Research Progress of PI3K Signaling Pathway Inhibitors in the Treatment of Pulmonary Fibrosis
-
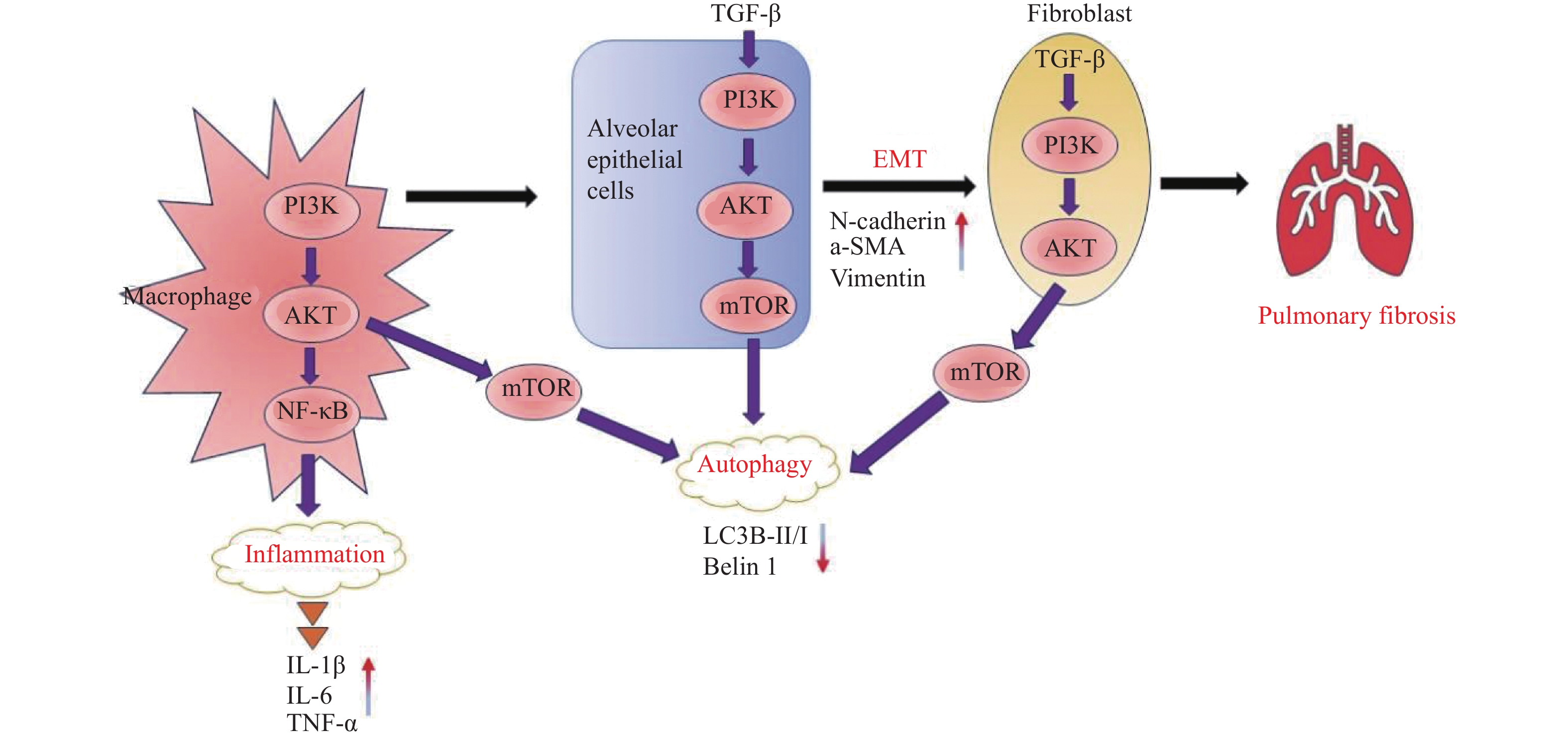
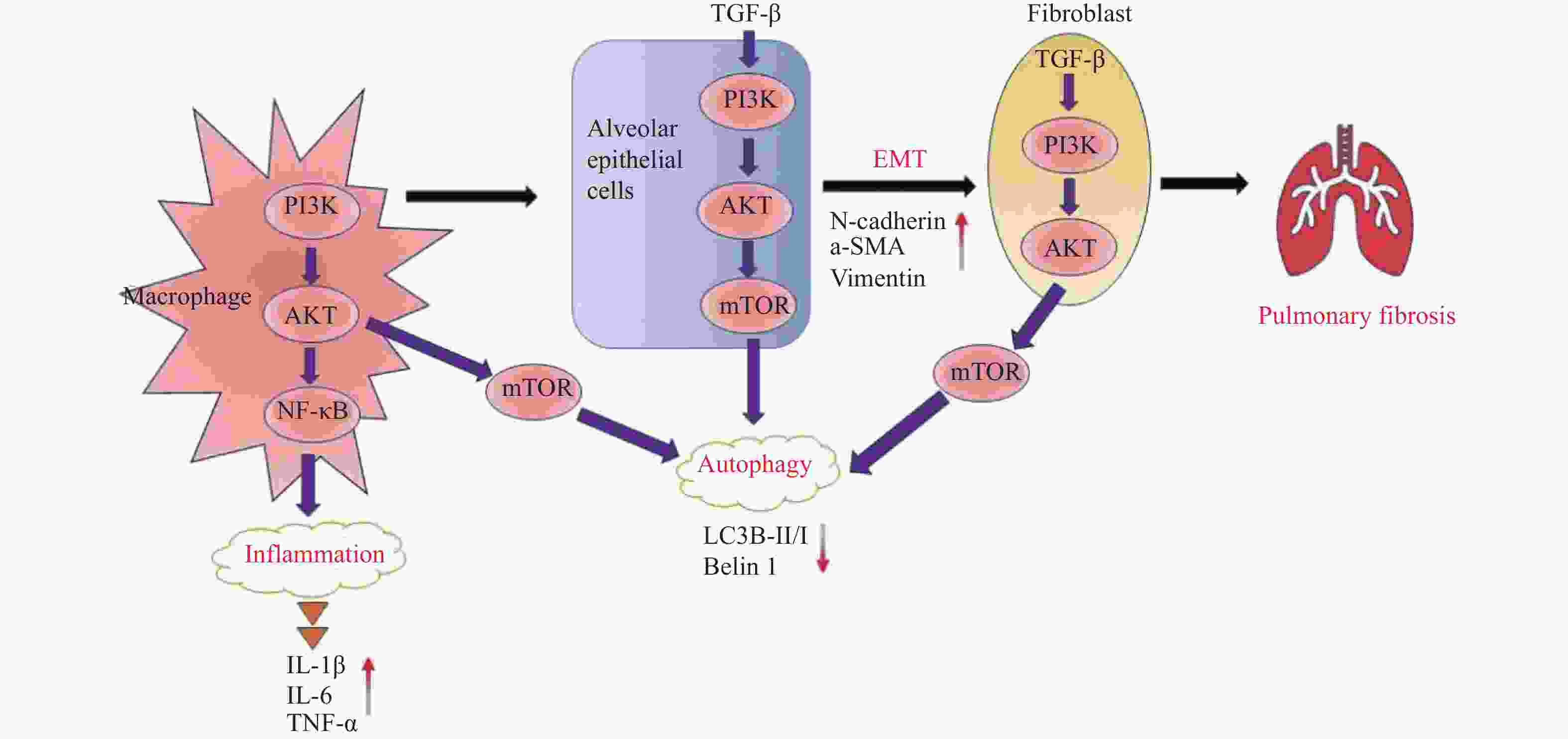
摘要: 肺纤维化(pulmonary fibrosis,PF)是一种多种病因引起的慢性进行性肺部疾病,也是多种慢性炎症性肺疾病的共同结局。肺纤维化发病率逐年上升,死亡率高,严重威胁患者生命健康。尽管已有吡非尼酮和尼达尼布两个药物上市用于治疗肺纤维化,但其仅能减缓疾病的进展,不能逆转或阻止肺纤维化进程,而且长期服用会产生多种不良反应。因此,研发更具有靶向性、高效性以及患者耐受良好的肺纤维化新药非常必要。磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶(phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase,PI3K)信号通路在肺纤维化发病过程中发挥了重要作用,靶向抑制PI3K信号通路可能是肺纤维化新药研发的重要方向。目前,已有一些PI3K信号通路抑制剂表现出较好的肺纤维化防治作用,但大多数仍处于研究阶段。对PI3K信号通路在PF中的作用进行综述,进一步总结有前景的具有PF治疗效果的PI3K通路抑制剂,包括处于临床试验和临床前研究中的抑制剂,并探讨其作用机制及开发前景。Abstract: Pulmonary fibrosis (PF) is a chronic progressive lung disease caused by a variety of etiologies and is also a common outcome of various chronic inflammatory lung diseases. The incidence of pulmonary fibrosis is increasing year by year, with a high mortality rate that seriously threatens the life and health of patients. Although two drugs, pirfenidone and nintedanib, are already on the market for the treatment of pulmonary fibrosis, they can only slow down the progression of the disease but cannot reverse or stop the process of pulmonary fibrosis, and long-term use can produce a variety of adverse reactions. Therefore, it is highly necessary to develop new drugs for pulmonary fibrosis that are more targeted, effective, and well-tolerated by patients. The phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) signaling pathway plays an important role in the pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis. Targeted inhibition of the PI3K signaling pathway may be an important direction for the development of new drugs for pulmonary fibrosis. At present, some PI3K signaling pathway inhibitors have shown good effects in preventing and treating pulmonary fibrosis, but most of them are still in the research stage. This article reviews the role of the PI3K signaling pathway in PF, further summarizes promising PI3K pathway inhibitors with PF therapeutic effects, including inhibitors in clinical trials and preclinical studies, and discusses their mechanisms of action and development prospects.
