9340 in MAPK1, rs14804 in NRAS, rs712 and rs7973450 in KRAS) in the 3'UTR of ERK1/2 signaling pathway-related genes and non-small cell lung cancer(NSCLC). Methods A total of 478 NSCLC patients and 480 healthy controls were enrolled in this study. Four SNPs were genotyped by using TaqMan assays. The association between the four SNPs and NSCLC was analyzed. Results The distribution frequency difference of the allele of rs9340 was statistically significant between the control group and the non-small cell squamous cell carcinoma(SCC) group(P = 0.009), suggesting that the G allele of rs9340 may be a protective factor for non-small cell lung squamous cell carcinoma(OR = 0.67, 95%CI: 0.50~0.91). In addition, in the < 50 years age group, the distribution frequency difference of the allele of rs9340 was statistically significant between the control group and the NSCLC group(P = 5.07 × 10-4), indicating that the G allele of rs9340 may be a protective factor for NSCLC(OR = 0.46, 95%CI: 0.29~0.72). Conclusion The SNP rs9340 in MAPK1 may be associated with the risk of NSCLC.
2024, 45(3): 18-29.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240303
Abstract:
Objective To identify inflammation-related genes in atrial fibrillation (AF) and explore the possible role and mechanism of these genes and infiltrating immune cells in the development of AF. Methods A series of bioinformatics analysis combined with machine learning algorithms to identify biomarkers of AF, the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were used to verify the prediction and diagnostic value of key genes, and Spearman correlation analysis was used to clarify the correlation between key genes and infiltrating immune cells. Results 593 differential genes (| log2 (fold change, FC) |> 1, P <0.05), 7 immune cell subtypes (P <0.05) were selected, 190 immune-related differential genes were obtained, 3 biomarkers (IGF1, PTGS 2 and PPARG), and the correlation analysis showed that 3 markers were significantly associated with infiltrating immune cells (P < 0.05). Conclusion IGF1, PTGS2 and PPARG are inflammation-related genes of AF, which are speculated to be closely related to the process and pathway of immune cell infiltration.
2024, 45(3): 30-34.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240304
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the effect of electromagnetic wave power density on the expression of glial fibrillary acidic protein(GFAP) in the hippocampus of SD rats under 1800 MHz electromagnetic wave irradiation, and whether it exhibits a “window effect”. Methods Ninety-eight 4-week-old SPF-grade SD rats were randomly divided into 14 groups, with 7 rats in each group. Seven groups were exposed groups (frequency: 1800 MHz, power densities: 0.1 mW/cm2, 0.3 mW/cm2, 0.5 mW/cm2, 0.7 mW/cm2, 0.9 mW/cm2, 1.0 mW/cm2, 1.2 mW/cm2) and corresponding 7 groups were control groups(power density: 0 mW/cm2). Exposure was conducted for 12 hours daily for 3 weeks. After exposure, Western Blot was used to detect the expression level of GFAP in the hippocampal tissue, and immunohistochemistry staining was performed to determine the average optical density(MOD) value of GFAP-positive expression products in the DG, CA3, and CA1 regions of the hippocampal tissue, to determine the power density window of GFAP expression in the hippocampus of SD rats under 1800 MHz exposure. Results At power densities of 0.1 mW/cm2 and 0.3 mW/cm2, Western Blot results showed increased expression of GFAP in the rat hippocampus(P < 0.05), and immunohistochemistry staining demonstrated increased MOD values of GFAP in the three regions(P < 0.05). Conclusion Long-term exposure to 1800 MHz electromagnetic radiation has a “window effect” on the expression of GFAP in the DG, CA3, and CA1 regions of the hippocampus in SD rats, with power density windows of 0.1 mW/cm2 and 0.3 mW/cm2.
2024, 45(3): 35-41.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240305
Abstract:
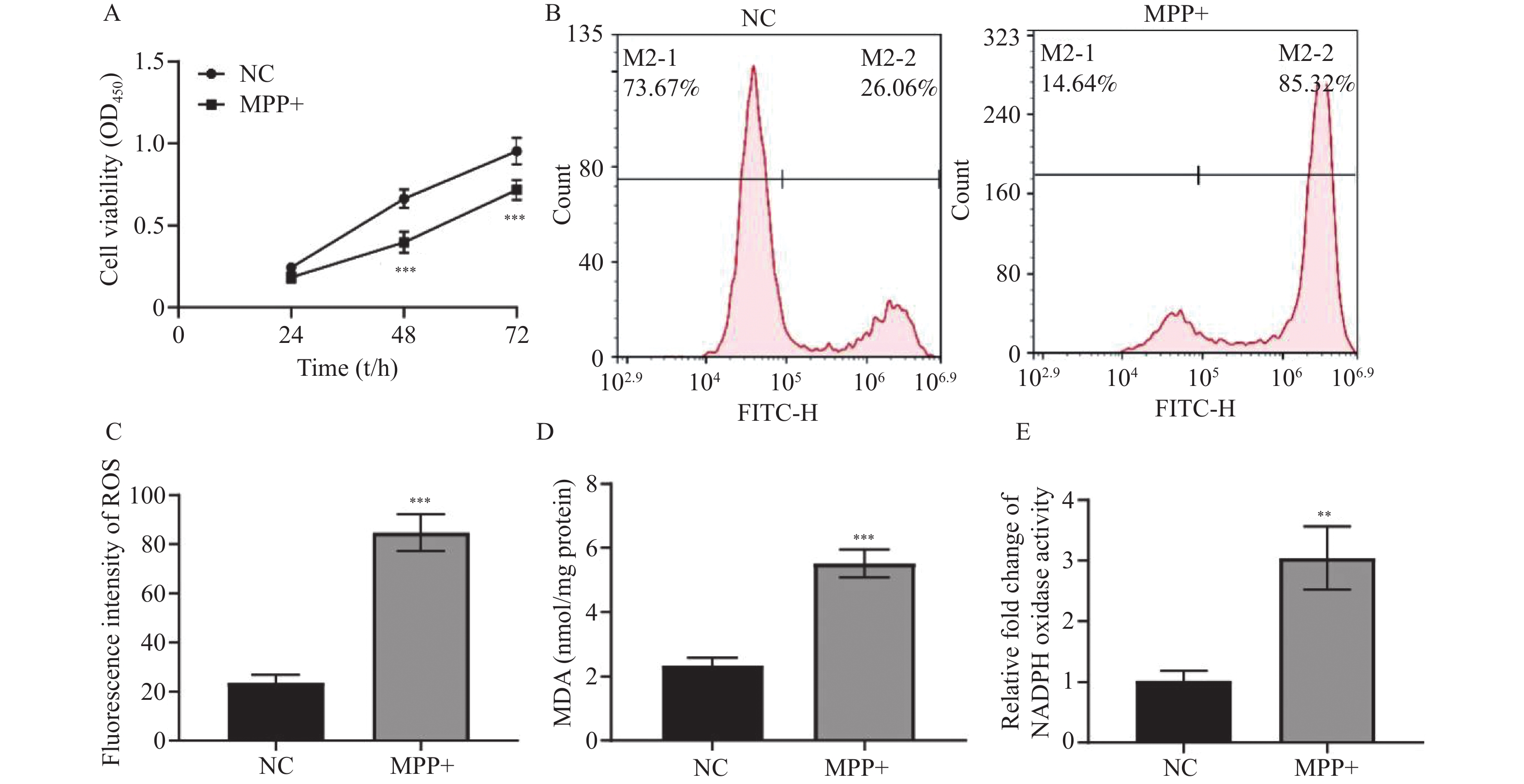
Objective To investigate the effects of different concentrations of PPF on oxidative stress and apoptosis of PD model cells induced by MPP+. Methods The human neuroblastoma cell SH-SY5Y was induced by 1 mM MPP+ to establish PD cell model. In PPF treatment group, SH-SY5Y cells were stimulated with 10, 20, 40 and 80 μM PPF for 4 h before MPP+ induction. Cell counting kit-8(CCK-8) was performed to evaluate cell proliferation activity. H2DCF-DA fluorescent probe was used to detect ROS in cells. The levels of MDA and NADPH oxidase were analyzed by the kit. Western blot examined the protein expression of cytochrome c in mitochondria and cytoplasm, as well as the relative expression of Bcl-2, Bax and cleaved caspase-3 in SH-SY5Y cells. Apoptosis rate was analyzed by flow cytometry. Results MPP+ significantly inhibited the proliferation of SH-SY5Y cells(P < 0.001), promoted the level of ROS(P < 0.001), MDA(P < 0.001), NADPH oxidase(P < 0.01), cytochrome c in cytoplasm(P < 0.01) and induced apoptosis(P < 0.001) and the relative expression of pro-apoptosis protein Bax and cleaved caspase-3(P < 0.01), reduced cytochrome c protein in mitochondria(P < 0.01) and the relative expression of anti-apoptosis protein(P < 0.01). PPF pretreatment alleviated the proliferation inhibition, oxidative stress and apoptosis promotion of SH-SY5Y cells induced by MPP+(P < 0.001), and the effects of 40 μM and 80 μM on cells were more significant. Conclusion PPF pretreatment can alleviate the oxidative stress of SH-SY5Y cells induced by MMP+ and reduce apoptosis rate.
2024, 45(3): 42-47.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240306
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the popularization of cardiopulmonary resuscitation(CPR) knowledge and science popularization needs among urban and rural residents in Tonghai County, Yuxi City, Yunnan Province, so as to explore the establishment of an efficient and appropriate science popularization model. Methods A total of 300 residents aged 15-60 years old were selected from Tonghai County, Yuxi City, Yunnan Province using stratified and simple random sampling methods. A self-designed questionnaire was used to conduct an anonymous questionnaire survey. Results Only 20.3% of Tonghai County residents master CPR skills, and 26.2% of Tonghai County residents have never heard of CPR. There is a statistically significant difference in the awareness rate of CPR between rural residents and non-rural residents(P < 0.01). There are differences in residents' age and CPR awareness( P < 0.01), the age and CPR are inversely proportional. The residents have a higher willingness to perform chest compressions and mouth-to-mouth resuscitation on strangers, 66.2% and 68.6% respectively. 63.79% of residents have never attended relevant training. But 92.76% of the people said they were willing to participate in the relevant training when they learned the training news. Conclusion Residents in Tonghai County generally lack knowledge of CPR first aid, but the demand for first aid knowledge of residential CPR is high and the attitude towards rescue is positive. It is recommended that relevant departments increase CPR science popularization and training efforts, and popularize CPR into villages.
2024, 45(3): 48-53.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240307
Abstract:
Objects To explore the effectiveness and safety of using the Cardio-O-Fix Plug occluder in the treatment of muscular ventricular septal defect(mVSD) in children. Methods 14 patients with mVSD were taken to the cardiology department of First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University from July 2015 to June 2021 as research subjects. They were divided into two groups: 14 children who received Cardi-O-Fix Plug occluder as the experimental group, and 10 children who received Cardi-O-O-Fix mVSD occluder as the control group. Electrocardiogram and transthoracic echocardiography were used to evaluate the occlusive efficacy and incidence of complications 1 day after surgery and 1 month, 3 months, and 6 months of follow-up. Results Among the 24 pediatric patients, 22 cases were successfully occluded, and 2 cases were unsuccessful(1 in the experimental group and 1 in the control group). The success rate of the experimental group was 92.8%(13/14), while the success rate of the control group was 90.0%(9/10). The average surgical duration of the experimental group was(71.93 ± 14.85) minutes, while the average surgical duration of the control group was(90.70 ± 19.78) minutes. There was a significant statistical difference between the two groups(P < 0.05). Both the experimental group and the control group did not experience serious complications during surgery and follow-up. There was no significant difference in cardiac ultrasound indicators(including left ventricular ejection fraction, left ventricular end-diastolic diameter, and pulmonary artery pressure) between the two groups at different time points( P > 0.05). Conclusion Transcatheter closure of mVSD using Cardi-O-Fix Plug occluder in children is both safe and effective. The incidence of arrhythmia is low in the short, medium and long term.
2024, 45(3): 54-58.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240308
Abstract:
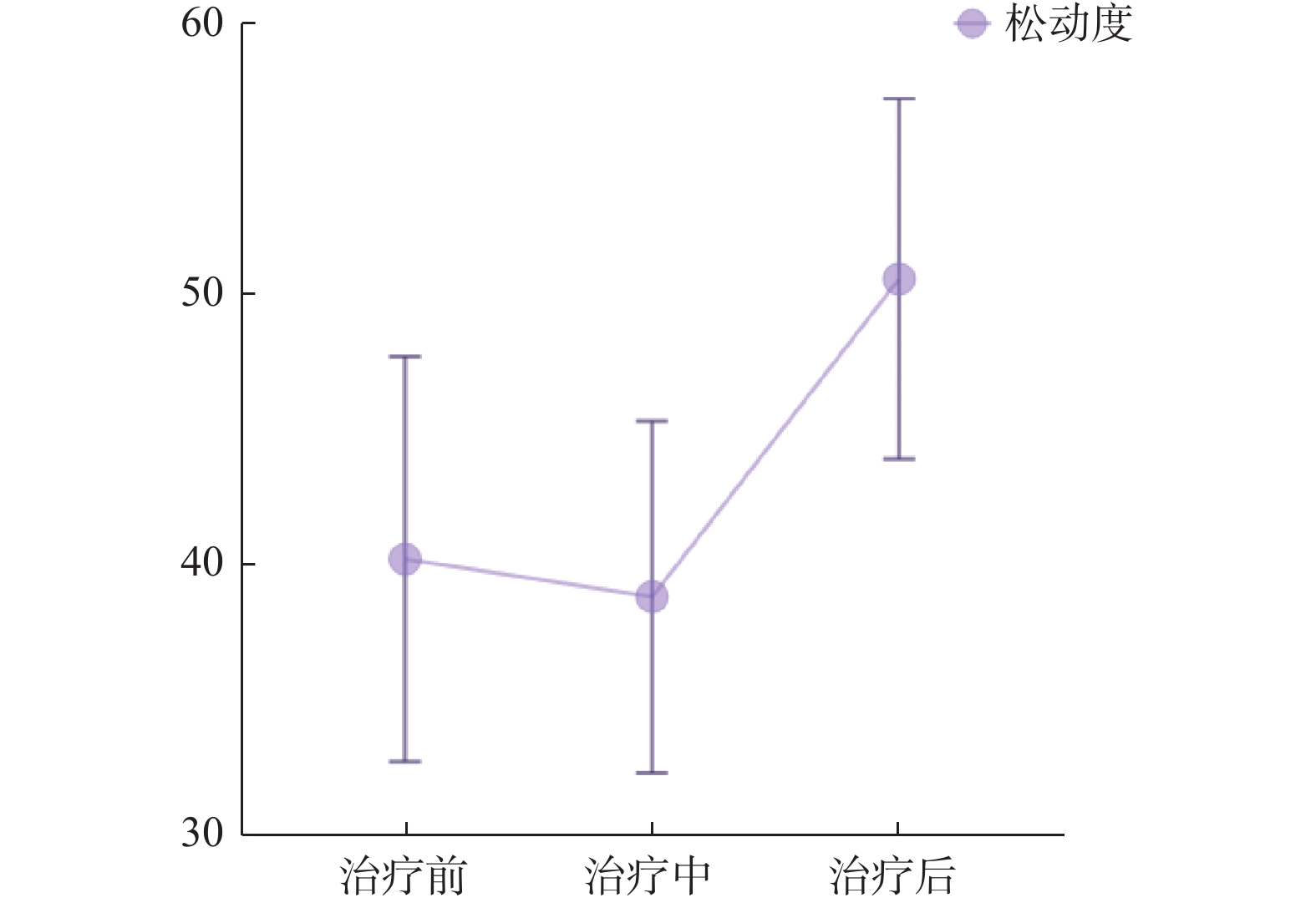
Objective To investigate the effect of dynamic monitoring of occlusal force on the final therapeutic effect and the change of periodontal supporting tissue during combined periodontal orthodontic treatment. Methods The periodontal clinical index of 20 patients with traditional periodontal orthodontic treatment and 20 patients with combined periodontal orthodontic treatment assisted by T-Scan III and Anycheck digital occlusion analysis system were compared before, during and after treatment, as well as the changes of bite force, bite time and tooth mobility in the experimental group. Results The depth of periodontal pocket(PD), loss of attachment(AL), bleeding index(BI) and tooth looseness were significantly reduced after combined periodontal orthodontic treatment in both groups. In the control group, the percentage of anterior and posterior biting force changed obviously, and the occlusion force balance was improved. Conclusion The combined treatment of periodontitis and orthodontics can improve the periodontal tissue of patients with periodontitis, and T-Scan system can observe and guide the adjustment of occlusal and better achieve occlusion force balance.
2024, 45(3): 59-64.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240309
Abstract:
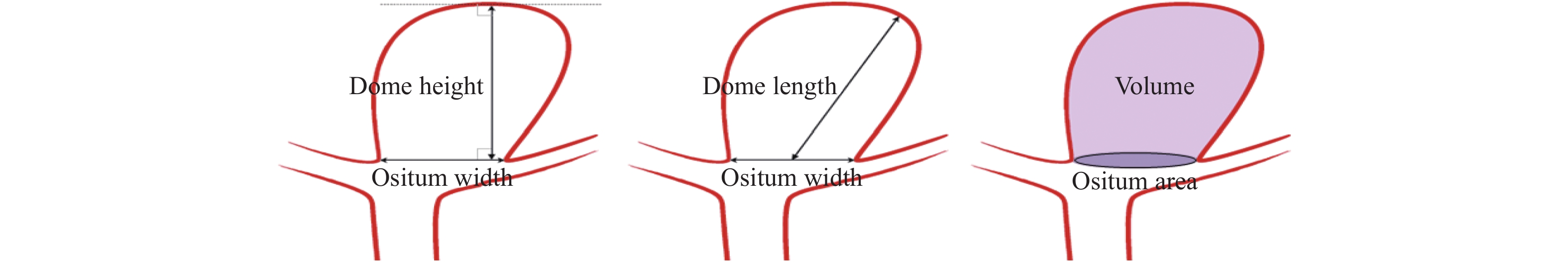
Objective To investigate the value of 4D-CTA combined with SDF-1a/CXCR4 signaling pathway in evaluating the risk of intracranial aneurysm rupture. Methods Fifty patients with unruptured intracranial posterior communicating aneurysms and 50 patients with ruptured intracranial posterior communicating aneurysms were divided into unruptured group 1 and ruptured group 1. All patients underwent 4D-CTA examination and serumSDF-1alevel was detected. Non-ruptured group 1 was followed up for 12 months(After conservative treatment), on this basis, patients with ruptured posterior communicating aneurysms were included in ruptured group 2, and patients with unruptured posterior communicating aneurysms were included in non-ruptured group 2. Results The AUC values of Wn, AR, L, SR, SDF-1a and their combinations in diagnosing ruptured intracranial posterior communicating aneurysms were all greater than 0.70.The AUC values of Wn, AR, L, SR, SDF-1a and their combinations in predicting ruptured intracranial posterior communicating aneurysms in ruptured group 2 were all greater than 0.70. Conclusion 4D-CTA combined with SDF-1acan effectively distinguish ruptured intracranial posterior communicating aneurysms and predict the risk of rupture.
2024, 45(3): 65-71.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240310
Abstract:
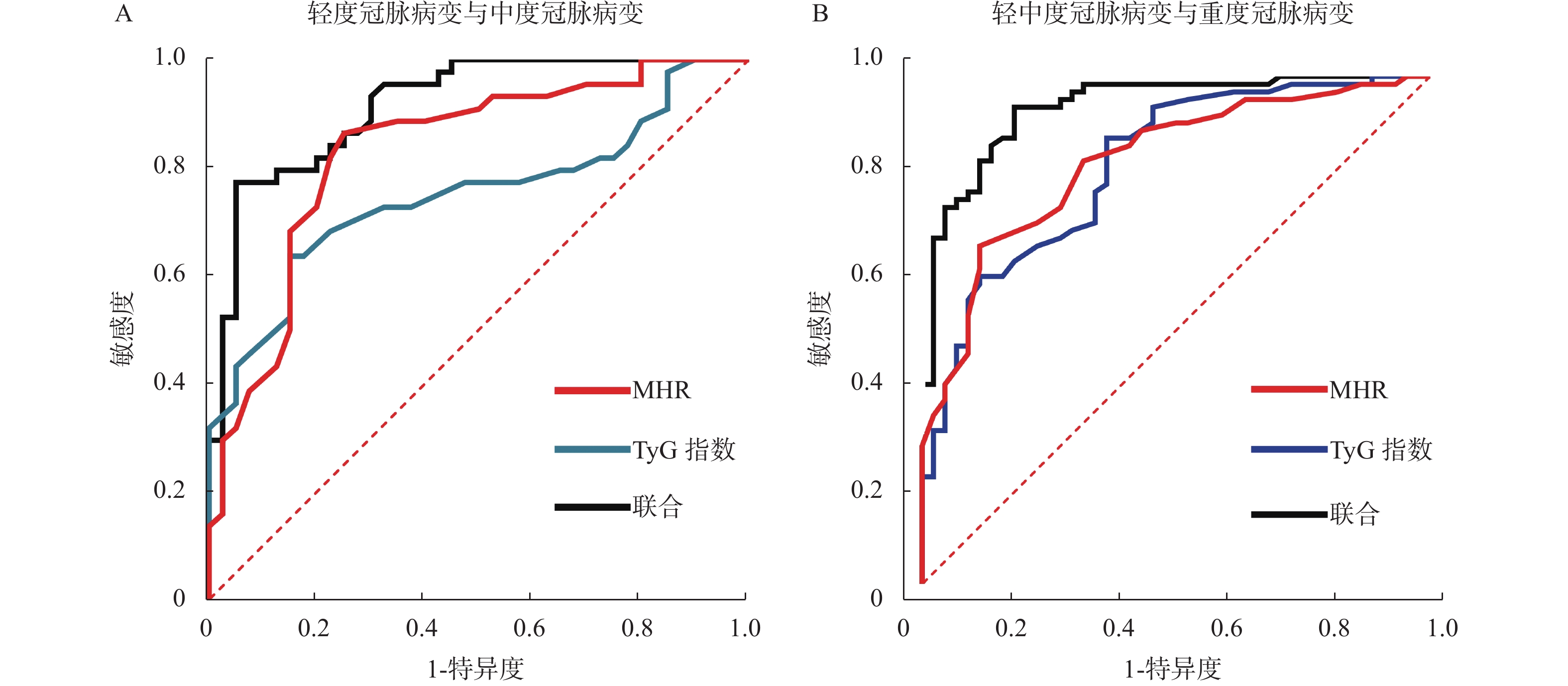
Objective To investigate the correlation of triacylglycerol glucose(TyG) index, monocyte to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio(MHR) with coronary artery disease and myocardial ischemia degree in coronary heart disease(CHD), and to analyze the two Predictive value of coronary artery disease and myocardial ischemia degree. Methods CHD patients from the 920th Hospital of the Chinese People's Liberation Army Joint Logistics Support Force from January 2019 to January 2022 were selected as the study group(n = 150), and healthy physical examination subjects from the same period were selected as the control group(n = 75). The TyG index and MHR of the two groups were compared and analyzed. The extent of coronary artery disease was evaluated based on the Gensini score, and the TyG index and MHR of patients with different coronary lesions and myocardial ischemia were compared, and their correlation with Gensini score and myocardial ischemia was analyzed. The predictive value of TyG index, MHR, and the combined detection of both for coronary lesions and myocardial ischemia was evaluated using receiver operating characteristic(ROC) curves and area under the curve(AUC). Results The TyG index and MHR of the study group were(4.12±0.35) and(0.26±0.08) ×109, respectively, which were higher than those of the control group(4.94±0.55) and(0.43±0.12) ×109, and the TyG index and MHR of severe coronary artery disease > moderate coronary artery disease > mild coronary artery disease, acute myocardial infarction TyG index, MHR > unstable angina pectoris > stable angina pectoris(P < 0.05); TyG index and MHR were positively correlated with Gensini score(r = 0.621, 0.635, P < 0.05), and positively correlated with the severity of myocardial ischemia(r = 0.617, 0.642, P < 0.05). The AUC of TyG index and MHR for the joint identification of mild coronary artery disease and moderate coronary artery disease was 0.917, which was greater than the AUCs of 0.749 and 0.832 for the two conditions individually. The AUC of TyG index and MHR for the joint identification of mild to moderate coronary artery disease and severe coronary artery disease was 0.935, which was greater than the AUCs of 0.770 and 0.767 for the two conditions individually(P < 0.05). The AUC of TyG index and MHR for the joint identification of stable angina pectoris and unstable angina pectoris was 0.922, which was greater than the AUCs of 0.812 and 0.824 for the two conditions individually. The AUC of TyG index and MHR for the joint identification of stable angina pectoris, unstable angina pectoris, and acute myocardial infarction was 0.913, which was greater than the AUCs of 0.708 and 0.714 for the two conditions individually(P < 0.05). Conclusions TyG index and MHR are positively correlated with Gensini score and myocardial ischemia degree. The combined detection of the two has a higher application value in the evaluation of coronary artery disease and myocardial ischemia degree.
2024, 45(3): 72-78.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240311
Abstract:
Objective To observe the clinical efficacy of acupuncture at Front Mu point in the treatment of ulcerative colitis. Methods Sixty patients with ulcerative colitis treated at the Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital in Kunming from August 2022 to June 2023 were collected. Using a random number table method, 30 cases were assigned to each of the control group and the combined group. The treatment method involved administering oral mesalazine to the control group for a continuous period of 8 weeks, while the combined group received both oral mesalazine and acupuncture at front Mu points. The clinical efficacy, colonoscopy results score (Baron score), and colonic mucosal healing score (Geboes) before and after treatment were compared. Follow-up was conducted at 3 months to calculate the recurrence rate in the combination and control groups. Results The total effective rate in the combination group was higher than that in the control group (P < 0.05), with rates of 93.33% and 67.67%, respectively. After treatment, the disease activity index, Baron score, and Geboes score decreased compared to before treatment (P < 0.05), and the combination group had a lower disease activity index, Baron score, and Geboes score than the control group after treatment (P < 0.05). Comparing the recurrence rates at 3 months post-treatment, the combination group was lower than the control group. Conclusion Acupuncture at Front Mu Point can significantly improve the clinical symptoms of ulcerative colitis, reduce the recurrence rate compared to patients in the control group, and is safe and reliable without serious adverse reactions.
2024, 45(3): 79-83.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240312
Abstract:
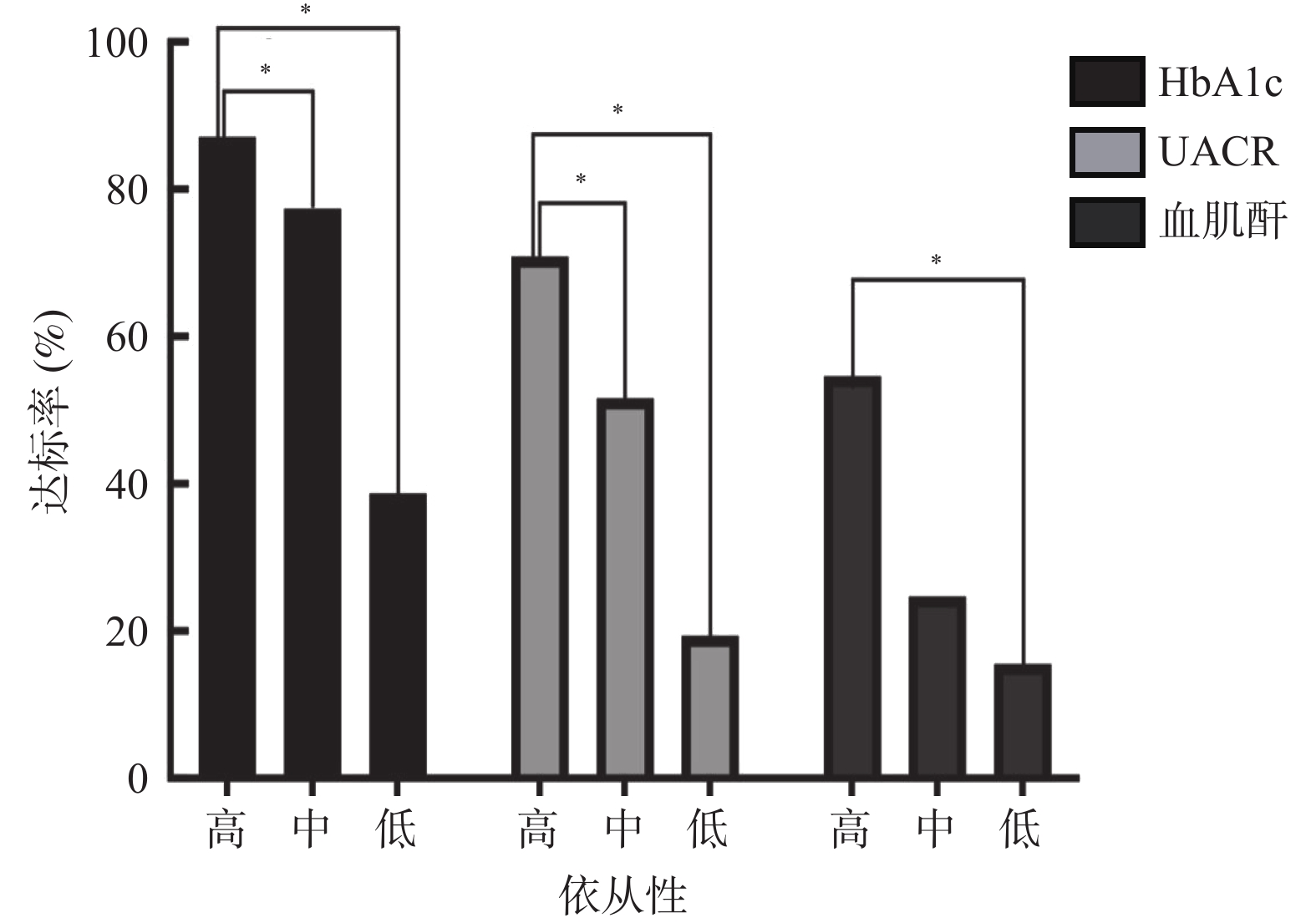
Objective To analyze the influence of medication compliance of chronic type 2 diabetes management patients on disease control in two communities in Kunming. Methods A total of 138 patients with type 2 diabetes who were included in chronic disease management in Guandu and Xiaobanqiao communities of Kunming were selected from December 2021 to September 2022. Basic information collection and HbAlc and other related tests were improved. A questionnaire survey of 8-item Morisliy medication adherence scale (MMAS-8) was conducted to analyze the levels of HbAlc and other indexes of three groups with high (group A), medium (group B), and low (group C) adherence, and to conduct statistical analysis. Results Group A accounted for 22.5%, group B for 44.9%, and group C for 32.6%. There were significance differences in urinary albumin creatinine ratio (UACR), HbA1c and blood creatinine among the three groups (P < 0.05). The levels of UACR, HbAlc and serum creatinine in group A were lower than those in group B and group C, and there was a negative correlation between UACR, HbAlc and serum creatinine and medication compliance rate ( P < 0.05). Conclusion In the Guandu Community and Xiaobanqiao community of Kunming, only 22.5% of patients with chronic type 2 diabetes had high medication compliance. The higher the compliance, the lower the level of UACR, HbAlc and serum creatinine, there is a correlation between the two, suggesting that medication compliance should be regarded as one of the key points in the management of chronic diabetes mellitus in the community, and the intervention of patients' medication compliance should be strengthened.
2024, 45(3): 84-91.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240313
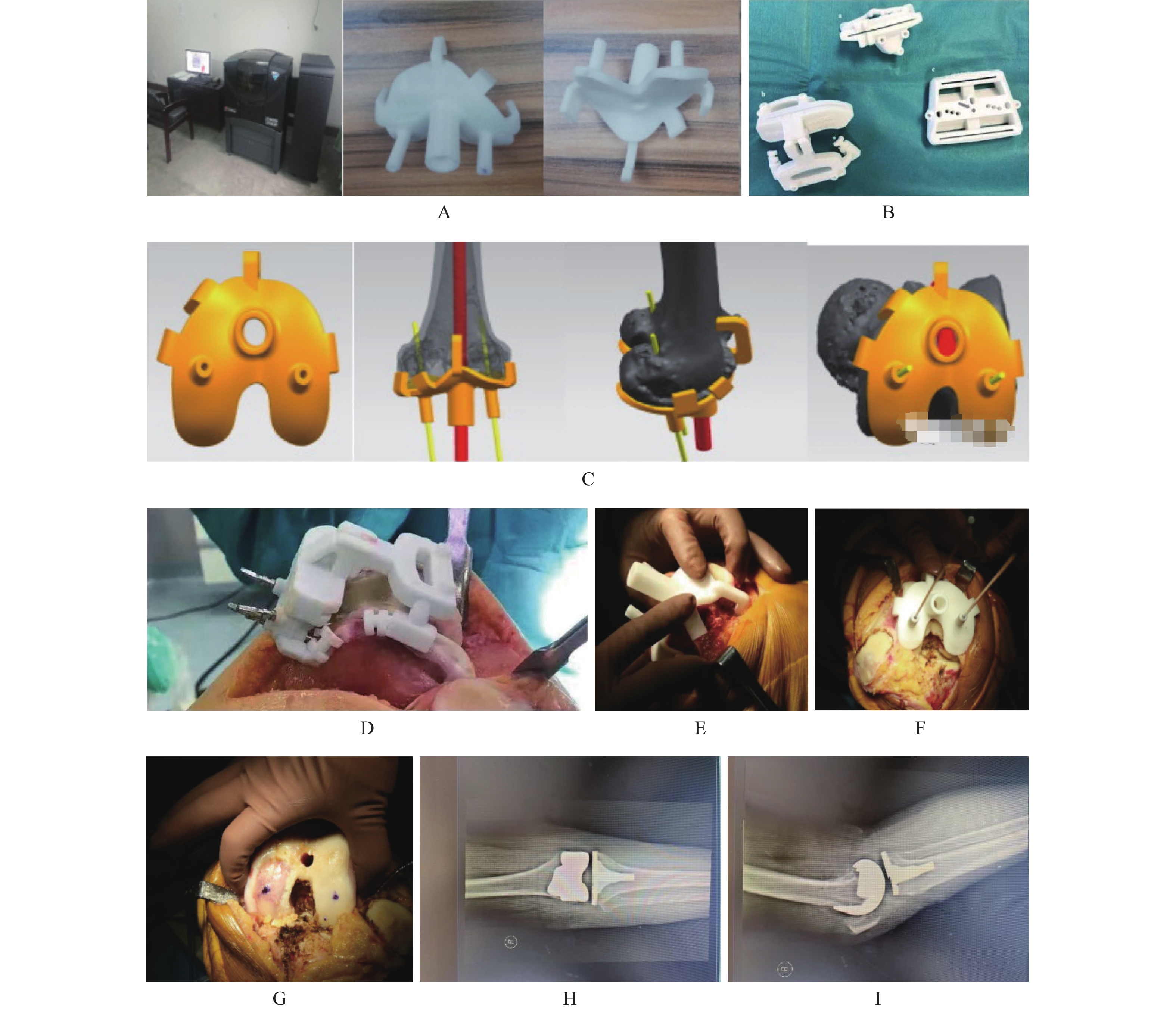
Abstract:
Objective To explore the application effect of new improved 3D printing individualized guidance (3D psi) in total knee arthroplasty (TKA) for knee osteoarthritis (KOA). Methods A total of 100 patients with KOA in 920th Hospital of Joint Logistics Support Force, PLA from January 2021 to January 2022 were selected, and were divided into 2 groups of 50 patients each using the randomized numerical table method. The control group was treated with conventional TKA, and the study group was treated with new improved 3D psi assisted TKA. The operation conditions, postoperative rehabilitation, complications, prosthesis component position deviation, knee range of motion (ROM), lower limb force line parameters [coronal distal femoral mechanical axis lateral angle (mldfa), lower limb mechanical axis angle (HKA)], gait parameters (percentage of support time, stride, pace), knee function(HSS score), quality of life (AIMS2 score) were observed. Results Compared with control group, the amount of intraoperative and postoperative blood loss and drainage volume 2 days after operation were less in the study group, and the operation time and hospital stay were shorter (P < 0.05). The deviations of LTC Angle, FFC Angle, HKA Angle, LFC Angle and FTC Angle in the study group were smaller than those in the control group (P < 0.05). At 3 months, 6 months and 12 months after surgery, the percentage of knee ROM, supporting time, stride length and walking speed of the research group were higher than those of the control group, while the coronal-position mLDFA and HKA were lower than those of the control group (P < 0.05). The proportion of WBC and PMN in joint fluid at 3 months, 6 months and 12 months after surgery was lower than that in control group (P < 0.05). The HSS score of the study group was higher than that of the control group at 3 months, 6 months and 12 months after operation, and the AIMS2 score was lower than that of the control group (P < 0.05). There was no statistically significant difference in the incidence of complications between the study group and the control group (P > 0.05). Conclusion The new improved 3D PSI-assisted TKA treatment of KOA can optimize the surgical situation, improve operating accuracy, improve the patient’ s lower limb alignment, promote limb function recovery, help improve the quality of life, and has high safety.
2024, 45(3): 92-98.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240314
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the mental health status and its influencing factors among elderly hypertensive patients from Rural Areas of Chuxiong and Honghe Prefecture in Yunnan. Methods Multi-stage random sampling method was adopted to select elderly hypertensive patients from rural Yi ethnic areas in Yunnan. Questionnaires were used to collect their basic information and mental health status. Multivariate logistic regression was performed to explore the influencing factors of mental health among the elderly hypertensives. Results 21.82%(209/958) of elderly people with hypertension have poor mental health status in Chuxiong and Honghe Prefecture, Yunnan. Age of 80-89 years(OR = 2.395, P < 0.05) and over 90 years( OR = 3.293, P < 0.05), as well as physical disability( OR = 2.037, P < 0.05), were risk factors for poor mental health. Compared with those who rated their economic situation as very difficult, rating as somewhat difficult( OR = 0.490, P < 0.05), moderate( OR = 0.632, P < 0.05) and relatively affluent( OR = 0.344, P < 0.05), having a spouse( OR = 0.655, P < 0.05), received full concern from the offspring( OR = 0.411, P < 0.05) and maintain good relationships with offspring( OR = 0.339, P < 0.05) were protective factors. Conclusions The mental health status of elderly people with hypertension is relatively poor in rural areas of Chuxiong and Honghe Prefecture in Yunnan Province. Special attention should be paid to the mental health of older and physically disabled elderly hypertensives. Economic and mental support from children was crucially important in improving the mental health of elderly hypertensive patients in rural areas of Chuxiong and Honghe Prefecture in Yunnan Province.
2024, 45(3): 99-105.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240315
Abstract:
Objective To build the early predictive model for chronic kidney disease (CKD) in hypertension and diabetes patients in the community. Methods The CKD patients were recruited from 4 health care centers in 4 urban areas in Kunming. The control group was residents without hypertension and diabetes (n = 1267). The disease group was residents with hypertension and/or diabetes (n = 566). The questionnaire survey, physical examination, laboratory testing, and 5 SNPs gene types in the PVT1 gene. The risk factors, which were filtered with logistics regression, were used to build predictive models. Four machine learning algorithms were built: support vector machine (SVM), random forest (RF), Naïve Bayes (NB), and artificial neural network (ANN) models. Results Thirteen indicators included in the final diagnostic model: age, disease type, ethnicity, blood urea nitrogen, creatinine, eGFR from MDRD, ACR, eGFR from EPI2009, PAM13 score, sleep quality survey, staying-up late, PVT1 SNP rs11993333 and rs2720659. The accuracy, specificity, Kappa value, AUC of ROC, and PRC of ANN are greater than those of the other 3 models. The sensitivity of RF is the highest among 4 types of machine learning. Conclusions The ANN predictive model has a good ability of efficiency and classification to predict CKD with hypertension and/or diabetes patients in the community.
2024, 45(3): 106-111.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240316
Abstract:
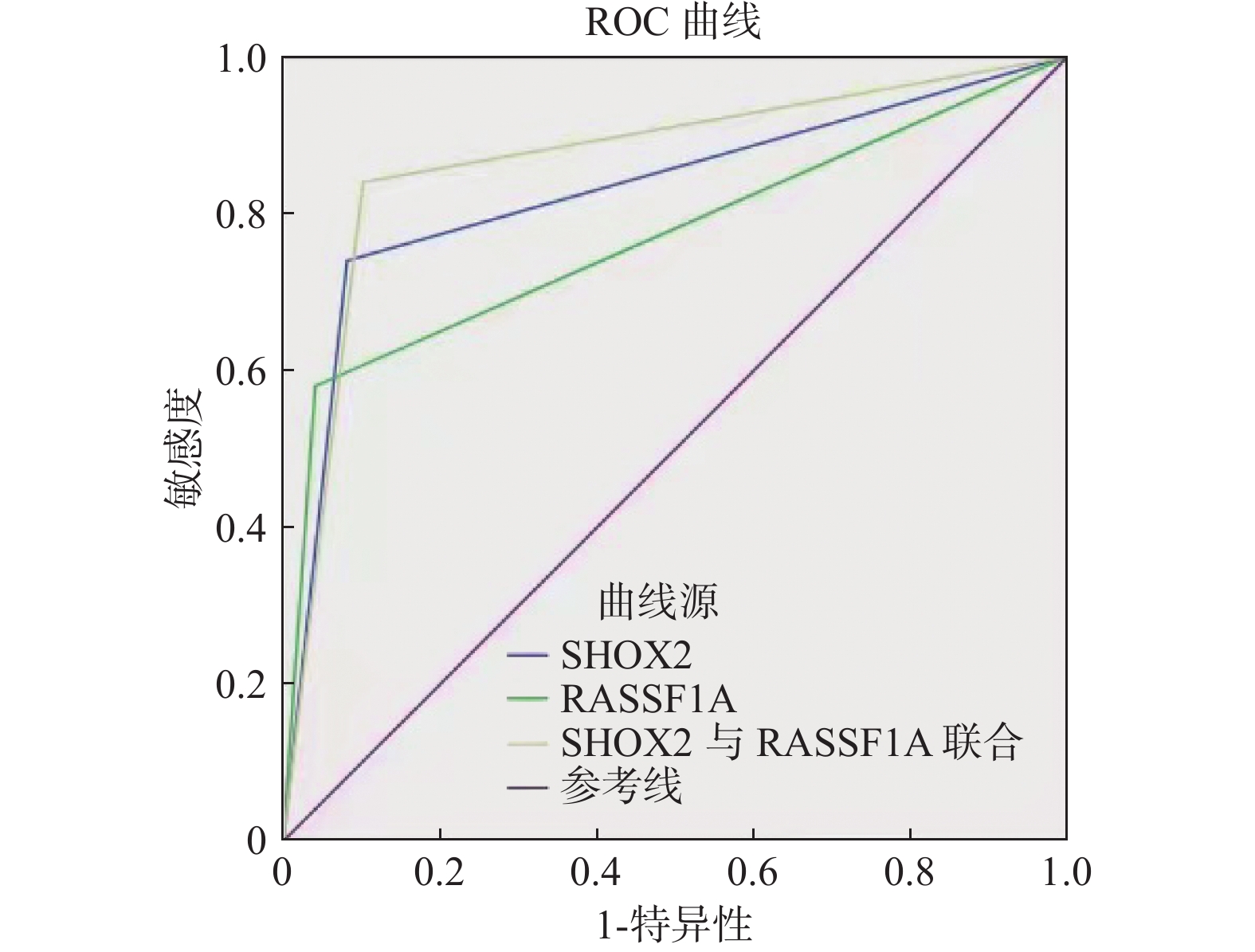
Objective The diagnostic efficacy of the two gene methylation indexes was verified by lung biopsy or postoperative disease examination results. Methods A prospective study was conducted to collect 99 patients diagnosed with pulmonary nodules and masses in the Third People's Hospital of Yunnan Province from March 2019 to March 2020. After bronchoscopy and BALF samples were collected, regular follow-up, lung puncture biopsy and post-operative disease examination were performed. Results Ninety-nine patients with pulmonary nodules and masses were divided into lung cancer group(n = 50) and benign lung disease group(n = 49) after pathological diagnosis. The age of patients in the lung cancer group was(62.64±9.71) years, and that of the benign lung disease group was(60.48±13.69) years, and there was a statistical difference between the two groups(P = 0.032). In the diagnosis of lung cancer, the sensitivity and specificity of SHOX2 and RASSF1A genes alone were found to be 72% and 58%, respectively, and 92.3% and 95.9%, respectively. The combined test of the two genes showed a higher sensitivity in the diagnosis of lung cancer, 0.84, compared to 0.102 in the benign disease group(P < 0.001). ROC curve analysis showed that the sensitivity of the two genes could be increased to 84% when methylation was combined. Conclusion The methylation test of SHOX2 and RASS1A gene in alveolar lavage fluid has a good value in the diagnosis of lung cancer patients with pulmonary nodules and masses and SHOX2 combined with RASSF1A can be an important supplementary tool for early diagnosis of lung cancer when imaging and histological diagnosis are unclear.
2024, 45(3): 112-117.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240317
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the correlation between bone mineral density(BMD) at different hip positions with muscle parameters and physical performance in middle-aged and elderly people in Kunming area. Methods 531 middle-aged and elderly volunteers were recruited from the Radiology Department of the First People's Hospital of Yunnan Province from May 2021 to April 2022. All study subjects completed the five-times-sit-to-stand test(FTSST) and hip quantitative CT (QCT)examinations. Volunteers’ total hip(TH), femoral neck(FN), and intertrochanteric(IT) BMD were measured by using QCT PRO workstation and using OsiriX software to measure the area and density of their gluteus maximus muscle, gluteus medius, and minimus muscle and midthigh muscle. Divide male and female volunteers into positive and negative groups respectively based on FTSST time ≥ 12 seconds or < 12 seconds, and analyze the differences in hip BMD between the groups; Also divide male and female volunteers into three groups(50~59 years old, 60~69 years old, 70 years old and above) at the age of 10, and analyze the correlation between hip BMD and muscle parameters in different age and gender stratification. Control for age and BMI, and then perform partial correlation analysis on the above indicators. Results The BMD of the hip in the female FTSST positive group was lower than that in the negative group(P < 0.001), while there was no statistically significant difference between the male groups( P > 0.05). After adjusting for age and BMI, among males, FN BMD was positively correlated with gluteus medius and minimus muscle density in the age groups of 50~59 and 60~69( P < 0.05), while TH BMD, FN BMD, and IT BMD were strongly positively correlated with gluteus medius and minimus muscle density in the age group over 70( P < 0.05). For females, the correlation between hip BMD and muscle density in the age groups of 50~59 and 60~69 was weak, while BMD in all parts of the hip was not correlated with muscle density in the age group over 70( P > 0.05). There was a negative correlation between TH BMD, FN BMD, and gluteus medius and minimus muscle area in the age group of 50~59 years old for males( P < 0.05), while there was a significant negative correlation between TH BMD, IT BMD, and gluteus maximus area in the age group of 70 years old and above for females( P < 0.05). Conclusion The BMD of various parts of the hip in the female FTSST positive group is lower than that in the negative group. The density of the gluteus medius and minimus muscle can to some extent serve as a predictive indicator of femoral neck bone strength in middle-aged and elderly men in Kunming area.
2024, 45(3): 118-126.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240318
Abstract:
Objective To explore the public's cognition and attitude towards general medicine, general practitioners, and pre-hospital first-aid knowledge in Ludian County, Yunnan Province, to find out the training and learning methods that are more acceptable to the public for this kind of related knowledge, and to propose targeted solutions. Methods A complete random sampling survey was conducted among the nucleic acid collection office at the gate of the vegetable market from October 15, 2022, to December 30, 2022, and the outpatient clinic of Wenping Street Health Center from January 1, 2023, to February 28, 2023, by using electronic questionnaire and paper questionnaire. Results Nearly 50% of the people in Ludian County of Yunnan Province lack the knowledge of general medicine and pre-hospital emergency care, especially the knowledge of electrical defibrillation. People with higher education and the medical profession have a higher understanding of general medicine, and people with a higher understanding of general medicine are more willing to participate in pre-hospital emergency care. The average Ridit value is: very familiar with general medicine (0.774) > Knowledge of some general practices (0.565) > Never heard of general practice (0.400). The higher education level and the more comprehensive understanding of general medicine had a positive impact on participation in pre-hospital emergency care, with B values of 0.624 and 0.619, OR 95% CI of 1.867 (1.544 ~ 2.257) and 1.857 (1.298 ~ 2.657), respectively. Taking medical staff as a reference, the B value of medical students was = 0.942, P = 0.234, the difference was not significant, and the B value of non-medical professional population was all less than 0, the effect is negative. In addition, most people have a positive attitude towards learning pre-hospital first aid, and more than 70% of people are willing to learn and train related knowledge of pre-hospital first aid. Conclusions People in urban areas of Ludian County, Yunnan Province have poor understanding of general practice, low recognition of general practitioners, low demand for general practitioners, and lack of awareness of the importance of pre-hospital emergency treatment. Because of the cognitive differences among different groups, it is necessary to conduct specific training for different groups.
2024, 45(3): 127-132.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240319
Abstract:
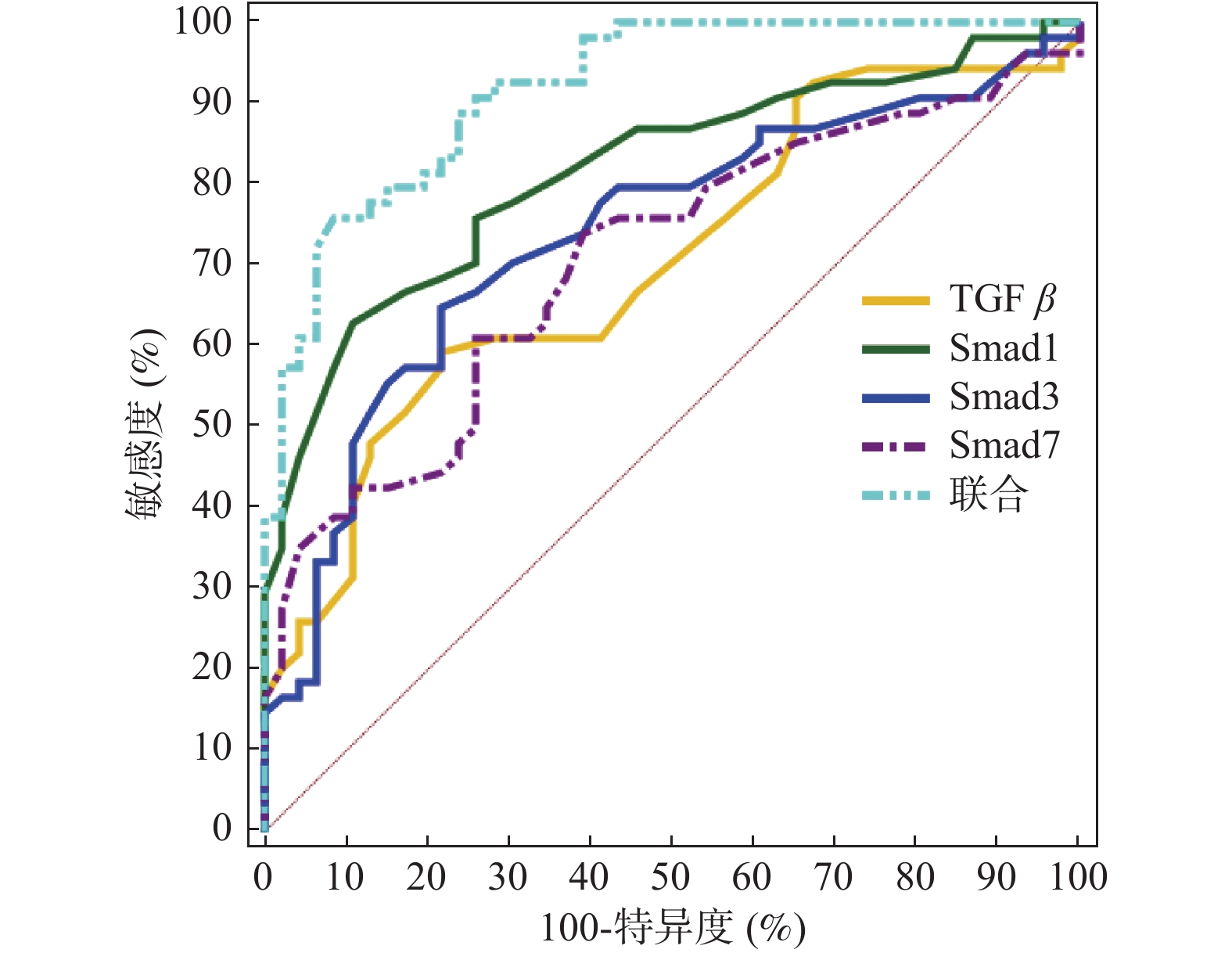
Objective To investigate the relationship between factors related to the transforming growth factor β(TGF-β)/Aerine-threonine kinase receptors(Smads) signaling pathway and cognitive dysfunction in peripheral blood of patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage(aSAH). Methods The clinical data of 100 patients with aSAH admitted to Chongzuo City People's Hospital from October 2018 to March 2022 were retrospectively selected and grouped according to the patients' Montreal Cognitive Assessment Scale(MoCA) scores, including 54 cases with cognitive dysfunction and 46 cases without cognitive dysfunction. The clinical data, peripheral blood TGF-β, Smad1, Smad3, and Smad7 mRNA expression levels of the two groups were compared. The relationship between pathway-related factors and cognitive dysfunction in patients with aSAH was analyzed in a multifactorial manner. The predictive value of pathway-related factors for cognitive dysfunction in aSAH patients was assessed using the receiver operating characteristic(ROC) curve. Results Peripheral blood TGF-β, Smad1, Smad3, and Smad7 mRNA expression levels were higher in the cognitively impaired group than in the group without cognitive impairment(P < 0.05). Multifactorial showed that pathway-related factors were significantly associated with cognitive impairment in patients with aSAH(P < 0.05). The ROC showed that the area under the curve(AUC) of pathway-related factors jointly predicted cognitive dysfunction in patients with aSAH was superior to that predicted alone(P < 0.05). Conclusion The high expression of factors related to the TGF-β/Smads signaling pathway in the peripheral blood of aSAH patients suggests that this pathway may be associated with cognitive dysfunction in patients.
2024, 45(3): 133-140.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240320
Abstract:
Objective To explore the influencing factors of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in patients with primary liver cancer complicated with ascites and establish a prediction model. Methods A total of 292 patients with primary liver cancer complicated with ascites who were hospitalized for the first time in the Third People’ s Hospital of Kunming from January 2012 to December 2021 were selected as the study objects. General data, etiological indicators, serological indicators and complications of these subjects were collected. Then they were divided into the infection group (n = 114) and the control group (n = 178) according to whether spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP) was complicated. Univariate and multivariate logistic regression were used to analyze the influencing factors of SBP in patients with primary liver cancer complicated with ascites. Finally, ROC curves were constructed to more intuitively represent the individual and combined predictive value of these targets. Results Among 292 hepatocellular carcinoma patients with ascites, there were 235 males (80.48%) and 57 females (19.52%), among which 114 patients with SBP were in the infection group and 178 patients without SBP were in the control group. The results of univariate analysis showed that compared with the control group, the levels of WBC, neutrophils, prothrombin time, total bilirubin, albumin, CD3 , CD4 , CD8 , CD4/CD8 ratio, CD19 procalcitonin, serum amyloid A, hypersensitive C-reactive protein, sodium , chlorine , alcohol consumption, shock, hepatorenal syndrome, hepatic encephalopathy, massive ascites in the infection group had statistically significant difference (P < 0.05). Multi-factor analysis revealed that CD8, CD4/CD8 ratio were protective factors for SBP in patients with liver cancer ascites, CD19, procalcitonin , serum amyloid A, and massive ascites were risk factors for SBP in patients with ascites. ROC curve construction showed that serum amyloid A, CD8, CD4/CD8 ratio, CD19, procalcitonin, massive ascites area under curve (AUC) of massive ascites were 0.724, 0.637, 0.653, 0.820, 0.705, 0.686, respectively. Conclusion CD8, CD4/CD8 ratio, CD19, procalcitonin, serum amyloid A, and a large volume of ascites are significant factors contributing to the development of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP) in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma ascites. The predictive value of combination is substantial, demonstrating a level of accuracy in forecasting SBP occurrence
2024, 45(3): 141-145.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240321
Abstract:
Objective To explore the occurrence of adverse reactions to vaccination in children with special health status in Kunming and the corresponding countermeasures. Methods The information data of 952 children with special health conditions who were vaccinated at the Child Healthcare Department of the Kunming Children's Hospital from October 2021 to February 2023 were collected, and descriptive methods were used for epidemiological analysis. Results The detection rate of adverse reactions in children with special health conditions in Kunming was 10.92% (104/952), all of which were mild adverse reactions. The top three vaccines with the highest detection rates of adverse reactions were adsorbed acellular pertussis-diphtheria-tetanus vaccine (Pertussis-Diphtheria-Tetanus), measles-mumps-rubella attenuated live vaccine (Measles-Mumps-Rubella), and meningococcal polysaccharide vaccine group A and C (Meningococcal A+C), with detection rates of 7.00%, 4.14%, and 3.08%, respectively. The detection rate of adverse reactions in children with premature birth, allergy, and anemia after vaccination was higher, with detection rates of 13.87%, 11.03%, and 10.05%, respectively. The detection rate of adverse reactions after more than two vaccinations was 73.08%, which was higher than the first vaccination detection rate of 26.92%. The clinical manifestations of vaccine adverse reactions were mainly fever, redness, and induration, with detection rates of 39.42%, 21.15%, and 18.27%, respectively. The detection rate of adverse reactions in children with special health conditions under the age of two was higher, accounting for 75.00%. The detection rate of adverse reactions within 24 hours after vaccination was higher, accounting for 62.50%. After timely symptomatic treatment and follow-up observation, all adverse reactions in children with special health conditions after vaccination recovered within 7 days. Conclusion Adverse reactions after vaccination in children with special health conditions in Kunming are predominantly mild. The detection rate of adverse reactions post-vaccination for pertussis, measles, mumps, and meningococcal A+C is notably high. Children under 2 years old with premature birth, allergy, and anemia are more likely to have adverse reactions after vaccination. These adverse reactions typically manifest within 24 hours post-vaccination and resolve within 7 days.
2024, 45(3): 146-150.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240322
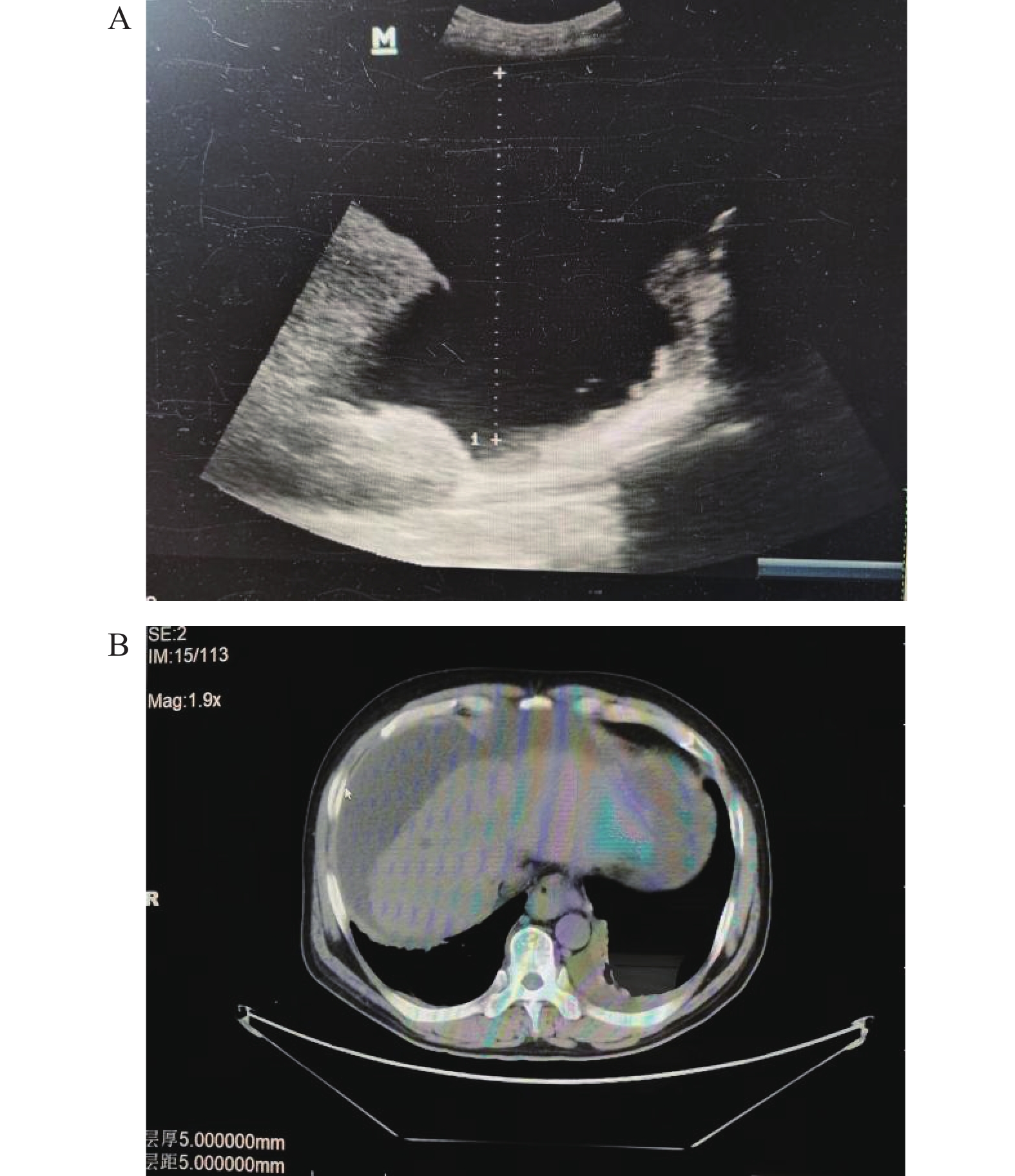
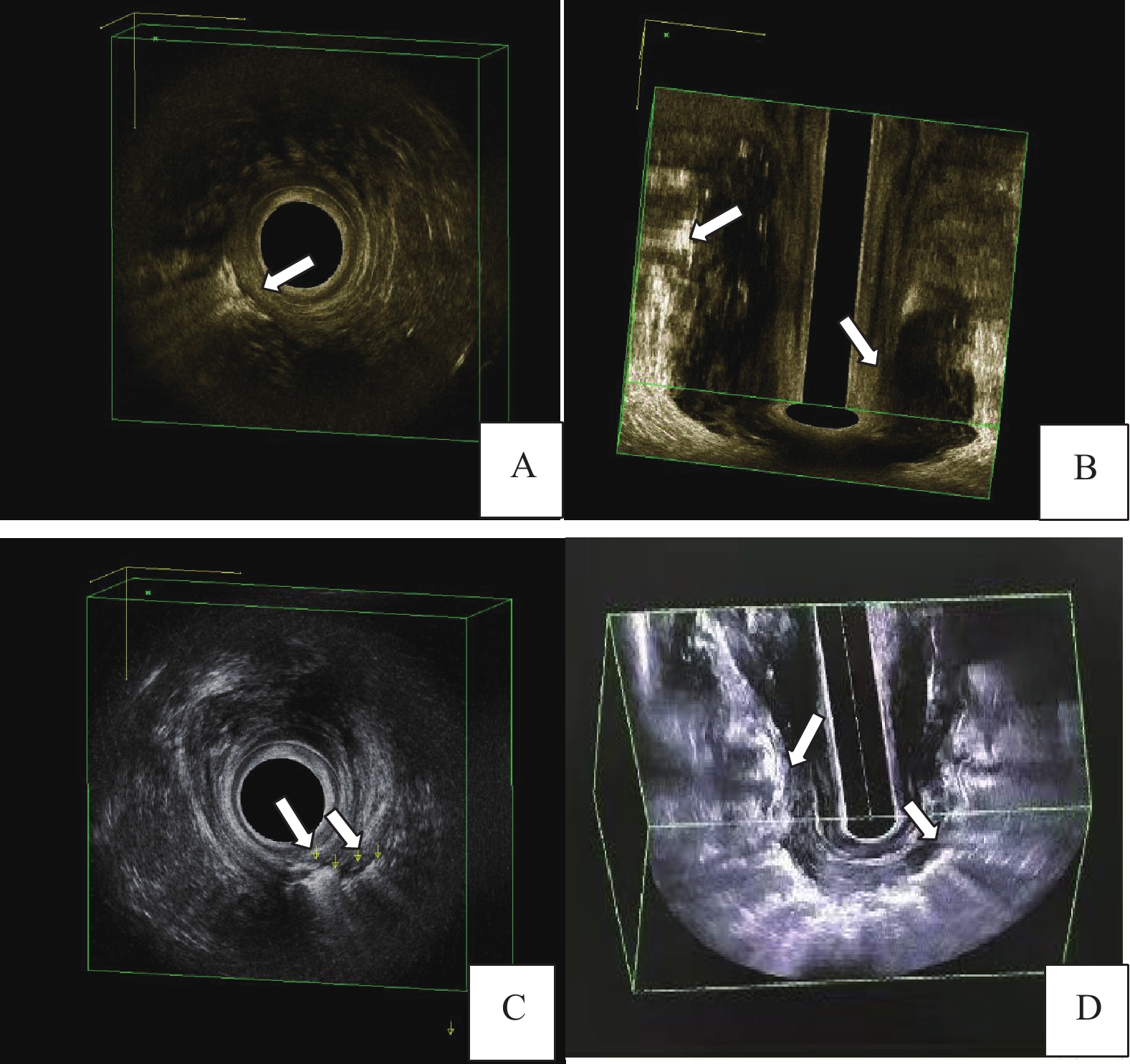
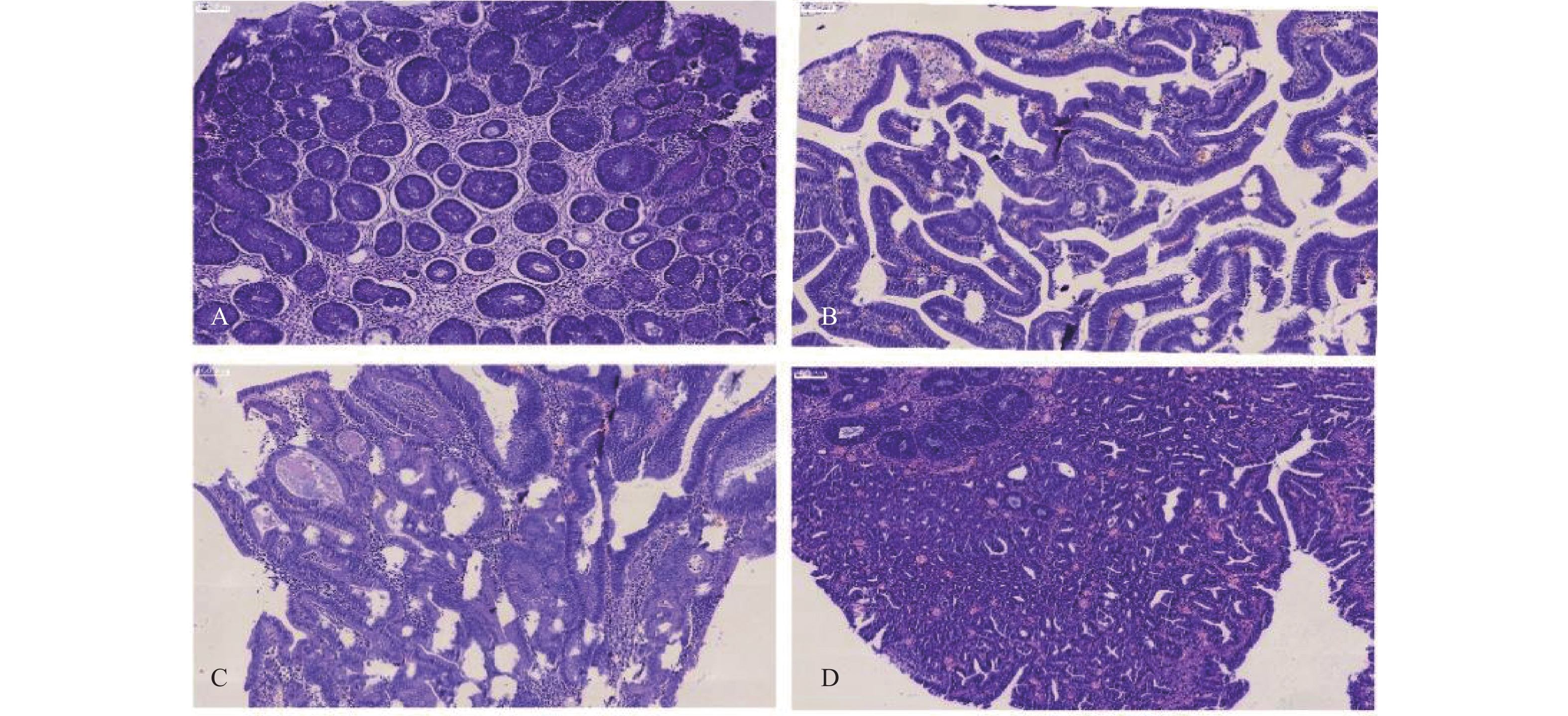
Abstract:
Objective To explore the application value of Three-Dimensional rectal cavity ultrasound combined with contrast agent imaging in necrotizing fasciitis of the anal region. Methods Before surgery, standard three-dimensional rectal cavity ultrasound examinations(referred to as the conventional group) and contrast agent imaging examinations(referred to as the imaging group) were conducted for 40 patients clinically diagnosed with anal region necrotizing fasciitis. Separate observations were made for the primary lesion, as well as for the depth and superficial necrosis of the fascia, and injuries to the anal sphincter muscle. Comparative analysis with surgical results was undertaken to assess the diagnostic sensitivity of both the conventional and imaging groups. Results In comparing the conventional group with the imaging group, the rates of primary lesion visibility rose significantly from 70% to 97.5%, deep fascial necrosis visibility increased from 50% to 88.8%, superficial fascia visibility improved from 70% to 100%, and the visibility of anal sphincter muscle injury escalated from 62.5% to 97.2%, all demonstrating statistical significance at P < 0.05. Conclusions Three-dimensional rectal cavity ultrasound combined with contrast agent imaging exhibits significantly enhanced accuracy in identifying primary lesions associated with perianal necrotizing fasciitis, as well as the necrosis affecting deep and superficial fascia, in contrast to conventional three-dimensional rectal cavity ultrasound. This advancement offers more precise guidance for clinicians in devising surgical plans, thereby augmenting the success rate of surgical interventions.
2024, 45(3): 151-156.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240323
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the predictive significance of Septin9 gene methylation(mSEPT9) in peripheral blood in the diagnosis of colorectal adenoma. Methods A total of 52 subjects were included, 31 patients with colorectal adenomas were collected as the experimental group in the Department of Pathology and 21 subjects with negative colonoscopy in the gastroenterology outpatient clinic were used as the control group from October 2020 to May 2022. mSEPT9 was detected in the two groups, and the results of CEA level in peripheral blood were collected. All the results were statistically analyzed using the Receiver Operating Characteristic(ROC). Results The area under the curve(area of the ROC: AUC)of mSEPT9detectionto predict the development of adenoma was 0.7205(P < 0.05), And the cut-off value(CT value) was 39.55, the corresponding sensitivity was 90.91% and the specificity was 56.67%. The AUC of CEA detection for predicting adenoma was 0.5333(P > 0.05). Conclusions The detection of mSEPT9 is better than that of CEA tumor marker detection in peripheral blood for screening colorectal adenomas with good sensitivity and relative specificity. Invasive colonoscopy for people with positive mSEPT9 screening results can be easier to accept by the general population.
2024, 45(3): 157-165.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240324
Abstract:
Objective To analyze the clinical characteristics of 310 patients with anti-tuberculosis drug-induced liver injury (ATB-DILI), to explore prognostic influencing factors, and to provide reference for its prevention and treatment. Methods Primary tuberculosis patients hospitalized in the Department of Tuberculosis of the Third People's Hospital of Kunming from November 2020 to November 2022 who met the diagnosis of ATB-DILI were enrolled. Statistics by gender, age, history, type of tuberculosis, co-morbidities, frequency of anti-tuberculosis regimens leading to liver injury, use of hepatoprotective drugs, and management and regression were performed to analyze the clinical characteristics of the patients and the factors influencing their prognosis. Results 310 patients were included, male, 148 (47.74%) and female, 162 (52.26%). The mean age was 44.33±17.47 years. Thirty-four patients had a history of allergy. The combination of isoniazid, rifampicin, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol (244 patients, 78.71%) was the anti-tuberculosis regimen that resulted in the highest number of cases of hepatic injury. The median time between initiation of the tuberculosis regimen and the development of hepatic injury in patients with ATB-DILI was 30 d, and the mean duration of hospitalization was 16.39±7.01 d. The most used hepatoprotective drug was reduced glutathione (154 patients, 49.68%), and most patients used a combination of 2 hepatoprotective drugs (128 patients, 41.29%). Liver injury improved in 257 cases (82.90%) and failed in 53 cases (17.10%). The differences in alcohol consumption, severity, clinical staging, TT, ALP, TBIL, DBIL, IBIL, and GGT were statistically significant compared to those who did not recover (P < 0.05), and severity and high ALP were independent risk factors for poor prognosis. Conclusions Patients should be carefully asked if they have a history of basic liver disease and alcoholism before using anti-tuberculosis drugs. In the course of anti-tuberculosis treatment, the combined use of anti-tuberculosis drugs is more serious than the use of single drugs to cause liver damage. Drugs that may cause liver damage should be used with caution and improved anti-tuberculosis programs should be explored. At the same time, liver function should be monitored regularly during anti-tuberculosis treatment, especially 30 days after medication, in order to reduce the occurrence of adverse reactions.
2024, 45(3): 166-173.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240325
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the clinical value of multimodal ultrasonography combined with clinical indicators in predicting the progression of ischemic stroke (IS). Methods A total of 134 patients with IS admitted to Third People's Hospital of Yunnan Province from January 2020 to October 2022 were selected as study objects and were divided into progressive ischemic stroke (PIS) group (n=20) and non-progressive ischemic stroke (NPIS) group (n=114) according to the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) score. The clinical indicators, multi-modal ultrasonic image manifestations and related parameters of the two groups were counted, the influencing factors of PIS were screened by Logistics, the nomogram model was drawn, and the predictive efficiency of the nomogram model was evaluated by ROC curve and calibration curve. Results There were significant differences in age, baseline nutritional risk index (GNRI) score, baseline homocysteine (Hcy) and baseline uric acid (UA) between the two groups (P < 0.05). The peak time (TTP), peak intensity (PI), the area under the curve (AUC), carotid plaque enhancement mode, the mean value of maximum elastic modulus (MEmax) and mean value of minimum elastic modulus (MEmin) were compared between the two groups, and the differences were statistically significant ( P < 0.05). Logistic analysis showed that baseline GNRI score, baseline UA, TTP, PI, AUCTC, carotid plaque enhancement pattern, MEmax and MEmin were the influencing factors of PIS ( P< 0.05). Based on the above factors, the nomogram model was drawn. ROC curve and calibration curve showed that the model had good prediction efficiency, and the prediction efficiency was in good agreement with the reality. Conclusion The influencing factors of PIS include baseline GNRI score, baseline UA, TTP, PI, AUCTC, carotid plaque enhancement pattern, MEmax, MEmin, and the neagram model based on the above factors has good differentiation and accuracy.
2024, 45(3): 174-179.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240326
Abstract:
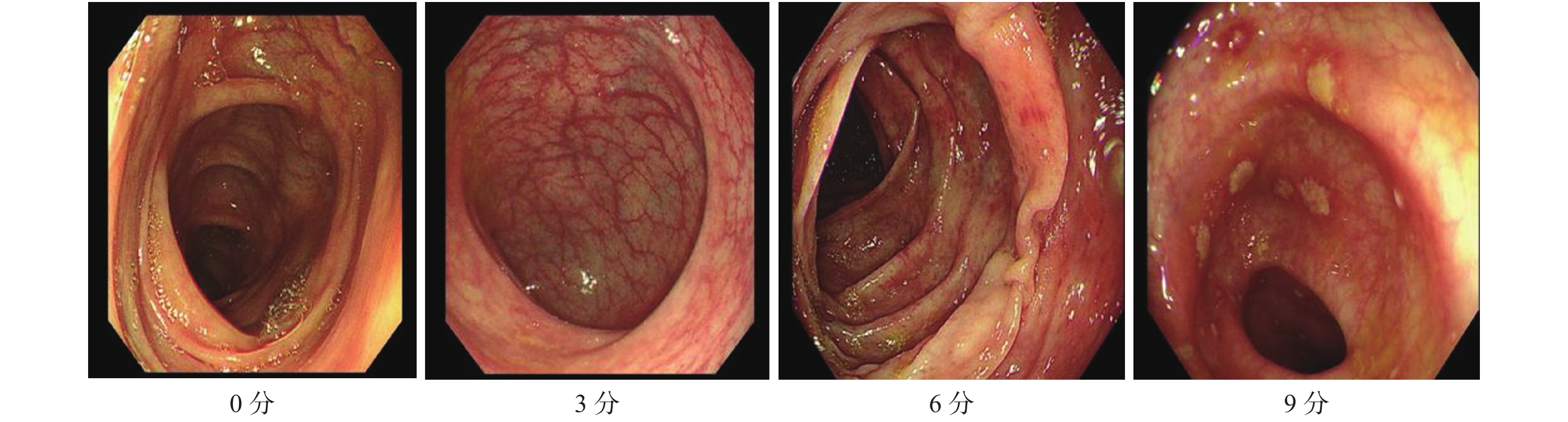
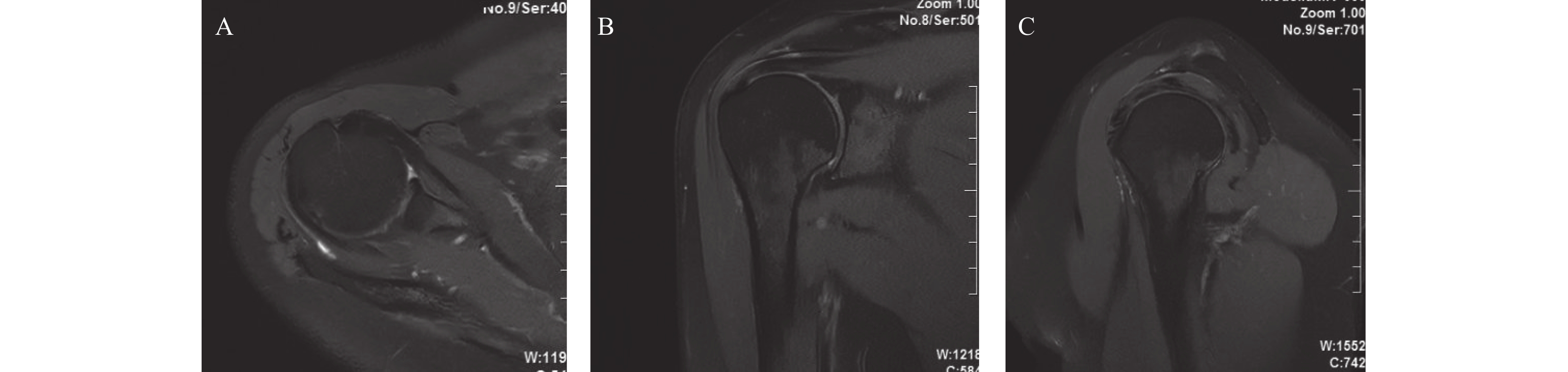
Objective To investigate the optimal display orientation of rotator cuff space(RI) structures on magnetic resonance(MR) scanning and arthrography. Methods A total of 80 patients who underwent MR scanning and arthrography in our hospital from January 2021 to March 2023 were selected and all of them were confirmed to have normal RI by shoulder arthroscopy. The RI and the superior glenohumeral ligament(SGHL), the long head of biceps tendon(LHBT), and the coracohumeral ligament(CHL) in the transverse axial, oblique sagittal, and oblique coronal positions were counted in the transverse axial, oblique sagittal, and oblique coronal positions on MR scanning and arthrography. Results The display rate of RI structure by oblique sagittal scan was 17.50% higher than that by horizontal scan, 0.00% and oblique coronal scan, 5.00%(4/80)(χ2 = 18.739, P < 0.001). The display of SGHL, LHBT and CHL in RI by MR Oblique sagittal scan was better than that in transverse axis and oblique coronal scan(χ2 = 26.036, P < 0.001). MR oblique sagittal arthrography showed a higher rate of RI structures 57.50% than transverse axial 5.00% and oblique coronal 17.50%(χ2 = 61.534, P < 0.001); MR oblique sagittal arthrography showed better display of SGHL, LHBT, and CHL structures in RI than transverse axial and oblique coronal(χ2 = 64.569, P < 0.001); MR oblique sagittal arthrography had a significantly higher rate of complete visualization of RI structures in 57.50% than MR oblique sagittal plain scanning in 17.50%(χ2 = 27.307, P < 0.05). Conclusion Oblique sagittal position is the optimal display orientation for MR scanning and arthrography to show RI structures.
2024, 45(3): 180-185.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240327
Abstract:
Cardiomyopathy is a group of heterogeneous myocardial diseases with a variety of specific phenotypes that can lead to cardiovascular death or progressive heart failure in severe cases. Because of the severity and complexity of these diseases, the search for new regulatory mechanisms to prevent and treat cardiomyopathy is particularly urgent. Iron death is a form of programmed cell death that differs from other forms of iron dependence and is characterized by the accumulation of iron-dependent lipid peroxides. Studies have shown that iron death can be involved in the occurrence and progression of cardiomyopathy through different signaling pathways. Therefore, targeted regulation of iron death is a new strategy to prevent cardiomyopathy. In this paper, the mechanism of iron death and its important role in cardiomyopathy were reviewed to find the potential relationship between iron death and cardiomyopathy and provide more ideas for the treatment of various cardiomyopathies in the future.
Cardiomyopathy is a group of heterogeneous myocardial diseases with a variety of specific phenotypes that can lead to cardiovascular death or progressive heart failure in severe cases. Because of the severity and complexity of these diseases, the search for new regulatory mechanisms to prevent and treat cardiomyopathy is particularly urgent. Iron death is a form of programmed cell death that differs from other forms of iron dependence and is characterized by the accumulation of iron-dependent lipid peroxides. Studies have shown that iron death can be involved in the occurrence and progression of cardiomyopathy through different signaling pathways. Therefore, targeted regulation of iron death is a new strategy to prevent cardiomyopathy. In this paper, the mechanism of iron death and its important role in cardiomyopathy were reviewed to find the potential relationship between iron death and cardiomyopathy and provide more ideas for the treatment of various cardiomyopathies in the future.
2024, 45(3): 186-191.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240328
Abstract:
Active physical exercise can effectively alleviate the pathological process of chronic cerebral ischemia(CCH) and improve learning and memory ability. This paper reviews the possible biological mechanisms of aerobic exercise to delay the pathological process of chronic cerebral ischemia and improve learning and memory. Previous studies have found that aerobic exercise can improve the neuroprotective effect, enhance the plasticity of hippocampal synapses, improve the activity of the upper and lower pathways of hippocampal tissue, and improve learning and memory ability. However, the intervention effect of aerobic exercise on chronic cerebral ischemia should be fully considered at the intervention time, and the intervention effect is also different.
Active physical exercise can effectively alleviate the pathological process of chronic cerebral ischemia(CCH) and improve learning and memory ability. This paper reviews the possible biological mechanisms of aerobic exercise to delay the pathological process of chronic cerebral ischemia and improve learning and memory. Previous studies have found that aerobic exercise can improve the neuroprotective effect, enhance the plasticity of hippocampal synapses, improve the activity of the upper and lower pathways of hippocampal tissue, and improve learning and memory ability. However, the intervention effect of aerobic exercise on chronic cerebral ischemia should be fully considered at the intervention time, and the intervention effect is also different.
2024, 45(3): 192-197.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240329
Abstract:
Objective To explore the application effect of the Mini-CEX evaluation model based on the OBE concept in the clinical Practice teaching of neurology. Methods We Selected 100 students who will Practice in the Department of Neurology from 2022 to 2023 as the research objects, and divided them into the experimental group (n=50) and the control group (n=50). Under the guidance of the OBE concept, the experimental group was guided by learning outcomes, refined the teaching objectives, and applied the Mini-CEX evaluation mode for evaluation and feedback. In contrast, the control group adopted the traditional teaching mode. Combined with the observation data, we analyzed and compared the data of various indicators of the two groups of students at the beginning and end of the internship. Results At the end of the internship, the scores of clinical consultation, Physical examination, humanistic medicine, clinical diagnosis, health consultation, organizational effect, and overall evaluation of the experimental group were significantly improved and were higher than those of the control group. After the Practice, in terms of skill test scores, the experimental group scored higher than the control group, the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05), and the experimental group also scored higher in satisfaction evaluation than the control group. Conclusion The Mini-CEX evaluation teaching model based on the concept of OBE is applied to the clinical practice teaching of the neurology department, which can enhance the training effect of students’ clinical practice skills.
2024, 45(3): 198-202.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240330
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the effect of intravertebral labor analgesia nursing intervened by anesthesia nurse on labor analgesia and delivery outcome. Methods Two hundreds cases of parturients who received intravertebral labor analgesia in The First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University from July to December 2022 were selected as research objects and randomly divided into observation group and control group by drawing lots, with 100 cases in each group. The control group was given routine nursing by midwives, and the observation group was given anesthesia nursing by an anesthesia nurse. The degree of labor pain, the outcome of labor, the incidence of anesthesia-related complications, and the satisfaction of labor analgesia nursing were compared between the two groups. Results The degree of labor pain in the observation group was significantly lower than that in the control group(P < 0.05). The duration of labor in the observation group was longer than that in the control group(P < 0.05). The incidence of anesthesia-related complications in the observation group was significantly lower than that in the control group(P < 0.05). The satisfaction of parturient analgesic care in the observation group was higher than that in the control group(P < 0.05). Conclusion Labor analgesia care intervened by anesthesia nurses can effectively reduce labor pain, shorten the labor process, reduce the incidence of anesthesia-related complications, improve the satisfaction of labor analgesia nursing, and provide a safe, comfortable, and effective labor process for women, which is worthy of clinical promotion.


 Email
Email RSS
RSS