-
Key words:
- Pulmonary fibrosis /
- PI3K signaling pathway /
- Inhibitors /
- New drug development
-
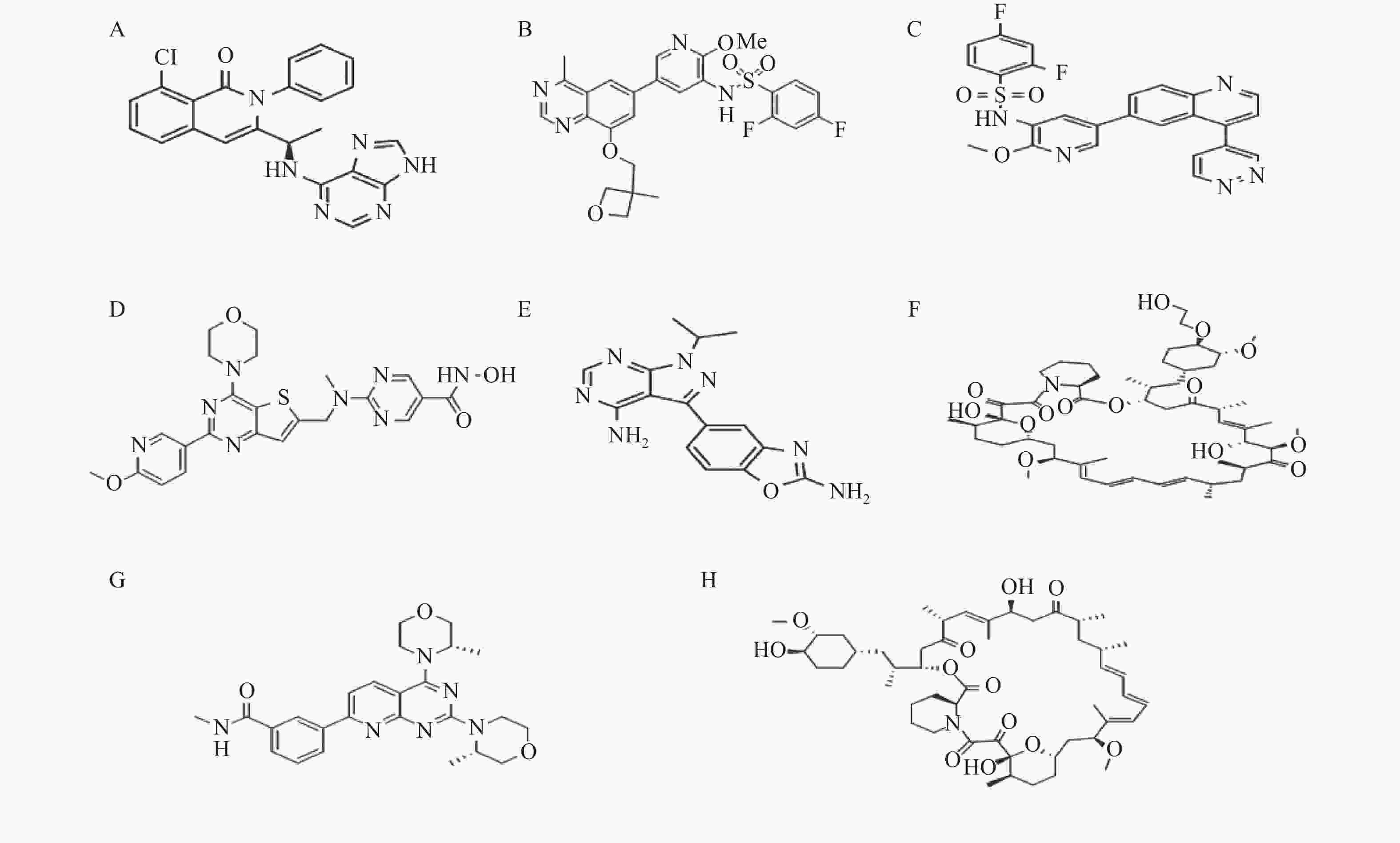
表 1 用于PF治疗的潜在PI3K通路抑制剂
Table 1. Potential PI3K pathway inhibitors for PF treatment
-
[1] Koudstaal T,Funke-Chambour M,Kreuter M,et al. Pulmonary fibrosis: From pathogenesis to clinical decision-making[J]. Trends Mol Med,2023,29(12):1076-1087. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2023.08.010 [2] Maher T M,Bendstrup E,Dron L,et al. Global incidence and prevalence of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis[J]. Respir Res,2021,22(1):197. doi: 10.1186/s12931-021-01791-z [3] Lancaster L H,de Andrade J A,Zibrak J D,et al. Pirfenidone safety and adverse event management in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis[J]. Eur Respir Rev,2017,26(146):170057. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0057-2017 [4] Wind S,Schmid U,Freiwald M,et al. Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of nintedanib[J]. Clin Pharmacokinet,2019,58(9):1131-1147. doi: 10.1007/s40262-019-00766-0 [5] Capuzzimati M,Hough O,Liu M. Cell death and ischemia-reperfusion injury in lung transplantation[J]. J Heart Lung Transplant,2022,41(8):1003-1013. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2022.05.013 [6] Wang J,Hu K,Cai X,et al. Targeting PI3K/AKT signaling for treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis[J]. Acta Pharm Sin B,2022,12(1):18-32. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.07.023 [7] Margaria J P,Moretta L,Alves-Filho J C,et al. PI3K signaling in mechanisms and treatments of pulmonary fibrosis following sepsis and acute lung injury[J]. Biomedicines,2022,10(4):756. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10040756 [8] Li X,Ma X,Miao Y,et al. Duvelisib attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis via inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signalling pathway[J]. J Cell Mol Med,2023,27(3):422-434. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17665 [9] Lukey P T,Harrison S A,Yang S,et al. A randomised,placebo-controlled study of omipalisib (PI3K/mTOR) in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis[J]. Eur Respir J,2019,53(3):1801992. doi: 10.1183/13993003.01992-2018 [10] Hettiarachchi S U,Li Y H,Roy J,et al. Targeted inhibition of PI3 kinase/mTOR specifically in fibrotic lung fibroblasts suppresses pulmonary fibrosis in experimental models[J]. Sci Transl Med,2020,12(567):eaay3724. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aay3724 [11] 朱武嫦,莫孝成,苏宏梅,等. 天然产物通过抑制PI3K信号通路抗肝纤维化的研究进展[J]. 中国药理学通报,2024,40(4):619-624. doi: 10.12360/CPB202208011 [12] Zhu K,Wu Y,He P,et al. PI3K/AKT/mTOR-targeted therapy for breast cancer[J]. Cells,2022,11(16):2508. doi: 10.3390/cells11162508 [13] Xu J,Li Y,Kang M,et al. Multiple forms of cell death: A focus on the PI3K/AKT pathway[J]. J Cell Physiol,2023,238(9):2026-2038. doi: 10.1002/jcp.31087 [14] Tian L Y,Smit D J,Jücker M. The role of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma metabolism[J]. Int J Mol Sci,2023,24(3):2652. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032652 [15] Mei Q,Liu Z,Zuo H,et al. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: An update on pathogenesis[J]. Front Pharmacol,2021,12:797292. [16] 罗成,叶远航,柯佳. 中药基于PI3K/AKT信号通路治疗肺纤维化的研究进展[J]. 沈阳药科大学学报,2025,42(4):311-321. [17] Zhang X L,Li B,Zhang X,et al. 18β-Glycyrrhetinic acid monoglucuronide (GAMG) alleviates single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNT)-induced lung inflammation and fibrosis in mice through PI3K/AKT/NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf,2022,242:113858. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.113858 [18] Pan L,Cheng Y,Yang W,et al. Nintedanib ameliorates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis,inflammation,apoptosis,and oxidative stress by modulating PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in mice[J]. Inflammation,2023,46(4):1531-1542. doi: 10.1007/s10753-023-01825-2 [19] Rahmani F,Asgharzadeh F,Avan A,et al. Rigosertib potently protects against colitis-associated intestinal fibrosis and inflammation by regulating PI3K/AKT and NF-κB signaling pathways[J]. Life Sci,2020,249:117470. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117470 [20] Huckestein B R,Zeng K,Westcott R,et al. Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 activation in macrophages contributes to persistent lung inflammation following respiratory tract viral infection[J]. Am J Pathol,2024,194(3):384-401. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2023.11.017 [21] Cadena-Suárez A R,Hernández-Hernández H A,Alvarado-Vásquez N,et al. Role of microRNAs in signaling pathways associated with the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A focus on epithelial-mesenchymal transition[J]. Int J Mol Sci,2022,23(12):6613. doi: 10.3390/ijms23126613 [22] 朱雨晴,韩彦琪,韩梁,等. 中药通过抑制上皮间充质转化缓解肺纤维化的研究进展[J]. 中草药,2025,56(7):2559-2570. [23] Sun H N,Ren C X,Lee D H,et al. PRDX1 negatively regulates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis via inhibiting the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and lung fibroblast proliferation in vitro and in vivo[J]. Cell Mol Biol Lett,2023,28(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s11658-023-00460-x [24] Weng C M,Li Q,Chen K J,et al. Bleomycin induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via bFGF/PI3K/ESRP1 signaling in pulmonary fibrosis[J]. Biosci Rep,2020,40(1):BSR20190756. doi: 10.1042/BSR20190756 [25] Zhao H,Wang Y,Qiu T,et al. Autophagy,an important therapeutic target for pulmonary fibrosis diseases[J]. Clin Chim Acta,2020,502:139-147. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2019.12.016 [26] Peng J,Xiao X,Li S,et al. Aspirin alleviates pulmonary fibrosis through PI3K/AKT/mTOR-mediated autophagy pathway[J]. Exp Gerontol,2023,172:112085. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2023.112085 [27] Gong H,Lyu X,Liu Y,et al. Eupatilin inhibits pulmonary fibrosis by activating Sestrin2/PI3K/Akt/mTOR dependent autophagy pathway[J]. Life Sci,2023,334:122218. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2023.122218 [28] Alsayed H A,Mohammad H M F,Khalil C M,et al. Autophagy modulation by irbesartan mitigates the pulmonary fibrotic alterations in bleomycin challenged rats: Comparative study with rapamycin[J]. Life Sci,2022,303:120662. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120662 [29] Li P,Hao X,Liu J,et al. miR-29a-3p regulates autophagy by targeting Akt3-mediated mTOR in SiO(2)-induced lung fibrosis[J]. Int J Mol Sci,2023,24(14):11440. doi: 10.3390/ijms241411440 [30] Campa C C,Silva R L,Margaria J P,et al. Inhalation of the prodrug PI3K inhibitor CL27c improves lung function in asthma and fibrosis[J]. Nat Commun,2018,9(1):5232. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07698-6 [31] Lin S,Jin J,Liu Y,et al. Discovery of 4-methylquinazoline based PI3K inhibitors for the potential treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis[J]. J Med Chem,2019,62(19):8873-8879. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b00969 [32] Zhang W,Zhang Y,Tu T,et al. Dual inhibition of HDAC and tyrosine kinase signaling pathways with CUDC-907 attenuates TGFβ1 induced lung and tumor fibrosis[J]. Cell Death Dis,2020,11(9):765. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-02916-w [33] Xu Z,Lv Y,Kong D,et al. Sapanisertib attenuates pulmonary fibrosis by modulating Wnt5a/mTOR signalling[J]. Basic & Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology,2023,133(3):226-236. [34] Pandolfi L,Marengo A,Japiassu K B,et al. Liposomes loaded with everolimus and coated with hyaluronic acid: A promising approach for lung fibrosis[J]. Int J Mol Sci,2021,22(14):7743. doi: 10.3390/ijms22147743 [35] González-Sánchez E,Muñoz-Callejas A,Gómez-Román J,et al. Targeted nanotherapy with everolimus reduces inflammation and fibrosis in scleroderma-related interstitial lung disease developed by PSGL-1 deficient mice[J]. Br J Pharmacol,2022,179(18):4534-4548. doi: 10.1111/bph.15898 [36] Shaikh T B,Chandra Y,Andugulapati S B,et al. Vistusertib improves pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis by modulating inflammatory/oxidative stress mediators via suppressing the mTOR signalling[J]. Inflamm Res,2024,73(7):1223-1237. doi: 10.1007/s00011-024-01894-5 [37] Gomez-Manjarres D C,Axell-House D B,Patel D C,et al. Sirolimus suppresses circulating fibrocytes in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in a randomized controlled crossover trial[J]. JCI Insight,2023,8(8):e166901. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.166901 [38] He Y,Sun M M,Zhang G G,et al. Targeting PI3K/Akt signal transduction for cancer therapy[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther,2021,6(1):425. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00828-5 [39] Xie J,Xu K,Cai Z,et al. Efficacy and safety of first-line PD-L1/PD-1 inhibitors in limited-stage small cell lung cancer: A multicenter propensity score matched retrospective study[J]. Transl Lung Cancer Res,2024,13(3):526-539. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-24-24 [40] Zhang L,Li Y,Hu C,et al. CDK6-PI3K signaling axis is an efficient target for attenuating ABCB1/P-gp mediated multi-drug resistance (MDR) in cancer cells[J]. Mol Cancer,2022,21(1):103. doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01524-w [41] Huang T,Gao J,Cai L,et al. Treating pulmonary fibrosis with non-viral gene therapy: From bench to bedside[J]. Pharmaceutics,2022,14(4):813. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14040813 -





 下载:
下载: